16. Anti-cancer Drugs
1/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
List the classifications of anti-cancer drugs and give examples of each.
Anti-metabolites: methotrexate
Alkylating agents: cyclophosphamide
Antibiotics: doxorubicin
Mitotic spindle poisons: vinca alkaloids; vincristine, vinblastine
Hormones: prednisone, tamoxifen, anastrozole
Monoclonal antibodies: trastuzumab
Anti-metabolites - Methotrexate
Describe anti-metabolites and their mechanism of action.
Structurally related to normal compounds that exist in cell
Interfere w/availability of normal purine or pyrimidine nucleotide precursors, either by inhibiting synthesis or by competing with them in DNA or RNA synthesis
Anti-metabolites - Methotrexate
Anti-metabolites are ____ _____ ________, and their maximal cytotoxic effects are in the ___ phase.
cell cycle specific
S-phase
Anti-metabolites - Methotrexate
List characteristics of methotrexate.
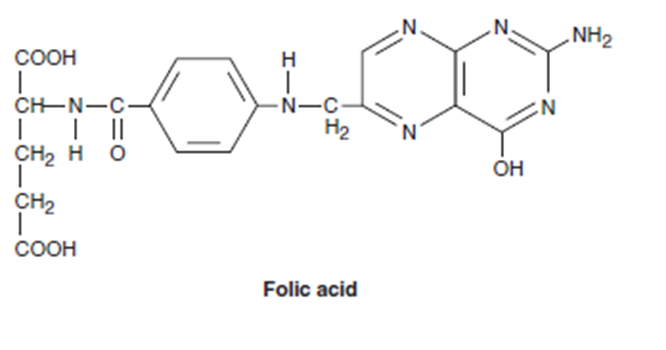
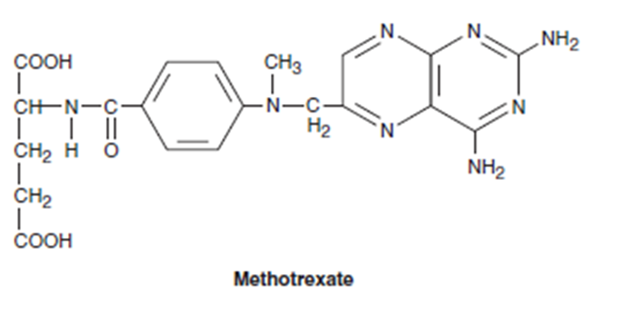
Folic acid analogue
Oldest
Highly efficacious anti-neoplastic drugs
Anti-metabolites - Methotrexate
Describe the mechanism of methotrexate.
Structurally related to folic acid
Acts as antagonists by inhibiting mammalian dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR); enzyme that converts folic acid to its active, coenzyme form, tetrahydrofolic acid
Also inhibits thymidylate synthase + other enzymes involved in folate metabolism and DNA synthesis
Anti-metabolites - Methotrexate
List the therapeutic uses of methotrexate.
Usually in combination with other drugs
Effective against acute lymphocytic leukemia, breast cancer, bladder cancer, and head and neck carcinomas
Low-dose MTX is effective as single agent against certain inflammatory diseases e.g. severe psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, and Crohn’s disease
Anti-metabolites - Methotrexate
List the adverse effects of methotrexate.
Nausea
Vomiting
Bone marrow depression
Alkylating Agents - Cyclophosphamide
Alkylation of ___ is probably the most crucial cytotoxic reaction that is _______ to the tumor cells. They exert their cytotoxic effects by __________ binding to ___________ groups on various cell constituents. Alkylating agents do not discriminate between _______ and _______ cells, even though they are most toxic for _______ ________ cells.
DNA
lethal
covalently
nucleophilic
cycling
resting
rapidly dividing
Alkylating Agents - Cyclophosphamide
Why is cyclophosphamide one of the most popular alkylating agents used in many solid tumors?
Prominent immunosuppressant property
Alkylating Agents - Cyclophosphamide
List the adverse effects of cyclophosphamide.
Alopecia and cystitis (due to another metabolite, acrolein)
Antibiotics - Doxorubicin
Antibiotics owe their cytotoxic action primarily to their _____________ with ___, which cause ___________ of DNA function. They are cell cycle ____________.
interactions
DNA
disruption
non-specific
Antibiotics - Doxorubicin
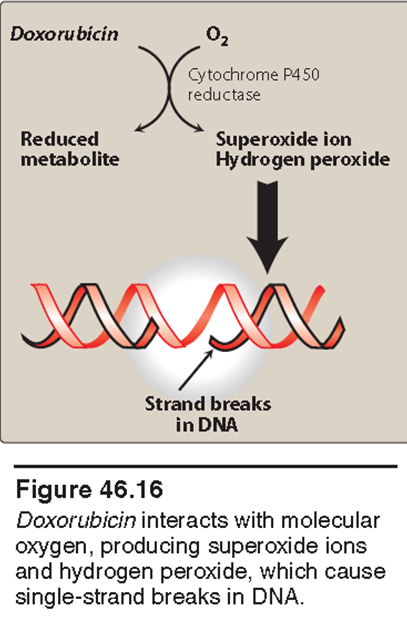
Describe the mechanism of doxorubicin.
Doxorubicin-derived free radicals can induce membrane lipid peroxidation, DNA strand scission, and direct oxidation of purine or pyrimidine bases, thiols, and amines
Antibiotics - Doxorubicin
What is the most serious adverse reaction of doxorubicin?
Irreversible, dose-dependent cardiotoxicity
Microtubule Inhibitors/Mitotic Spindle Poisons
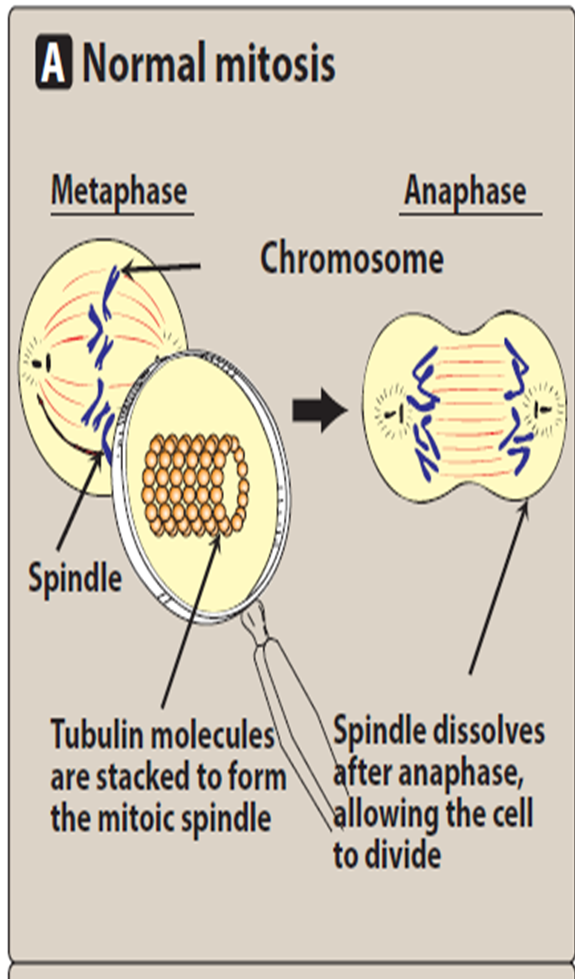
Vincristine and vinblastine are _____ _________. They bind to microtubular protein ‘_______’, prevent its _____________ and ________ of microtubules, cause disruption of mitotic _______, and interfere with ____________ function. They are cell cycle ________ and act in the ________ phase.
mitotic inhibitors
tubulin
polymerization
assembly
spindle
cytoskeletal
specific
mitotic
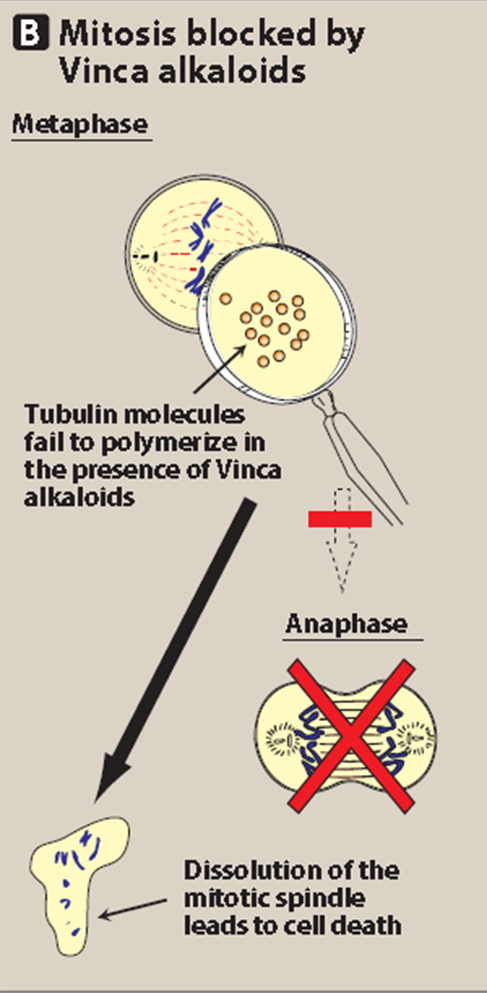
Microtubule Inhibitors/Mitotic Spindle Poisons
Vincristine and vinblastine are _______-acting drugs, useful in inducing __________ in childhood acute _____________ _______.
rapidly
remission
lymphoblastic leukemia
Microtubule Inhibitors/Mitotic Spindle Poisons
List the adverse effects of microtubule inhibitors.
Peripheral neuropathy and alopecia
Steroid Hormones and their Antagonists
Describe prednisone and what it is used for.
Potent
Synthetic
Anti-inflammatory corticosteroid
Primarily employed to induce remission in patients with acute lymphocytic leukemia & in treatment of both Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphomas
Steroid Hormones and their Antagonists
Describe tamoxifen and what it is used for.
Estrogen antagonists with some estrogenic activity
Classified as selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM)
Used for first-line therapy in treatment of estrogen receptor positive (ER+ve) breast cancer
Used prophylactically in reducing breast cancer occurrence in high-risk women
Steroid Hormones and their Antagonists
Anastrozole is an _________ inhibitor. The aromatase reaction is responsible for extra-adrenal synthesis of _________, which takes place in _____, fat, muscle, skin, and breast tissues, including breast _____________. __________ aromatization is an important _____ of estrogen in _______________ women. Aromatase inhibitors ________ the production of estrogen in these women. They are ______ active and cause almost a total suppression of estrogen synthesis.
aromatase
estrogen
liver
malignancies
Peripheral
source
postmenopausal
decrease
orally
Define and describe targeted therapy.
Drugs targeted at pathways, processes, and proteins which are uniquely disrupted in cancer cells or in tumor microenvironment
E.g. receptors, genes, angiogenesis, tumor pH
List the advantages of targeted therapy.
More effective treatments that can attack specific breast cancer cells without harming normal cells
Commonly used in combination with traditional chemotherapy with fewer severe adverse effects
Monoclonal Antibodies - Trastuzumab
Describe trastuzumab and its functions.
Humanized monoclonal antibody, specifically targets extracellular domain of HER2 growth receptor
In patients w/metastatic breast cancer, overexpression of transmembrane human epidermal growth factor receptor protein 2 (HER2) is seen in 25-30% of patients
Monoclonal Antibodies - Trastuzumab
Describe the mechanism of trastuzumab.
Binds to HER2 sites in breast cancer, gastric cancer, etc, and inhibits proliferation of cells that overexpress the HER2 protein → decreasing no. of cells in S-phase
By binding to HER2, it blocks downstream signaling pathways, induces antibody-dependent cytotoxicity, and prevents release