JCCC EMT Trauma (EMS 132)
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
119 Terms
the area inside skull
cranial vault
how many cranial and spinal nerves
12 cranial
31 spinal
how many vertebrae do we have
33
how many injuries are there in there to a head trauma
2
primary - the blow itself (coup-contrecoup)
secondary- the after effects (Swelling)
concussion
least severe head injury
no physical damage, but interrupts normal brain function
concussion, headache, and memory loss, N/V, dizzy
loss of consciousness is not always the case
the two types of memory loss
retro amnesia and antero amnesia
contusion
a bruise on the brain- worse than concussion
think more severe concussion s/s
epidural hematoma
blood between skull and dura mater
arterial bleeding in epidural space will result in rapidly progressing symptoms
usually goes “unconscious>conscious>unconscious
DAI
diffuse axonal injury
shearing stretching or tearing of nerve fibers from rapid accel. or. decel. of nerve fibers from falls, SBS, and falls
subdural hematoma
blood beneath dura mater but outside brain
most common TBI
usually after falls or injuries with strong decel forces
usually veinous bleeding so more gradual progression
fluctuating LOC and slurred speech
subarachnoid hemorrhage
bleeding subarachnoid space where CSF is
causes: rupture of aneurysm and trauma
usually results in death
another exp ? for decreased LOC
any recent head trauma
intracranial hematoma
basically a hem. stroke
increased ICP- what does it do
The MAP stays the same, so the perfusion to the brain decreases.
compresses the tissues in brain
tissues pushed out the foramen magnum
this causes cushing’s triad bc the brain stem is being damaged
what is cushing’s triad
htn
bradycardia
abnormal resp.
SBS main s/s
lethargy
decreased appetite
behavior changes in general
the two signs of basal skull fracture
raccoon eyes and battle sign
general head injury s/s
AMS
N/V
seizure
cushings triad
combative behavior
repetitive ?s
Dizzy
amnesia
CSF leaking
behavior change
blown pupils
posturing
facial trauma s/s that aren’t obvious
limited ocular movement (a fractured bone snags the muscle)
facial assym.
malocclusion (bad bite)
diplopia (double vision)
are alkali eye burns or acid worse
alkali
blow out orbital fracture
direct blow causes eye to push on thin base plate and fractures it.
s/s
flattened face
periorbital swelling
diplopia
inopthalmos (sunken eye)
impaired ocular movement
globe trauma in eye
an injury to the eyeball itself
pain
pupil irregularity
blood
blurry vision
hyphema
blood in anterior chamber of eye
hyphema
what do the vertabrae connect by
ligaments called disks
types of spinal cord injuries
extension
flexion
distraction compression
the higher up the spinal cord injury…..
the more body is effected
neurogenic shock
the area below the injury no longer can connect to the sympathetic NS so no vasoconstriction.
They are not cool pale and clammy usually and will have a slow pulse bc of no sympathecic response
head injury treatment
continuous ETCO2
c-spine
BP monitoring
Administer high-flow oxygen via NRB (non-rebreather) as a precaution against
unanticipated deterioration, keep SPO2 from falling below 90%
Target Etco2 level of 40
Moist sterile dressing to any potential open skull wound
Severe head injury – Elevate head of bed 30 degrees
chemical eye burns how long to irrigate
20 mins
thermal/light eye burns care
cover eyes with moist sterile dressing
conjunctivia
the membrane that lines eyelids and covers surface of eye
cornea
transparent tissue layer infront of pupil and iris
the iris
the muscle that dilates and constricts pupils
lens
transparent part of eye through which images are focused on retina
retina
the light sensitive area at back of eye that sends signals to brain
sclera
white fibrous portion of eye
What should you do before caring for evisceration
Primary and physical exam
If ear or nose cartilage is showing you should
Cover with moist sterile dressing
how many sets of ribs do we have
12
pulmonary contusion
bruise of lung tissue
damaged tissue cant perform
fluid ends up in alveoli
may hear crackles
give 02 if needed
can lead to ARDS
ARDS
acute resp distress syndrome
lungs get irritated after injury (secondary drowning, trauma, smoke inhalation, etc…)
blunt myocardial injury
can lead to arrythmias
chest pain
SOB
cardio/obstruc. shock
when bluntbtrauma to chest causes cardiac arrest
commotio cordis
leads to v-fib
traumatic asphyxia- what? s/s?
chest gets crushed and pushes blood to head and rest of body
bluish red to bluish black skin on head, neck, upper thorax
massive subconjunctival hemorrhage
def of flail chest. Care?
2 or more ribs broken in 2 or more places
BVM internal splinting
cardiac tamponade s/s
hypotension/narrowing pulse pressure, muffled heart sounds, JVD- becks triad
irregular pulse, chest pain
Trauma to male genitalia
Wrap contents in moist dressing
Stop bleeding with direct pressure
Put ice on scrotum
Ask “can you urinate”
rule of 9s
TBSA is calculated only based on percent of second- and third-degree burns – First
degree/superficial burns are not included in this calculation
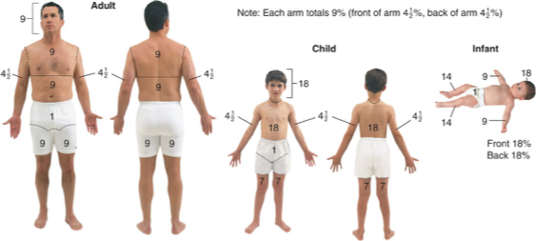
classification: red/white, moist, burns with blisters
partial thickness
complications with burns
dehydration/fluid shift
loose thermoregulation
infection
swelling/compartment syndrome- circumferential burns
airway
what could happen if there is a burn around the chest
compartment syndrome. They cant breathe
what places/types are considered critical burns
hands, feet, face, genitalia, butt, thighs, major joints
circumferential
over 15%
any respiratory
burn care
Stop the burning
Remove clothing (if not stuck to the patient)
Remove jewelry
Leave blisters intact
(No water bc of heat loss)
Minimize burn wound contamination
Cover burns with dry dressing or clean sheet (seperate fingers and toes)
Do not apply gels or ointments
Monitor SPO2, EtCO2 and cardiac monitor
High flow supplemental oxygen for all burn patients rescued from an enclosed space
Prevent systemic heat loss and keep the patient warm
for small burns (basic red cross first aid, not EMS)
run under cold water for 20 mins
cover with clean dressing
consider burn ointment if no hospital needed
escharotomy
they cut the chest so it can expand and breathe again
electrical burns considerations
remember reverse triage
can cause more internal injuries
which skeleton? skull, ribs, spine, sternum
axial skeleton
which skeleton? extremities, pelvis, scapula
appendicular skeleton
a femur fracture can loose about _____ of blood
1-2 liters
a pelvic injury can loose ____ of blood
all of it
dislocations considerations
May spontaneously reduce
may cause a fracture of adjoining bone
sprain
excessive twisting causes ligaments and tendons to stretch and tear
strain
overworking, stretching, or exertion
can cause a snap sound upon tearing
when to use a traction splint
when its an isolated, closed, midshaft femur fracture
shoulder injury splinting
sling and swath with padding between arm and chest
anterior hip dislocation
rotated outward (lateral) may be shorter
posterior hip dislocation
knee is usually bent and leg rotated inward
orthopedic trauma care
Expose (and remove jewelry)
palpate
inspect
cover and dress open wounds
PMS
is PMS there? No- gently try one time to put angulated body part back in proper place.
Tell the pt before you do this. Ask them to tell you if there is any resistance, unbearable pain, or crunching sounds
Apply splint
PMS
Ice
elevate it
Recheck PMS and 6 Ps every 5 minutes
if open fracture, cover bone with moist dressing.
MARCH
Massive hemorrhage
body sweep for holes and blood
Airway
Open and self-maintained?
Respiratory
Rate- adequate or not?
Sounds
Patency and tracheal deviation
Oximetry
02
Etco2
Circulation
strength and quality of pulses
skin
note low bp by feeling pulses
Head injury/hypothermia
cover with blanket
PMS all extremities
AVPU
Pupils
Triage/Transport
MVC significant MOI cues
death of occupant
rotation or flip
severe deformity or intrusion
ejection
how many collisions in MVC
3
car to object
body to car
organs to body
frontal collisions common injuries
extremities
internal organs
chest
head
Rear end collisions common injuries
whiplash injuries (body goes forward while head stays back)
coup-contrecoup
Lateral crashes common injuries
very common cause of death
lateral whiplash
pelvic injury
rib injury
rollover crashes common injuries
ejection
hit by objects inside
car vs motorcycle common injuries
bilateral femur fractures
crush injury from bike
abrasions
Falls exp ?s and considerations
how high
what surface
what body part
what was the cause
more than 2-3x body height is significant
internal injuries pose the greatest threat
children usually fall on their heads
GSW considerations
bullet may ricochet
fragmentation may increase injury
the path the bullet takes is called
trajectory
high velocity weapons can cause ________. What is it?
cavitation- bullet generates pressure waves damaging nearby tissues that may be distant from bullets path
the two time standards for trauma
platinum ten and golden hour
In major MOI situations with broken bones, you should…
use the back board as a splint, then go back as time permits
GCS
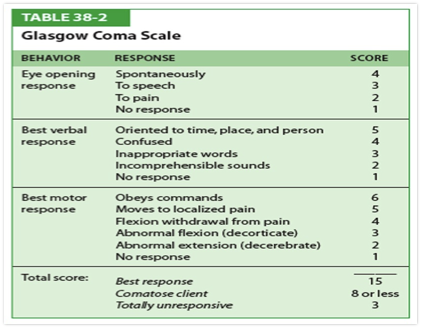
when to call for air medical
MCI
Need ALS with no ground ALS available
extended period required for extrication
When you cant get out (locked down highway)
level 1 trauma center
every aspect of trauma at all times
rehab to prevention
level 2 trauma center
surgical specialties available in < 30 min
capable of definitive care for all trauma pts
level 3 and 4 trauma centers
3- prompt resus and stabilization
4- provide ALS before transport to higher level
Johnson county level 1 trauma centers
Childrens mercy
research medical center
st lukes hospital- plaza
KU medical center
Stroke centers in Johnson county
Advent health shawnee mission and OP- p
OPR- p
research med center- c
st lukes hospital plaza- C
KU med- C
SMR
indicated when:
AMS with trauma- manual
neuro deficits (pms)- manual
midline pain- manual or verbal
evidence of intox- manaul
other severe or distracting injuries- manual or verbal
cant communicate (language)- manual
major MOI- manual or verbal
DO NOT USE C COLLAR when penetrating injury neck
only do manual when AMS, cant communicate, or movement deficits
self extricate unless worsen injuries, AMS, or neuro deficits
pts should not stay on backboard unless
used as splint
unstable pts and you dont have time
index of suspicion
awareness that unseen lifethreatening injuries may exist
trauma exp ?s and observations: MVC
spider web
airbags
# of cars
how fast
break on?
car off?
seatbelts
exterior damage (intrusion)
steering wheel damage
what angle did they get hi from
what was the cause? Medical?
headrest position?
big objects that could hit someone inside
trauma exp ?s and observations: GSW
how many shots heard
how many holes
type of gun
how long ago did it happen
trauma exp ?s and observations: bike injury/crash
helmet look like
how far away from bike?
how did they fall?
bleeding exp ?s
beta blockers?
blood thinners?
alcohol?
hemophilia?
age?
what 2 things are most important with trauma secondary assessments
the story and the physical exam
you should always give _____ for shock regardless of _____
02, SP02
the 6 p’s
what does it go with and what are they
compartment syndrome/blocked blood flow
Pain, Paresthesia, Paralysis, Pallor, Pulselessness, and Poikilothermia
ALS assist: fluid resuscitation considerations
we aim for permissive hypotension- dont turn them to coolaid but dont let them die
pediatrics need continuous infusion
geriatrics have higher BP needs
OB pts need to be within normal so that fetus stays perfused (mom shunts when hypoperfused)
bandaging care
wrap distal to proximal
dont cover fingers or toes unless they are injured
watch for 6 ps
for closed soft injuries, you should
compare both sides with the following
range of motion (ROM)
bear weight?
PMS
swelling
remove jewelry if swelling