Bacteria: Structure, Growth, Taxonomy
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Understanding of the structure of a bacterial cell State the Structural differences between bacteria and Eukaryotes Taxonomy and diagnosis of bacteria Structure/function features of cell envelope Growth conditions for bacterial growth
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
what are bacteria?
unicellular microorganism (can be free living or host dependant).
What kingdom are bacteria in?
Monera- single cells
difference between Monera and protists?
Monera - prokaryotes, unpaired chromosomes, no nucelus
Protits - eukaryotes, paired chromosomes, nuclear structure.
table comparing Prok vs Euk
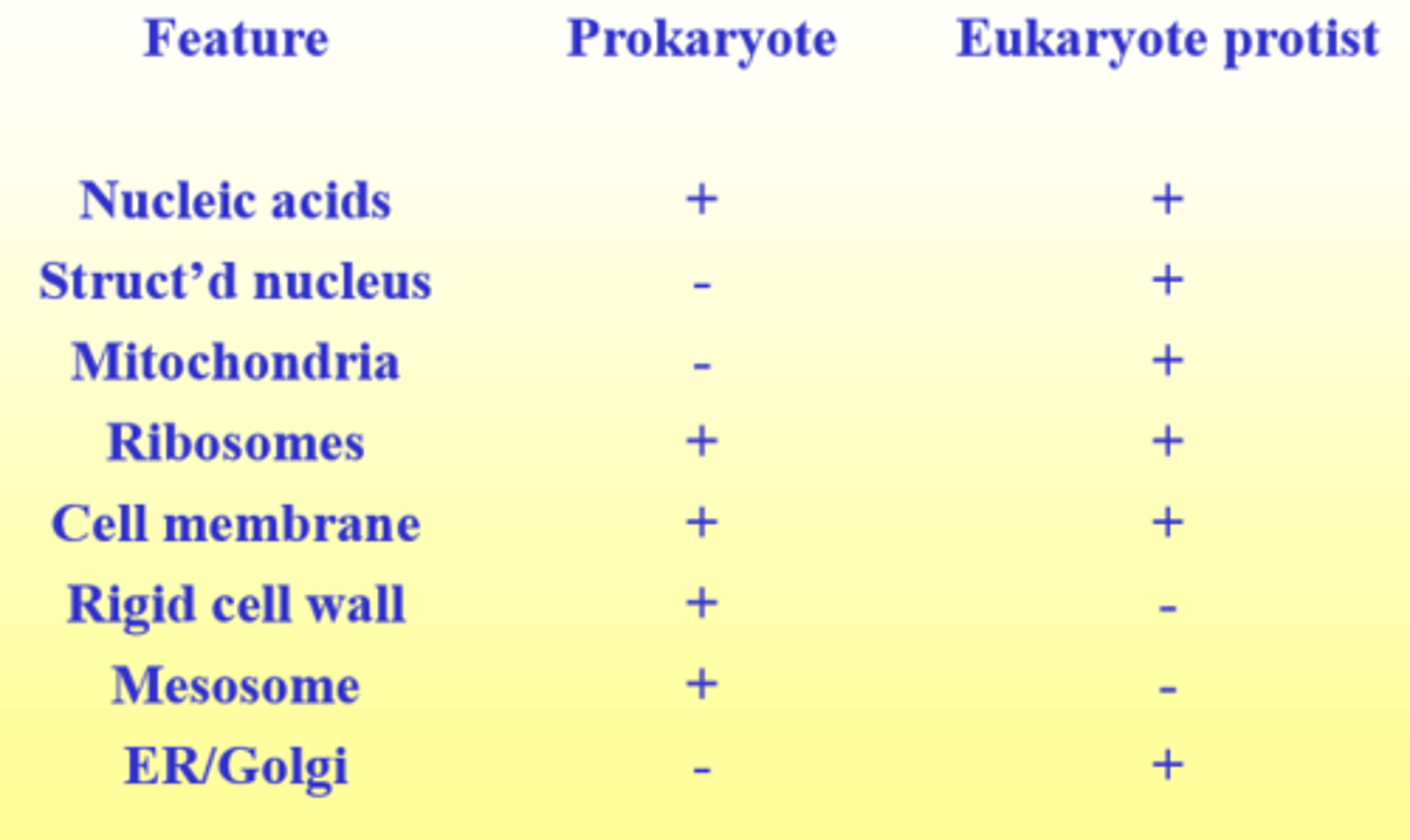
What structure do both prokaryotes an eukaryotes have?
Nucleic acid, ribosomes, cell membrane
What structures are in eukaryotes and not prokaryotes ?
Structured nucleus, mitochondria, ER/Golgi
typical bacterial cell structure
Coiled DNA, Ribosomes, pili, inner membrane, cell wall, outer membrane, flagellum in the inner membrane,
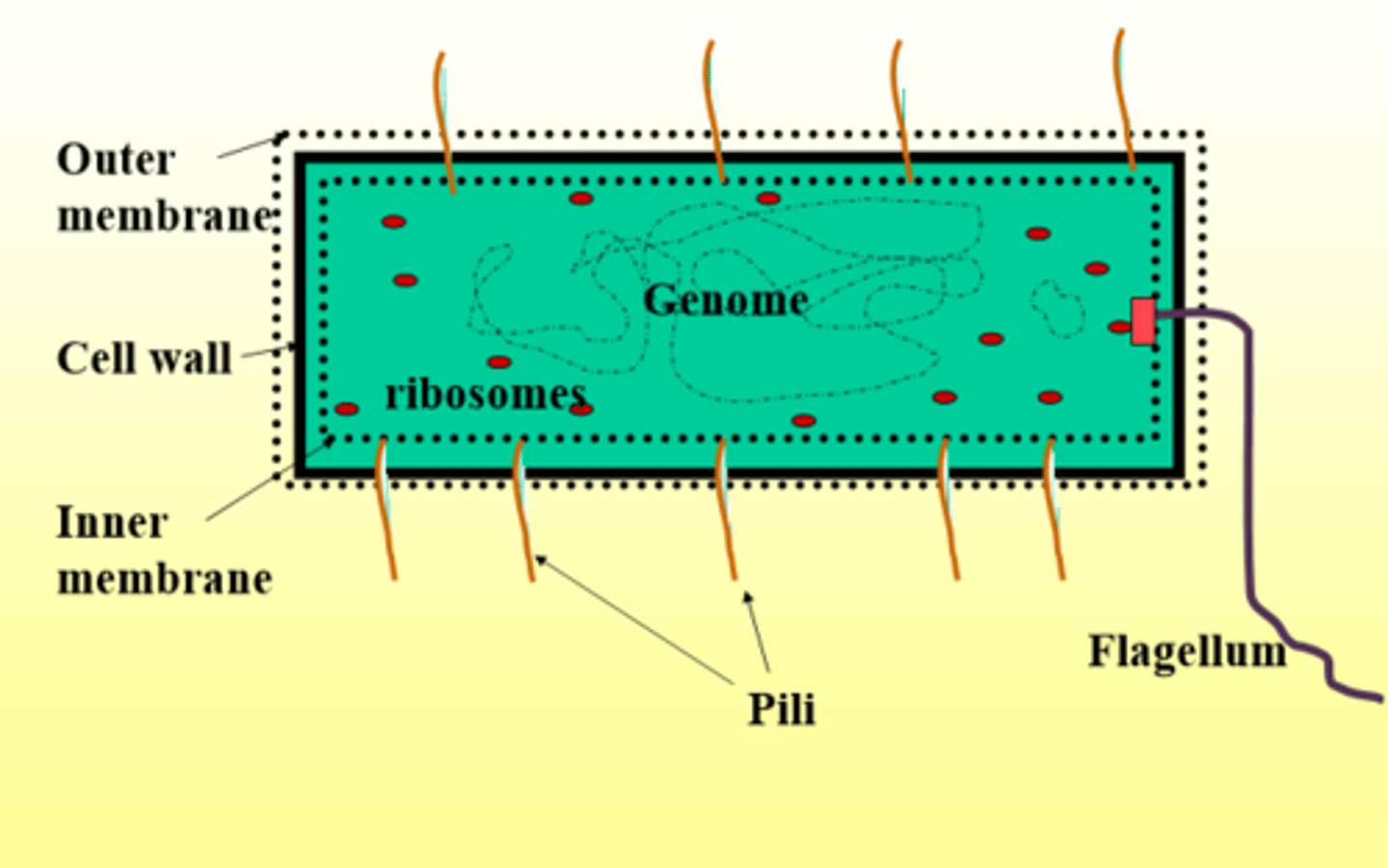
Which bacteria has outer memebrane
gram - negative
What is binomial nomenclature?
two word naming system.
Genus then species.
why is bacterial taxonomy important?
- Handling information
- Learning
- Communication
- Identification
- Evolution
methods of classification - phenotypic
morphology - macroscopic/ microscopic
bio typing - biochemical tests
serotyping - differences in antigenic determinants on the outside of the cell
macroscopic morphology (growth on agar medium)
-shape
- margin
- elevation
- size
macroscopic morphology
- texture (smooth/rough)
- appearance (glistening (shiny) or dull)
- pigmentation (none = cream, tan, white/ pigmented = purple, red, yellow)
- optical density (opaque/translucent)
microscopic morphology characteristics?
- shape (rod, club, coccus, etc.)
- size
- staining characteristics (gram stain 'truce bacteria'. acid-fast stain 'mycobacteria')
- arrangements (individual , clusters)
-Optical density
genotypic characteristics?
- %G+C ratios → Amount of bases
- PCR/DNA sequencing → Banding patterns
- ribotyping (classifying based on sequence of ribosomal RNA (16s RNA)
what does a gram stain do?
differentiated bacteria on basis of their cell wall structure.
Generally first line test in diagnosis of bacterial infections.
what does gram positive mean?
thick cell wall
what is gram negative?
thin cell wall
what is added to perform gram staining?
- crystal violet - stains all cells
- gram's iodine - Thickens the crystal violet in the cell wall
- decolouriser (alcohol/acetone) - if gram-positive then can’t remove the crystal violet
- safranin red only applies to gram-negative
examples of morphological characterisation
In terms of cell envelope characteristics. What are the difference between both gram + and - have?
+ = Thicker, teichoic acid on top, sporulation, sensitive to lysozyme, more susceptible to penicillin
- = thiner wall , LPS , less susceptible to penicillin

In terms of cell envelope characteristics. What does both gram + and - have?
capsules
what is the function of porins?
Within the Plasma Membrane, they are proteins that allow certain ions and small polar molecules to pass through the membrane.
functions of cell wall?
- rigidity and cell shape and structure
- maintains osmolarity
- survival
- cell division
how is the bacterial cell wall synthesised?
peptidoglycan precursor synthesised inside the cell.
→
exported across the cell membrane X bacitracin (prevents secretion of the precursor unit of the cell wall)
→
a site is created in the existing wall by enzymes (PBPs).
→
new nucleotide minus the terminal D-ala is incorporated.
→
cell grows.
Different cell wall morphologies - Mycobacterium
- modified peptidoglycan layer
- covalently attached to arabinogalactan
- mycolic acid waxy coat - lipids → causes cells to clump
- poor gram stain
- acid fast - carbolfuchsni.
mycoplasma
- Type of bacteria
-no cell wall
- cell membrane contains steroids (host)
what is the cell membrane like?
- lipid bilayer - hydrophobic
- similar gram +ve and -ve bacteria
- no steroids (except mycoplasmas)
role = ion transport and energy production
- mesosome - cell division
- electron transport (energy production)
What other morphological features : spores?
spores
- cell survival in adverse conditions
- desiccation, heat, starvation
- gram +ve only
what other morphological features like capsule
capsules
- protection against phagocytosis
- both gram +ve/-ve
- gelatinous material, polysaccharide/polypeptide
Flagella + Fimbriae
Flagella:
- cell motility
- coiled in structure
- anchored in bacterial membranes
Fimbriae:
- smaller length and diameter
- not coiled
Main role of flagella and fimbirae ?
flagella =–Chemotaxis , Movement by ATP-driven ‘motor’ membrane potential
fimbirae - Adhesin
morphological virulence factors (What can you find? ) - Gram-negative
LPS
- lipid A/core ploysacc
- shedding - meningos
- inflammatory response
- cytokines/septic shock
Porins
Pili
morphological virulence factors (What can you find? ) - gram positive
Teichoic acids - in the inner membrane
Lipoteichoic acids
Peptido fragments
surface protein
- afimbrial adhesins
- protein F
Inflammatory response
Cytokines/shock
physical growth characteristics
- oxygen/carbon dioxide
- temperature
- water
- pH
- light
- osmolarity
nutrition requirements growth characteristics
- carbon source
- nitrogen source
- inorganic salts (Fe/Na/K/P/Ca/Mg)
- organic compounds (ammino acids?)
Medical relevance?
cell wall synthesis - for antibiotic killing
capsules - vaccines
cell membranes - antibiotics (only negative )/ vaccines
ribosomes - antibiotics that target ribosomes like tetracyclines