ap psych 7.2
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Effortful Processing
Type of memory encoding that requires active work and attention to embed information into long term memory.
Automatic Processing
The unconscious encoding of information about space, time, frequency, and well learned tasks.
Shallow Encoding
A basic level of processing that focuses on surface characteristics of information such as the sound or appearance of words without engaging with its meaning.
Structural
Type of shallow processing that focuses on the physical structure of information.
Phonemic
Shallow processing that focuses on the auditory aspects of information.
Deep Encoding
Involves thoroughly processing information by focusing on its meaning and connecting it to existing knowledge.
Semantic processing
Encoding information based on its meaning.
Self Reference Effect
Our improved memory of information that is personally meaningful to us.
Storage
The process of retaining information in the brain over time.
Flashbulb Memories
Vivid memories of emotionally significant events that are stored in the amygdala.
Hierarchy of Memory
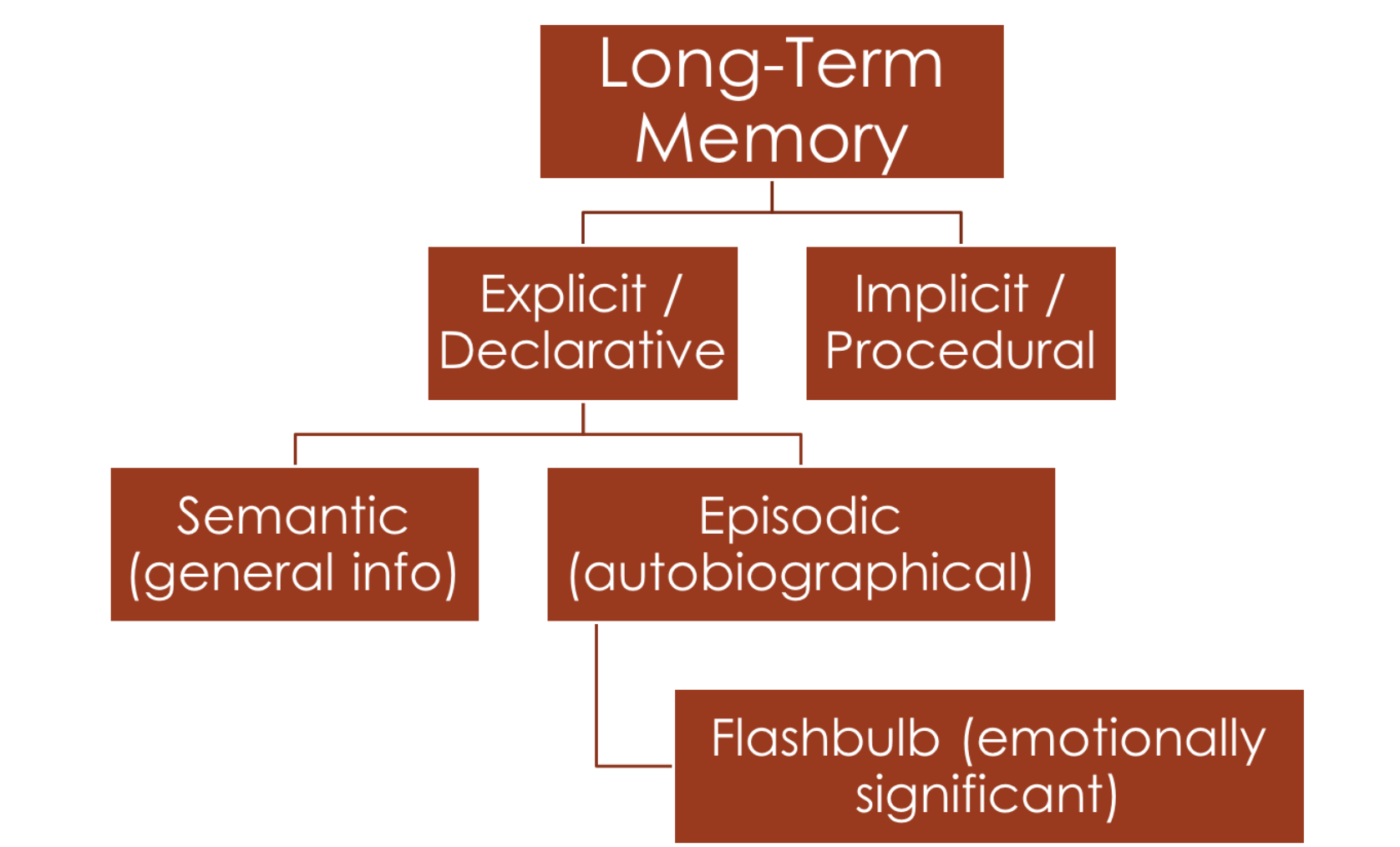
Prospective Memory
Remembering to perform a planned action or recall a planned intention at some point.
Massed Practice
Learning strategy where content is studies intensively over a short period without breaks.
Distributed Practice
Where learning is more effective when study sessions are spaced out over time, rather than crammed into one session.
Maintenance Rehearsal
Learning technique that involves repeatedly reviewing information to keep it in short term memory.
Elaborative Rehearsal
Memory technique that involves deep processing of information by adding meaning or connecting it to existing knowledge.
Retreival
The process of accessing and ringing stored information back into conscious awareness.
Retrieval Cues
Stimuli that help bring preciously learned information to mind. lThey play a critical role in the procedss of retrieving memories.
Internal Cues
Thoughts or feelings associated with the original learning.
External Cues
Environmental factors or objects that can trigger memories
Recall
Type of memory retrieval that involves accessing information without the aid of cues.
Recognition
Type of memory retrieval that involves identifying information when it is presented.
Familiarity
Sensing something that has been encountered before.
Identification
Matching new information with stored knowledge.
Context Dependent Memory
When you remember information better in the same environment where you first learned it.
State Dependent Memory
The phenomenon where memory retrieval is most effective when an individual is in the same state of consciousness as they were when the memory was formed.
Mood Congruent Memory
The tendency to recall information that is consistent with one’s current mood.
Serial Position Effect
The tendency to remember items at the beginning and end of a list better than those in the middle.
Testing Effect
Phenomenon where long term memory is enhanced when some of the learning period is devoted to retrieving the information through testing.
Metacognition
The awareness and understanding of one’s own thought processes in relation to learning and memory.