Topics 3,4,5,6,8 Quiz - Plasma Membrane & Membrane Permeability
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
What are the 2 parts of the phospholipid head?
1.) Phosphate group
2.) Glycerol
Why are the heads of phospholipids hydrophyllic?
The phosphate group carries a negative charge, making it a polar, hydrophyllic component that can form H-bonds with H2O molecules.
What is the plasma membrane composed of and what is its function?
It is comprised primarily of phospholipids, and it separates the internal cell environment from the external environment.
Phospholipids are classified as….
Amphipathic (hydrophobic & hydrophyllic)
Why is the membrane selectively permeable?
Hydrophobic interior
Why is the plasma membrane called a fluid mosaic model?
Fluid: The membrane is held together by weak, hydrophobic interactions and can therefore move and shift. Mosaic - comprised of many macromolecules.
What helps to maintain fluidity at low temps?
Unsaturated hydrocarbon tails: Kinked tails prevent tight packing of phospholipids
Cholesterol
What helps to maintain fluidity at high temps?
Cholesterol: reduces movement
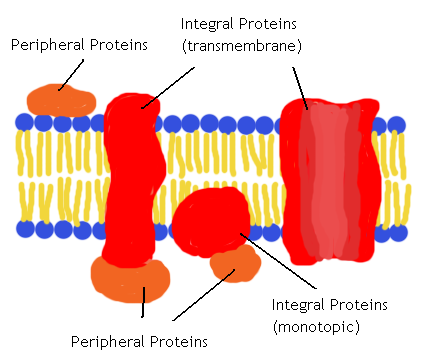
What are the 2 major categories of proteins in the membrane?
Integral Proteins & Peripheral Proteins
Integral Proteins
embedded into lipid bilayer, hydrophyllic and hydrophobic regions are determined by the R group side chains
-Hydrophyllic regions make up interior of channel and are exposed to cytosol
-Hydrophobic regions are the non-polar side chains that make up the protein surface and interact with fatty acids on the interior of the membrane
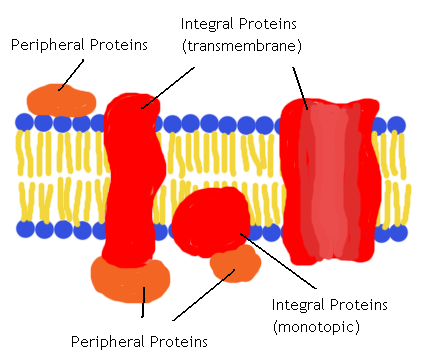
Peripheral Proteins
Proteins that are not embedded into the lipid bilayer and are loosely bonded to the surface
Membrane Carbohydrates
Important for cell-to-cell recognition (recognize harmful pathogens)
1.) Glycolipids: carbs bonded to lipids
2.) Glycoproteins: carbs bonded to proteins (most abundant)
Which substances have easy passage across the membrane?
Small, nonpolar, hydrophobic molecules
ex: hydrocarbons, CO2, O2, N2
Which substances have difficult or protein-assisted passage across the membrane?
Hydrophyllic polar molecules, large molecules, ions (Na+, Cl-, K+, Ca2+)
**small polar, uncharged molecules like water and ammonia can pass through in small amounts
Which organisms have cell walls that cover their plasma membranes?
Plants, Bacteria, Archaea, Fungi
What is the function of cell walls?
-provide structure
-permeability barrier
-protection from osmotic lysis (cell bursting when water goes into cell)
What is the plant cell wall composed of?
-composed of cellulose
-contain plasmodesmata (hole-like structures filled with cytosol that connect adjacent cells)
Selective permeability creates & maintains __________ of solutes across the membrane.
Concentration gradients
Passive Transport
transport of a molecule that does not require energy from the cell because a solute (salt or sugar) is moving with its concentration gradient
ex: diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion
Diffusion
Substances move from high to low concentration
-move down the concentration gradient
-different rates of diffusion (depend on size, weight, distance, etc.)
Osmosis
diffusion of water down its concentration gradient
-can be thought of as the diffusion of water from areas of low solute concentration to high solute concentration (hypotonic→ hypertonic)
Faciliated Diffusion
diffusion of molecules through the membrane via channel/carrier proteins - still moving down concentration gradient
Channel Proteins
type of integral protein, has an open hydrophyllic pore/channel that moves charged ions
-”Gates” can open/close in response to stimuli (signaling molecules, changes in electric potential)
-movement can polarize the membrane (making one side more pos/neg than the other side)
Aquaporins
specialized channel proteins for large amounts of water/osmosis (not necessary for small amts)
Carrier Proteins
Alternate between 2 conformations
-transport large polar molecules (glucose/sugars, amino acids, nucleosides)
Dialysis
Process used to remove waste products & excess water from the blood
-replaces function of kidneys when not functioning properly
-filters blood outside of the body then returns it back
Why is glucose added to the dialysis fluid?
So that the water in the blood filters out to a hypertonic dialysis fluid solution
Cellular _________ depends on cell size
metabolism
True or False: at a certain size, it begins to be too difficult for a cell to regulate what comes in and out of the plasma membrane
True
Cells need a ______ SA:V ratio to optimize the exchange of material through the plasma membrane
high
Cells tend to be small because..
small cells have a high SA:V ration, which optimizes the exchange of materials at the plasma membrane
Large Cells
have a low SA:V ratio
-lose efficency exchanging materials
-cellular demand for resources increases
-rate of heat exchange decreases
**tend to store materials (fat cells)
How are eukaryotic cells able to become so much larger than prokaryotic cells while still efficiently exchanging material through the plasma membrane?
Eukaryotic cells have internal membranes and membrane-bound organelles that allow for increased surface area & compartmentalization of reactions and functions
Per unit body mass, mice have a higher metabolic rate than do elephants, why is this?
Smaller animals have a higher SA:V ratio, so they lose heat faster. To replace the heat they lose, they have a higher metabolism.
Why might smaller organisms lose heat more quickly than larger organisms?
They have a higher SA:V ratio. More surface area=more space to give off heat.