geography - option G
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
- changing urban systems - variety of urban environment - urban environmental and social stresses - building sustainable urban systems for future
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
living trends
for the first time in the history more people are living in urban areas rather than rural
reasons: natural change, migration
trends in migration
centripetal (moving or tending to move towards a center) population movements:
job opportunities (less in rural areas, lower wage, less physical jobs, less changing factors)
social aspect (entertainment, better place to socialize, not everybody knows you)
people are forced to move towards urban areas, if they are pushed out and there is not enough land for them in rural areas
centrifugal (moving or tending to move outside of the center) population movements:
social aspect (peace, feeling of community)
air pollution
safety risks (traffic, crime rates)
lack of space (not many free places to live)
high cost of living (expensive apartments, parking spaces, etc.)
commuting
as we get older we cannot drive so well, so we depend on public transport
time spent on public transport and commuting is a big disadvantage
gentrification
the process whereby the character of a poor urban area is changed by wealthier people moving in, improving housing, and attracting new businesses, often displacing current inhabitants in the process
higher in MEDC
urban growth over time
case study: Lagos and Sao Paulo
aspects:
transport
infrastructure improvements
sanitation
water
waste disposal
telecommunication
deindustrialization
a city loses its industrial power
example: Detroit and Walbrzych
aspects:
many buildings are abandoned
poverty
crime rates are higher
divorce
characteristics of urban places
site - precise location (geographical coordinates)
situation - describes location with relation to other circumstances (ex. that it is located near a river)
function - justification of its presence (ex. residential, economic, administrative, transportation, scientific/educational)
land use
hierarchy of settlement
growth process
model of a city (types)
1) Burgess’ concentric model
2) Hayt’s sectoral model
3) multiple nuclei model
brownfield vs greenfield site
brownfield site - any land that has already been built on
requires some compromises
often in the city, therefore attractive for businessmen
difficulties with the city (traffic jams, problems with delivery, etc.)
greenfield site - any land that hasn't been built on before
cheaper
more flexible with the design
has to be built from scratch
CBD (central business district)
more offices than apartments (because it will be expensive for occupants + office generates profit)
low population density
highest buildings
high number of workers (low number of residents)
traffic restrictions
population density (factors)
water access
natural obstacles (temperature, mountains, rivers, etc.)
natural advantages [usually for rich people] (lower temperature in the hills)
land values (poorer people have to live wherever it is available and don't have choice)
ethnicity
bid-rent theory
price and demand of real estate changes depending on the distance from the city center
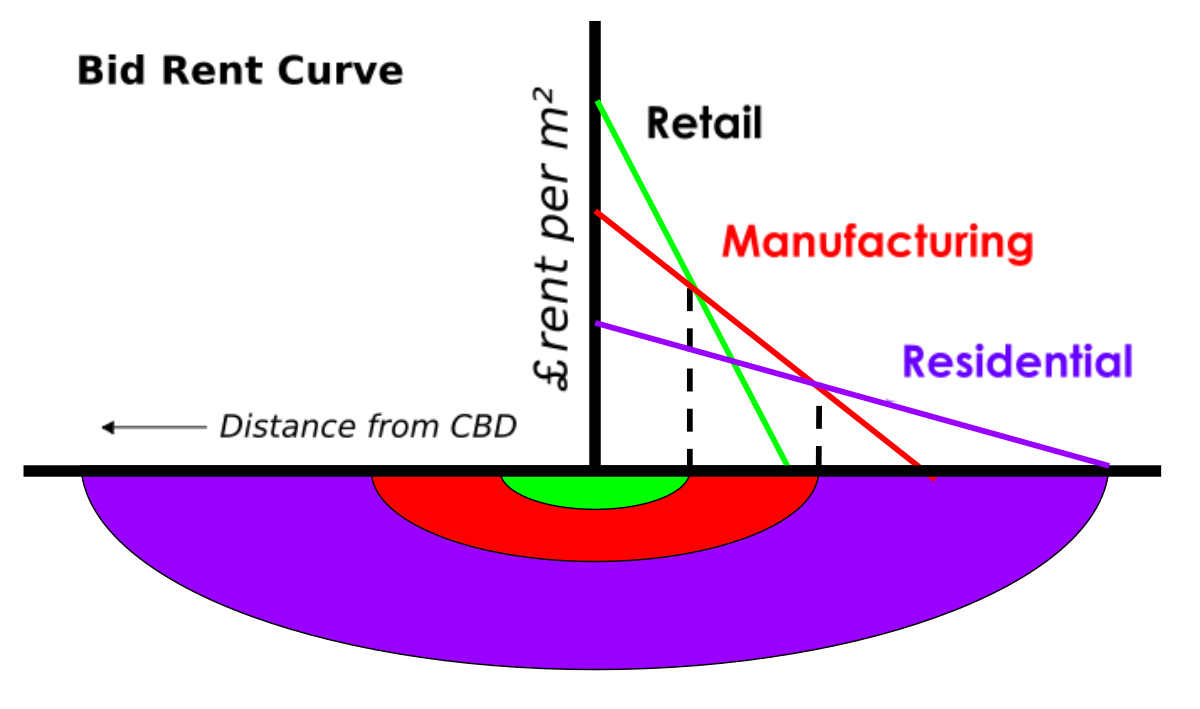
why ethnicities live together?
same language (social, economic)
similar food taste (social)
same skin color and clothing (social)
similar religion
national holidays
areas of deprivation
space of people who lack something (usually basic)
Kibera, Kenya
biggest slum in Africa
only two train rails
near the river -> water source <- the water is polluted and can result in diseases
cheap living (not favorable place to live)
deprivation of basic security (especially for women)
favelas in Rio
additional risks (apart from those already connected to the reality of slums) connected with a massive slope (land-slides)
differences in rural and urban areas
temperature
air humidity
wind
overcast
precipitation
urban heat island effect
refers to an urban area being significantly warmer than its rural are surroundings due to human impact
concrete having low albedo (doesn't reflect the energy)
more air pollution (more greenhouse gases)
use of lots of electricity (ex. AC)
industrial buildings that generate a lot of energy (heat)
heat leads to water bodies to evaporate more (higher temp >> lower air humidity)
quick exchange of water (no time for evaporation)
taller buildings are a barrier for wind
specific patter of winds in a city
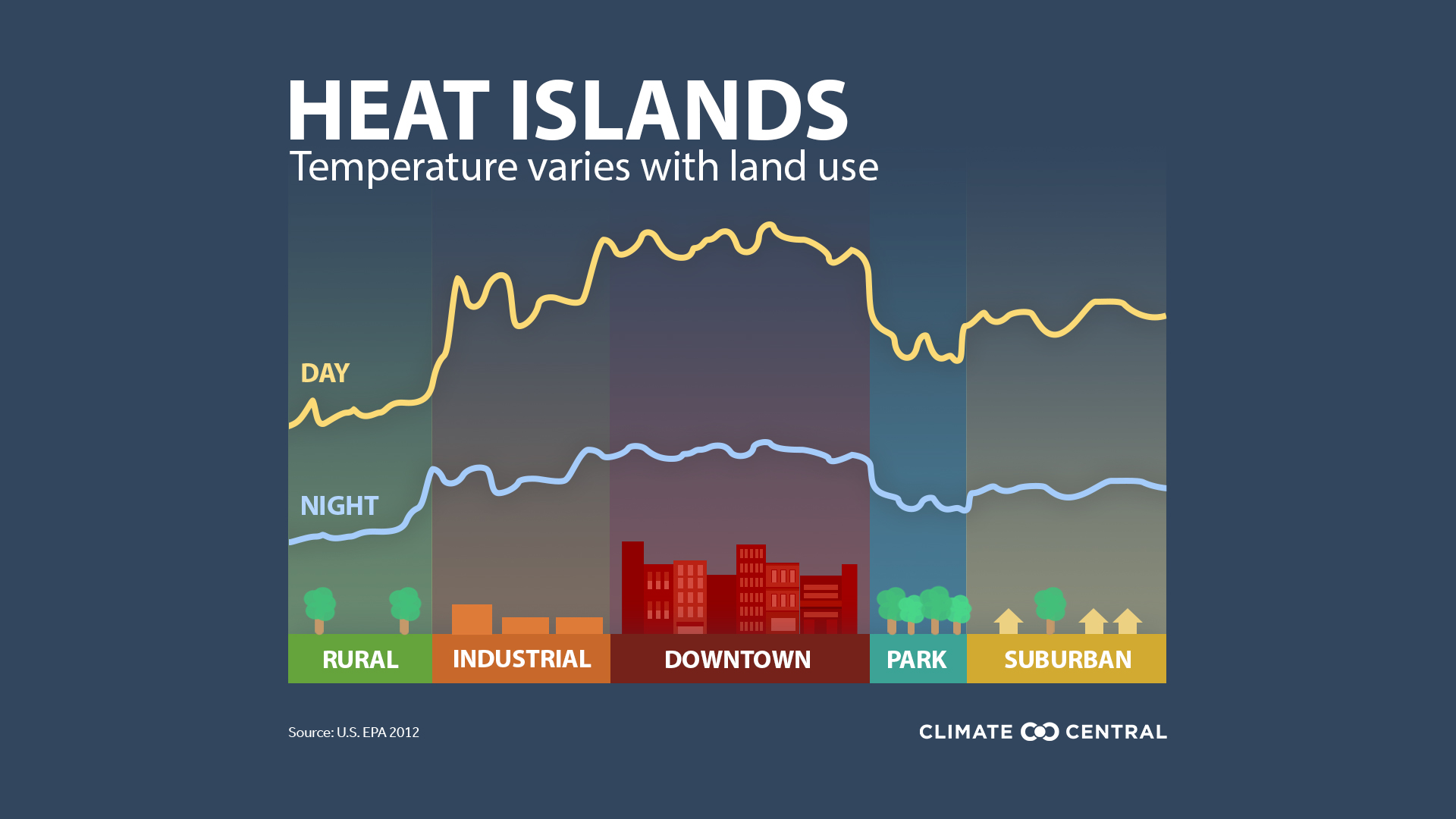
social and environmental stresses of urban heat island effect
poses a danger to people's health (heat strokes, dehydration, etc.)
people being bad-tempered during heat waves
long term building deterioration
adds up to the global warming
management of urban heat island effect
replanting trees
reducing air pollution
constructing better buildings to reduce air conditioning use
finding ways to help people manage the heat (ex. water curtains)
increasing albedo of buildings (painting them white)
smog
(smoke + fog) = CO2 + SOx + soot
photochemical smog //L.A. type// (created when there is a lot of NOx from combustion engines)
smog management
KAWKA in Wroclaw (replacing old stoves)
Large cities like Shanghai, Shenzhen, and Guangzhou restricted the number of cars on the road and started introducing all-electric bus fleets.
traffic congestion impacts
road rage
pollution
worse health
lower economic productivity
higher traffic congestion --> higher population
lower traffic congestion --> lower population
pattern: city center more congested than outer city parts
trend: depending on working hours and/or season congestion can be higher or lower
noise impacts
lack of rest
disturbance during work
reduced hearing
congested land
land that cannot be used twice
example: Park Mieszczanski in Wroclaw
before it was a military base, but it was changed into residential area
citizens wanted a green area, while developers wanted to build up the area
not a lot of green areas in the city center so it would serve others too
example: Vila Autodromo in Rio
people were evicted from their homes, because they didn't represent "luxury"
example: Nigeria
the city destroyed houses of poor people despite court ruling otherwise
social deprivation
limited access to society's resources due to poverty, discrimination, or other disadvantage
posting some initiatives online >> people without internet
written information >> people who are illiterate
providing only one language in school >> kids from abroad can't learn
racial segregation/racism
cycle of deprivation
this is a shorthand for what can happen when people or areas suffer from a combination of linked problems such as unemployment, poor skills, low incomes, poor housing, crime, bad health and family breakdown; these problems are linked and mutually reinforcing
managing social deprivation
study cases: krzywy komin (Wroclaw), Brazil
managing crimes
big fat cat in Barcelona
lights on the street
more police and police patrols
cctv
urban ecological footprint
measured in gha (a theoretical measure) // its theoretical since it measure different aspects that can't be added together
how much a city needs to satisfy its needs compared to how much is needed to tackle the waste it generates
how to calculate?
PL x WRO = 4,5 x 700 000 = 3 150 000
area of WRO --> 3150000 / 250000 = 126 --> so Wroclaw should be 126 times bigger to tackle the waste it generates
eco city
a human settlement modeled on the self-sustaining resilient structure and function of natural ecosystems
strategies:
changing habits
car-free zones
renewable sources of energy
disadvantages:
expensive
hard to implement in the whole city
smart city
is a technologically modern urban area that uses different types of electronic methods and sensors to collect specific data
strategies:
Masdar, UAE - an isolated city on a desert built using smart technological solutions to make living there bearable
for concrete they are using recycled metal waste and timber(?), as the usual material would be destroyed by underground salt water
they are using their wood waste and reusing it in the project
for transport they are using smart cars, with no drivers and sensors that could determine whether there is some obstruction on the road
a system that collected data and made sure that the citizens are environment friendly
Songdo, South Korea - a city created from scratch
they took ideas from cities that "work" and put them together
at first there were no people there, but that changed in 2014
every aspect of public life can be dealt with using a single keycard, which is a door key, public transport ticket, and payment device, all in one
the city uses the data generated to optimize energy usage, educate the inhabitants, and make them aware of how resources are being used; for example, in the apartments, monitors are installed which praise – or admonish – the persons living there, depending on whether they are reaching ambitious energy-saving goals or not
trash is automatically moved to the collection point (no traditional pick-up system); there are no trashcans around the city
CCTV around the city monitoring basically everything from traffic to actual people; its goal is to improve safety
there is little culture and entertainment around Songdo
against:
a city in Mexico refused to be "smart", because that meant that their culturally significant landmarks were destroyed