Plant cell anatomy terms (picture with label)
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
nucleus
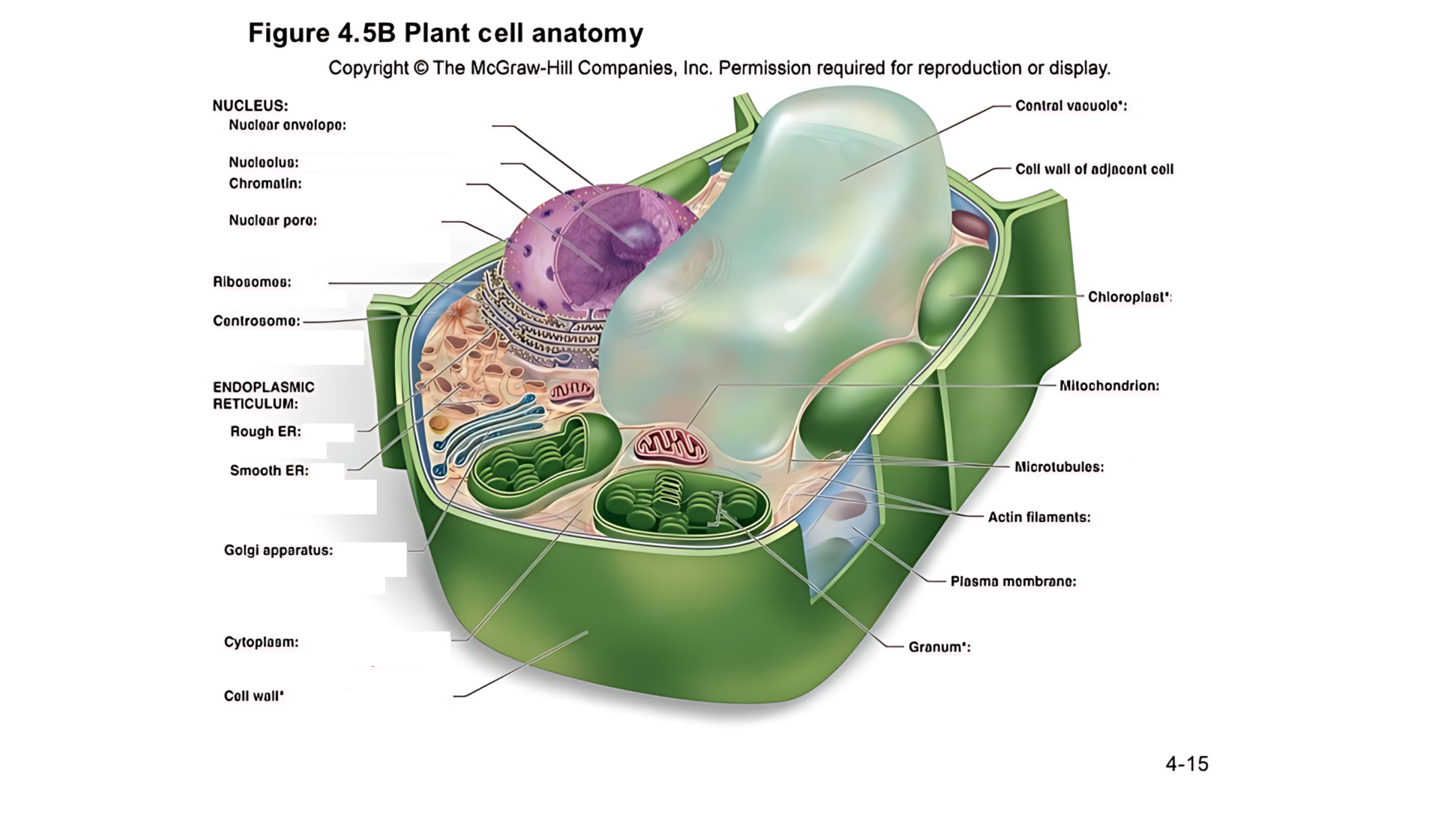
The cell's command center that contains DNA, which dictates the cell's activities and functions.
nuclear envelope
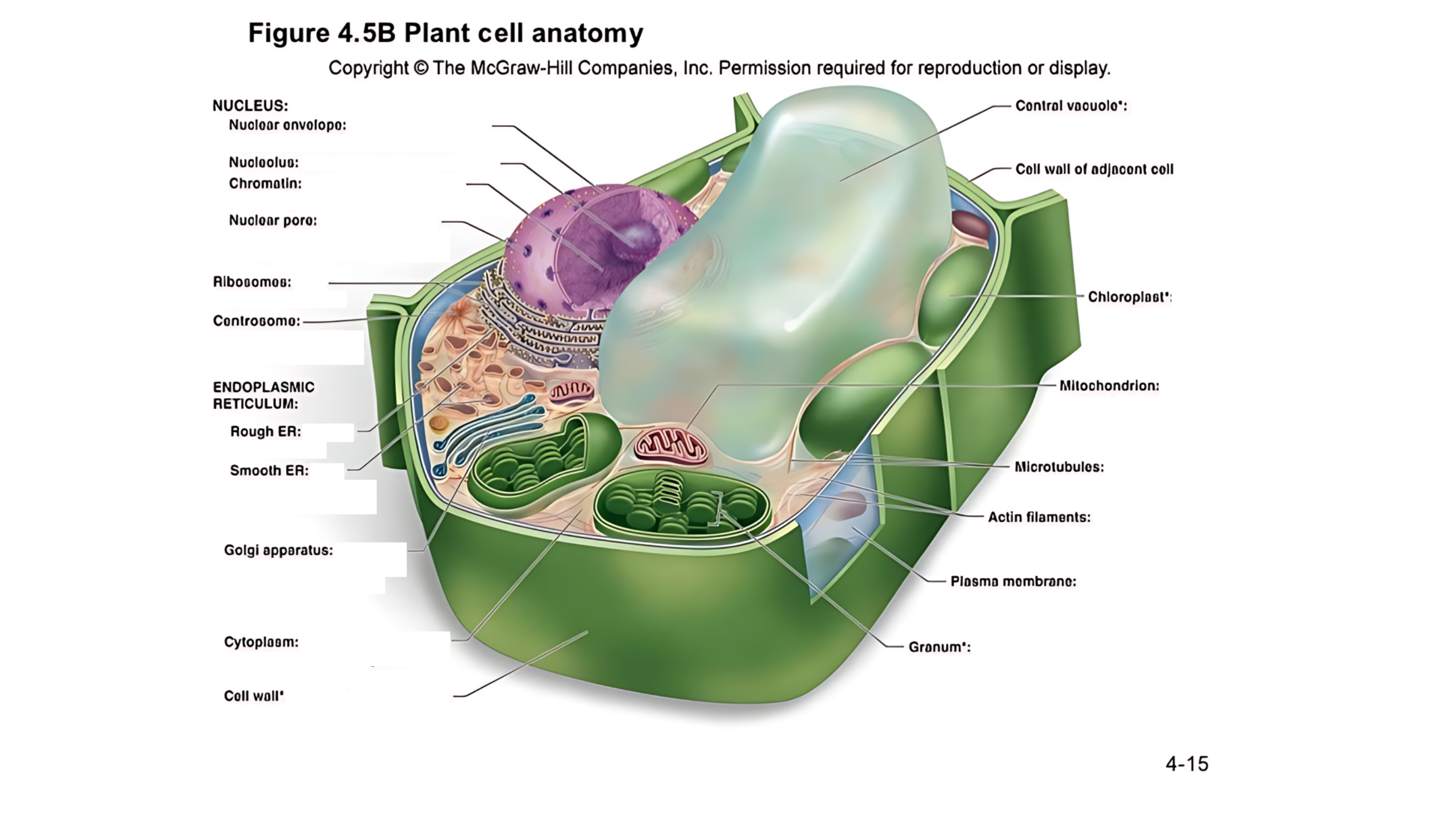
A double membrane with pores that control the flow of materials in and out of the nucleus.
nucleolus
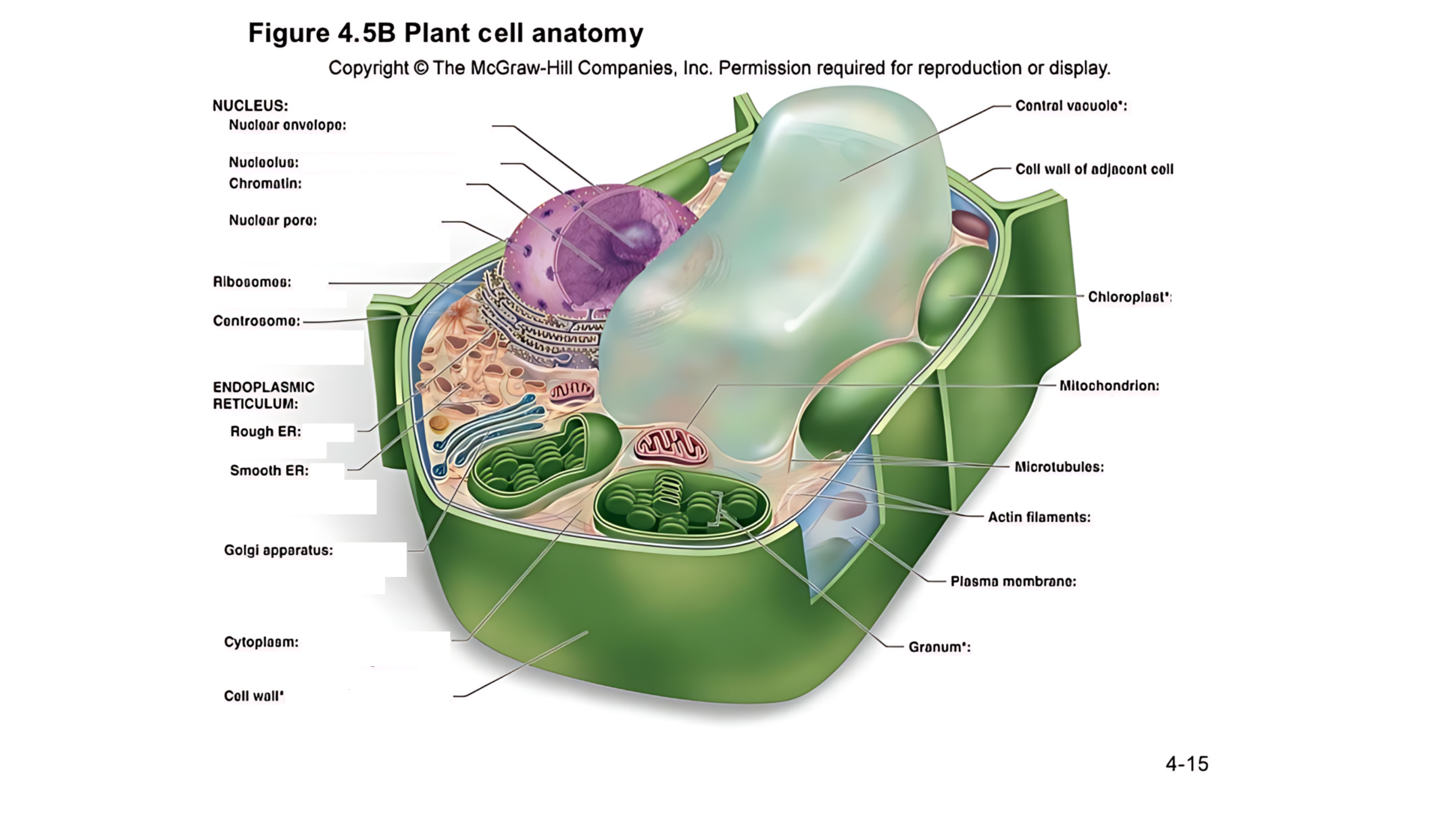
A region within the nucleus where ribosomes are produced.
chromatin
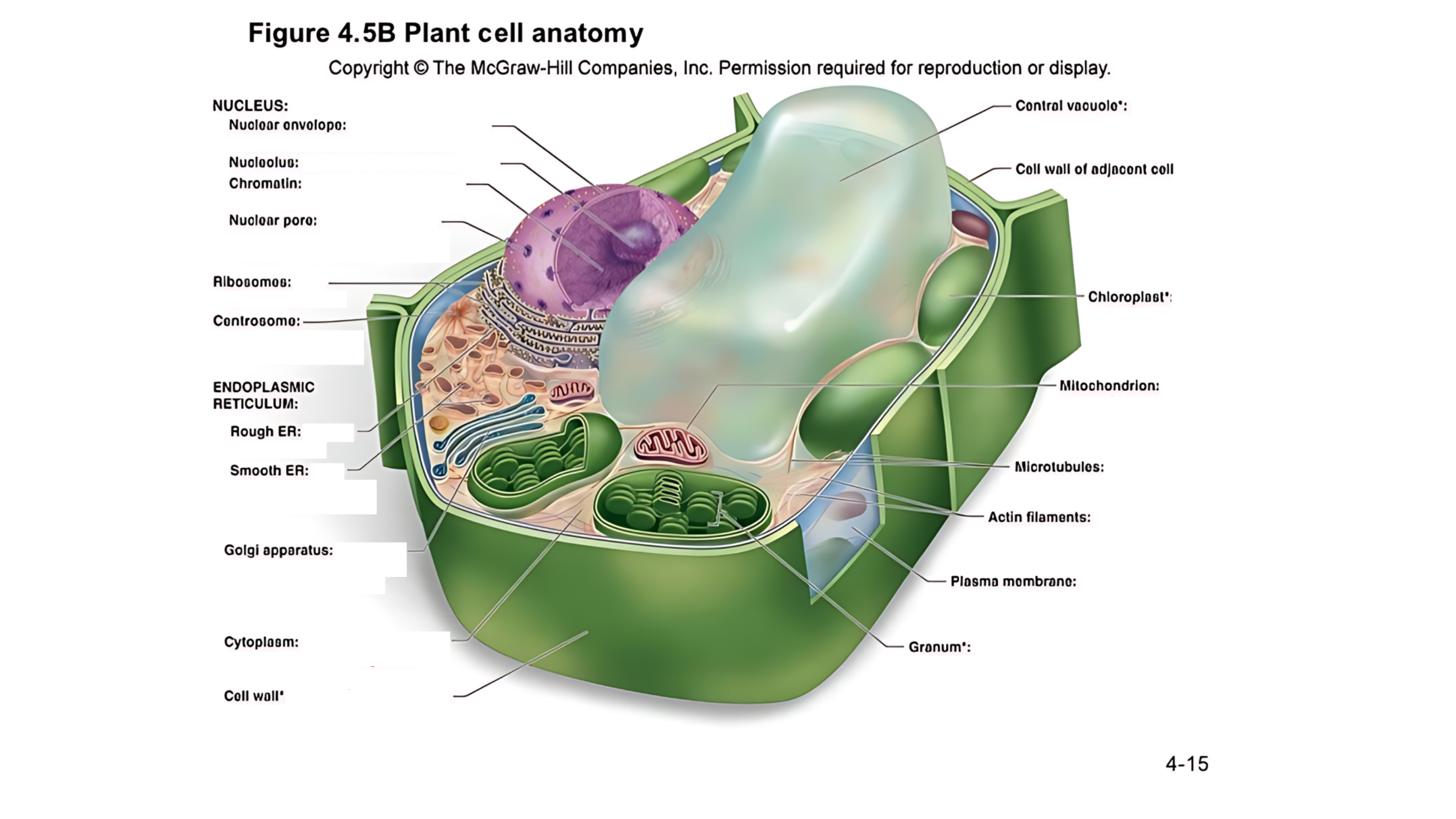
Made of DNA and proteins; it carries genetic information and condenses into chromosomes during cell division.
nuclear pore
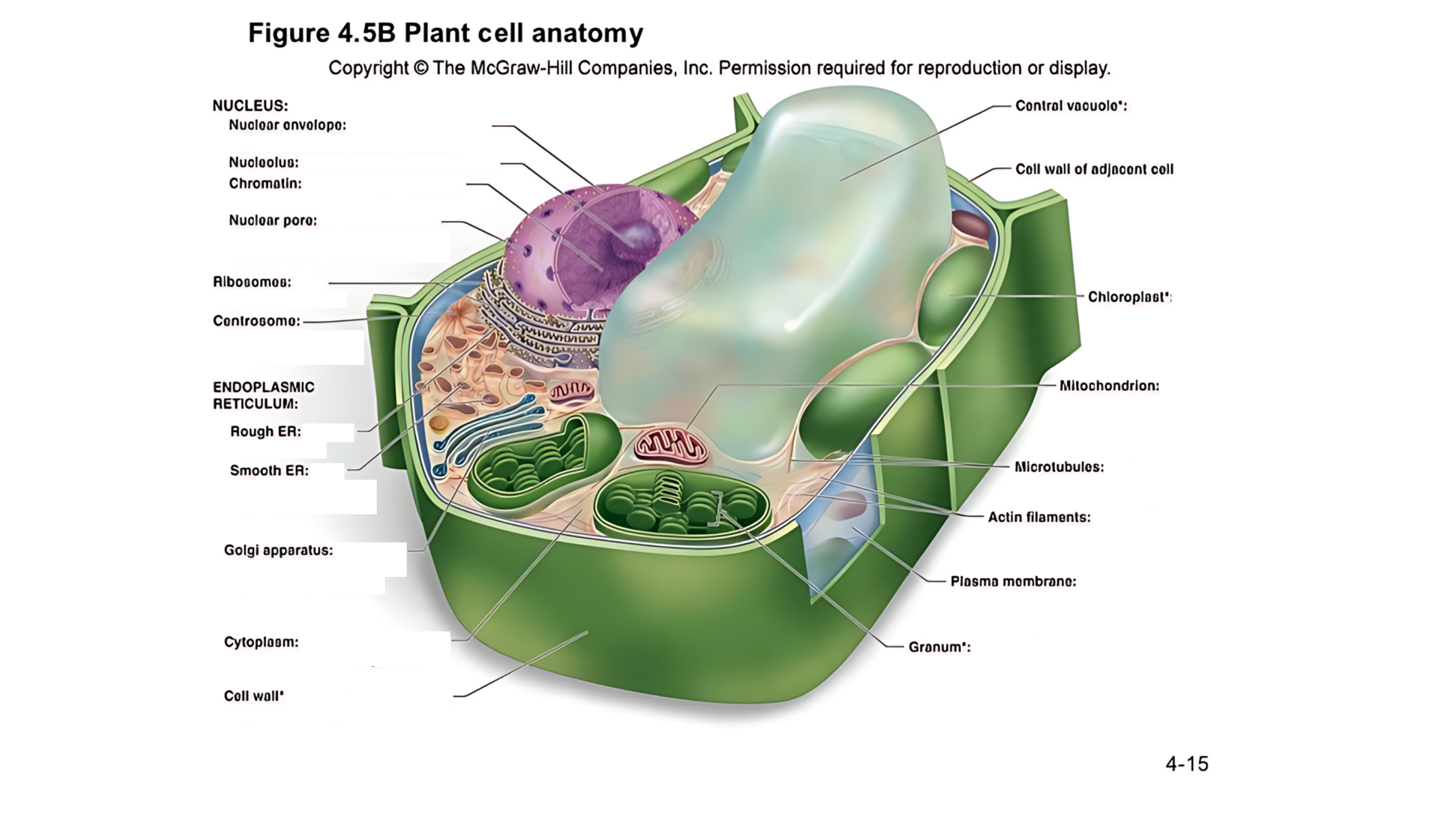
permits passage of proteins into the nucleus and ribosomal subunits of the nucleus
ribosomes
carry out protein synthesis
Small structures that make proteins by following the instructions in the DNA.
centrosome
microtubule organizing center (lacks centrioles)
Organizes microtubules and plays a role in cell division.
endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
protein and lipid metabolism
works as an intracellular highway, providing a passage for the movement of proteins and other molecules throughout the cell.
It is also involved in transporting synthesized proteins to the Golgi apparatus for further processing and transport.
rough ER
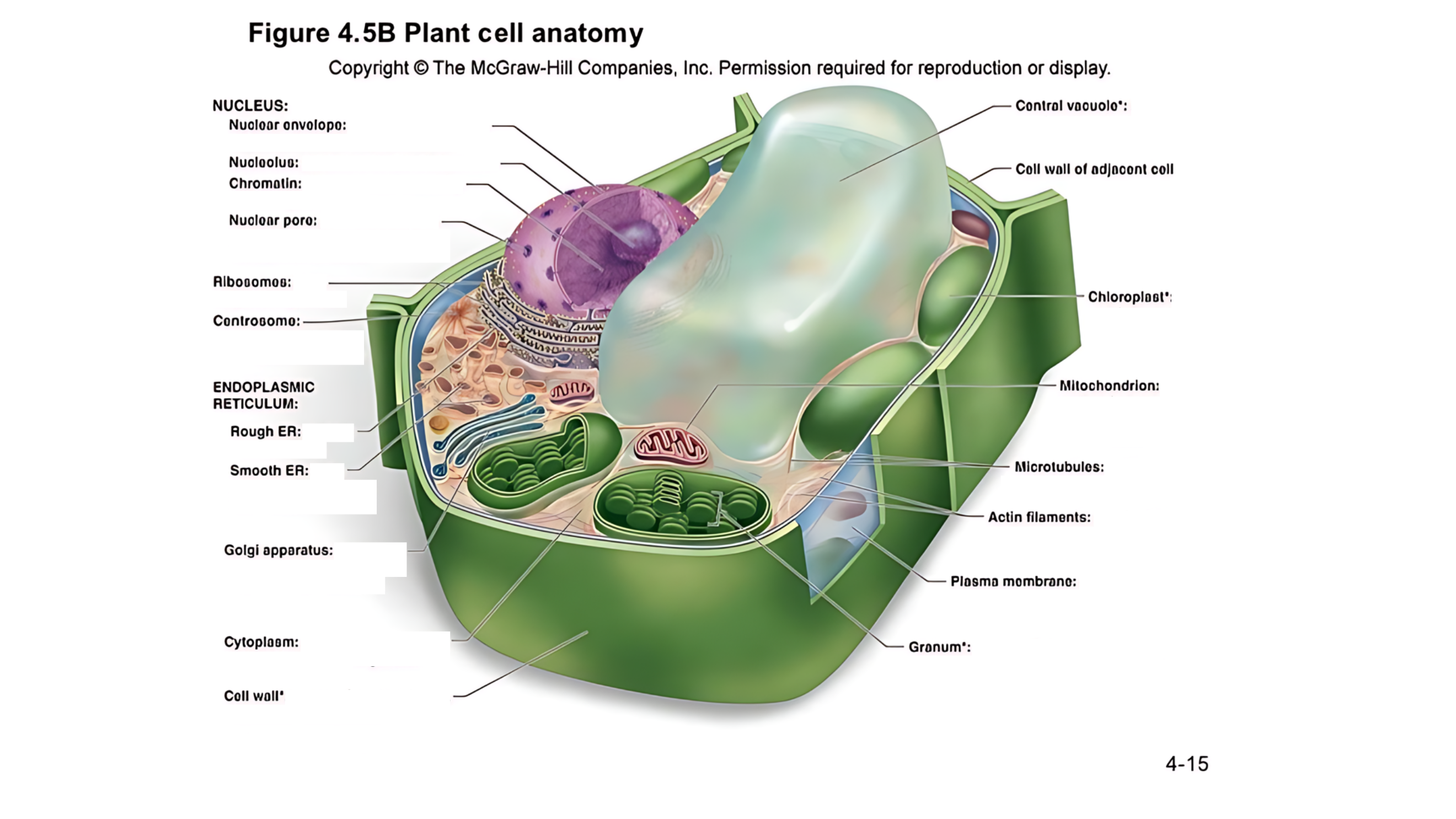
Has ribosomes on its surface and helps in making proteins.
smooth ER
Lacks ribosomes and is involved in lipid (fat) synthesis and detoxification.
peroxisome
vesicle that is involved in fatty acid metabolism
Involved in breaking down fatty acids and detoxifying harmful substances.
golgi apparatus
processes, packages, and secretes modified proteins
Packages and modifies proteins and lipids made by the ER for transport within or outside the cell.
cytoplasm
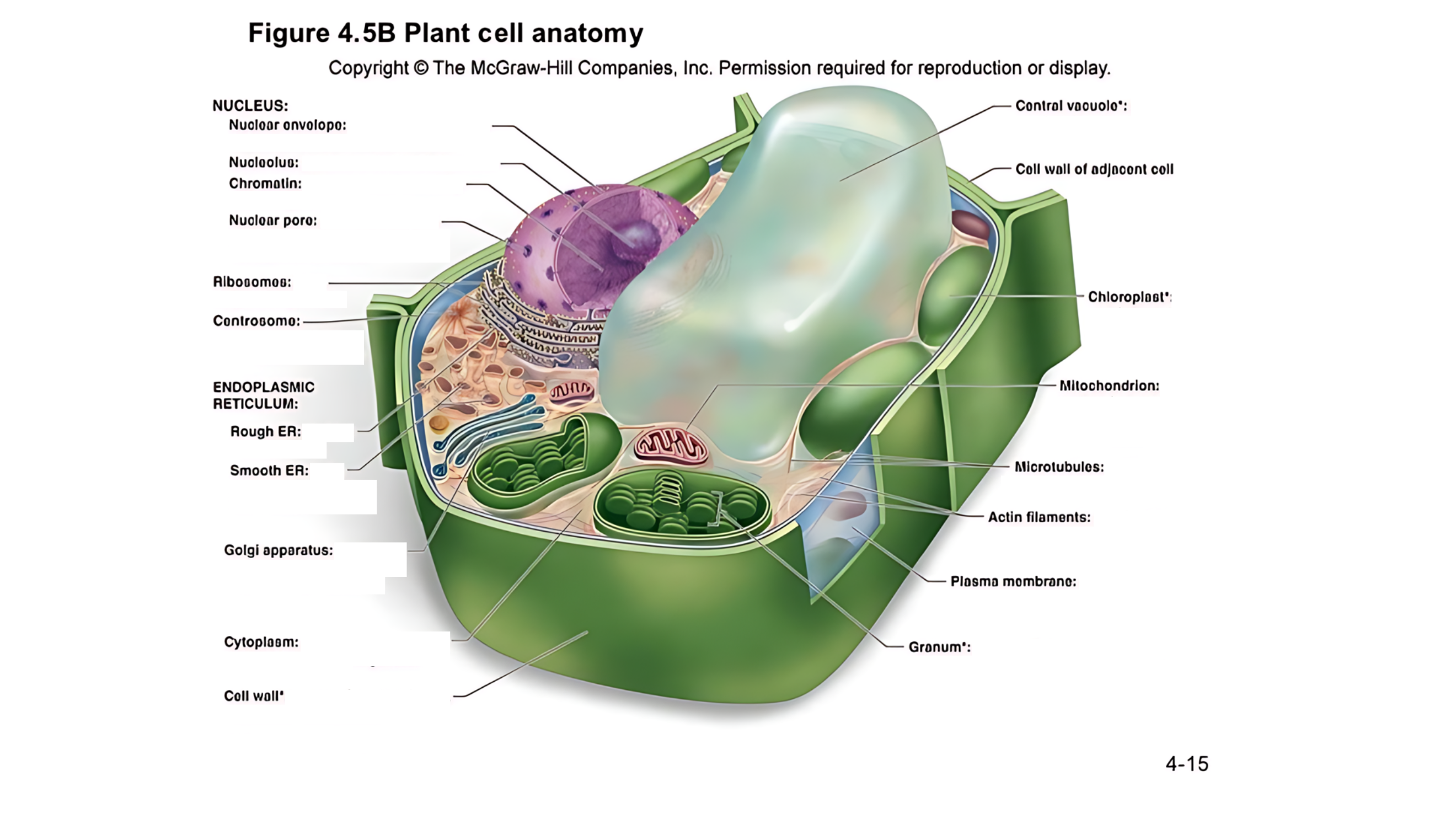
semifluid matrix outside the nucleus that contains organelles
the jelly-like substance that fills the cell and holds all the organelles in place
central vacuole
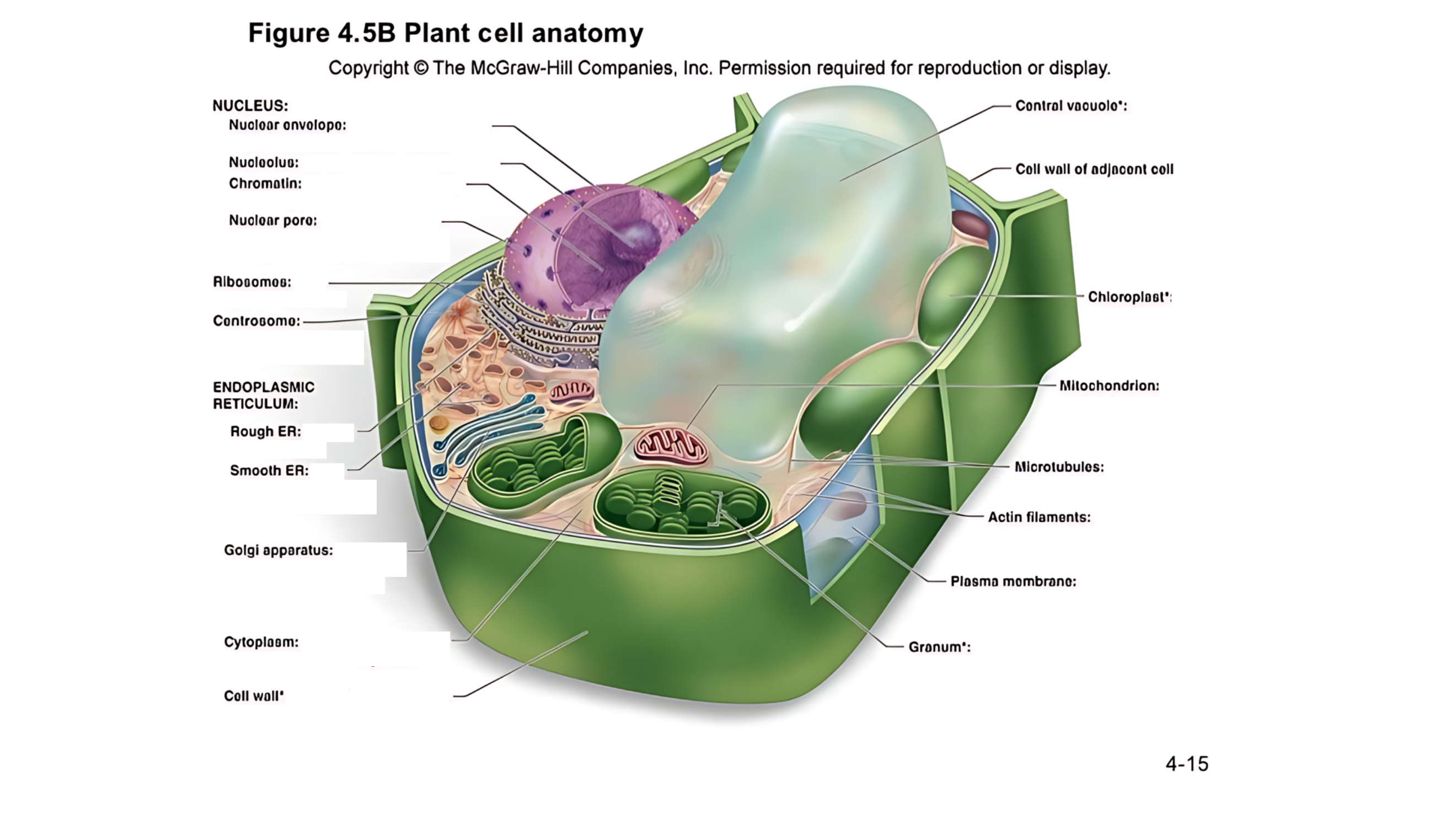
A large, fluid-filled sac that stores metabolites and helps maintain turgor pressure-the force within the cell that pushes the plasma membrane against the cell wall.
A large, fluid-filled sac that stores nutrients, and waste products, and helps maintain turgor pressure to keep the plant rigid.
cell wall of adjacent cell
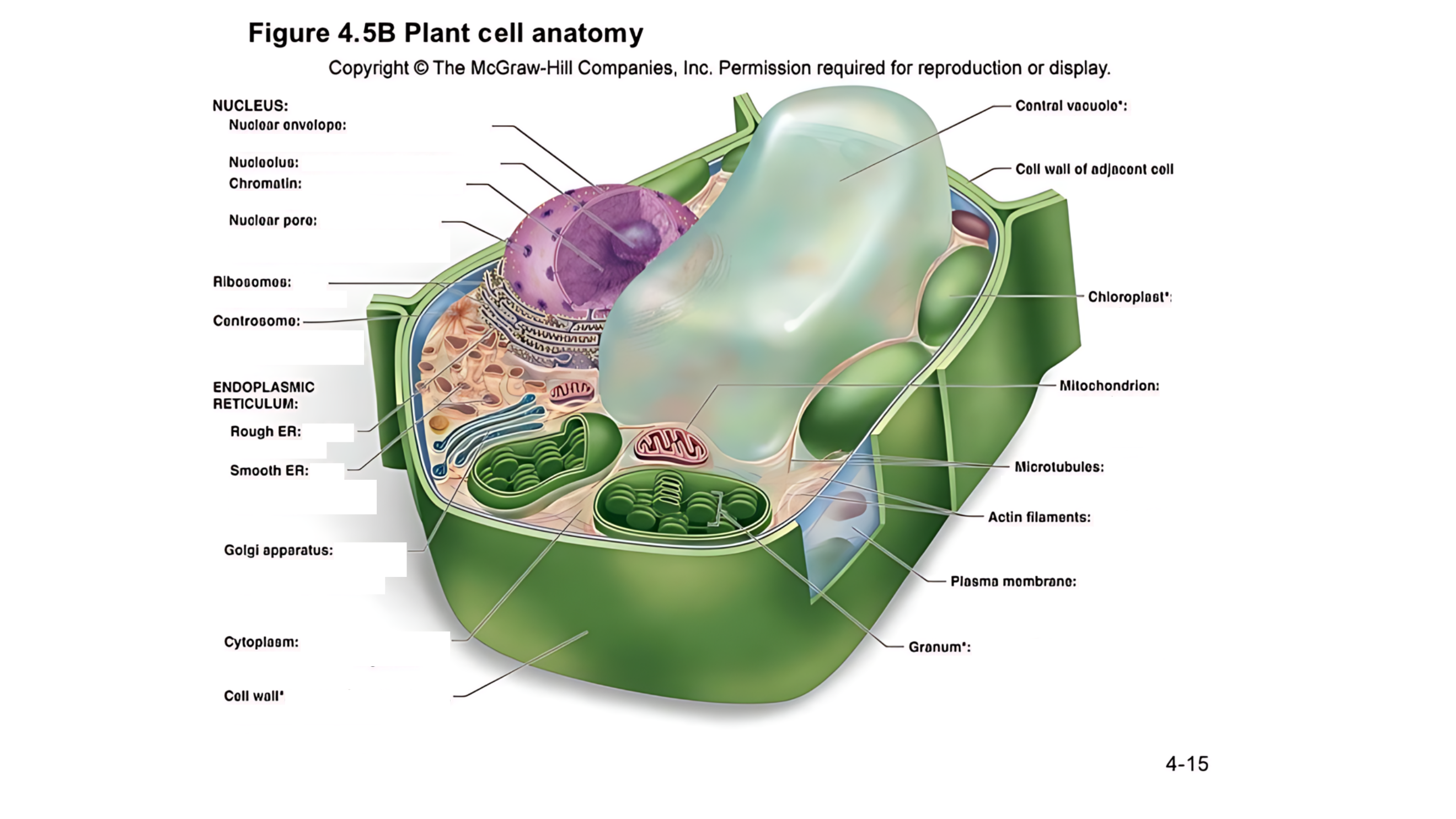
This refers to the cell walls of neighboring cells that are next to each other. In plants, these walls are often connected by structures called plasmodesmata, which allow for communication and nutrient transfer between cells. These are aligned closely and can sometimes be connected by a middle lamella, which is a layer of pectin that helps cement the cells together.
middle lamella
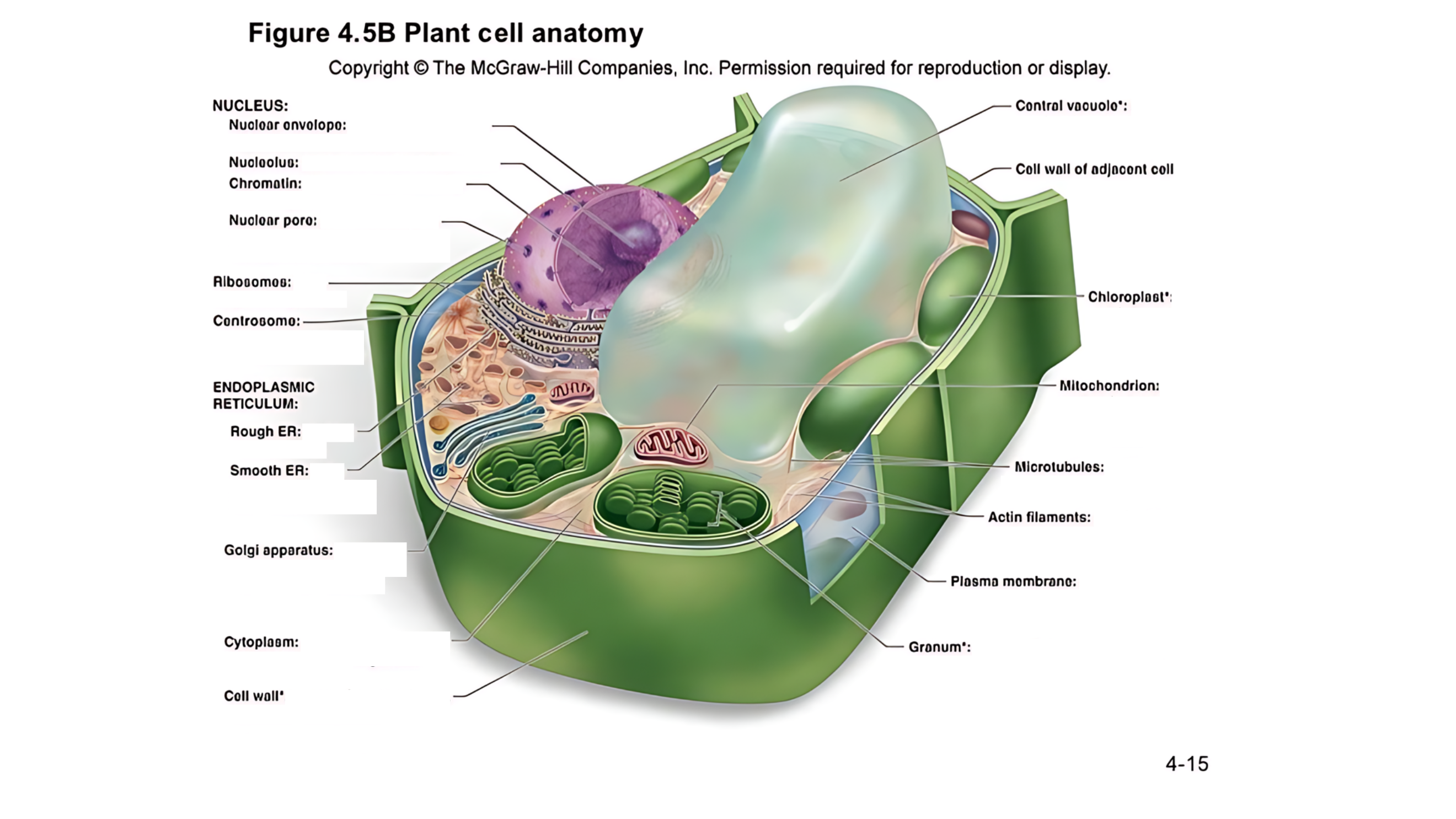
a layer of pectin that helps cement the primary cell walls of adjacent plant cells together.
A layer that helps stick plant cells together.
chloroplast
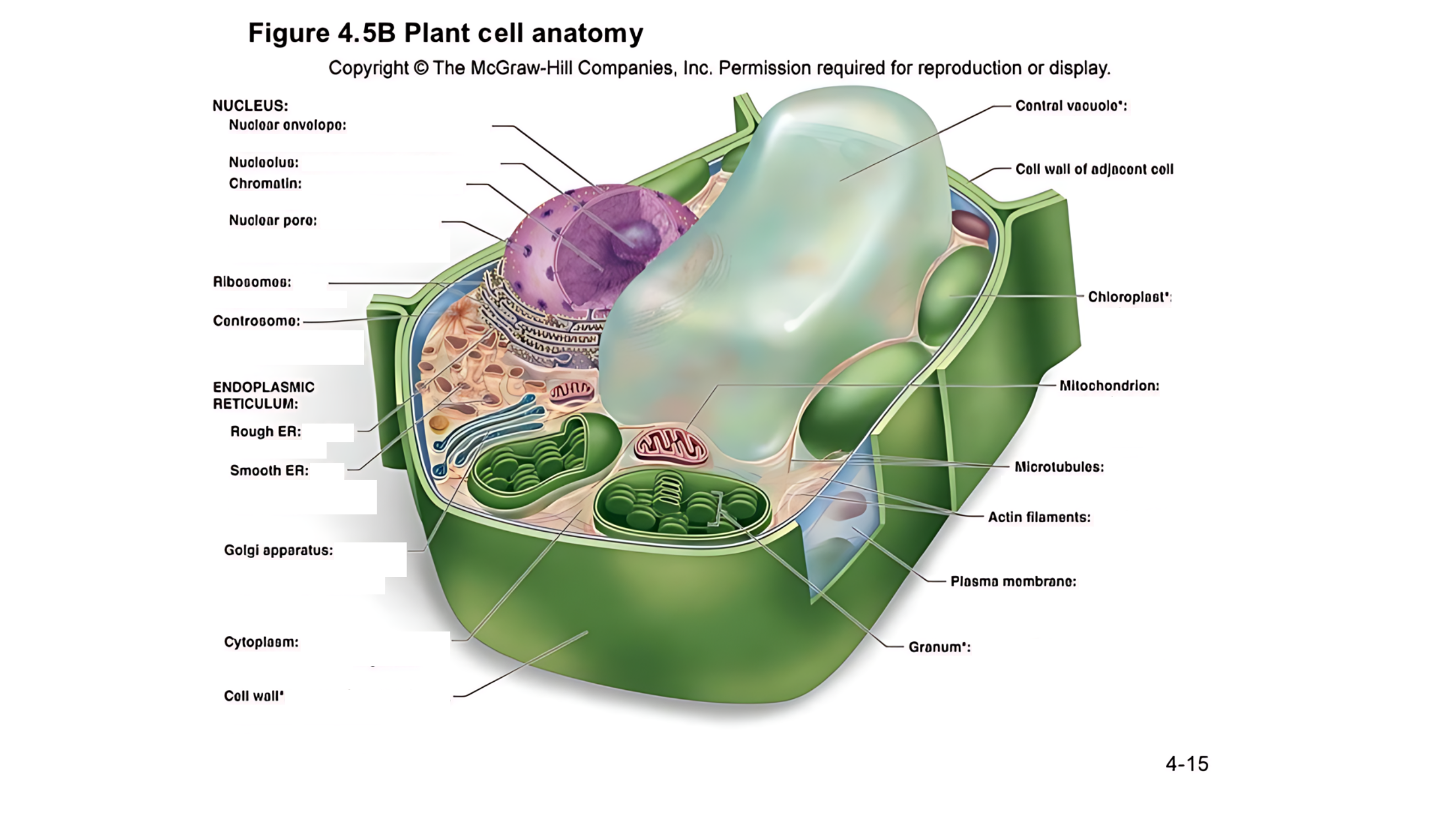
carries out photosynthesis, producing sugars
Contains chlorophyll (green pigment) and is the site of photosynthesis, where light energy is converted into chemical energy (sugar).
granum
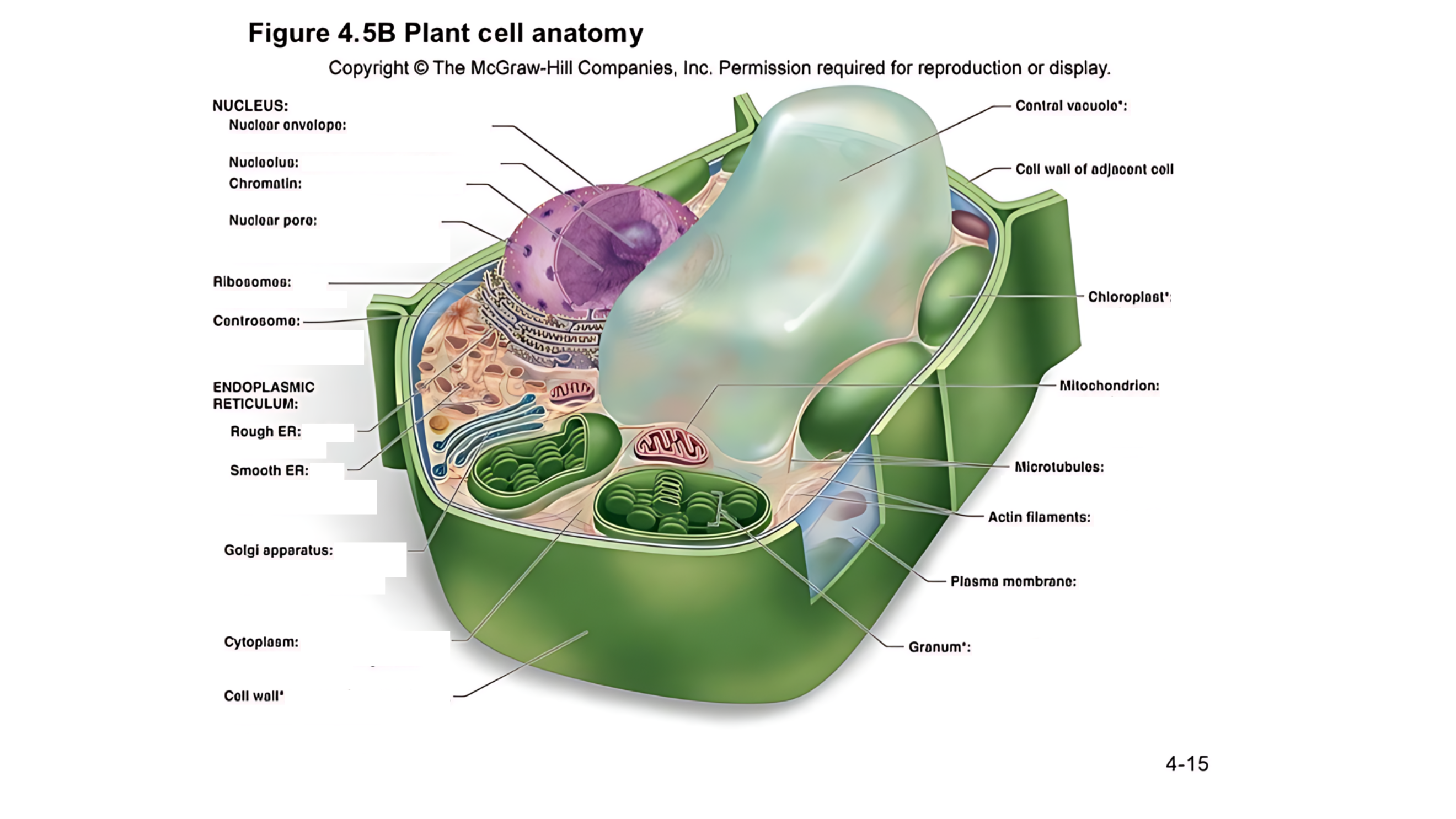
is a stack of thylakoid membranes found within the chloroplasts
mitochondrion
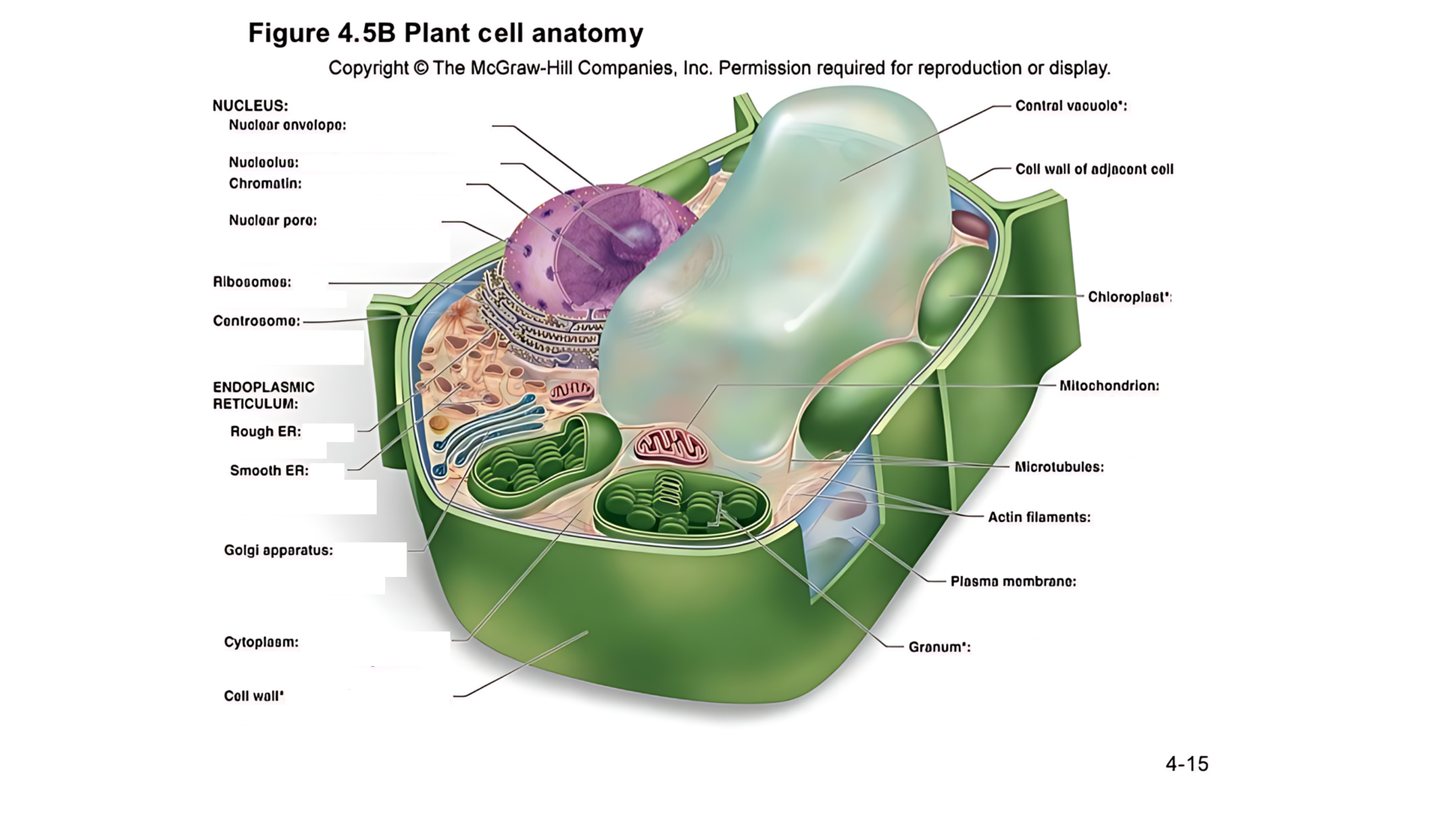
organelle that carries out cellular respiration, producing ATP molecules
produces energy (ATP) through a process called cellular respiration.
microtubules
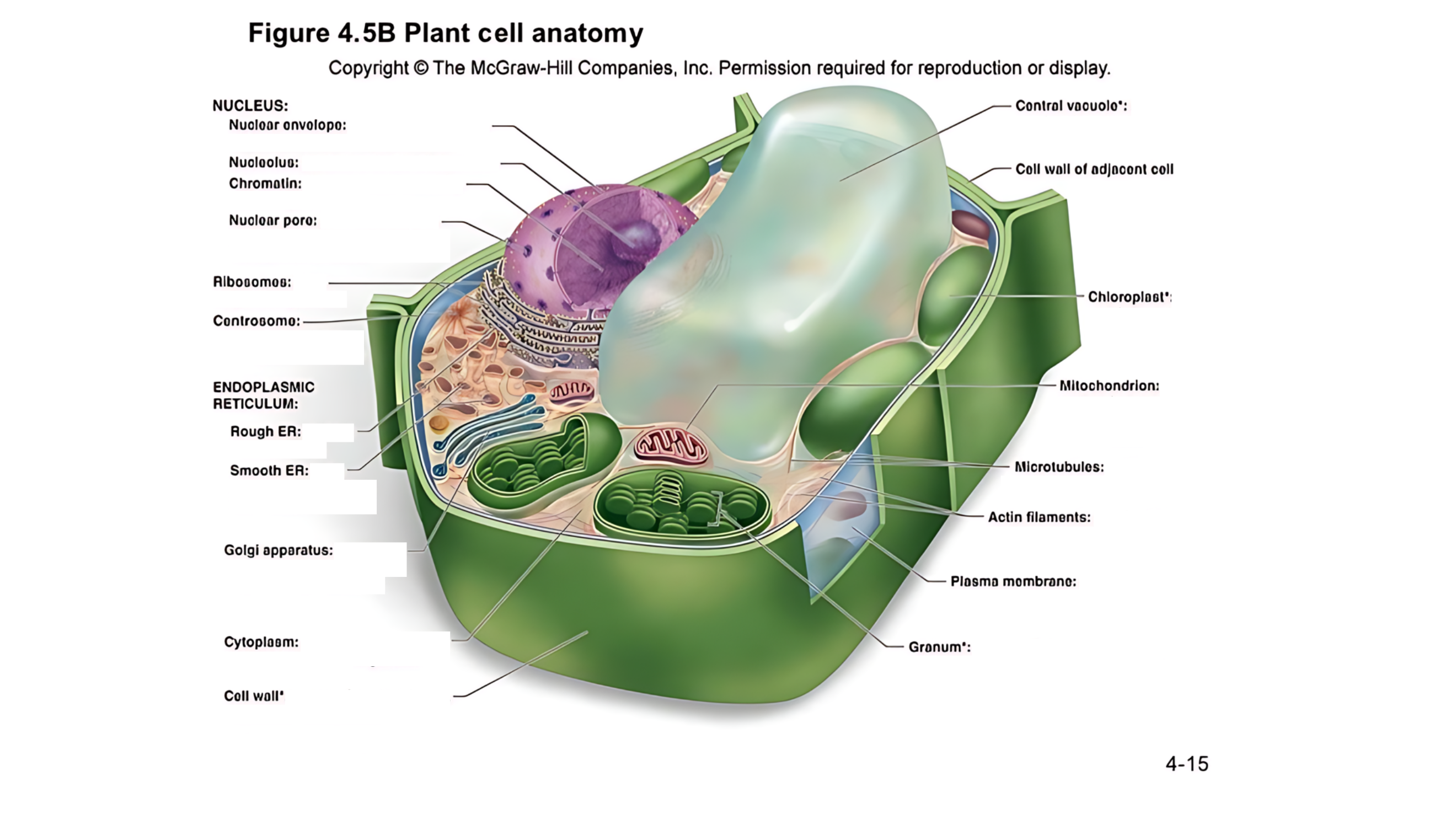
protein cylinders that aid the movement of organelles
are cylindrical structures composed of tubulin proteins. They are hollow tubes
actin filaments
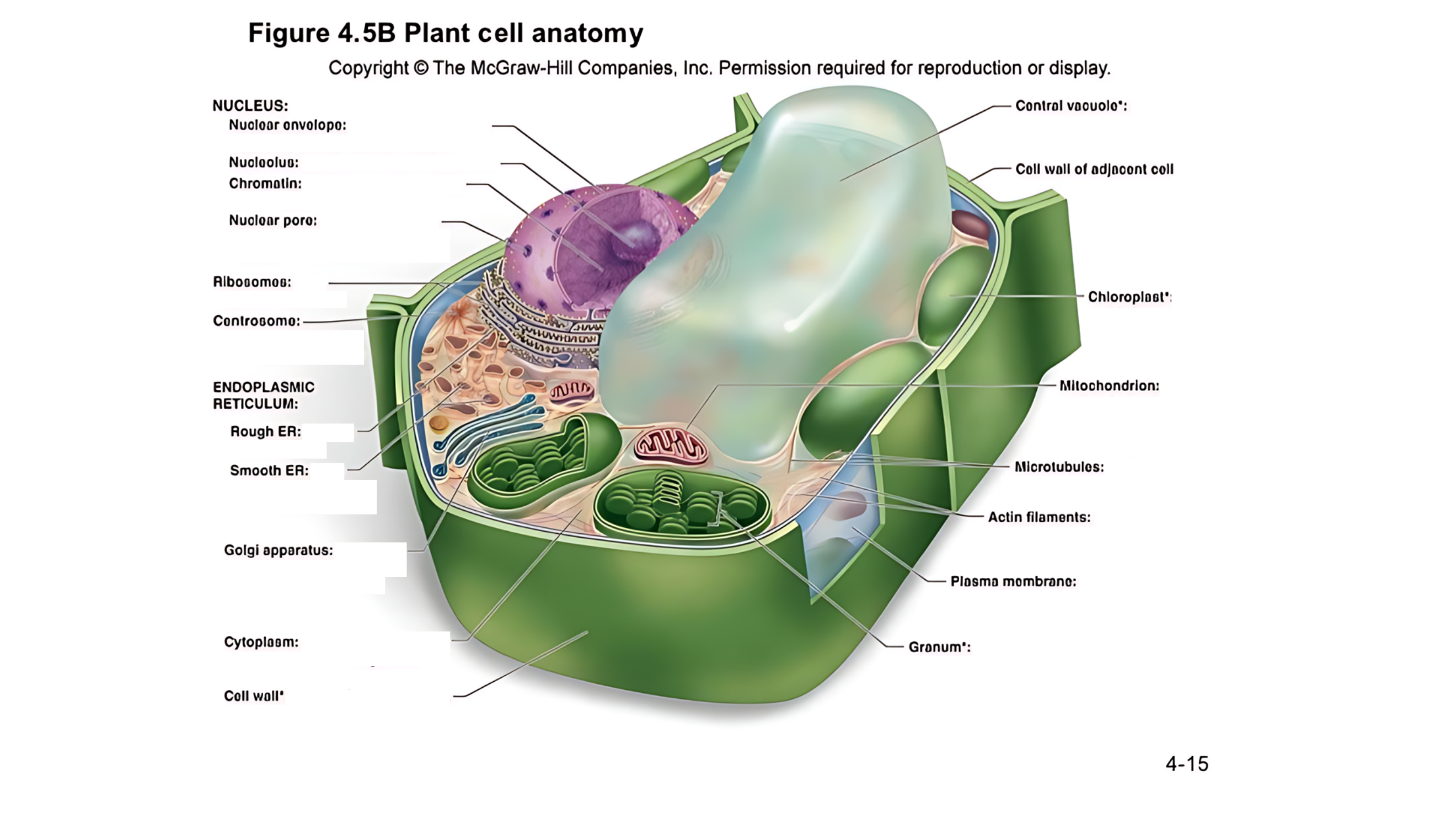
protein fibers that play a role in the movement of cell and organelles
These are very thin, flexible threads made of proteins. They help the cell maintain its shape and assist in movement and division.
plasma membrane
surrounds cytoplasm, and regulates entrance and exit of molecules
cell wall
outer surface that shapes, supports, and protects cell