Molecular Diagnosis of Fungal Infections Seminar
1/144
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
145 Terms
How many people do fungal diseases kill globally each year?
Over 1.5 million people.
What is the global impact of fungal infections on public health?
Fungal infections are neglected by public health authorities despite many deaths being preventable.
What conditions are associated with INCREASED risk of serious fungal infections? CLUE: HACOC
Asthma, HIV/AIDS, cancer, organ transplantation, and corticosteroid therapies.
What type of studies were reviewed to improve the accuracy of fungal infection diagnosis?
85+ country-specific studies and data from 120+ countries.
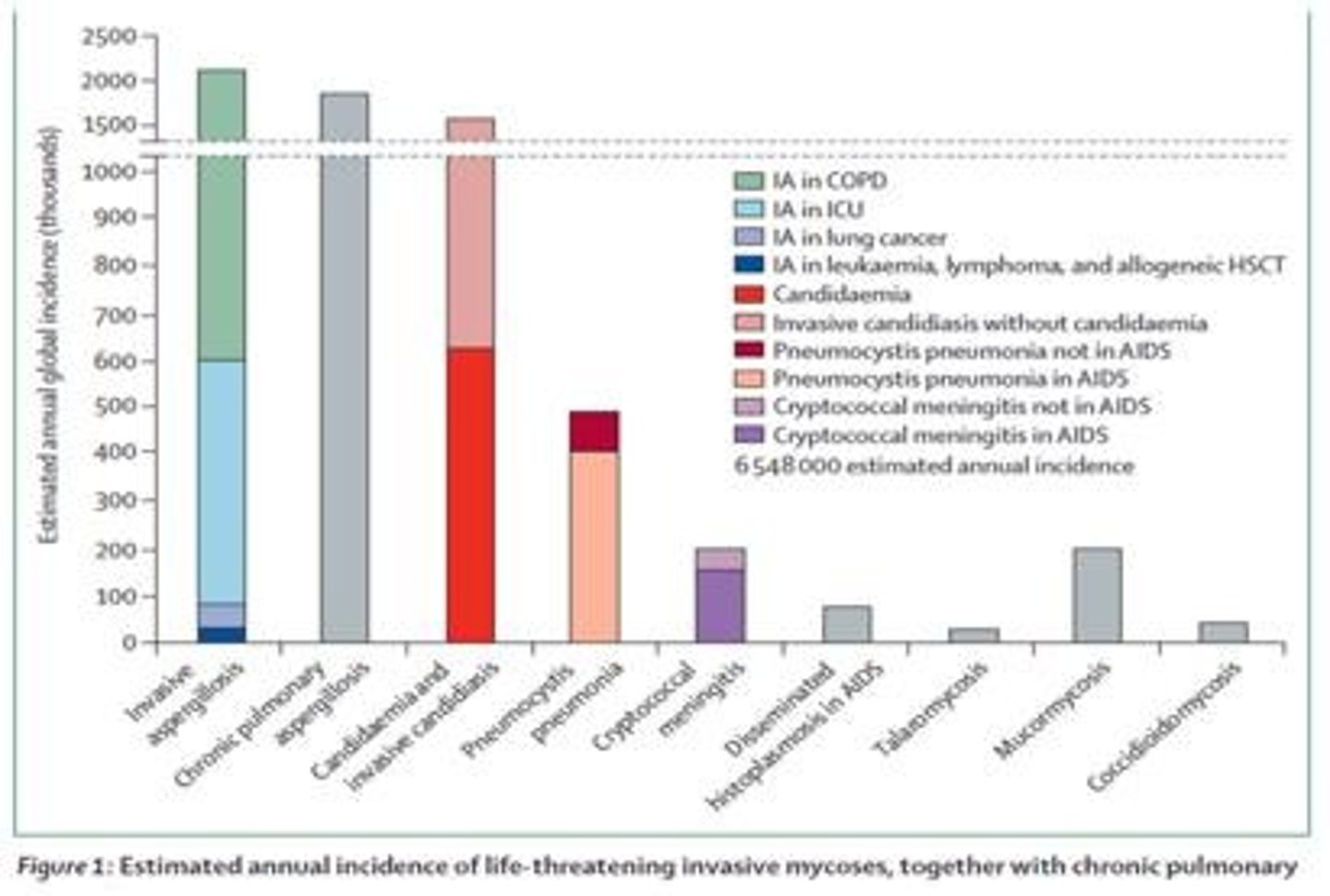
Based on the ESTIMATED ANNUAL INCIDENCE chart, Invasive aspergillosis cases are related to?
COPD 2,113,000+ cases
Green: COPD
Skyblue: ICU px
Lavender/purple: Lung
Blue: Hematologic malignancies
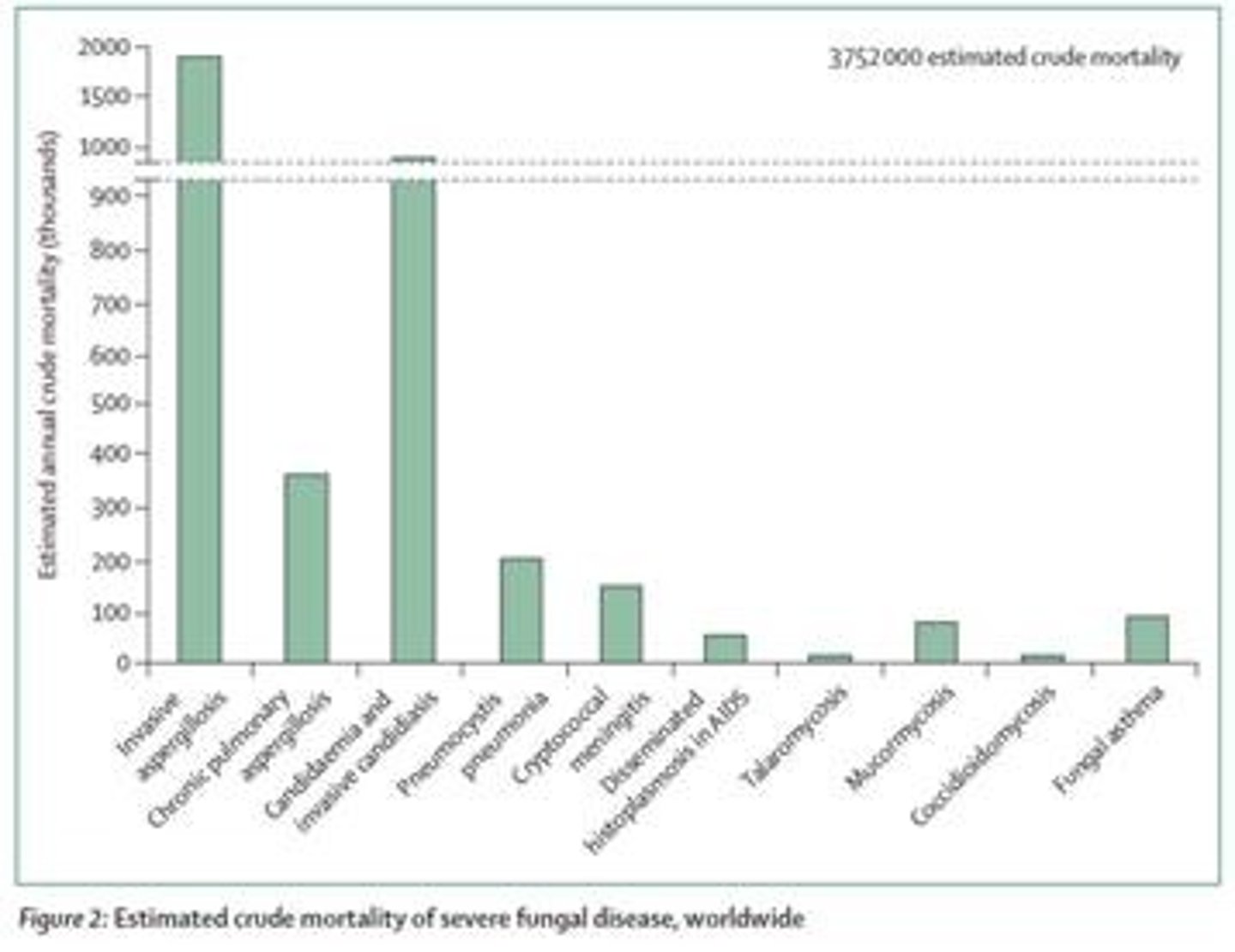
Based on ESTIMATED CRUDE MORTALITY chart, invasive aspergillosis has
1,801,000 deaths/years with 85.2% mortality rate
How many cases of CANDIDA BLOODSTREAM infection occur annually?
1,565,000 cases per year, with 995,000 deaths (63.6%)
If non-sterile specimens are used, there is high risk of isolating?
Commensal organisms and environmental contamination.
What indicates colonization of Aspergillus in immunocompetent patients?
Recovery of Aspergillus from the respiratory tract.
What does recovery of Aspergillus suggest in immunocompromised patients?
It strongly suggests invasive disease.
What are the ADVANTAGES of molecular methods in diagnosing fungal infections? CLUE: THIA
Timely diagnosis, higher sensitivity and specificity, improved patient outcomes, and antimicrobial stewardship.
What is the role of PCR-based methods in clinical microbiology laboratories?
They are becoming more commonly used and allow for faster and more accurate diagnosis.
What does PCR stand for in the context of molecular diagnosis?
Polymerase Chain Reaction.
What are the three main cycles of conventional PCR?
Denaturation, annealing, and extension.
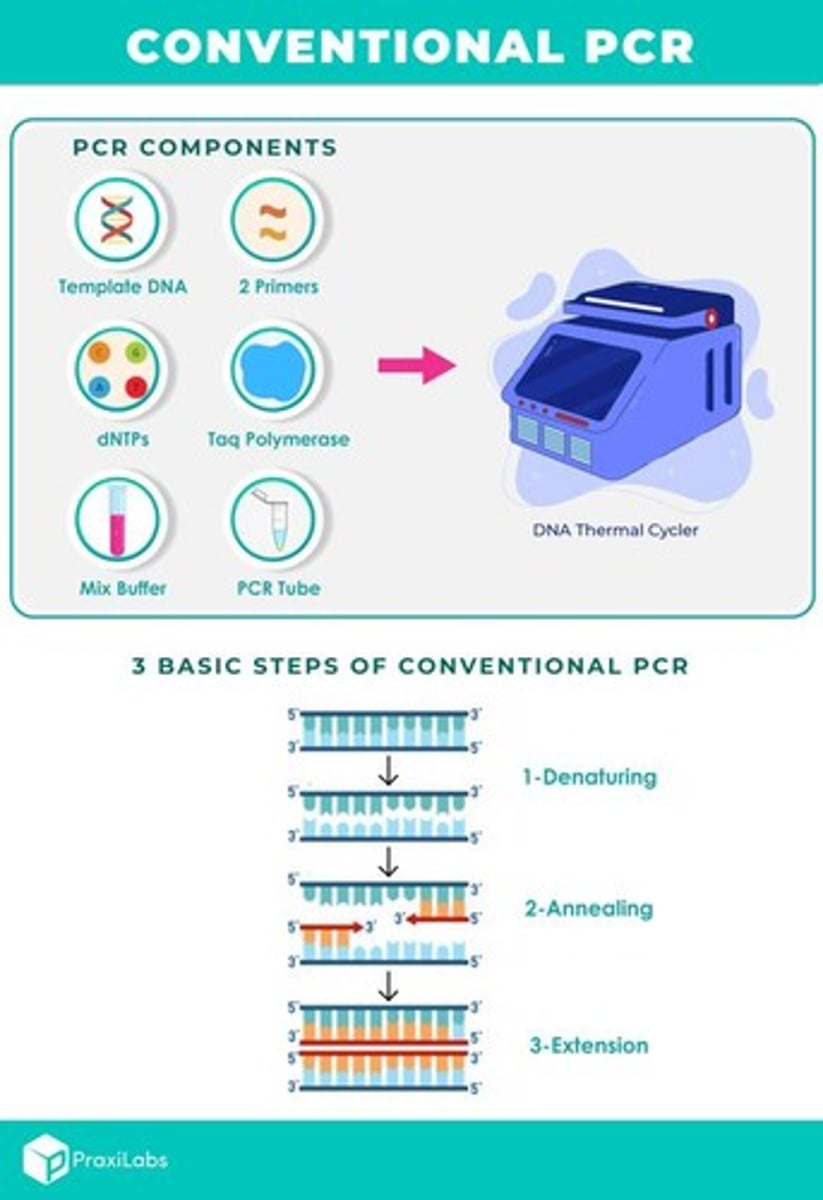
What is the function of Taq Polymerase in PCR?
It builds new strands of DNA.
What are dNTPs in the context of PCR?
Deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates that are raw materials used to synthesize new DNA strands.
What are primers in PCR?
Short custom-made sequences that adhere to the start of the target region, telling Taq Polymerase exactly where to start building.
What is the purpose of buffers in PCR?
They help maintain optimal conditions for the reaction.
What role do cofactors like Magnesium chloride play in PCR?
Help the primer adhere to the correct site and assist Taq Polymerase in functioning.
What is the estimated annual incidence of invasive fungal infections?
6.5 million invasive fungal infections per year.
How many DEATHS are attributed to fungal infections annually?
3.8 million deaths, with about 2.5 million directly due to fungal infections.
What are the LIMITATIONS of traditional diagnostic methods for fungal infections? CLUE: LTC
Low sensitivity, time-consuming processes, and contamination risk --> which lead to higher hospital costs
What is the MORTALITY RATE associated with invasive Aspergillosis based on the Estimated Crude Mortality chart?
85.2% mortality rate.
What is the estimated number of cases from Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP) annually?
505,000 cases, with 214,000 deaths
What is the estimated number of cases of Cryptococcal meningitis per year?
194,000 cases, with 147,000 deaths (75.8%)
What is the impact of fungal asthma on public health?
It affects approximately 1.5 million people & may contribute to 46,000 asthma deaths per year.
What is the purpose of direct microscopy in fungal diagnosis?
To look for fungal morphological structures in infected biopsy tissue or fluid.
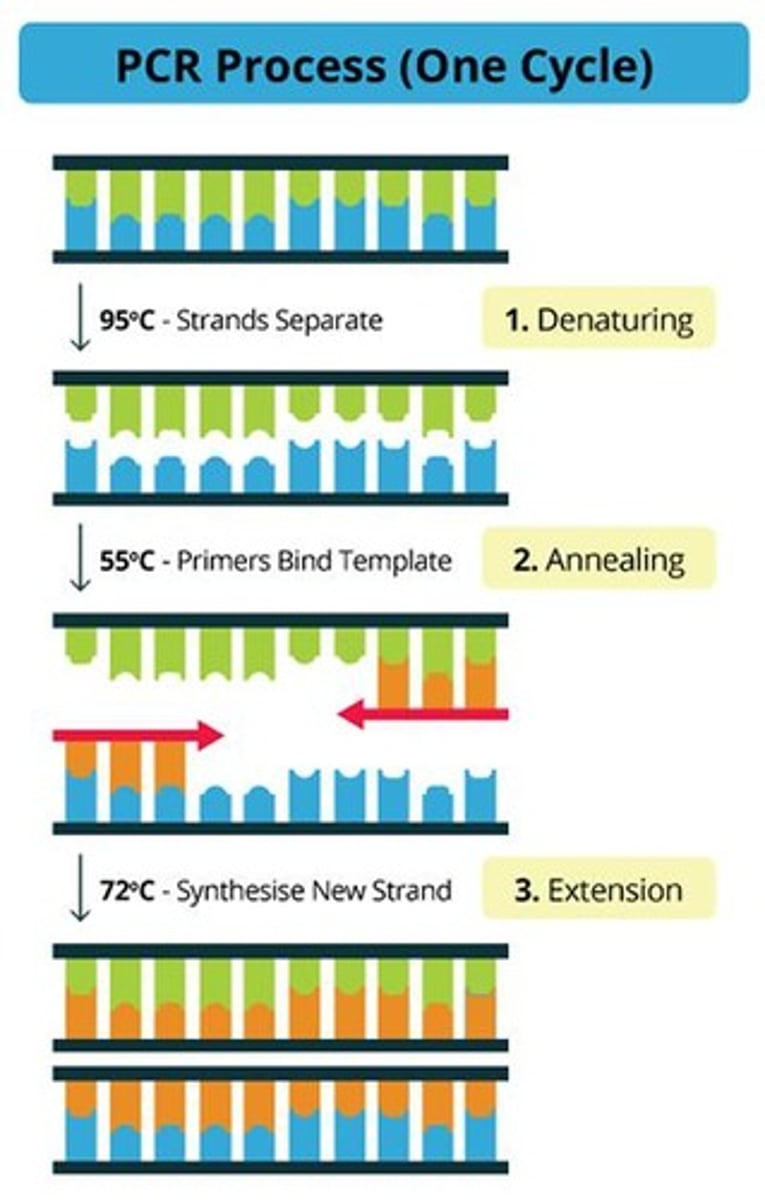
What is the temperature at which DNA is heated to break hydrogen bonds during PCR?
90°C.
What occurs during the annealing step of PCR?
Primers bracket the sequence of interest at 55°C to prepare for copying.
Why is visualization alone insufficient for identifying fungal species?
Structures can be similar across various fungal species, making specific identification difficult.
What is the sensitivity of blood cultures for diagnosing Candidemia?
Blood cultures have low sensitivity for diagnosing Candidemia.
What are the limitations of non-blood cultures in diagnosing fungal infections?
Non-blood cultures are non-specific and may take too long to turn positive.
What is the recovery rate of Aspergillus from sputum in patients with invasive Aspergillosis?
8-34%.
What is the recovery rate of Aspergillus from bile/bronchoalveolar lavage in patients with invasive Aspergillosis?
45-62%.
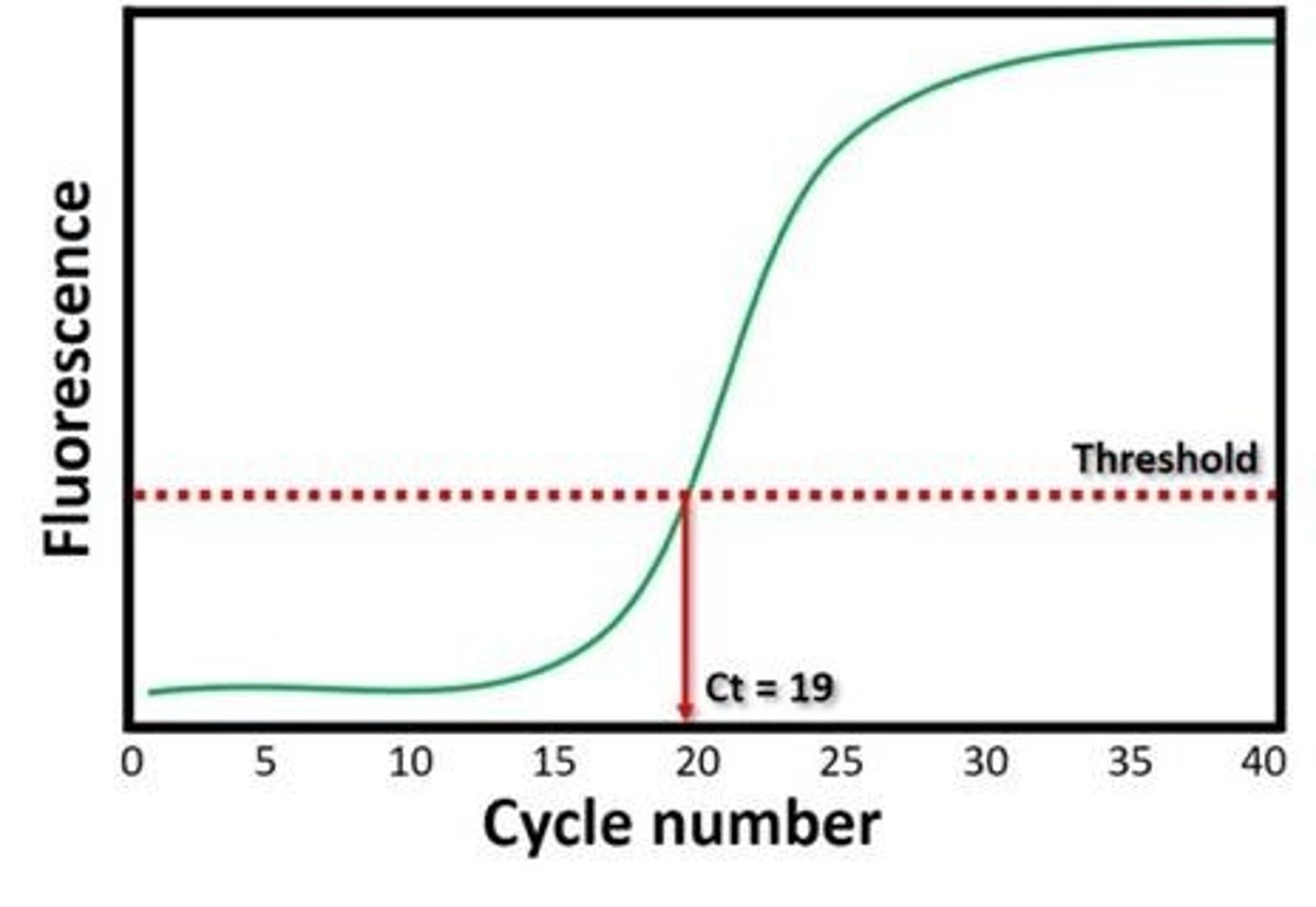
What does a low Ct value indicate in real-time PCR?
A high DNA concentration.
What does a high Ct value indicate in real-time PCR?
A low DNA concentration.
What occurs during the extension step of PCR?
Taq polymerase synthesizes a new complementary DNA strand at 72°C.
What is the effect of magnesium ions during PCR?
Magnesium helps orient the primer for proper binding and forms bonds between the primer and dNTPs.
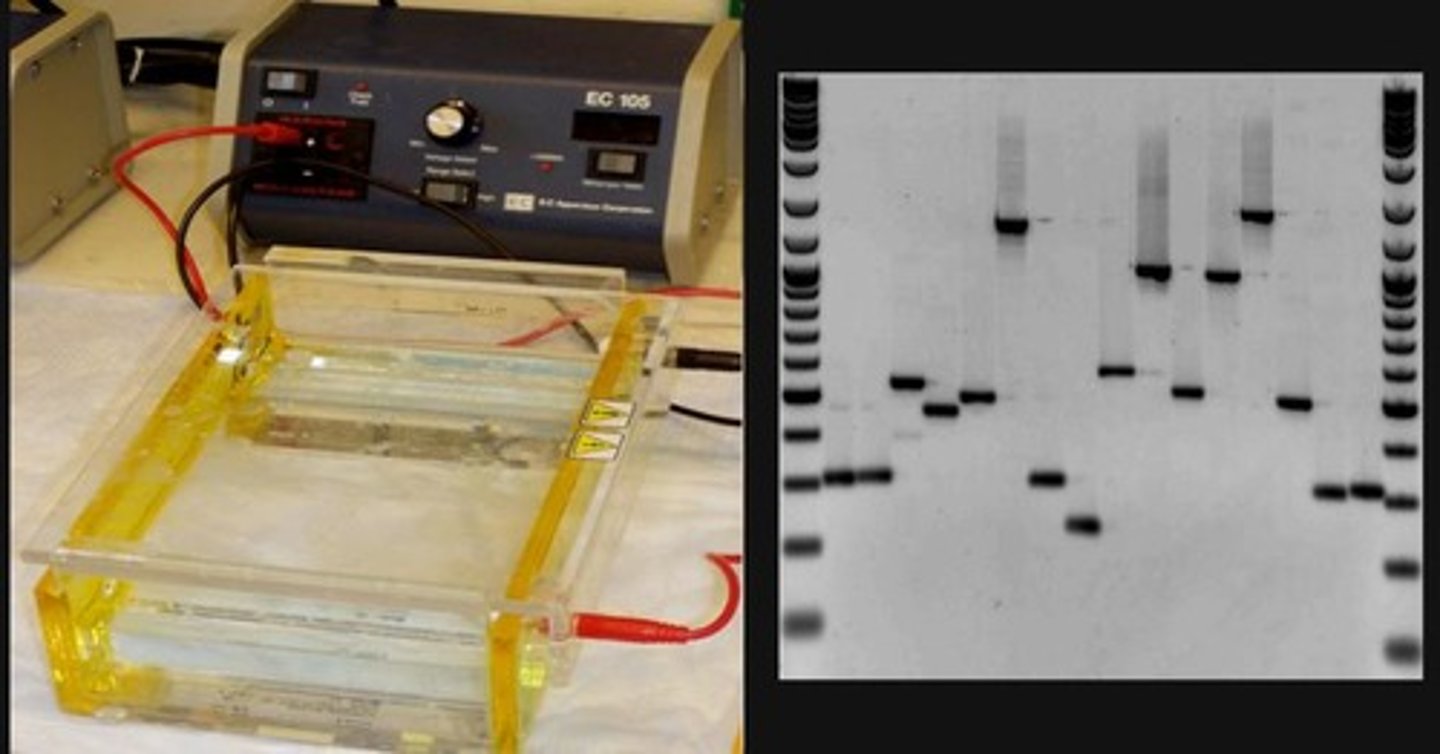
What is the purpose of DNA gel electrophoresis after PCR?
To analyze the amplified DNA samples.
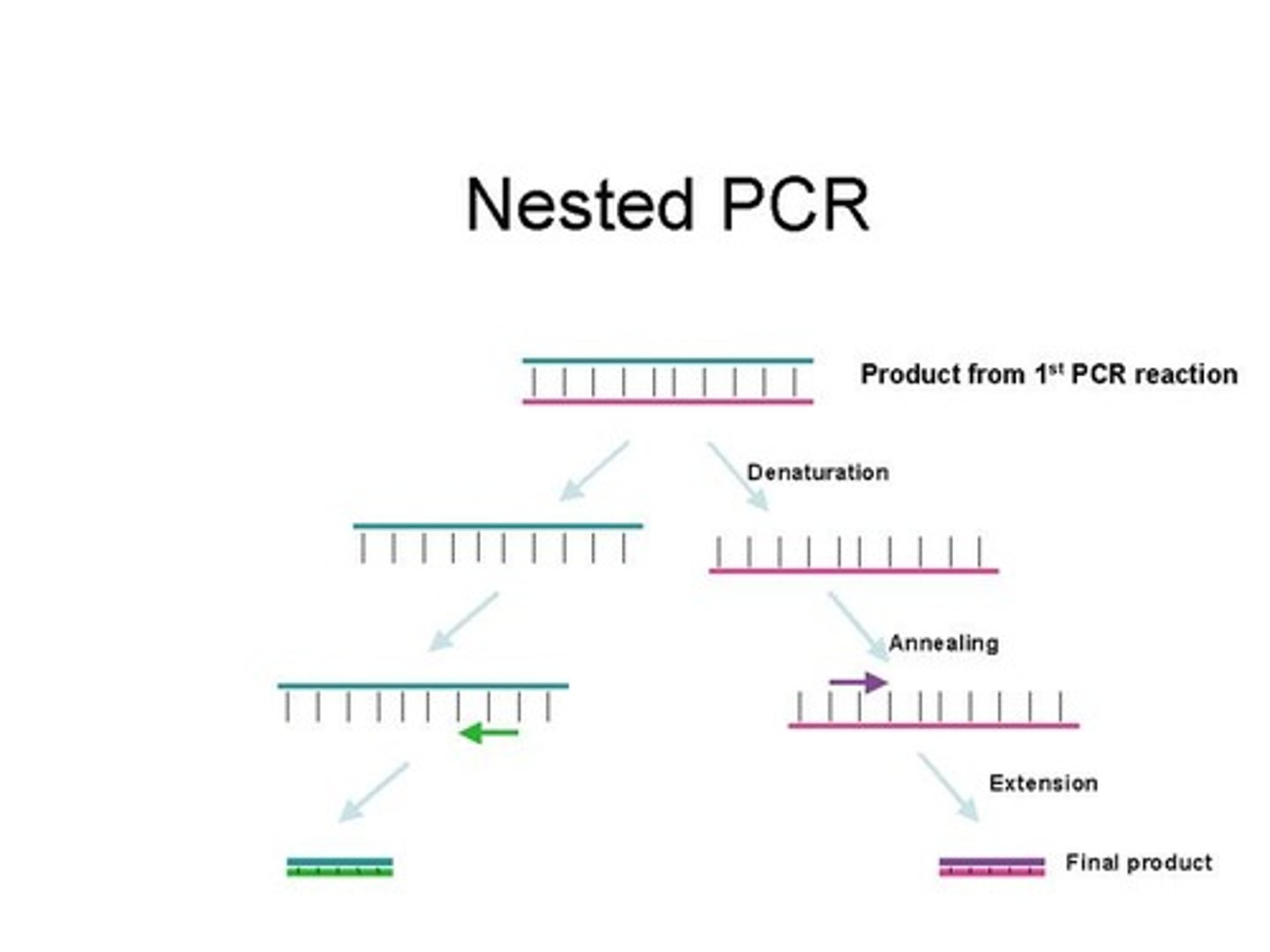
What is nested PCR?
A modification of PCR designed to improve specificity and sensitivity using two primer sets and two successive reactions.
What are the two types of primers used in nested PCR?
Outer primers amplify a larger target region, while nested primers amplify a smaller, internal region.
What is the advantage of using nested PCR?
Increased sensitivity and enhanced specificity, making it ideal for difficult samples.
What is the role of reverse transcriptase in real-time PCR?
It builds DNA from RNA templates, creating complementary DNA (cDNA).
What is the first step of the PCR cycle?
The denaturation step, where DNA is heated at 90C too separate strands.
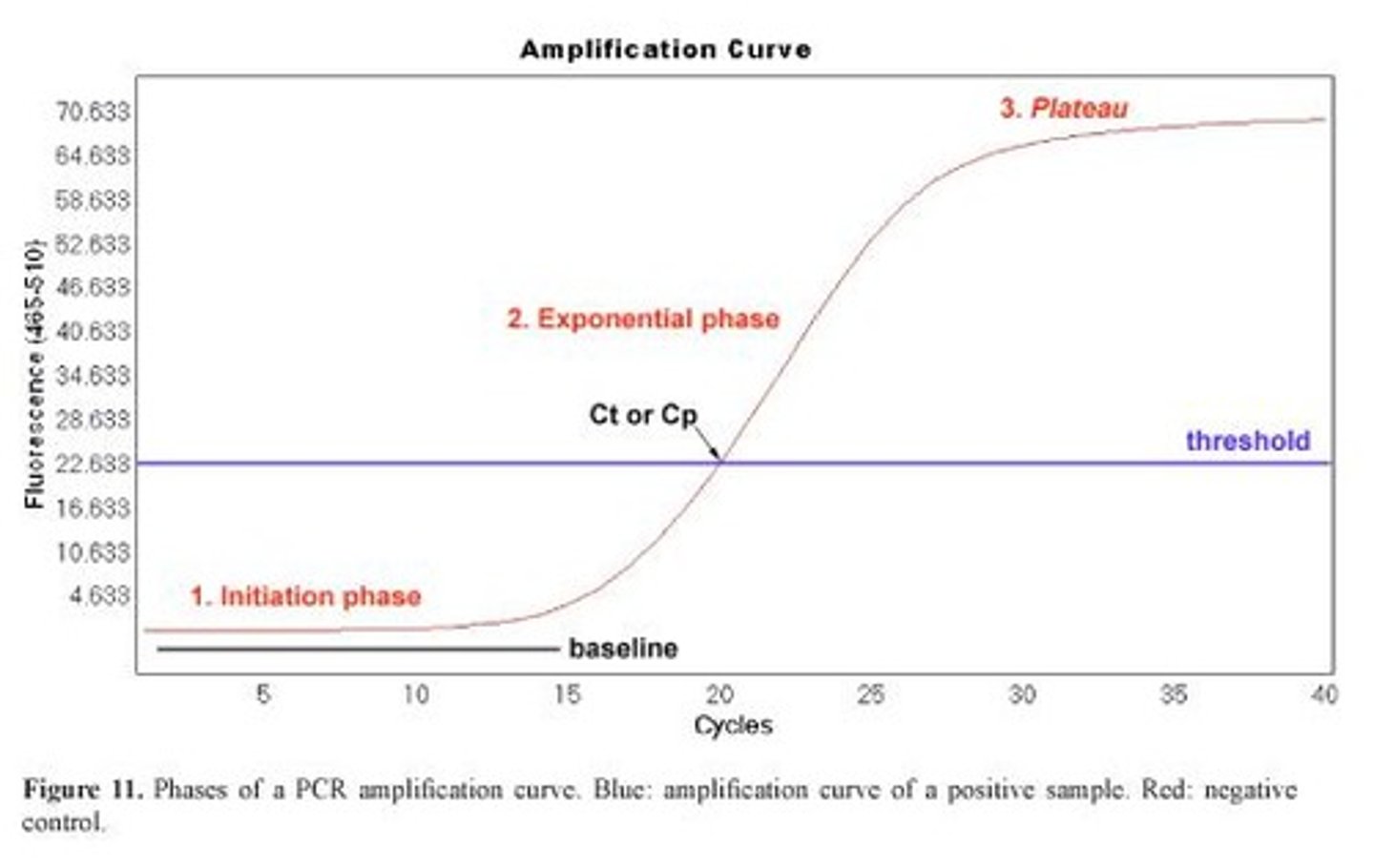
What is the significance of the Ct value in quantitative PCR?
It indicates the point where the amplified product exceeds the threshold.
What is the purpose of primers in PCR?
Primers are designed to stick to specific parts of the DNA template for amplification.
What happens to the amount of DNA after the extension step in PCR?
The amount of DNA doubles.
What is the typical cycle progression in PCR amplification?
1 → 2 → 4 → 8 → 16 copies, and so on.
What is the primary function of RTQ-PCR?
To quantify DNA in real time.
What are the main components of RTQ-PCR?
Primers, fluorescent probes, and DNA polymerase.
What does the Master Mix in RTQ-PCR contain?
Primers, Taq polymerase, dNTPs, buffer, and magnesium chloride.
What are the four main steps in the PCR process?
Denaturation, annealing, extension, and fluorescence detection.
What is the role of green primers in RTQ-PCR?
They attach only to double-stranded DNA and are used to shorten the region containing the target segment.
What is SYBR Green used for in RTQ-PCR?
It is a common fluorescent reagent that binds to double-stranded DNA.
What is a TaqMan probe?
A short sequence that attaches to a specific target sequence and contains a glowing reporter component along with a quencher.
How does the Taq polymerase affect the TaqMan probe during DNA synthesis?
As Taq polymerase builds the new complementary strand, it dislodges the probe, causing the reporter to glow.
What is Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP)?
A rapid DNA amplification technique that requires only a single constant temperature (67°C).
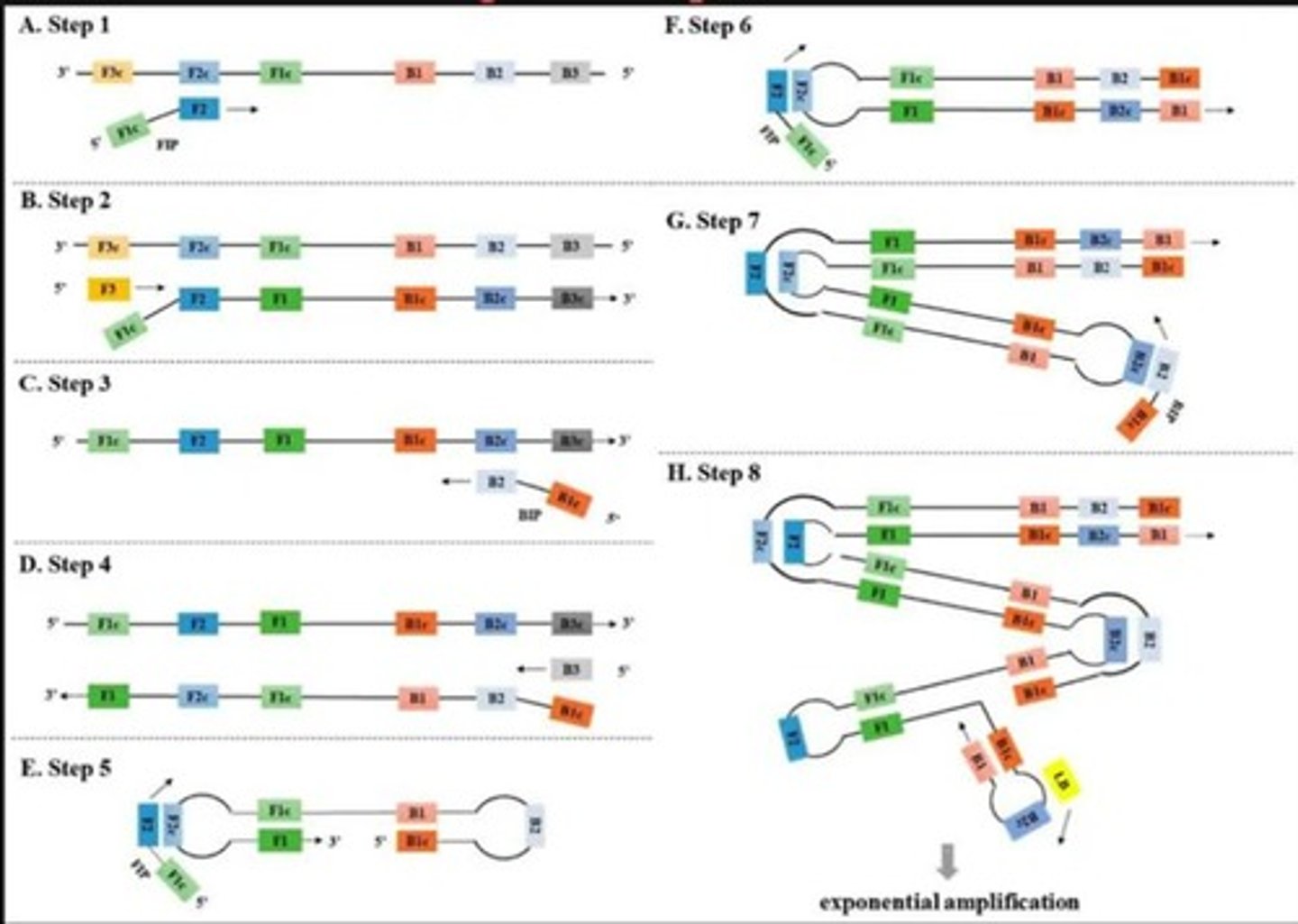
How many primers are typically used in LAMP?
4 to 6 primers, including essential and optional loop primers.
What is the sample type commonly used in LAMP for pathogen detection?
Sputum.
What is the significance of the constant temperature in LAMP?
It eliminates the need for a thermocycler.
Describe the workflow summary of LAMP amplification.
FIP binds → DNA synthesis → F3 displaces strand → loop forms → BIP binds → reverse synthesis → B3 displaces strand → dumbbell DNA → self-priming & loop primers bind → massive amplification.
What are the advantages of LAMP?
Fast results, simplicity with minimal equipment, high sensitivity, and portability.
What is the role of the Forward Inner Primer (FIP) in LAMP?
It hybridizes to the target DNA, initiating synthesis and forming a 5' overhang.
What does the Backward Inner Primer (BIP) do in LAMP?
It binds to the target DNA and includes a sequence that aids in amplification.
What are the target pathogens commonly detected using LAMP?
Aspergillus spp. and Candida spp.
What gene is often targeted for detecting Aspergillus spp.?
anxC4.
Which sequences are typically used for detecting Candida spp.?
ITS1, ITS2, ACT1, 5.8S/18S/28S.
What is the function of the Forward Outer Primer (F3) in LAMP?
It binds upstream of the target region to facilitate amplification.
What happens during the Outer Primer Action in LAMP?
The Forward Outer Primer (F3) binds to its target, enhancing the amplification process.
What is the purpose of loop primers in LAMP?
They are optional but enhance the amplification speed.
What primers are involved in the initial DNA synthesis for amplification?
The Forward Outer Primer (F3) and the Backward Inner Primer (BIP) are involved.
What is the role of the Forward Outer Primer (F3) in DNA synthesis?
F3 binds to F3c upstream of F2, initiating synthesis and displacing the previous strand containing the FIP.
What structure forms as a result of the displaced single-stranded DNA during amplification?
A loop forms at one end due to self-hybridization between F1 and F1c.
What is the result of the reverse synthesis initiated by the Backward Inner Primer (BIP)?
It forms another loop on the opposite side by hybridizing with B1, resulting in a dumbbell-shaped DNA structure.
How does the dumbbell DNA structure contribute to amplification?
It serves as a template for exponential amplification, allowing loop primers (LF and LB) to bind to single-stranded rRNA genes.
What types of specimens are used for DNA detection in this method?
Sputum, blood, bone marrow, bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL), clinical samples, and nail clippings.
What are some detection methods used in this DNA amplification process?
Colorimetry, fluorescence, gel electrophoresis, turbidity, and Lateral Flow Biosensor (LFB).
What does a color change in colorimetry indicate?
It indicates the presence of DNA amplification.
What is the significance of the studies by Fallahi et al. (2019) and Jiang et al. (2021)?
Both studies reported 100% sensitivity and specificity in their detection methods for fungal pathogens.
What target gene is commonly used for detecting Candida spp.?
ITS2 is commonly used for Candida spp.
What is the specificity of the target gene 5.8S/18S/28S rRNA for Candida spp. as noted by Watanabe et al. (2019)?
The specificity is only 12.9%, possibly due to contamination or detection of non-pathogenic species.
What is LAMP and its significance in fungal pathogen detection?
LAMP is a highly sensitive tool for detecting fungal pathogens, particularly Candida spp. and Aspergillus spp.
What factors greatly affect the performance of the tests?
Specimen type and target gene significantly affect test performance.
What is the Chain Termination Method in DNA sequencing?
It is a method developed by Frederick Sanger in 1977 for determining the nucleotide sequence of DNA.
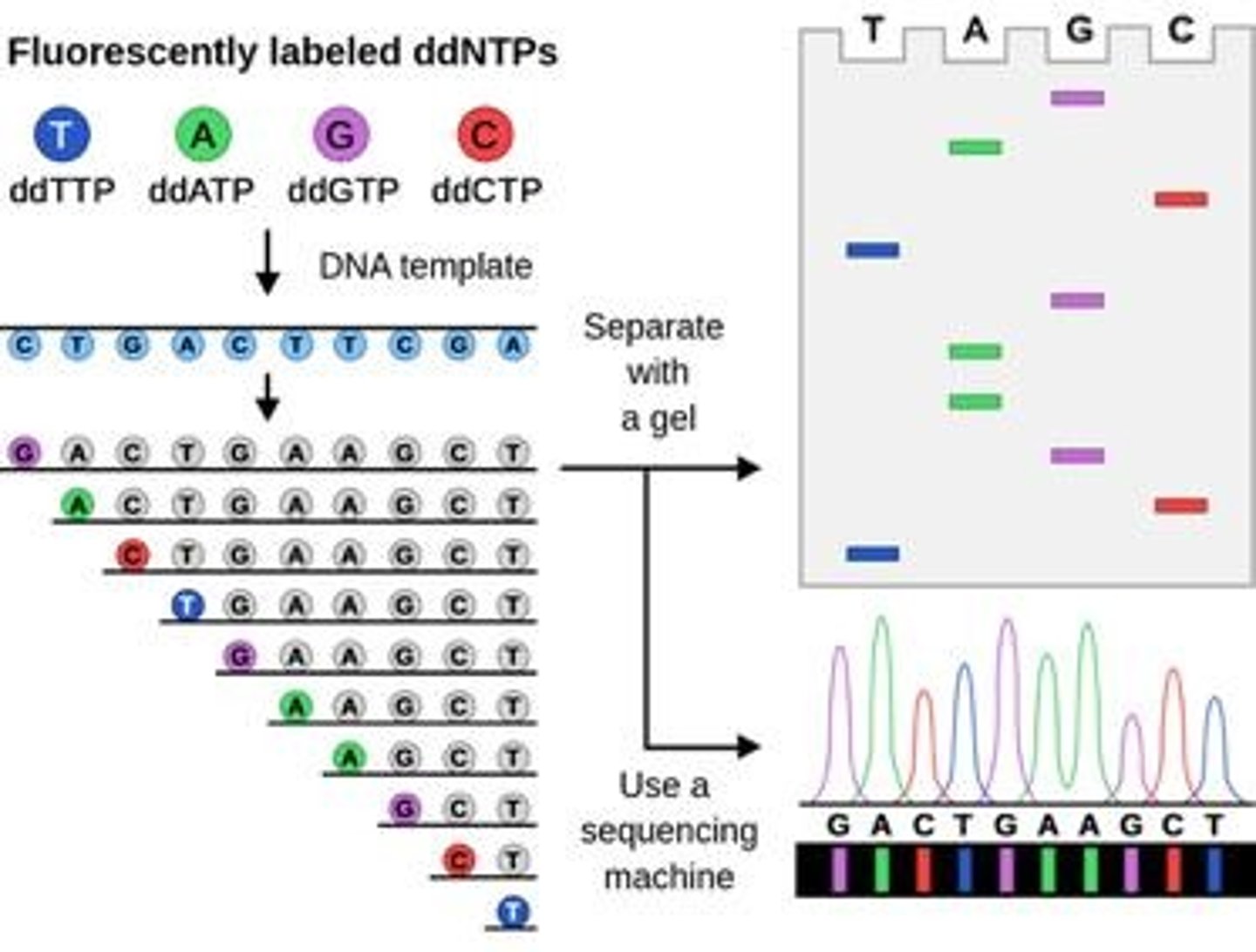
What is the mechanism of Sanger sequencing?
It uses a single primer to initiate DNA synthesis.
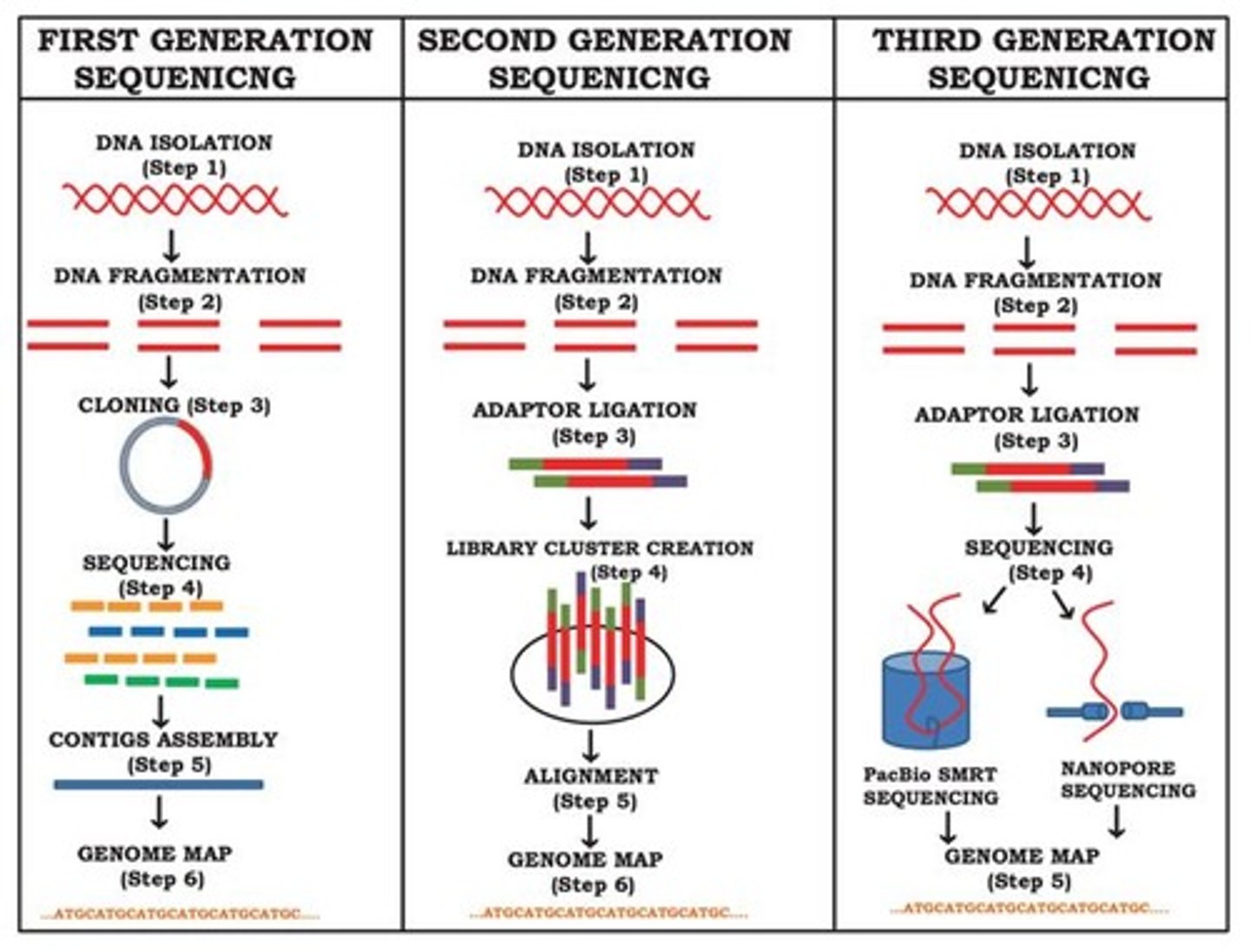
What is Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) also known as?
It is also known as Massive Parallel Sequencing.
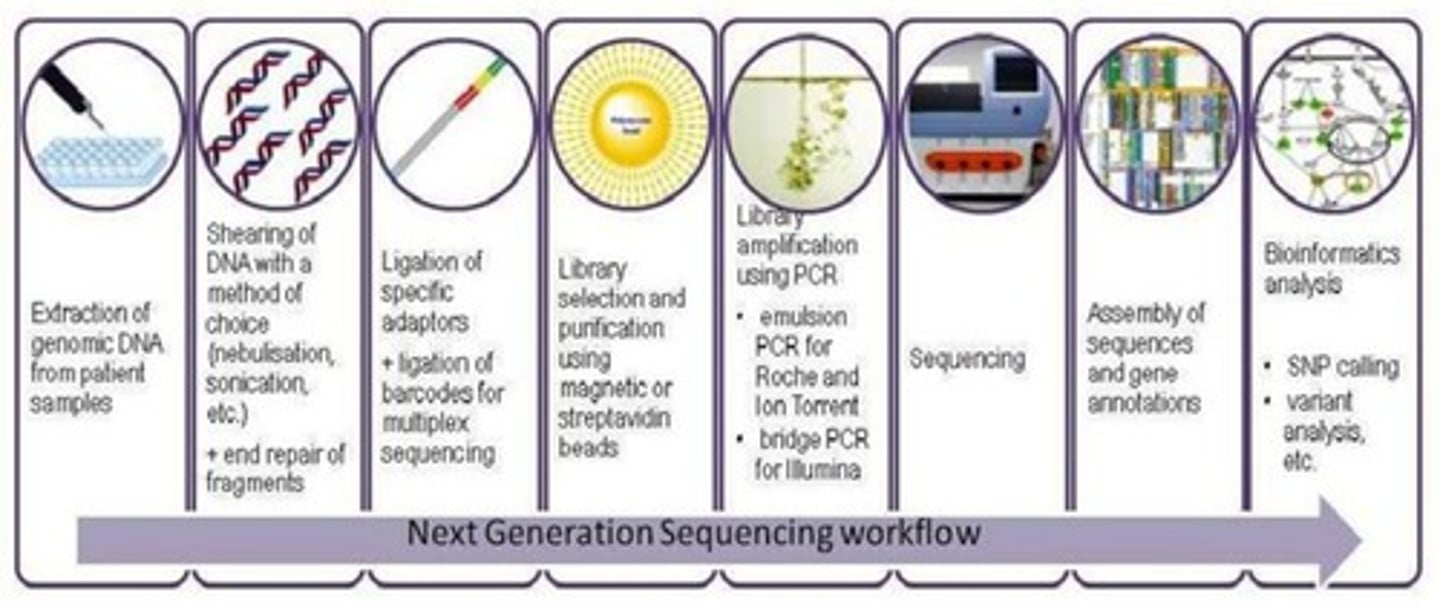
What is the overview of Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS)?
NGS allows simultaneous sequencing of millions of DNA fragments.
What is a key difference between standard PCR and Chain Termination PCR?
Chain Termination PCR includes dideoxynucleotides that cause chain termination during DNA synthesis.
What are the final products of the amplification process described?
Large amounts of double-stranded DNA and looped structures or concatemers with multiple repeats of the target sequence.
What detection methods provide reliable results for DNA amplification?
Detection methods like LFB, fluorescence, and turbidity provide reliable results.
What is the role of loop regions in DNA synthesis?
Loop regions speed up DNA synthesis and result in multiple concatemeric DNA products.
What are dideoxynucleotides (ddNTPs) used for in DNA sequencing?
ddNTPs are modified nucleotides that lack a 3' OH group, causing DNA strand extension to stop when incorporated.
What is the purpose of using a low ratio of ddNTPs to normal dNTPs in sequencing?
It allows for the termination of DNA fragments at various lengths, resulting in millions to billions of terminated DNA fragments.
List three applications of DNA sequencing techniques.
Genomics, Transcriptomics, Metagenomics.
What is the first step in the Sanger sequencing process?
Sample Extraction, where DNA is extracted from the patient's sample.
What does library preparation involve in DNA sequencing?
It involves preparing a sequencing library from RNA or DNA samples, which includes amplification and addition of sequencing adaptors.
What is the purpose of PCR amplification in library preparation?
To yield a pool of appropriately sized target sequences.
How are ddNTPs tagged in the sequencing process?
Each ddNTP is tagged with a unique fluorescent label.
What is the role of gel electrophoresis in DNA sequencing?
It separates chain-terminated fragments by size, allowing for the arrangement of fragments from smallest to largest.
What happens during the adaptor ligation step in library preparation?
Amplified DNA/cDNA fragments are bookended with specific oligonucleotide sequences that interact with the sequencing flow cell.