Exotics
1/207
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
208 Terms
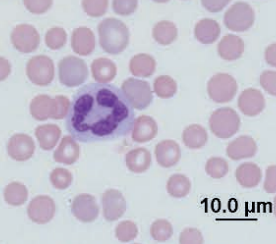
African hedgehog
Toxic neutrophil
Mouse and rat, what cell type?
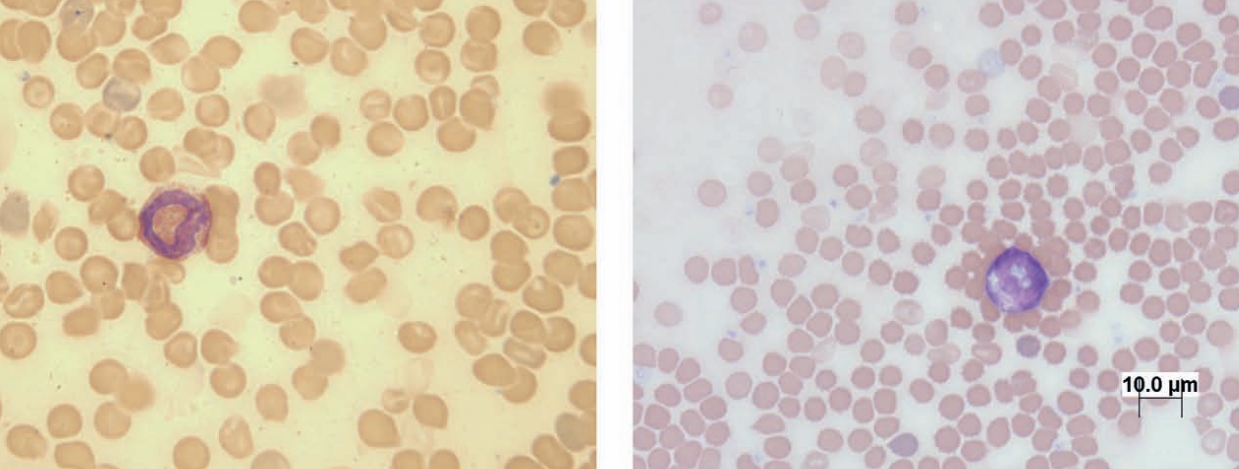
Eosinophil
Mouse
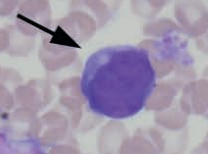
Monocyte
Guinea pig
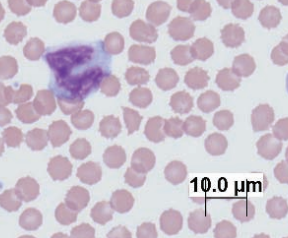
Monocytes
Guinea pig
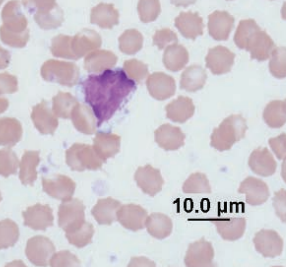
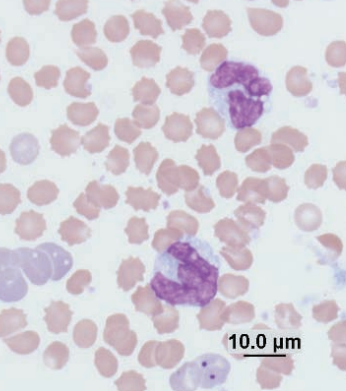
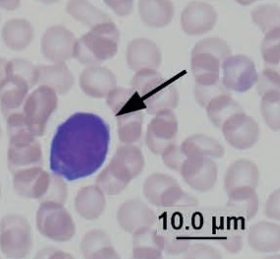
Large granular lymphocyte
Guinea pig
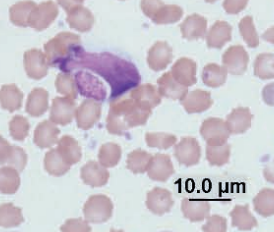
Lymphocyte with Kurloff body
Chinchilla
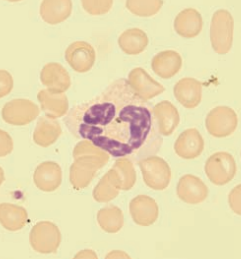
Heterophil
Rabbit
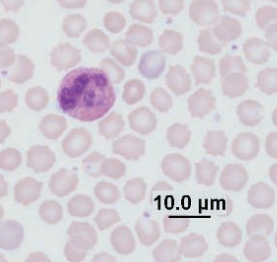
Heterophil
Rabbit
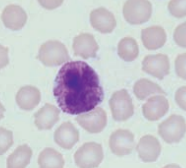
Basophil
Rabbit
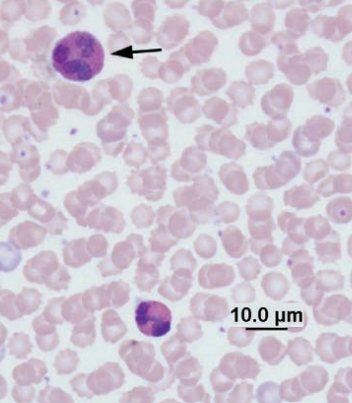
Eosinophil arrow, heterophil below
Rabbit
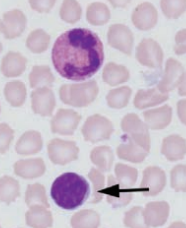
Heterophil and lymphocyte
Rabbit
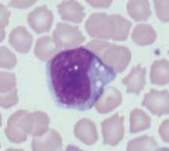
Monocyte
Ferret
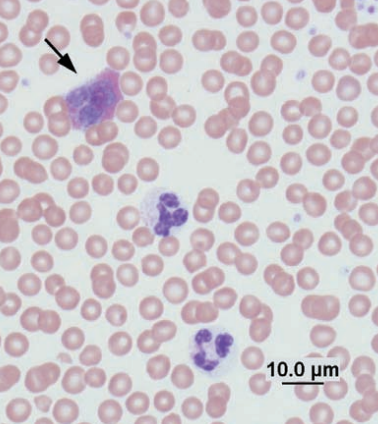
Eosinophil and neutrophils
Hedgehog
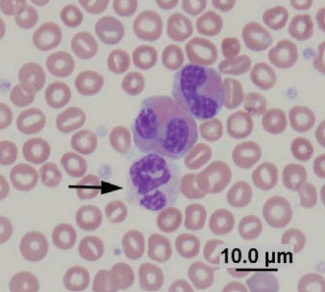
Neutrophil and eosinophils
Hedgehog
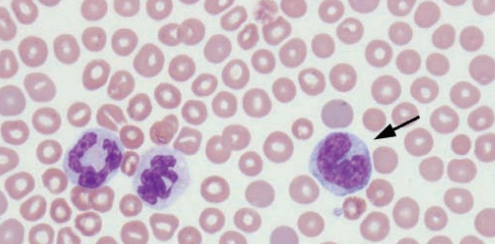
Neutrophils and monocytes
Guinea pig bone marrow, identify each
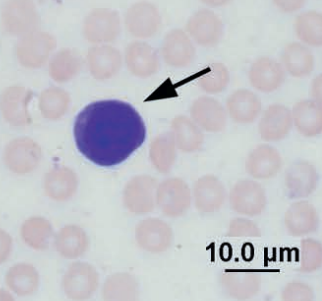
Rubriblast, prorubricyte, rubricyte and band
Guinea pig bone marrow
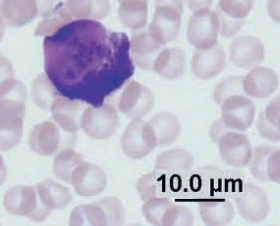
Myeloblast
Guinea pig bone marrow
Promyelocytes
Guinea pig bone marrow
Basophil myelocyte
Guinea pig bone marrow
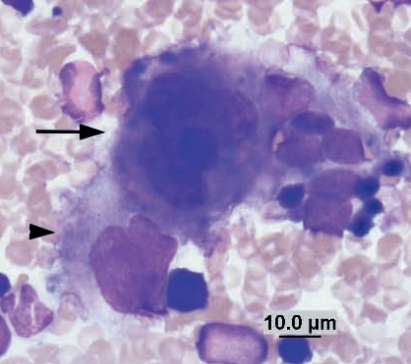
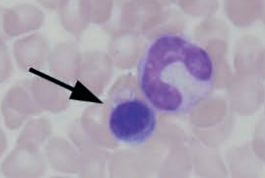
Promegakaryocyte next to megakaryocyte
Guinea pig bone marrow
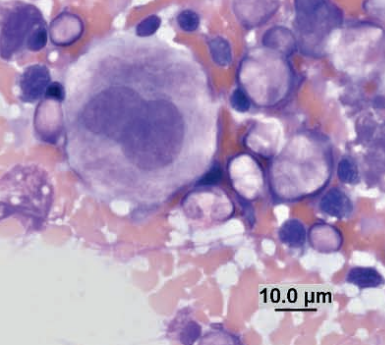
Promegakaryocyte
Chinchilla
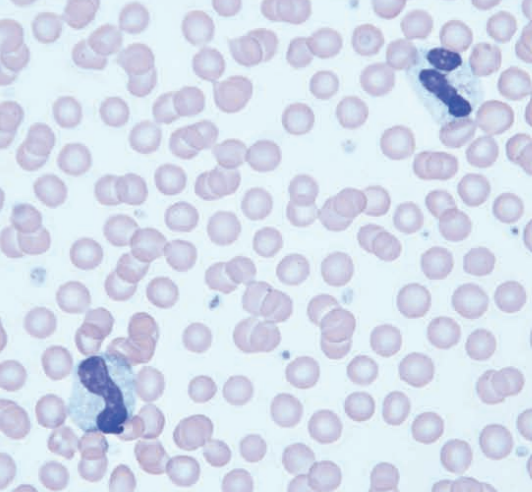
Toxic seg and band
Chinchilla
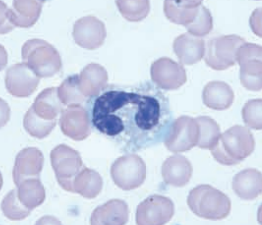
Toxic band
What infectious agent causes diarrhea in ferrets, often with green mucus, and in chronic conditions a bird-seed-like appearance?
Two main ddx?
Ferret enteric coronavirus (epizootic catarrhal enteritis, ECE)
Ddx: foreign body and Helicobacter mustelae gastritis
Cytospin from tracheal wash of a guinea pig
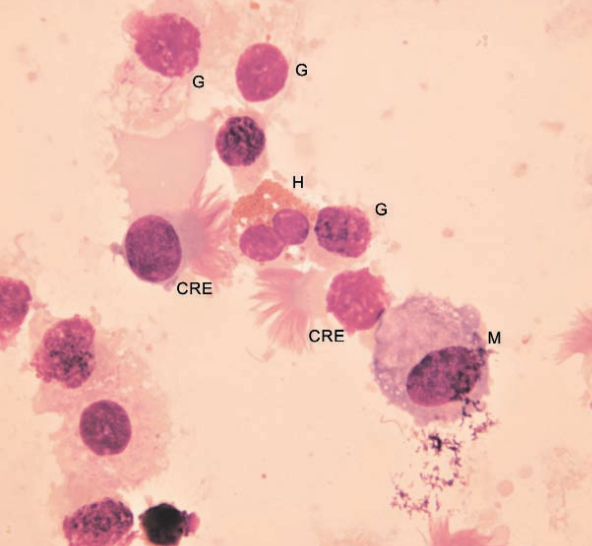
Normal. Ciliated respiratory epithelial cells (CRE), goblet cells (G), heterophil (H), macrophage (M)
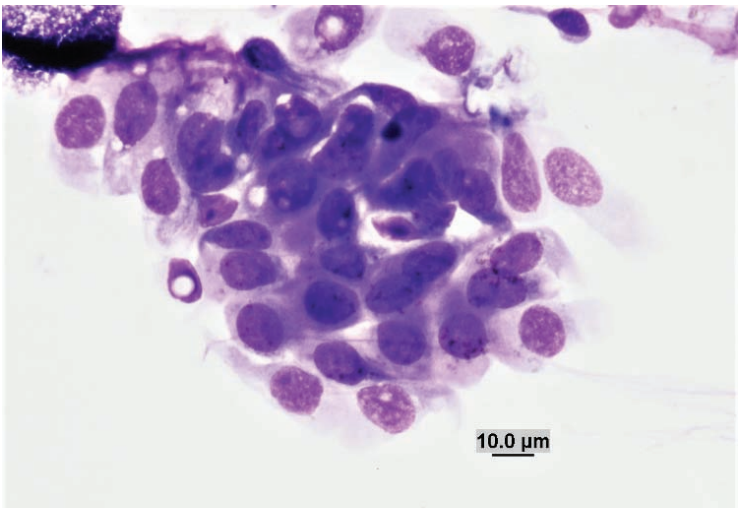
Conjunctival scraping from a guinea pig
Normal melanocytes
Choroid plexus imprint (from CNS)
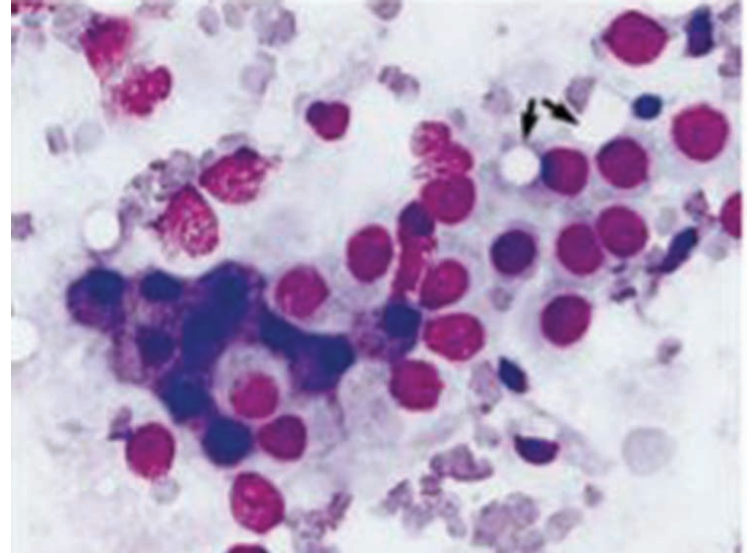
Alpha cells have dark blue cytoplasm and densely stained nuclei, and beta cells have paler nuclei with a cribriform chromatin distribution. Two gamma cells with intracellular vesicles are seen (arrows).
Guinea pig conjunctival scraping

Normal epithelium
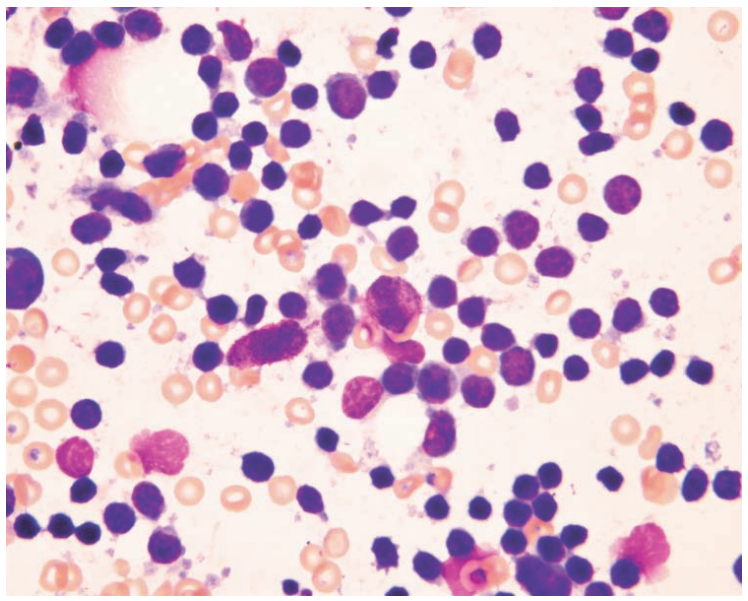
Ferret lymph node
Normal, two mast cells in centre
Ferret, liver
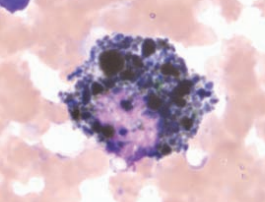
Intracytoplasmic bile pigment
Rabbit, nasal flush
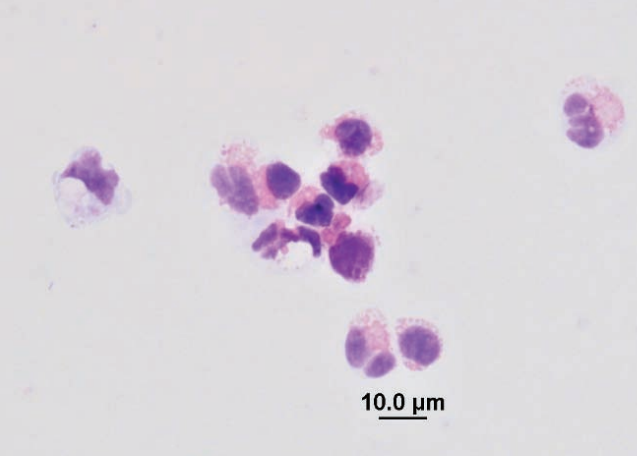
Heterophilic rhinitis
Ferret, subcutaneous mass
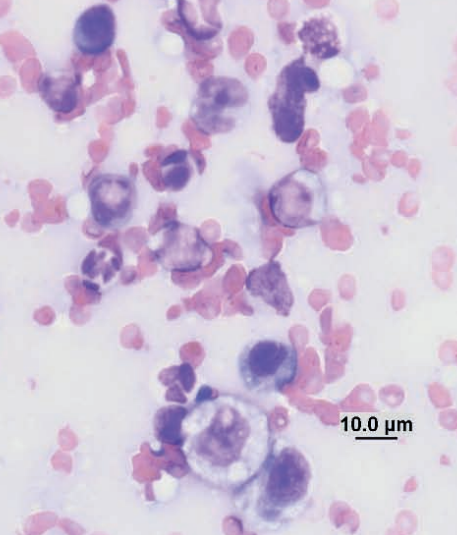
Mixed-cell inflammation
Mass from a hamster
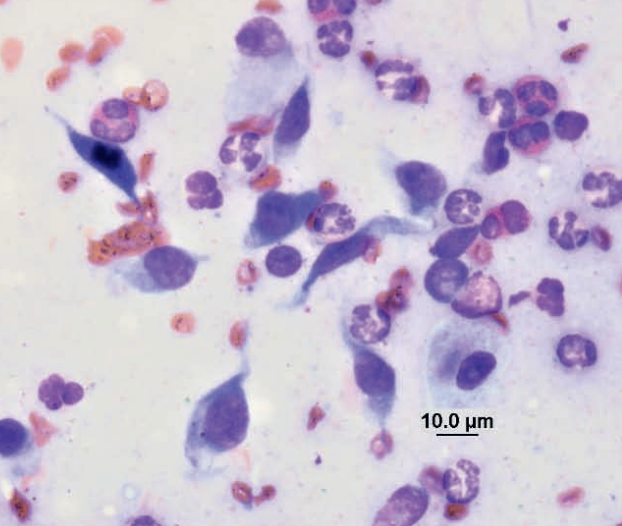
Fibroblasts from an abscess
Ferret abdominal fluid
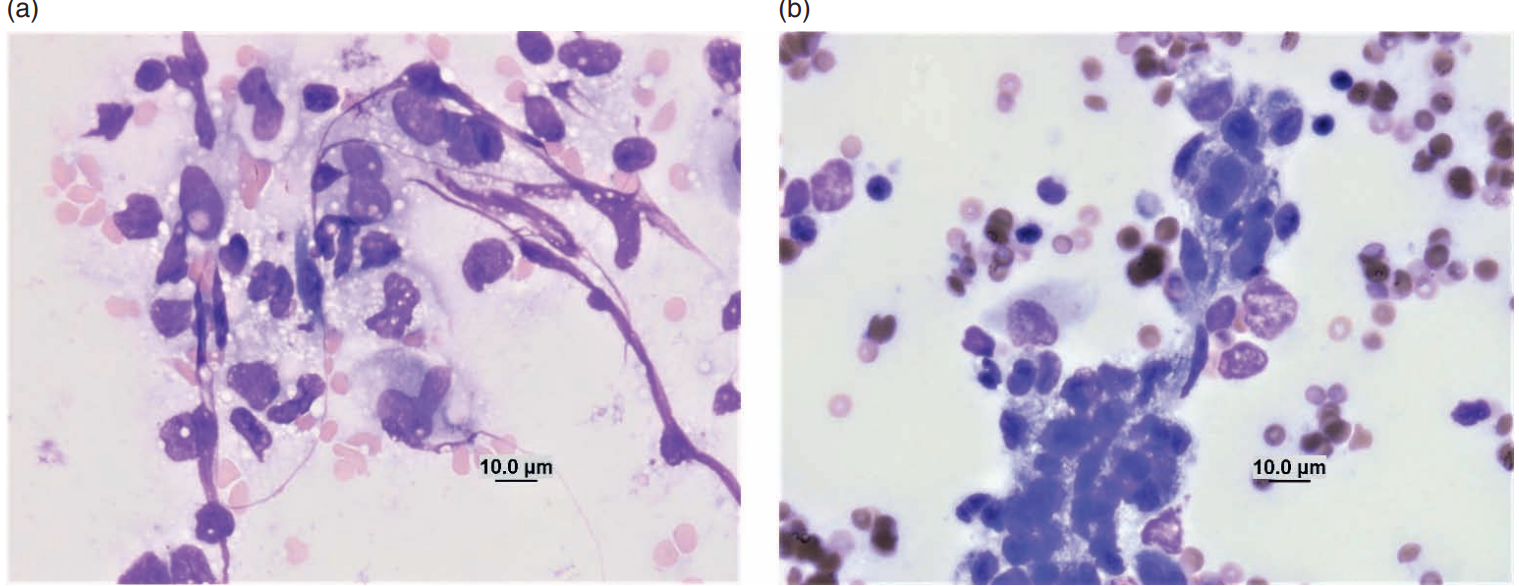
Macrophagic inflammation in peritonitis
Hedgehog, skin
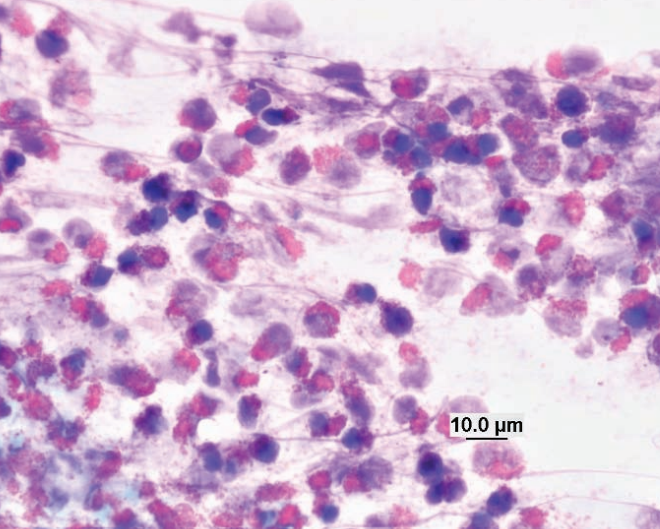
Eosinophilic inflammation
Tiger, tongue
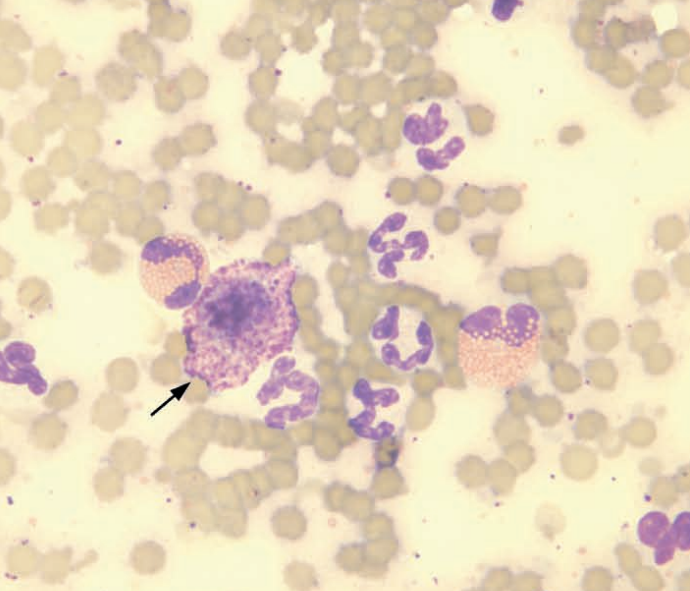
Neutrophils, eosinophils, and a mast cell
Sugar glider, skin
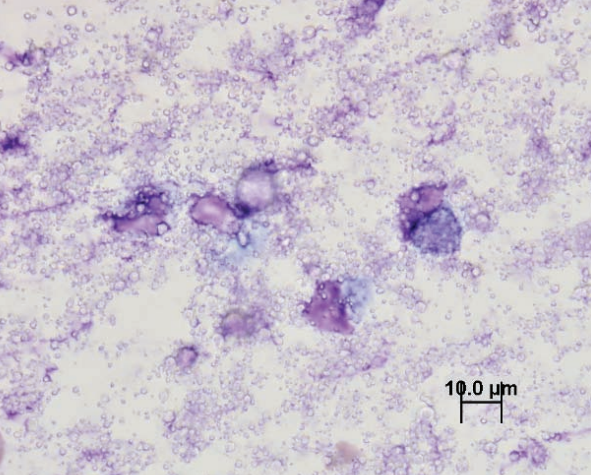
Calcinosis circumscripta
Ferret, liver
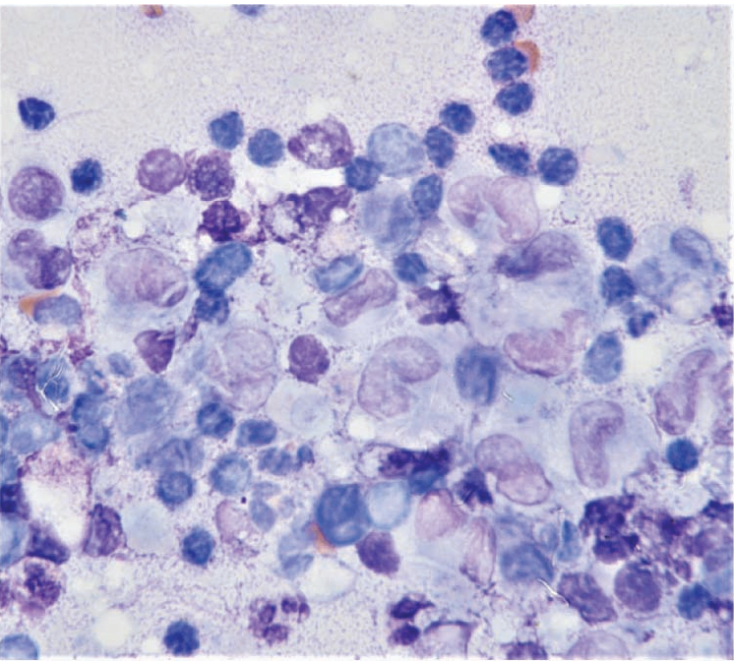
Macrophagic inflammation with Mycobacterium (goodii)
Rabbit, conjunctival swab
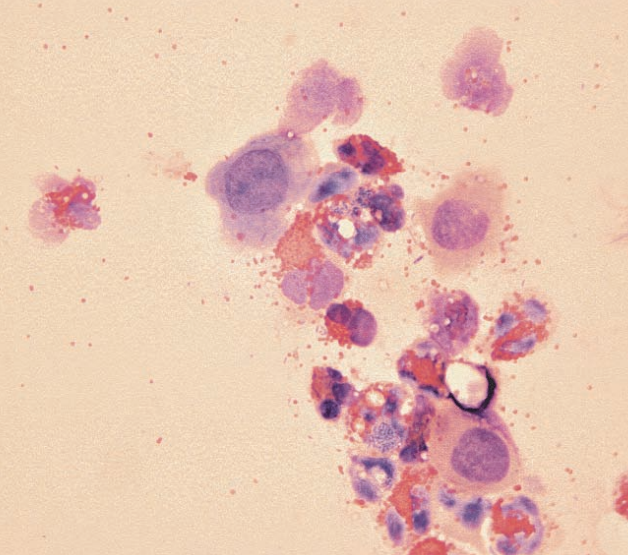
Heterophilic inflammation
Rat, skin
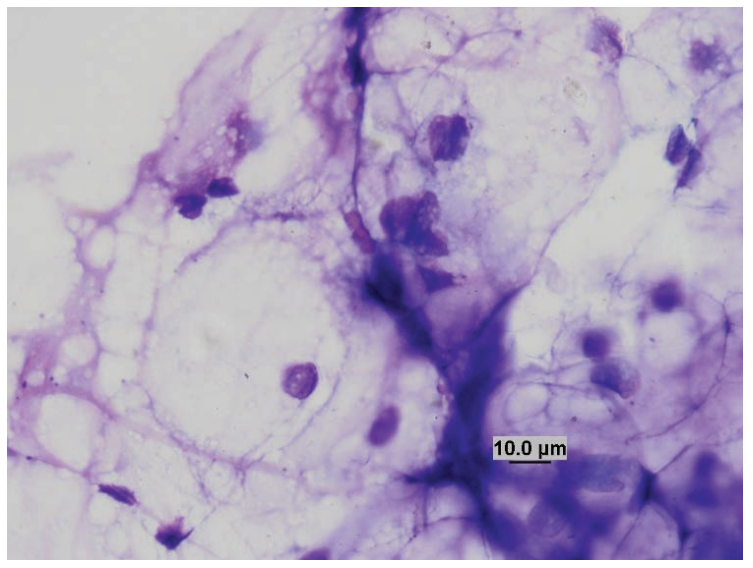
Lipoma
Ferret, skin
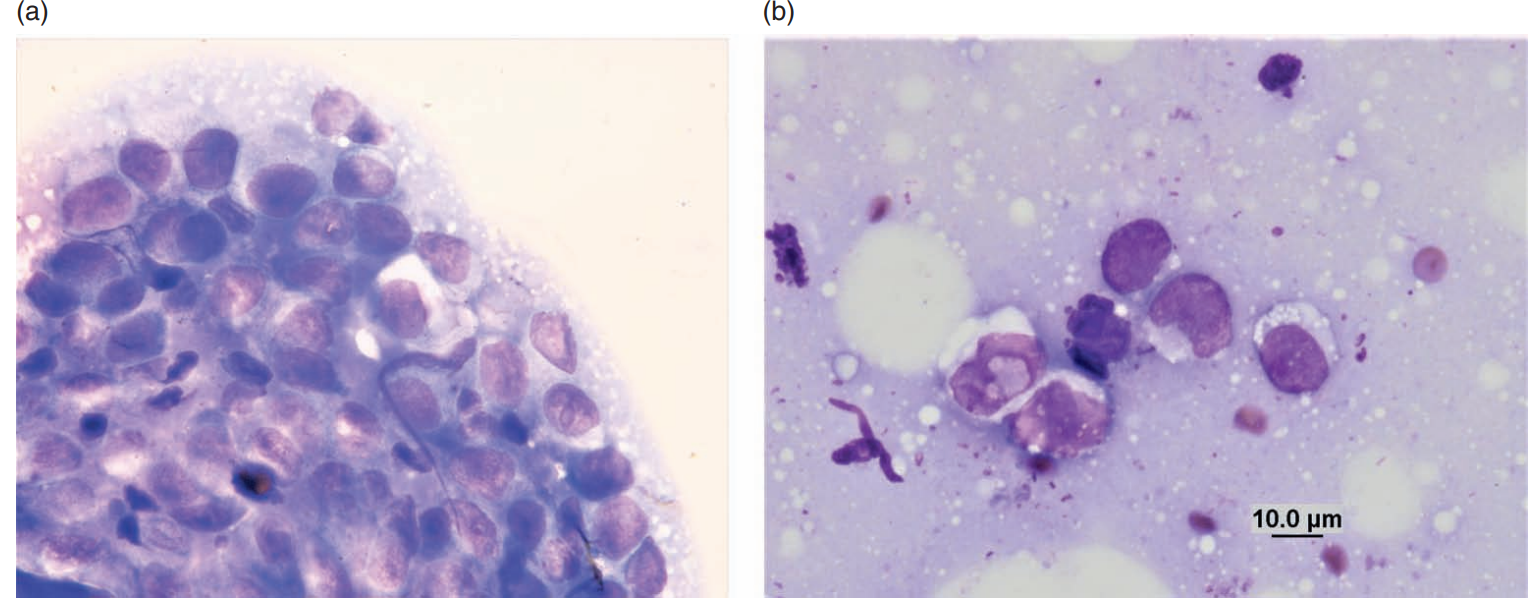
Histiocytoma
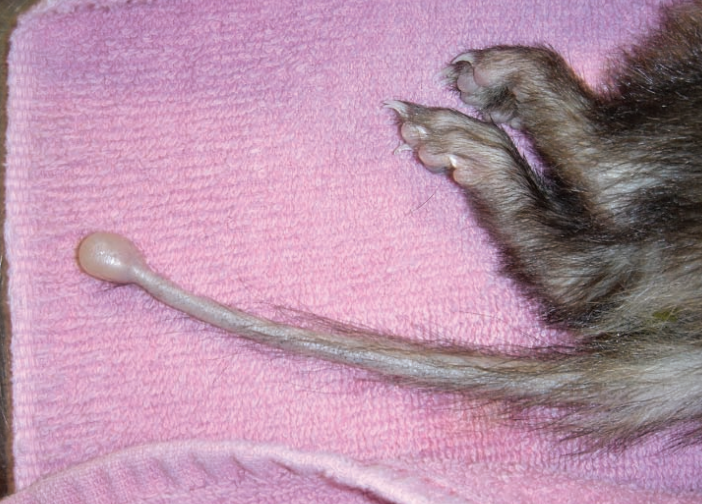
Ferret, chordoma
Ferret, tail
Chordoma
Large foamy physaliphorous cells with a background of mucinous pinkish material
Ferret, tail
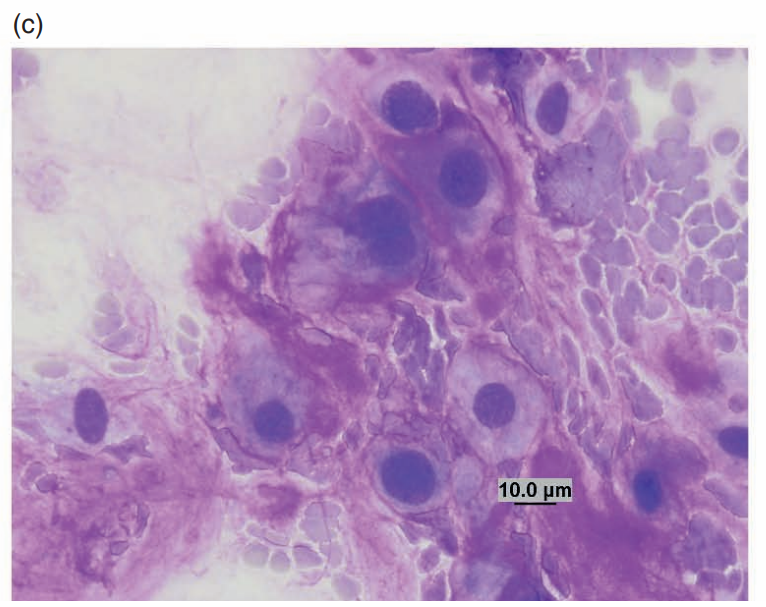
Chordoma
Large foamy physaliphorous cells with a background of mucinous pinkish material
Rat, ear
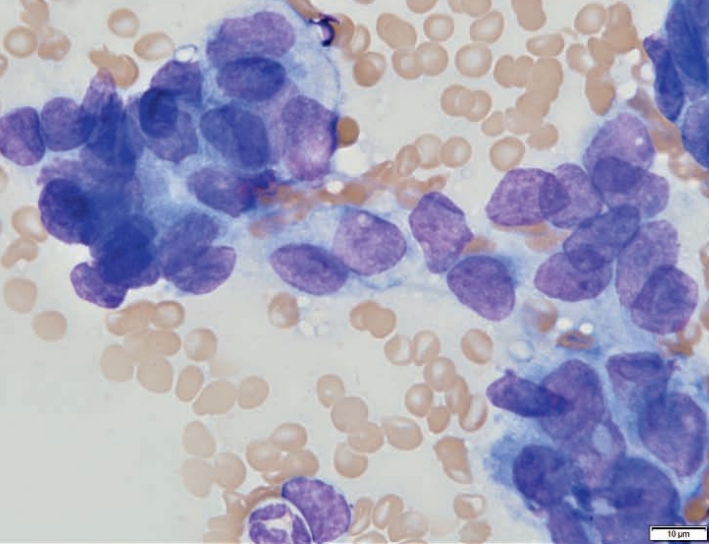
Zymbal gland adenoma
Rat, ear
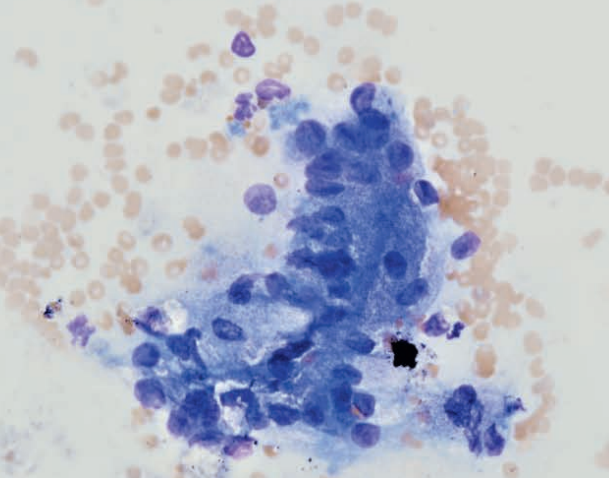
Zymbal gland adenoma
Caudal abdominal mass in a hedgehog
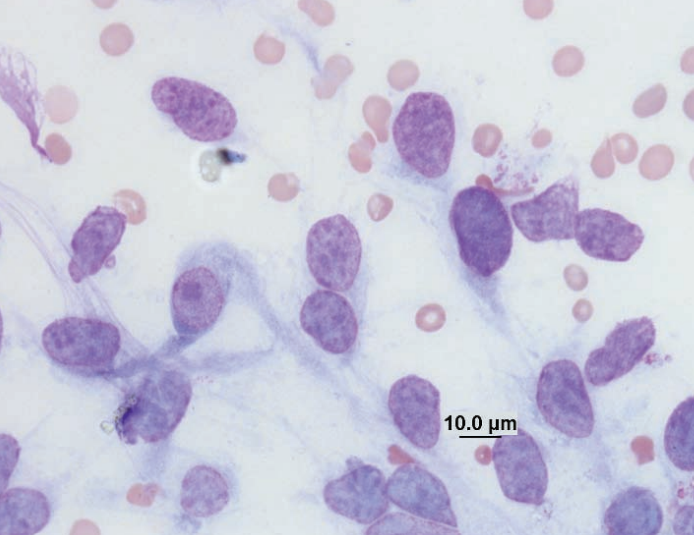
Uterine leiomyoma
Ferret, prostate
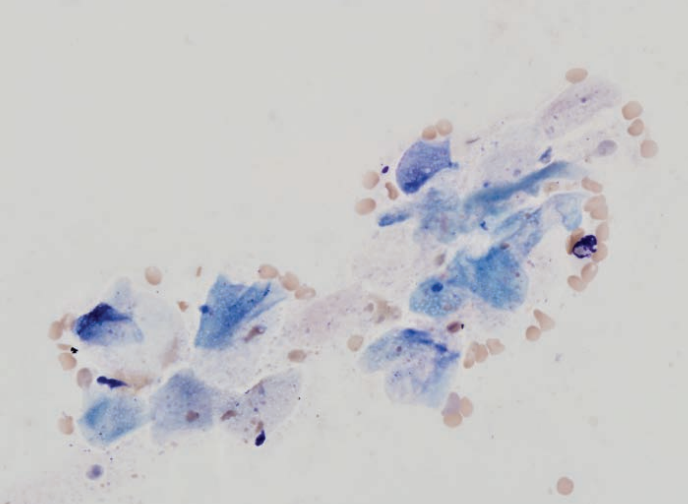
Squamous metaplasia
Ferret, lymph node
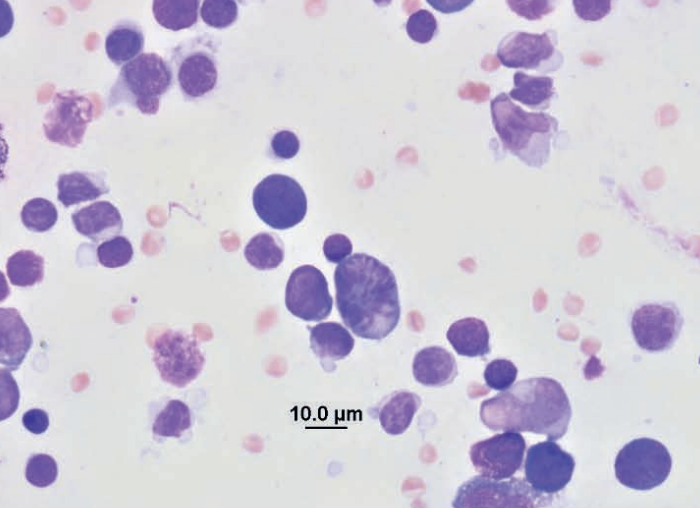
Reactive
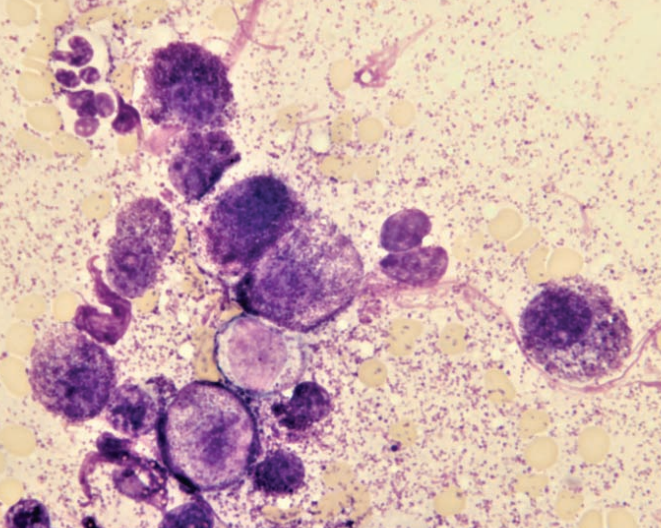
Ferret, spleen
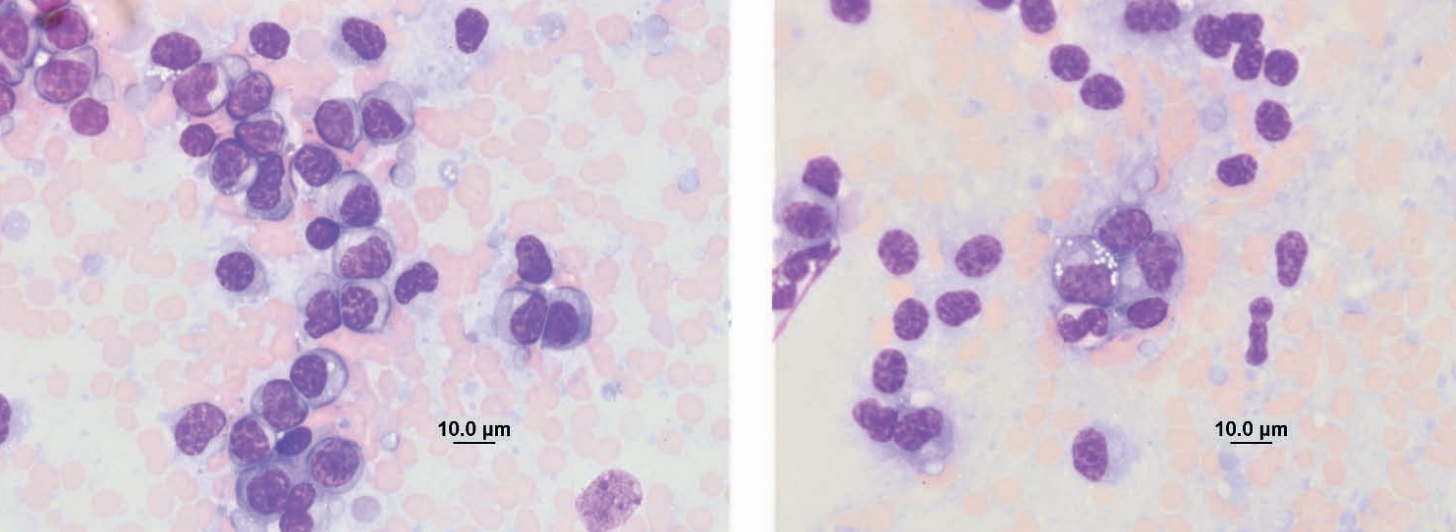
Multiple myeloma
Guinea pig, neck mass
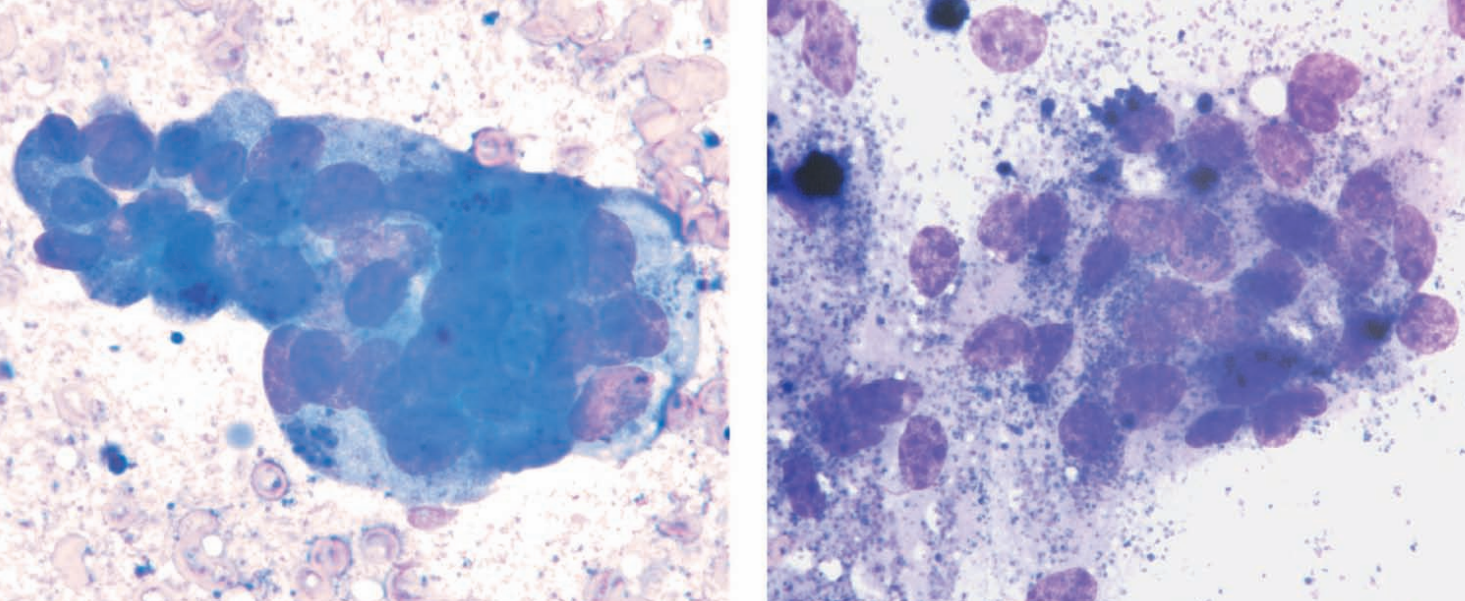
Thyroid adenoma
Tiger, skin
MCT
Rat
Histiocytic sarcoma
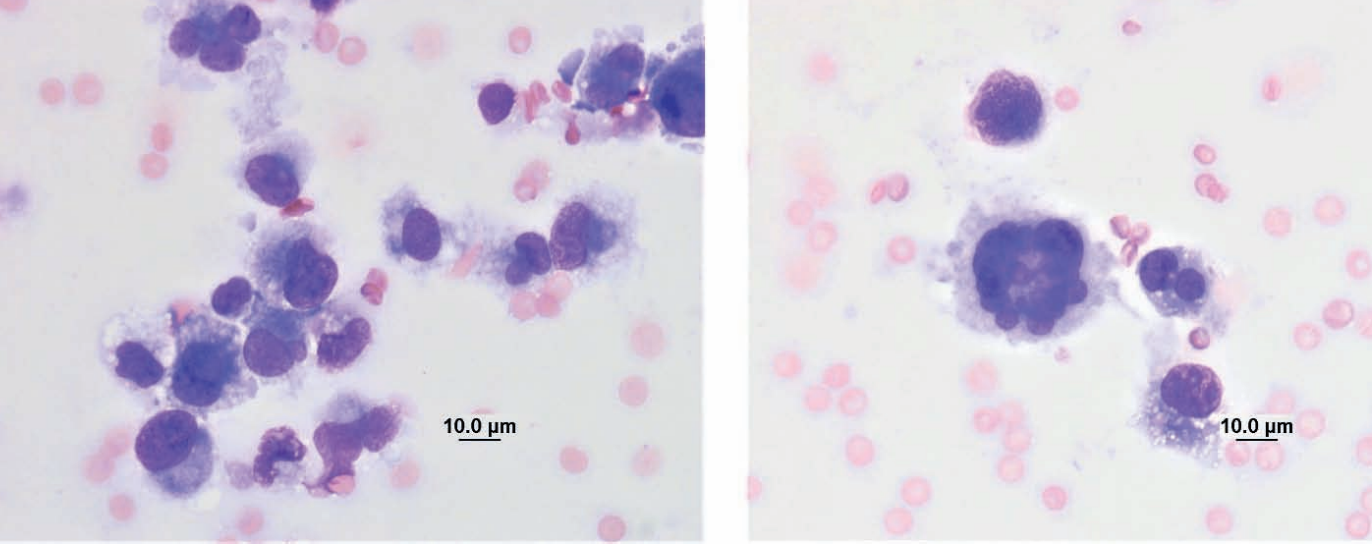
Ferret, lymph node
Lymphoma
Ferret, lymph node
Lymphoma
Ferret, abdominal mass
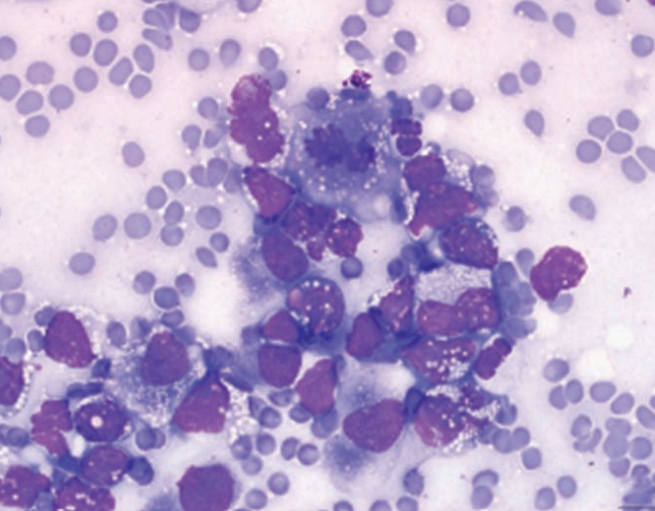
T-cell lymphoma with pleomorphism
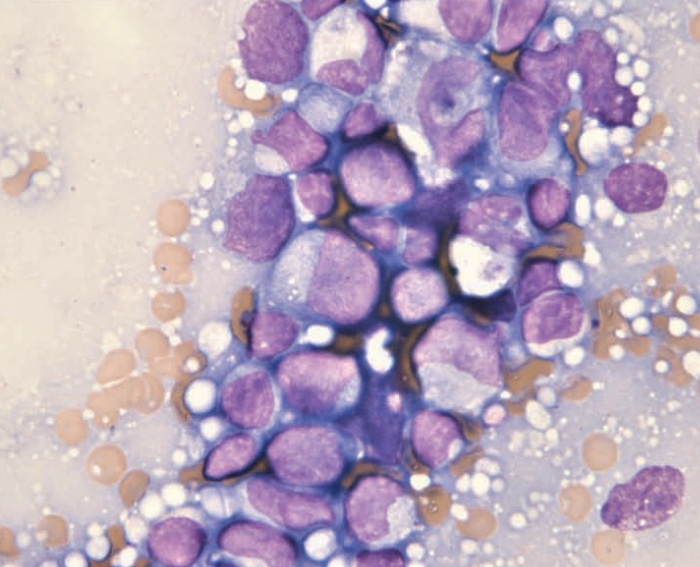
Ferret, spleen
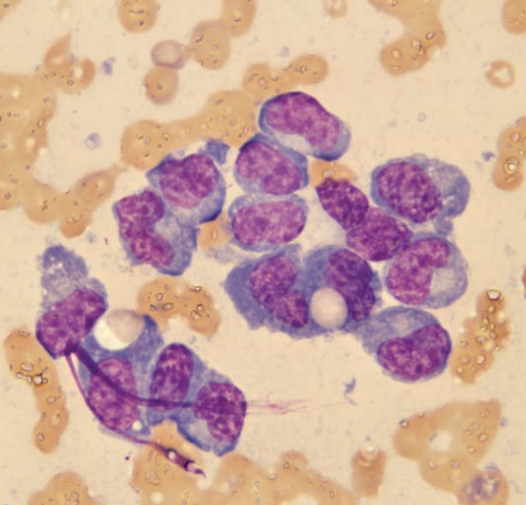
Multiple myeloma
Ferret
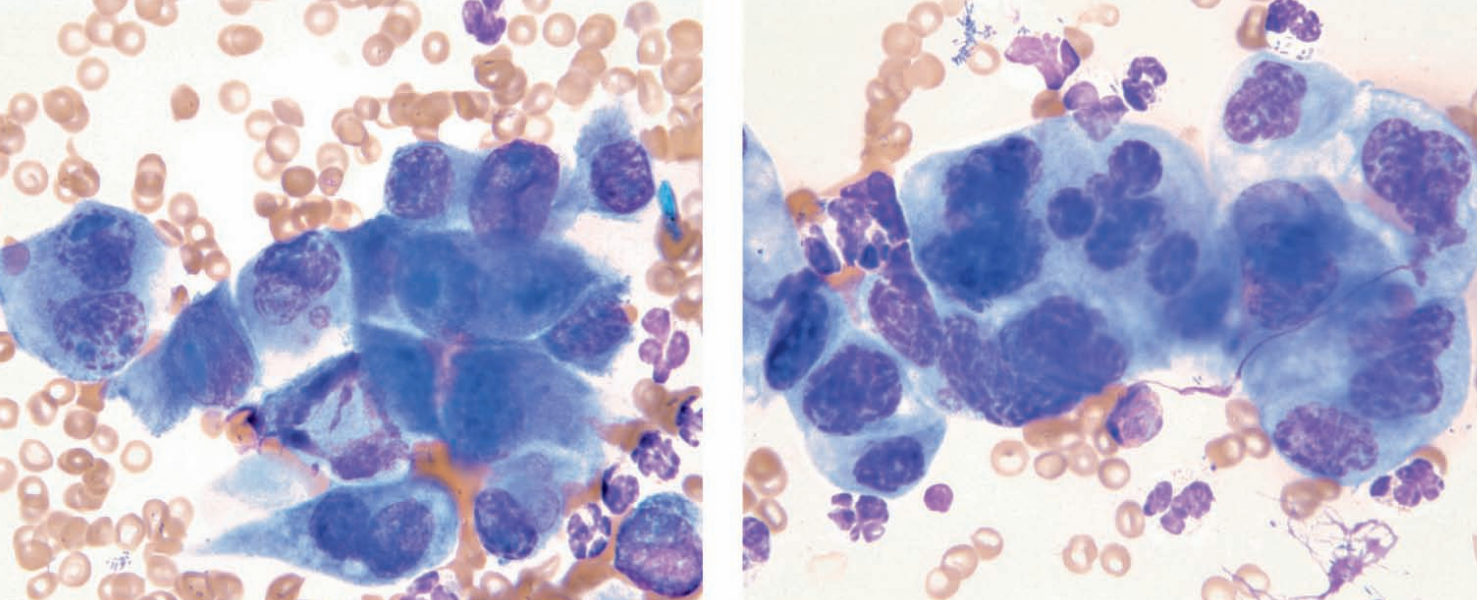
Carcinoma
Guinea pig, uterine impression
Endometrial adenoma
Hamster, ventral skin
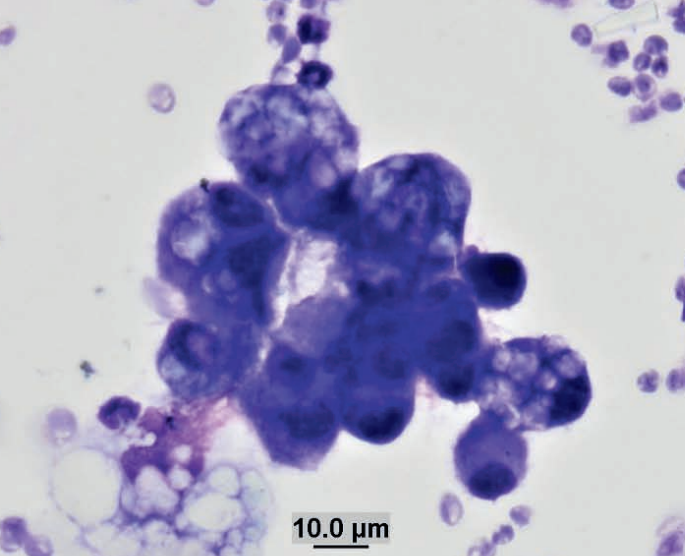
Mammary adenocarcinoma
Ferret, abdominal mass
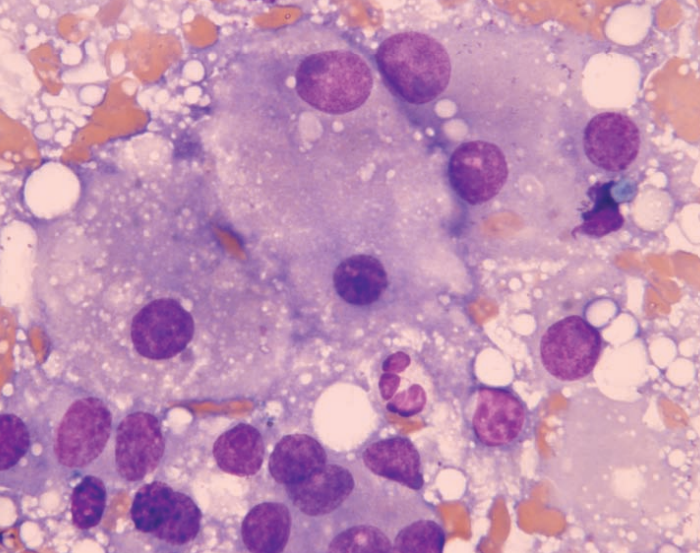
Adrenal adenocarcinoma
Ferret, abdominal mass
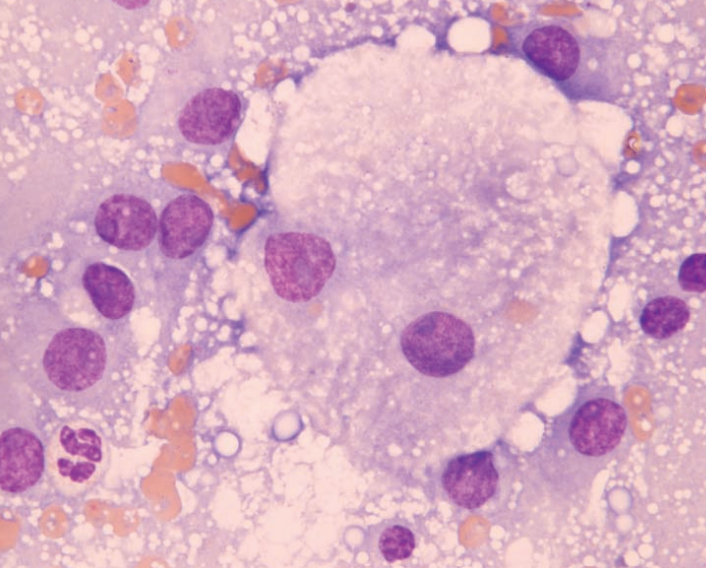
Adrenal adenocarcinoma
Hedgehog, oral FNA
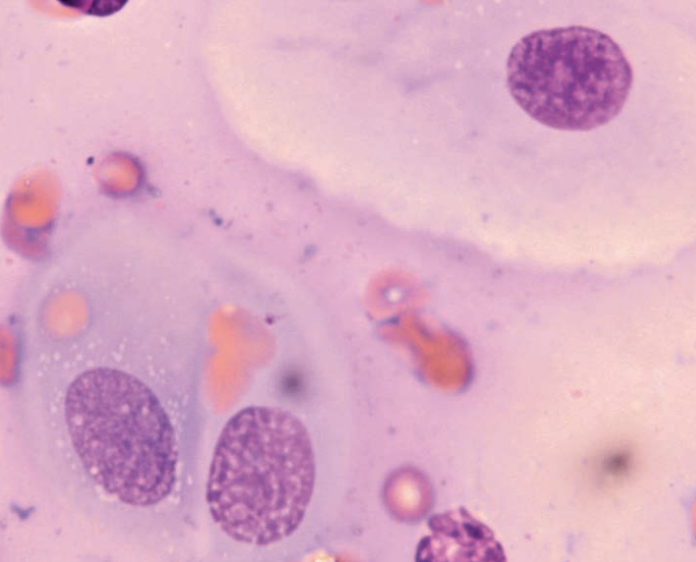
SCC
Gerbil, abdominal mass
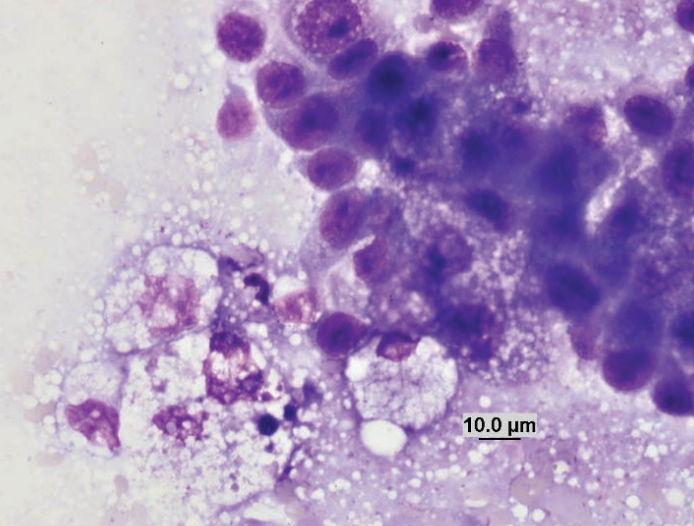
Poorly-differentiated sarcoma
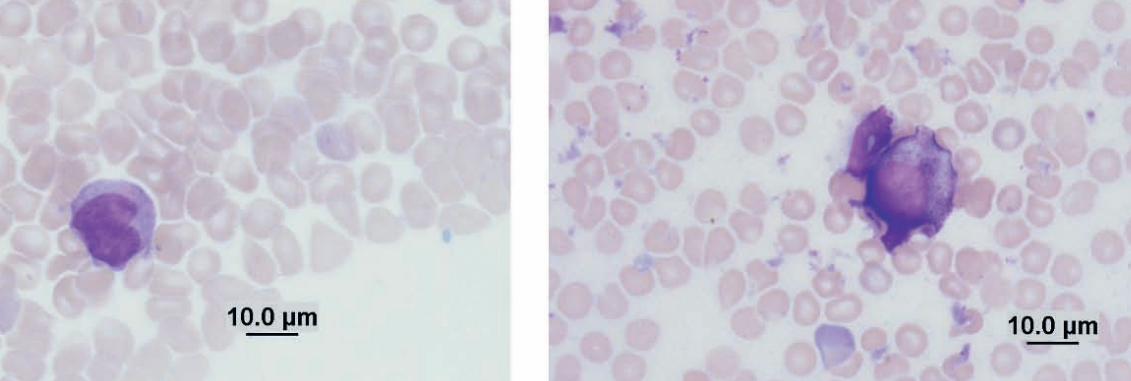
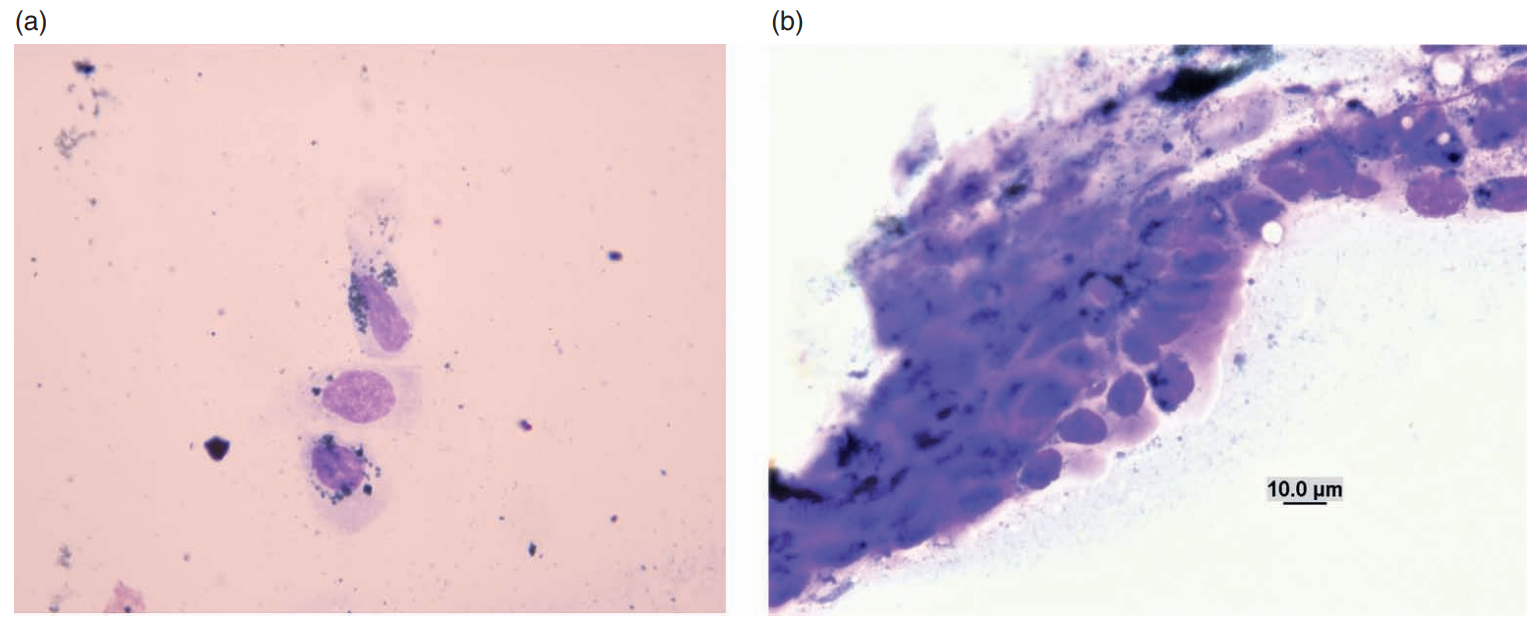
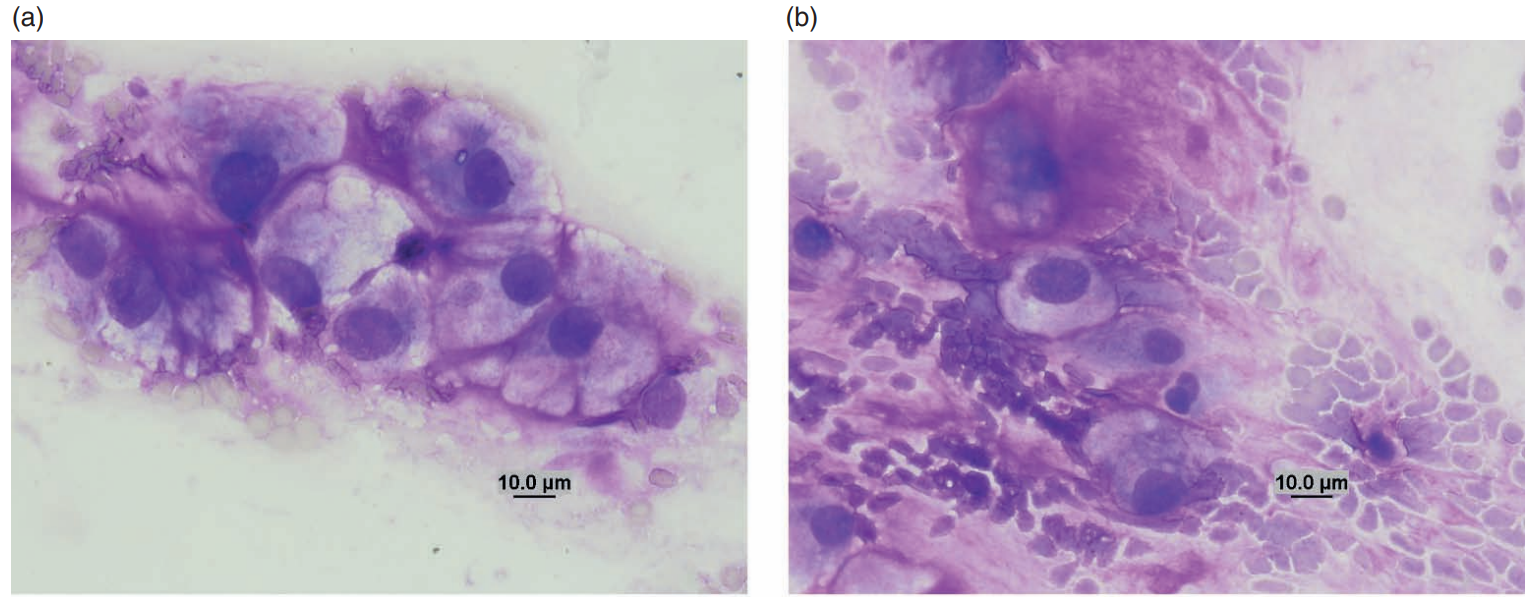
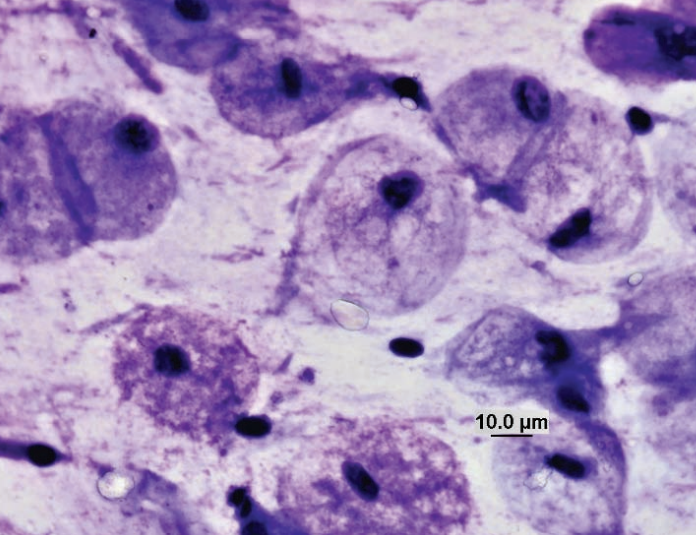
Rabbit, nodule on muzzle
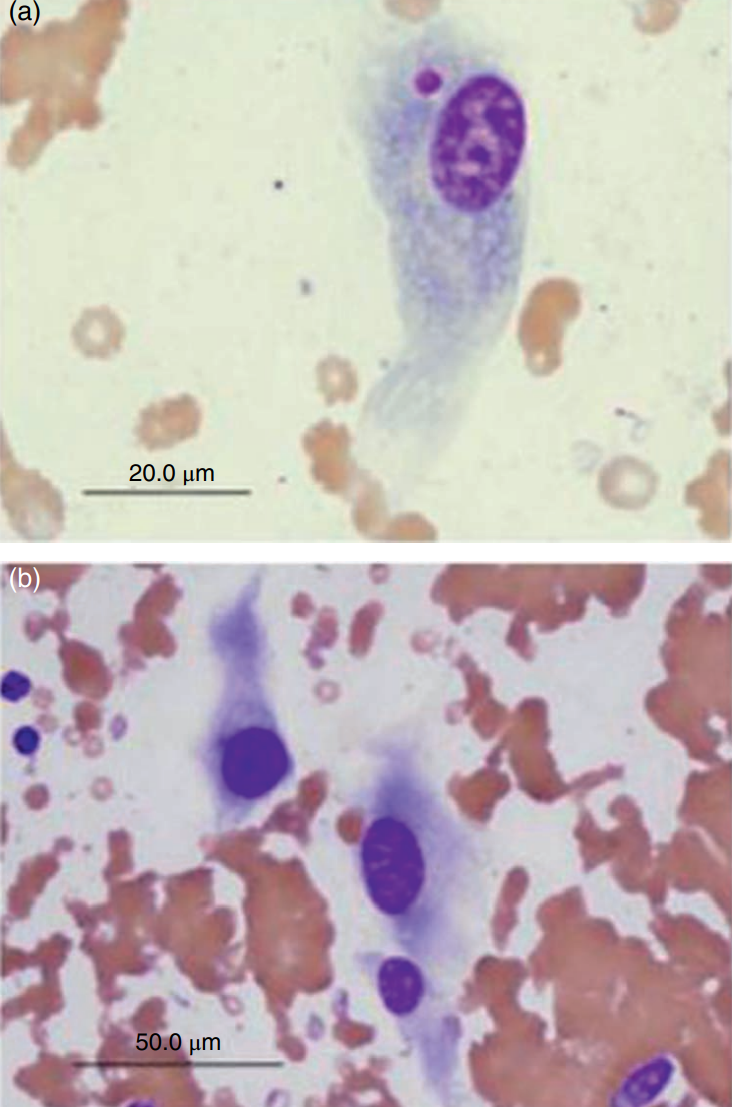
Shope fibroma
Rabbit (Shope) fibroma virus (Poxviridae)
The virus ordinarily produces localized fibromas where cytologic preparations consist of spindle-shaped cells exhibiting moderate anisocytosis and anisokaryosis (Figures 7.86a and 7.86b). The nuclei are large (1–3 times the size of erythrocytes), round to oval, eccentric, and exhibit finely stippled chromatin with multiple nucleoli. The basophilic cytoplasm occasionally contains round to oval eosinophilic inclusions that vary in size (3–5 μm) and shape
Sugar glider, mass projecting from right aspect of marsupium
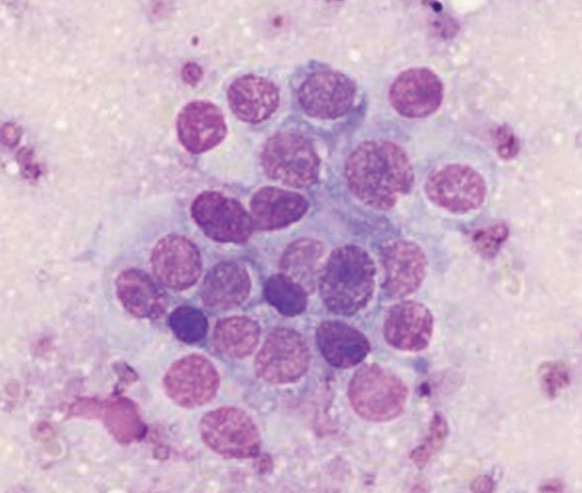
Carcinoma or ACA, ddx amelanotic melanoma
Ferret, perianal mass
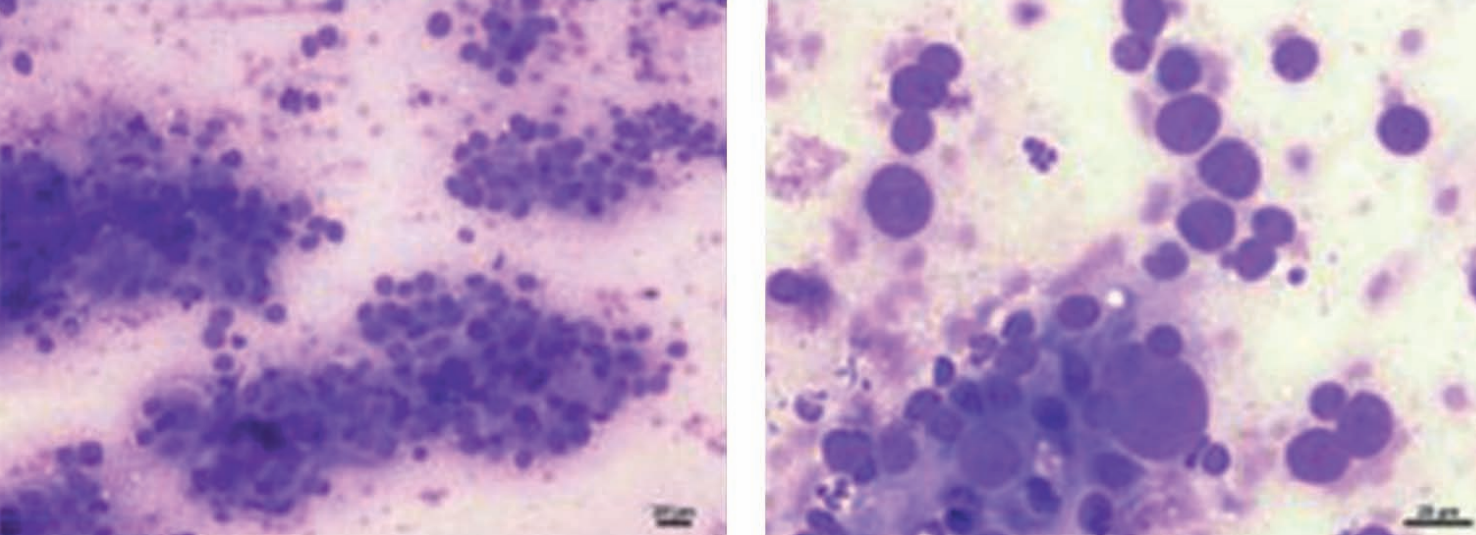
Anal sac adenocarcinoma
Guinea pig, skin
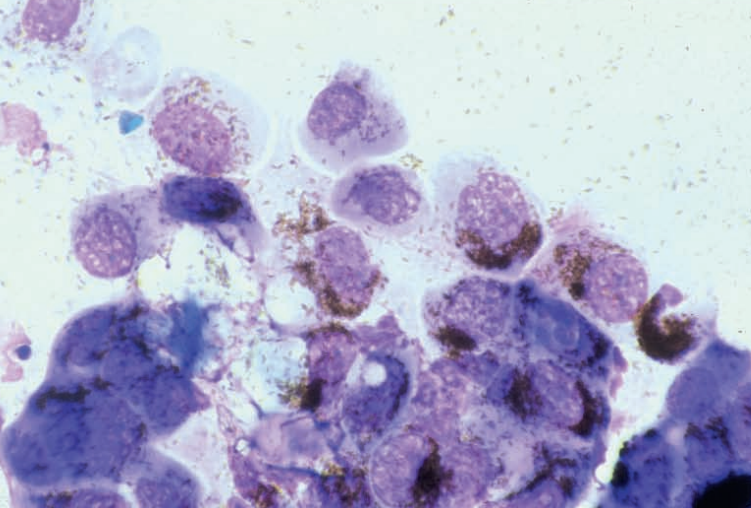
Melanoma
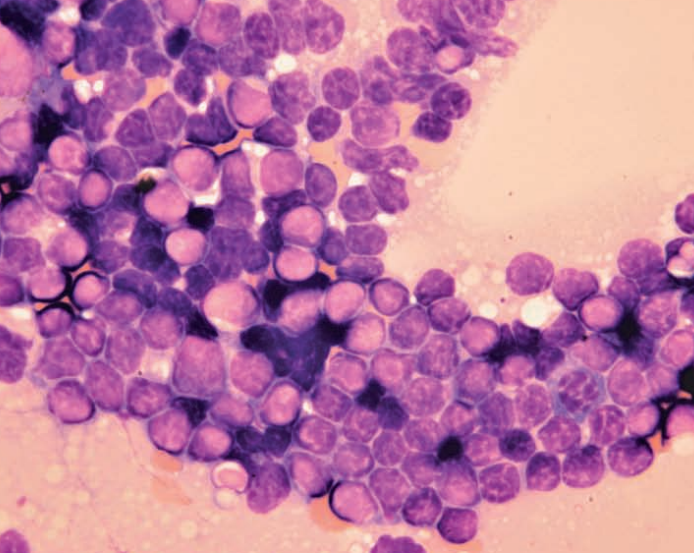
Ferret, abdominal mass
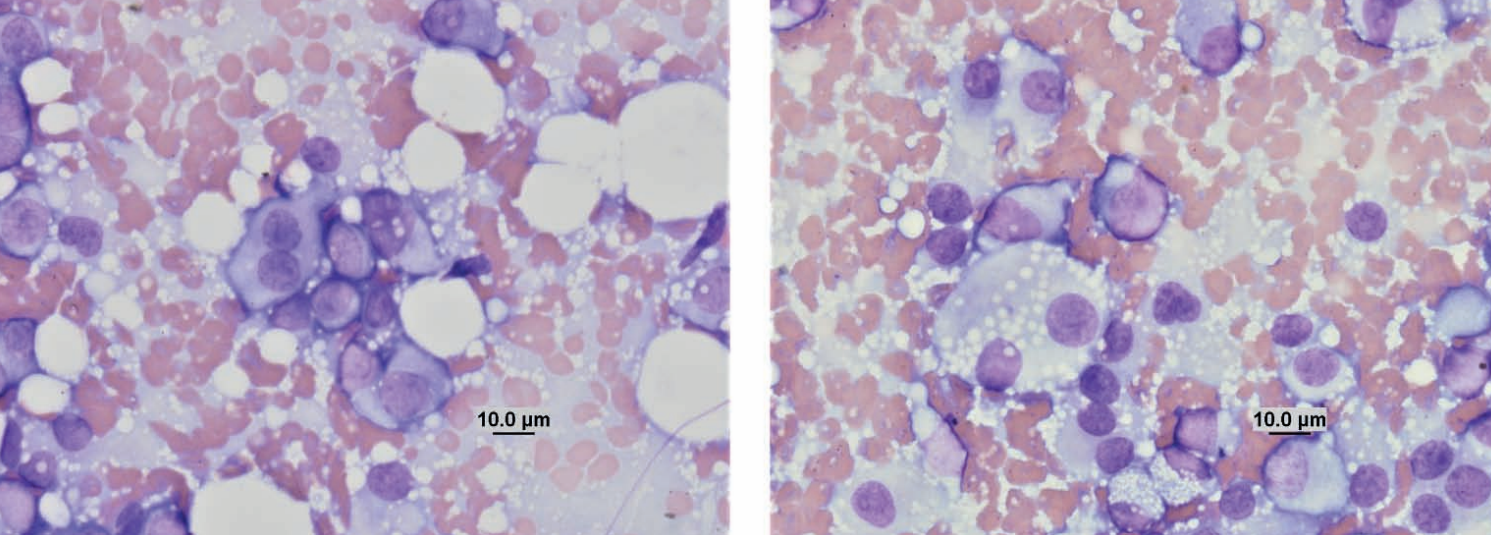
Ferret, abdominal mass
Term
Adrenal gland adenoma
Hedgehog, right cervical mass
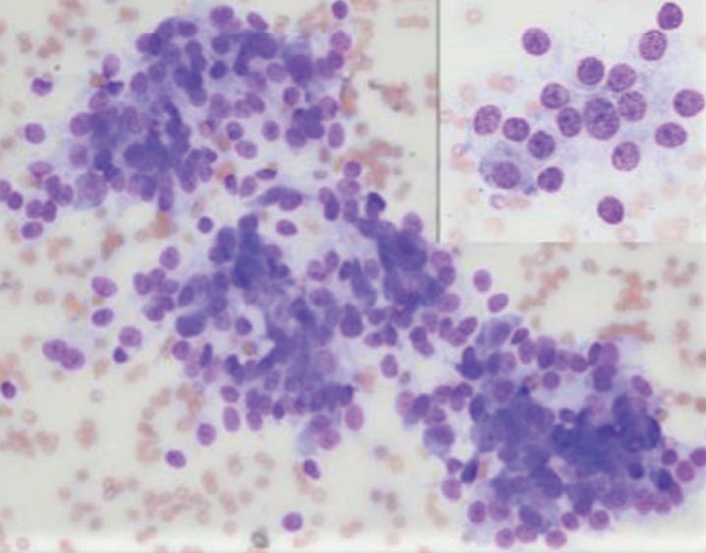
Thyroid carcinoma
Ferret, abdominal fluid cytospin
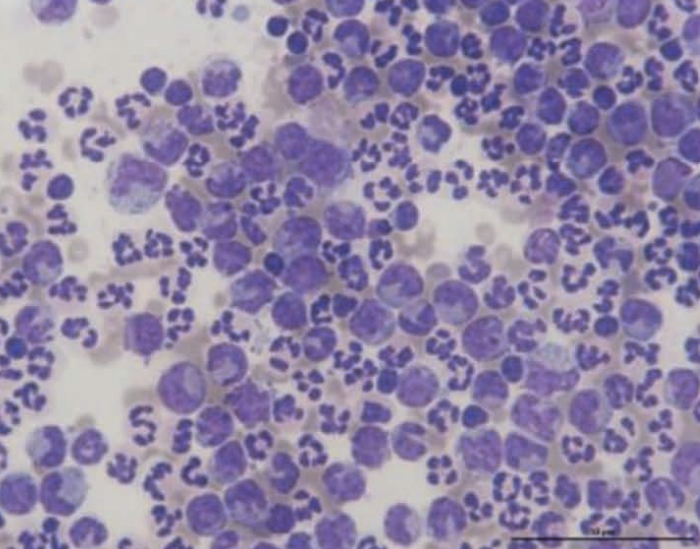
Chylous effusion, but see mixed population of nondegenerate neutrophils and macrophages that show intermittent foamy cytoplasm. Small lymphocytes are in low numbers.
Ferret, abdominal mass
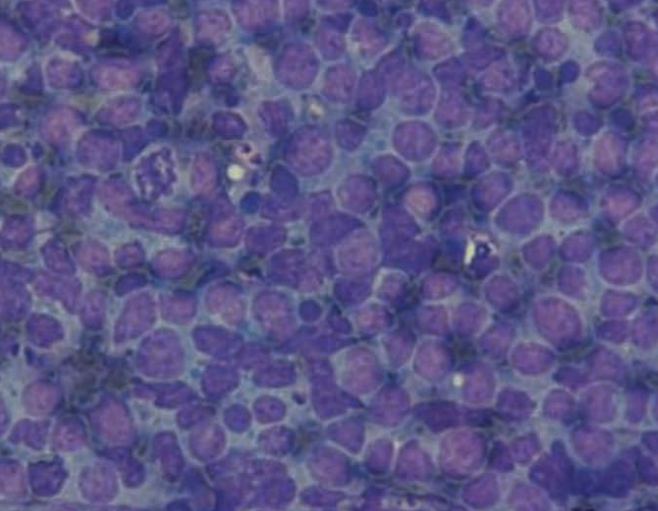
Lymphoma
Ferret, fluctuant mass on the head
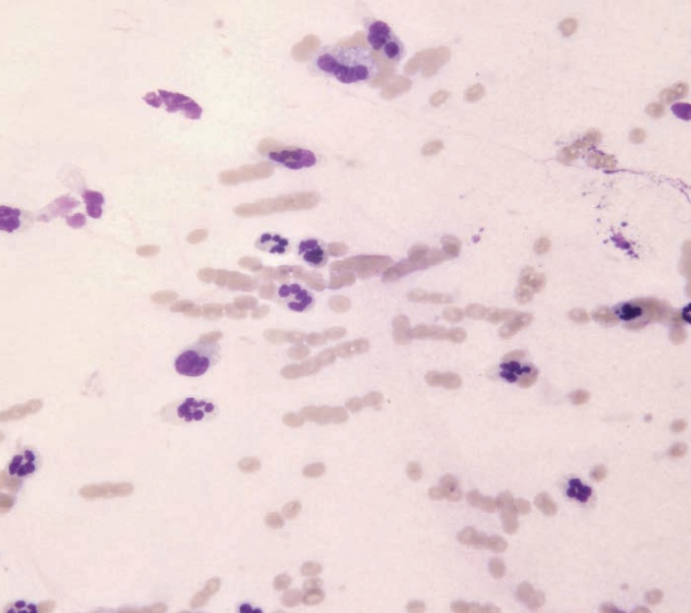
Mucocele
Hamster, fecal smear
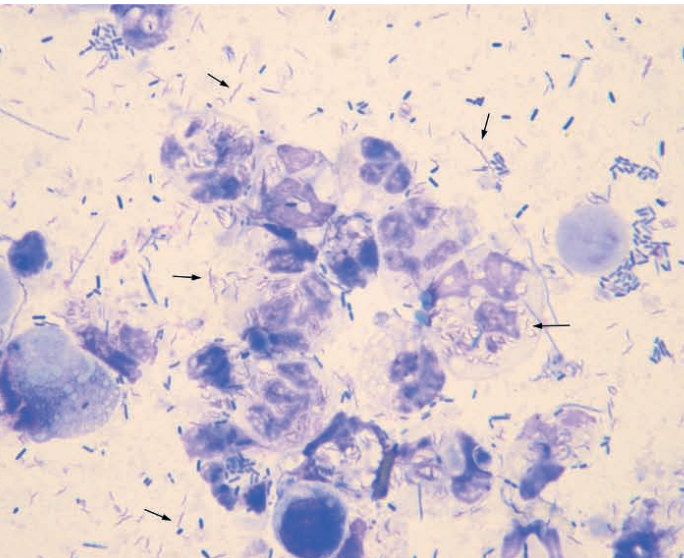
Campylobacter-like organisms in case of septic colitis
Hamster, rectal swab
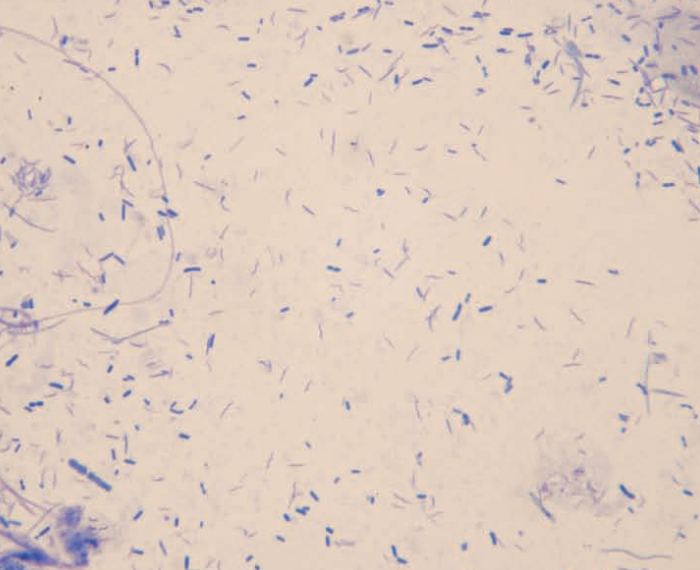
Campylobacter-like organisms in a case with colitis
Hamster, fecal smear
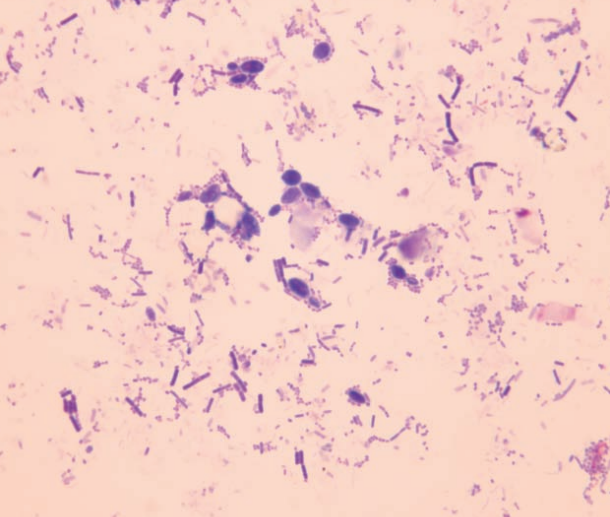
Budding yeast in a case with diarrhea
Ferret, lung
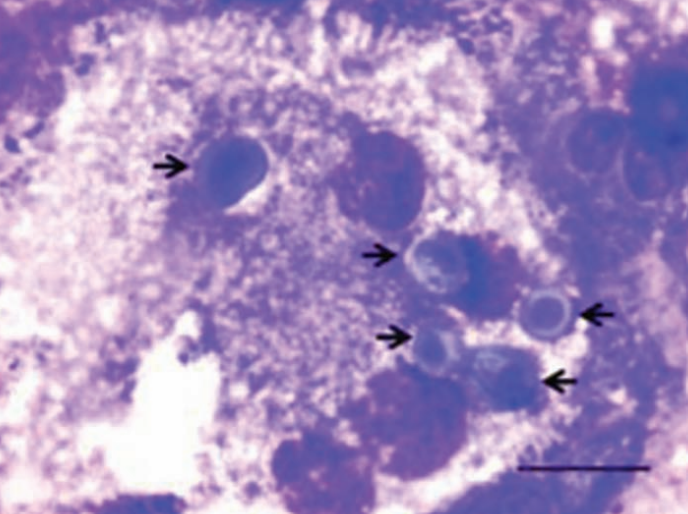
Blastomyces dermatitidis
Rabbit, fecal smear
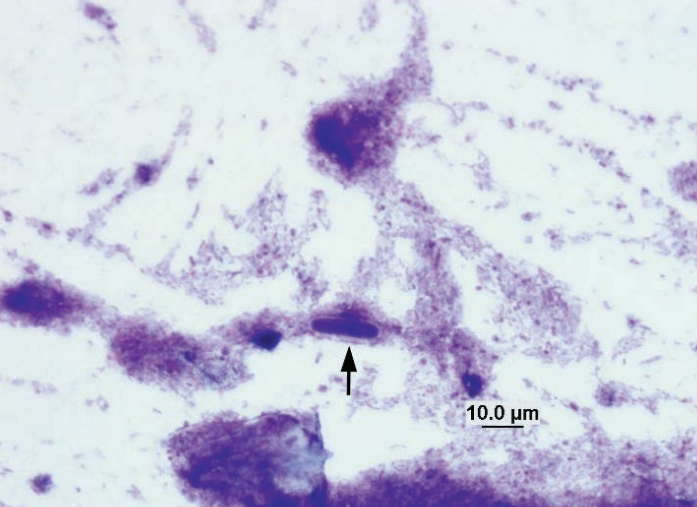
Saccharomyces spp. yeast, part of normal flora of the cecum
Rabbit, fecal smear
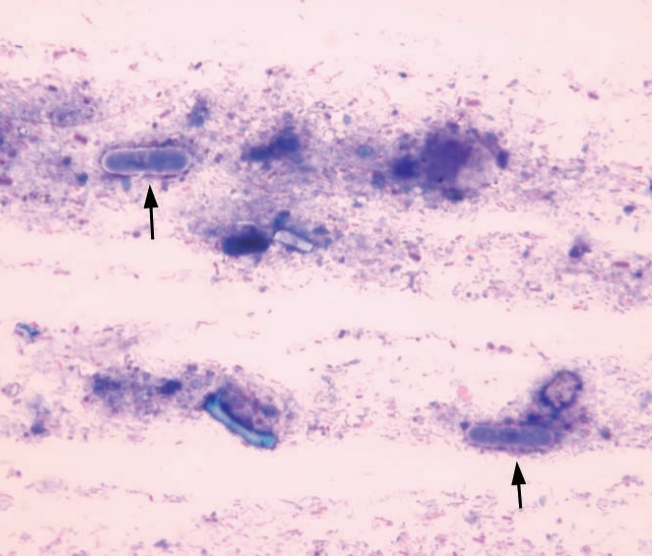
Saccharomyces spp. yeast, part of normal flora of the cecum
Rat, fecal smear
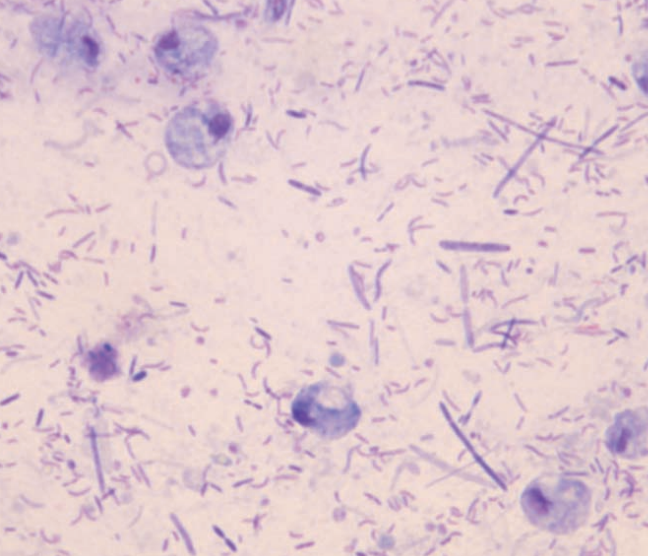
Trichomonas in a case with diarrhea
Hedgehog, swelling under right forelimb
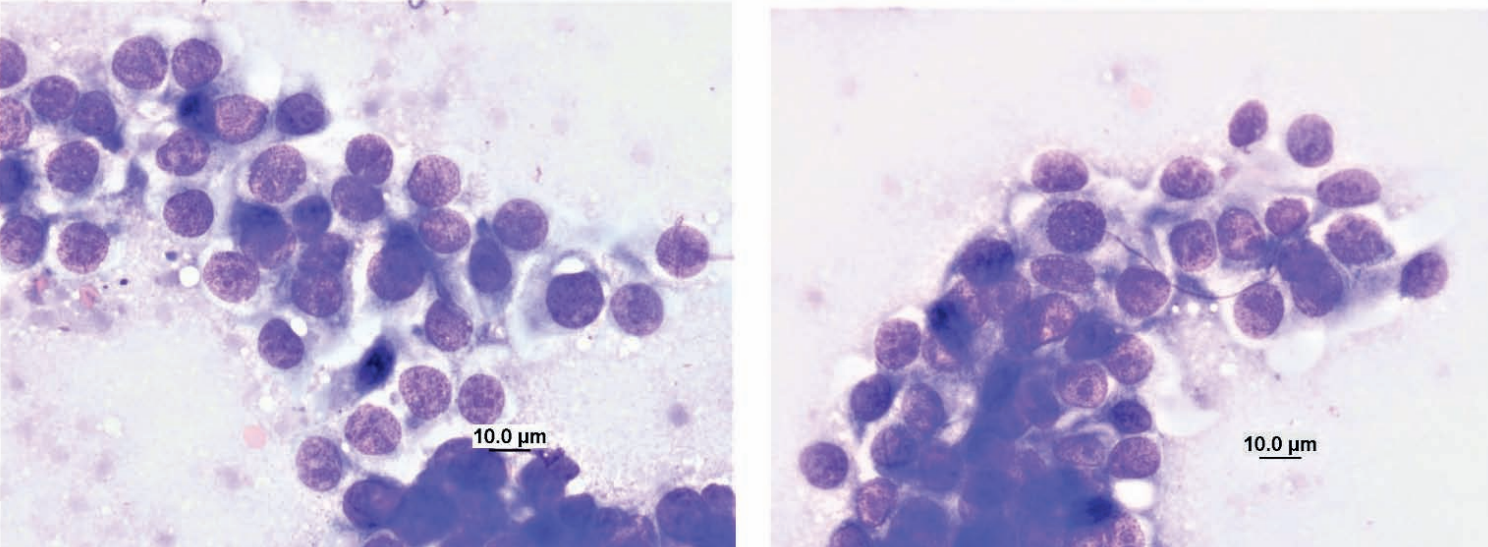
Mammary adenocarcinoma
Rat, rapidly growing mass on face
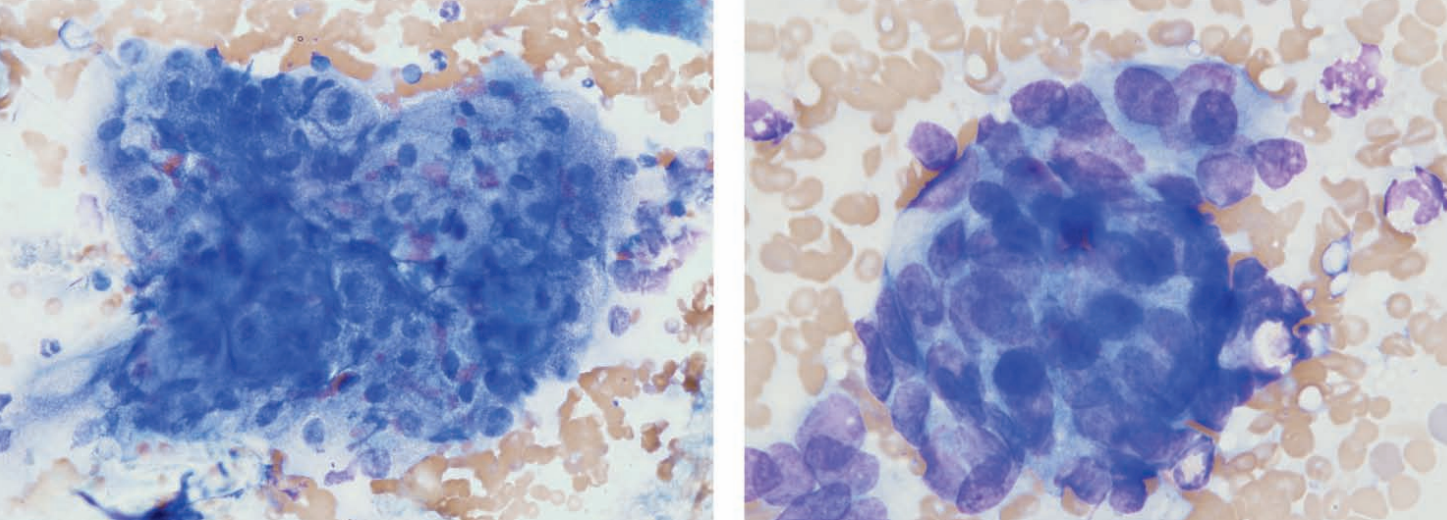
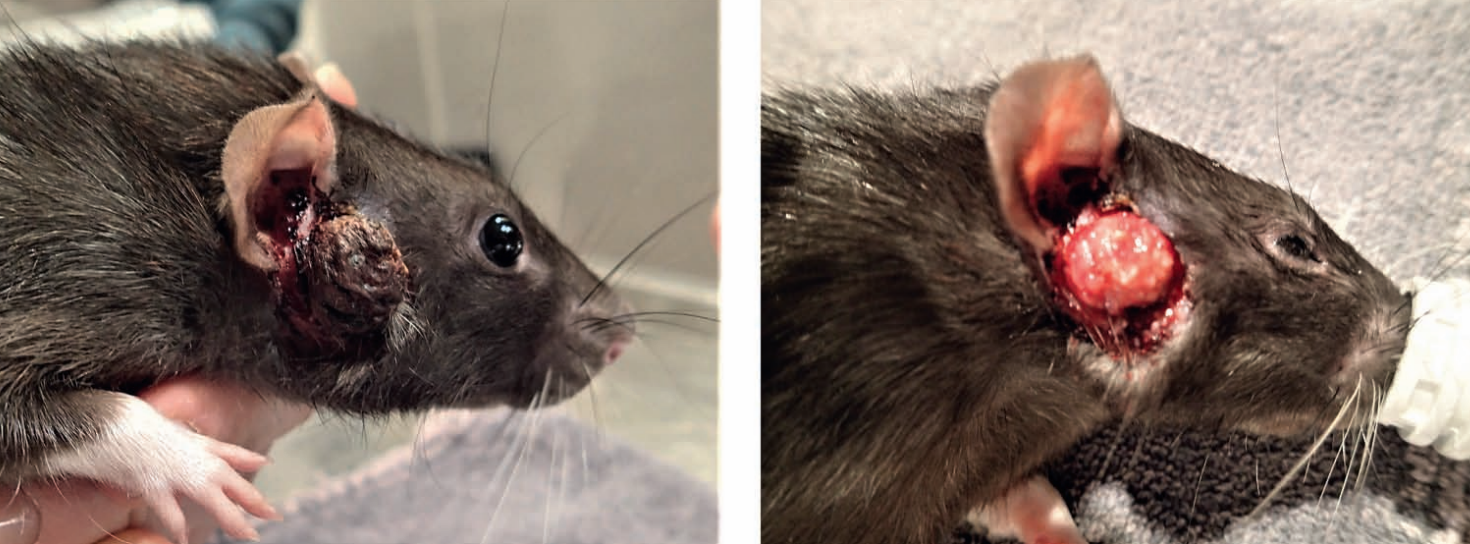
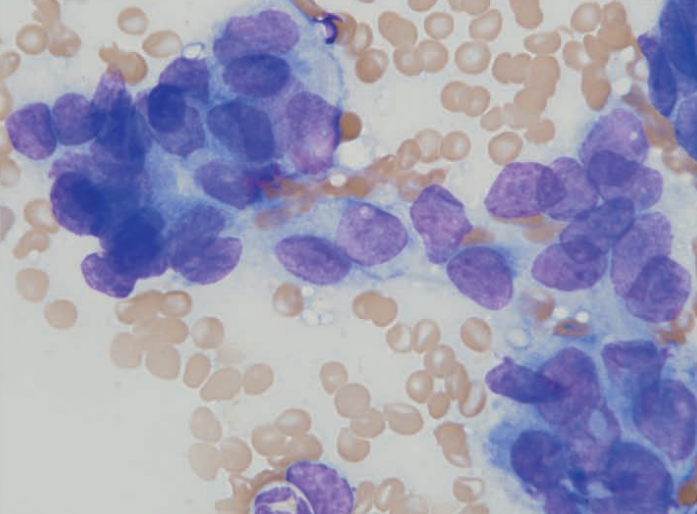
Ddx sebaceous carcinoma, Zymbal gland adenocarcinoma based on location
Hedgehog, vaginal mass
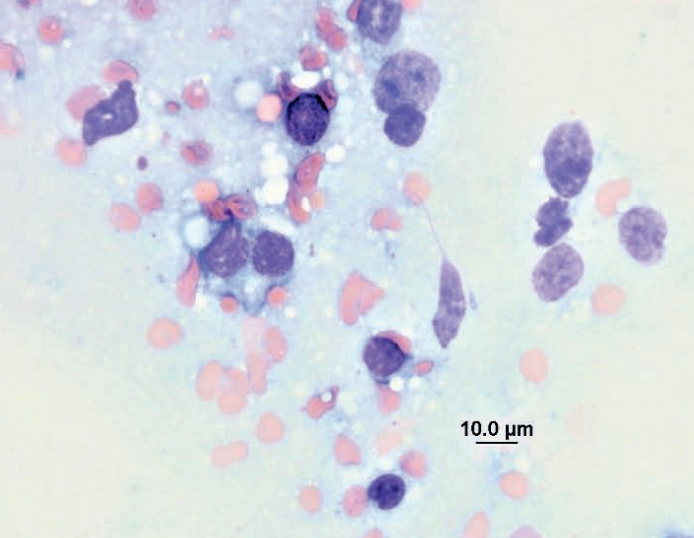
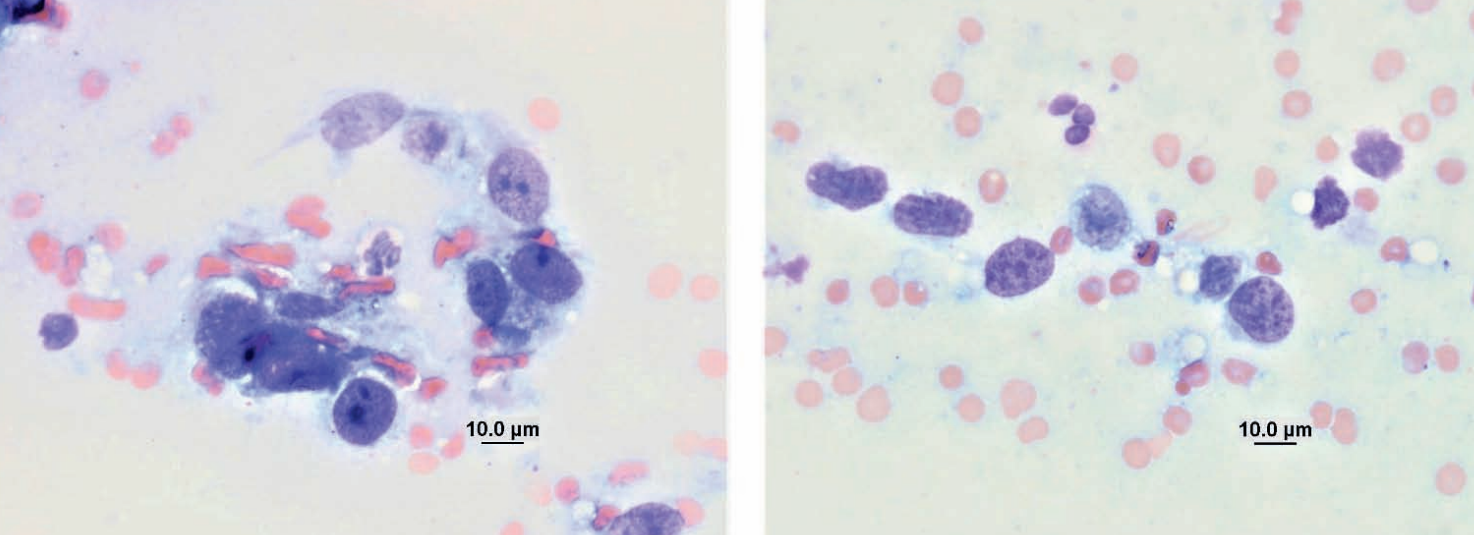
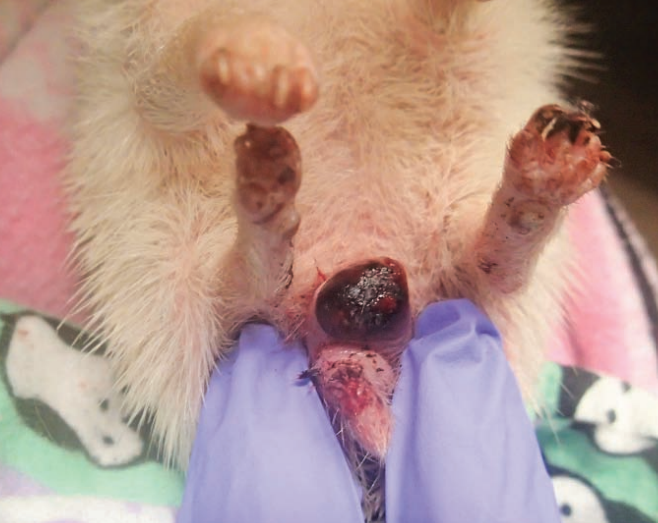
Leiomyosarcoma, was also within the uterine horn
Sugar glider, mass in left axilla
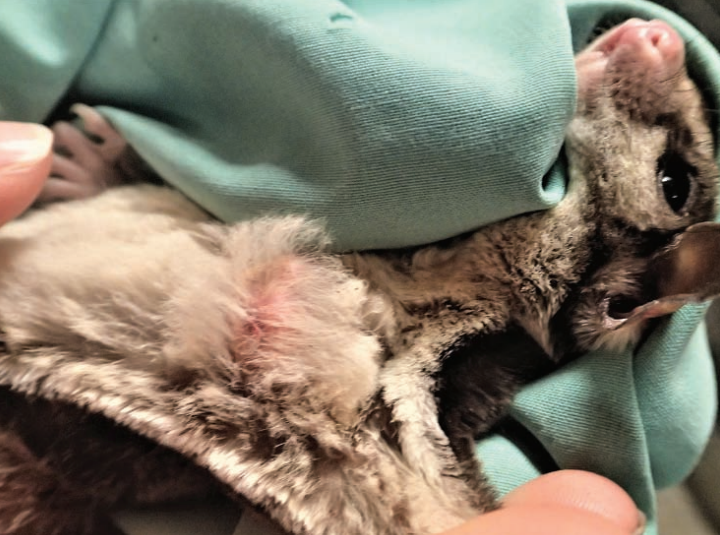
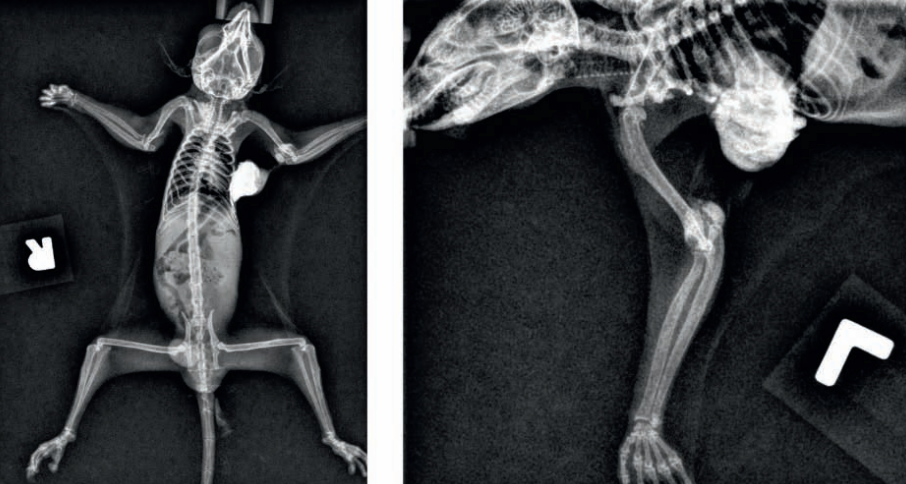
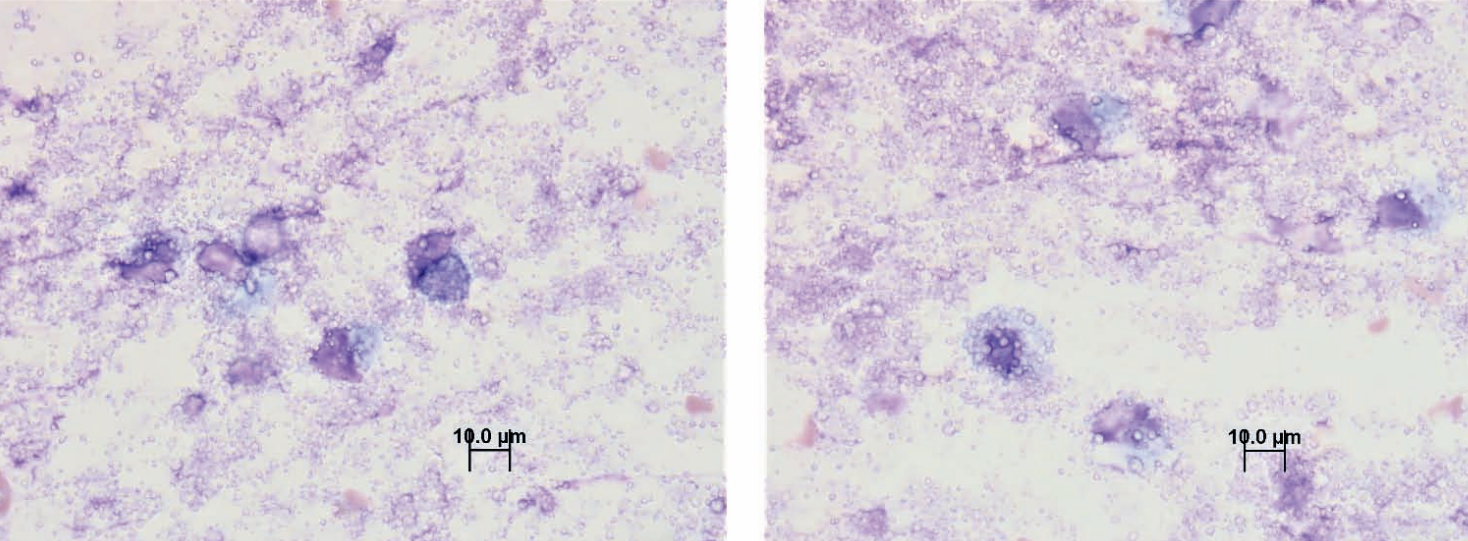
Calcinosis circumscripta
Blood smear from a turkey
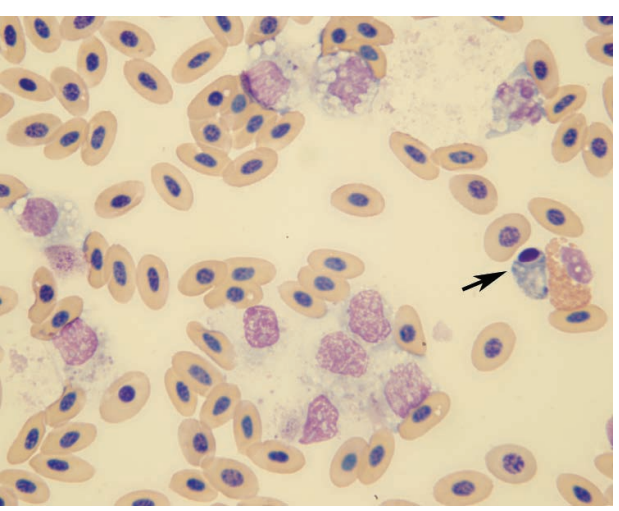
Clumping, vacuolation, and pyknotic nuclei from 48h in EDTA
Avian blood smears
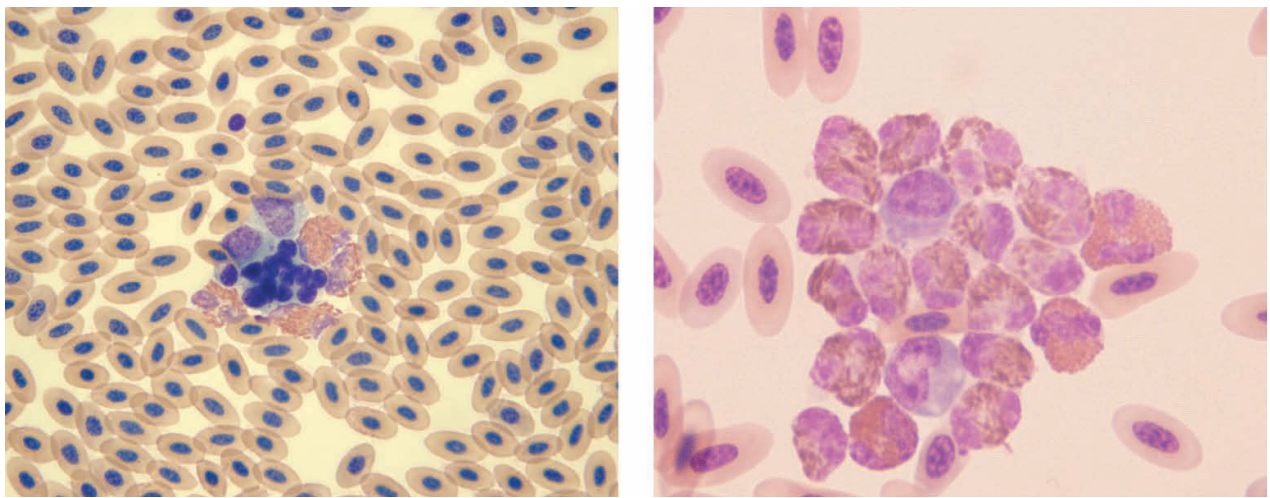
Clumping due to heparin
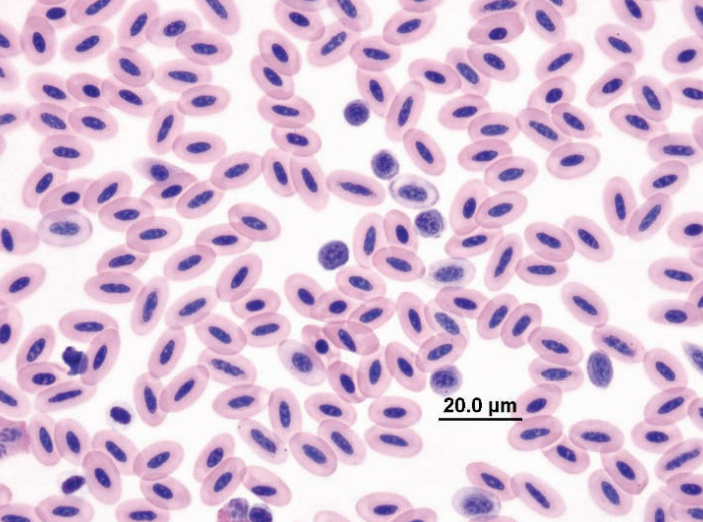
Blood smear from eclectus parrot
Hypochromic RBCs
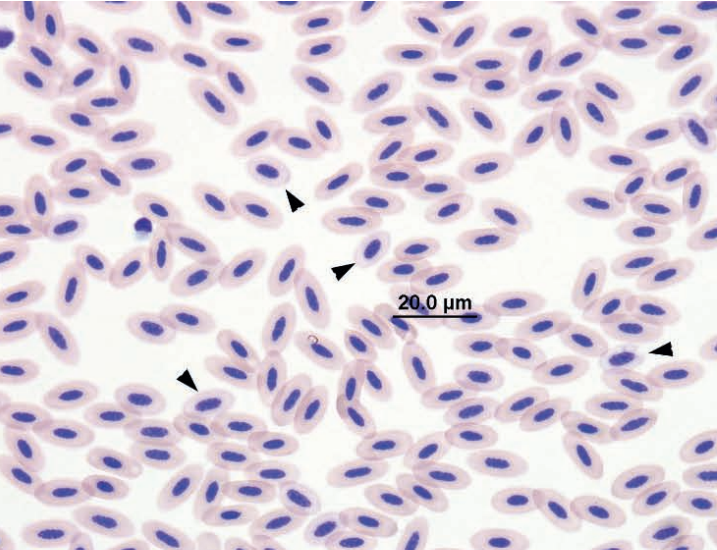
Blood smear from a turkey vulture
Increased numbers of immature erythrocytes (early and mid-polychromatic rubricytes) without an appropriate increase in polychromasia due to lead poisoning
Avian blood smear
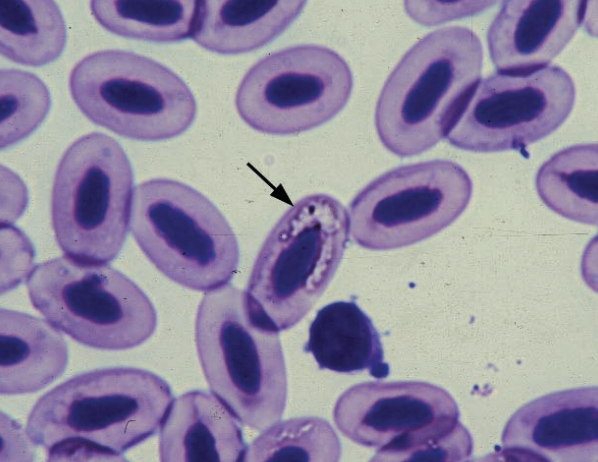
Artifact from slow drying
Blood smear from an eclectus parrot
Agglutination and erythrophagia
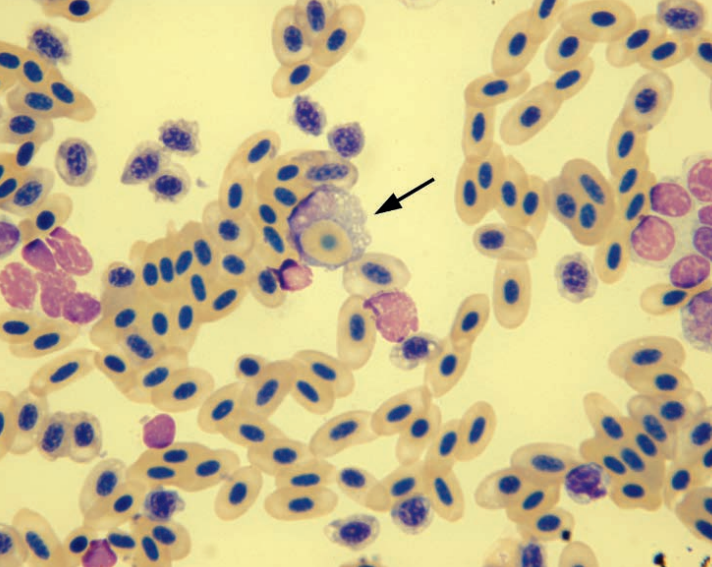
Blood smear from a hawk
Basophilic rubricyte and increased polychromatophils
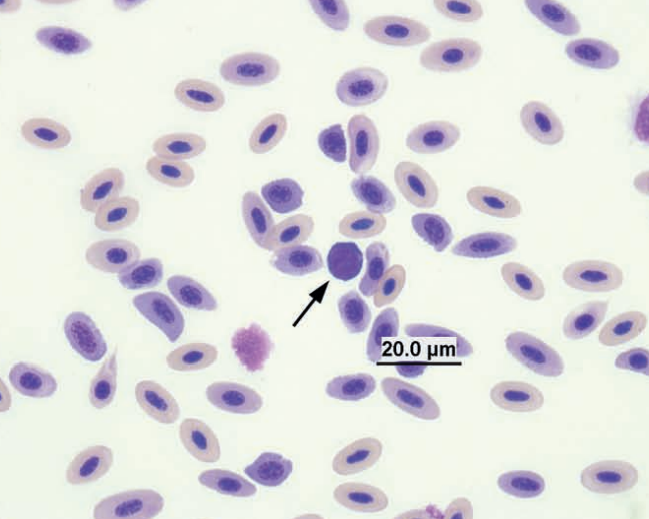
Amazon parrot blood
Lymphocyte
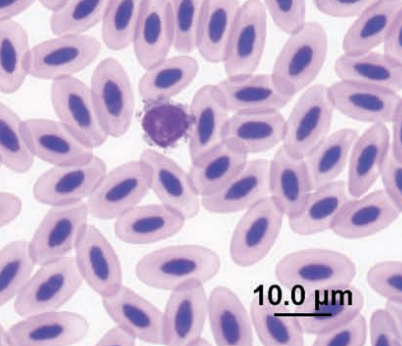
Conure blood
Immature erythrocyte—early polychromatic rubricyte (arrow), lymphocyte (arrowhead), and thrombocytes
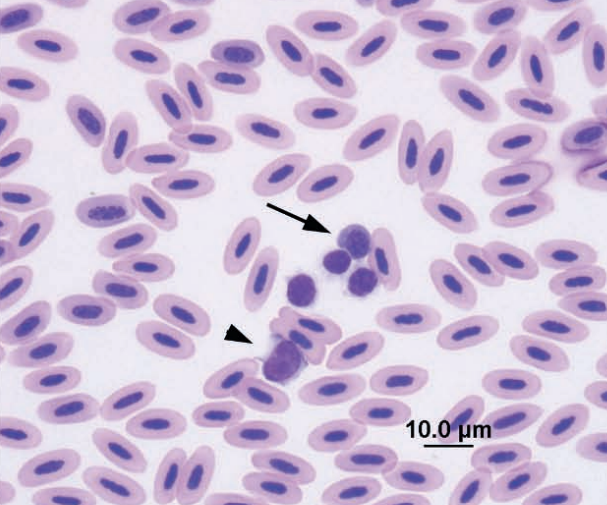
Domestic chicken blood
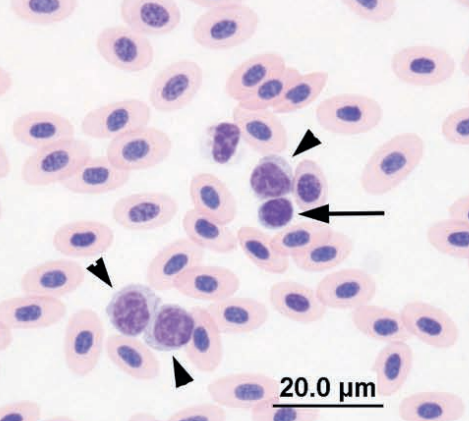
Large lymphocytes (arrowheads), medium lymphocyte (arrow), and thrombocyte
Amazon parrot
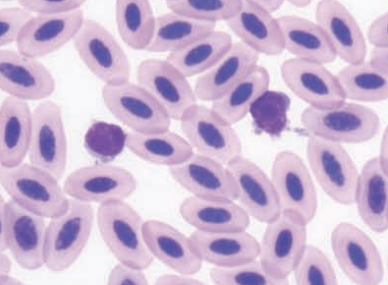
Lymphocytes
Barred owl
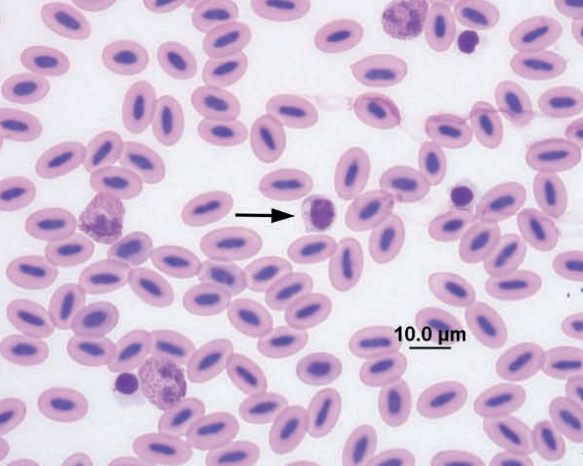
Lymphocyte with azurophilic cytoplasmic granules (arrow) and thrombocyte
Domestic duck
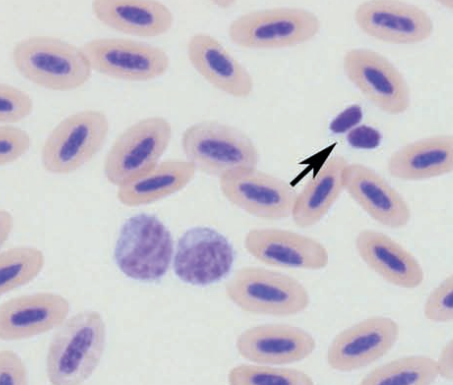
Two large lymphocytes (center) and two thrombocytes (arrow)
Conure
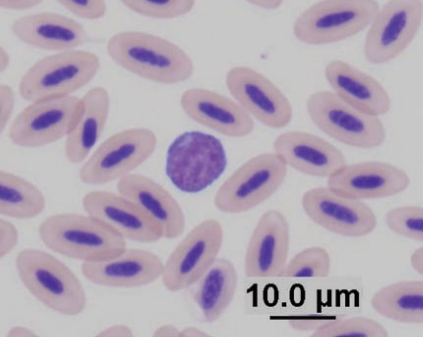
Large reactive lymphocyte
Gannet (a sea bird) blood smear
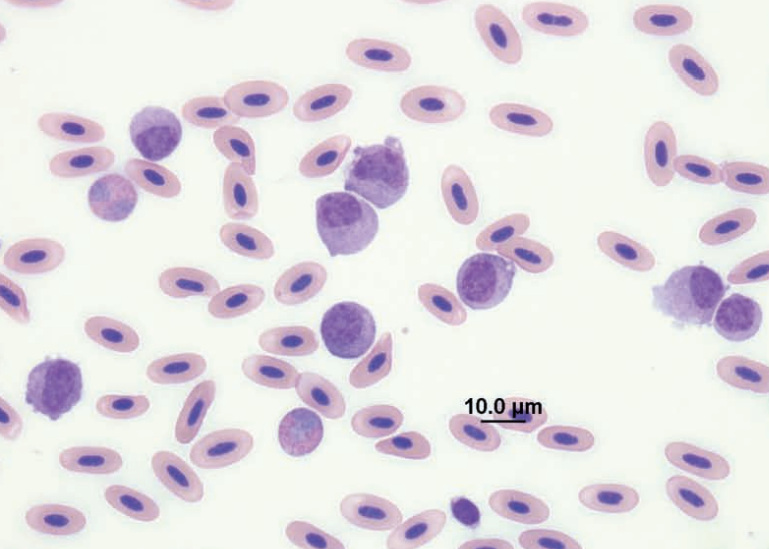
Monocytosis