Histo 21 | Male Reproductive System L
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
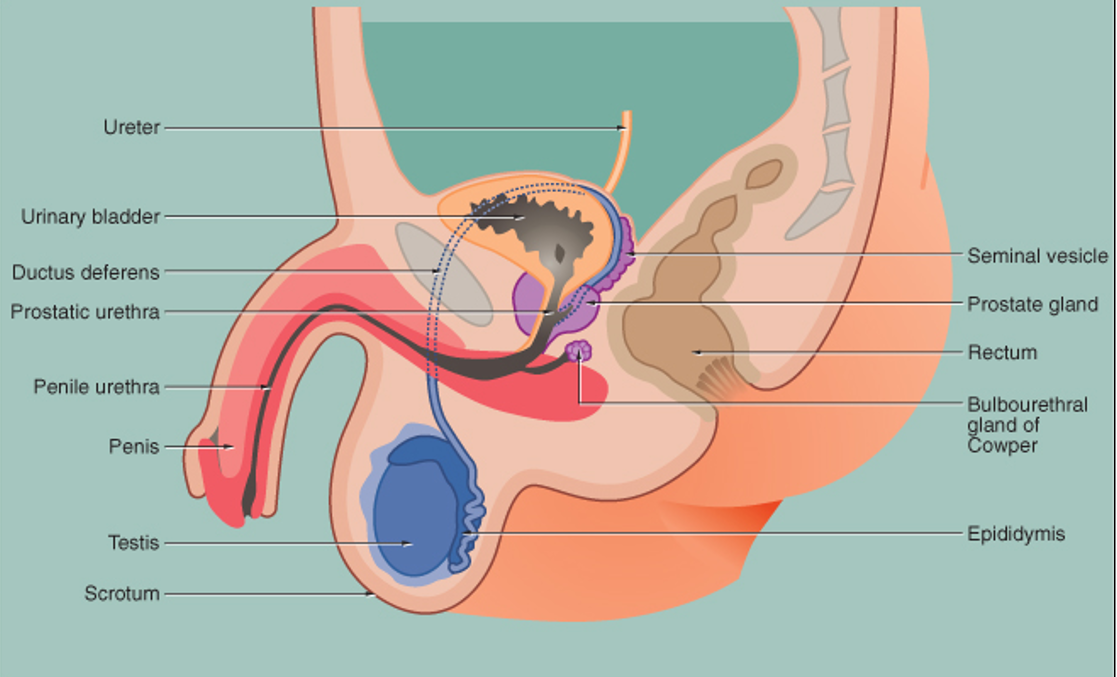
Where are the testes located?
In the scrotum, suspended like abdominal organs.
What lines the scrotum?
The tunica vaginalis, which has a visceral and parietal layer (like the peritoneum).
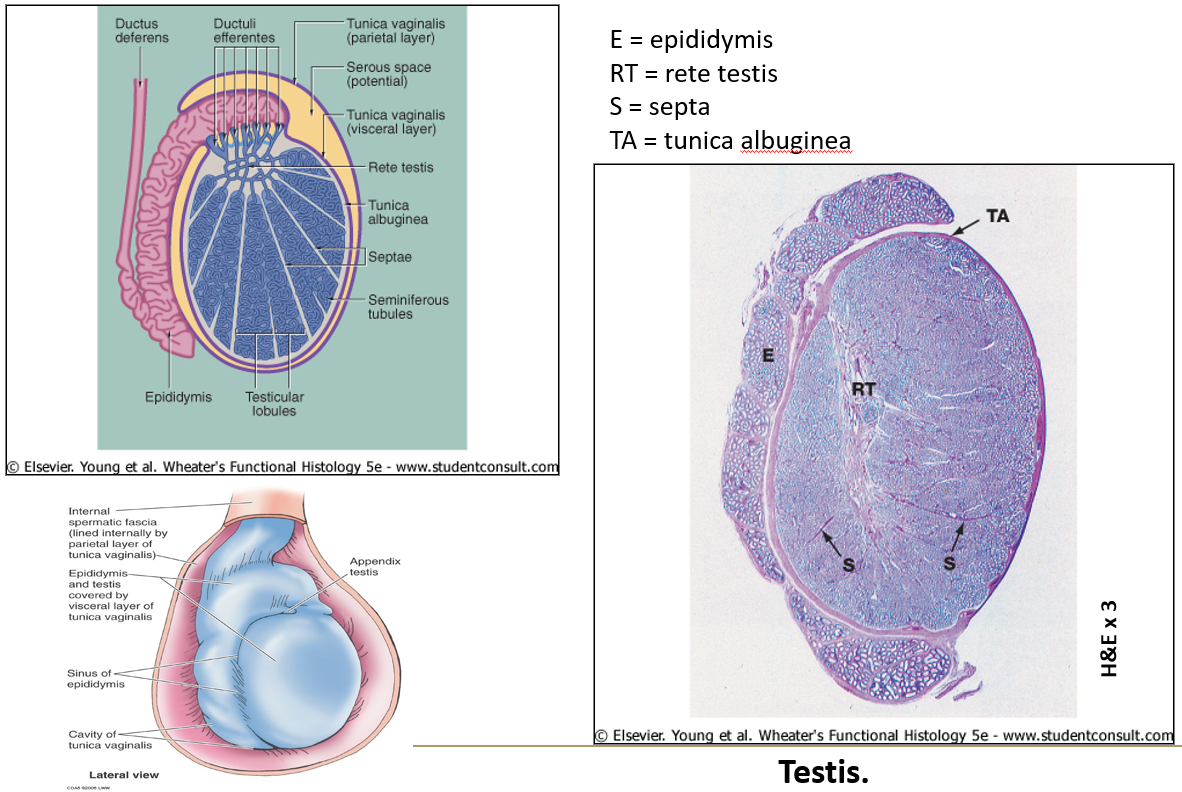
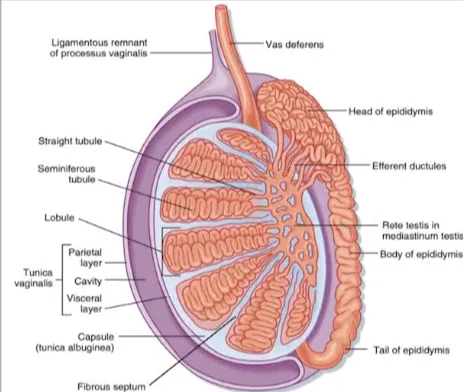
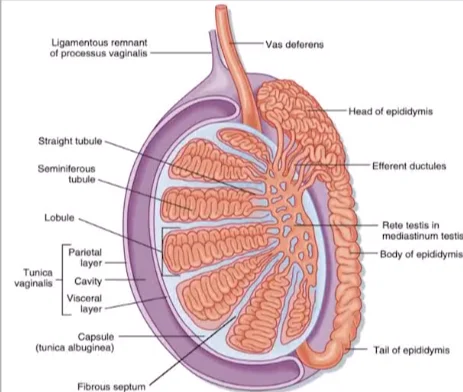
What is the tunica albuginea?
A thick capsule made of dense irregular connective tissue around the testis.
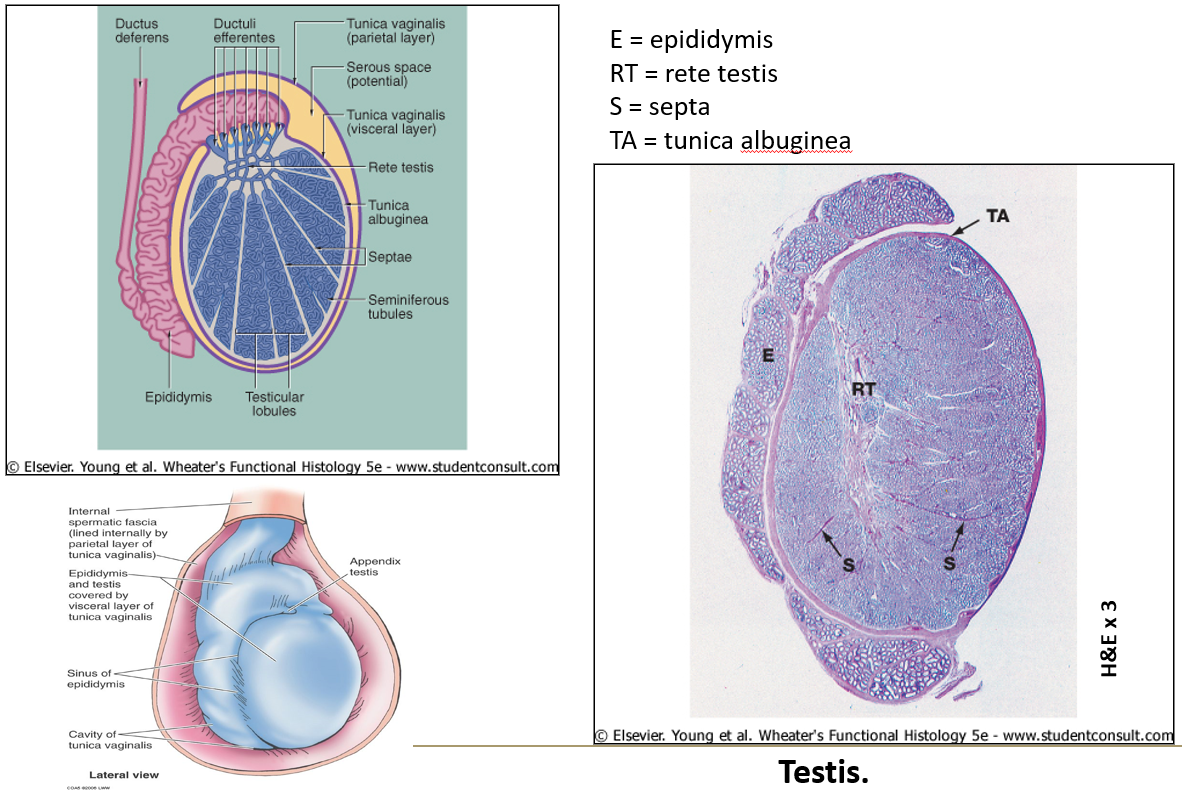
What are seminiferous tubules?
They are long coiled tubes (about 400 per testis, 70 cm each) where sperm are produced.
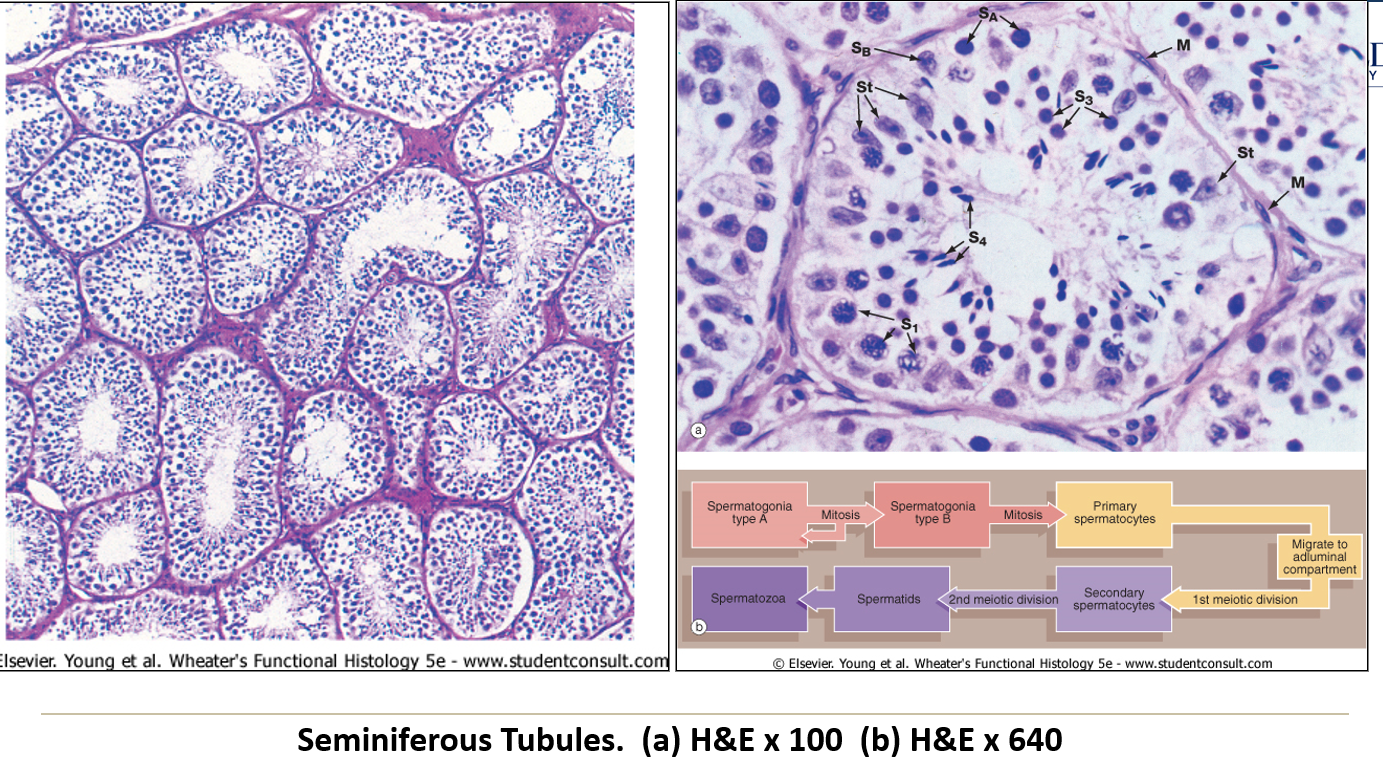
What is the boundary layer of seminiferous tubules?
A thick basement membrane with myoid cells, which thicken with age or disease.
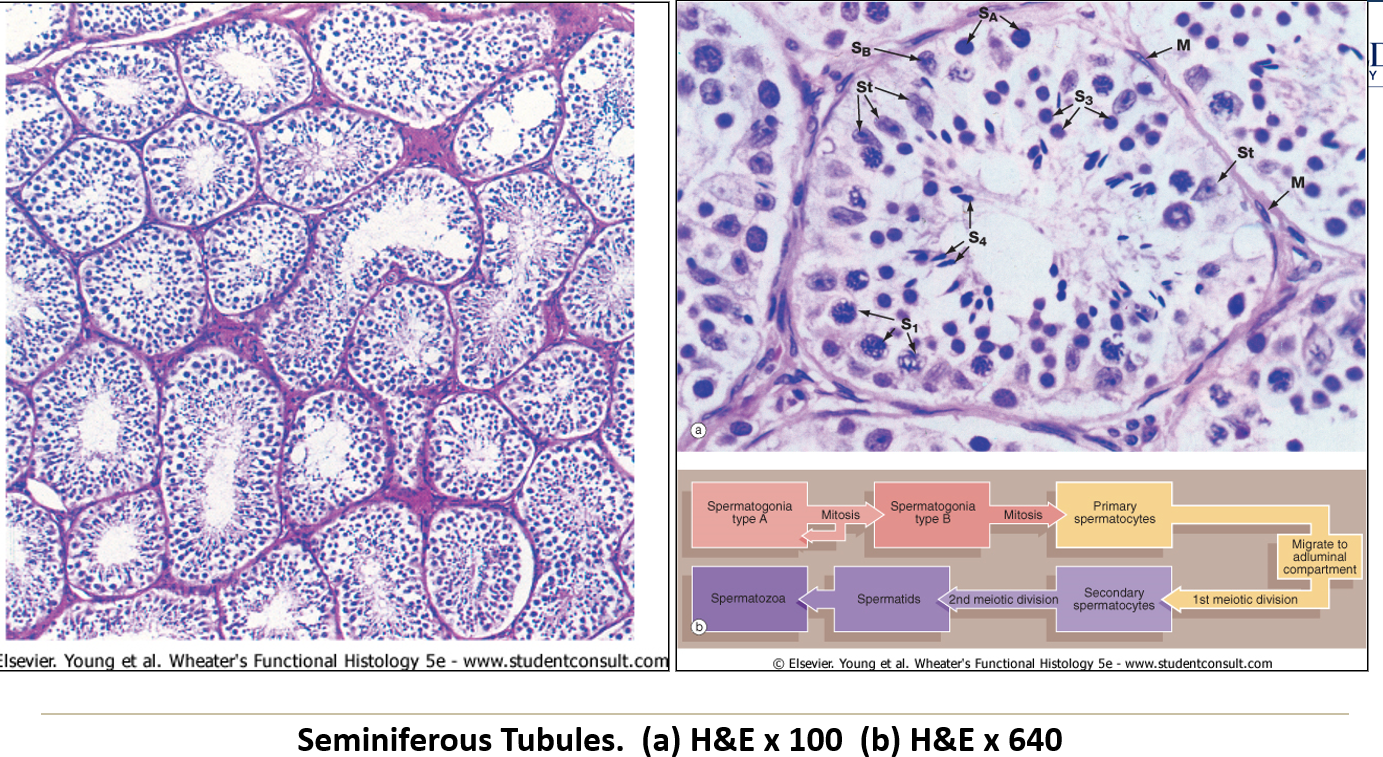
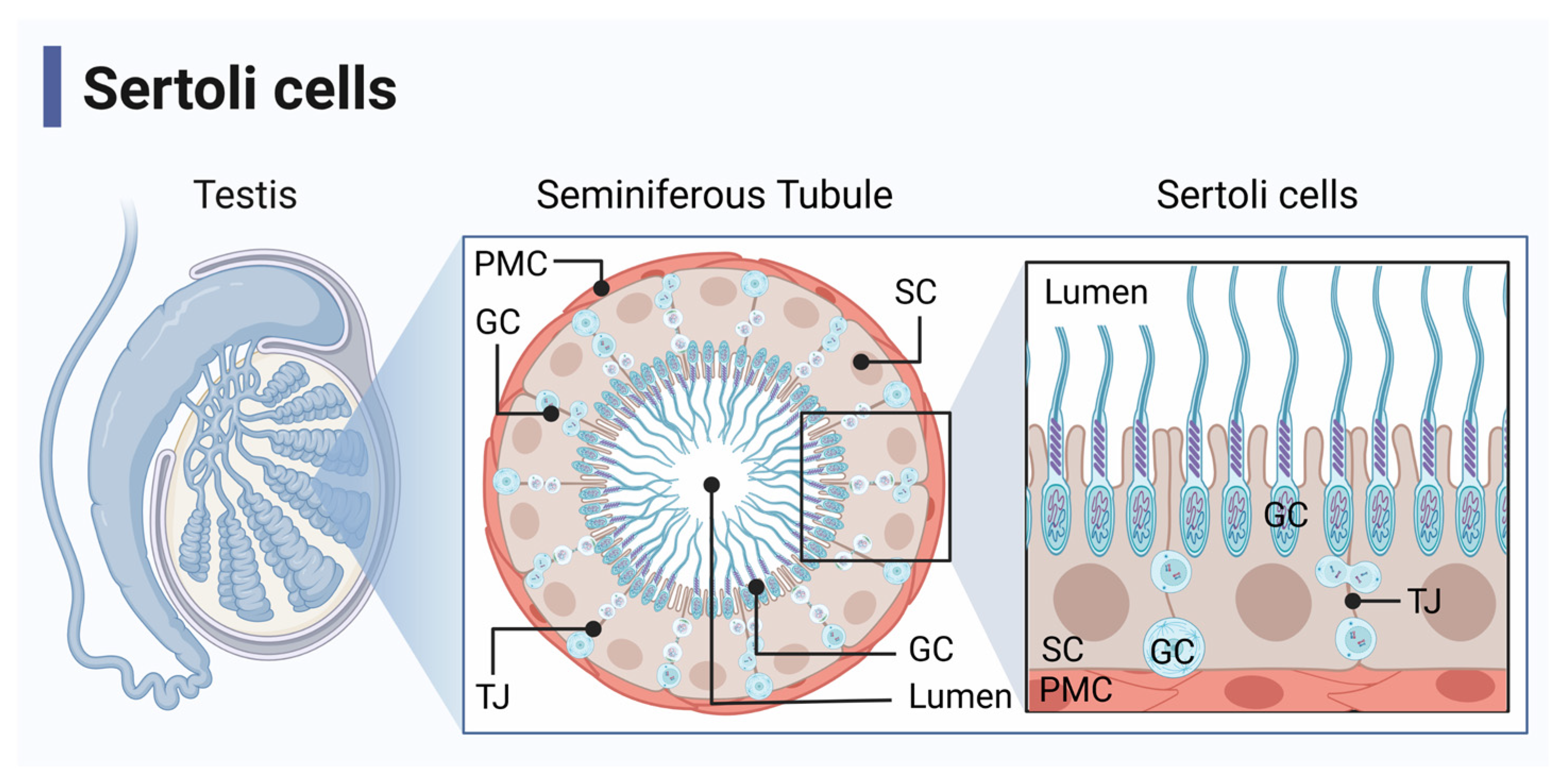
What are Sertoli (sustentacular) cells?
Large supportive cells with clear cytoplasm and oval nuclei, forming part of the blood-testis barrier.
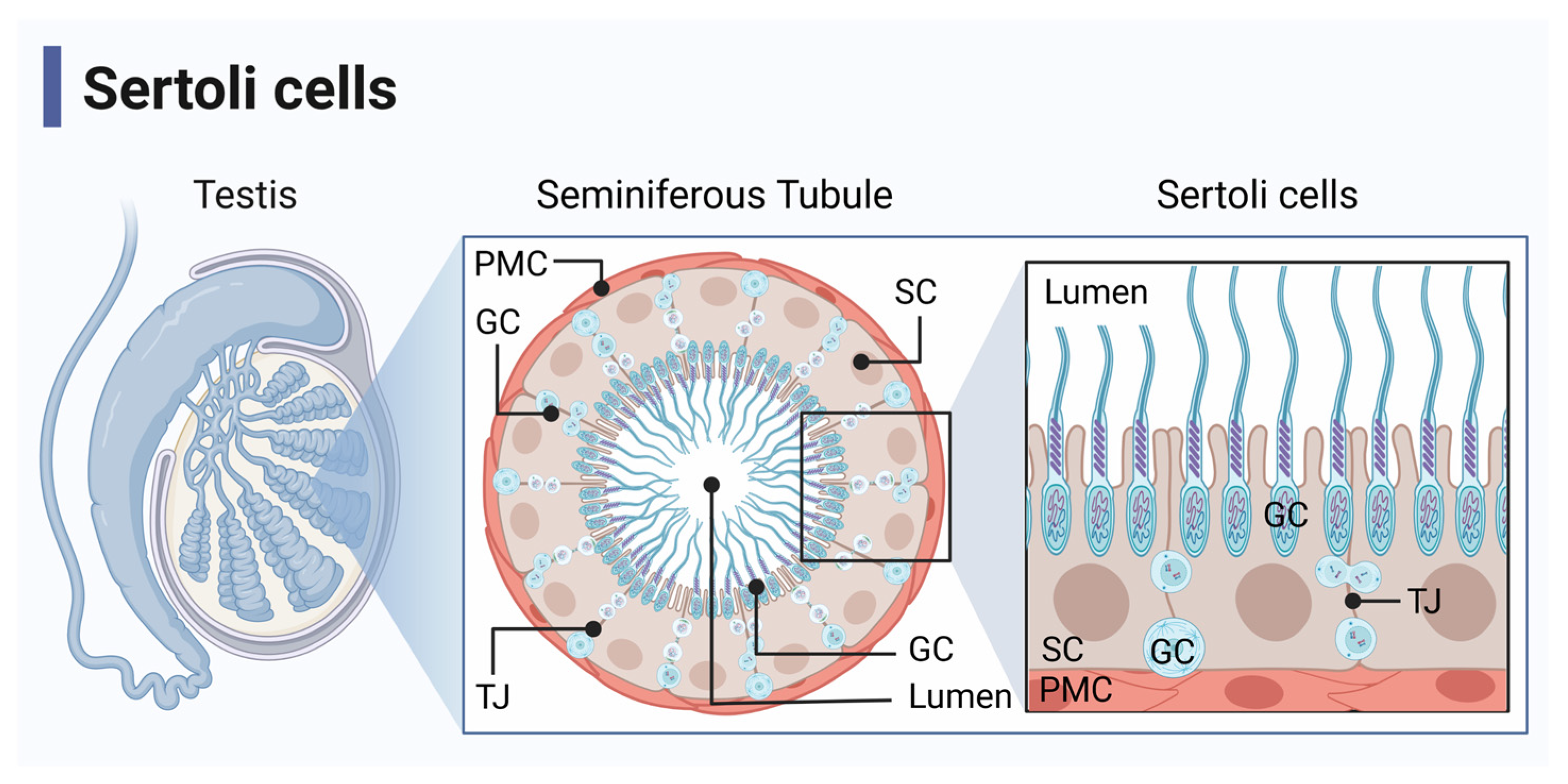
What do the zonula occludens (tight junctions) in Sertoli cells do?
They form the blood/testis barrier at the base of the seminiferous tubule.
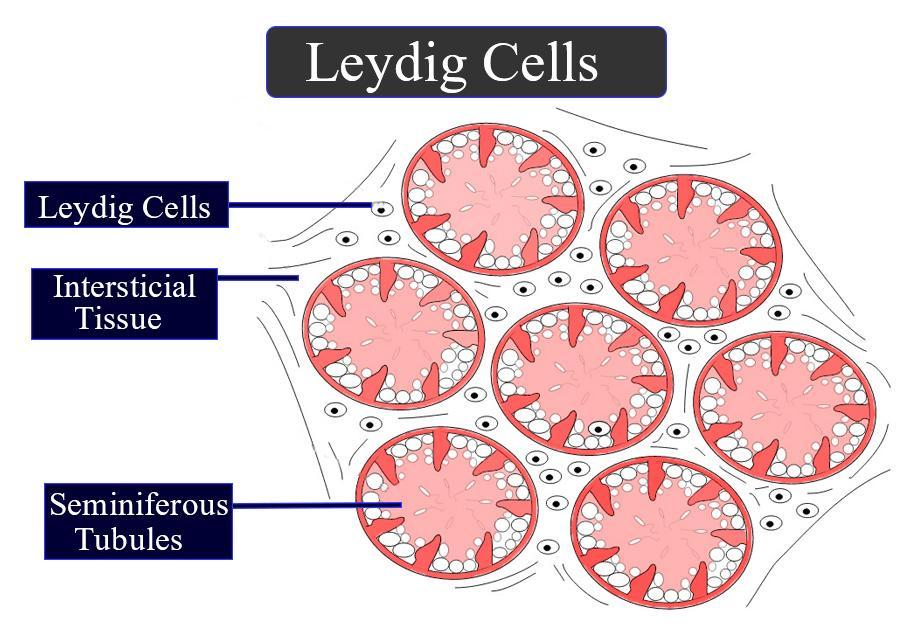
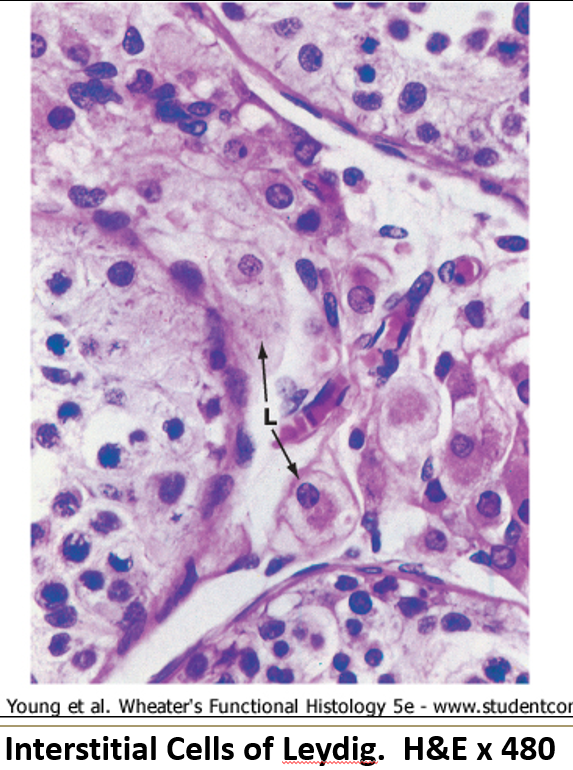
What do Leydig cells do?
Found between seminiferous tubules, they produce androgens (like testosterone) when stimulated by LH.
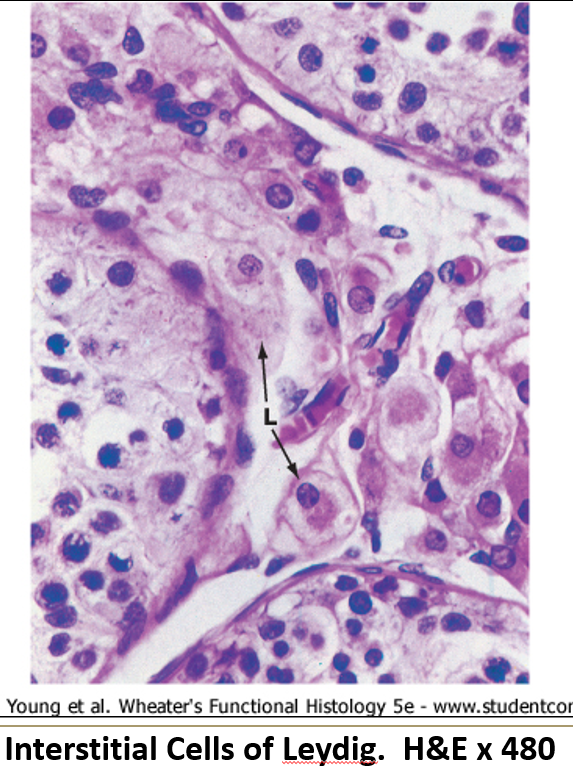
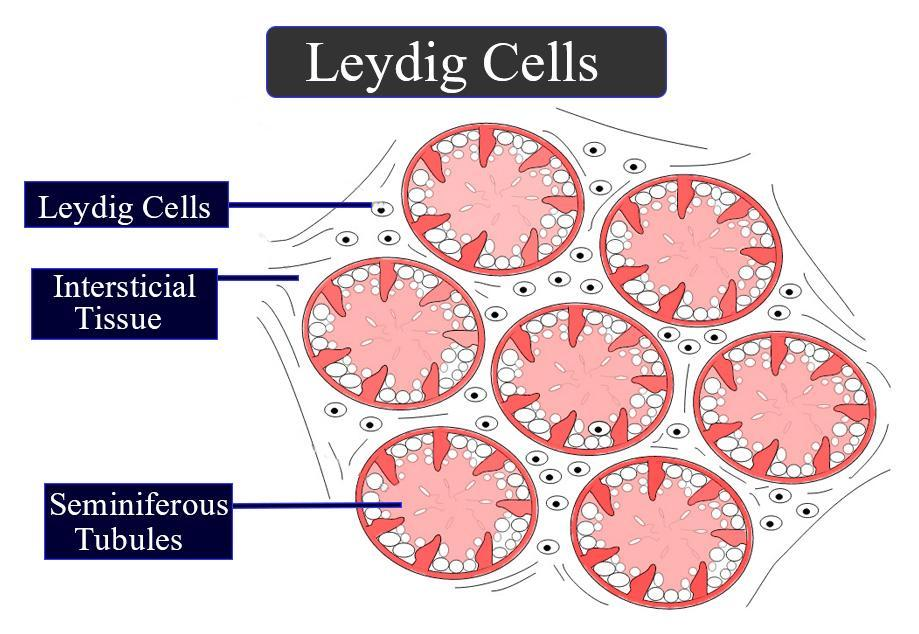
What do Leydig cells look like?
They have a central round nucleus, eosinophilic cytoplasm (due to SER), and may show lipid droplets.
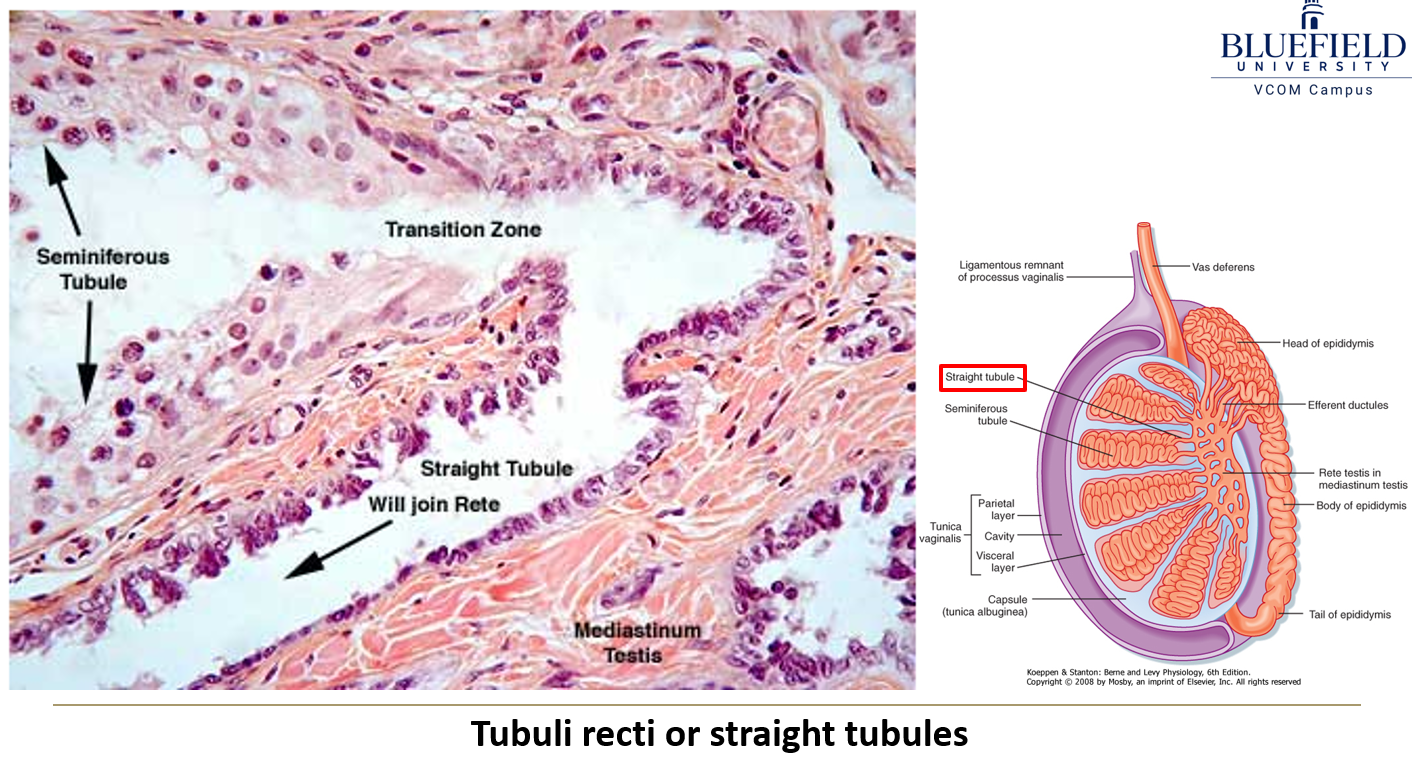
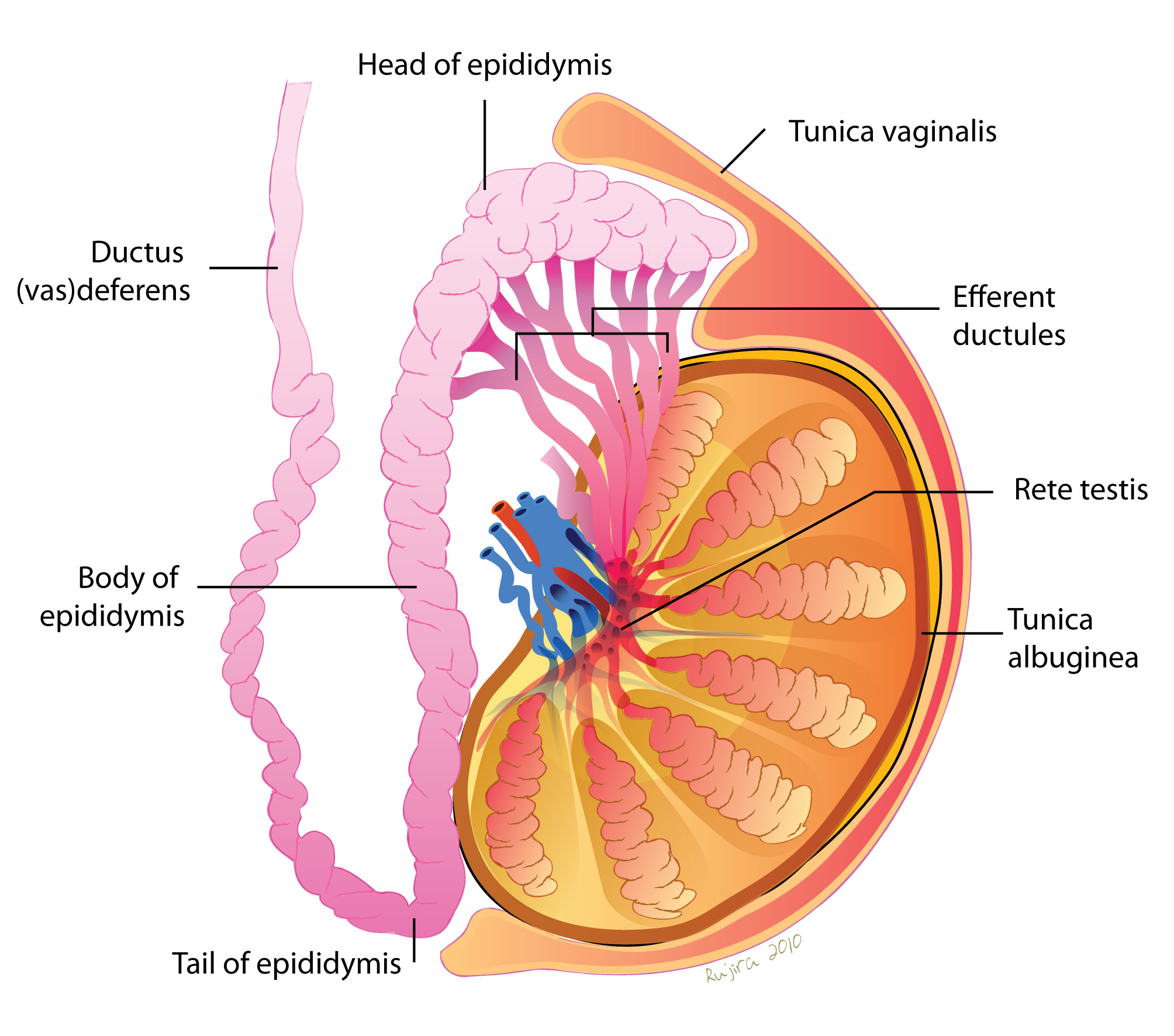
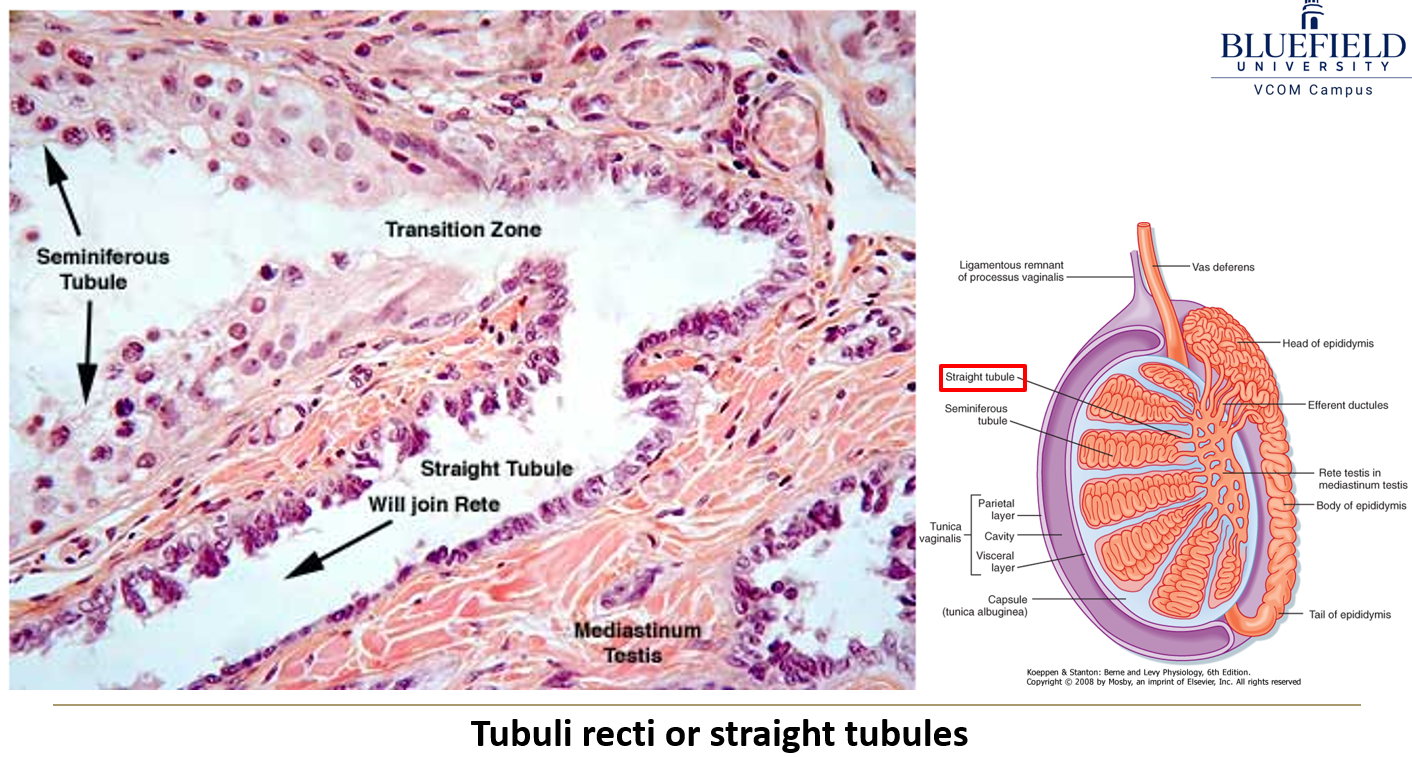
What are the tubuli recti?
Straight tubules that connect seminiferous tubules to the rete testis. They start with Sertoli cells and transition to cuboidal epithelium.
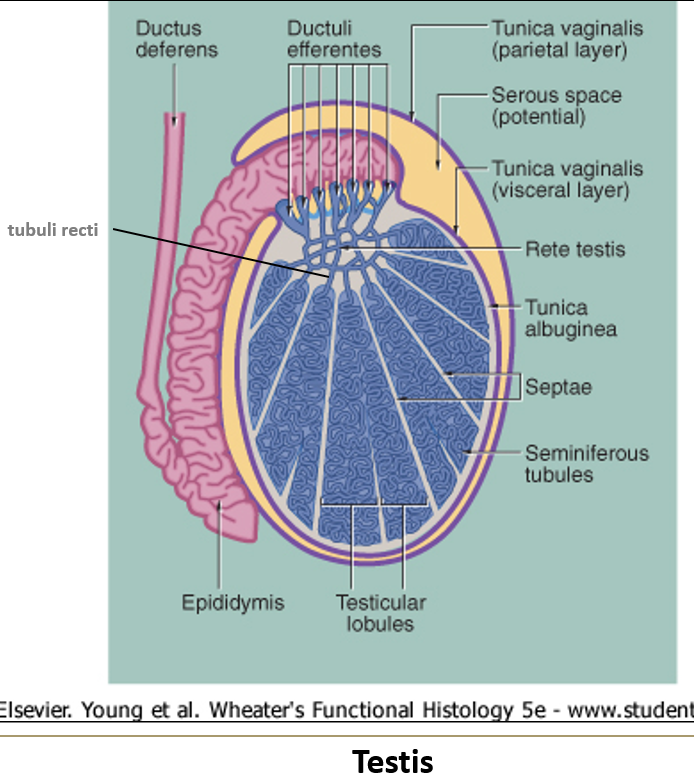
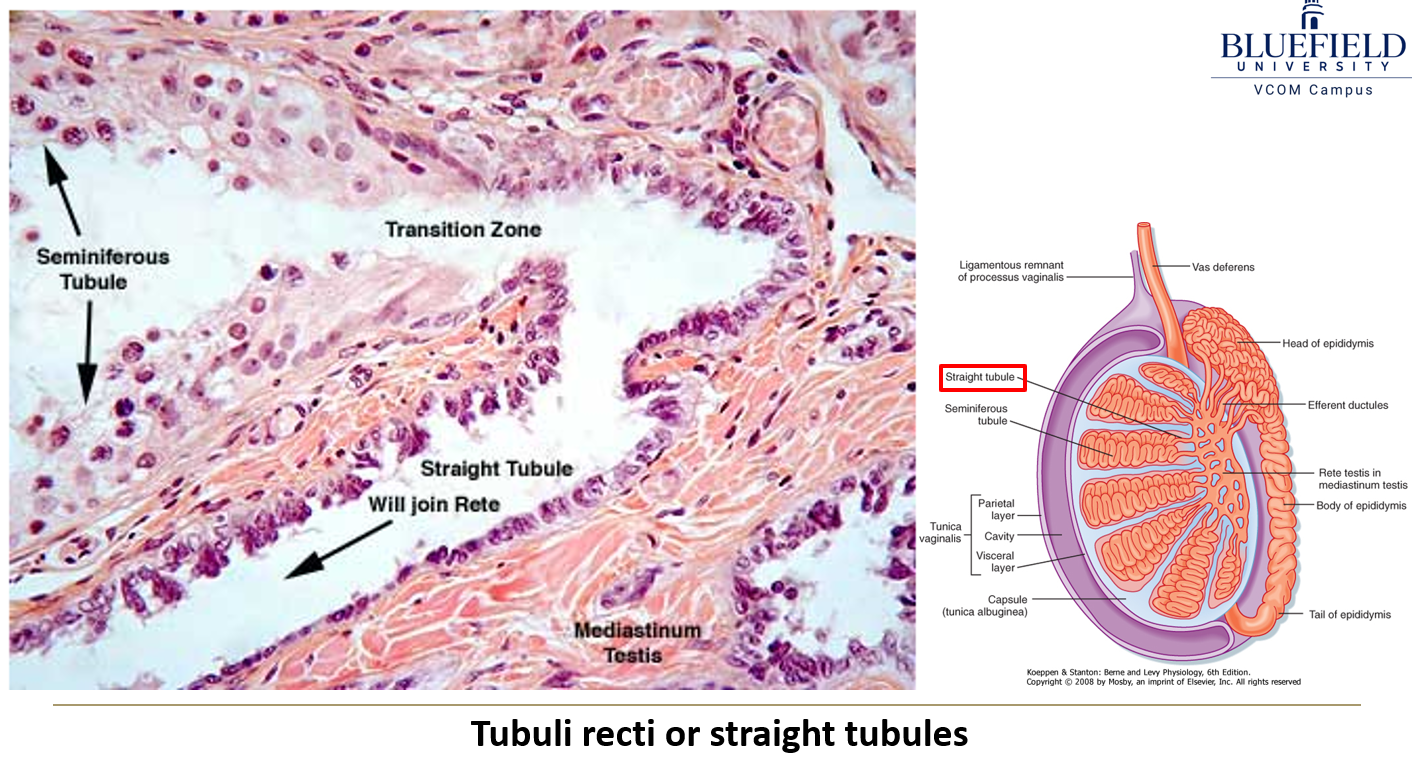
What is the rete testis?
A maze of passageways that look like a sponge, lined by low cuboidal or simple squamous epithelium. Some cells have a single flagellum.
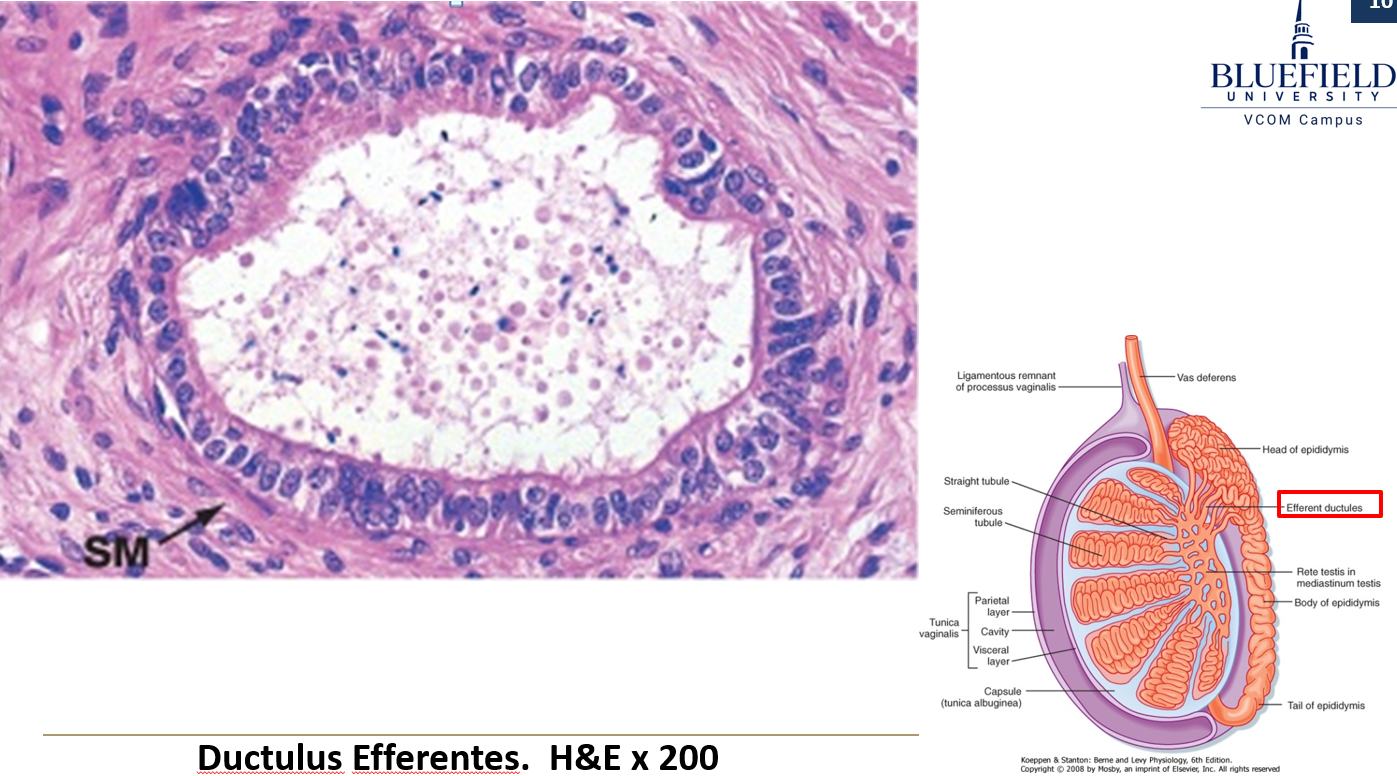
What lines the ductuli efferentes?
Alternating cuboidal and columnar epithelium, creating a folded appearance.
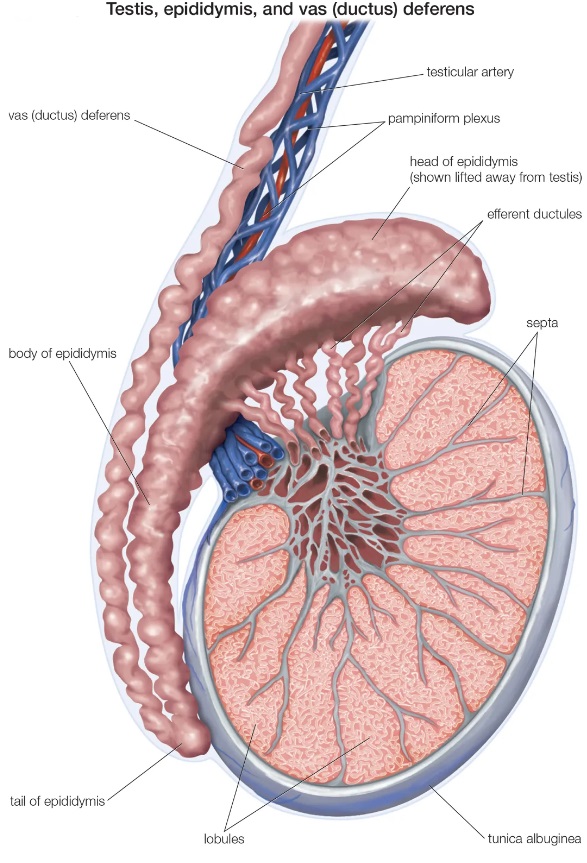
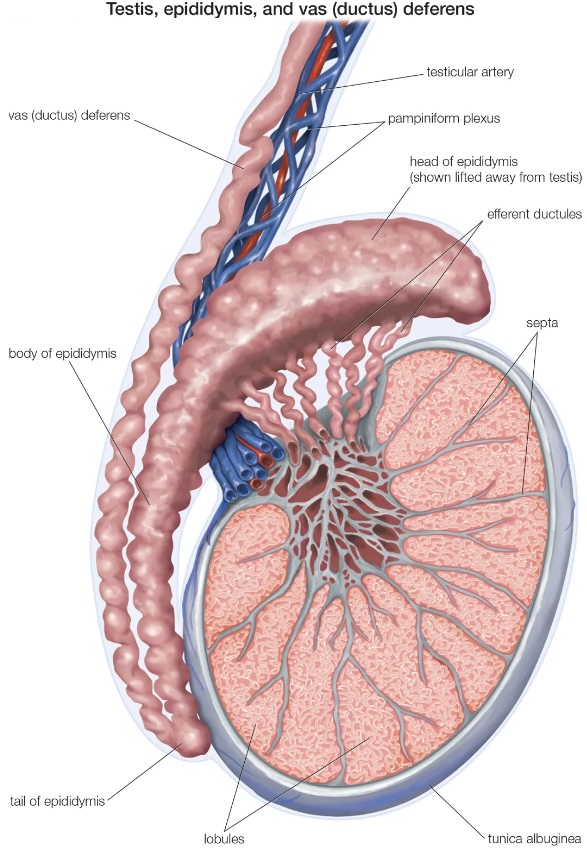
What is the function of the epididymis?
It's a long coiled tube where sperm mature.
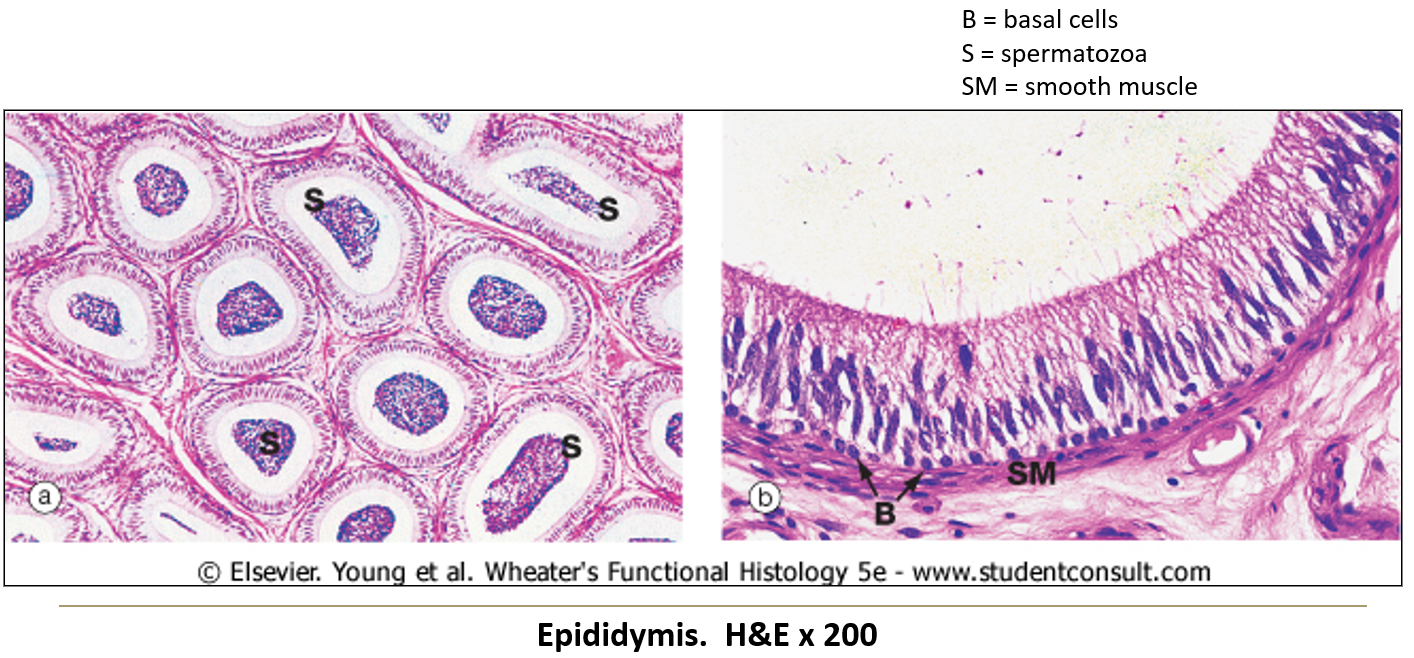
What kind of epithelium lines the epididymis?
Tall pseudostratified epithelium with stereocilia (not motile, just for increased surface area).
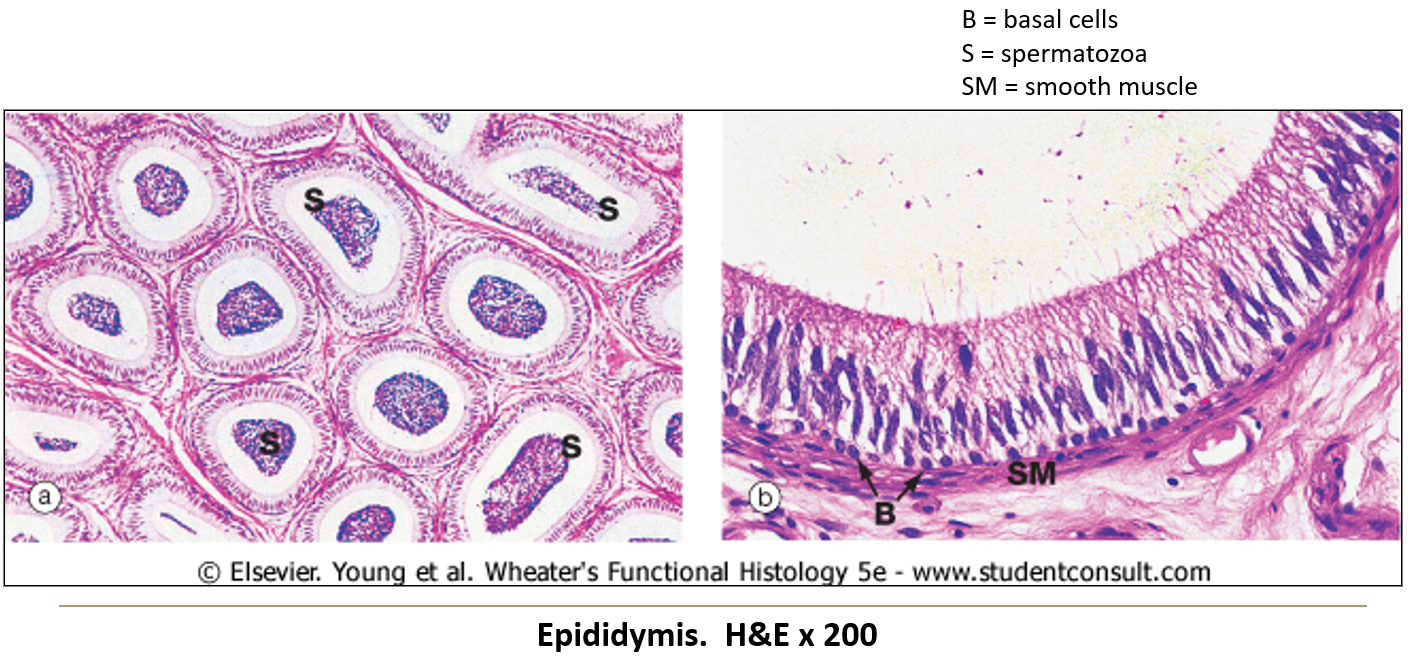
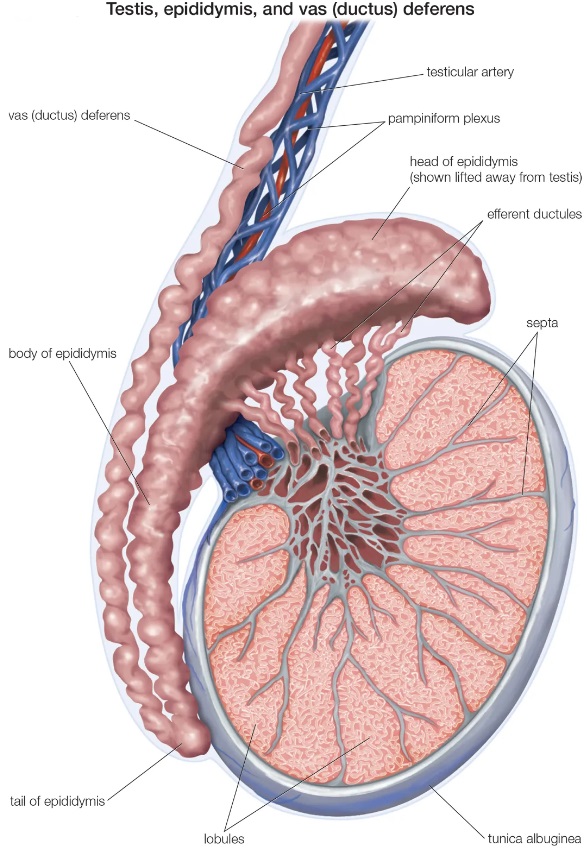
What are the two known functions of the epididymis?
Reabsorbs excess fluid from seminiferous tubules
Supplies sperm with glycerophosphorylcholine, an energy-rich molecule

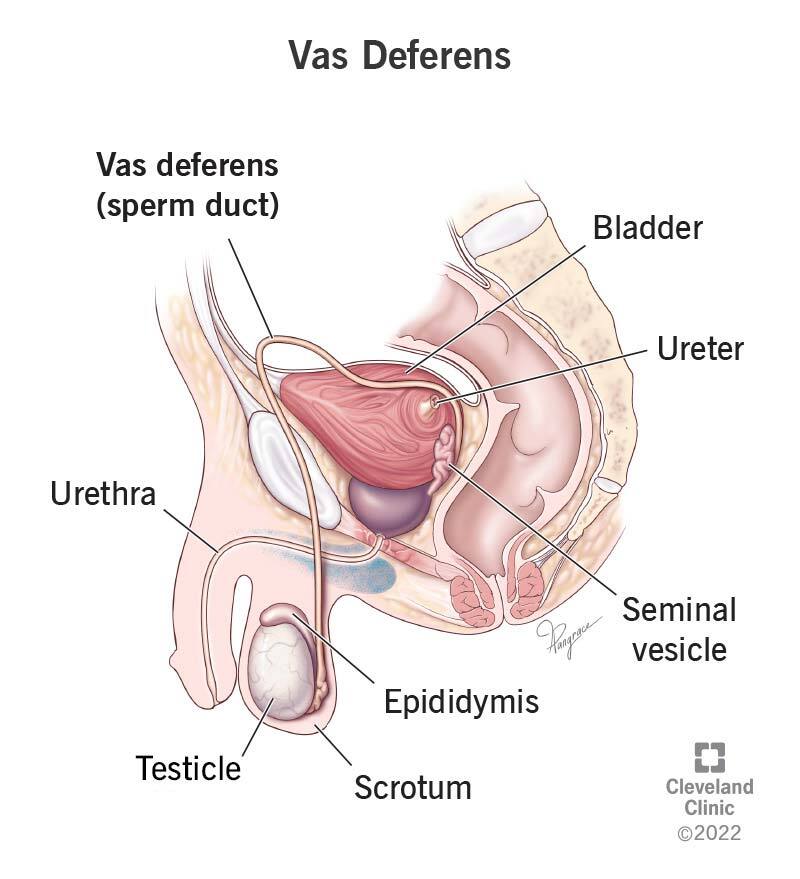
What does the vas deferens connect?
It connects the epididymis to the urethra and stores/transports sperm.
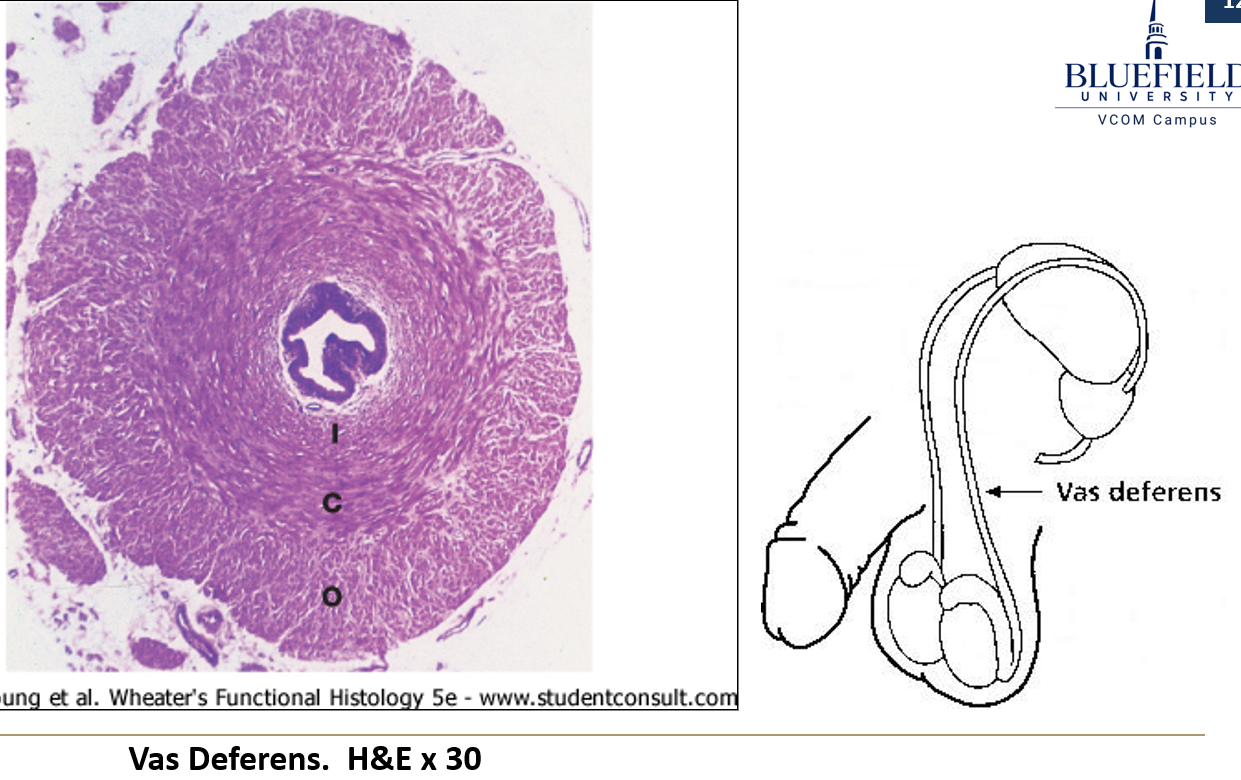
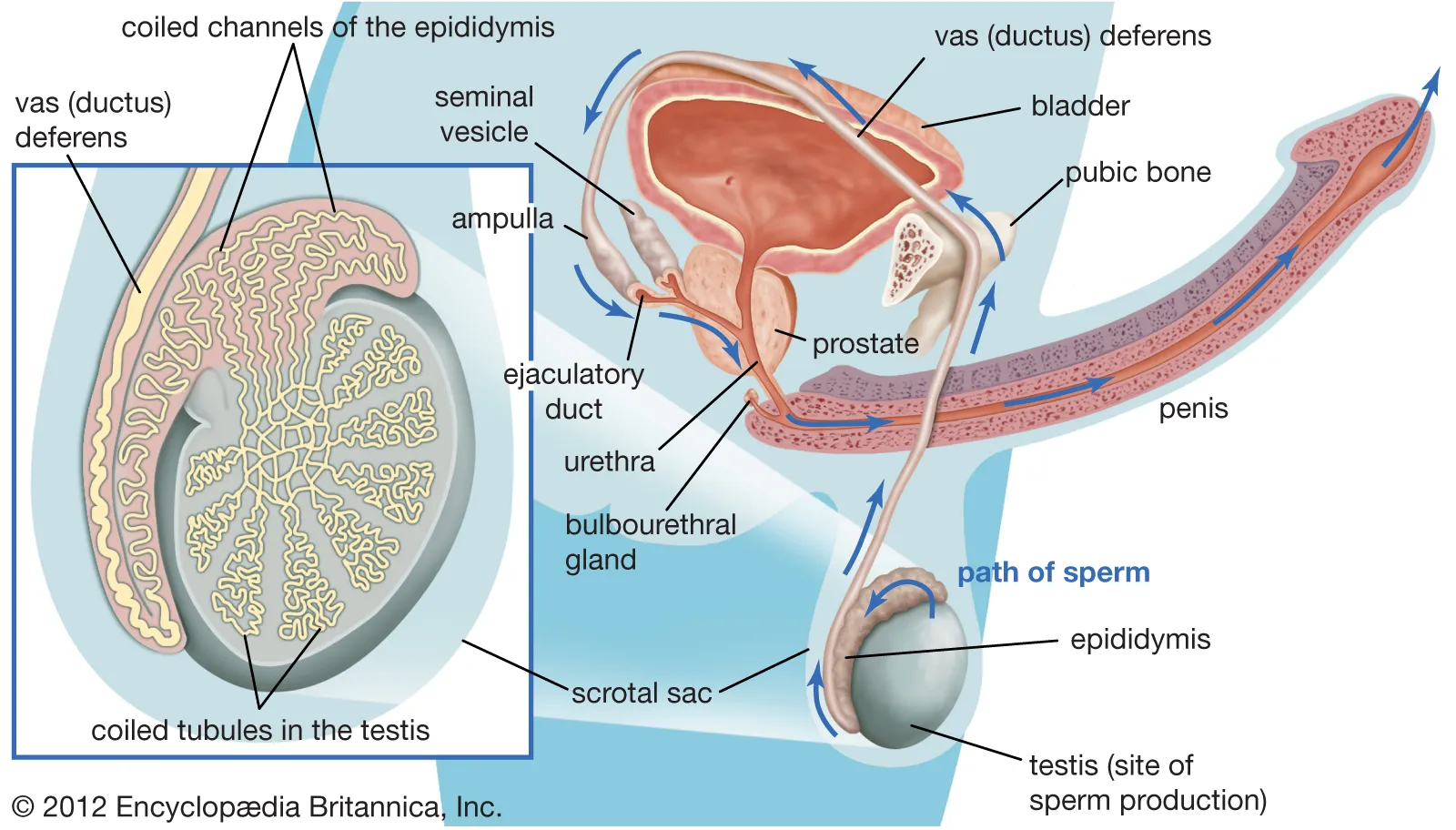
What is the ampulla?
The dilated distal end of the vas deferens before it joins the ejaculatory duct in the prostate
How does the vas deferens appear on histology?
Lined with pseudostratified epithelium with stereocilia
Thick muscularis: inner circular, middle spiral, outer longitudinal
Lumen appears stellate-shaped (star-like) except in the ampulla
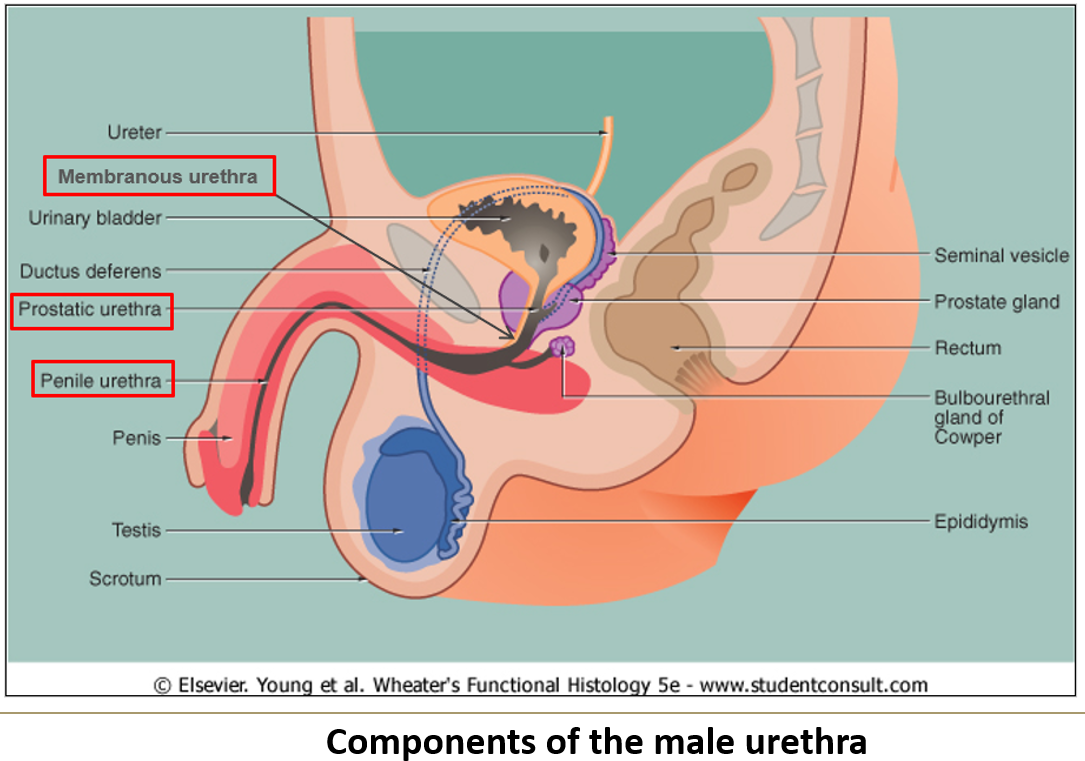
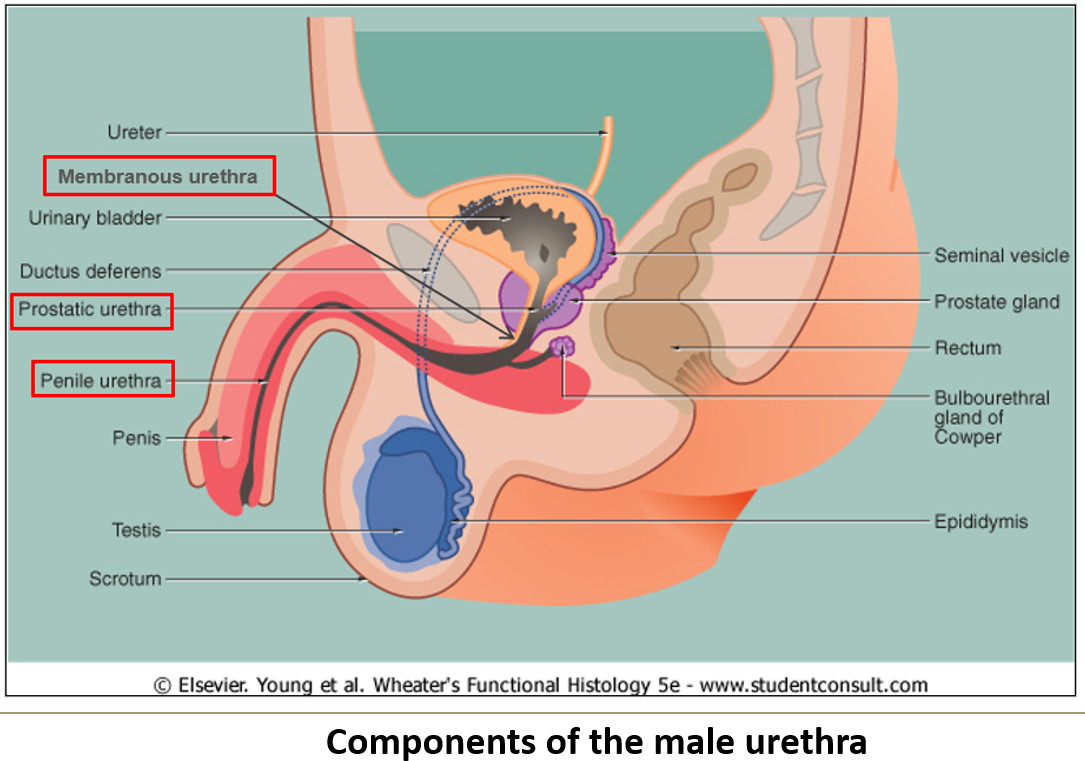
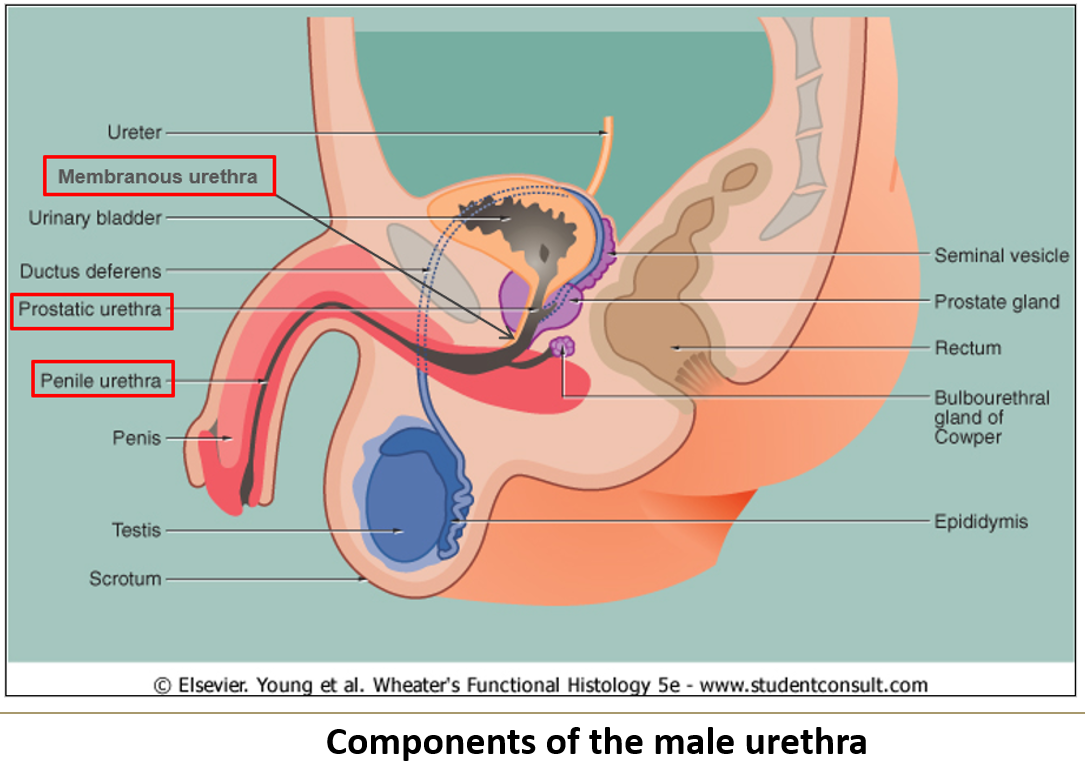
What are the three subdivisions of the male urethra?
Prostatic urethra (through prostate)
Membranous urethra (through pelvic floor)
Cavernous/spongy urethra (through penis)
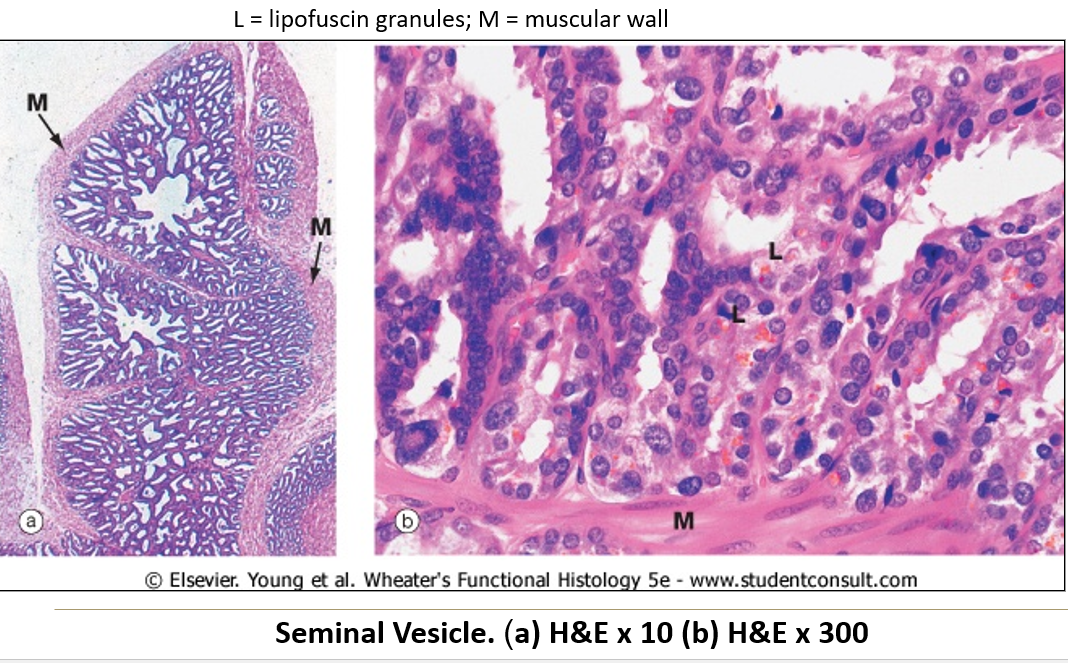
What are seminal vesicles and where are they located?
Paired, narrow, folded sacs located at the posterior base of the bladder.
What do seminal vesicles secrete?
A complex fluid with flavins, ascorbic acid, globulin protein, and fructose.
What kind of epithelium lines the seminal vesicles?
Pseudostratified epithelium that varies in height, giving a false simple columnar appearance.
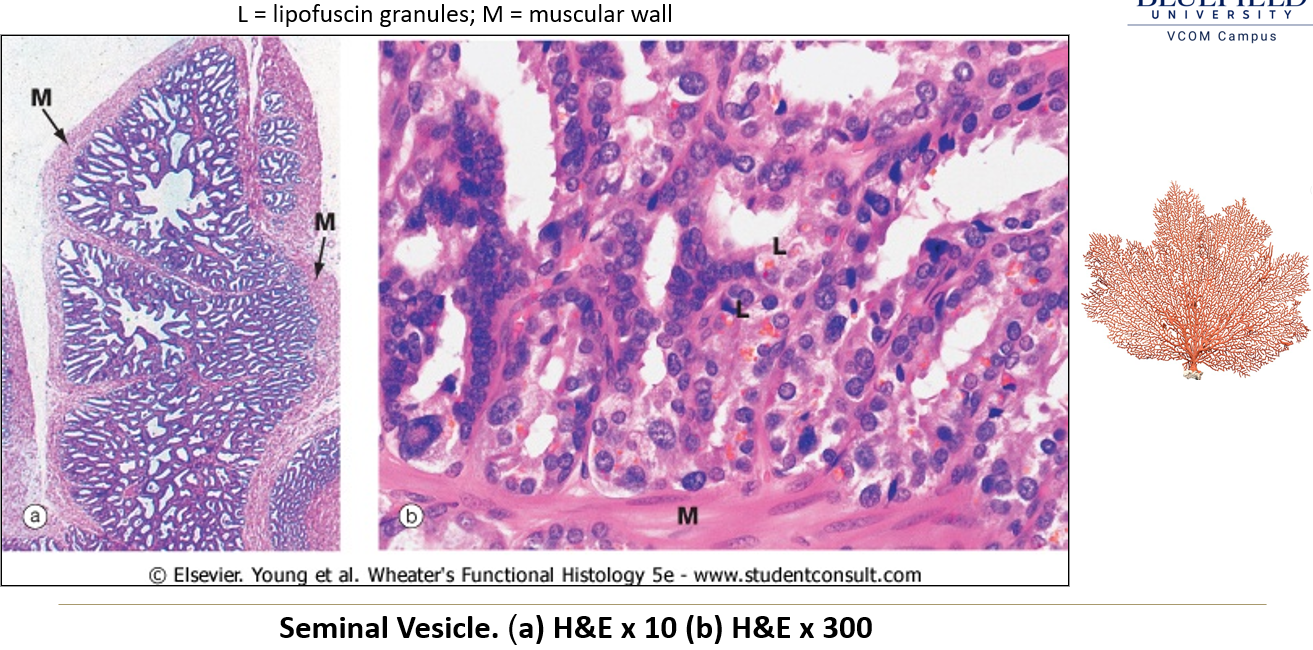
What’s special about the lamina propria and muscularis in the seminal vesicles?
Lamina propria = can be very thin
Muscularis = present but layers are ill defined
Where is the prostate gland located?
It wraps around the urethra at the base of the bladder.
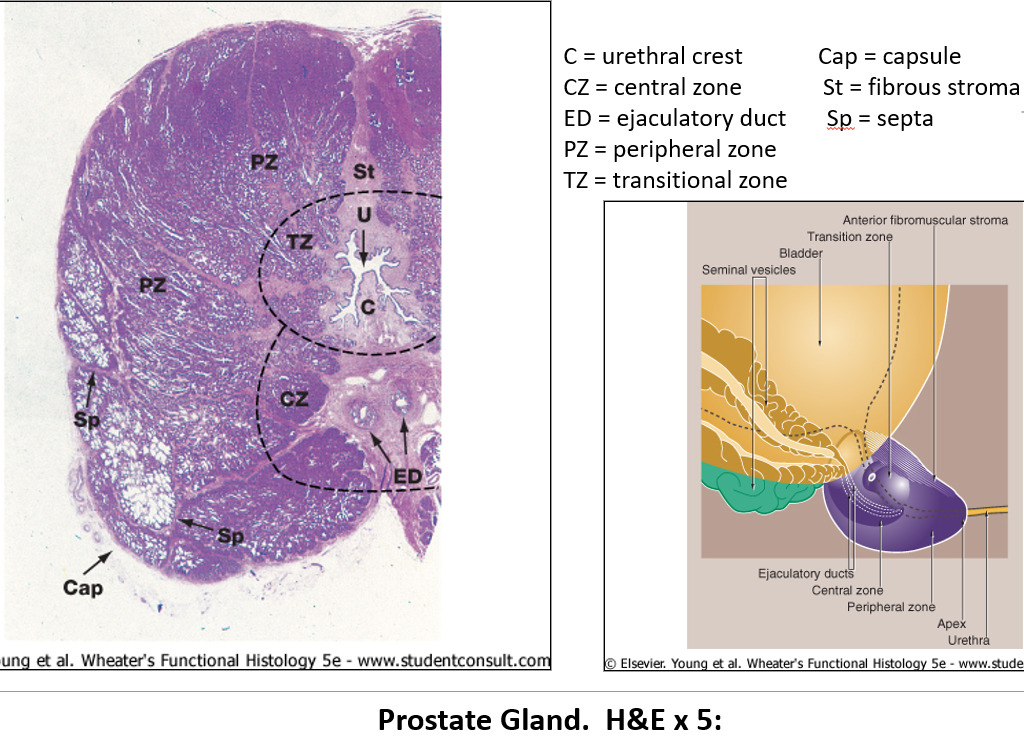
What is the prostate made of?
About 20 tubuloacinar glands, each with its own duct that opens into the urethra.
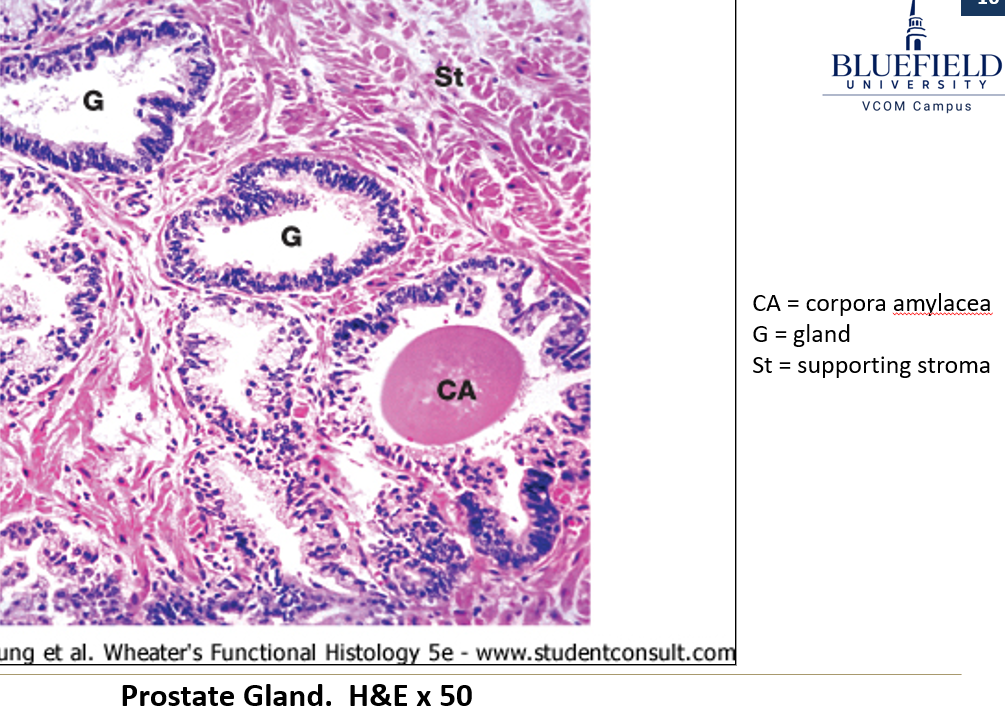
What kind of epithelium lines the prostate?
Pseudostratified epithelium of varying height, influenced by testosterone levels.
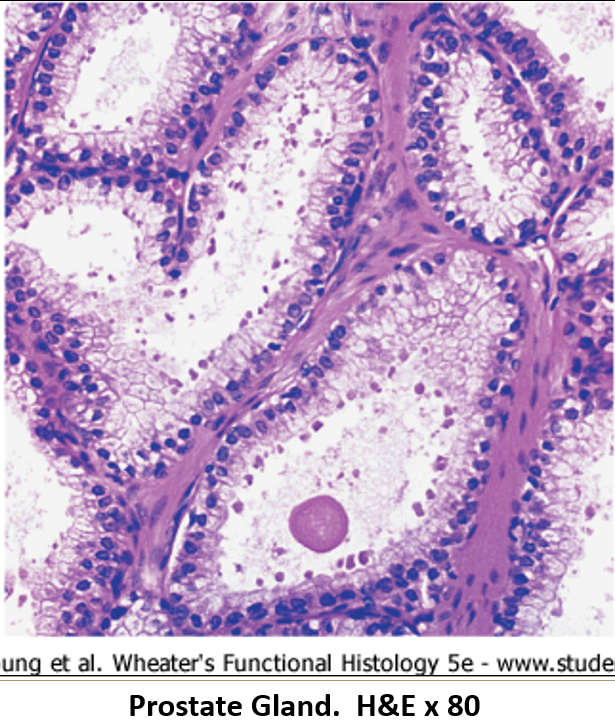
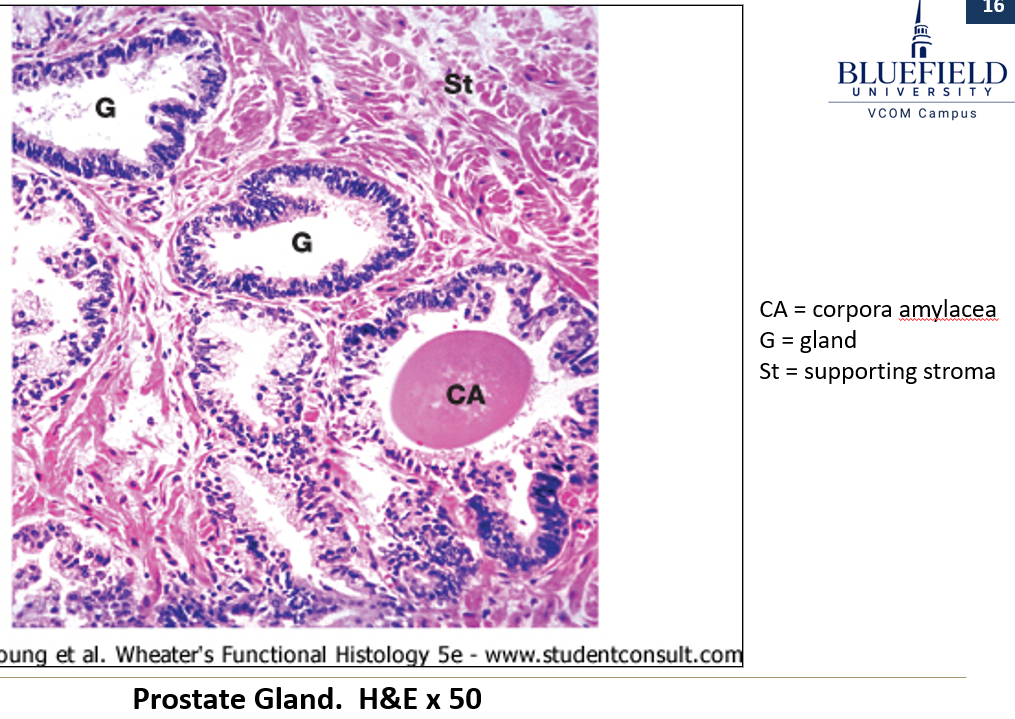
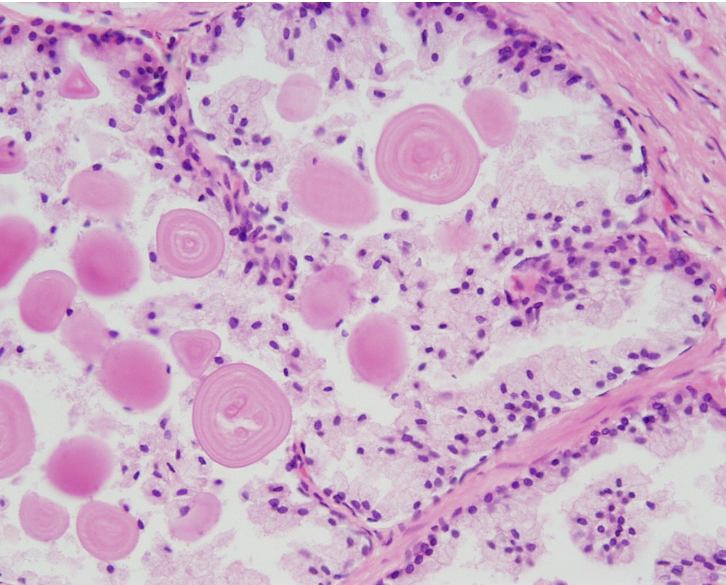
What are corpora amylacea?
Glycoprotein concretions (clumps) found in that commonly form inside the prostate glands
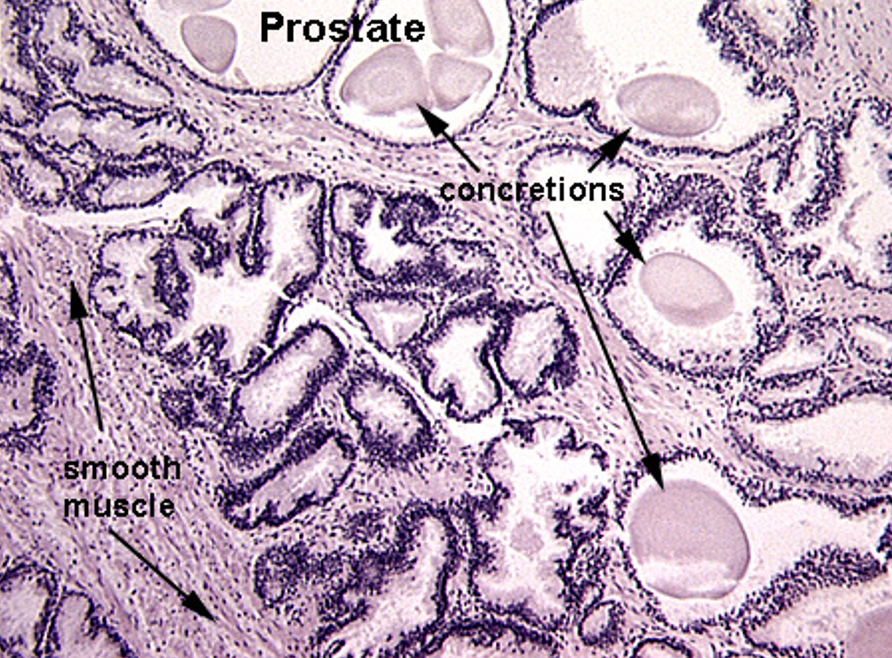
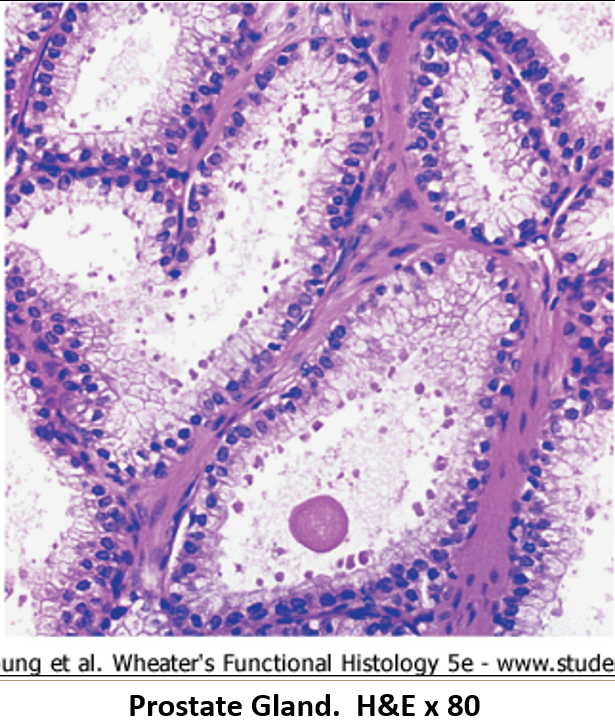
Which substances are secreted by the prostate?
Acid phosphatase (also goes into blood)
Citric acid
Fibrinolysin
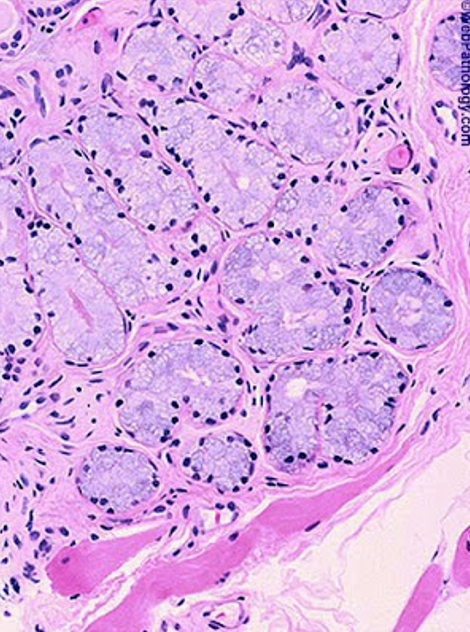
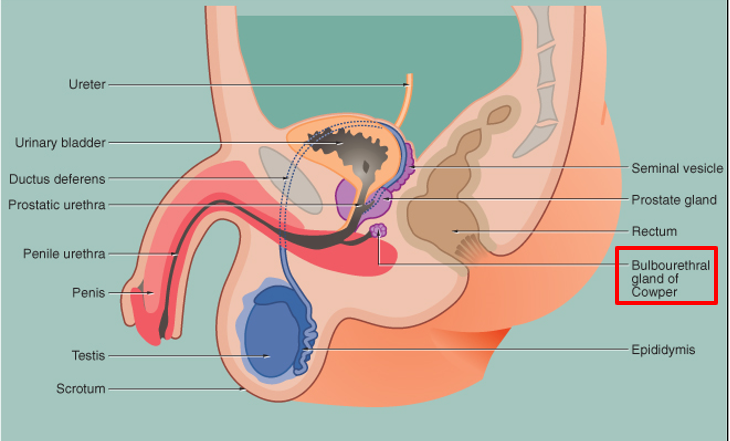
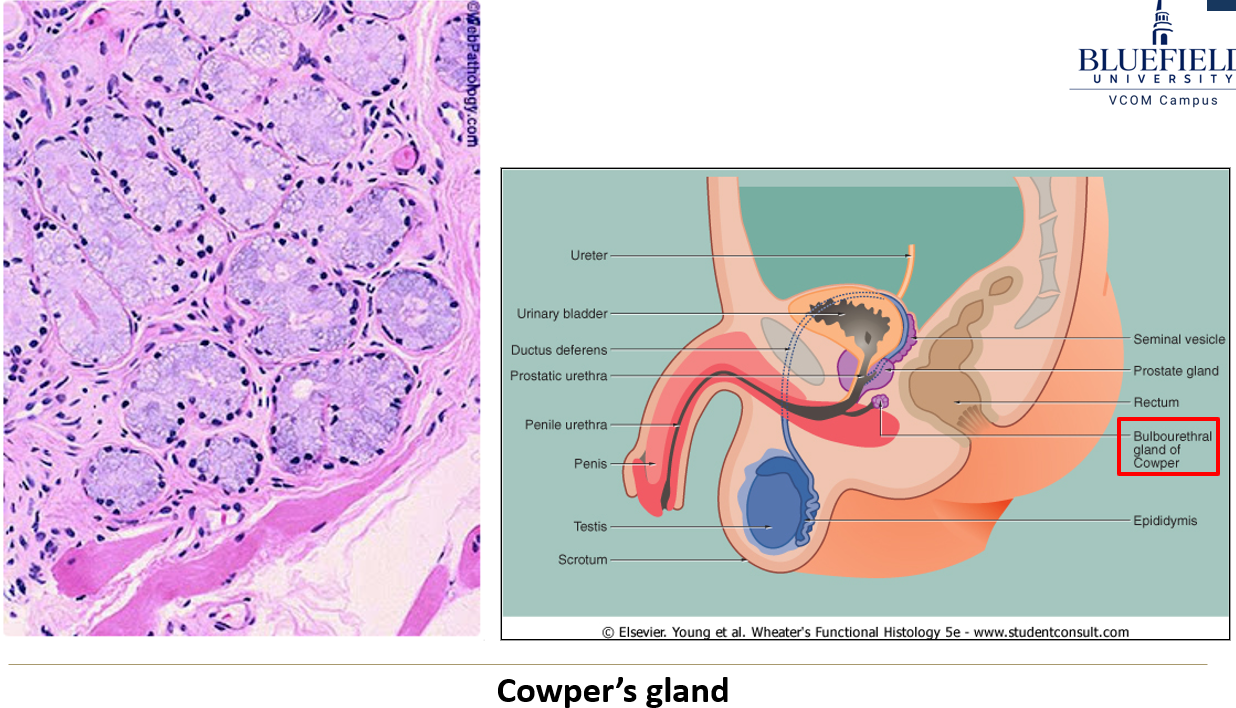
Where are Cowper’s glands located?
Paired pea-sized glands near the base of the penis, beside the urethra.
What kind of glands are they?
Tubuloacinar glands with irregular lumens, lined with columnar to cuboidal cells.
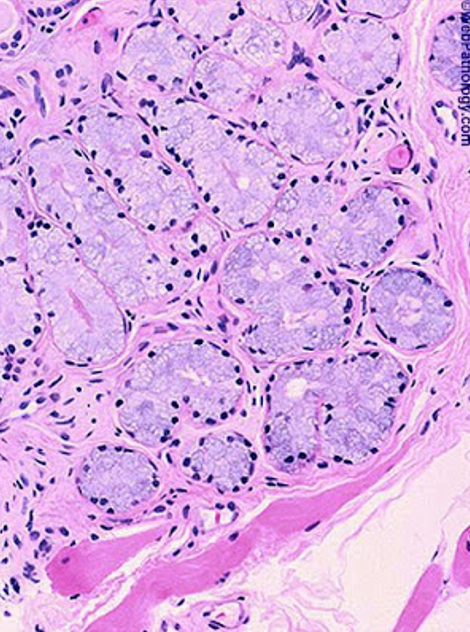
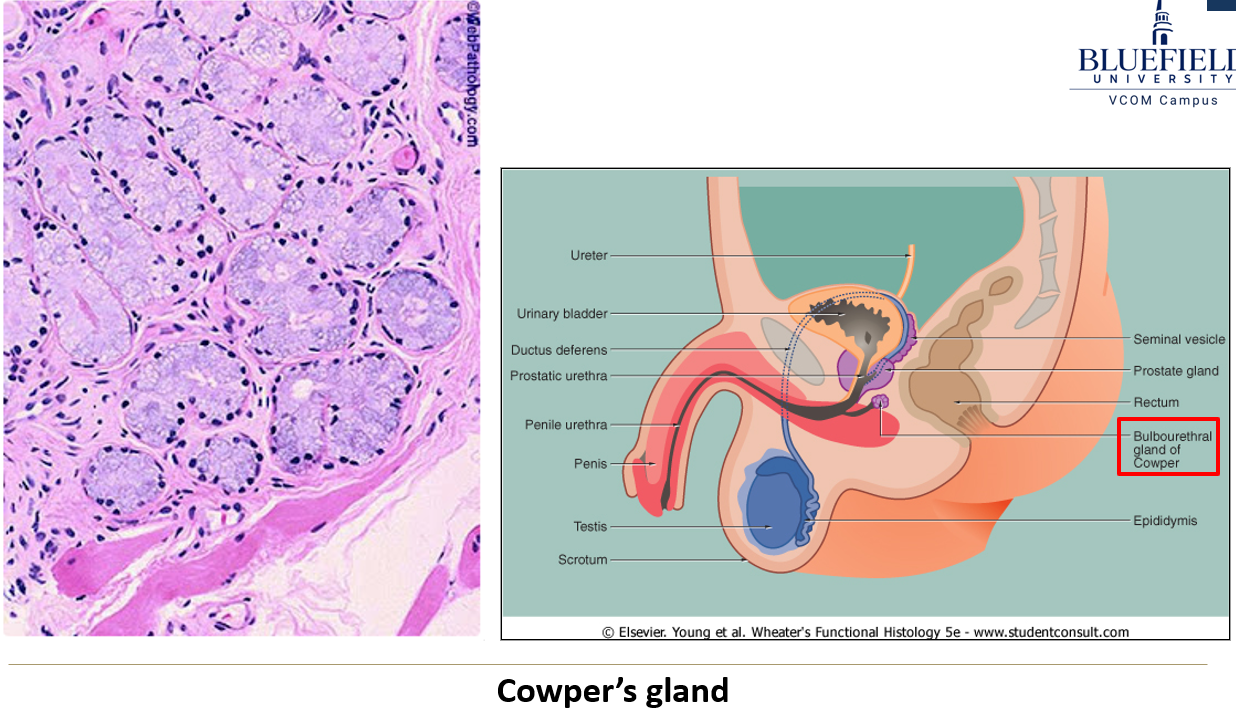
What do cowper’s glands secrete?
An alkaline mucous.
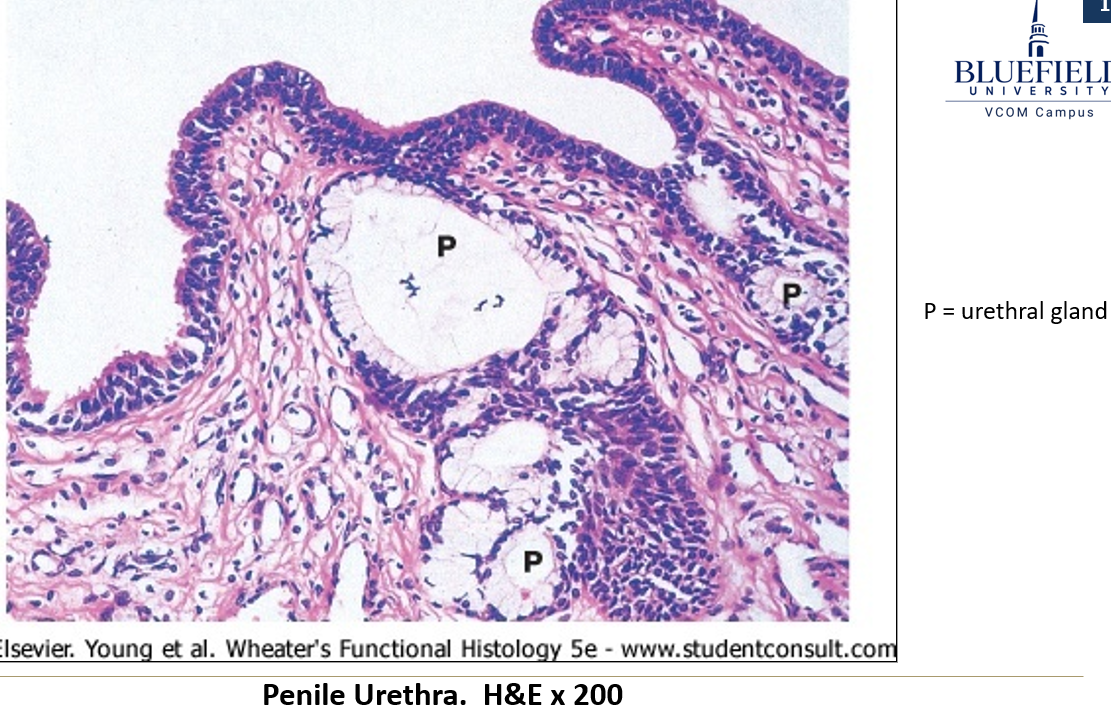
Where are urethral glands found and what do they secrete?
Found along the penile urethra and they secrete alkaline material.
What are the main components of erectile tissue?
Connective tissue and smooth muscle surrounding blood sinuses lined with endothelium.
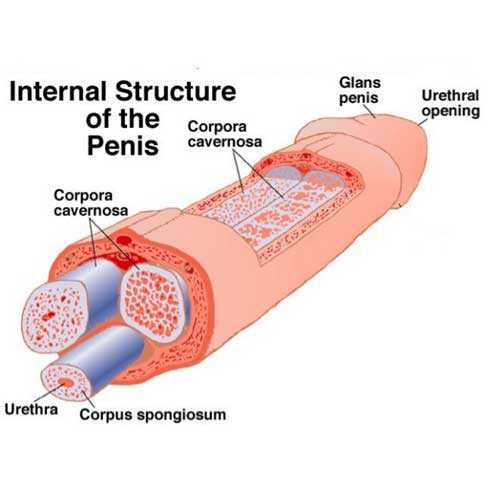
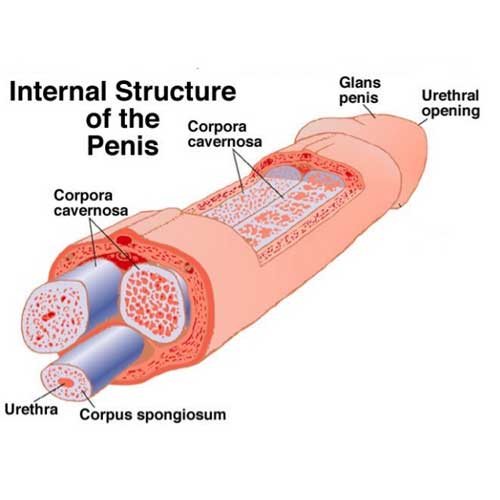
What are the corpora cavernosa?
Two paired columns of erectile tissue located dorsally in the penis.
What surrounds the corpora cavernosa?
A dense capsule called the tunica albuginea.
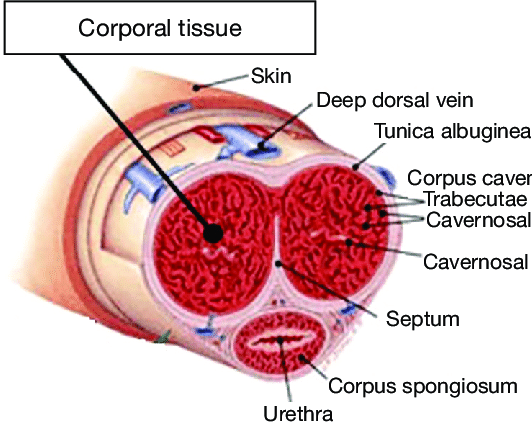
Are the two corpora cavernosa completely separate?
No, they are not completely separated at the midline.
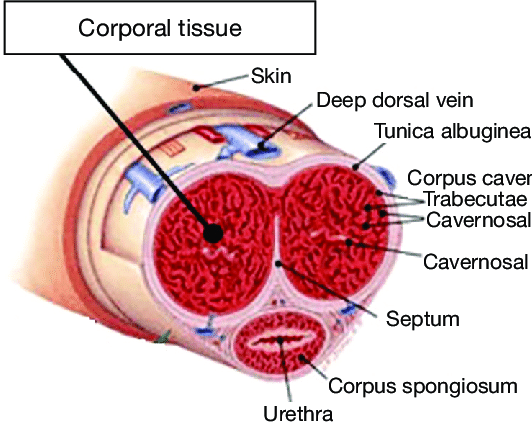
Where is the corpus spongiosum located?
It lies anteriorly and surrounds the urethra along its entire length.
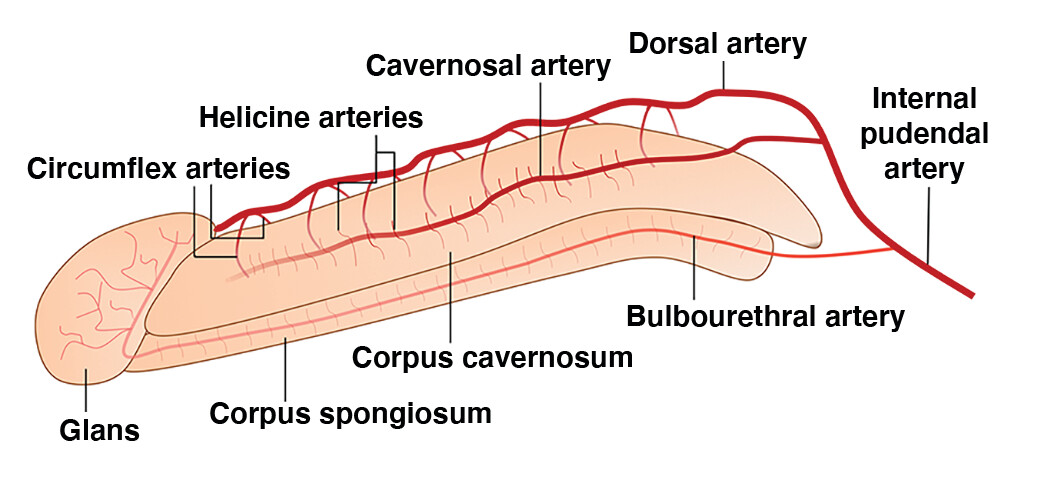
What arteries supply the corpora?
Helicine arteries, which have a very thick tunica media.
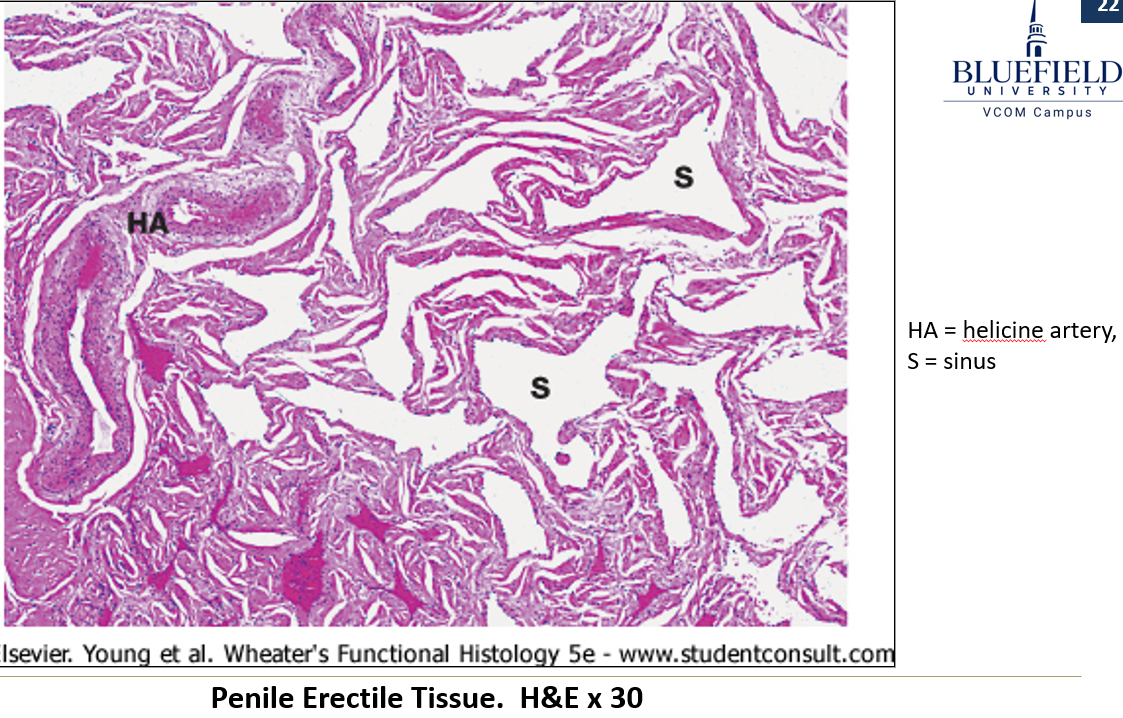
What keeps helicine arteries constricted normally?
Sympathetic input.
What causes an erection?
When sympathetic input is reduced, the helicine arteries dilate, causing blood inflow to exceed outflow, resulting in erection.
What is the epithelium of the prostatic urethra?
Starts as transitional epithelium, then changes to pseudostratified or stratified cuboidal/columnar distally.
What type of epithelium lines the membranous urethra?
Pseudostratified or stratified cuboidal/columnar epithelium.
How does the epithelium change in the cavernous urethra?
Starts as stratified cuboidal/columnar and shifts to stratified squamous near the opening of the penis.
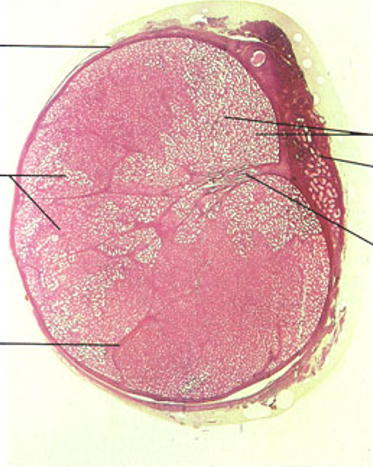
Identify this structure
Testis
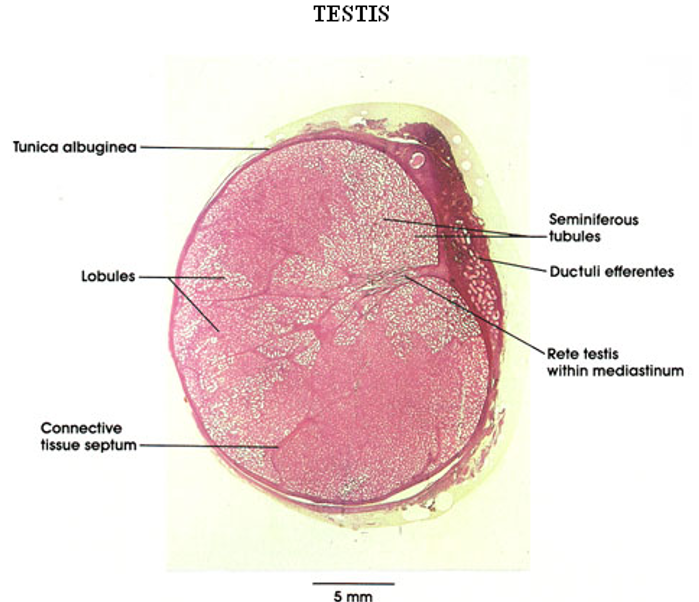
Identify this structure
Testis
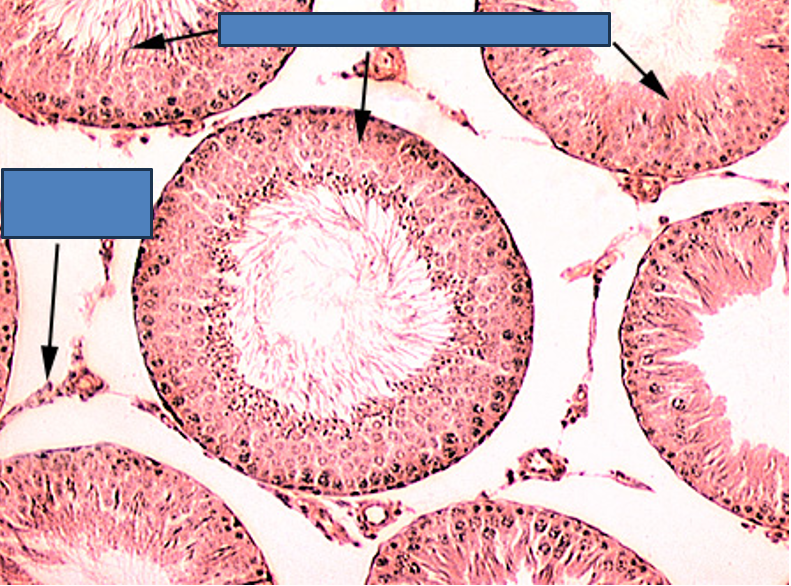
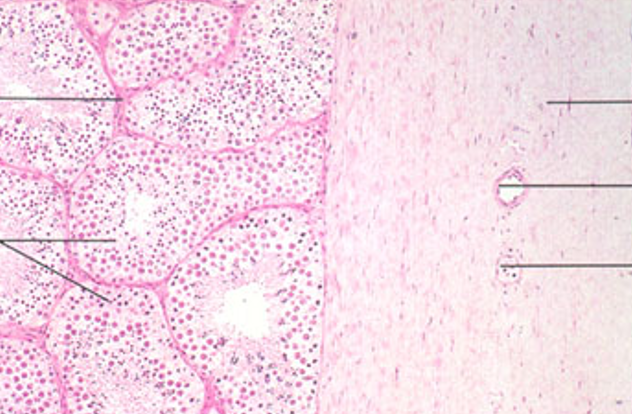
Identify this structure
Seminiferous tubules
Round or oval tubules with a stratified epithelium
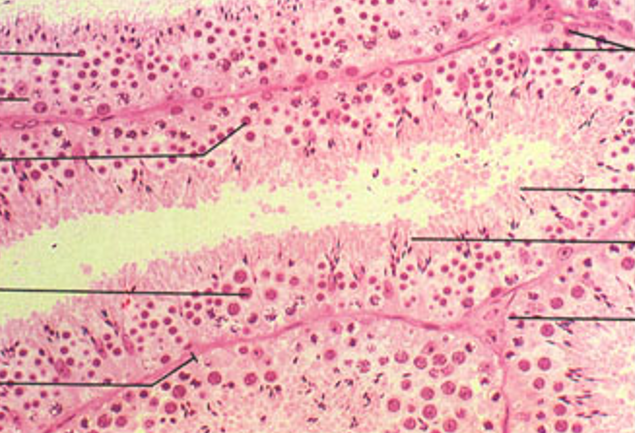
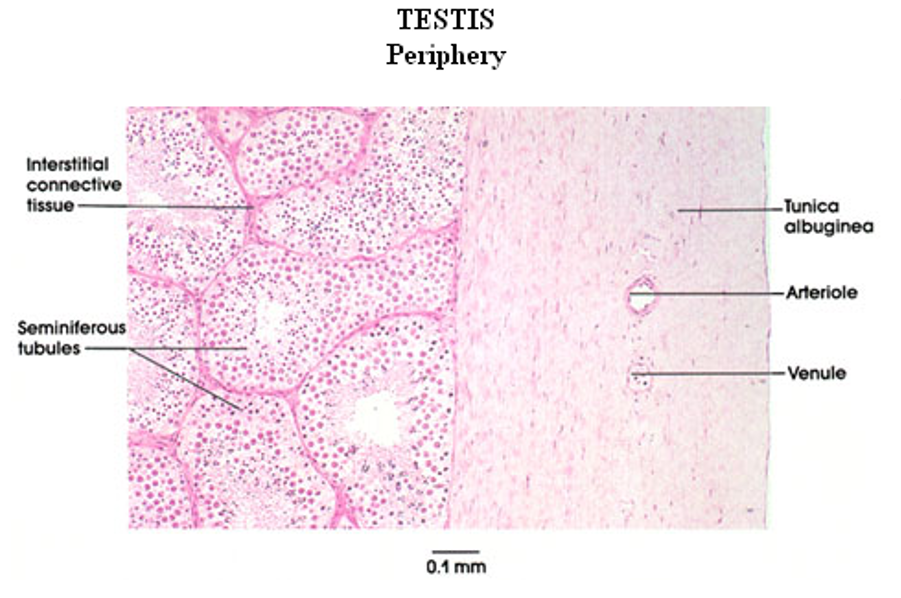
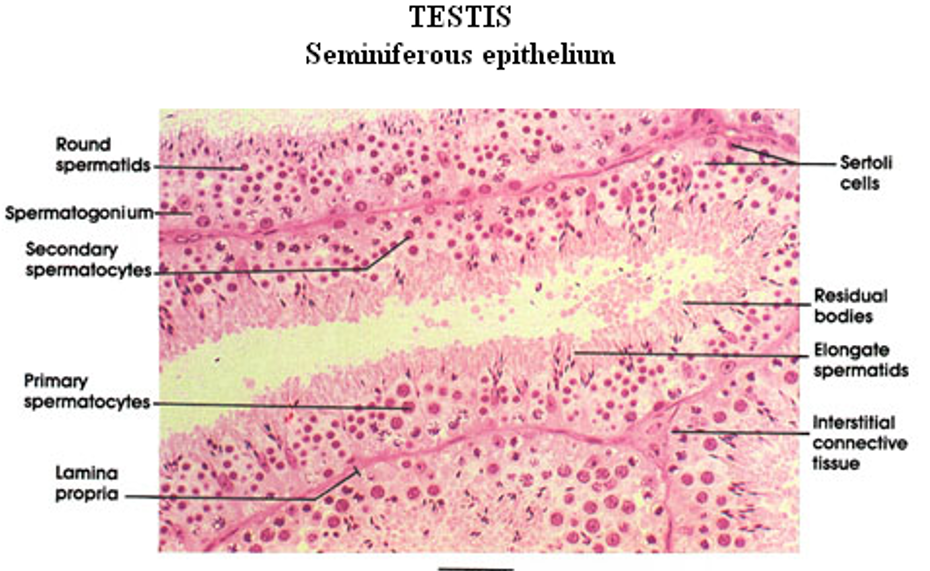
Identify this structure
Testis—Seminiferous epithelium
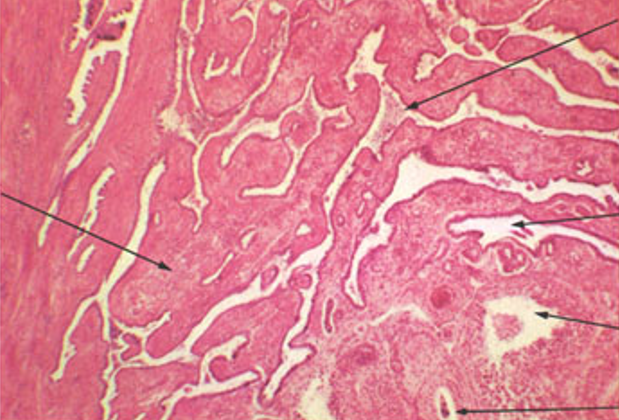
Identify this structure
Rete testis
Appears like a “flattened sponge”
Located in the mediastinum testis (central region of testis)
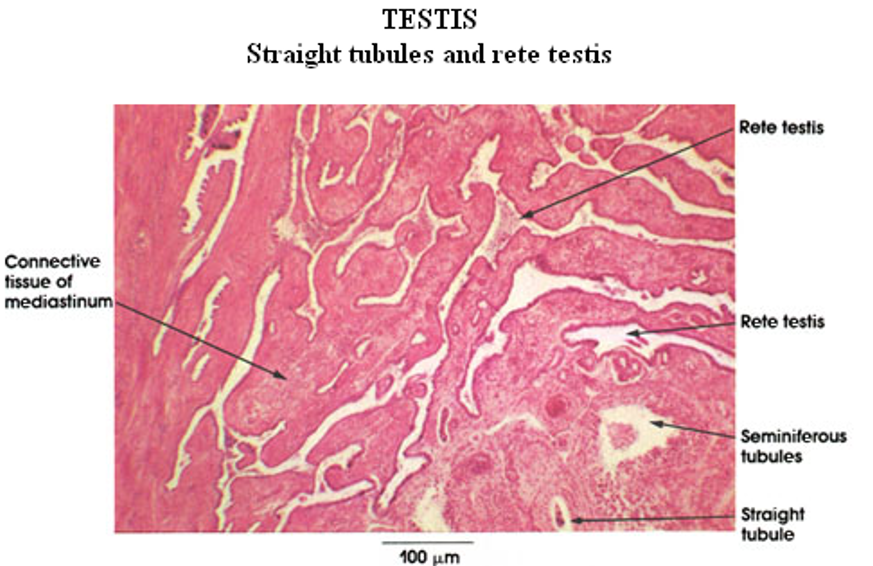
Identify this structure
Rete testis
Appears like a “flattened sponge”
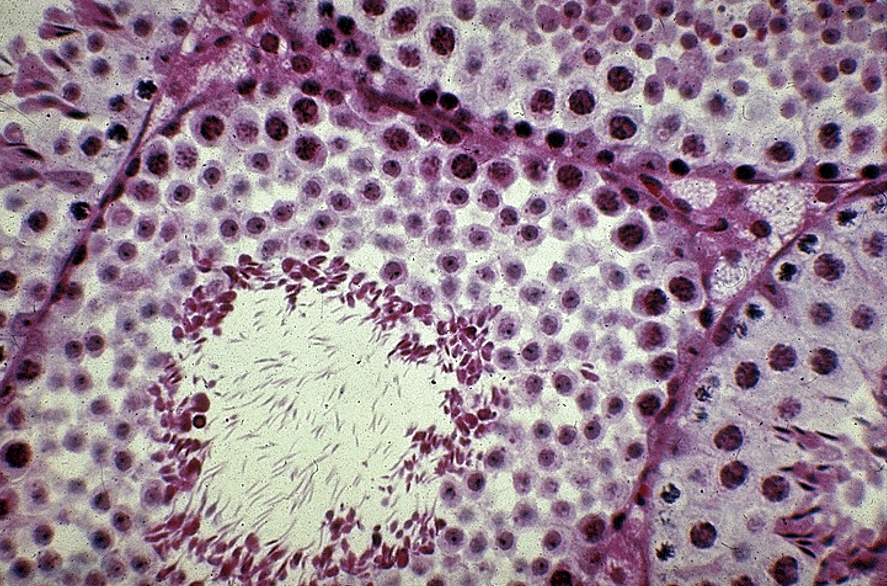
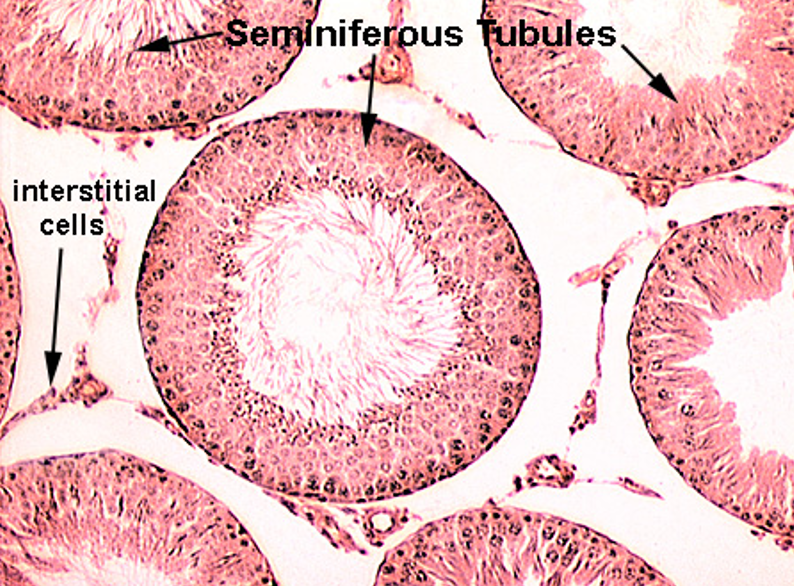
Identify Sertoli cells, spermatogenic cells and the boundary layer. Also identify Leydig cells.
Seminiferous tubule.
Nuclei visible surrounding lumen (unlike epididymis)
Leydig = testosterone factory (outside seminiferous tubules)
Sertoli = sperm babysitters (inside seminiferous tubules)
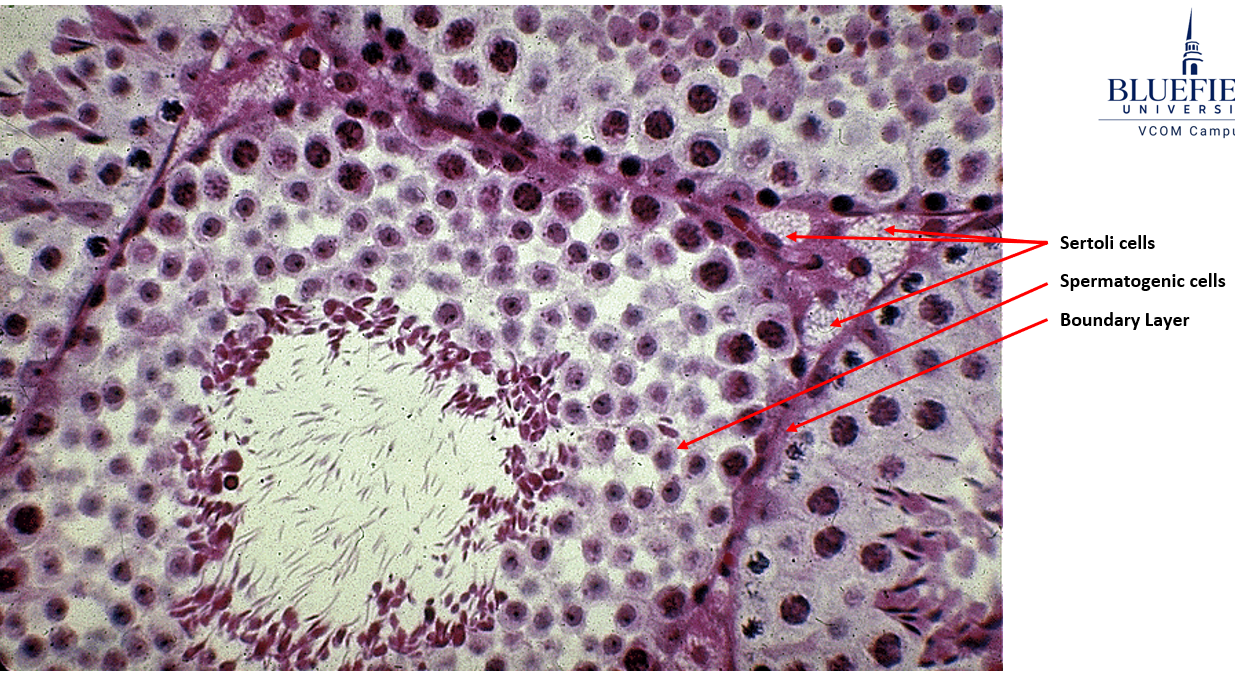
Identify this structure
Seminiferous tubule.
Nuclei visible surrounding lumen (unlike epididymis)
Leydig = testosterone factory (outside seminiferous tubules)
Sertoli = sperm babysitters (inside
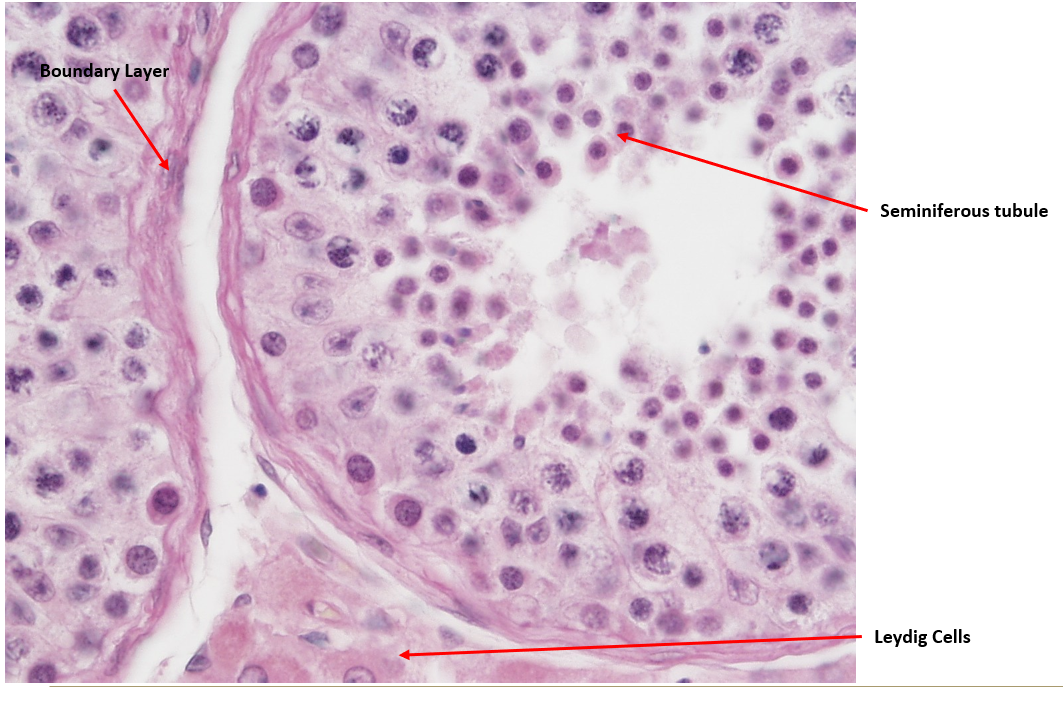
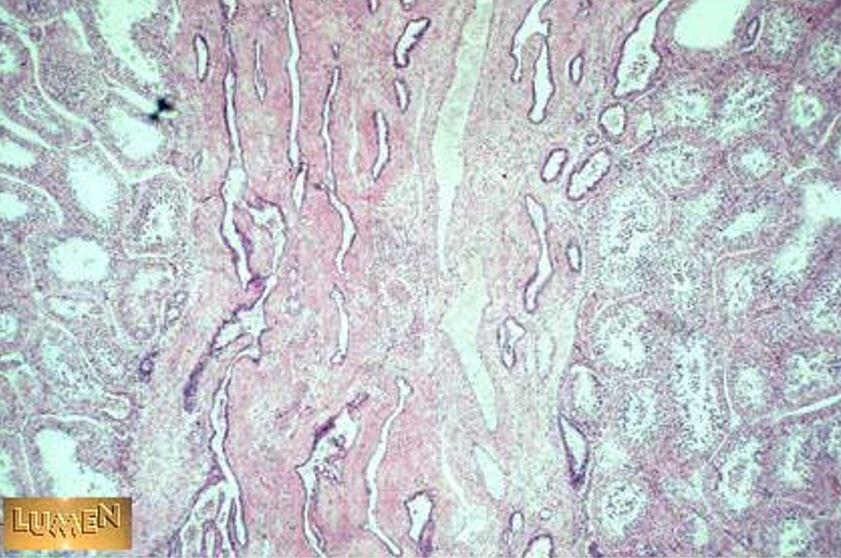
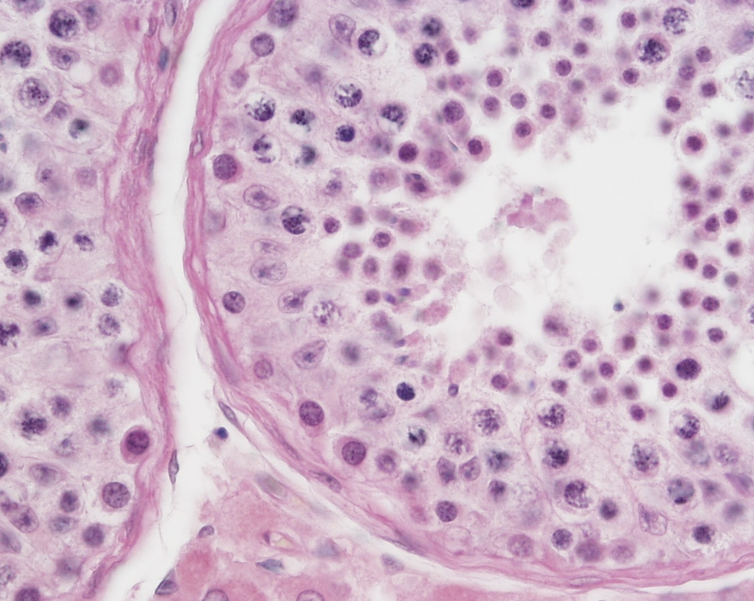
Identify this structure
Seminiferous tubules and rete testis.
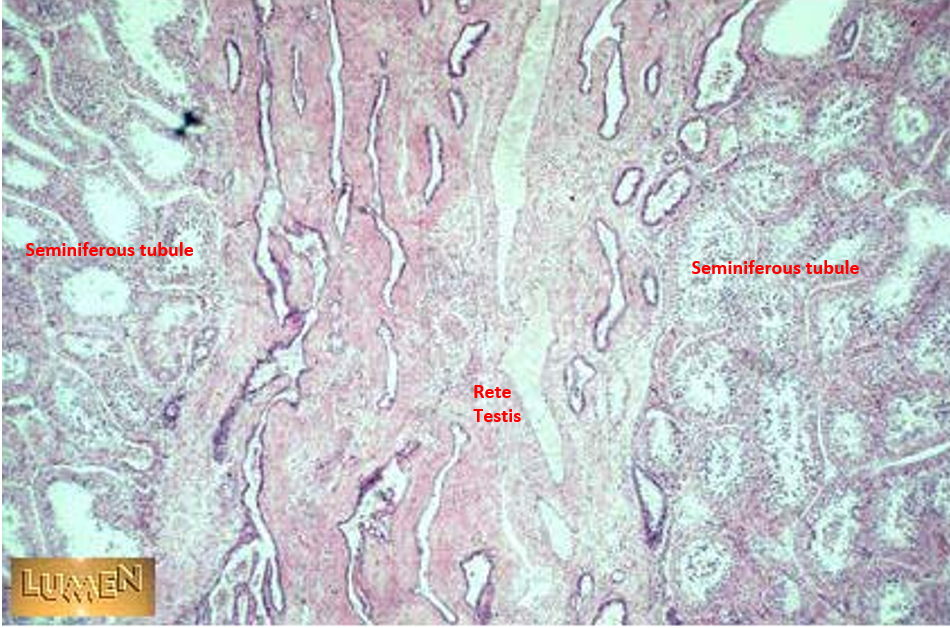
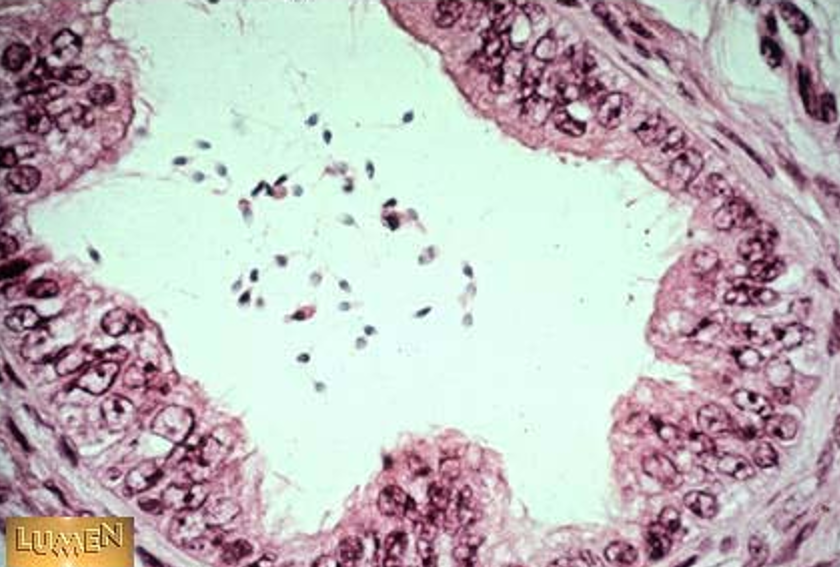
Identify this structure
ductuli efferentes
Wavy or scalloped lumen
Lined by alternating tall ciliated and short non-ciliated simple columnar cells
Thin smooth muscle layer around each duct
Found between rete testis and epididymis
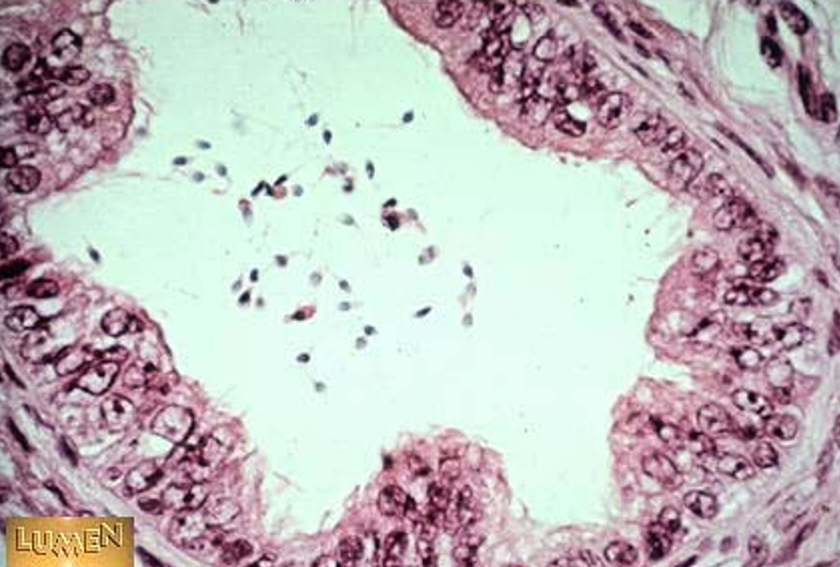
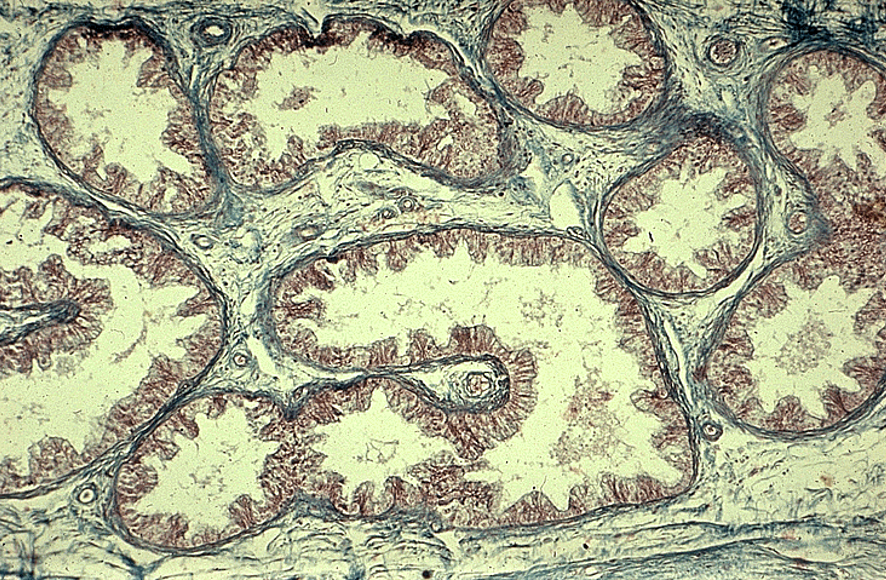
Identify this structure
ductuli efferentes
Wavy or scalloped lumen
Lined by alternating tall ciliated and short non-ciliated simple columnar cells
Thin smooth muscle layer around each duct
Found between rete testis and epididymis
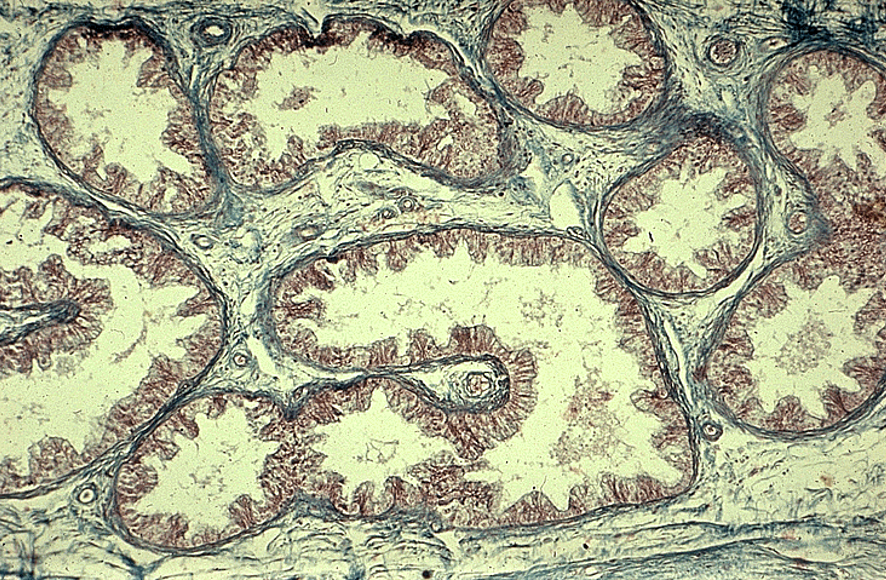
Identify this structure
Epididymis
Long, coiled duct with a regular, round lumen
Cytoplasm has no nuclei in it (unlike seminif. tubules)
Lined by pseudostratified columnar epithelium with stereocilia
Surrounded by smooth muscle
Sperm often visible in the lumen
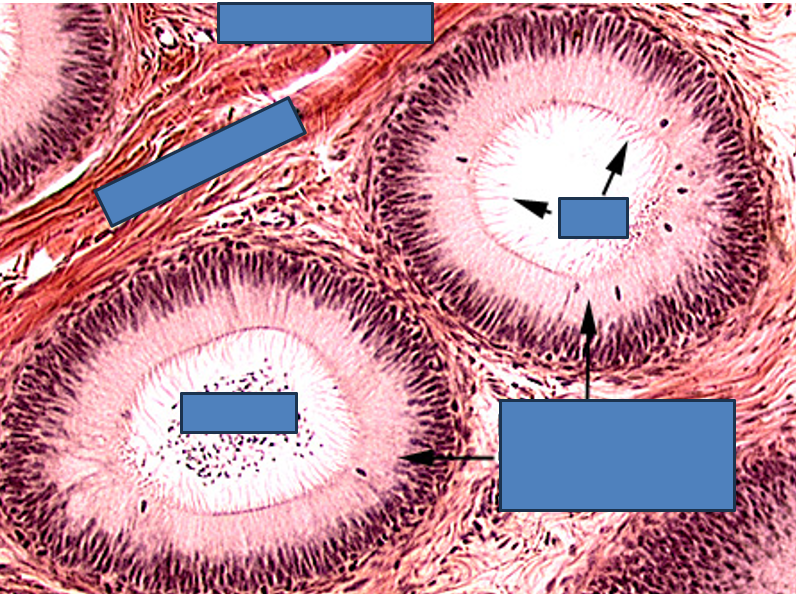
Identify this structure
Epididymis
Long, coiled duct with a regular, round lumen
Cytoplasm has no nuclei in it (unlike seminif. tubules)
Lined by pseudostratified columnar epithelium with stereocilia
Surrounded by smooth muscle
Sperm often visible in the lumen
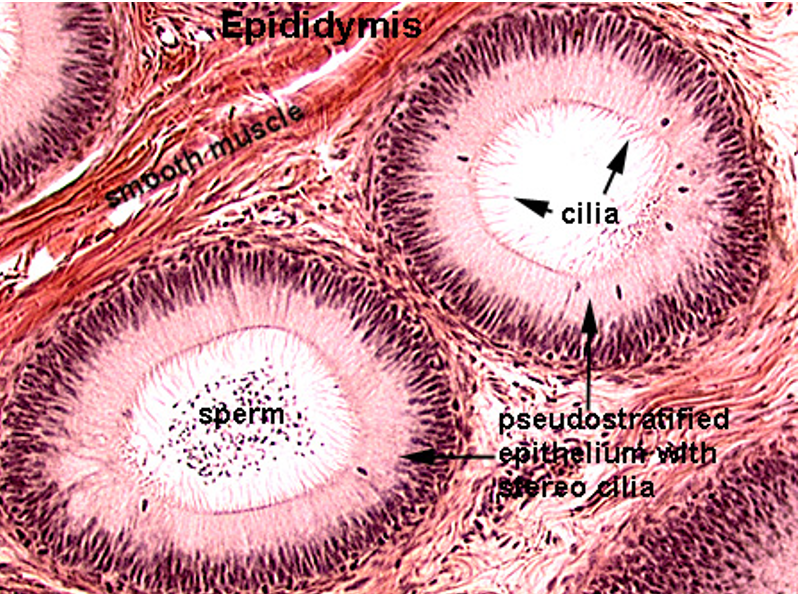
Identify this structure
Epididymis
Long, coiled duct with a regular, round lumen
Cytoplasm has no nuclei in it (unlike seminif. tubules)
Lined by pseudostratified columnar epithelium with stereocilia
Surrounded by smooth muscle
Sperm often visible in the lumen
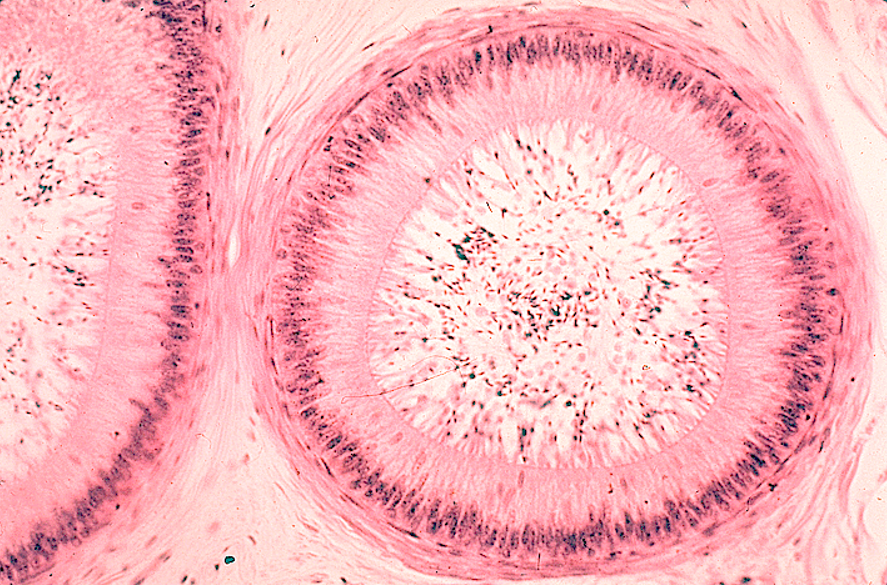
Identify this structure
Epididymis
Long, coiled duct with a regular, round lumen
Cytoplasm has no nuclei in it (unlike seminif. tubules)
Lined by pseudostratified columnar epithelium with stereocilia
Surrounded by smooth muscle
Sperm often visible in the lumen
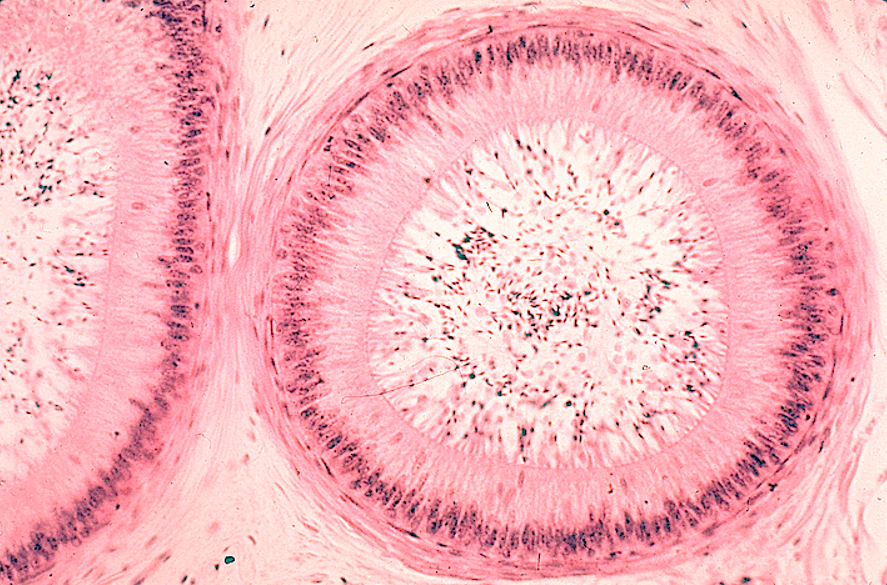
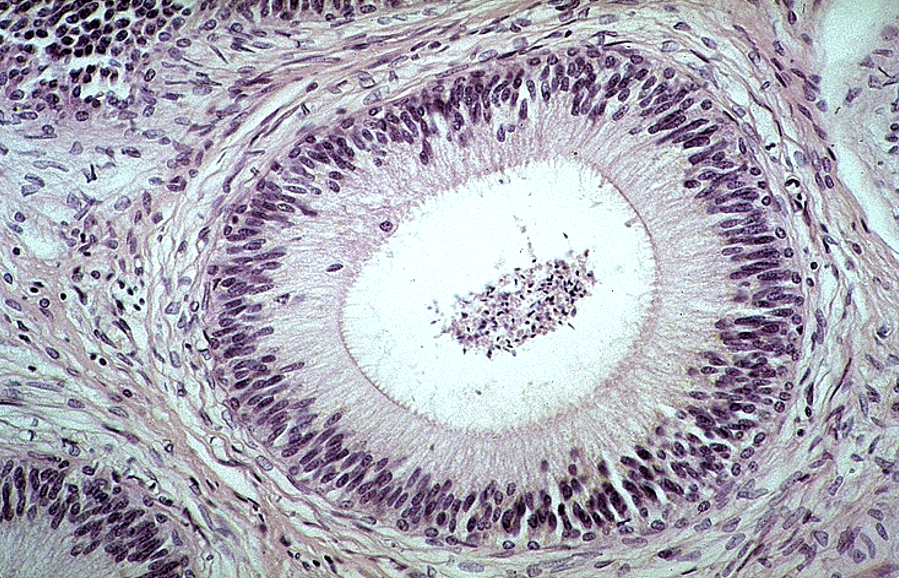
Identify this structure
Epididymis
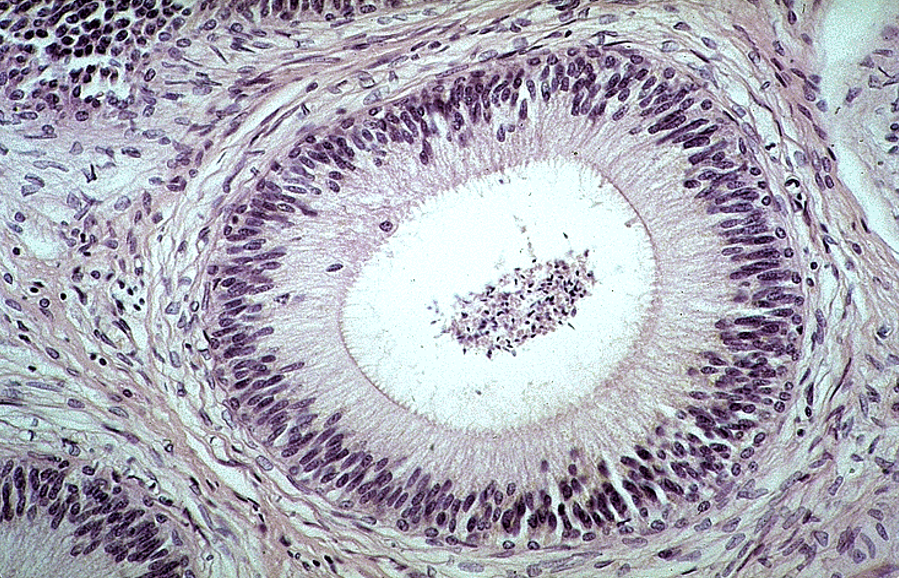
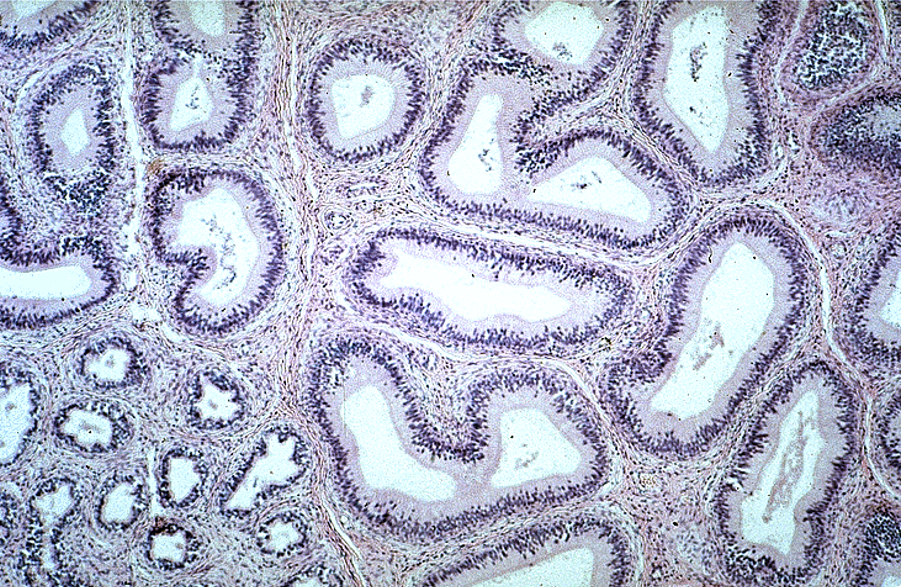
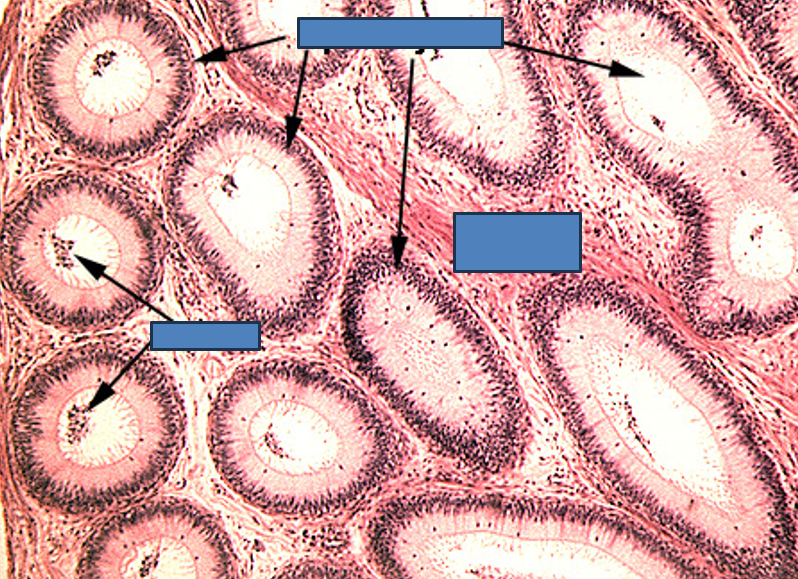
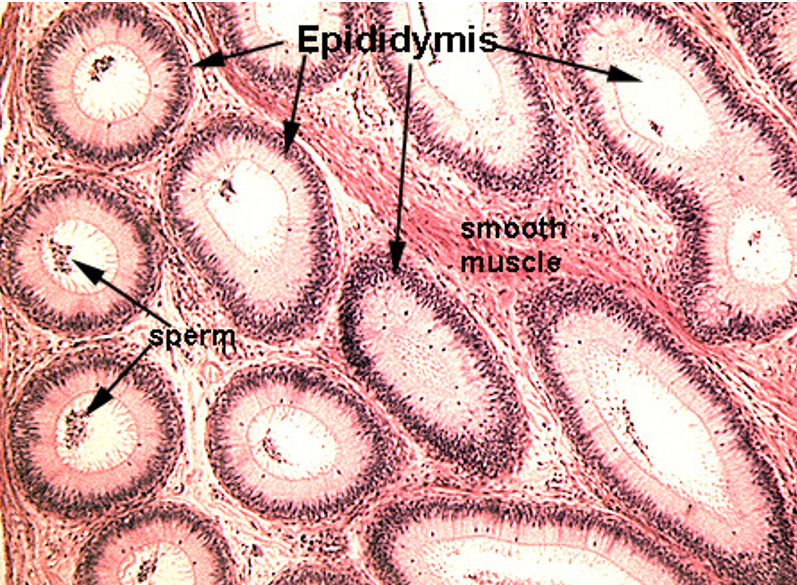
Identify this structure
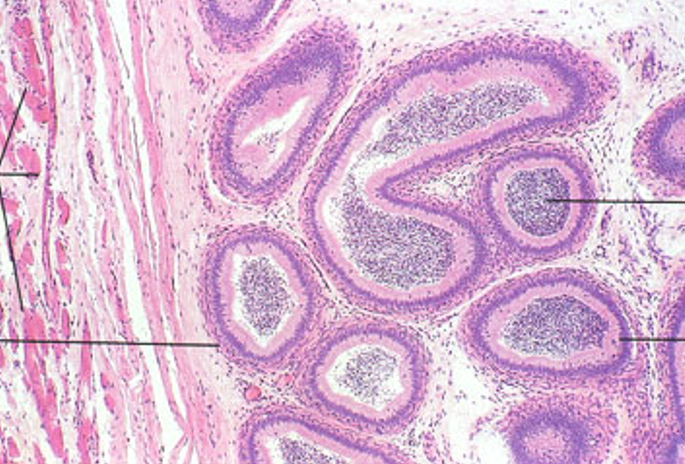
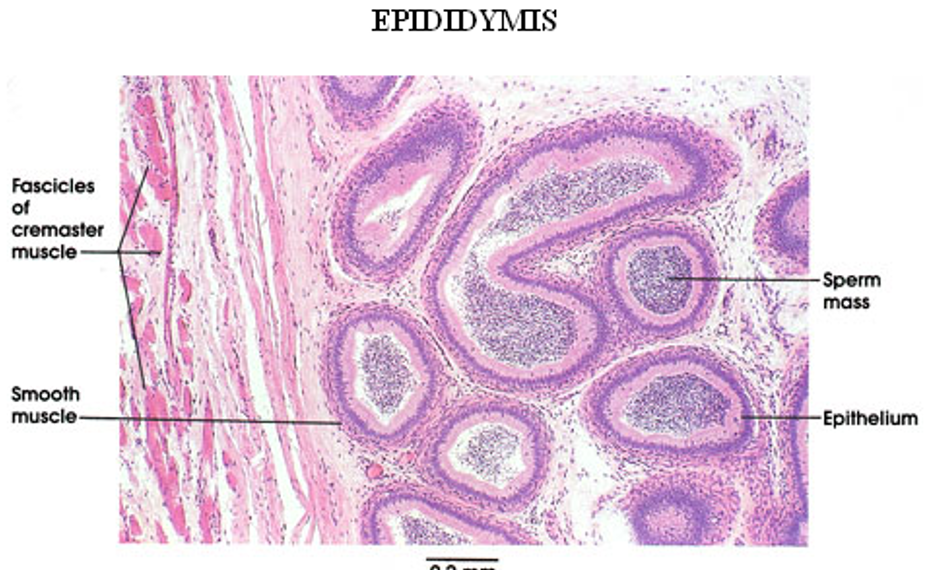
Epididymis, in both tangential and longitudinal sections. Note also some ducti efferentes in the lower right corner.
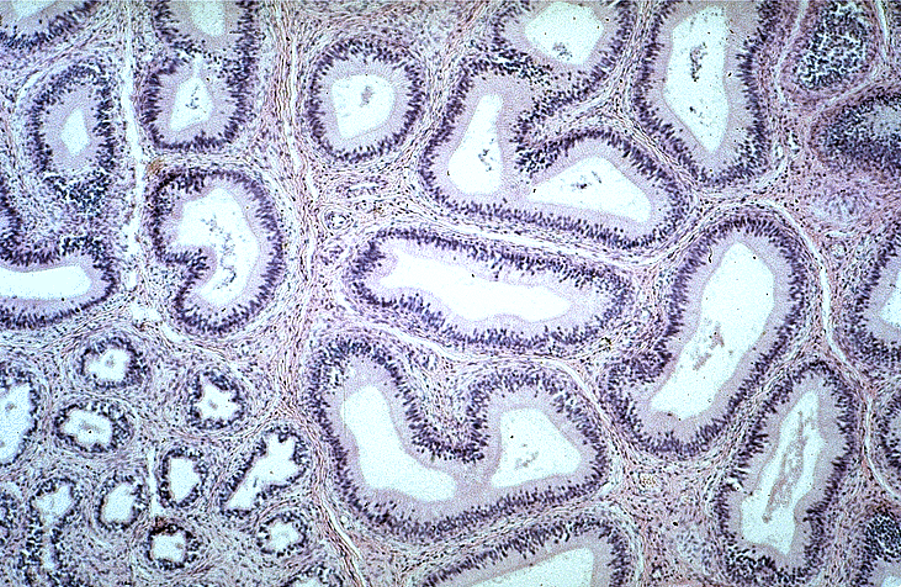
Identify this structure
Epididymis
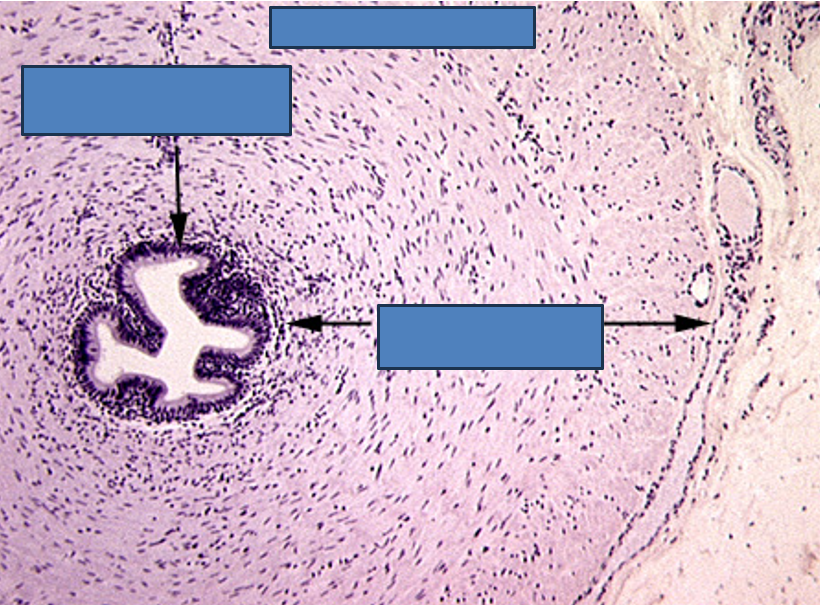
Identify this structure
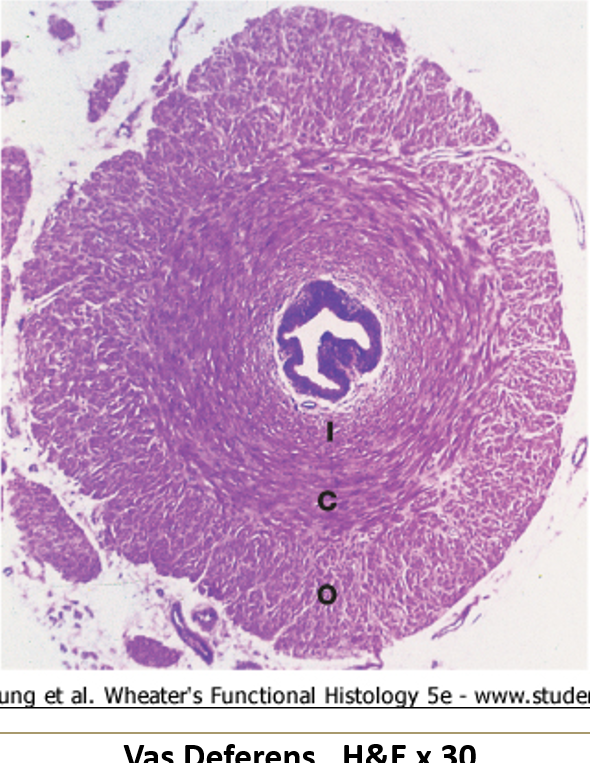
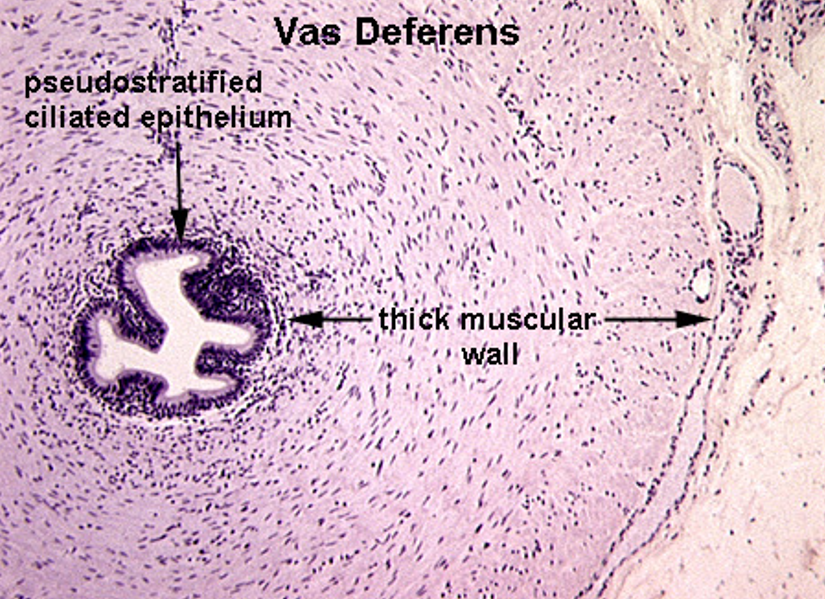
Vas deferens
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium with stereocilia
Small, irregular lumen compared to thick wall
Surrounded by a very thick muscularis with three layers: inner longitudinal, middle circular, outer longitudinal
Often has a folded mucosa
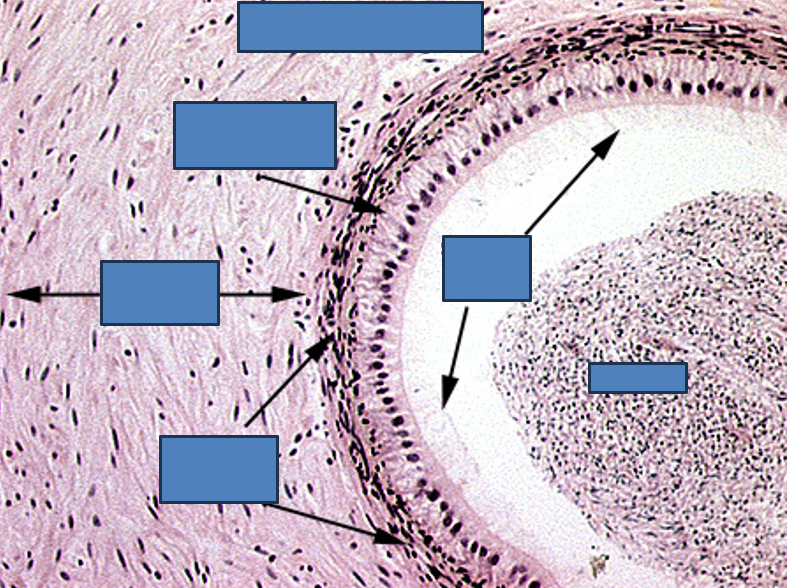
Identify this structure
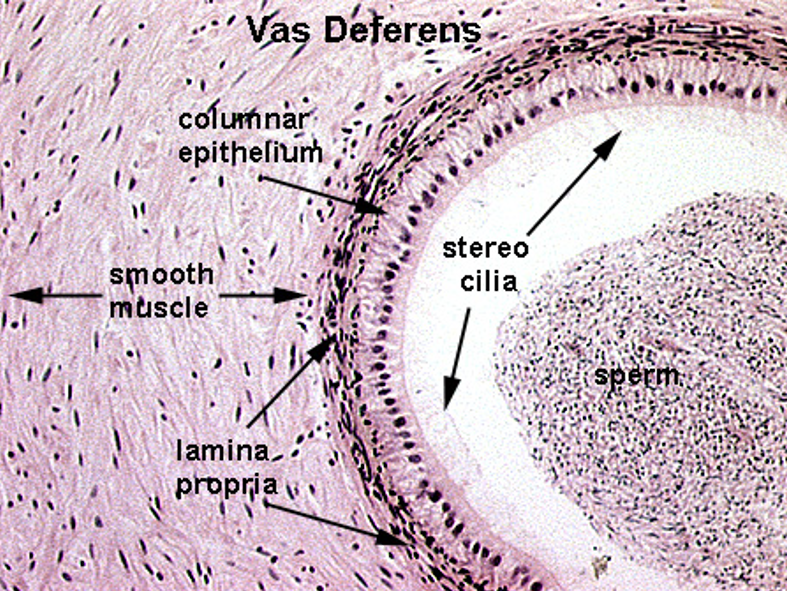
Vas deferens
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium with stereocilia
Small, irregular lumen compared to thick wall
Surrounded by a very thick muscularis with three layers: inner longitudinal, middle circular, outer longitudinal
Often has a folded mucosa
Vas deferens stores sperm
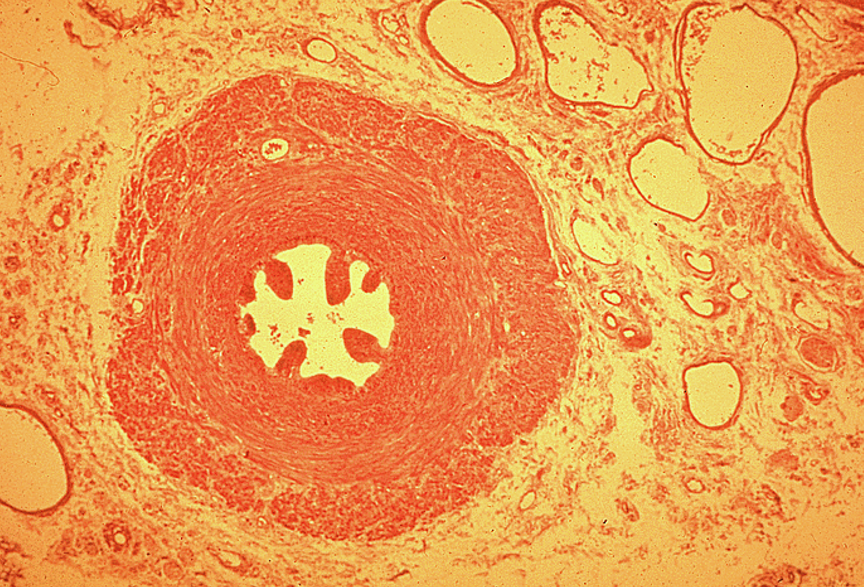
Identify this structure
Vas deferens
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium with stereocilia
Small, irregular star-shaped lumen compared to thick wall
Surrounded by a very thick muscularis with three layers: inner longitudinal, middle circular, outer longitudinal
Often has a folded mucosa
Vas deferens stores sperm
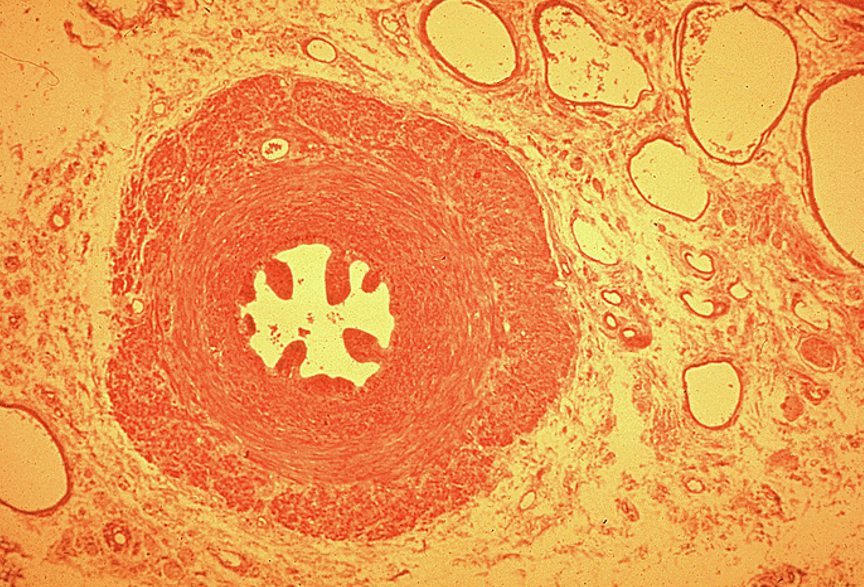
Identify this structure
Vas deferens
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium with stereocilia
Small, irregular star-shaped lumen compared to thick wall
Surrounded by a very thick muscularis with three layers: inner longitudinal, middle circular, outer longitudinal
Often has a folded mucosa
Vas deferens stores sperm
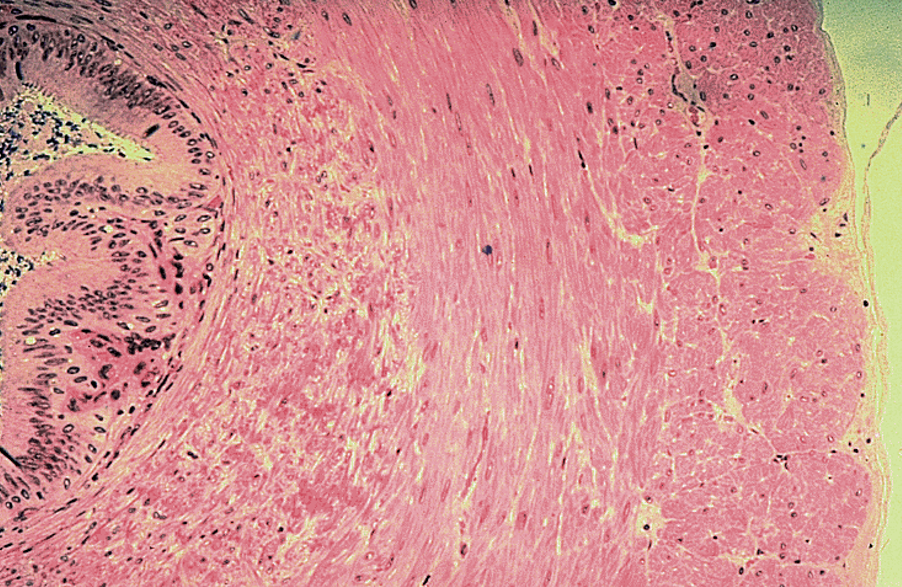
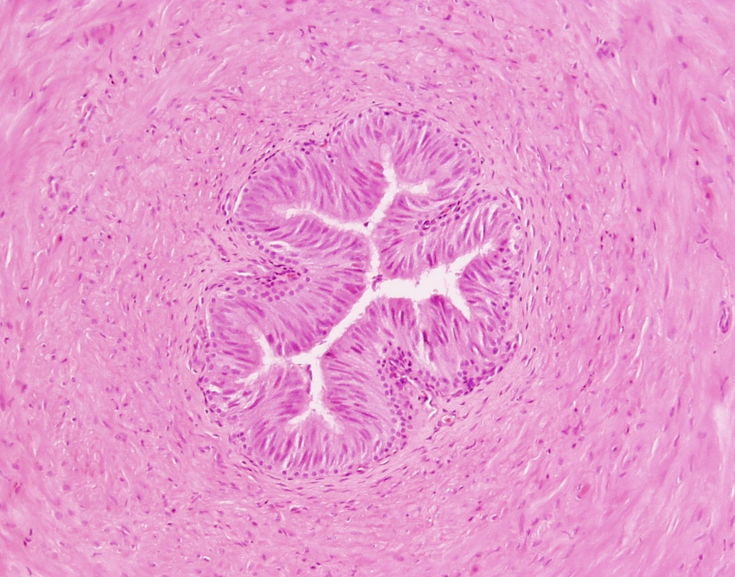
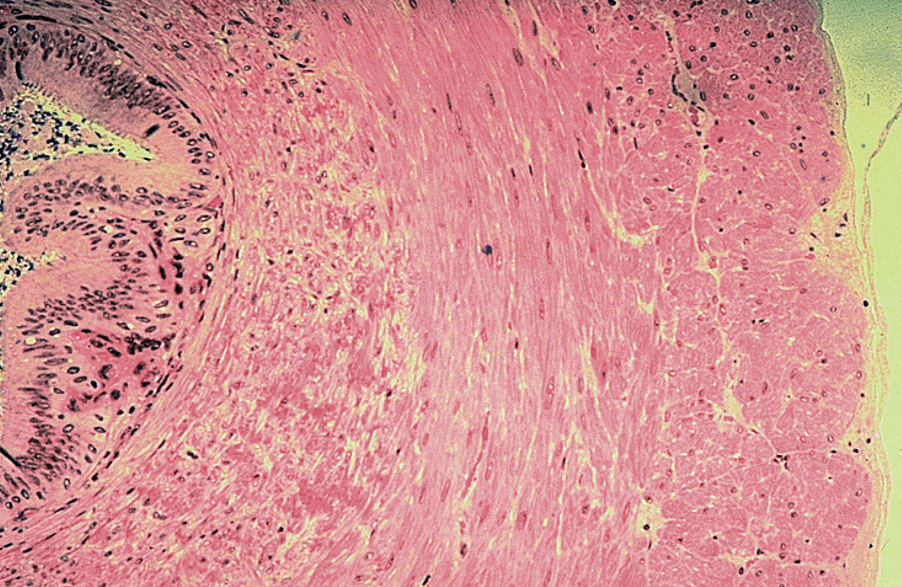
Identify this structure
Vas deferens
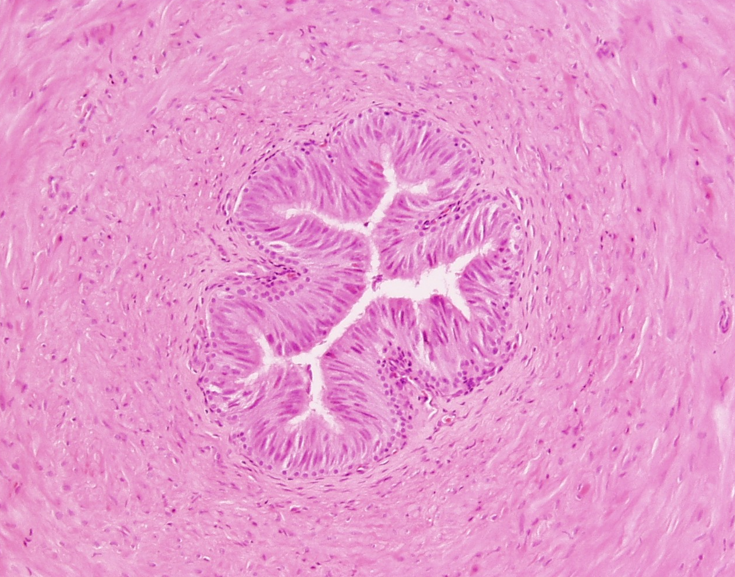
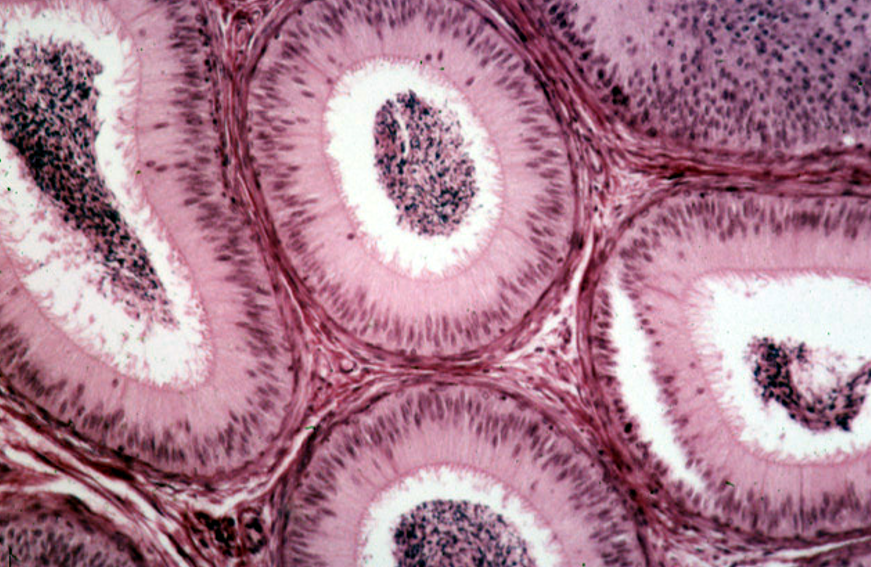
Identify this structure
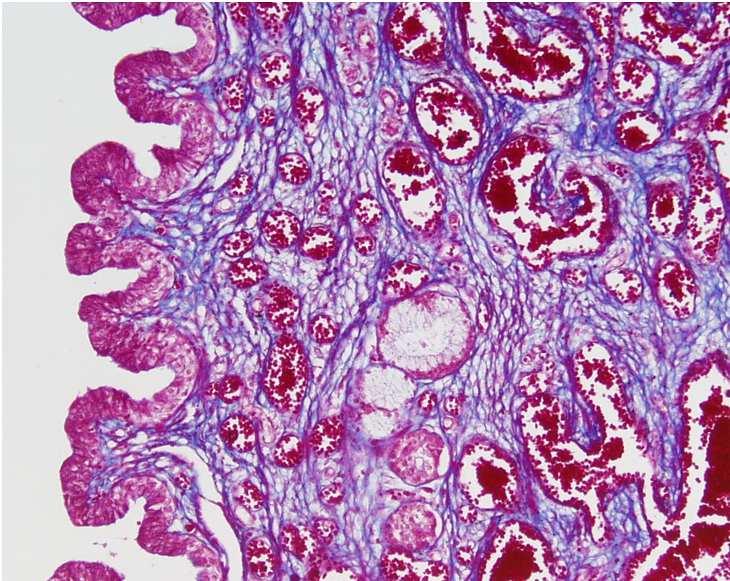
Seminal vesicle
Highly folded mucosa, giving a honeycomb or maze-like appearance
Lined by pseudostratified columnar epithelium with secretory cells
No sperm in the lumen
Thin smooth muscle layers: inner circular, outer longitudinal
Lumen often contains eosinophilic secretion
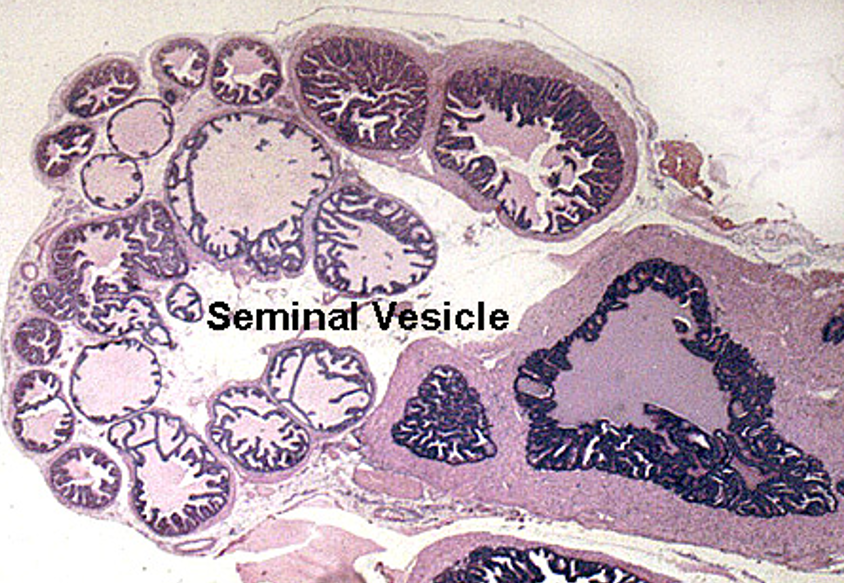
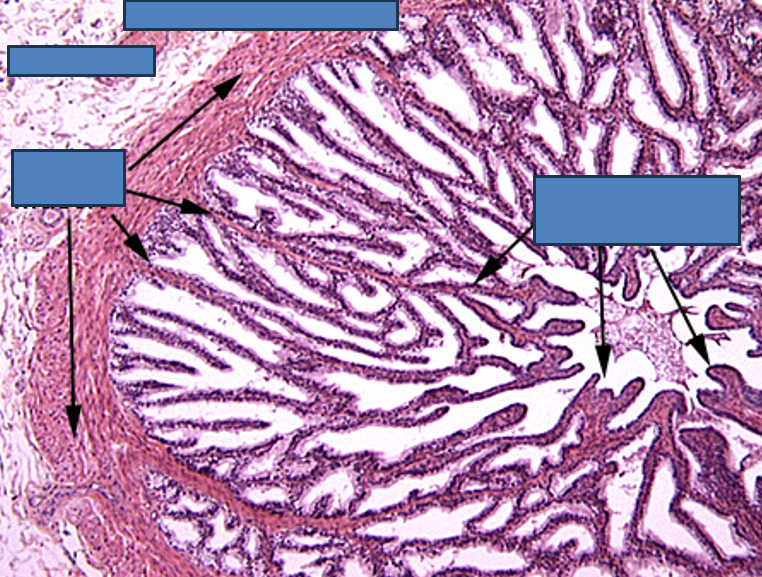
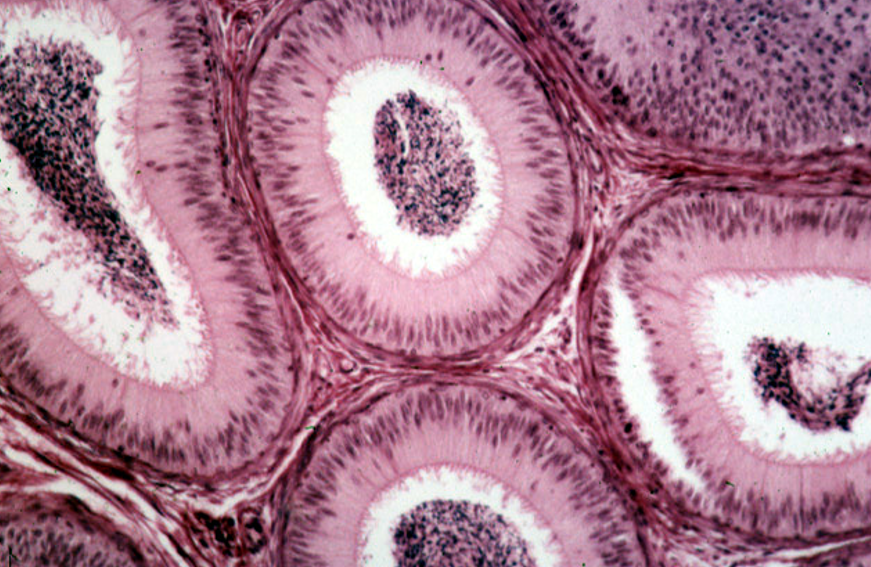
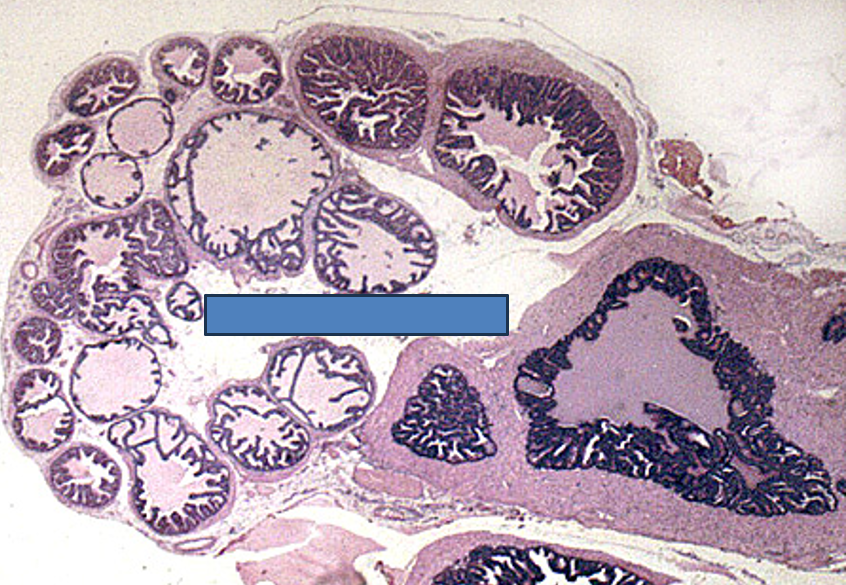
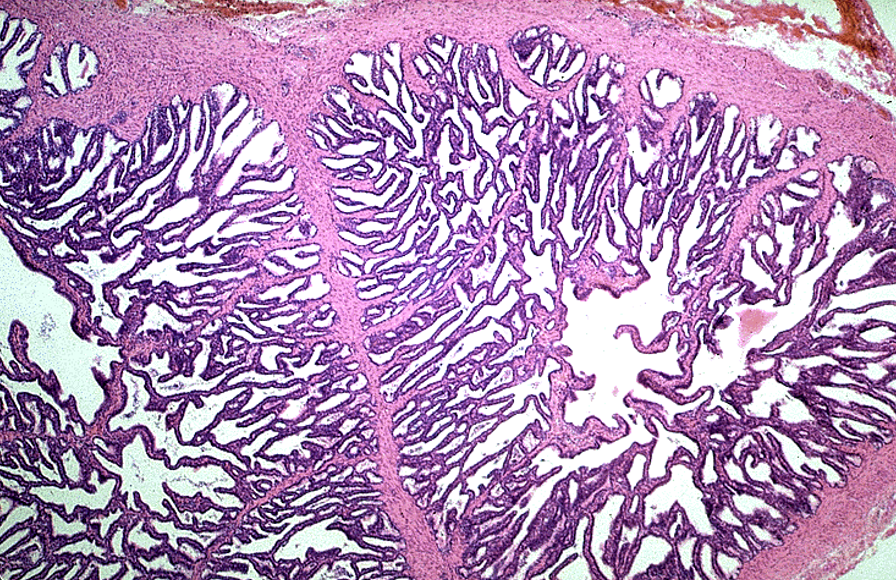
Identify this structure
Seminal Vesicle
Maze-like appearance
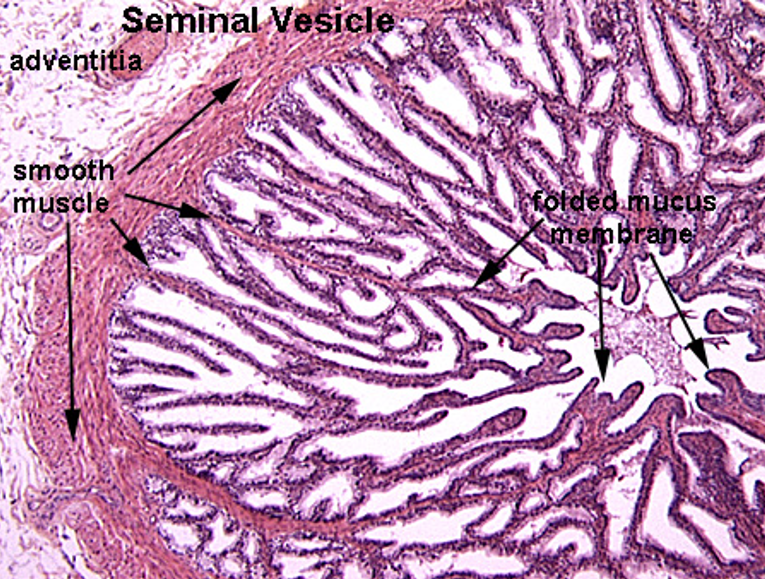
Identify this structure
Seminal vesicle
Highly folded mucosa, giving a honeycomb or maze-like appearance. C-shaped appearance
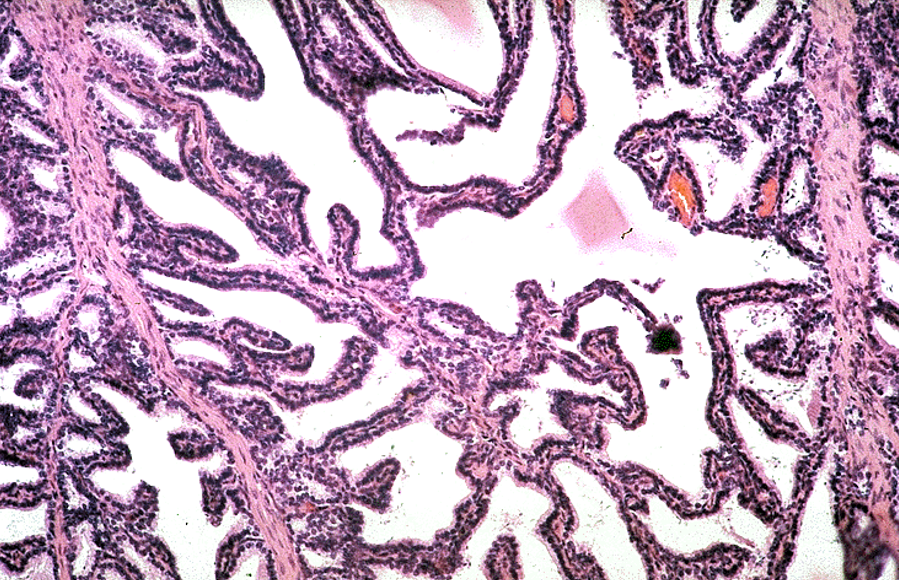
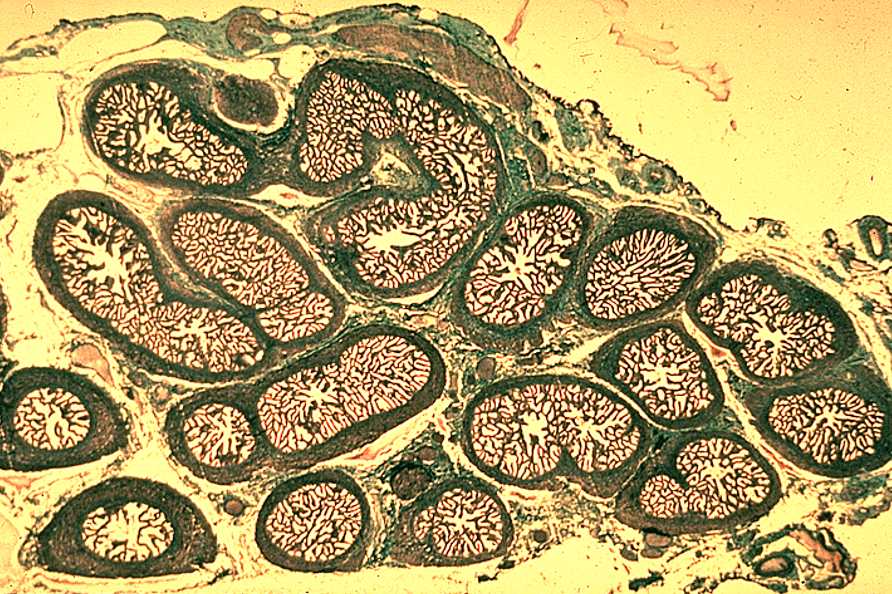
Identify this structure
Seminal vesicle
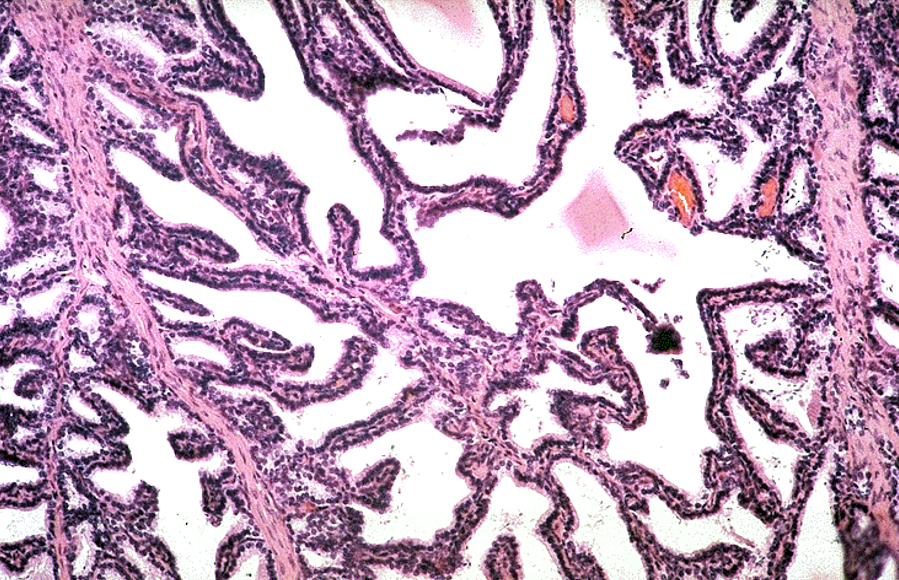
Identify this structure
Seminal Vesicle
Maze-like appearance

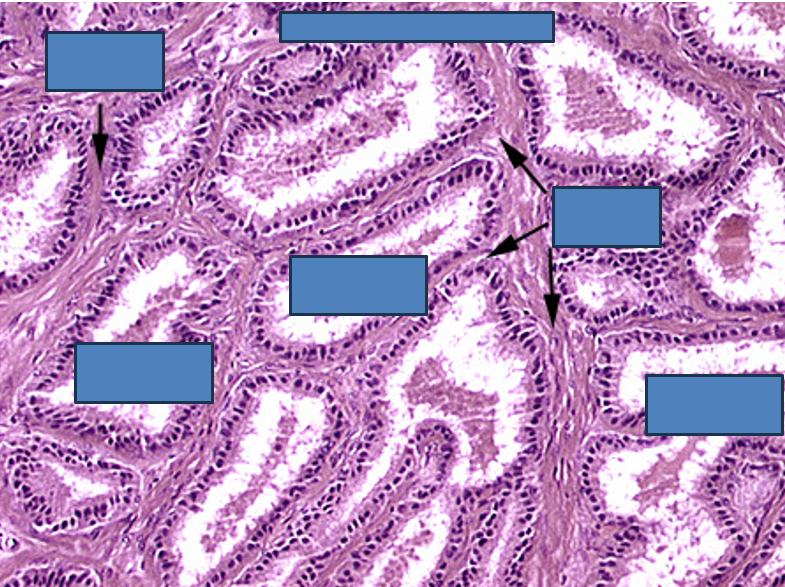
Identify this structure
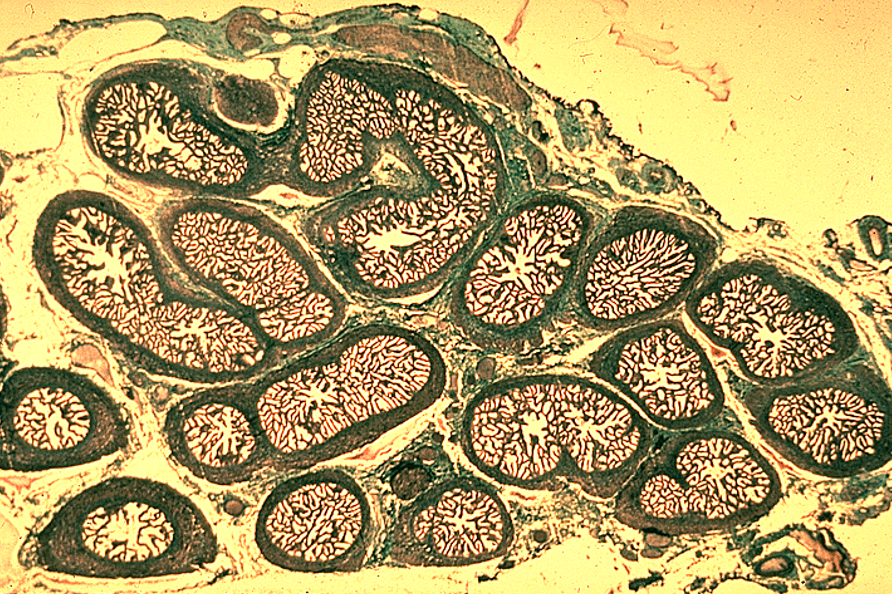
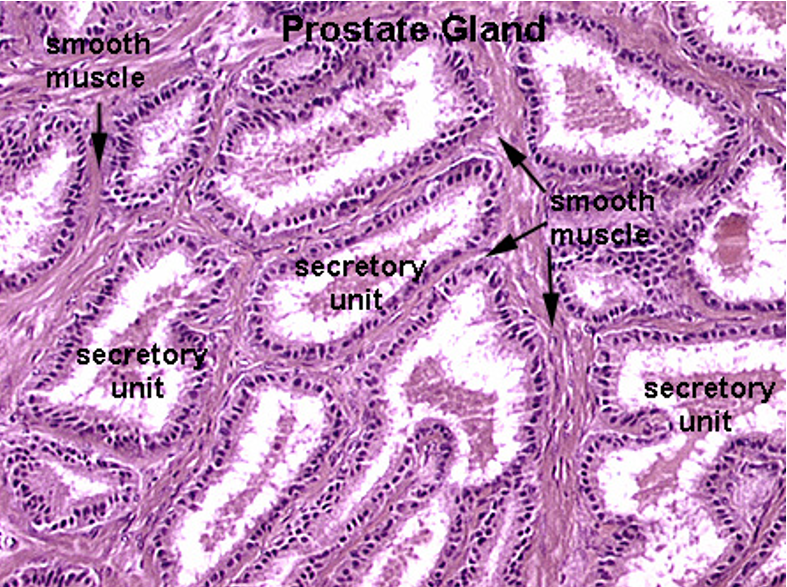
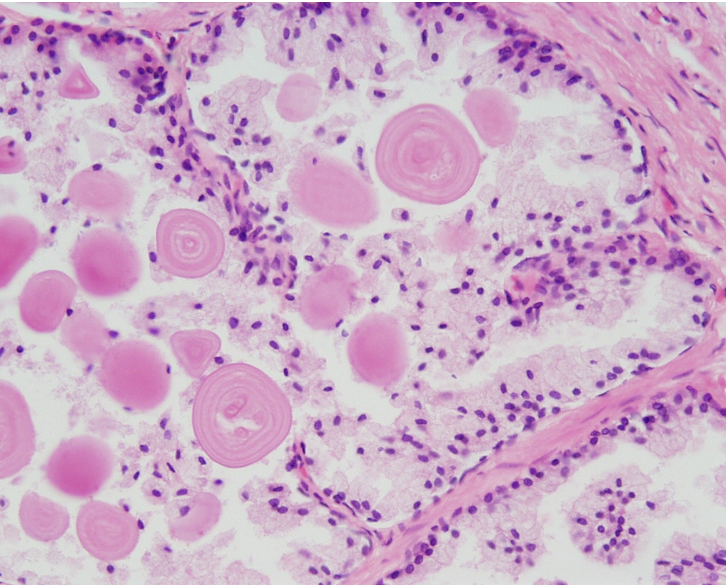
Prostate
Multiple secretory glands
Corpora amylacea (round, eosinophilic concretions) often seen in gland lumens
Glands vary in size and shape
Identify this structure
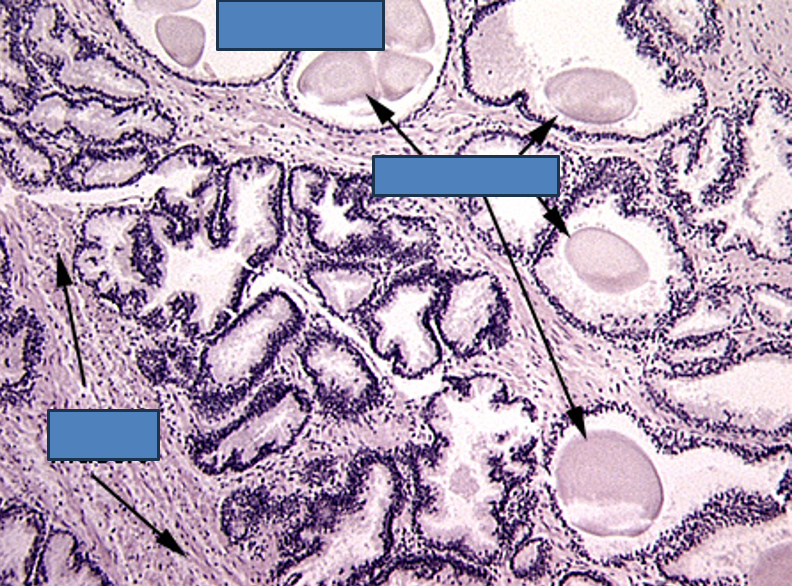
Prostate
Multiple secretory glands
Corpora amylacea (round, eosinophilic concretions) often seen in gland lumens — the circles inside the lumen
Glands vary in size and shape
Identify this structure
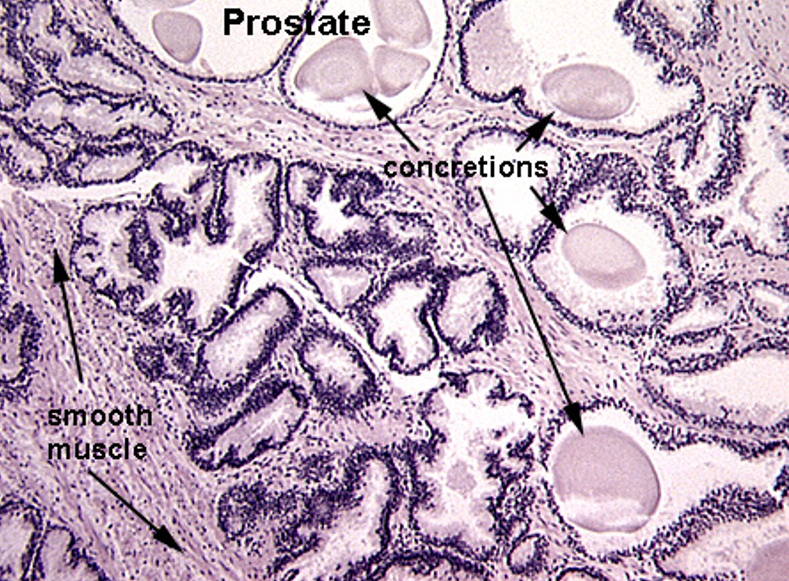
Prostate
Multiple secretory glands
Corpora amylacea (round, eosinophilic concretions) often seen in gland lumens
Glands vary in size and shape
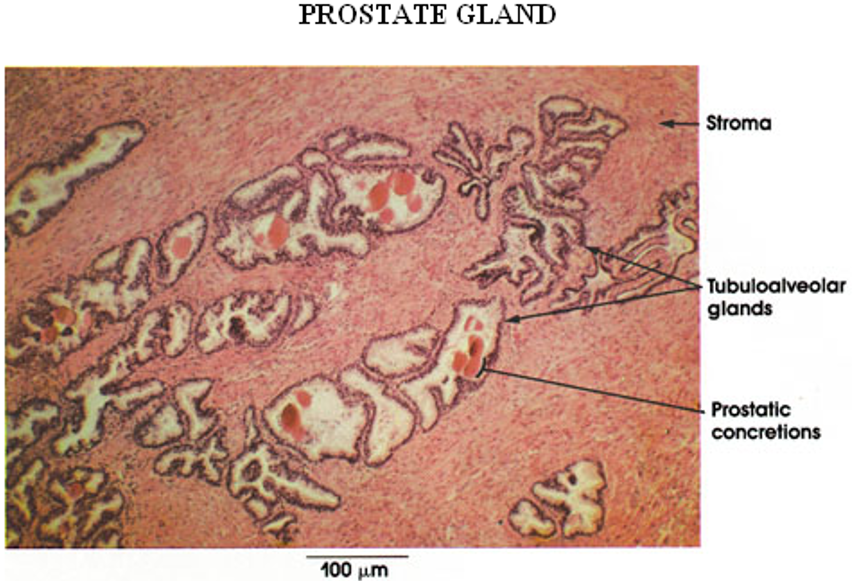
Identify this structure
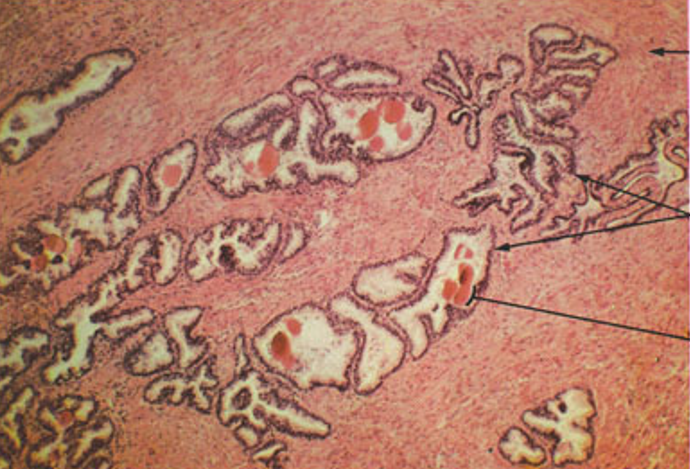
Prostate
Multiple glands
Thin & flat epithelium (older individual)
Corpora amylacea (round, eosinophilic concretions) often seen in gland lumens. Multiple layers over time
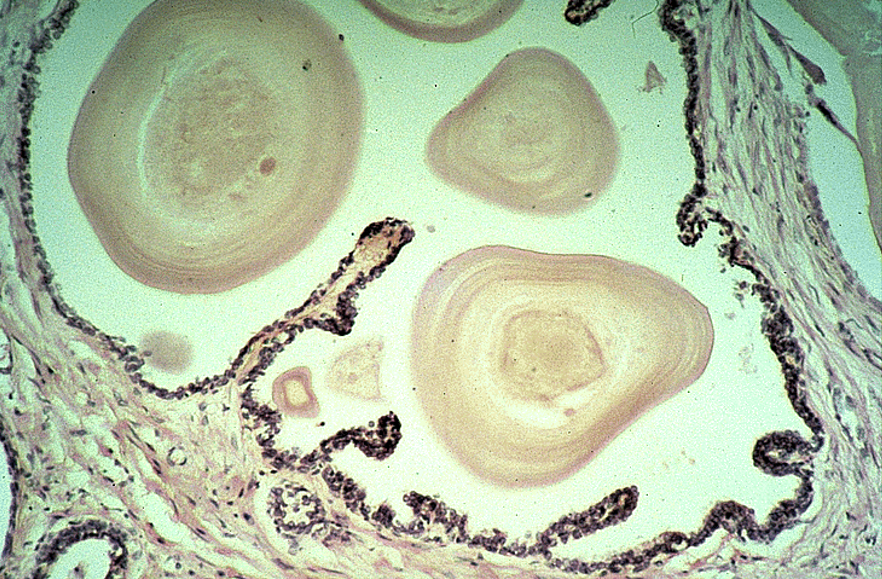
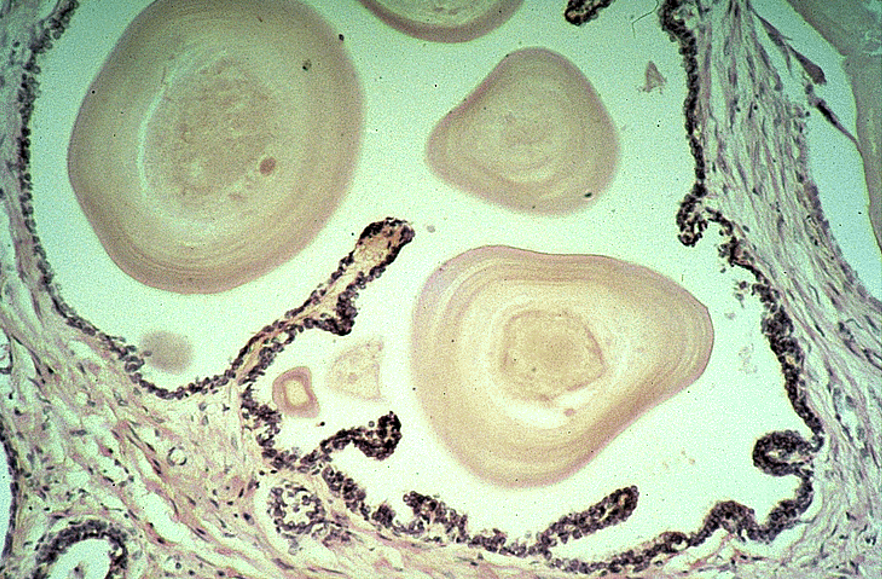
Identify this structure
Prostate
Identify this structure
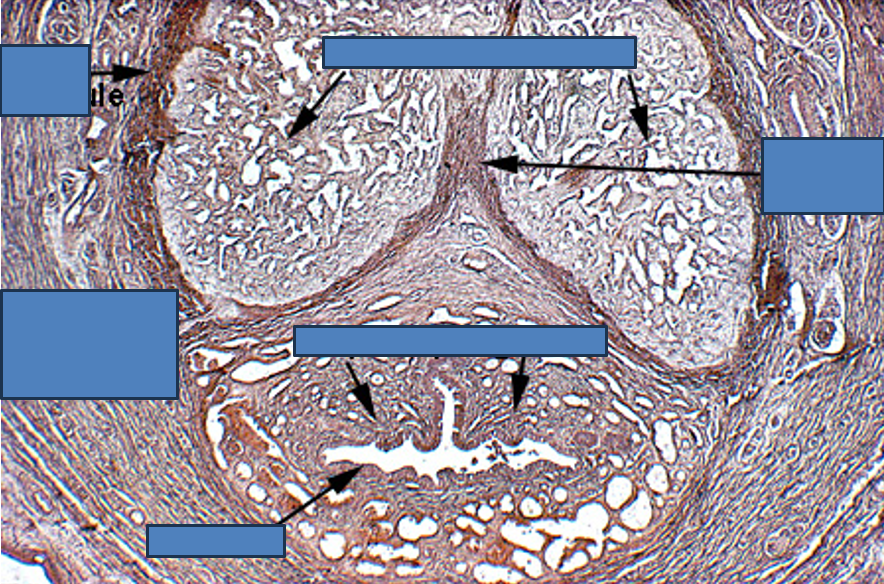
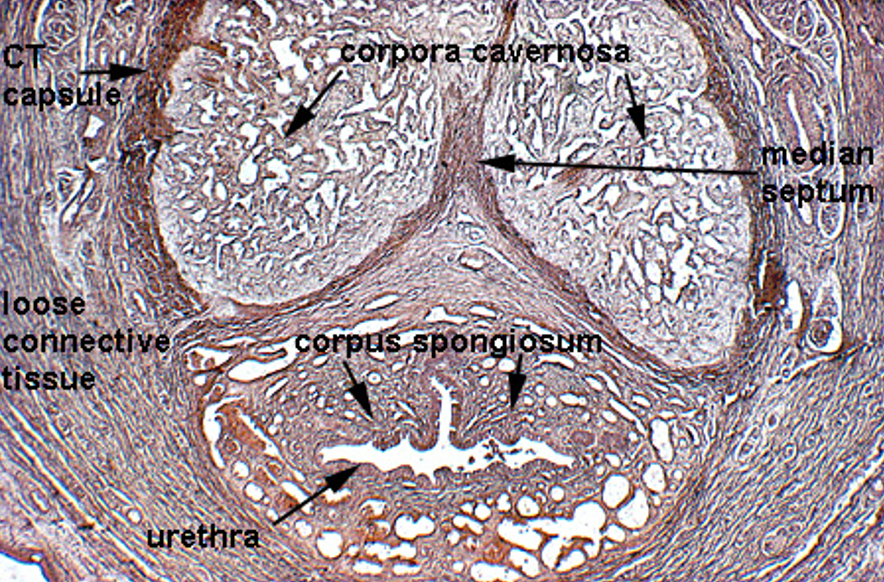
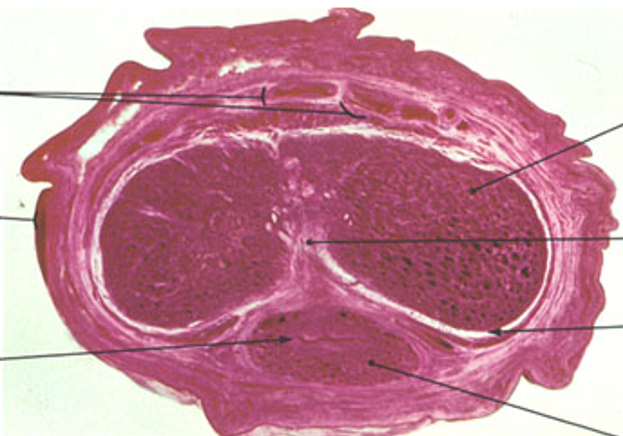
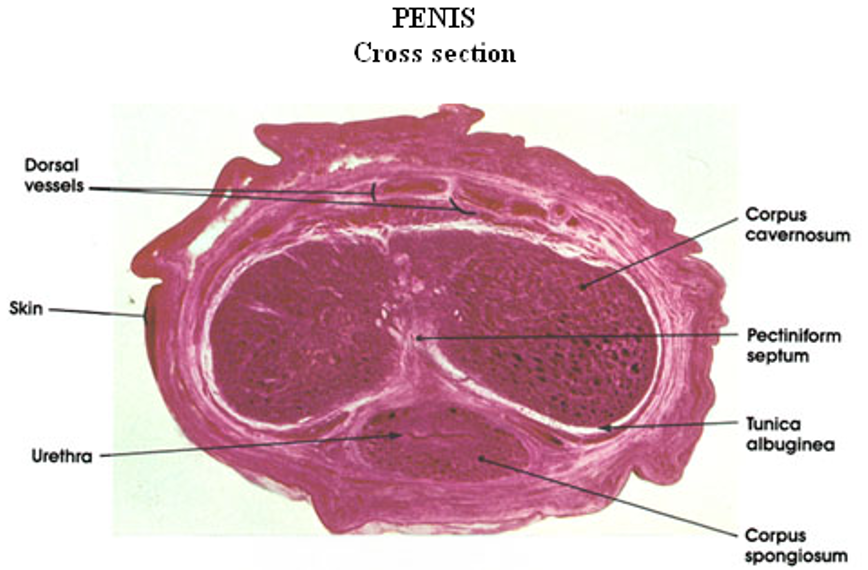
Penis
Two corpora cavernosa (top) and one corpus spongiosum (bottom)
Each erectile body is surrounded by tunica albuginea
Urethra runs through the corpus spongiosum, lined by transitional or pseudostratified epithelium
Identify this structure
Penis
Two corpora cavernosa (top) and one corpus spongiosum (bottom)
Each erectile body is surrounded by tunica albuginea
Urethra runs through the corpus spongiosum, lined by transitional or pseudostratified epithelium
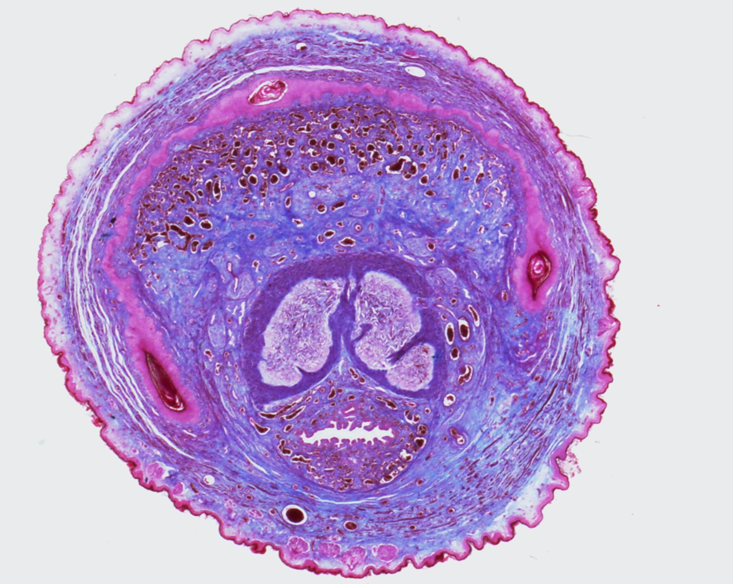
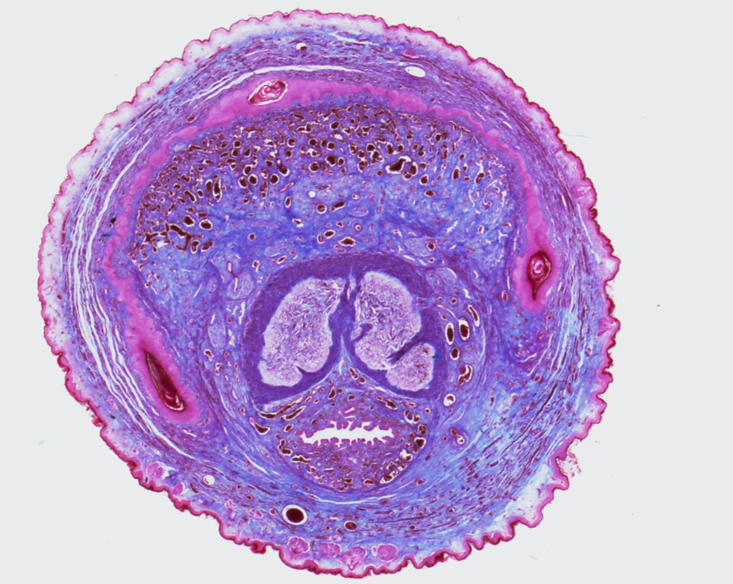
Identify this structure
Penis
Two corpora cavernosa (top) and one corpus spongiosum (bottom)
Each erectile body is surrounded by tunica albuginea
Urethra runs through the corpus spongiosum, lined by transitional or pseudostratified epithelium
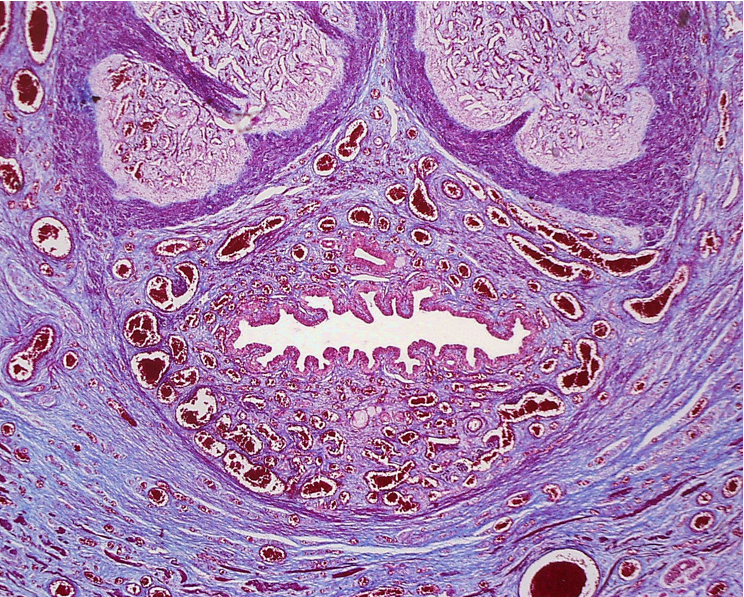
Identify this structure
Penis
Two corpora cavernosa (top) and one corpus spongiosum (bottom)
Each erectile body is surrounded by tunica albuginea
Urethra runs through the corpus spongiosum, lined by transitional or pseudostratified epithelium
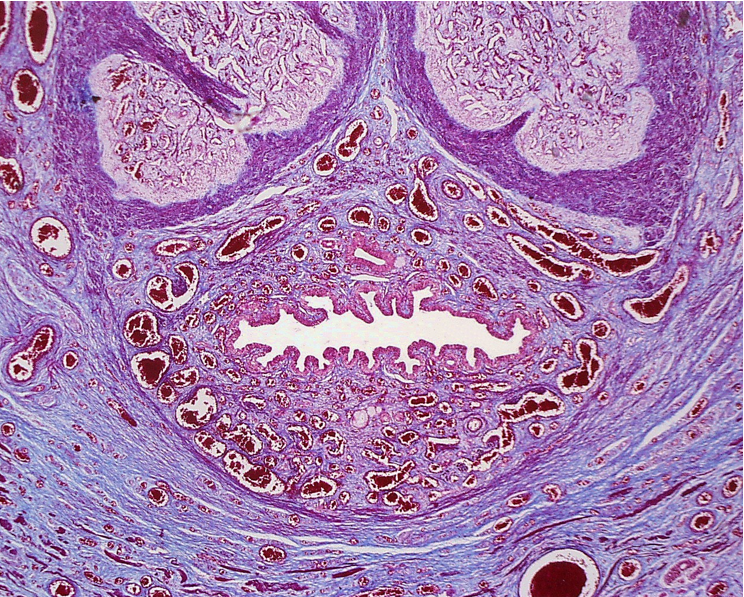
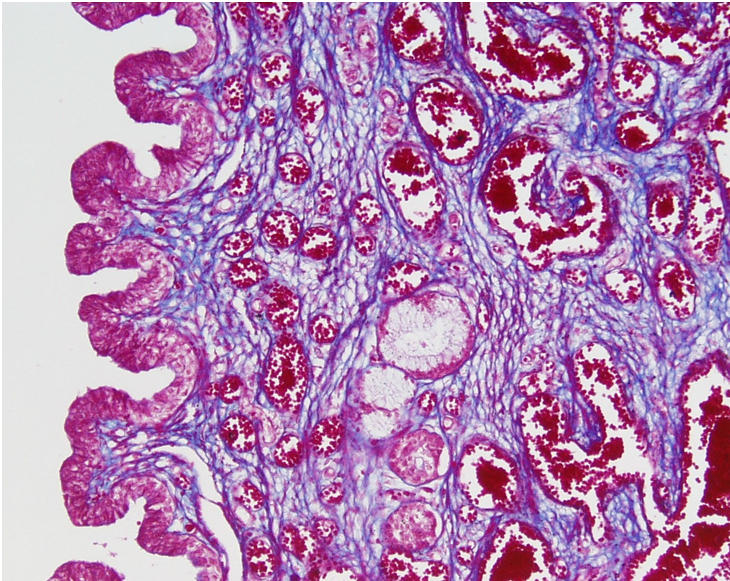
Identify this structure
The lumen of the urethra is to the right. Note the abundance of blood vessels within the corpus spongiosum.