Bloodstain Pattern Analysis
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Blood structure
Plasma: 52-62%
White Blood Cells and Platelets: <2%
Red Blood Cells: 38-48%
There is no DNA in mature blood cells
True
White blood cells contain DNA
True
Classifying Bloodstain Patterns
Spatter: occurs when a blood mass is broken up into small droplets and put into free flight by some mechanism. When these droplets strike a surface, they produce circular or elliptical shaped stains
Non-Spatter Stains: Passive and Altered
Spatter, Passive, Altered
Spatter:
Impact
Cast-off
Expiration
Splash
Projected
Forward
Back
Passive:
Drip Stain
Drip Trail
Drip pattern (liquid into blood)
Pool
Flow
Saturated Stain
Altered:
Transfer
Wipe
Swipe
Insect
Void
Data: Shape
Shape of the individual stains
• Circular
• Elliptical
• Pattern
• Irregular
Data: Distribution
Refer to Picture

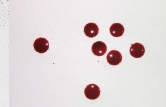
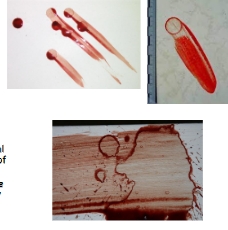
Drip
A bloodstain resulting from a falling drop that forms due to gravity

Drip Trail
A bloodstain pattern resulting from the movement of a source of drip stains between two points
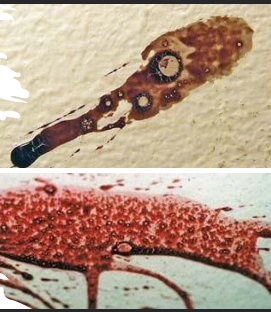
Drip Pattern
A bloodstain resulting from a liquid that dripped into another liquid, at lead one of which was blood.
Parent Stain – a bloodstain
from which a satellite stain
originated.
Satellite Stain – a smaller
bloodstain that originated
during the formation of the
parent stain as a result of
blood impacting surface or
blood into blood.

Flow
A bloodstain resulting from the movement of a volume of blood on a surface due to gravity or movement of the target surface

Pool
A bloodstain resulting from an accumulation of liquid blood on a surface.

Saturation Stains
A surface bloodstain soaked in liquid blood on a surface
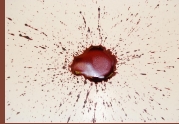
Expiration Pattern
A bloodstain pattern resulting from blood forced by airflow out of the nose, mouth, or a wound.

Projected Blood (arterial spurt)
A bloodstain pattern resulting from the ejection of blood under hydraulic pressure, typically from a breach in the circulatory system
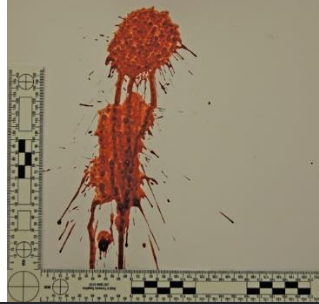
Splash Pattern
A bloodstain pattern created from a large volume of liquid blood falling onto a surface

Cast-off
A bloodstain pattern resulting from blood drops released from an object due to its
motion.

Cessation Pattern
A bloodstain pattern resulting from blood drops released from an object due to its
abrupt deceleration.
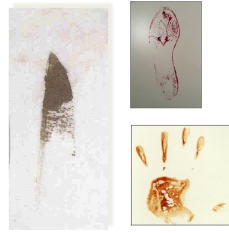
Transfer
A bloodstain resulting from contact between a blood-bearing surface and another surface

Swipe
A bloodstain resulting from the transfer of blood from a blood- bearing surface onto another surface, with characteristics that indicate relative motion between the two surfaces
Wipe
An altered stain resulting from an object moving through a pre-existing wet bloodstain.

Insect Stain
A bloodstain resulting from insect activity. It can mimic impact spatter, however no logic or overall pattern to it.

Void
An absence of blood in an otherwise continuous bloodstain or bloodstain pattern
Area of Convergence
• By considering the directionality of a
number of stains in a pattern, the CSI
can visualize the general area from
which the droplets originated.
• The reverse vectors defined by the
individual stains; directionality may (if
the stains are related) converge in the
scene.
• This convergence in a two-dimensional
area referred to as the pattern’s
convergence area (point)
Area of Origin
• Considered together the impact and
directional angles for a number of stains
associated with an impact event (a point
source dispersion of blood) may define
the origin of the stains in three
dimensions.
• Typically 10-15 individual stains are
selected in order to determine the area
of origin.