tax final
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
3 methods of cost recovey
depreciation, amortization, or depletion
cost recovery
business must capitalize the cost of assets with a useful life of more than one year on the balance sheet rather than expense the cost immediately
Depreciation
•Deducting the cost of tangible personal and real property (other than land) over a specific period of time.
Amortization
Deducting the cost of intangible property over a specific period of time.
Depletion
deducting the cost of natural resources over time
Basis for cost recovery
asset adjusted tax basis= asset’s initial basis - accumulated deprecation
Asset type: personal property comprised of tangible assets such as automobiles, equipment, and machinery
cost recovery method: depreciation
Asset type: real property comprises building and land
cost recovery method: depreciation
asset type: intangible assets
cost recovery method: amortization
asset type: natural resources
cost recovery method: depletion
•Scrap-Happy Inc., a scrapbooking retail chain, purchased an old office building for $175,000 for use in expanding its current operations. An additional $15,000 was spent painting and remodeling the building in preparation for its opening.
•Two years later, a Scrap-Happy employee discovered that several leaks in the roof were causing serious water damage to the store’s inventory; the company spent $50,000 to reroof the building.
•Every six months, Scrap-Happy pays $500 to have the carpet professionally cleaned.
initial: 190000 (175000+15000)
added: 50000 (reroofing)
no effect for carpet cleaning = maintenance
Tax Depreciation System
MACRS
What to know for MACRS (5 factors)
•Asset’s initial basis.
•Date it was placed in service.
•Applicable depreciation method.
•Asset’s recovery period (or depreciable “life”).
Applicable depreciation convention
Personal Property Depreciation.
•Includes all tangible property such as computers, automobiles, furniture, machinery, and equipment, other than real property.
•Personal property (not real property) and personal-use property (used for personal purposes) are not the same.
3 methods for personal property depreciation
•200 percent (double) declining balance.
•150 percent declining balance.
•Straight-line.

Recovery Period for Cars, light trucks, computers, and peripheral equipment
5 years
recovery period: office furniture, fixtures, and equipment
7 years
recovery period: qualified improvement property
15 years
Depreciation conventions
half-year
half-quarter
half year convention
•One-half of a full year’s depreciation is allowed in first and last year of an asset’s life.
•If an asset is disposed of before it is fully depreciated, only one-half of the table’s applicable depreciation percentage is allowed in the year of disposition.
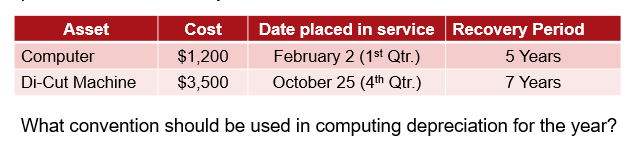
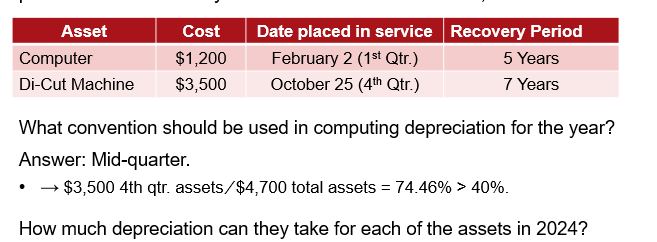
,mid-quarter convention
applicable when more than 40% of the qualified property is placed in service in the last quarter of the year
Calculating depreciation for personal property
•Determine the appropriate convention (half-year or mid-quarter).
•Locate the applicable table provided in Rev. Proc. 87-57.
•Select the column that corresponds with the asset’s recovery period.
•Find the row identifying the year of the asset’s recovery period.
Real Property: Residential
Recovery period 27.5 years
Real Property: Nonresidential property placed after May 13. 1993
Recovery Period: 39 years
Real Property: Nonresidential property placed before May 13 1993
31.5 years
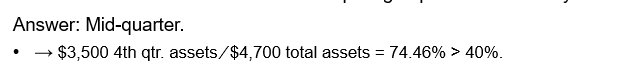
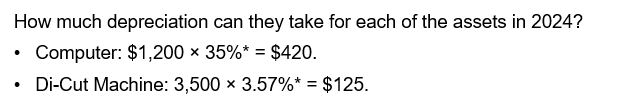


Immediate Expensing is also known as
179 expense
Limits of immediate expensing
Property limitation
taxable income limitation
What can 179 expenses be used for?
qualified property, needs to be acquired by an unrelated person, can be a used property as long as you or unrelated person hasn’t used it befor, regular depreciation life of 20 years or less
Bonus Depreciation
additonal depreciation allowed in the acquisition year for tangible personal property with a recovery period of 20 years or less
Listed Property
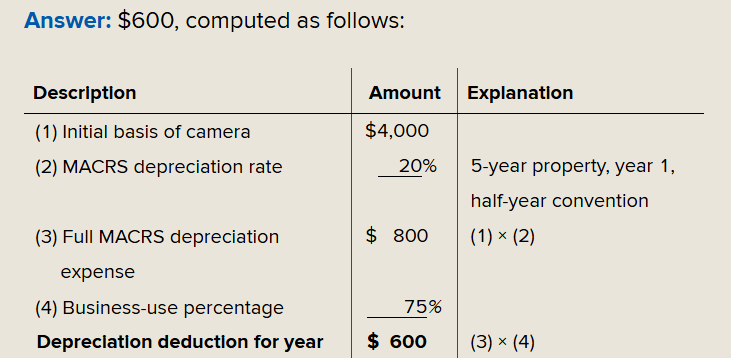
business assets that are often used for personal purposes. Depreciation on listed property is limited to the business-use portion of the asset.
if business use is more than 50%, deduct full annual depreciation*business percentage
Below 50%, depreciation for all previous years is retroactively restated using the MACRS straight line method

MACRS depreciation *business use percentage
Amortization
businesses recover cost of intangible assets through amortization
Examples of intangible assets
-197 intangibles
-start-ups/organization costs
-reserach and experimentation costs
-patents and copyrights
197 intangibles
recovery period of 15 years regardless of their actual life
Patents and Copyrights
if you buy it, amortize it over the remaining life
if you self-created, amortize over 5 years
why would someone choose to apply bonus depreciation
mandatory unless elected out
accelerate tax deductions
Depletion
recover their capital investment in natural resources
cost and percentage depletion —> take the larger of the 2 expenses
can deplete more than you paid
AMT
Alternative minimum tax to make sure people pay tax even if they get certain breaks
If you need to fix one asset write it as a
repair expense
if you replaced all 10 assets
capitalize the cost

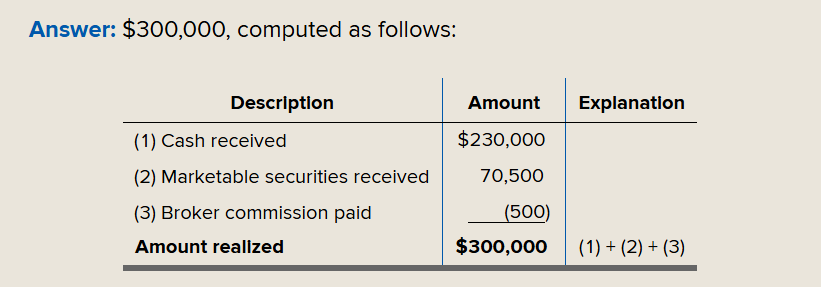

yr 1: 240 yr 2:384 adjusted basis: 576 (1200-240-384)



Netting and Look-Back Rule
§1231 gains and losses from individual asset dispositions are annually netted together. Net §1231 gains may be recharacterized as ordinary income under the §1231 look-back rule.
Like-kind property
Real property All real property used in a trade or business or held for investment is considered “like-kind” with other real property used in a trade or business or held for investment.
Ineligible property Personal property. Domestic property exchanged for property used in a foreign country and all property used in a foreign country. Real property held for sale.
Timing Requirements of a Like-kind exchange
May involve intermediaries
Identify replacement “like-kind” property within 45 days of giving up their property
must be received within 180 days of when the taxpayer transfers property in a “like-kind” exchange
Involuntary Conversions
Gain is deferred when appreciated property is involuntarily converted in an accident or natural disaster
Basis of property directly converted is carried over from the old property to the new one
In an indirect conversion, gain realized is the lessor of gain realized or amount of reimbursement the taxpayer does not reinvest in qualified property
Qualified replacement property must be of a similar or related use to the original property
Installment Sales
Sale of property where the seller receives the sale proceeds in more than one period
Must recognize a portion of gain on each installment payment (gross profit percentage=gross profit/contract price)
Related-Person Loss Disallowance Rules
Treat related persons as though they are the same taxpayer
Losses on sales to related persons are not deductible
Related person may deduct the previously disallowed loss to the extend of the gain on the sale to the unrelated third person
Amount realized =
cash recieved + Fair market value + buyer’s assumptions of liabilities - seller’s expense
Realized Gain or Loss on disposition =
the amount of gain or loss taxpayers realize on a sale or other dispositions of assets is simply the amount they realize - adjusted basis in the disposed assets
Gain or (loss) realized =
amount realized - adjusted basis
Adjusted basis
initial basis minus depreciation or other types of cost recovery deductions allowed (or allowable) on the property (initial basis - cost recovery allowed)
Adjusted basis for Gifts
AKA carryover
Fair market value > donor’s basis → carryover basis (initial basis is same as donor’s basis)
Fair market value < donor basis → carryover basis if sold at a gain, FMV is sold at a loss
Adjusted basis for Inherited Property
FMV on the date of death, or 6 months after the death if elected by the estate
AKA stepped up
Personal use to business use
Basis depends on whether the property appreciated or declined in value during the time the property was used personally
Appreciated: taxpayer uses the basis
Declined in value: taxpayer uses FMV
Ordinary Assets
Assets created or used in trade or business
Held for less than a year
Ex: inventory, A/R, machinery, equipment
Sold at a gain → gain is taxed at ordinary rates
Sold at a loss→ deduct the loss against other ordinary income
Capital Assets
Assets held for investment, for the production of income, or for personal use
1231 assets
Assets and land used in trade/business held for more than one year
Net gain → long term capital gain
Net loss → ordinary loss
Gains can be recharacterized as ordinary income
3 types of 1231 assets
1231 - Land
1245 - personal property and intangible
1250 - depreciable real property
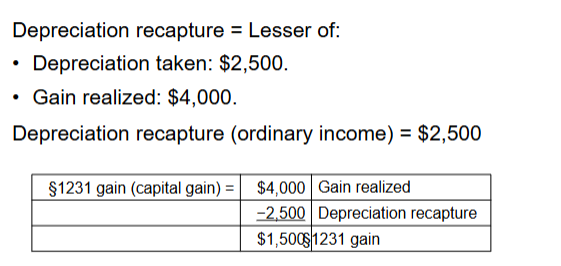
Depreciation Recapture
Conversion of 1231 gain into ordinary income on a sale based on the amount of accumulated depreciation on the property at the time of sale or exchange
Applies to gains ONLY
1245 Assets
Personal property and amortizable intangible assets
The lessor of:
Gain recognized
Total accumulated depreciation
Any remaining gain is a 1231 gain
3 scenarios of depreciation recapture
Gain created through only depreciation deductions
Gain created through both depreciation deductions and actual asset appreciation
Recognize a loss
1250 Depreciation Recapture for Real Property
Depreciable real property sold at a gain is NOT subject to recapture
Unrecaptured 1250 gain for individuals
Depreciable real property sold at a gain is 1250 but is no longer subject to recapture
Involuntary conversions
Lost his asset from something outside of his control
Circumstance most is eminent domain, when the state comes and takes your property, or the state condemns your property
Replacement asset must be of a similar or related use to the original property
Installment Sales
Sale of property where the seller receives the sale proceeds in more than one period
Must recognize a portion of gain on each installment payment received
Gross profit percentage = gross profit/contract price
Inventory, marketable securities, and depreciation recapture cannot be accounted for under installment sale rules
Does not apply to losses
When boot is given as part of a like-kind transaction
The asset received is recorded in two parts: property received in exchange for like-kind property and property received in a sale
Own a different property (the replacement asset)
Based on the basis that you had on your original asset
If i sold the new asset, that gain will come back and be recognized
Calculating 1231 gain or loss if gains>loss
net gain is long-term capital gain
Calculating 1231 gain or loss if gains<loss
net loss is ordinary
when boot is received
creates recognized gain
gain recognized is lessor of gain realized or boot received
Adjusted basis of boot received is the FMV of the boot
Simple Depreciation Recapture thinking
Recapture Potential is limited to the depreciation you claimed before selling. Any additional gain is considered a 1231 gain.