Lecture 1: Class I Anti-Arrhythmics (Sodium Channel Blockers)
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Class I Anti-Arrhythmics
A classification of antiarrhythmic medications that primarily block sodium channels and affect Phase 0 in the cardiac action potential.
Class Ia
Includes Disopyramide, Quinidine, and Procainamide.
Class Ib
Includes Lidocaine and Mexiletine.
Class Ic
Includes Flecainide and Propafenone.
Mnemonic for Class 1 Anti-Arrthymics
Double Quarter Pounder Lettuce Mayo Fries Please
Disopyramide, Quinidine, Procainamide, Lidocaine, Mexiletine, Flecainide, Propafenone

Proarrhythmic effects
Potential life-threatening drug-induced arrhythmias caused by Class I antiarrhythmics.
QTc prolongation
measure of delayed ventricular repolarization
must be monitored when using Class I antiarrhythmics
Black Box Warning for Class I antiarrhythmics
mortality → should be reserved for patients with life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias.
Ventricular arrhythmias
Includes vfib, vtach, and PVCs
Bradycardias
Includes sinus bradycardia, sinus pause, sick sinus syndrome, and heart block.
Supraventricular arrhythmias
Includes atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, atrial tachycardia, and AV nodal reentrant tachycardia.
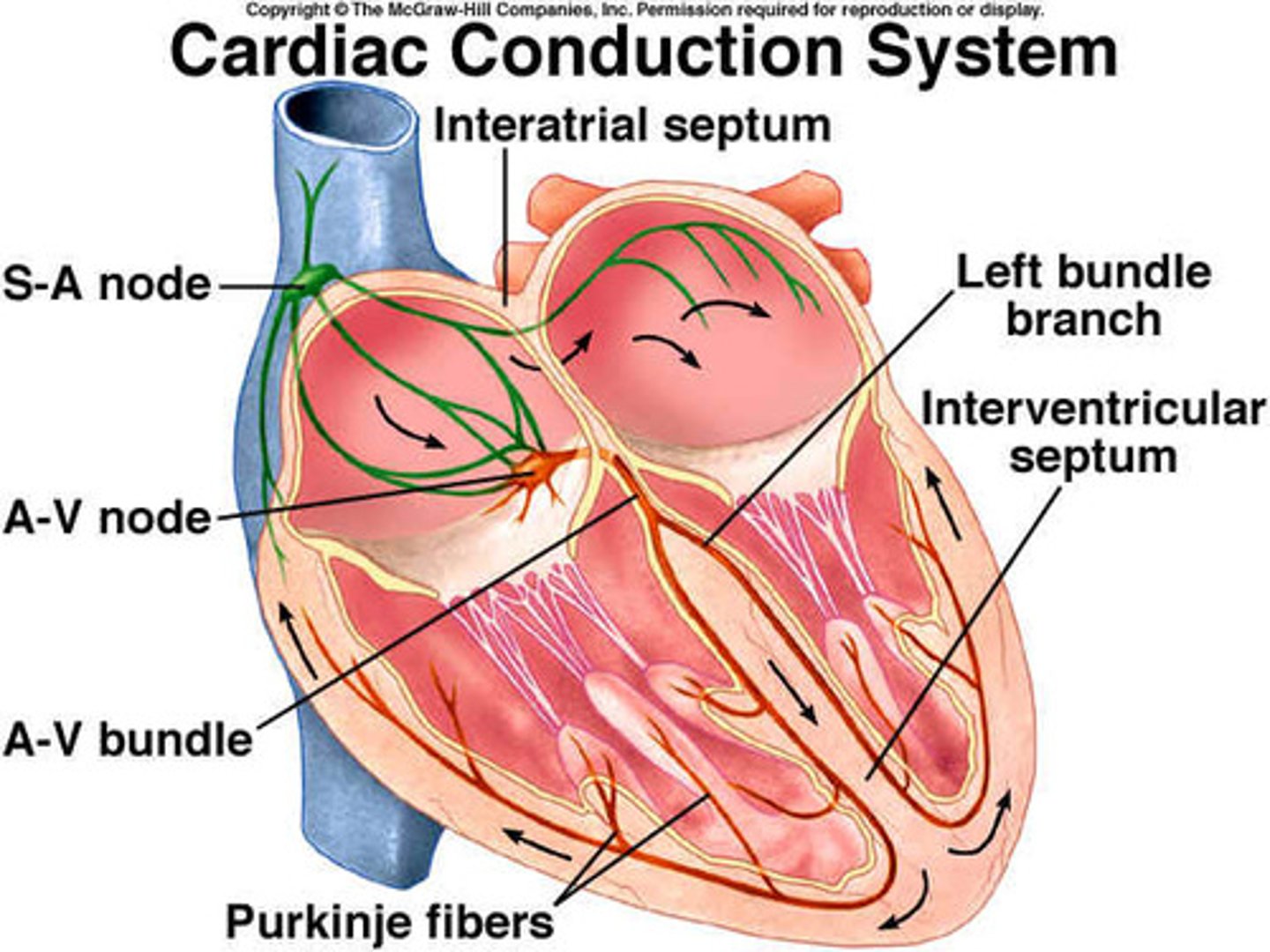
Cardiac Conduction Pathway
Includes SA Node, Right and Left Atriums, AV Node, Bundle of His, Right and Left Ventricles, and Purkinje Fibers.
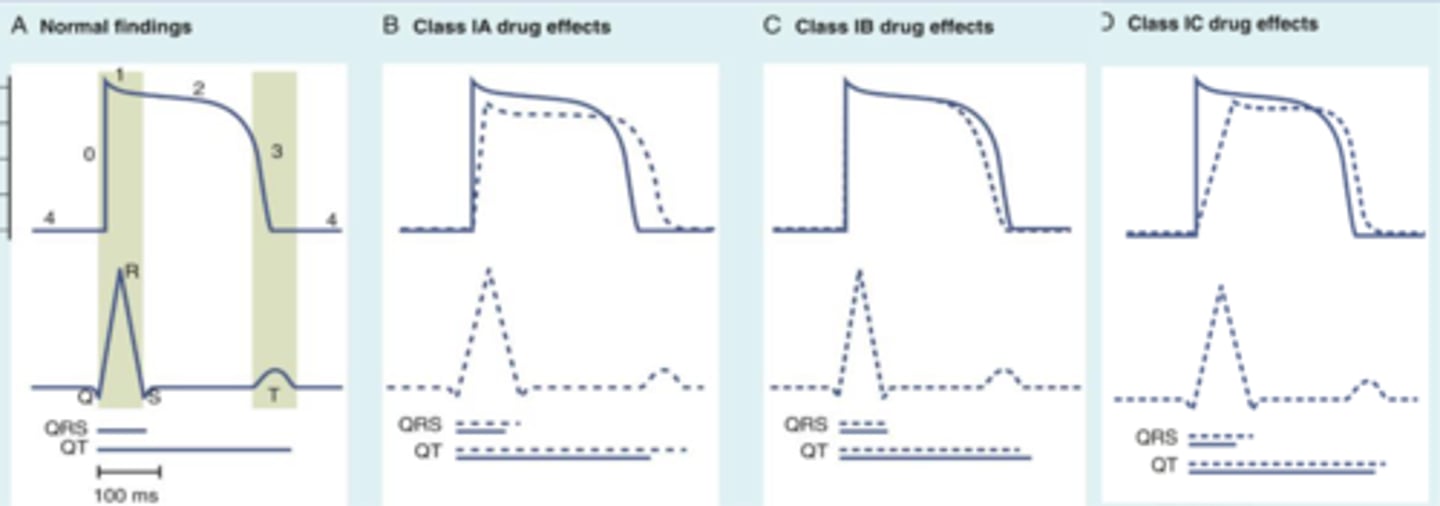
Cardiac Action Potential Phase 0
Rapid ventricular depolarization in response to an influx of sodium, leading to ventricular contraction (QRS Complex).
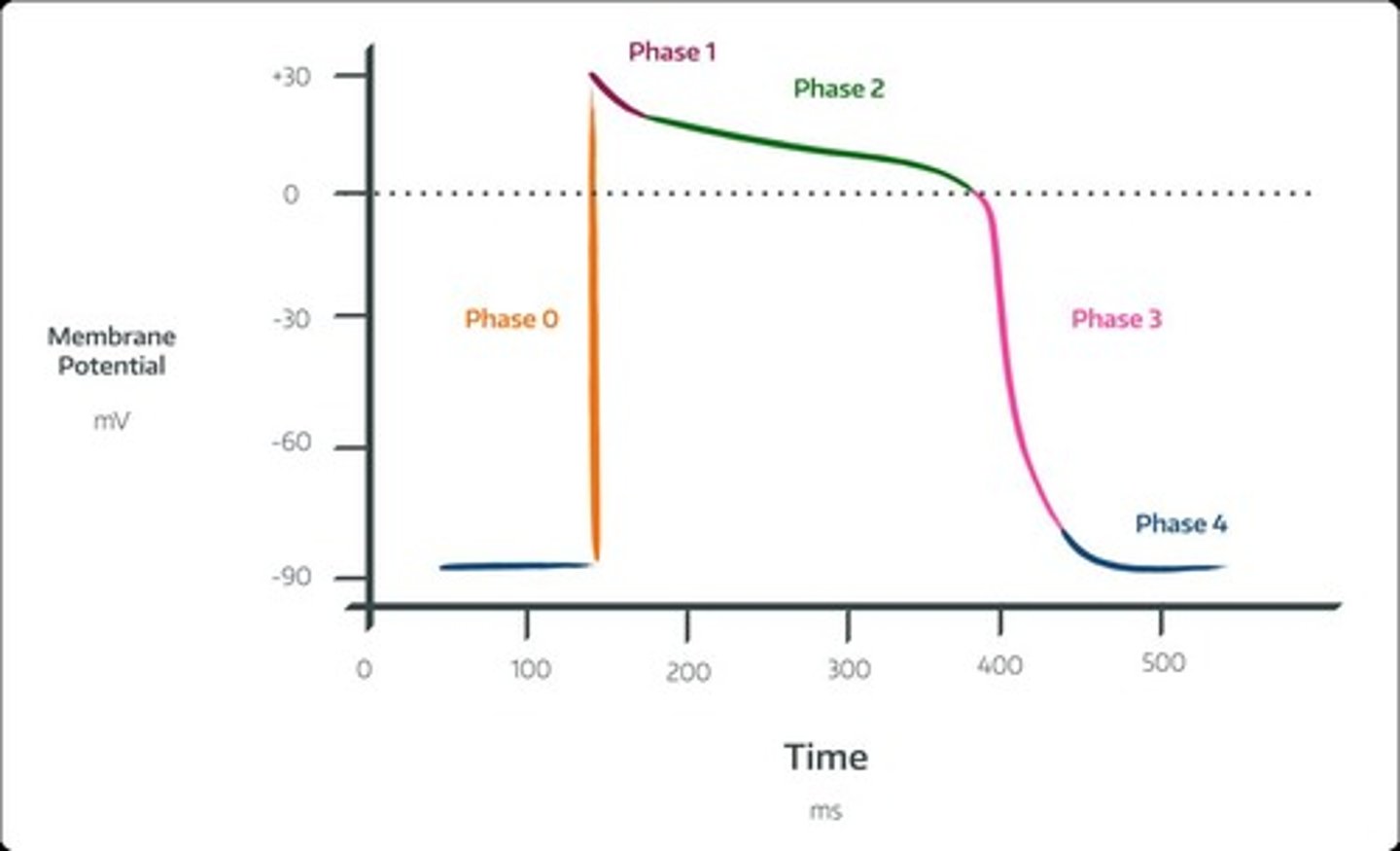
Cardiac Action Potential Phase 1
Sodium channel closes, leading to rapid repolarization.
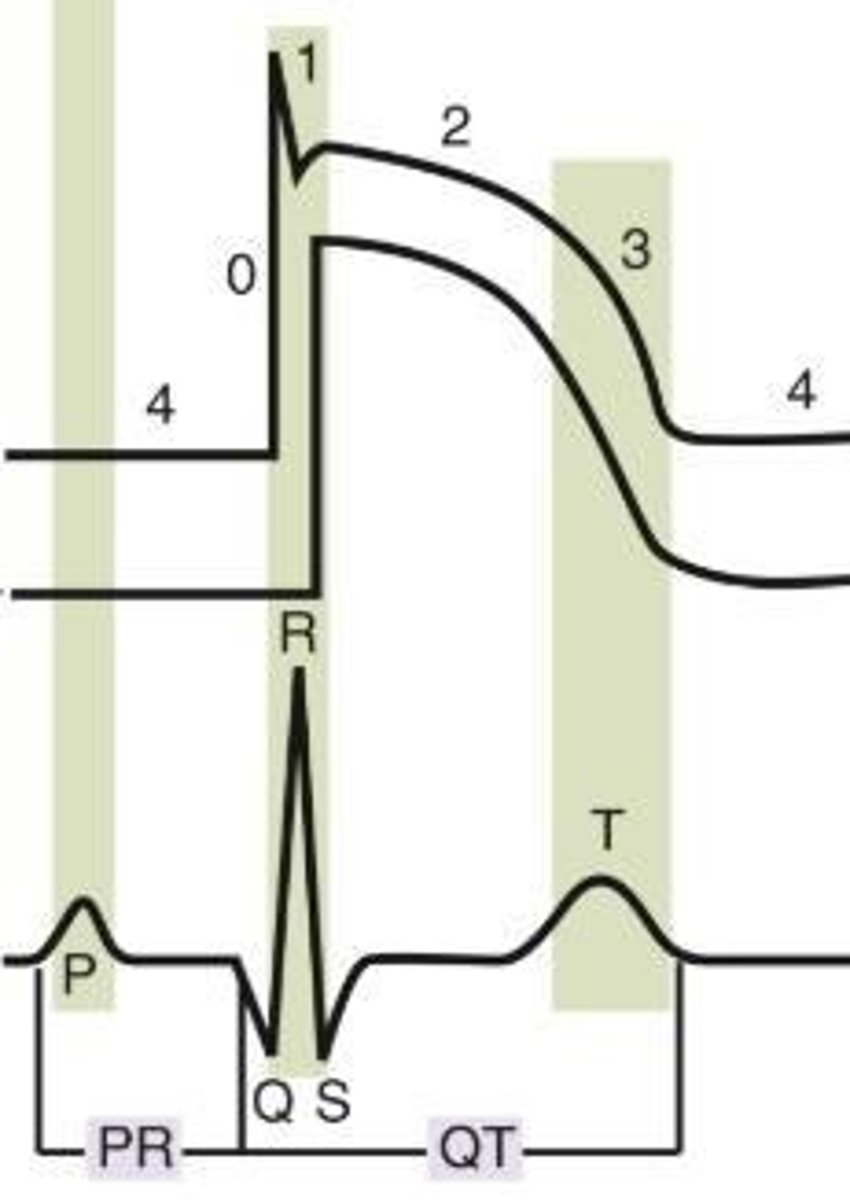
Cardiac Action Potential Phase 2
Plateau phase in response to an influx of calcium and efflux of potassium.
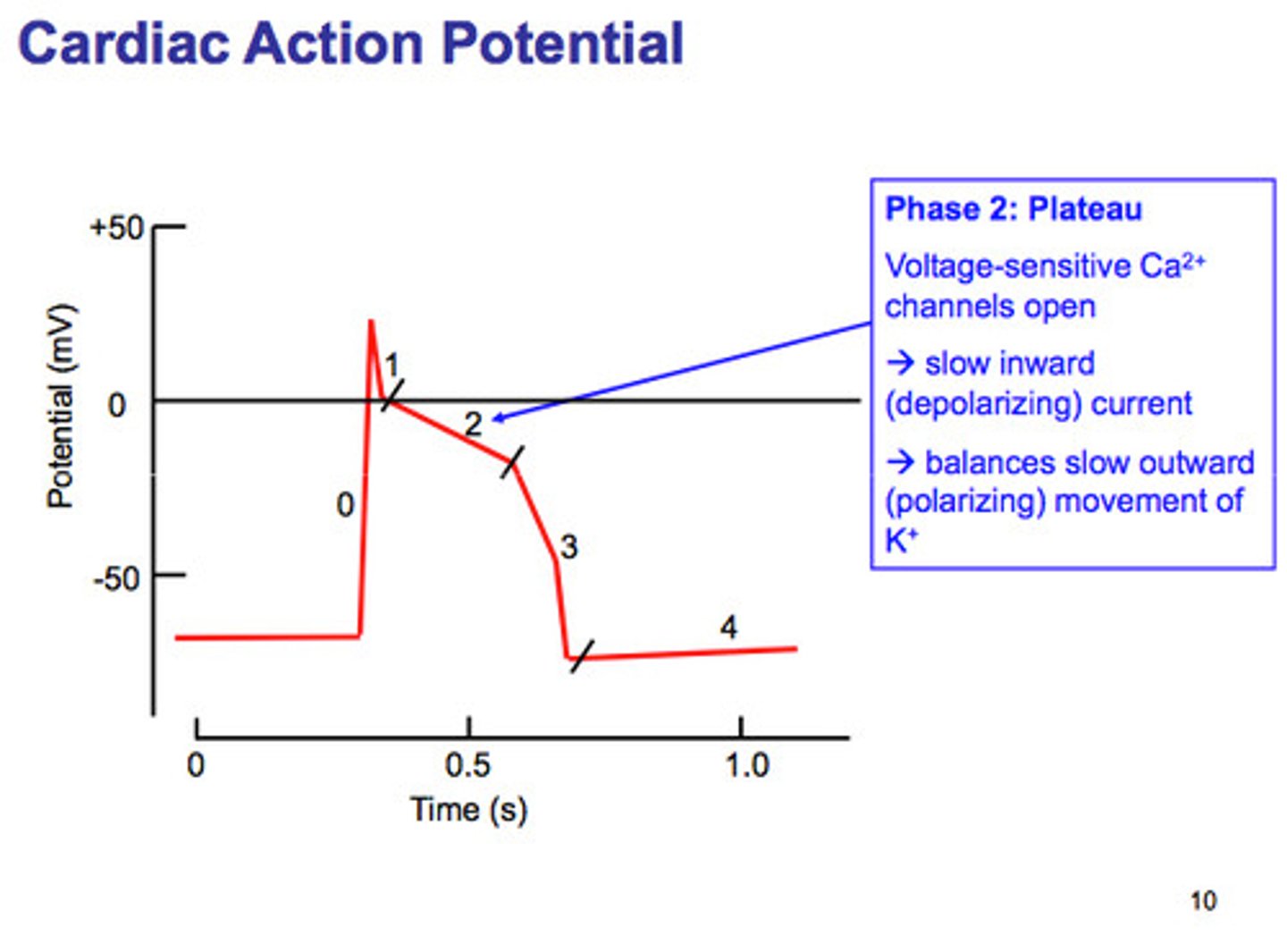
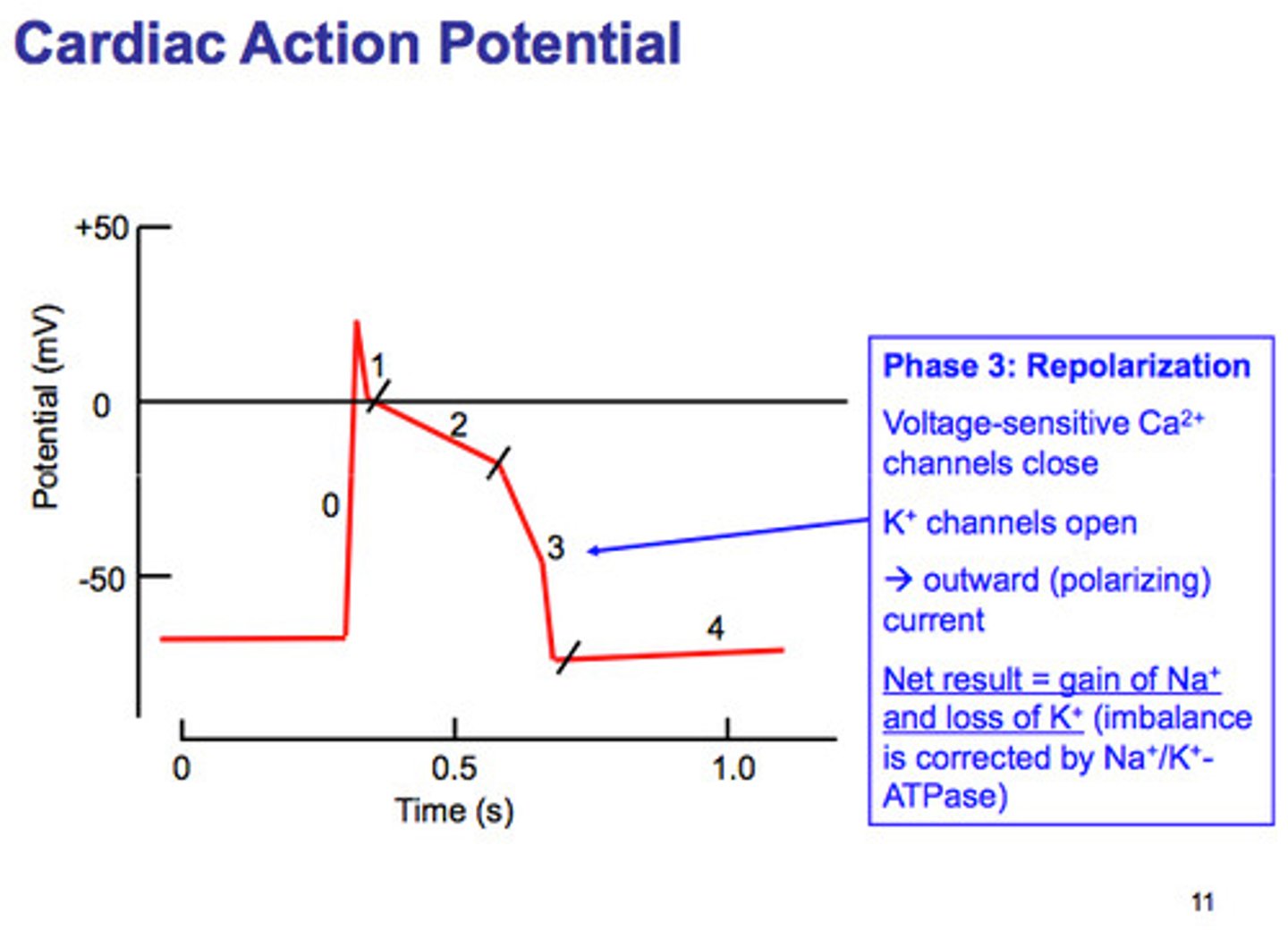
Cardiac Action Potential Phase 3
Efflux of potassium causing ventricular relaxation and ventricular repolarization (T wave).
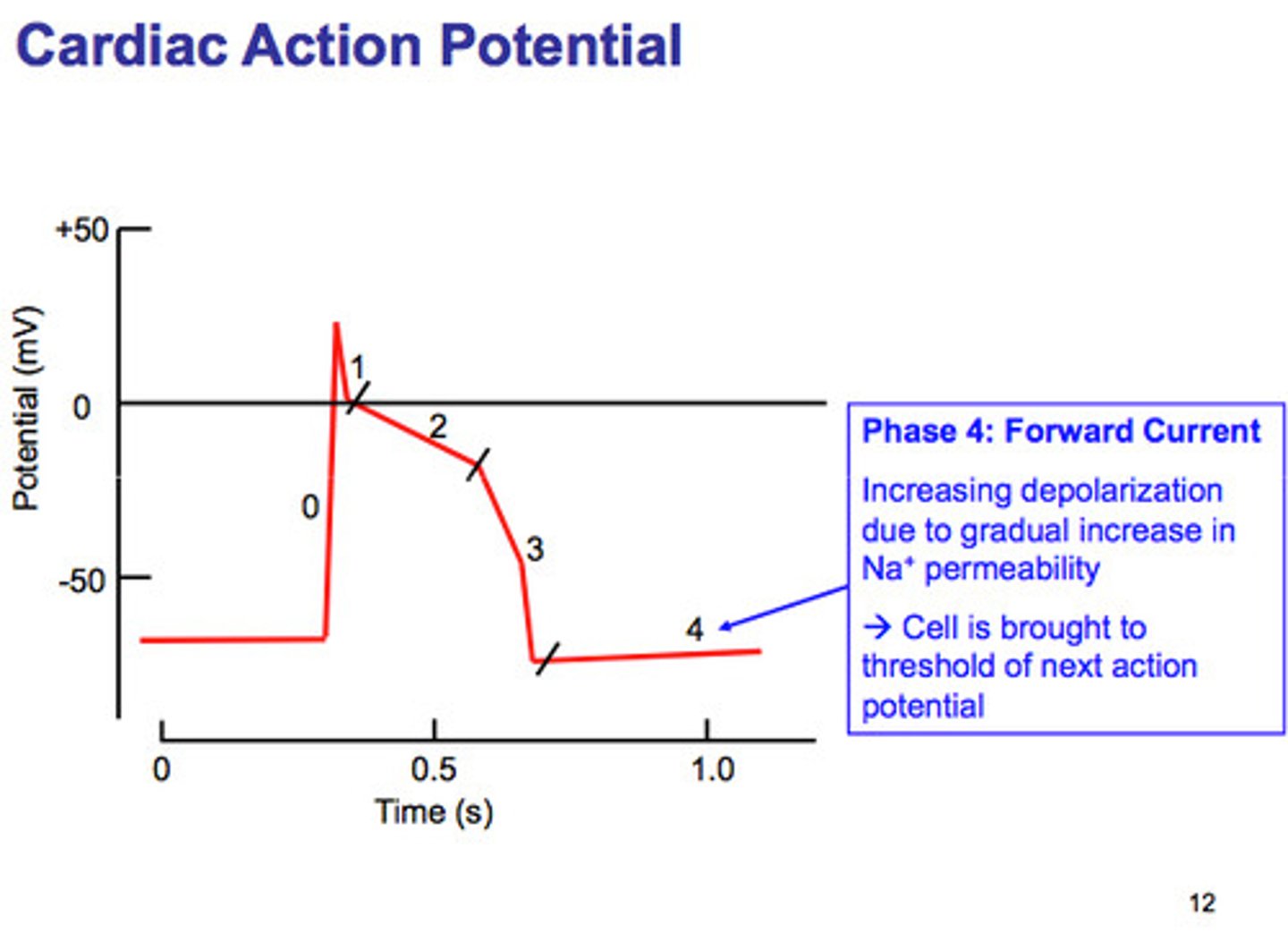
Cardiac Action Potential Phase 4
Resting membrane potential and atrial depolarization (P wave).
Disopyramide Brand Name
Norpace, Norpace CR
Disopyramide Mechanism of Action
Decreases myocardial excitability and conduction velocity; reduces disparity in refractory between normal and infarcted myocardium.
Indication for Disopyramide
Ventricular arrhythmias.
Route of Administration for Disopyramide
Oral.
Preparation for Disopyramide
Capsule, Capsule Extend-Release.
Side Effects of Disopyramide
Decreases heart contractility, urinary retention, dry mouth.
Warnings/Precautions for Disopyramide
Dry eye, heart failure, blurred vision, increased IOP, confusion.
Contraindications for Disopyramide
Hypersensitivity, cardiogenic shock, preexisting second- or third-degree heart block (except in patients with a functioning artificial pacemaker), congenital long QT syndrome.
Dosing for Disopyramide
Based on weight, Q6hrs! (not four times daily), renally dosed adjusted.
Monitoring Parameters for Disopyramide
ECG, blood pressure, urinary retention, CNS anticholinergic effects.
Special Populations for Disopyramide
May stimulate contractions in pregnant women.
Quinidine Mechanism of Action
Depresses phase 0 of the action potential
decreases myocardial excitability and conduction velocity, and myocardial contractility by decreasing sodium influx during depolarization and potassium efflux in repolarization.
Quinidine Indications
Atrial fibrillation/flutter, pharmacological conversion; paroxysmal atrial fibrillation/flutter, maintenance of sinus rhythm; ventricular arrhythmias; malaria (children).
Route of Administration for Quinidine
Oral.
Preparation for Quinidine
Tablet, ER Tablet.
Quinidine Contraindications
Hypersensitivity, thrombocytopenia; thrombocytopenic purpura, heart block greater than first degree, idioventricular conduction delays (except in patients with a functioning artificial pacemaker).
Quinidine Warnings
Hemolysis risk - G6PD deficiency, hepatotoxicity.
Quinidine Monitoring Parameters
ECG, CBC, liver function, renal function.
Quinidine Dosing
IR: q6hrs, ER: q8-12hrs, take with food to decrease GI upset.
Quinidine Side Effects
QT prolongation, thrombocytopenia, diarrhea, stomach cramping, gastrointestinal distress including esophagitis, heartburn, dizziness, drug-induced lupus, cinchonism (tinnitus, hearing loss, blurred vision, headache, delirium).
Procainamide Mechanism of Action
Decreases myocardial excitability and conduction velocity and may depress myocardial contractility, by increasing the electrical stimulation threshold of ventricle, His-Purkinje system and through direct cardiac effects.
Procainamide Indications
Ventricular tachycardia, atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia (off-label), atrial fibrillation with preexcitation (off-label).
Route of Administration for Procainamide
Injection.
Preparation for Procainamide
Continuous infusion, IV, IM.
Procainamide Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to procainamide, procaine, other ester-type local anesthetics, or any component of the formulation; complete heart block; second-degree AV block or various types of hemiblock (without a functional artificial pacemaker); systemic lupus erythematosus; torsade de pointes.
Black Box Warning for Procainamide
Drug-induced lupus erythematosus-like syndrome. Positive ANA Tests.
Blood Dyscrasias
Agranulocytosis, bone marrow depression, neutropenia, hypoplastic anemia and thrombocytopenia.
Procainamide Dosing
Renal adjustment for CrCl <50.
Procainamide Therapeutic Range
4-10 mcg/mL.
N-Acetyl Procainamide (NAPA) Therapeutic Range
15-25 mcg/mL
Procainamide Monitoring Parameters
ECG, Blood Pressure, Kidney function, Liver Function, CBC with differential, Blood concentration (in kidney/liver impairment or continuous infusion >12 hrs).
Procainamide Side Effects
Agranulocytosis, Hypotension, Bradycardia, Rash, Lupus like-syndrome (joint/muscle pain, flu-like syndrome, butterfly-like rash) (reversible), Diarrhea.
Procainamide Onset
10 -30 mins (IM).
Procainamide Metabolism
hepatic via acetylation to active metabolite
procainamide half-life in children
1.7 hrs
procainamide half-life in adults
2.5-4.7
NAPA half-life in children
6 hours
NAPA half-life in adults
6-8 hours
procainamide time to peak
15 to 60 mins (IM)
Procainamide Excretion
>50% renally cleared.
urine > feces
NAPA Excretion
>80% Renally cleared.
Lidocaine brand name
Xylocaine
Lidocaine Mechanism of Action
Suppresses automaticity of conduction tissue, by increasing electrical stimulation threshold of ventricle, His-Purkinje system, and spontaneous depolarization of the ventricles during diastole by a direct action on the tissues.
Blocks the initiation and conduction of nerve impulses by decreasing the neuronal membrane permeability to sodium ions, which results in inhibition of depolarization with resultant blockade of conduction
Lidocaine Indication
Ventricular arrhythmia - especially in refractory cases (Vfib, Pulse-less VT).
Lidocaine Route of Administration
Injection (IV)
Lidocaine Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to lidocaine or another local anesthetic of the amide type, Adam-Stokes syndrome, Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, Severe degrees of SA, AV, or intraventricular heart block (except in patients with a functioning artificial pacemaker), Corn-derived dextrose (premixed injections).
Lidocaine metabolism
via CYP1A2 and CYP3A4
Lidocaine IV onset and duration
IV bolus onset: 45-90 secs
Duration: 10-20 mins
Lidocaine Monitoring Parameters
LFTs, ECG, Neurologic signs.
Lidocaine Side Effects
Bradycardia, Hypotension, Vomiting, Tinnitus, Blurred vision, CNS toxicity with accumulation of metabolites.
Mexiletine Mechanism of Action
Decreases rate of rise of phase 0, increases effective refractory period/action potential duration ratio.
Mexiletine Indication
Ventricular arrhythmias.
Mexiletine Route of Administration
Oral.
Mexiletine Black Box Warning
Acute Liver Injury. abnormal liver function tests especially in the setting of congestive heart failure or ischemia.
Mexiletine Preparation
Capsule.
Mexiletine Dosing
Administer with food or antacid (needs alkaline environment), Can use loading dose, Maximum: 1.2g/day.
Mexiletine
A medication contraindicated in cardiogenic shock and second- or third-degree AV block (except in patients with a functioning artificial pacemaker).
Contraindications of Mexiletine
Cardiogenic shock; Second- or third-degree AV block (except in patients with a functioning artificial pacemaker).
Side Effects of Mexiletine
Blood dyscrasis; Drug reactions with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS); Arrhythmia exacerbations; Dizziness.
Monitoring Parameters for Mexiletine
Ataxia; Liver function tests; ECG; Nervousness; GI distress; Nausea and vomiting; Tremor.
Mexiletine onset
30-120 mins
Mexiletine half-life
10-12 hrs
- CrCl<10: 15 hrs
- Hepatic impairment: 25 hrs
Mexiletine metabolism
via CYP2D6
Mexiletine Excretion
urine
Mexiletine time to peak
2-3 hrs
Flecainide Mechanism of Action
Slows conduction in cardiac tissue by altering transport of ions across cell membranes
Causes slight prolongation of refractory periods
↓ rate of rise of the action potential without affecting its duration;
↑ electrical stimulation threshold of ventricle, His-Purkinje system;
Possesses local anesthetic and moderate negative inotropic effects.
Indications for Flecainide
Ventricular arrhythmias (prevention); Atrial fibrillation/flutter or supraventricular tachycardias in patients with no structural heart disease.
Flecainide Route of Administration
Oral.
Flecainide Preparation
Tablet.
Flecainide Dosing
Renal adjustment CrCl <35
avoid in severe hepatic and renal impairment.
Flecainide Contraindications
Hypersensitivity; Pre-existing second- or third-degree AV block or with right bundle branch block when associated with a left hemiblock (bifascicular block) (except in patients with a functioning artificial pacemaker); Cardiogenic shock; Concurrent use of ritonavir.
Flecainide Monitoring Parameters
ECG; Heart Rate; Blood Pressure; Serum concentrations.
Flecainide Side Effects
Proarrhythmic effects (ventricular arrhythmia); 1:1 AV conduction; Fatal complications with structural heart disease (heart failure, MI); Dizziness; Visual disturbances (blurred vision, seeing spots).
Propafenone Mechanism of Action
Possesses local anesthetic properties; Blocks the fast inward sodium current and slows the rate of increase of the action potential; Prolongs conduction and refractoriness in all areas of the myocardium; Reduces spontaneous automaticity and exhibits some beta-blockade activity.
Indications for Propafenone
Ventricular arrhythmias; Atrial fibrillation/flutter and Supraventricular tachycardia, maintenance of sinus rhythm in patients without structural heart disease.
Propafenone Route of Administration
Oral.
Propafenone Preparation
IR tablet, ER capsule.
Propafenone Contraindications
Hypersensitivity; Sinoatrial, atrioventricular, and intraventricular disorders of impulse generation or conduction (except in patients with a functioning artificial pacemaker); Known Brugada syndrome; Bradycardia; Cardiogenic shock; Heart failure; Marked hypotension; Bronchospastic disorders or severe obstructive pulmonary disease; Marked electrolyte imbalance.
Propafenone Drug Interactions
Increase digoxin concentrations
Increase warfarin concentrations.
Propafenone Monitoring Parameters
ECG; Blood pressure; Pulse.
Propafenone Side Effects
Nausea and vomiting; Metallic taste; Dizziness; Visual disturbances.
Flecainide Pharmacokinetics
Half-life: Extensive metabolizer: 2-10 hrs; Poor metabolizers: 10-32 hrs; Time to peak: Children: 8 hrs; Adolescents: 11-12 hrs; >12: 12-27 hrs; Kidney impairment: 58 hrs; Time to peak: 1-6 hrs; Excretion: Urine > feces.
Propafenone Pharmacokinetics
Half-life: IR: 3.5 hrs; ER: 3-8 hrs; Excretion: Urine and feces.