Fundamentals Module 7, 8, 9 review
1/128
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
129 Terms
1. inspect
2. auscultate
3. percussion
4. palpation
what is the order of the abdominal assessment?
1. lower right
2. upper right
3. upper left
4. lower left
what is the order of auscultating the abdomen?
5 minutes
before saying someone has absent bowel sounds you have to listen to each quadrant for _____ minutes
bowel obstruction
absent bowel sounds
normal active bowel sounds
high-pitched, gurgling, cascading
-irregular 5-30 times per minute
hyperactive bowel sounds
increased motility; loud, high-pitched, rushing tinkling
->30 sounds/minute
1. IBS
2. Neurovirus
3. Food poisoning
what are three reasons for hyperactive bowel sounds?
hypoactive bowel sounds
diminished bowel sounds, -<5 sounds/minute
1. constipation
2. recent out of surgery
3. abdominal surgery
what are three reasons for hypoactive bowel sounds?
so you do not disrupt any bowel sounds
why do you percuss and palpate last?
constipation
infrequent/difficult bowel moevements
1. Increase fluid intake
2. Exercise
3. High fiber diet
what are 3 early interventions for constipation?
IV fluids
what is an early intervention for constipation if someone can't eat or drink?
stool softeners
what is a later intervention for constipation if early interventions do not work?
colace
what is an example of stool softeners?
makes it easier for them to go
how do stool softeners work?
1. laxatives
2. enema
3. suppository
what are three interventions to use for constipation that will make the patient need to go to the bathroom if stool softeners do not work?
laxatives
medicine that promotes bowel movements
enema
inserting fluid into rectum through a small tube
suppository
solid medical preparation (cylindrical shape) that is inserted into the rectum
1. painful hemorrhoids
2. rectal trauma
3. recent rectal surgery
4. don't have a rectum anymore (ostomy bag)
what are four reasons to not give someone an enema or suppository to?
fecal occult test
used to find hidden blood in the stool that is not visible to the eye
-three small stool samples are taken 1 day apart
-a special diet is prescribed 48 to 72 hours before test
1. bright red streaks
2. upper GI problem = black
what are two colors that we can see blood in stool with the naked eye?
Upper GI problem
what causes stool to be black?
1. abumin
2. pre-albumin
what are two nutrition lab tests?
albumin lab
used to determine liver function
pre-albumin lab
measures amount of protein contained in the internal organs
1. creatinine
2. Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN)
what are two tests that assess for kidney function and hydration?
1. 24-hour diet recall
2. food journal
what are two examples of subjective data about someone's nutrition status?
soft, non-tender or sometimes can't feel it
what should the lymph nodes feel like?
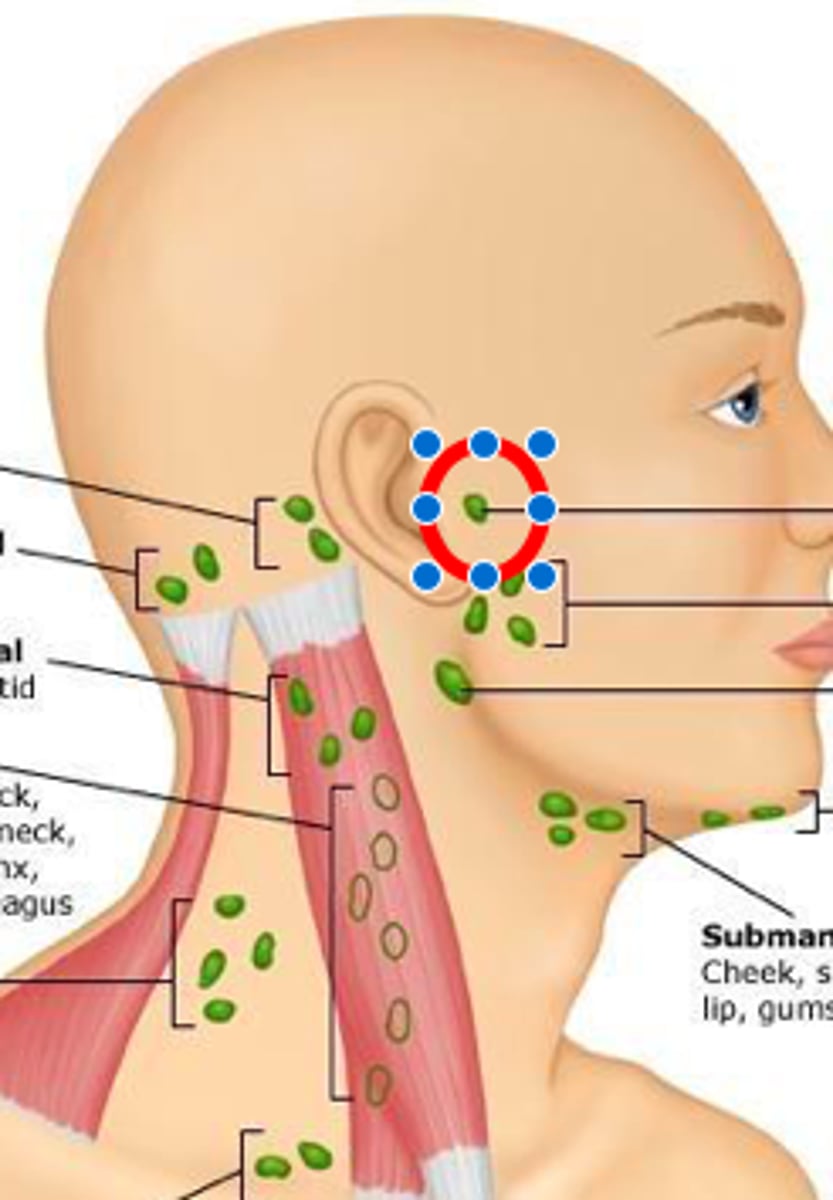
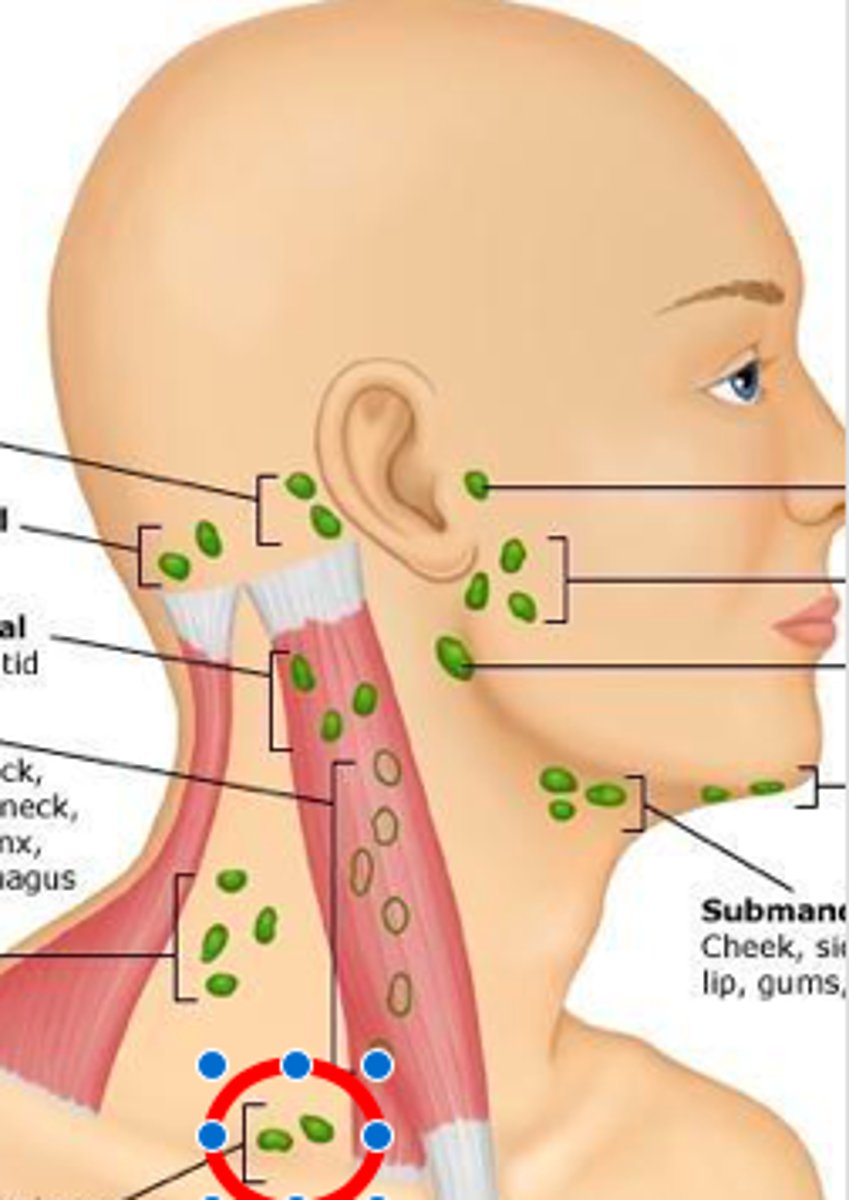
preauricular lymph node
in front of the ear
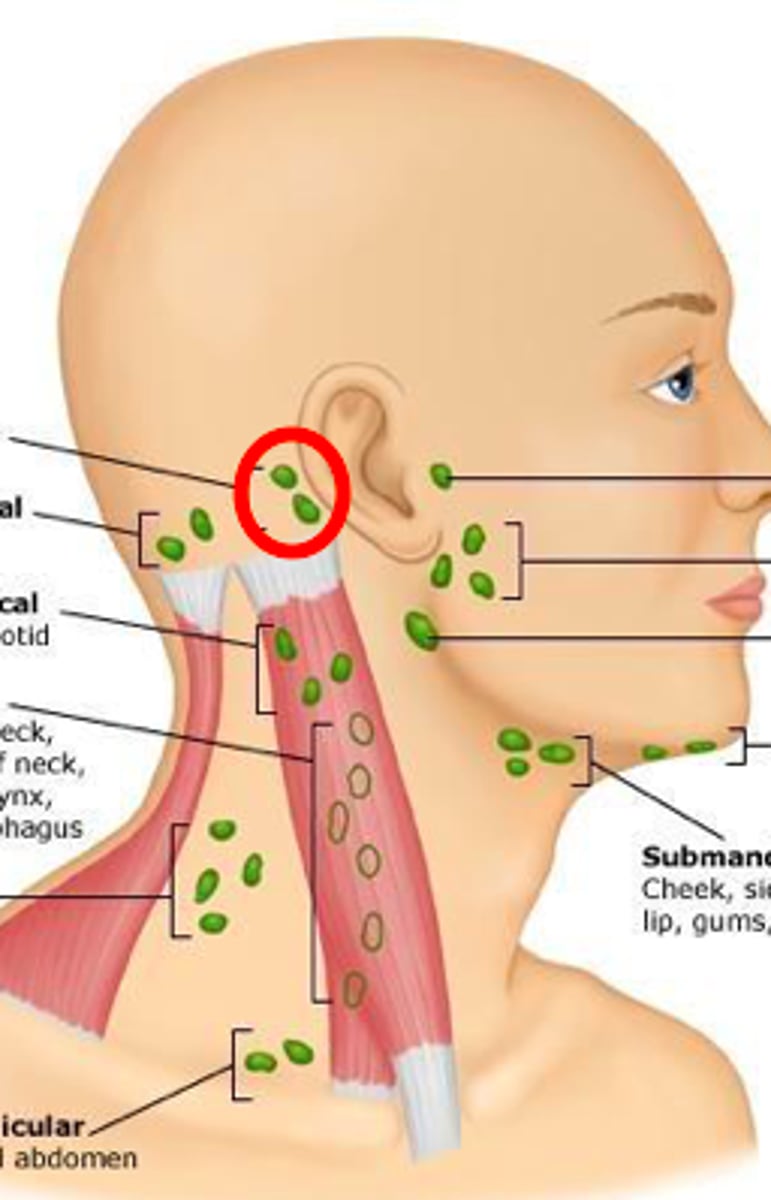
posterior auricular lymph node
behind the ear
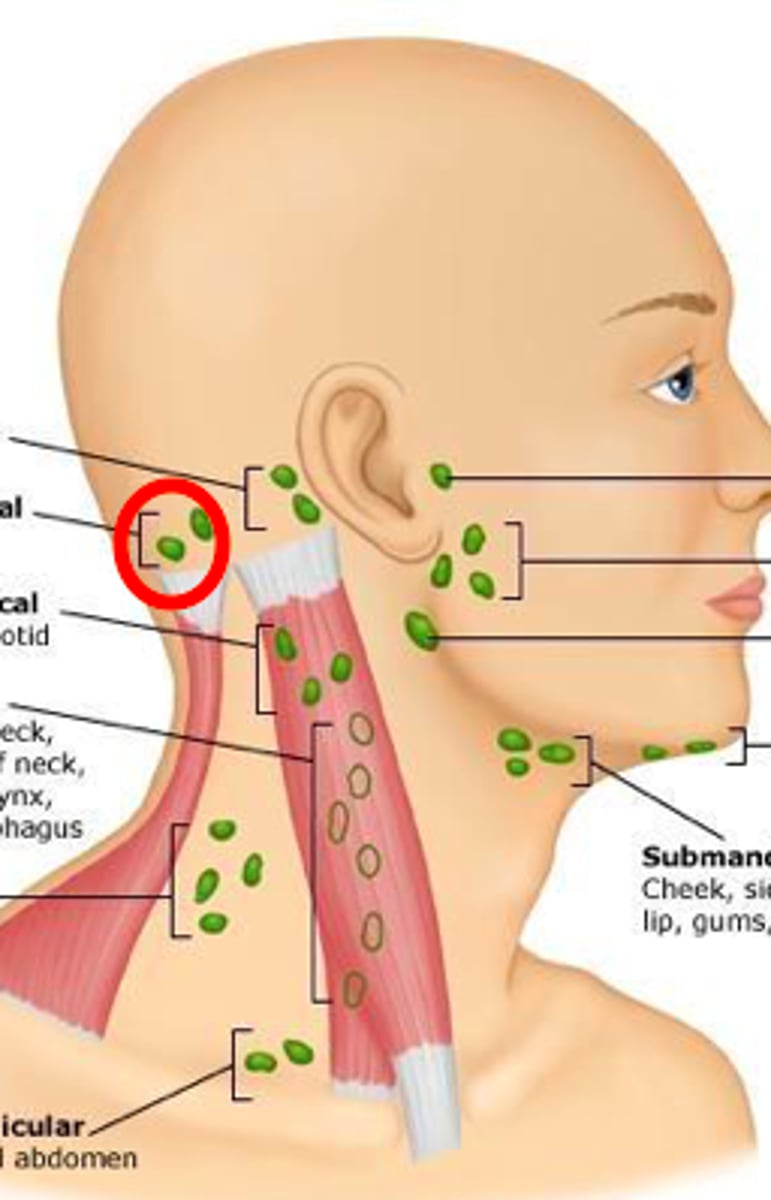
occipital lymph node
Located at the base of the skull
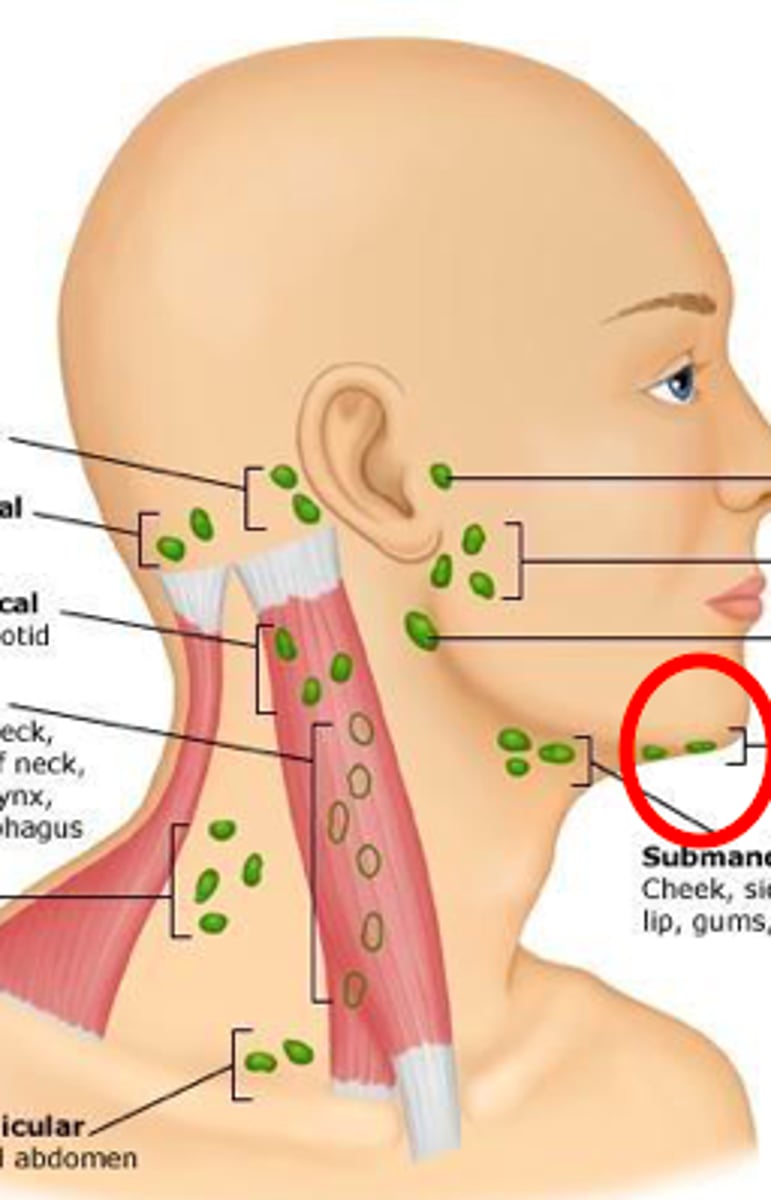
submental lymph node
under the chin
submandibular lymph node
halfway between the angle and the tip of the mandible
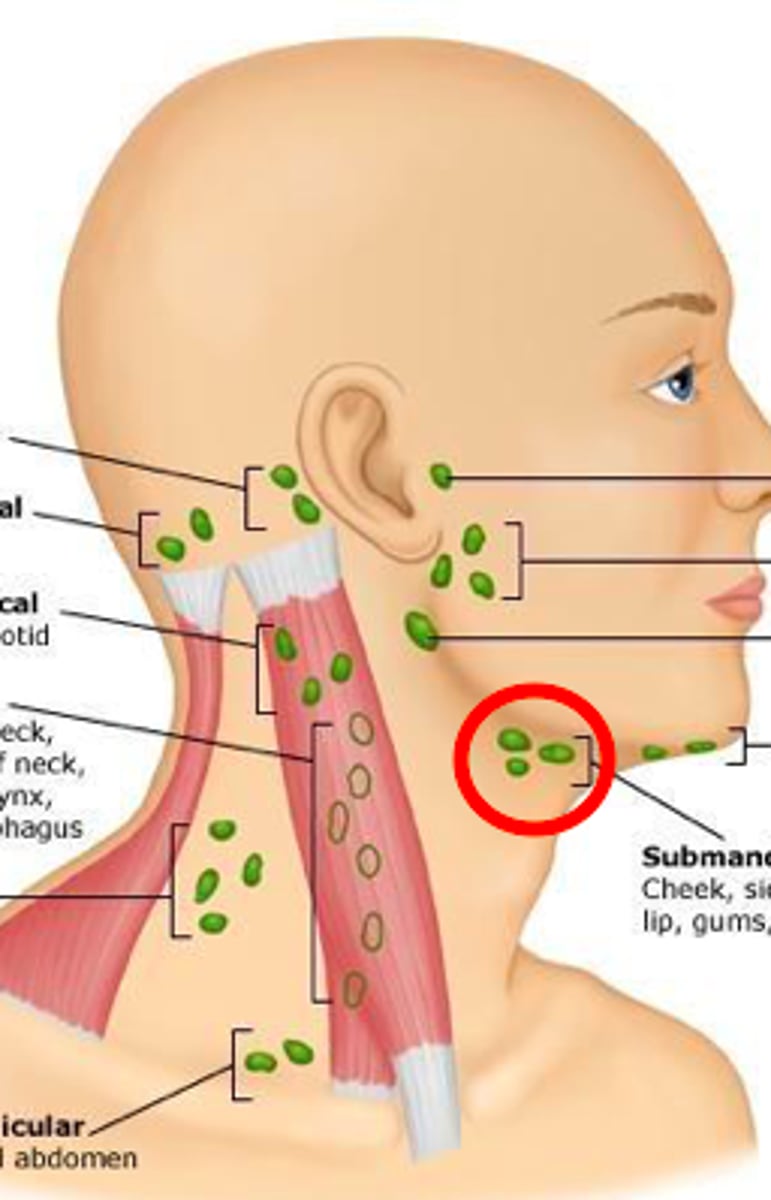
tonsilar lymph node
angle of jaw
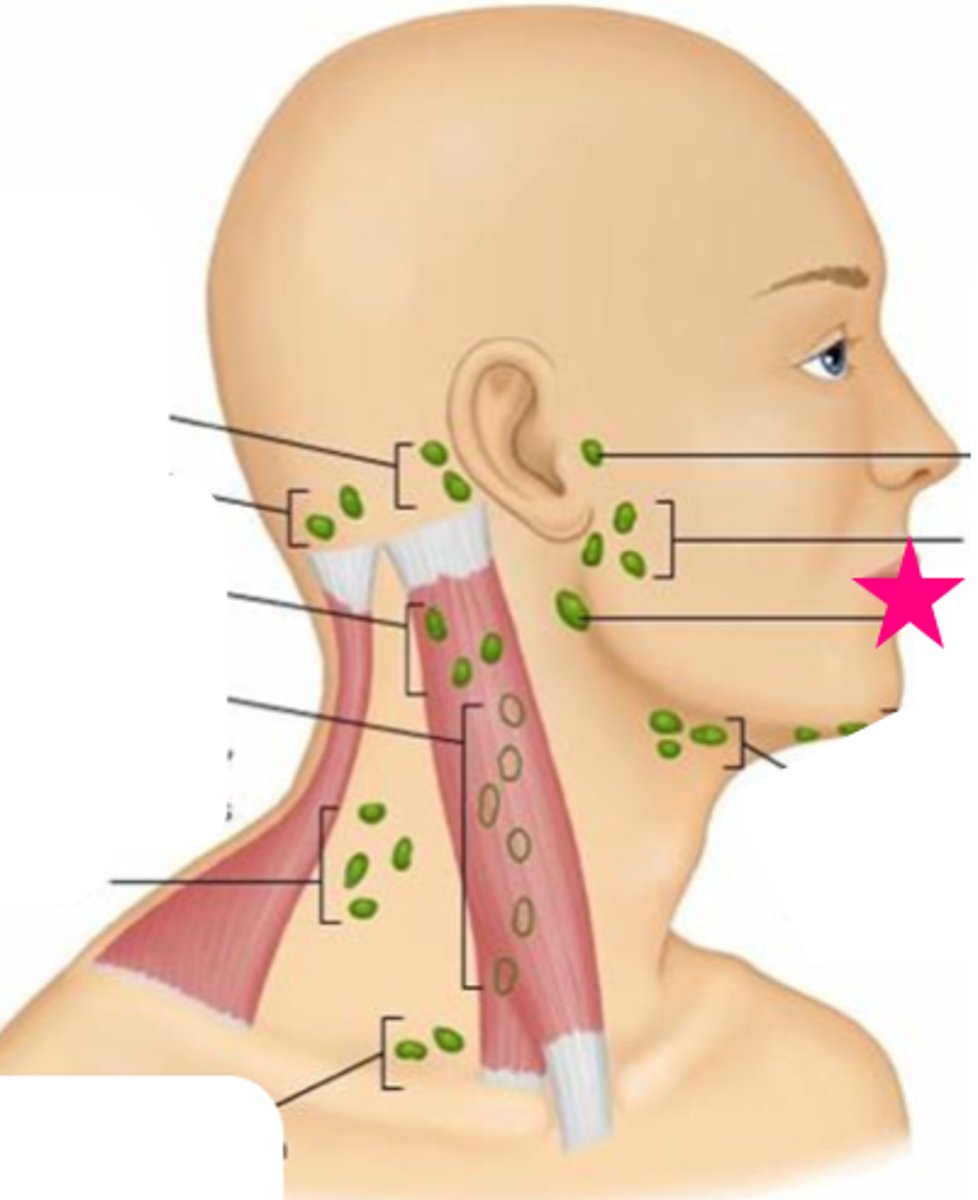
superficial cervical lymph node
overlying the sternomastoid muscle
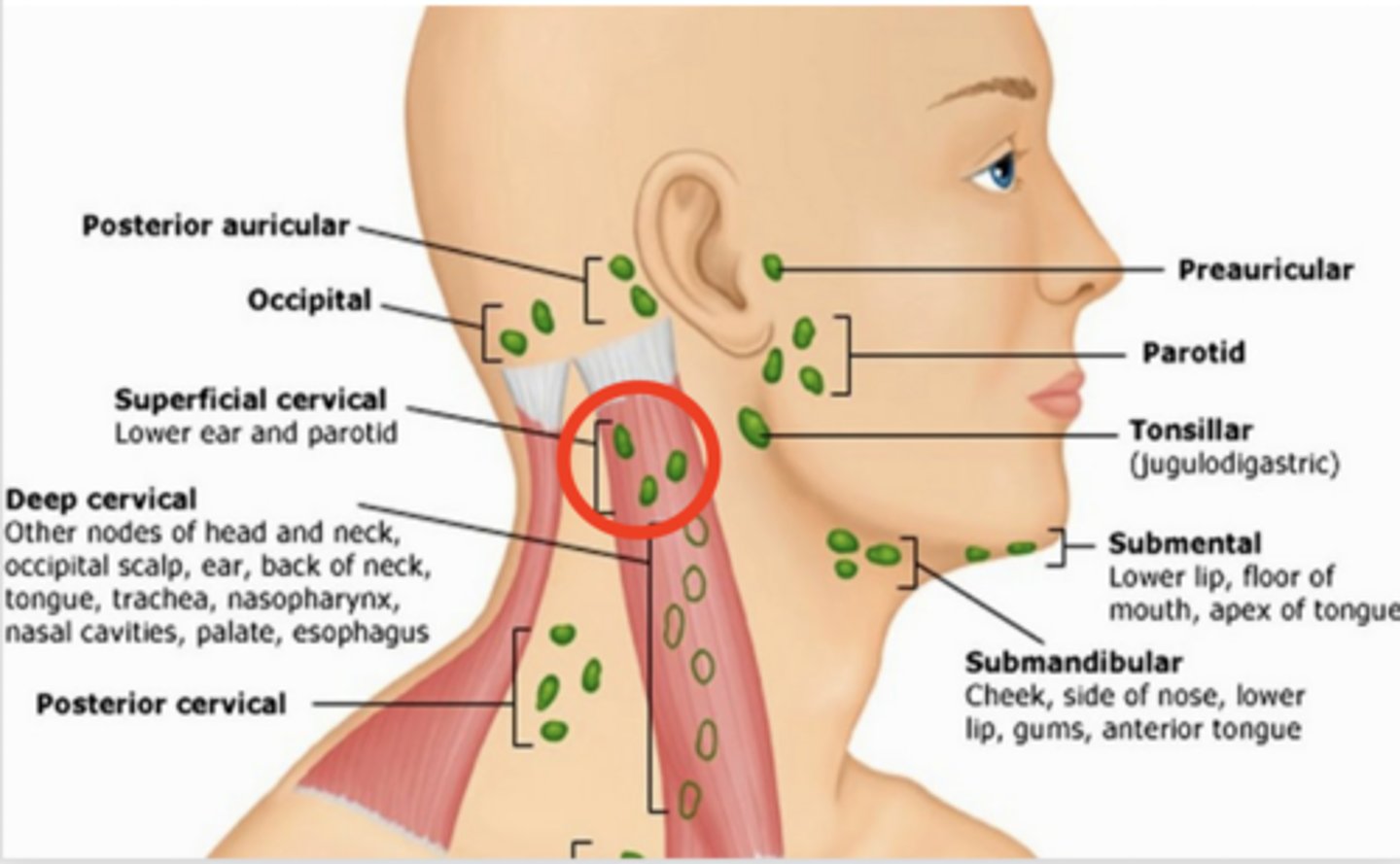
deep cervical lymph node
deep under the sternomastoid muscle
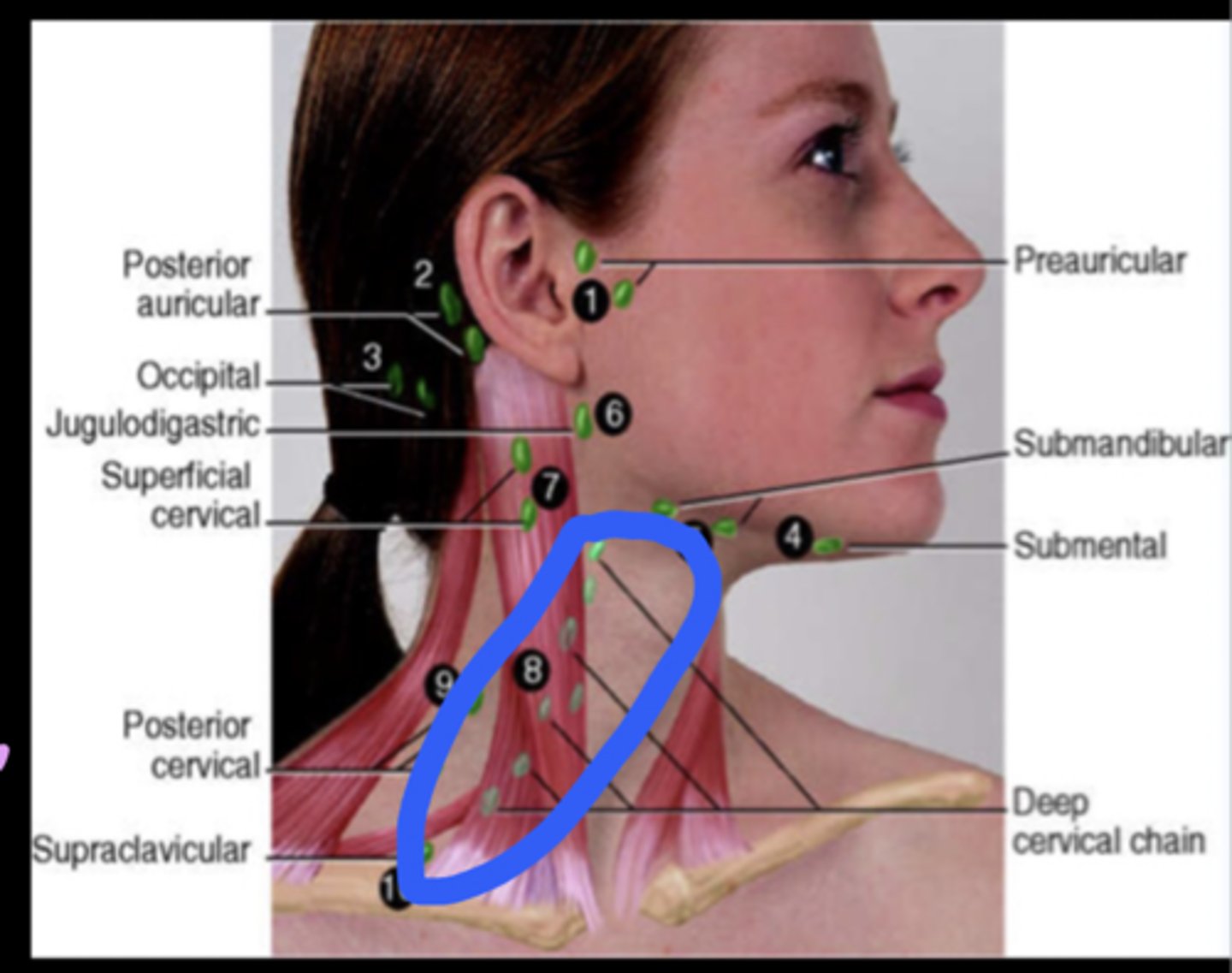
posterior cervical lymph node
Along the edge of the Trapezius Muscle
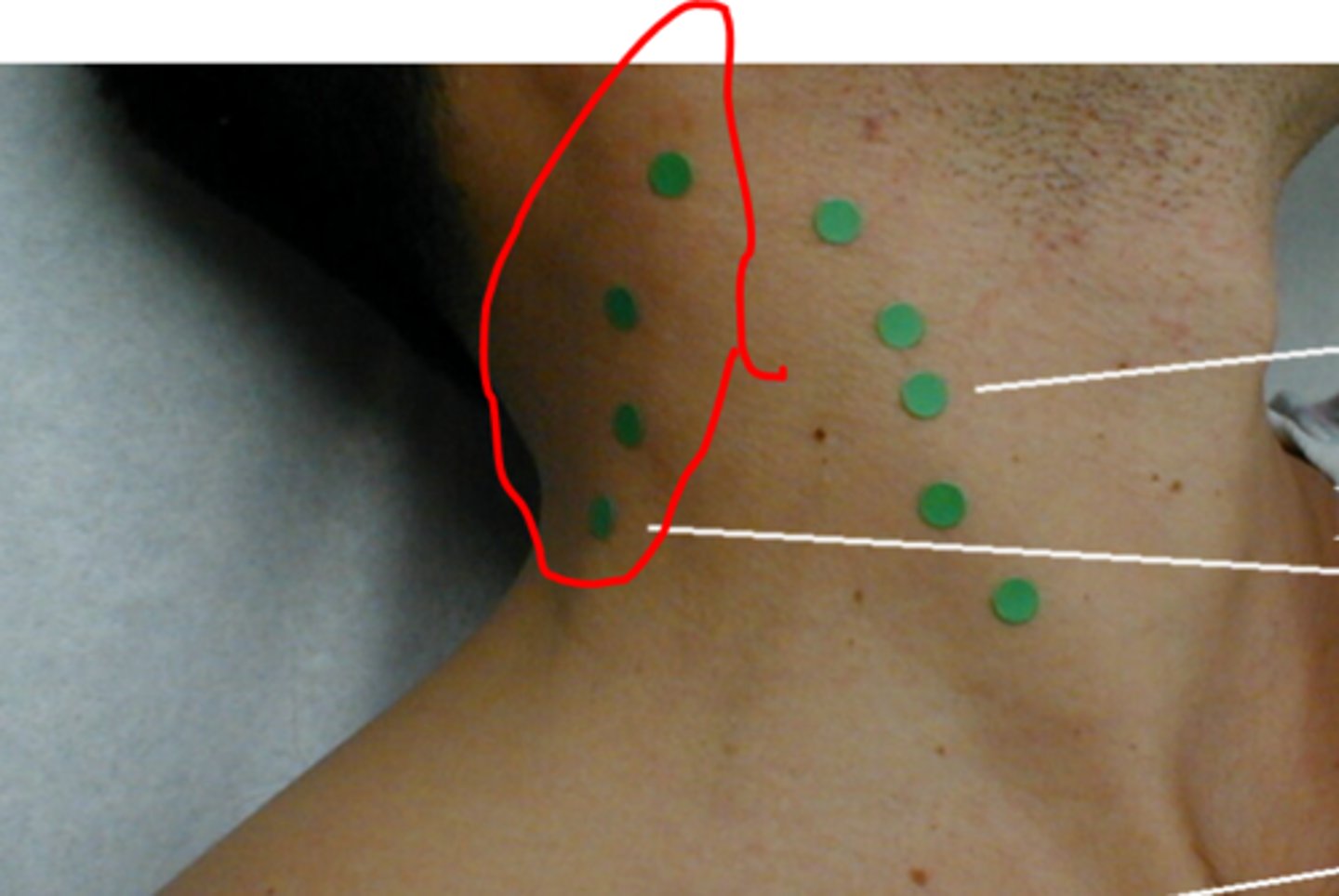
supraclavicular lymph node
just above and behind the clavicle, at the sternomastoid muscle
pupils are equal round and reactive to light and accomodation
what does PERRLA stand for?
pupillary light reflex
tests pupillary constriction using a light
consensual constriction
The simultaneous response of one pupil to the stimuli applied to the other
testing accommodation
pt looking at far object , as you move object close to pt nose, pupils should constrict and shift nasally
snellen chart
tests visual acuity
6 cardinal field of gazes
tests of eye movements
nystagmus
rapid movements of the eyes
peripheral vision test
use fingers and start from side and detect when patient can see the finger
1. neurologic conditions
2. stroke
what two things is the peripheral vision test common in?
tympanic membrane
when assessing inside the ear, what structure should you see?
pearly white/gray, seashell looking
what should the tympanic membrane look like?
1. sinus
2. cluster
3. tension
4. migraine
5. tumor-related
what are the 5 different types of headaches?
sinus headache
-character = deep, constant, throbbing pain; pressure-like pain in one specific area of the face or head (e.g. behind eyes); face tender to touch
-onset = occurs with or after a cold or acute sinusitis, or acute febrile illness with purulent discharge from the nose
-location = may occur in one area of the face or along eyebrow ridge and below the cheek bone
-duration = lasts until associated condition is improved
-severity = may be moderately severe, not debilitating
-pattern = pain worse with sudden movements of the head, bending forward, lying down; in the morning, or sudden temperature changes
-associated factors = other symptoms of sinusitis, such as nasal drainage and congestion, fever and foul-smelling breath. May be confused with tension headaches and migraines.
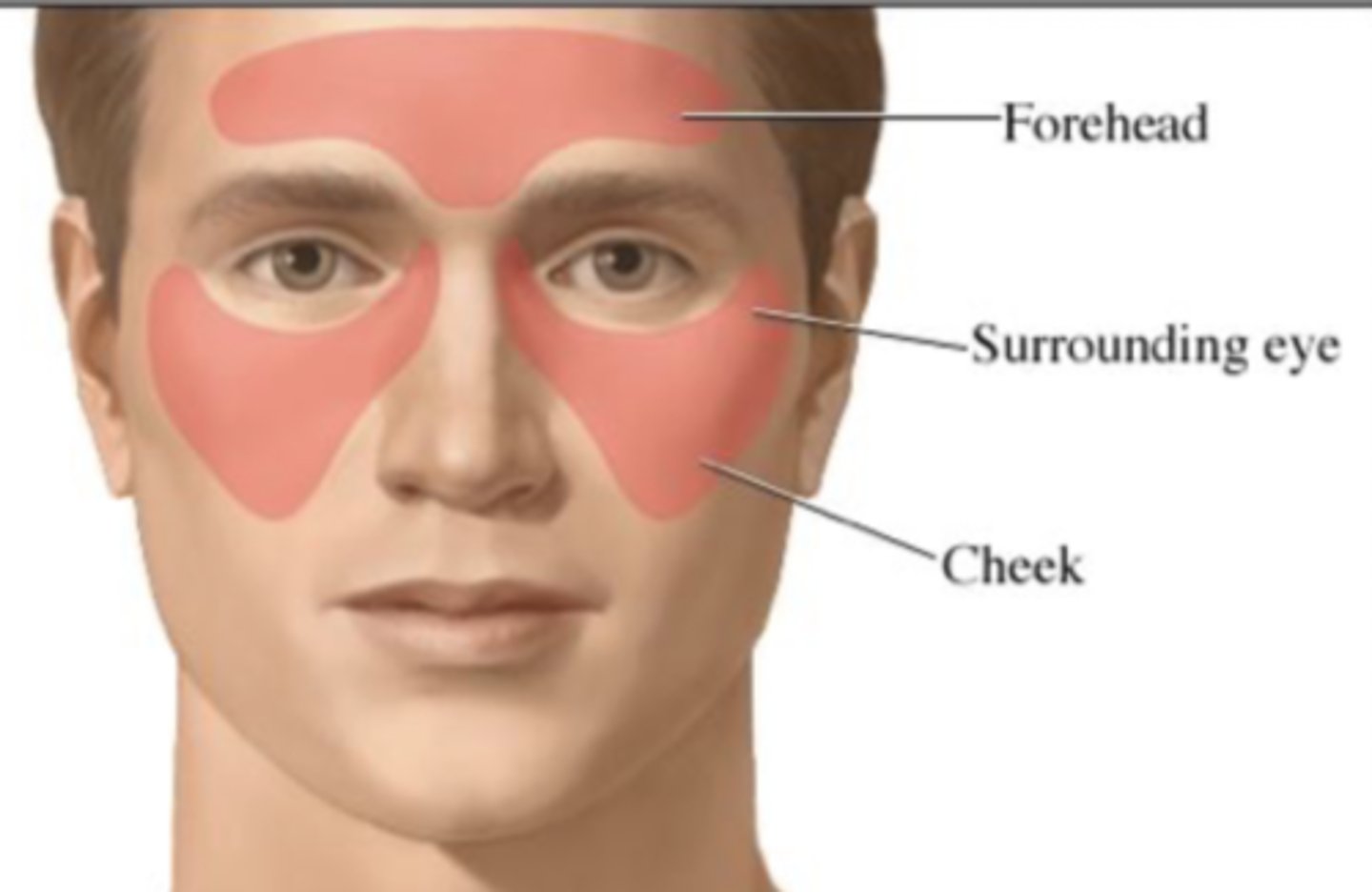
cluster headache
-character = stabbing pain, may be accompanied by tearing, eyelid drooping, reddened eye, or running nose
-onset = has sudden onset; may be precipitating by ingesting alcohol
-location = localized in the eye and orbit, and radiating to the facial and temporal regions
-duration = typically occurs in the late evening or during the night
-severity = intense
-pattern = movement or walking back and forth may relieve discomfort
-associated factors = occurs more in young males
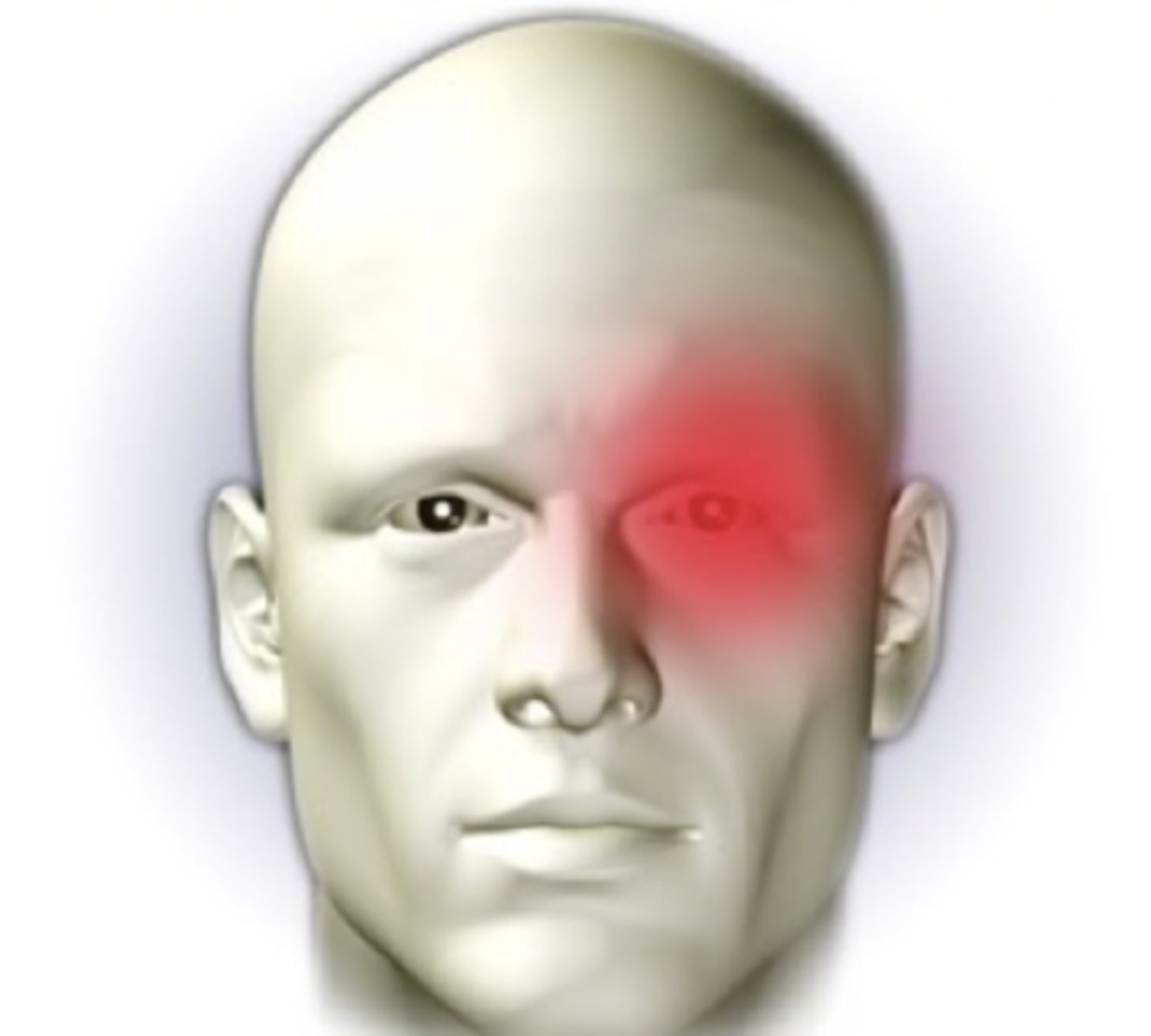
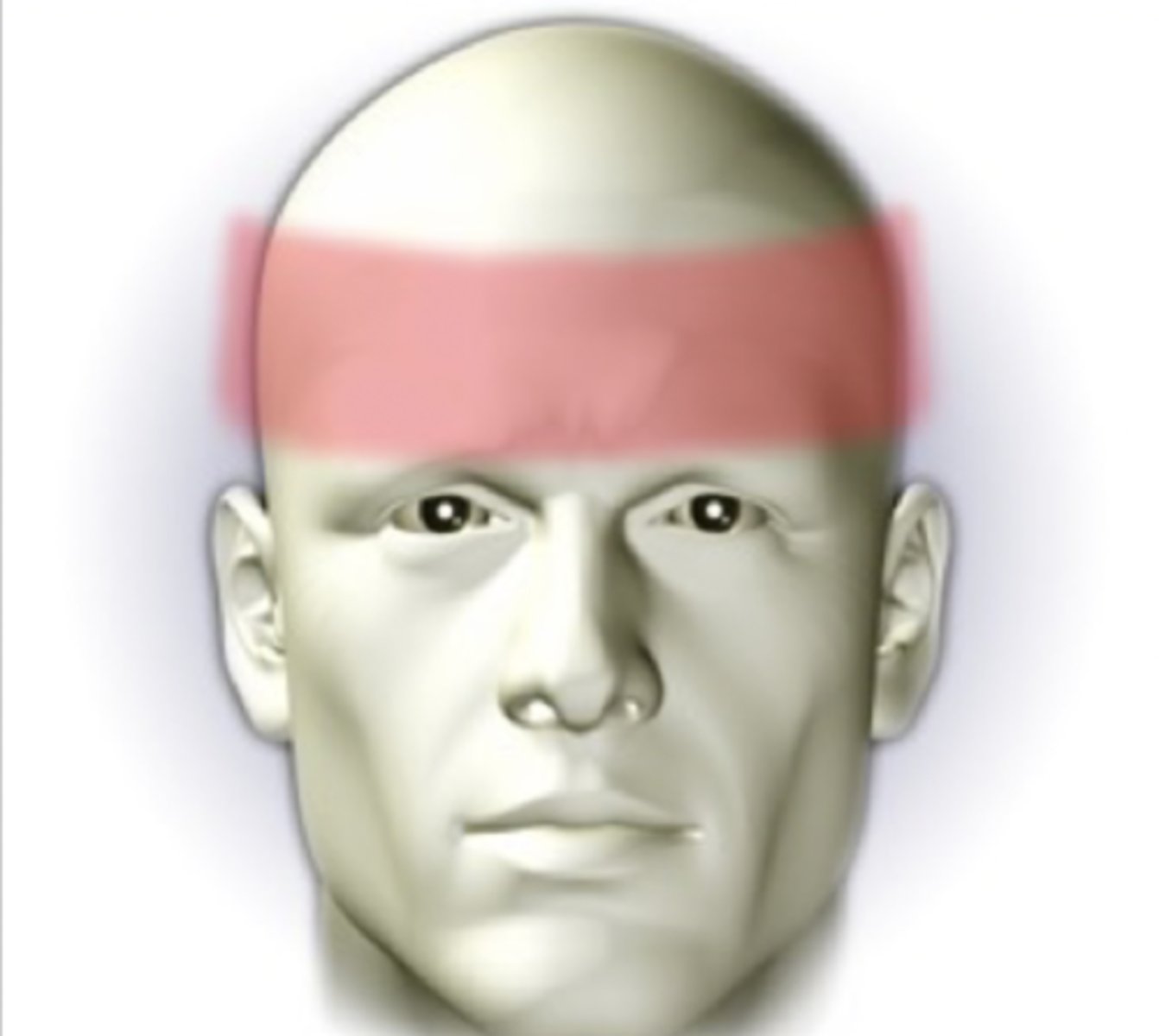
tension headache
-character = dull, light, diffuse; feels like a 'hatband' around the head
-onset = no prodromal stage, may occur with stress, anxiety or depression
-location = usually located in the frontal, temporal, or occipital region
-duration = lasts days, months, or years
-severity = aching
-pattern = symptomatic relief may be obtained by local heat, massage, analgesics, antidepressants, and muscle relaxants
-associated factors = affects women more than men

migraine headache
-character = accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and/or sensitivity to noise or light
-onset = may have prodromal stage (aura), may be precipitated by emotional disturbances, anxiety, ingestion of alcohol, cheese, chocolate, or other foods and substances to which the person is sensitive
-location = located around the eyes, temples, cheeks, or forehead; may affect only one side of the face
-duration = aura may last up to 1 hour; headache lasts up to 3 days
-severity = throbbing, severe
-pattern = rest, medication may be given daily for prevention and also to abort headache
-associated factors = occurs more often in women
migraine with aura
visual disturbances that occur before the migraine starts
tumor-related headache
-character = aching, steady; neurologic and mental symptoms as well as nausea and vomiting may develop
-onset = no prodromal stage; may be aggravated by coughing, sneezing, or sudden movement of the head
-location = varies with tumor location
-duration = commonly occurs in the morning and lasts for several hours
-severity = variable in intensity
-pattern = usually subsides later in the day
facial symmetry
what do facial landmarks help to show?
1. Nasolabial folds
2. Palpebral fissure
what are the two facial landmarks?
1. stroke
2. Bell's Palsy
what two disease/conditions can you test facial symmetry for?
dysphagia
modifying food and liquid textures to make them safer to swallow
1. full-liquid diet
2. pureed diet
3. mechanical soft diet
4. thickened liquid diet
5. clear liquid diet
what are 5 types of dysphagia diets
1. regular diet
2. cardiac diet
3. diabetic diet
4. renal diet
what are four diets not associated with dysphagia?
speech
Using a collaborative approach with someone with dysphagia who should you consult?
aspiration
inhalation of food or liquid into lungs
1. Coughing
2. Anxiety related to eating
3. Drop in O2 saturation
4. Lung sounds get junky
5. Choking
what are 5 signs of aspiration?
stop feeding them
What should you do when you suspect someone is aspirating?
both
you should always look at _______ sides for symmetry
1. scoliosis
2. atrophy
3. osteopenia
4. osteoporosis
5. fracture
6. gout
7. arthritis
8. bursitis
what are 8 alterations in the musculoskeletal system?
scoliosis
curvature of the spine
one should is higher than the other
what would someone look like if they have scoliosis?
atrophy
muscle wasting
osteopenia
reduced bone mass
osteoporosis
what can osteopenia lead to?
osteoporosis
loss of bone density and decreased bone strength
1. older women
2. thin women
3. asian and caucasian women
what three type of people is osteoporosis more common in?
fractures
what does osteoporosis cause and increase in?
fracture
break in a bone
1. open fracture
2. closed fracture
what are the two types of fractures?
open fracture
fracture where bone is exposed
closed fracture
fracture where skin is still intact
gout
-pain and inflammation in big toe
-Tophi
tophi
p-like structures in ear cartilage
arthritis
inflammation and pain in joints
1. rheumatoid arthritis
2. osteoarthritis
what are the two types of arthritis?
rheumatoid arthritis
chronic, autoimmune inflammatory disease of connective tissue
-affects people bilaterally
-most common in hands
1. ulnar deviation
2. swan-neck deformity
3. boutonnière deformity
what are the three main deformities associated with rheumatoid arthritis?
osteoarthritis
degenerative change in articular cartilage
-can be bilateral or unilateral
1. Heberden's nodes
2. Bouchard's nodes
what are the two deformities associated with osteoarthrities?
in distal interphalangeal joints
where is heberden's nodes located?
in peripheral interphalangeal joints
where is bouchard's nodes located?
bursitis
inflammation of the bursa
-may be precipitated by arthritis, infection, injury, or excessive exercise
herniated nucleus pulposus (HNP)
occurs when fibrocartilage surrounding an intervertebral disk ruptures and nucleus pulposus is displaced and compresses adjacent spinal nerves
-Rupture frequently occurs in lumbar spine with increased strain on vertebrae, such as lifting a heavy object improperly
carpal tunnel syndrome
occurs when median nerve compressed between flexor retinaculum (carpal ligament) and other structures within carpal tunnel.
-May be caused by repetitive movements of hands and arms, injury to wrist, and systemic disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis, gout, and hypothyroidism.
-It may also occur with fluid retention that occurs with pregnancy and menopause
1. burning
2. numbness
3. tingling in hands, often at night.
what are three symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome?
1. Phalen's sign
2. Tinel's sign
what are two ways to assess for carpal tunnel syndrome?
morse fall scale
tool used to identify risk factors for falls in hospitalized patients
higher
for the morse fall scale the higher the number = __________ the risk
1. Frequent check-ins (hourly rounding)
2. Scheduled toileting
3. Bed alarms
4. Non-skid socks
5. Bed in lowest position
6. Gait belt
7. Proper assessment of morse fall scale
8. Call light in reach
what are 8 ways to prevent falls?