Youngstock Disease: Sudden Death and Ill Thrift
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
What are the differentials for sudden death in the UK?
Anthrax
Blackleg (Clostridium chauvoei)
Cl. sordelli
Electrocution
Bloat
White muscle disease
Acute trauma
Plant poisonings (Yew, Rhododendron)
What type of bacteria is Clostridium chauvoei (blackleg)?
Large gram positive rod
Anaerobic
Describe the pathogenesis
Spores circulate in blood and settle in muscle tissue
Cause bruising of tissue
Fall in oxygen tension
Spores germinate
Digest muscle within fascia
Diffusion of toxin outside muscle
Death - often all you see is sudden death
Low morbidity high mortality
What ages are susceptible? What seasons?
All but peak 6-24 months
Summer/autumn
Clinical signs
Sudden death - PM change very bloated and blood at orifices
If alive:
Severe depression - unwilling to move
Anorexia
Pyrexia, tachycardia, tachypnea
Rumenal stasis
Very lame
Hot painful swelling of affected muscle areas
Convulsions
What would you see on PM?
Welling
Subcutaneous edema and emphysema over site
Muscle blackened with gas bubbles
Classic sour odor
How do you diagnose?
Gross pathology at knackery or farm after ruling out Anthrax
or submit to diagnostic lab - smears, stain with fluorescent antisera, PCR
Treatment?
Very sensitive to penicillin
Clinical cases: sodium benzylpenicillin IV very high dose
In contacts: LA penicillin products
Prevention?
Vaccinate!!
Clinical signs of Cl. sordelii?
Abomasitis/enteritis
Sudden death
Clinical signs of Cl. Haemolyticum?
Sporatic/western areas
Hemoglobinuria, jaundice, hepatitis, sudden death
What PM findings will you see for electrocution?
Singe marks
Capillary congestion
Ingesta in mouth
Normal rumen content
What causes pasture bloat?
Legumes (such as clover)
How does this cause bloat?
Makes a stable foam in the rumen that blocks air from leaving for eructation
What sounds might you hear a cow with bloat making?
Treatment?
Stomach tube
Anti-foaming agent (Simethicone, fairy liquid)
Can prevent with mineral oil in water troughs
What causes white muscle disease?
Selenium and/or vit E deficiency
Often just after turnout since they are getting more exercise
Clinical signs/pathogenesis
Lactic acid builds up and causes muscle damage
Found dead or very lame/stiff
Heart is included in this muscle damage and it stops → death
Treatment? Prevention?
P: Proper mineral balance in food
T: Supplemental selenium and vit E injection (act quick)
What toxin does rododendron have?
Andromedotoxin
What animals are susceptible to rhododendron toxicity?
cattle, sheep, goats, cats and dogs
Clinical signs?
Projectile vomiting (this is the only condition that causes this)
Intense abdominal pain
Ataxia, anorexia
Convulsions, trembling, collapse, death
Treatment? Prognosis?
T: Astringents/tannins (tea!)
Poor ☹ if recumbent probably just euthanize, if still walking like 50% chance of recovery
What species are susceptible to yew (Taxus baccata) toxicity?
Cattle, sheep, horses, goats
Clinical signs?
Can be sudden death
Onset variable (hours-days)
Excitation, agitation
Tympany
Depression
Death
Treatment?
Gastrotomy to remove leaves, symptomatic with tannins etc
How does grazing vs housed affect susceptibility to ill thrift?
Grazing usually has less infectious disease challenge
Housed has better opportunity for observation
Nutrition varies based on different factors for both
What ill thrift diseases are most often seen when housed?
Respiratory disease
Ringworm
Coccidia
Chronic bloat
Under/poor nutrition
What is the pathogenesis of botulism?
Affects motor neuron binding (at synapse) - prevents Ach release
Leads to flaccid paralysis
How do farms get infected with botulism?
Associated with use of poultry litter fertilizer
Big bale silage (poor fermentation)
Clinical signs?
Stiff, weak, wobble, progressing to recumbent
Dysphagia → can’t swallow water → manically thirsty
Tongue hangs out
Death from respiratory paralysis, cardiac failure, or dehydration
Diagnosis?
Eliminate other causes of paralysis
Epidemiological evidence of exposure
Submit dead to PM for toxin detection
Submit feedstuffs/suspect casual sources to lab for toxin detection
Treatment?
Supportive therapy: stomach tube with fluids and feed, move recumbent cattle frequently
Notify Animal Health Office - NOT a notifiable disease but issues with food chain safety
Control/prevention?
Remove contact with suspect source
Do not use poultry litter near animals
Vaccine available in Ireland but don’t really need it just manage the pasture well
What bacteria causes tetanus?
Clostridium tetani: anaerobe, toxin producing
Describe the pathogenesis of tetanus
Spore enter wound (castration, penetrating wound, etc)
Germinate in anaerobic environment
Produce toxin → local or systemic effects, spasmodic muscle contraction
Clinical signs?
Stiffness
Raised tail-head
Bloat
Hyperesthesia
Dysphagia
Longer duration of progression os signs
How do you diagnose?
Clinical signs and history of wound
Toxin in serum
Gram stain smears from wound
Treatment?
In early cases antitoxin in available but VERY expensive and hard to get
Antibiotics
Supportive care
Sedatives
In severe cases euthanasia
Prevention?
Hygiene around castration, calving, etc
Vaccinate!!!
What is the scientific name for ringworm?
Trichophyton verrucosum
How do you treat ringworm?
You usually don’t
Could use topical enilconazole
Can vaccinate (Bovillus Ringvac) and this is therapeutic at double dose
What causes chronic bloat?
Primary: GIT motility disorder, poor weaning management
Secondary: papilloma, other GIT/abdo/thoracic pathology such as multiple bouts of bloat or scour
But often don’t find the cause
Can be associated with chronic low rumenal acidosis - rumen is huge from being stretched multiple times
Treatment?
Full clinical exam
Trumen trochar - leave in situ for 3-4 weeks
Is chronic bloat something you see at housing or pasture?
Housing
What are the different types of papillomas?
BPV1 - Fronds
BPV2 - Head and neck
BPV3 - Smooth warts
BPV4 - GIT warts
BPV5 - “Rice grain”
*BPV4 + bracken exposure = GIT carcinoma
How do you treat and prevent papillomas?
Autogenous vaccine, fly control
Minor warts are self limiting but can use topical creams on teats if needed
What is degenerative arthropathy (OCD)?
Degeneration of cartilage and sub-chondral bone
Joint effusion and osteophyte production
Occurs in hip, stifle, and hock
Which animals are more predisposed?
Youngstock
Based on genetics, nutrition, and conformation
Symptoms?
Gradual, shifting, progressive lameness
Treatment?
Palliative (NSAIDs)
Euthanize
What animals are most prone to sporadic bovine leukosis (SBL) and which forms?
Juvenile < 6 mo (multi lymph node)
Youngstock < 2 years (thymus) - most common
Occasional adult disease (skin)
Clinical signs of thymic SBL?
CHF, bloat
So with CHF you’ll see brisket edema, distended jugular
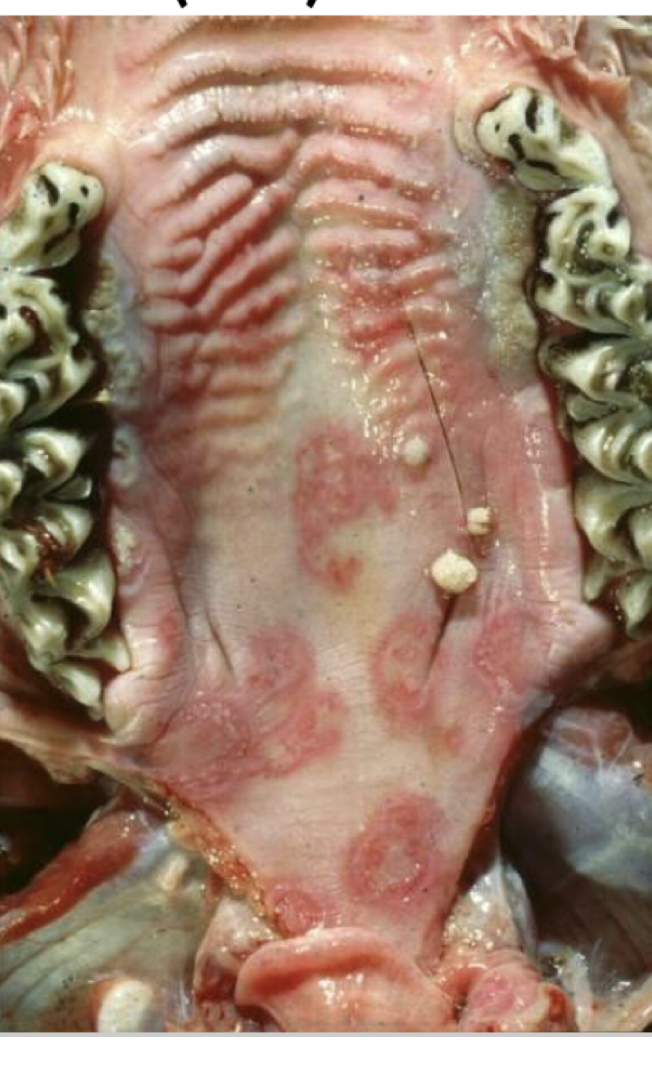
How significant is bovine papular stomatitis (BPS)?
It is usually innocuous but zoonotic
Treatment?
None