NPTE Non-systems
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
JACHO
Joint Commission on Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations
-Hospitals, SNF, Home Health, PPO, HMO, Mental institutions
-The FBI of healthcare
CARF
Commission on Accreditation of Rehabilitation Facilities
-Free standing rehab programs/facilities
CMS
Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services
OSHA
Occupational Safety and Health Administration
-keeps us safe at work
Documentation mistakes
-Strike out with single line and initialed and dated by PT
-Never use white out
PPE: MRSA, VISA, C-diff, Lice Scabies, Hep-B, Dermatitis, Rota Virus
Contact Precautions: Gloves and Gown
PPE: Mumps, Meningitidis Pneumonia, Flu, Strep
Droplet: Mask
PPE: Measles, Tuberculosis, Chicken Pox, Herpes Zoster, SmallPox, SARS
Airborne: N95
May add Contact if infection is severe (gown and gloves)
- must use (-) air flor room and keep door closed
MTV= airbone
Measles, Tuberculosis and Varicella
CPR basics
-chest compressions at least 5cm (2 in) deep
-30:2
-Allow full recoil
-minimize pauses in compressions
Levels of Evidence
Meta-analysis
Systematic reviews of multiple well-designed controlled studies
Randomized controlled trials
Cohort Studies
Case Control Studies
Cross sectional studies
Case series/case reports
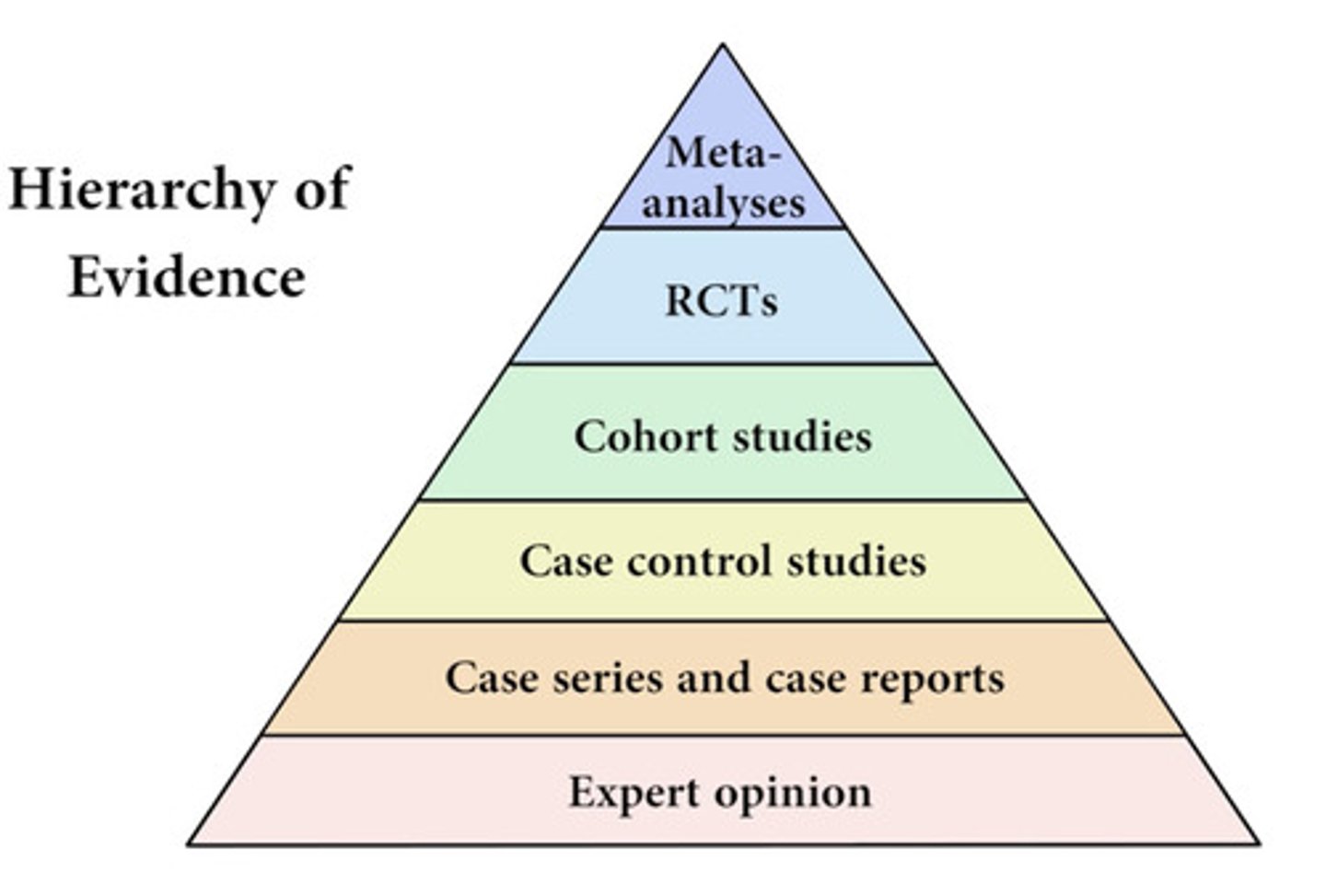
What is the difference between meta-analysis and systematic review?
Meta has a statistical analysis but a systematic review does not (its just synthesizing information out there)
Levels of Measurement for Qualitative Data: Non-parametric
Qualitative data: no numbers
Used for Non-parametric data
NOn= Nominal and Ordinal
Nominal: data that is mutually exclusive categories (Gender and blood type)
Ordinal: data that is ranked and no quantifiable differences between ranks (MMT)
Levels of Measurement for Quantitative Data: Parametric
Quantatiative: Numbers
Interval: Hold no true zero and can be below zero (Temperature)
Ratio: Highest level of measurement and can have True 0, ROM measurements
Rati0= True 0
Define reliability
Will you get the same results every time when used in the same situation
Types of Reliability
Intra-rater: Can 1 PT get the same outcome each time with several attempts
Inter-rater: Can 2 or more PTs get the same result
Test-retest: 1 test on 1 person on 2+ occasions get the same result (look for key words of new equipment, same test different week)
Define Validity
does the test measure what you want
Types of validity
Content: Measure specifically what the pt problem is (Fall risk-> use TUG)
Construct: Measure what is it supposed to measure (Goniometer measures ROM)
Concurrent: Comparing GOLD standard to other test (HHD vs MMT)
Face: the outcome measure should measure what is looks like it will measure related to patient problem (appears to measure; surveys?)
Types of Errors
Type 1: False Positive
1 can be turned into a P
ex: Telling a male he is pregnant
*Type 2: False Negative
II can be turned into a N
ex: Telling a pregnant woman she is not pregnant

Sensitivity and SNOut
-Someone will get (+) if they have the condition
-A (-) result = better able to rule OUT the diagnosis
-has few false negatives
-Very low likelihood ratio

Specificity and SPIn
-Identifies pt who DON'T have the condition
-Someone will get (-) if they DON'T have the diagnosis
-A (+) result = better able to rule IN the diagnosis
-high likelihood ratio

T-Test
-Determines if there is a difference BETWEEN 2 groups
-Can be done when 2 diff groups are matched and tested
OR
-if one group is tested (pretest/posttest)
-ONLY used if there is one dependent and one independent variable in the study
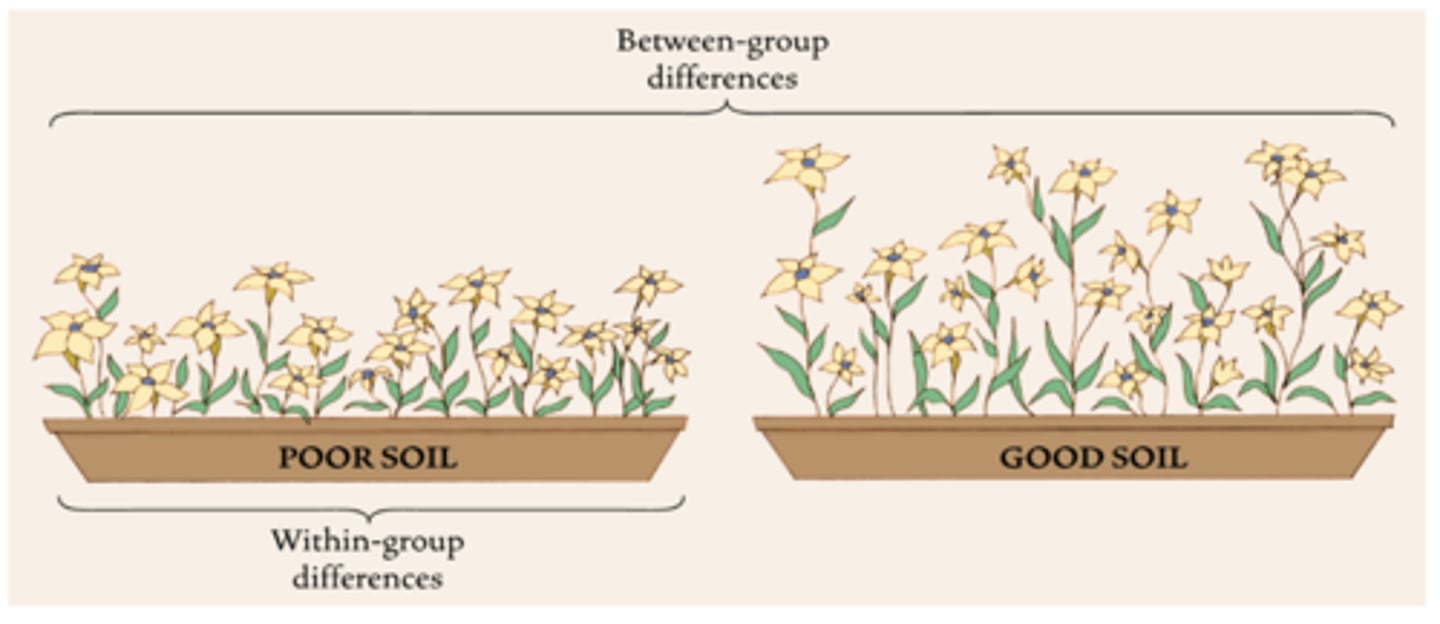
Analysis of Variance (ANOVA)
-statistical test used to determine whether there are differences among 3 or more groups
-Can analyze 2 or more independent variables and any interaction between the variables
-Ex: looking to determine difference btwn 3 exercise protocols that increase ROM following shoulder immobilization

Chi Square Test
-tells whether the observed pattern, trait or distribution is different that what would have been expected by chance alone
-often in genetics or with population statistics
-chi square test is commonly used to test relationships and differences btw categorical variables

Effect Size
-the magnitude of the difference btw groups
-Absolute effect size provides the difference btw the average outcomes in 2 diff intervention groups
-P values tells us whether an effect exits but does not share the size of the effect
-Effect Size btw groups is shared as Cohen's D, Odds or Risk ratio
-Effect size for associations is shared as Pearson's Coefficient
Statistical Significance
-The probability of level of confidence as to whether or not the results of the experiment happened by chance
- P values often set to 0.5 or 0.01
-p=0.05 there is probability that the results obtained would occur by chance 5% of the time and would occur from tx 95% of the time
-p=0.01 there is probability that the results obtained would occur by chance 1% of the time