Forensic Biology: Lecture 5 – STRs & SNPs in Forensic Analysis
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Homozygote
both alleles are the same length
Heterozygote
alleles differ and can be resolved from one another
STRs are the preferred genetic markers because they:
are highly variable within various populations.
Simple repeats
Variation is due to differences in the number of repeats
Simple repeats with non-consensus alleles
In addition to number of repeats, some of the repeats may be incomplete
Microvariants
STRs with altered repeat units
Compound repeats
Two or more types of repeat units
Compound repeats with non-consensus alleles
Two or more types of repeat units and some of the repeats may be incomplete
Complex repeats
They can have several types of repeat units, with interruptions between them
replication slippage.
During replication the newly synthesized DNA strand can be displaced, and a loop of unpaired DNA is formed between the old and new DNA strands. The result is that after replication, there may be a gain or loss of a repeat unit
STRs show two important differences with respect to other genetic markers (SNPs)
1. A much faster mutation rate (the average is around 10-3).
2. Instead of only two alleles, they typically have multiple allelic forms.
SNPs are
single base pair changes in DNA
How often, on average, do SNPs occur?
once every 300 base pairs
Polymorphism
The coexistence of two or more distinct forms in the same population.
There were originally 13 STRs for identification, but the CODIS panel newly upgraded to:
20
Genotyping of the CODIS STRs (plus Amelogenin for sex determination) is done by:
capillary electrophoresis
RFLPs are
varying DNA sequences that are recognized by restriction enzymes
Endonucleases
enzymes that cut RNA or DNA at specific sites; restriction enzymes
Exonuclease
enzyme that removes successive nucleotides from the end of a polynucleotide molecule
Genotyping the CODIS panel requires just 1 or 2 days, while the RFLP markers required:
1 week or more
Probability of a random match using 13 CODIS STR markers:
1 in 594 trillion
Multiplex PCR is:
the simultaneous amplification of several markers in the same PCR reaction
Capillary Electrophoresis (CE)
A method of separating DNA samples based on the rate of movement of each component through a gel-filled capillary while under the influence of an electric field
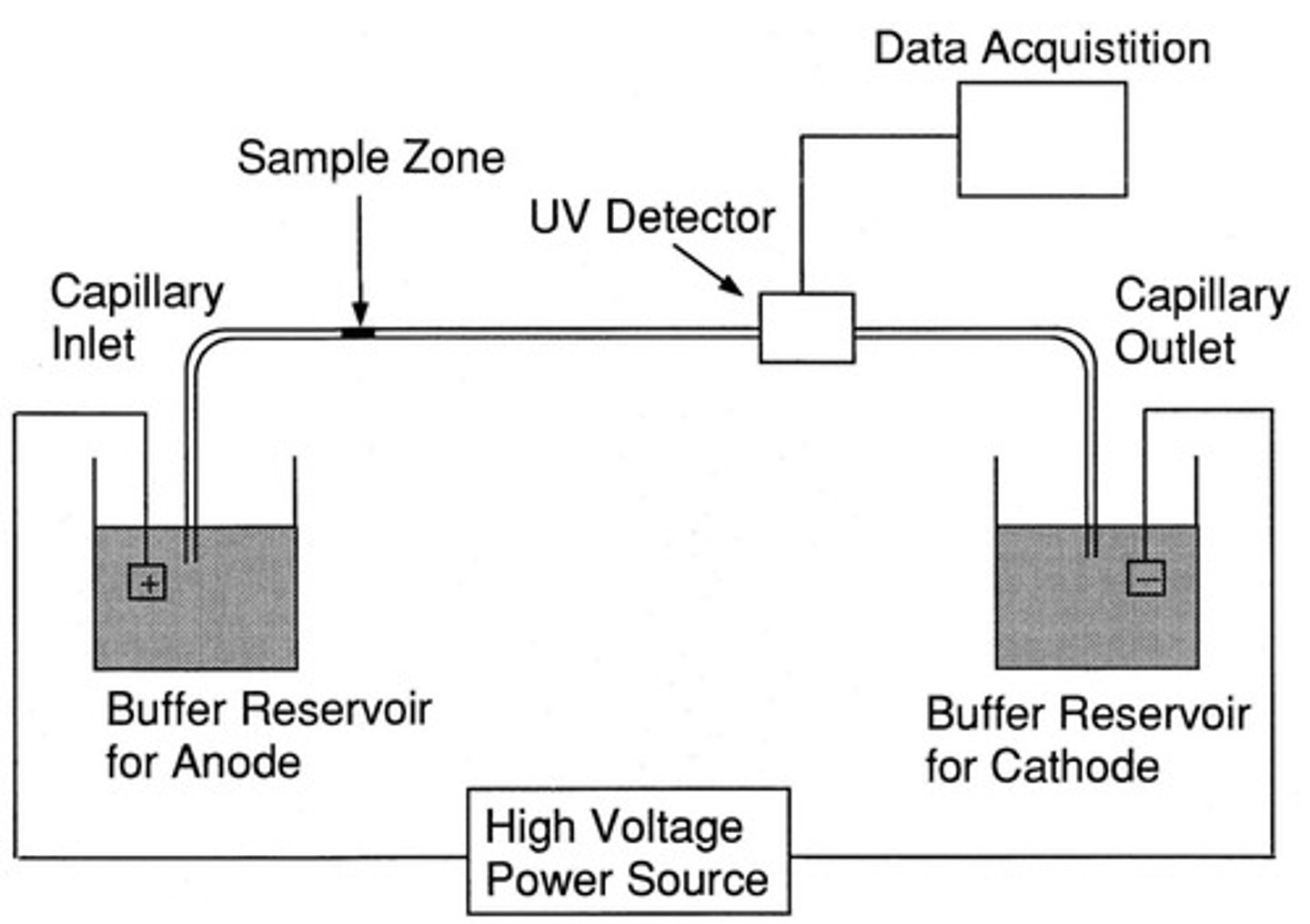
Internal size standards
combined with PCR product; set of DNA fragments of known size used to correlate results from run-to-run, allow allele sizing.
Allelic ladder
set of fragments representing all possible alleles of a repeat locus (STR)
STR genotyping is performed by comparison of sample data to:
allelic ladders
Ability to identify sample as male or female is useful for:
- Sexual assault cases
- Missing persons cases
- Mass disaster investigations
Amelogenin assay is the most useful for sex determination because:
it can be performed in conjunction with STR analysis
Rare mutation where the Y chromosome amplicon is absent, m ost common in South Asian populations:
Male samples falsely appear to be female
Mutation in primer binding sites on X chromosome causes amelogenin X allele dropout:
Only Y amplicon is present
Most abundant markers in the human genome:
SNPs
dbSNP
database for human SNPs maintained by the NCBI
Genotyping SNPs requires
use of PCR to amplify the region where the SNP is located
SNPs classified into four general uses:
- Human identification
- Ancestry informative markers (AIMs)
- Lineage informative SNPs
- Phenotype informative SNPs
SNPs have a low mutation rate and are therefore more likely:
to become fixed in a population making them population specific, which is helpful in determining ancestry of perpetrator or found remains.
Disadvantages of SNPs
They are diallelic, meaning they have a lower power of discrimination than STRs, which are multiallelic.
Advantages of SNPs
Work better for severely degraded DNA samples; amplicons can be as small as 40-50 bp, whereas STRs amplicons are typically between 100-500 bp.
What is RFLP mostly used for?
Genome mapping and in variation analysis (genotyping, paternity tests, hereditary disease diagnostics, etc.)
The McSNP Principle
In addition to distinctive lengths, DNA fragments have diagnostic melting points where the two strands separate.
TaqMan and molecular beacons:
methods based on the hybridization of an oligonucleotide (also known as a probe) to the sequence where the SNP is located (target sequence).
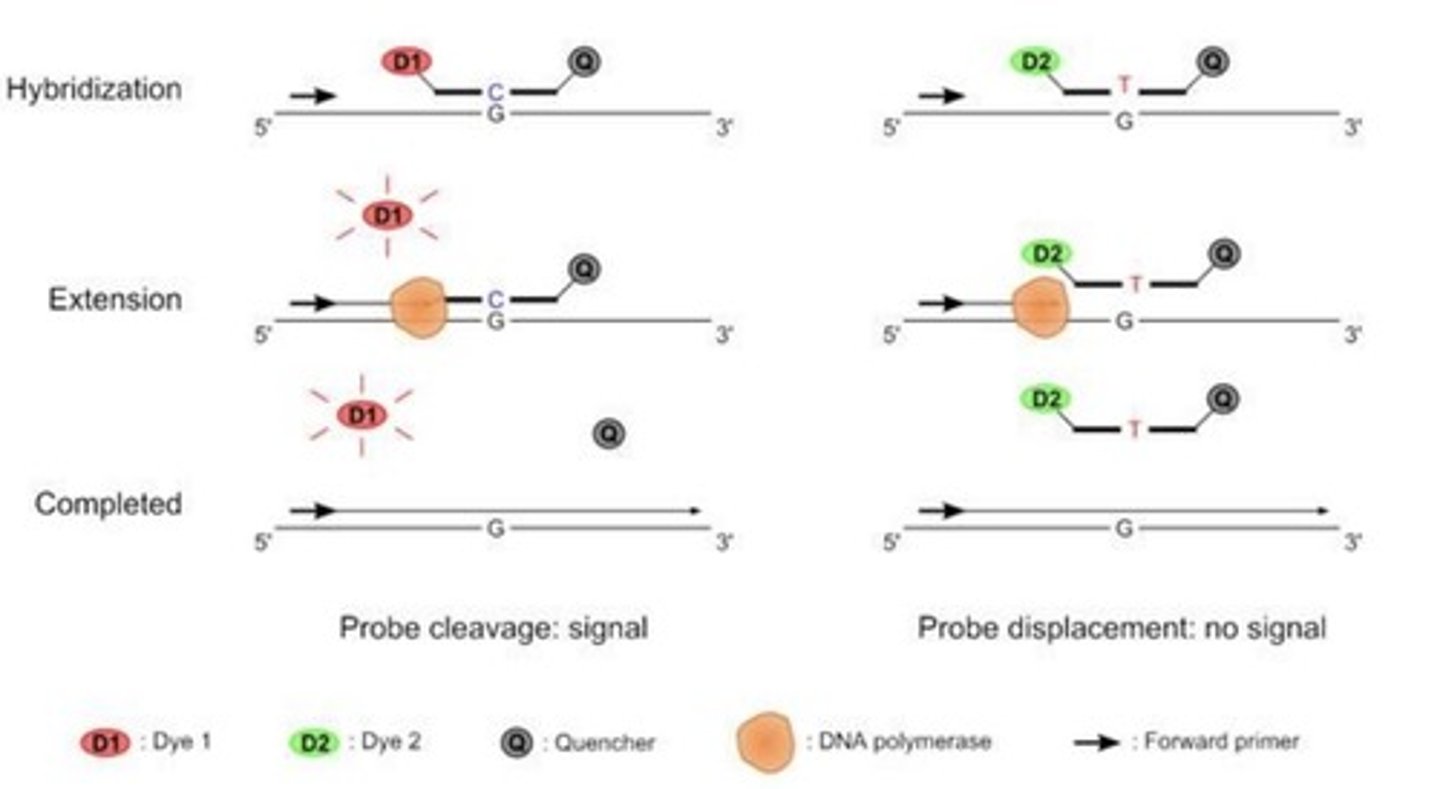
TaqMan Probe
Two probes per reaction; each is complementary to a different allele; labeled with a dye (fluorescent molecule) and a quencher (absorbs the energy of the dye); a perfect match of the probe to the target DNA will give a signal.
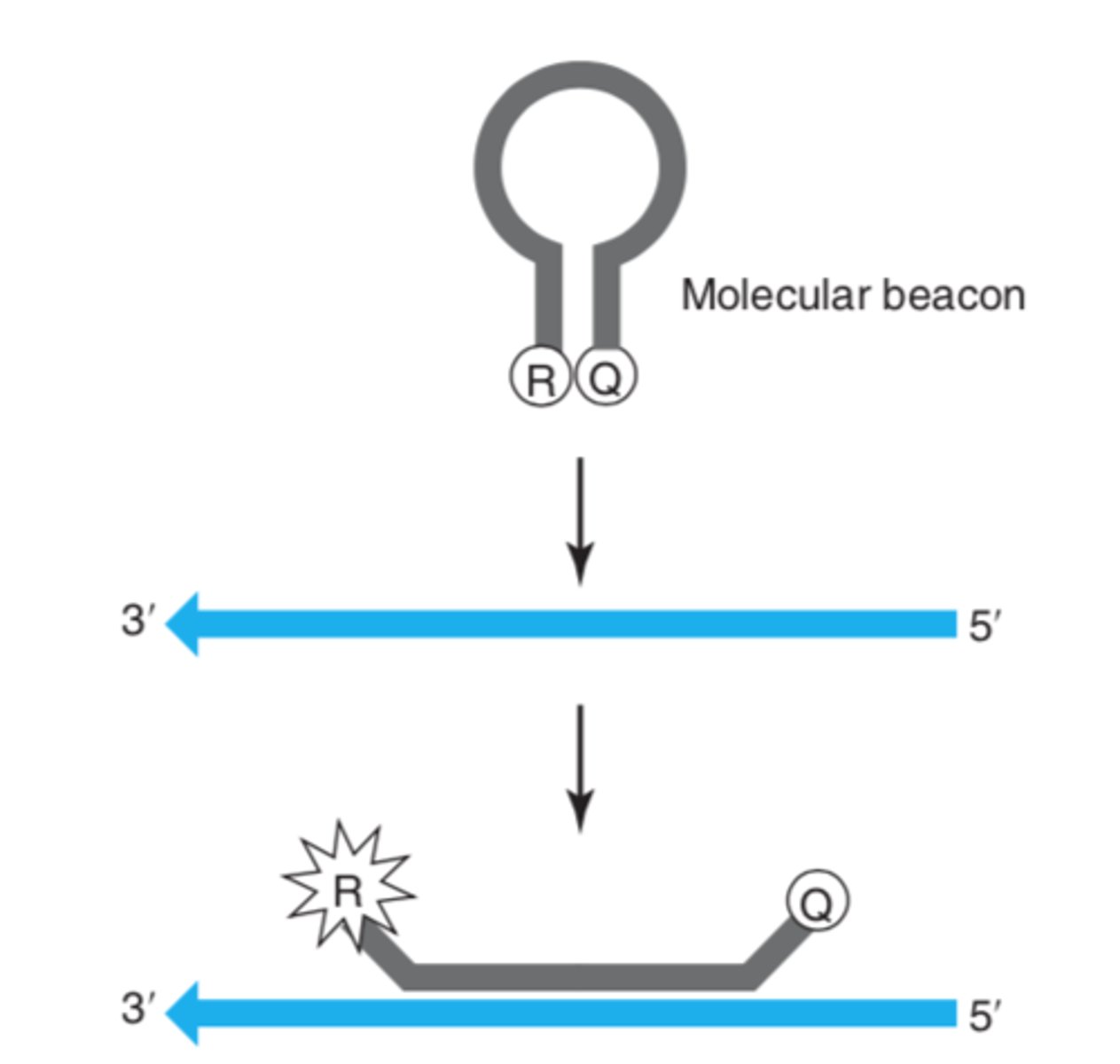
Molecular Beacons
Two probes are used, each complementary to a different allele; in the absence of the target DNA, the probe has a stem-loop structure; in the presence of the target DNA, the probe hybridizes to the complementary sequence, the quencher and reporter are driven apart, and there is fluorescence.
mini-sequencing
primers flank the polymorphic site of interest; two nucleotides labeled with different fluorophores are added to the primers by the action of Taq polymerase; the genotype is detected by the difference in fluorescence.