Changes in Abiotic Factors
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Changes in abiotic factors
Human activities may change the abiotic features of a habitat, making it more or less suitable for the survival of wildlife.
How can changes in abiotic factors be caused by inactivity?
Stopping a plagioclimax

How do human activities change water availability?
- Land drainage
- Flooding land
Water Availability - Land Drainage
Wetlands are drained to reclaim land. The land is often then used as farmland.

How else can land be drained by human activity?
- The over exploitation of groundwater resources can lower the water table in the ground
- This causes the surface wetland habitats to dry out
- It then is impossible for wetland species to survive
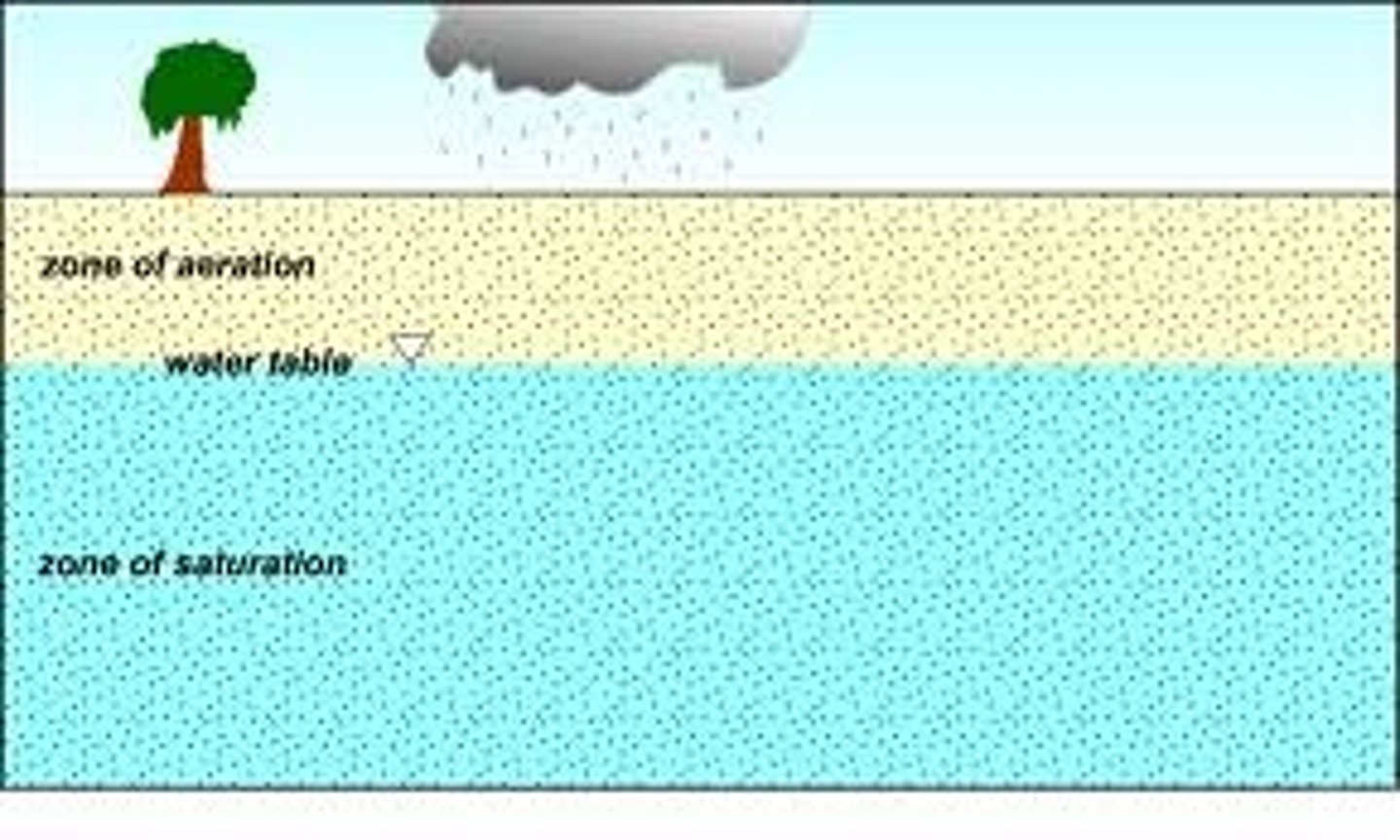
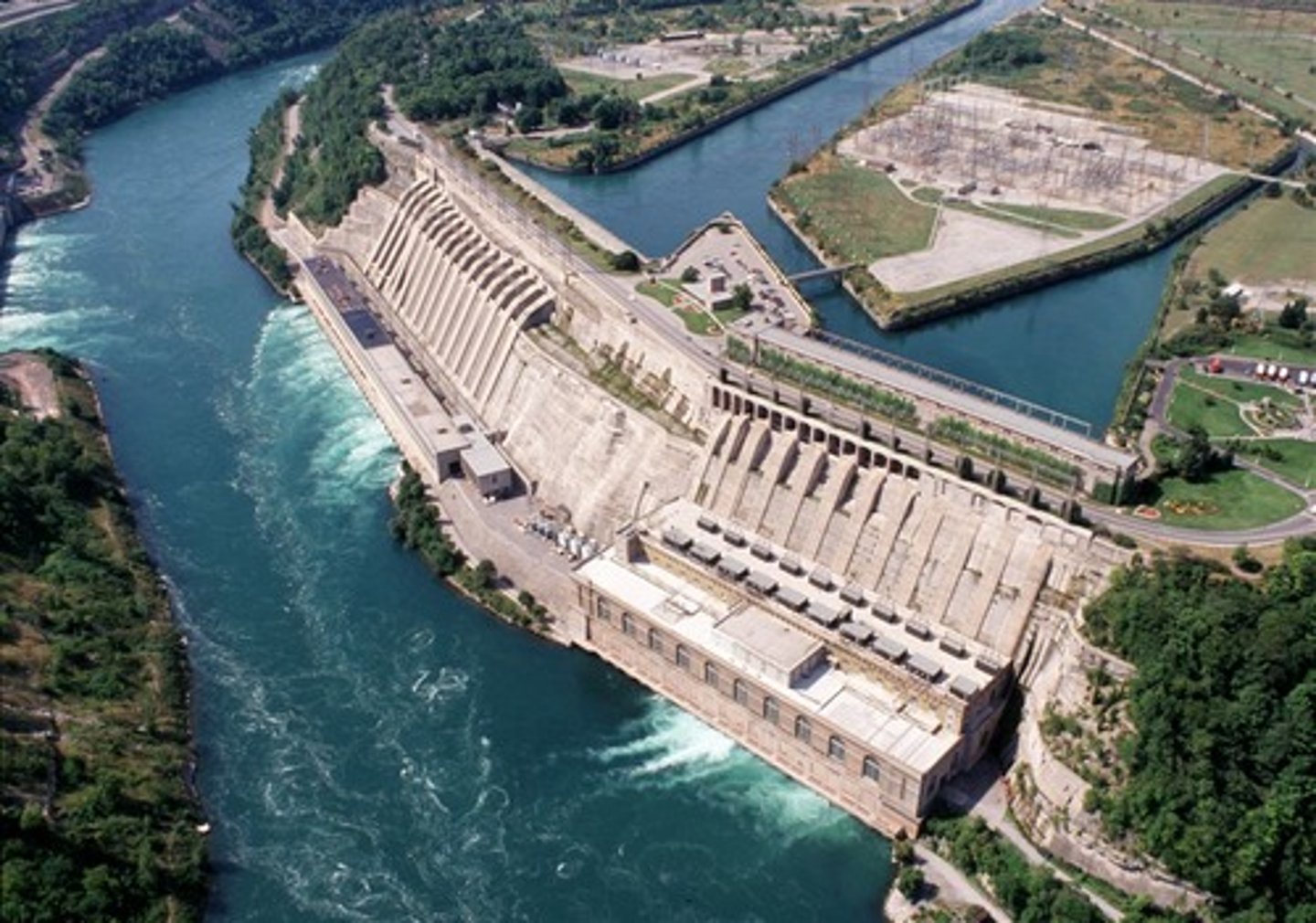
Water Availability - Flooding
The water level in tropical rivers may naturally rise and fall with the wet and dry seasons. Sandbanks and riverbanks that are exposed during the dry season may be important nesting sites for freshwater turtles or water birds.
Hydroelectric power may cause sudden changes in water levels that flood the nests, killing the eggs

Light levels
Forest clearance increases light levels

Oxygen availability
- Dissolved oxygen levels in water is reduced by hot water discharges from power stations
- It is also reduced by discharging organic wastes, such as sewage, which deoxygenates the water as it decomposes.

Why is a drop in dissolved oxygen levels bad?
It can reduce the survival of aerobic organisms such as fish and insect larvae.

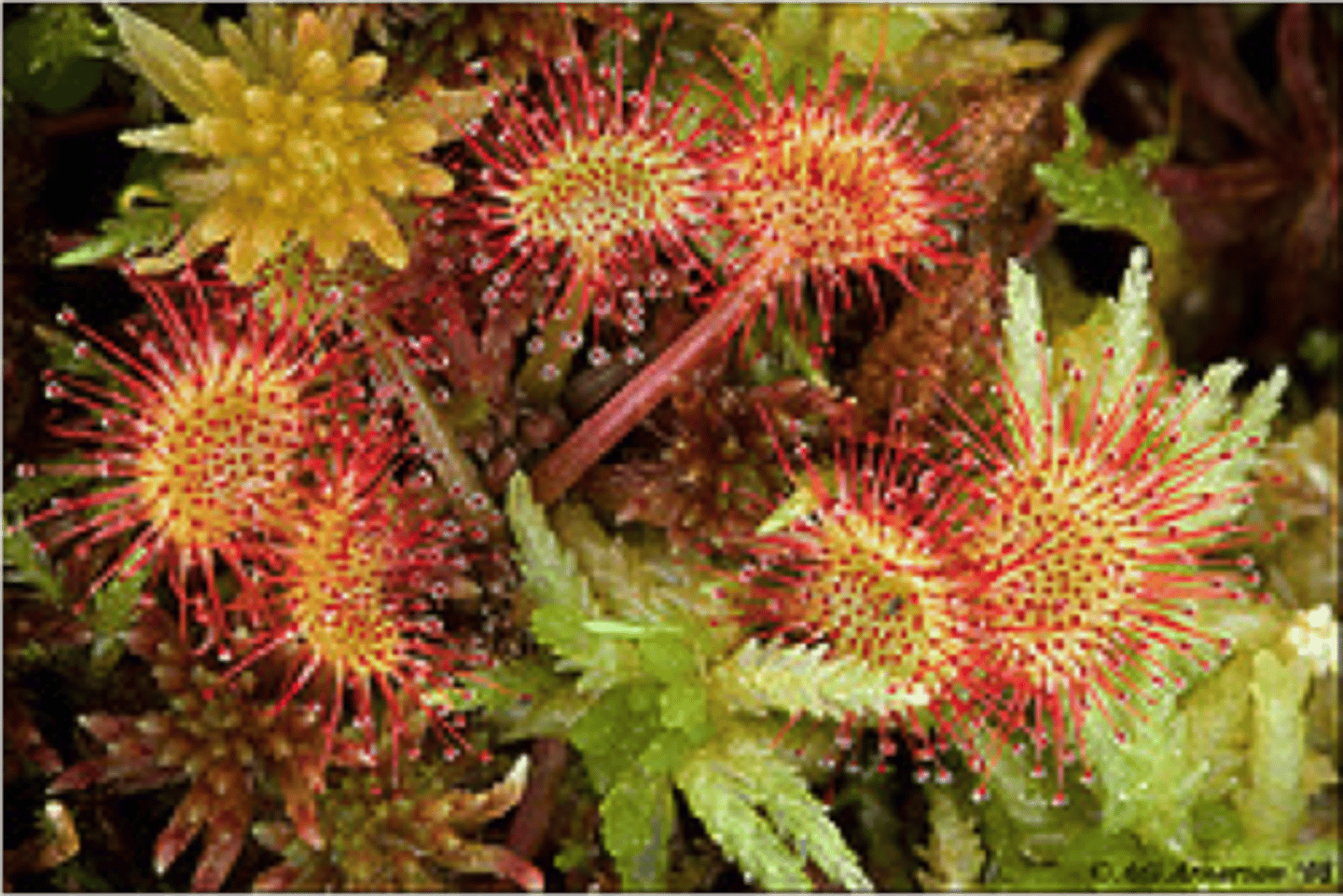
The impact of oxygen availability for sundew
Marshland plants such as sundews grow in waterlogged, anaerobic soil where tall plants can't survive due to low nitrogen levels (sundews trap and digest insects for nitrogen)
Drainage schemes that produce more aerobic soil may allow taller competitors to colonise the area, causing the sundew to die out.

Nutrient levels
Fertiliser runoff from farmland
pH
- Mine drainage water and pollutant gases from burning fossil fuels can produce acidic conditions
- Acid denatures the cell proteins of exposed tissues
- Some organisms or tissues are particularly vulnerable to acidic conditions, for example, fish eggs and gills, or invertebrates with calcium-based exoskeletons such as crayfish.

Temperature
A change in temperature can affect wildlife species in many ways. The growth or survival of some species will increase but others may not be adapted to survive the change.
- Global climate change
- Hot effluent water
Temperature: Hot effluent water
An increase in water temperature can increase the growth rates of aquatic vegetation, providing more food for aquatic animals, or it may increase the rate of decomposition causing deoxygenation.
Temperature: Global climate change
The temperature changes will cause changes in the distribution of species as they colonise areas which become suitable, or die out in areas where they can no longer survive
