geograpgy urban environments
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
urbanisation
increase of people living in urban areas (towns or cities)
rates in LICs or NEEs much faster than HICs mostly bc of rapid economic growth
causes of urbanisation
rural- urban migration (movement of people from rural to urban areas)
push and pull factors: natural disasters, war, conflict, employment, education, healthcare, quality of life...
natural increase- when birth rate exceeds death rate
increased birth rate: high % population child bearing age- high fertility rate; lack of contraception/ education about family planning
lower death rate: higher life expectancy due to better living conditions and diet; improved medical facilities- lower infant mortality rate
process of urbanisation
1. agglomeration
2. suburbanisation
3. commuting
4. urban regeneration
5. counter urbanisation
6. urban re imaging
7. urbanisation of suburbs
agglomeration
concentration of people and economic activites at favourable locations eg river crossing points/ close to mineral resources
(everyone moves into cities, where things come towards eg city centers)
commute
come from outside to inside urban area and still making use of urban services (eg shops colleges hospitals)
(suburbs to city, edge to center, then back again)
suburbanisation
towns expanding outwards adding to built up area
(from city center to countryside people moving)
urban regeneration
re using areas in old parts of cities abandoned as people and businesses have moved to suburbs or beyond
(improving run down areas with jobs and services)
urban re imaging (or rebranding)
regeneration of buildings/ areas from urban regeneration
urban characteristics
jobs mostly manufacturing and services
larger population and area
high density people and buildings
busy way of life
rural characteristics
agricultural jobs
sparse and small villages/ hamlets, small population, large area
low density people and buildings
simple quiet way of life
urban area
built up area such as town/ city
lee's migration model
origin, intervening obstacles, destination
push and pull factors (+ve and -ve)
push away from rural areas
pull to urban
(food availability, discrimination, violence, gov)
urbanisation pathway
1. developing- early urbanisation eg Sri Lanka 18%
2. emerging- accelerating urbanisation eg thailand 51%
3. developed- mature urbanisation eg japan 91%
4. developed- counter urbanisation eg UK 83%
problems of rapid urbanisation
1. housing
LIC: squatter settlements and shanty towns
HIC: demand outstips supply
2. access to water and electricity
LIC: clean and safe running water, sanitaion, electricity supplies hard to come by, basic services cannot keep up with rapid population growth
3. traffic congestion and transport
traffic systems become overloaded as areas grow
LICs and HICs: pollution issues- smog
4. health
LICs: not enough doctors, dirty water, air pollution- health suffers
5. education
LIC: only provide small primary schools with few pupils continuing to secondary schools because so few of them
6. employment
many unable to find work despite hope and lure of city- informal sector booms (cash in hand, not in bank- not paying tax, pension etc, not to gov)
LIC and HIC: many travel huge distances for work
natural increase
growth in population resulting in excess births over deaths
birth rate
number of live births per 1000 people per year
death rate
number of deaths per 1000 people per year
unemployment
state of not having a job
underemployment
employed yet does not make use of or acknowledge full ability/ training
push factors
why people encouraged to leave rural areas
pull factors
why people are attracted to urban areas
rural urban migration
movement of people from countryside to towns and cities to live permanently
infant mortality
average number of deaths of children under one year per 1000 live births
urban growth
expansion of towns and cities so they cover more land and gain larger populations
megacity
urban areas with populations greater than 10 million
most current are NEEs (brazil) and LICs (nigeria)
factors to growth of megacities
economic development
population growth
multiplier effect
once a city is prospering, it gathers momentum to carry forward- prosperity = growth
economies of scale
financial savings in terms of transport (distances much less) (communication easy- people and businesses)
global/ world city
any size, recognized worldwide as places of great prestige, status, power and influence
(most important: tokyo, new york, london- financial centers of global economy)
urban land use patterns -HIC
burgess/ concentric zone model (4 zones)- HIC
core: oldest, city center; CBD (central business district), retail gathers as shops can afford high rent
inner city: early suburbs, old housing, non residential land uses (industry/ factories- cannot afford rent in CBD)
suburban ring: present suburbs, housing as dominant land use
urban fringe: countryside eroded by growth (outward spread of built up area for housing and non residential uses)
development on urban fringe
areas between built up towns and open spaces of fields
countryside being taken for outward growth of towns and cities (most evident in suburbs)
land types on urban fringe
retail parks- deal with traffic and parking
industrial estates- built around working people
business parks- created by property developers to attract leisure and firms needing office accomodation
science parks- near university/ research centers
brownfield sites
land previously used for commercial/ industry- may be contaminated- hazardous waste pollution
advantages:
reduced loss of land to agricultural/ recreational use; revive old and disused urban areas; located near main areas of employment
disadvantages:
more expensive- clear old buildings and pollution; surrounded by rundown areas- not appealing as residential area; higher pollution levels
greenfield sites
flat, away from large cities, open land- demand for housing, industry, public works (eg sewage)
advantages: relatively cheap; healthier environment; proximity of countryside
disadvantages: valuable farmland and attractive scenery lost; development = light and noise pollution; wildlife and habitats lost; encourages further suburban sprawl
urban land use patterns- LIC
hoyt model
sectors grow out in wedges around CBD along traditional communication routes
1. center- CBD
2. transportation and industry
3. low class residential (together w 2)
4. middle class residential
5. high class residential
low quality housing next to industrial zone, middle class next to low, high class as far as possible from industry and low class
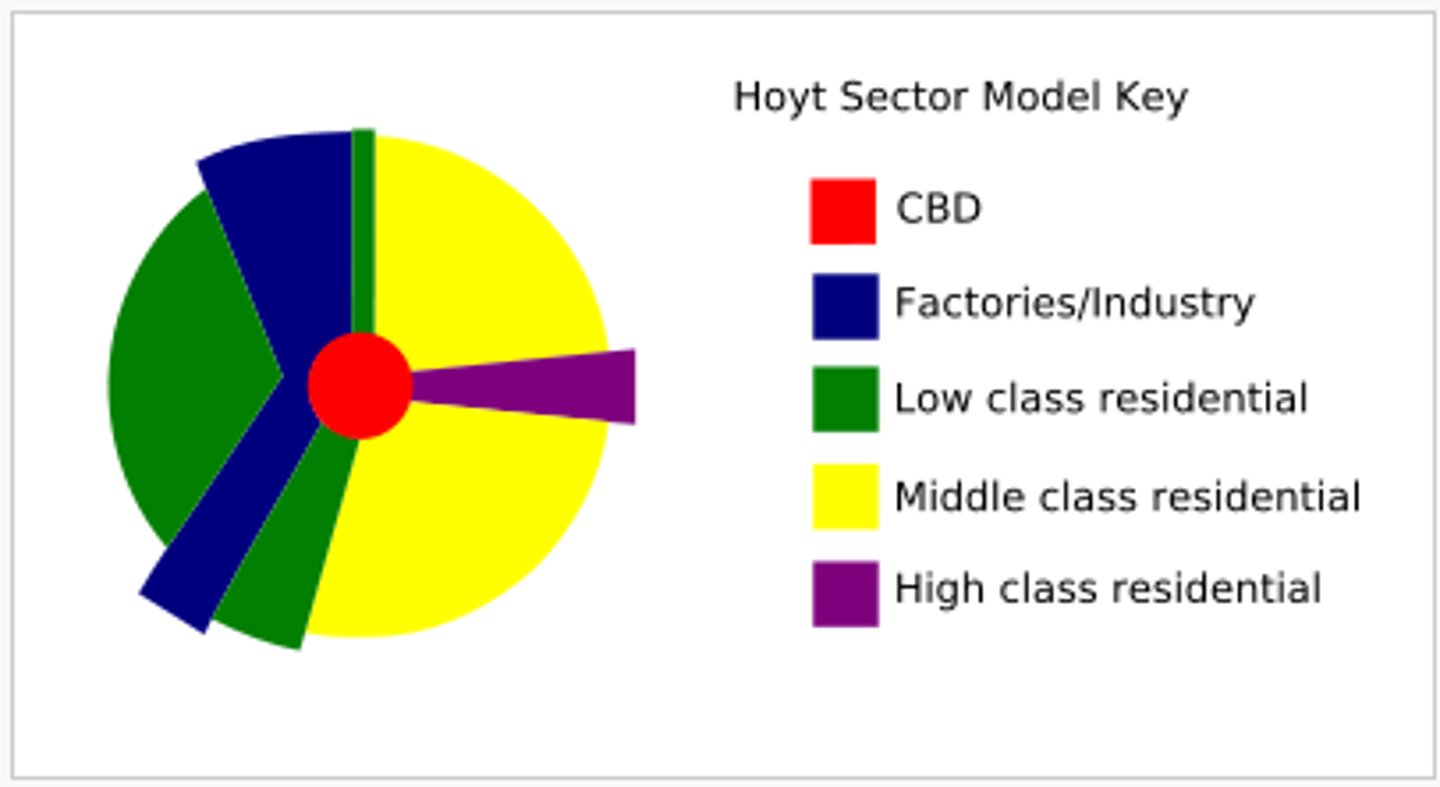
variation in land use patterns
value of land
values varies across urban areas- decrease away from CBD but also high value land where roads meet
location
important to value- close to key functions = higher value (eg railway stations, road intersections)
problems of urbanisation- HIC (HK)
1. housing
top 5 most densely populated= high demand, gov rent, high rise apartments, cage homes for poorest- up to 10 in a room
2. food, water, electricity
limited lakes and rivers, water pumped from river in China
3. traffic and transport
very good integrated public transport system- 90% journeys taken by public transport, increase in growth in traffic capacity and air pollution
4. social (poverty and deprivation)
large gap between wealthiest and poorest, segregation within society- income inequality, socio economic status of people
5. energy and environmental
6.4m tonnes a year of waste, most dumped in landfills (30% recycled), tried to implement 'waste charge' but cancelled, 99% energy from fossil fuels, not sustainable, smog
6. employment
7. education
8. health
HK
economically very strong- financial and trade services
few natural resources for energy
traffic congestion major issue
public transport good
social and education services good
densely populated- growth upwards, rented housing from gov, areas of poverty
problems of urbanisation- LIC and NIC (kenya/ dharavi)
informal economy huge- very low wages but will stop starvation
education very low
squatter settlements very densely packed and help house population of rapidly urbanising LIC and NIC
sustainable urban living
being able to live in citiesi n ways that do not pollute environment and using resources in ways that ensure future generations can also use them
sustainable urban living- water conservation
reducing amount of water used
collecting rainwater for gardens, toilets
water meters and toilets that flush less water
educating on using less water
sustainable urban living- energy conservation
using less fossil fuels can reduce rate of climate change
promoting renewable energy sources
making homes more energy efficient
encouraging people to use less energy
sustainable urban living- creating green space
can improve urban areas for those who live there
natural cooler areas to relax
encourages excercise
reduce risk of flooding from surface runoff
sustainable urban living- waste recycling
more recycling = fewer resources used
less waste = less landfill
collection of household waste
more local recycling facilities
greater awareness in benefits of recycling
sustainable urban living- case studies
masdar city (UAE)
one of world's most sustainable cities
all energy supplies renewable (location long hours of sun)- solar
energy efficient buildings, smart water consumption- desalination plants solar
waste nearly 0
curitiba (brazil)
older system based on improved transport
bus only zoned off area w/ dual carriages
CBD surrounded by parks so no shanty towns
waste disposal system- get fruit and veg
self help suburbs- people trained to fix and make basic amenities
afghanistai
trying to raise food production
females trained in business, nutrition, hygiene (self help)
crop growing, greenhouses, storing harvests, rain water collection
inhabitants given small plots, training in crop growing
managing urban challenges
organisations:
gov- local and national
charities- NGOs, where gov corrupt/ unable to help poorest of population
self help schemes- giving people skills- teaching eg plumbing
slums:
bulldoze and clear, clear but relocate, redevelop, improve- self help and services, ignore
traffic management- problems
environmental:
increases air pollution, releases greenhouse gases leading to climate change
economic:
congestion can make people late for work, business deliveries longer, can cause companies to lose money
social:
greater risk of accidents- frustration, health issues pedestrians
traffic management- solutions
wider roads- traffic flow easier
ring roads and bypasses- traffic out of city centers
park and ride schemes- reduce car use
encourage car sharing schemes- workplaces
public transport, cycle lanes, cycle hire schemes
congestion charges- discourage drivers from entering busy city centers
traffic management example: bristol
2012 most congested city in uk
now aims to develop integrated transport system- more public transport use; cycle routes and hiring schemes