AP World Map test Units 3 and 4
5.0(4)
Card Sorting
1/132
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:42 PM on 12/2/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
133 Terms
1
New cards
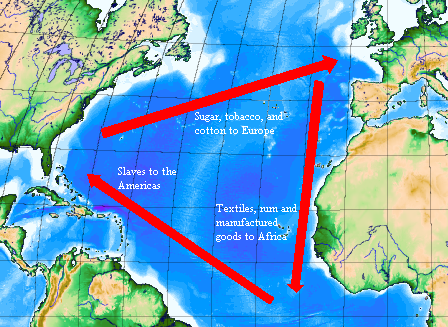
Atlantic Slave Trade
2
New cards
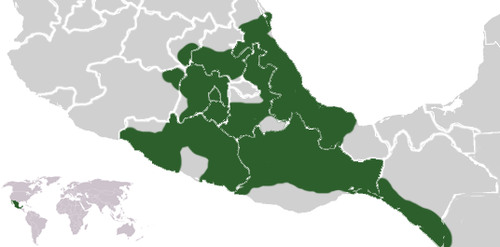
Aztec Empire
3
New cards
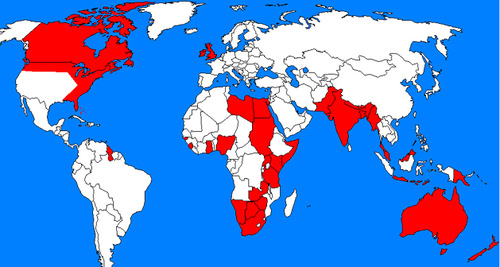
British Empire
4
New cards
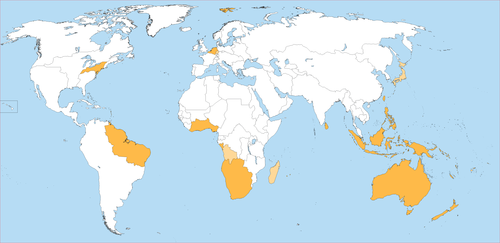
Dutch
5
New cards
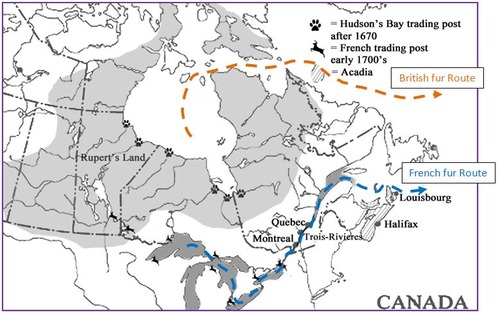
Fur Trade
6
New cards
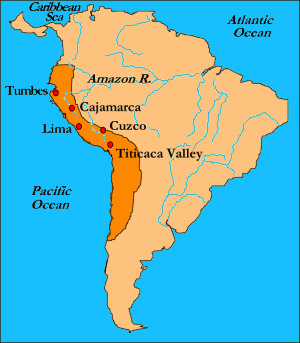
Inca Empire
7
New cards
Portugese
8
New cards
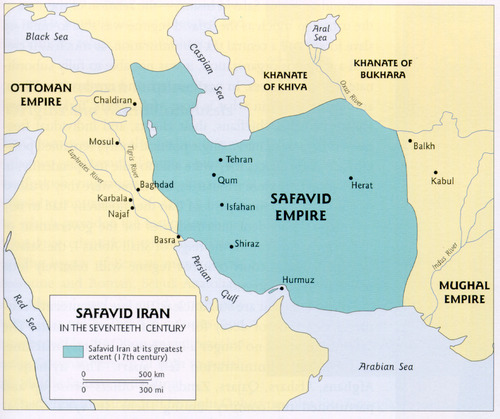
Safavid Map
9
New cards
Songhay
10
New cards
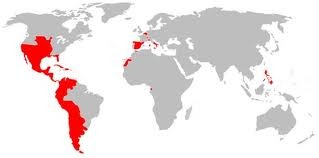
Spanish empire
11
New cards
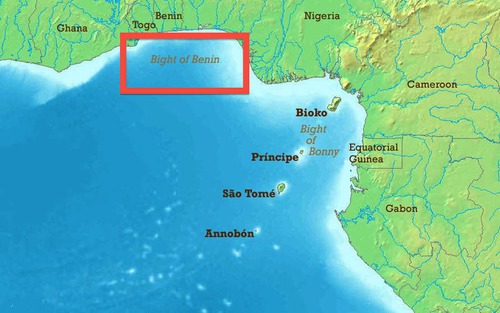
bight of benin
12
New cards
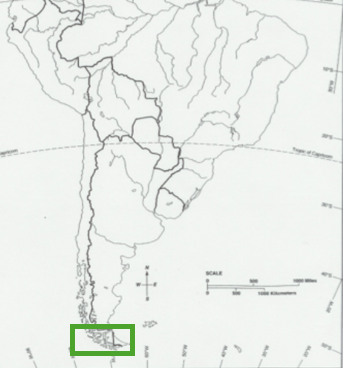
Cape Horn
13
New cards
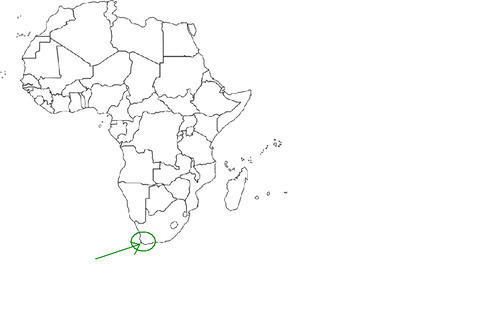
Cape of Good Hope
14
New cards
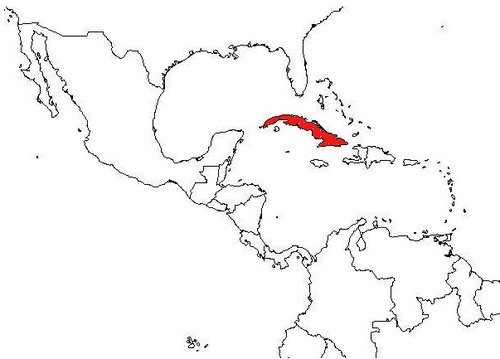
Cuba
15
New cards
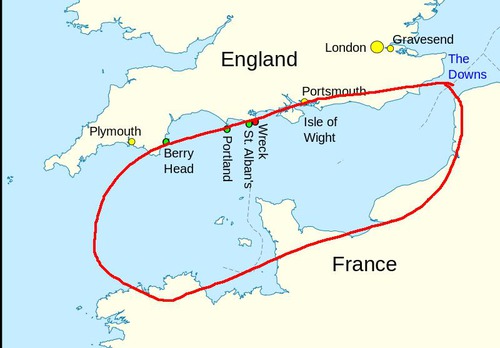
English Channel
16
New cards
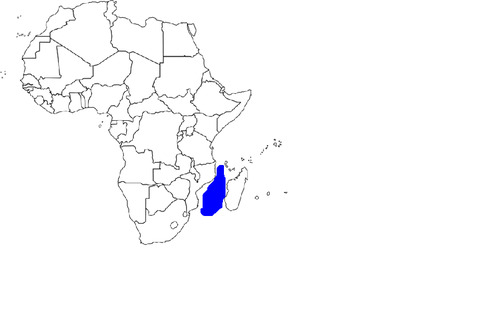
Mozambique Channel
17
New cards
Philippine Islands
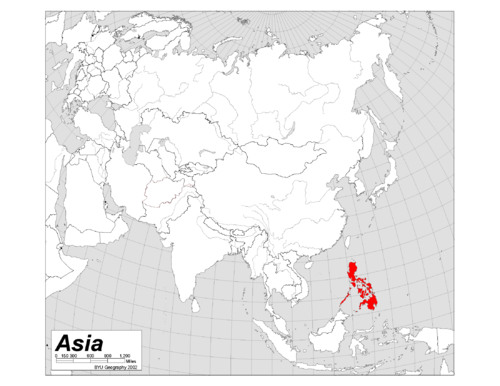
18
New cards
Strait of Hormuz
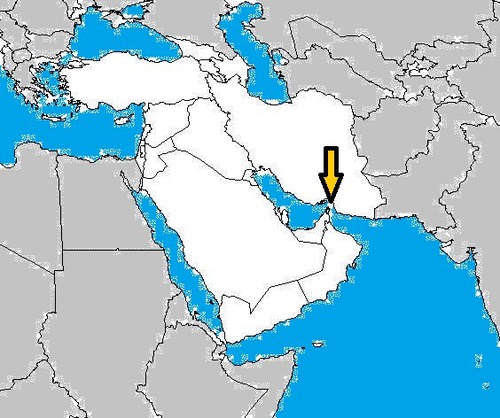
19
New cards
North America
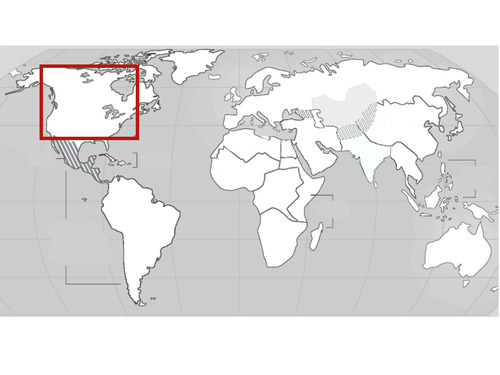
20
New cards
Central America
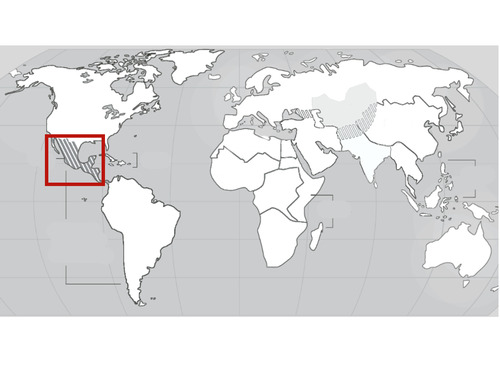
21
New cards
Caribbean
22
New cards
South America
23
New cards
The Americas
24
New cards
Western Europe
25
New cards
Mediterranean
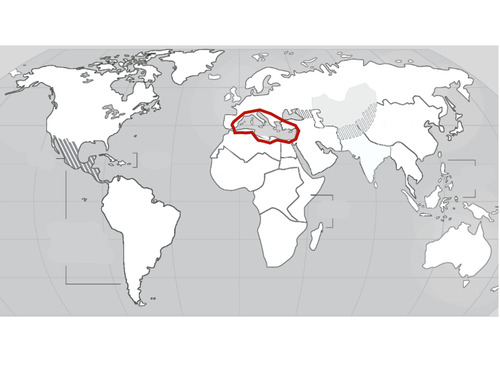
26
New cards
Eastern Europe
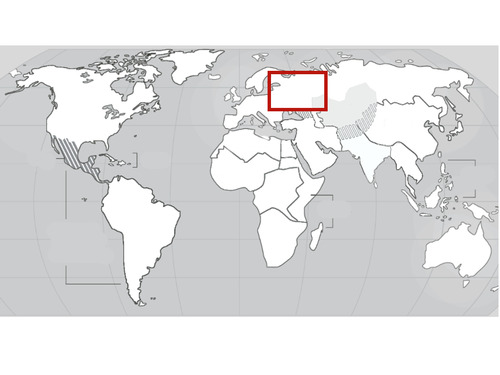
27
New cards
Central Asia
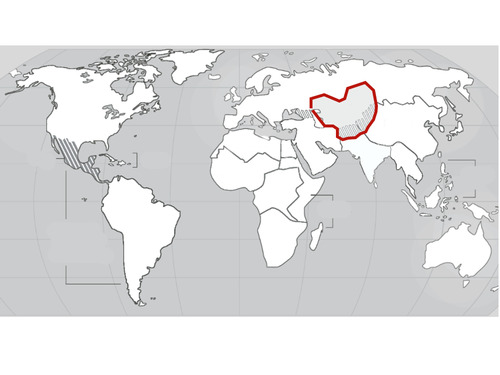
28
New cards
Middle East
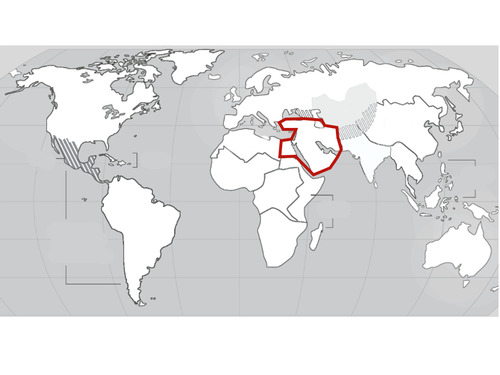
29
New cards
South Asia
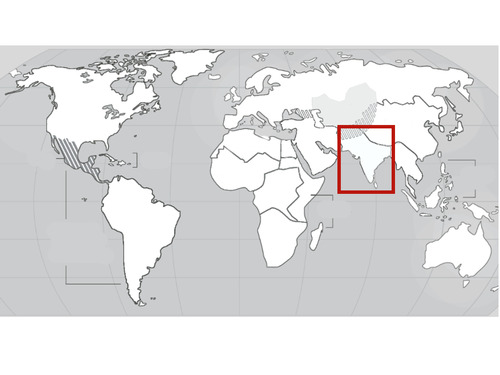
30
New cards
East Asia
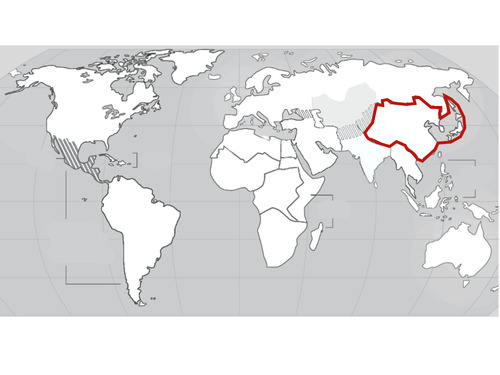
31
New cards
Southeast Asia
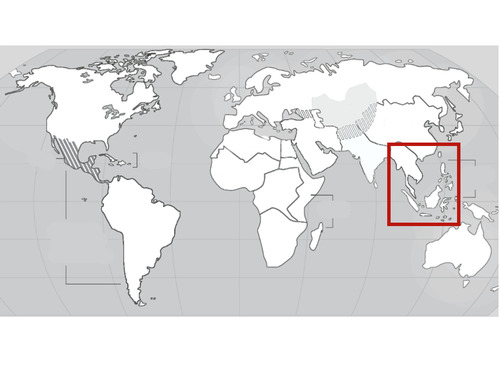
32
New cards
Oceania
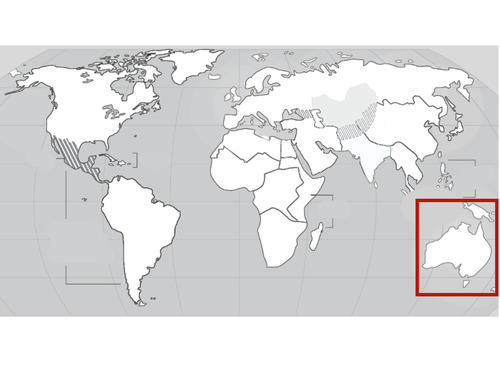
33
New cards
North Africa
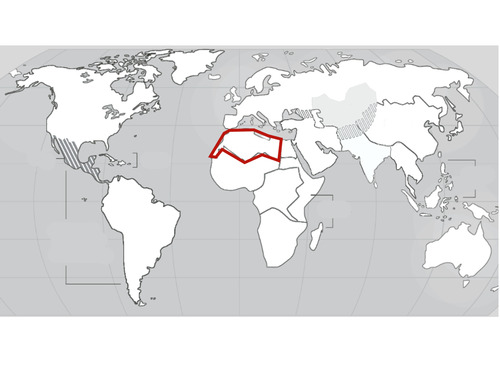
34
New cards
West Africa
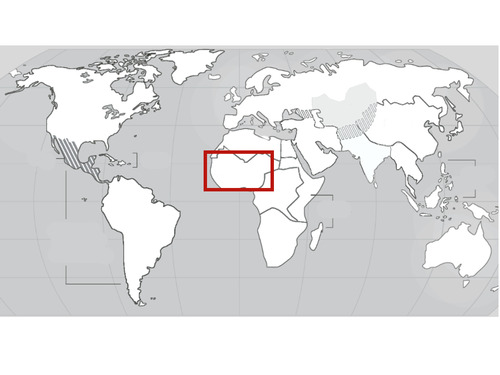
35
New cards
Central Africa
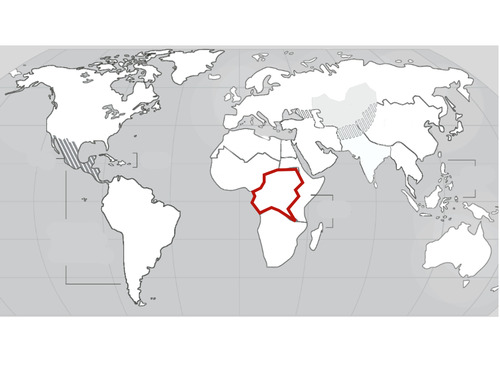
36
New cards
South Africa
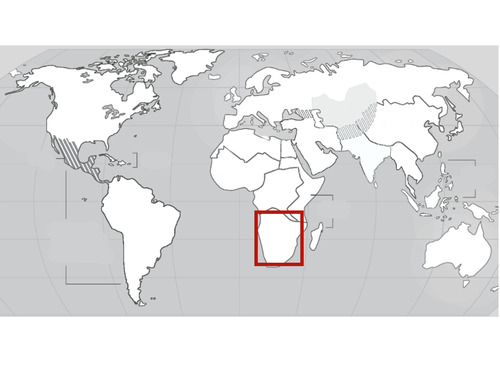
37
New cards
East Africa
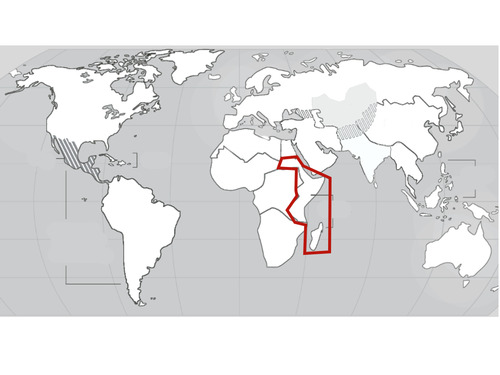
38
New cards
Africa
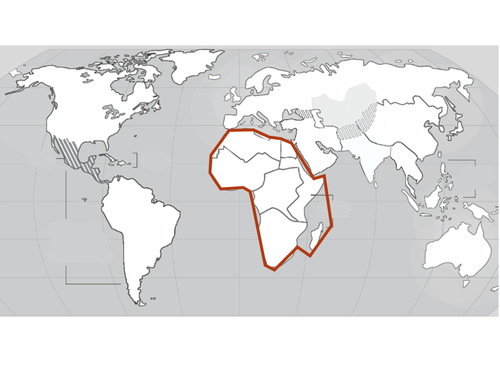
39
New cards
Pacific Ocean
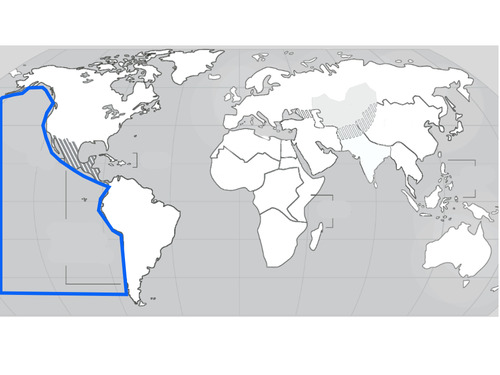
40
New cards
Atlantic Ocean
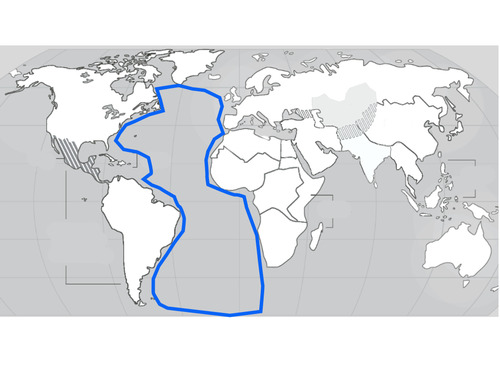
41
New cards
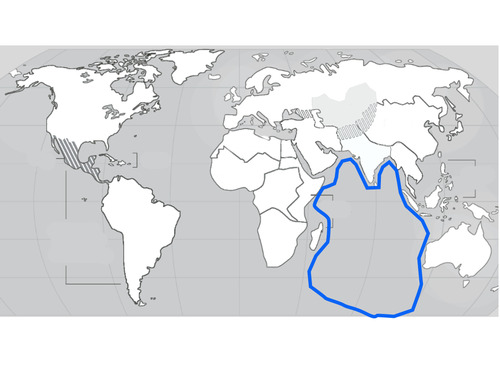
Indian Ocean
42
New cards
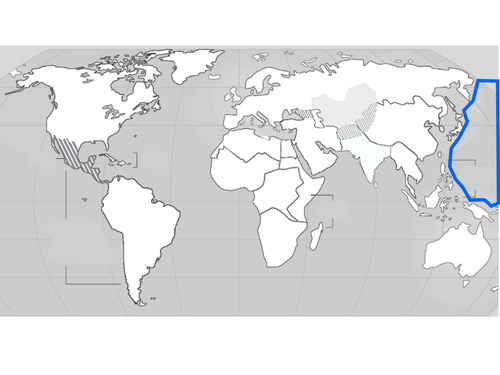
Pacific Ocean
43
New cards
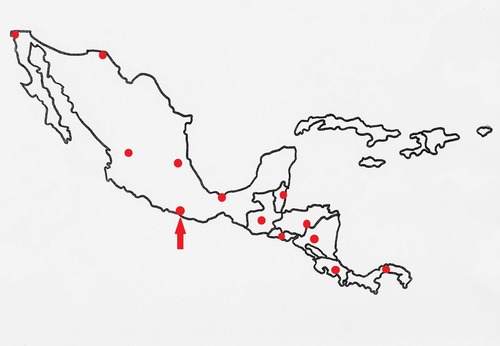
Acapulco
44
New cards
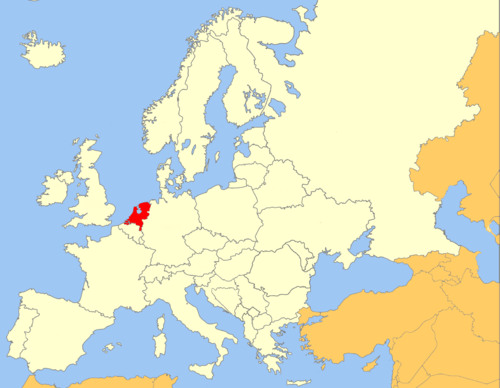
Amsterdam
45
New cards
Beijing
46
New cards
Calicut
47
New cards
Canton
48
New cards
Delhi
49
New cards
Goa
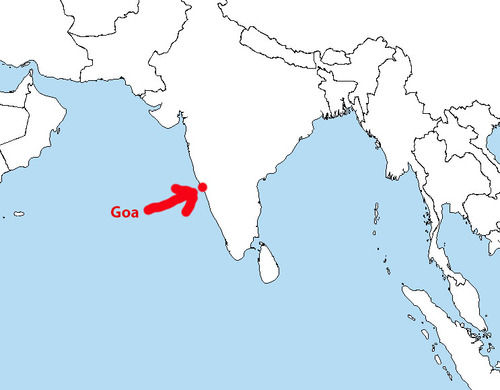
50
New cards
Isfahan
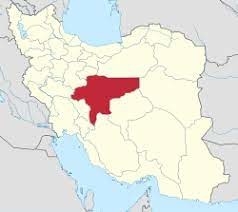
51
New cards
Istanbul
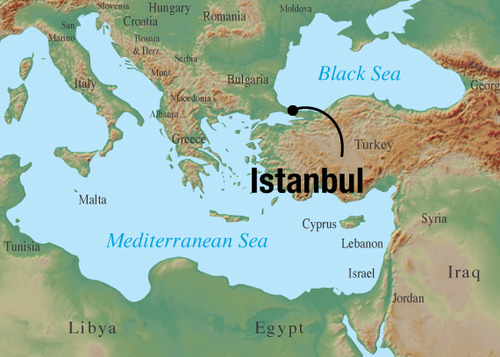
52
New cards
Kyoto
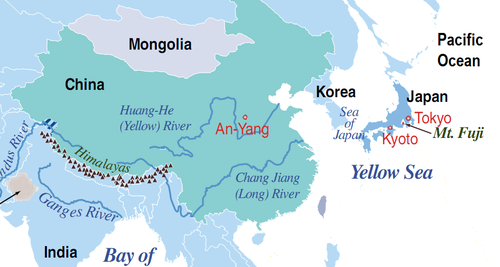
53
New cards
Lima
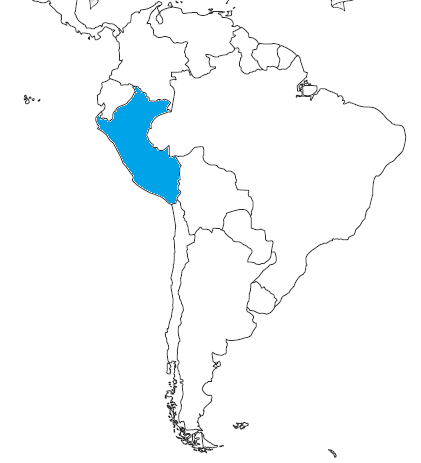
54
New cards
London
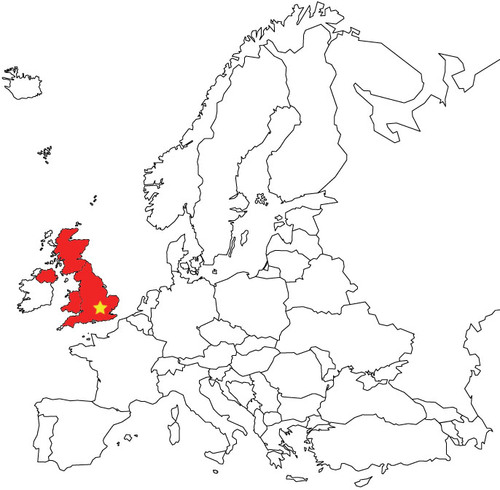
55
New cards
Macao
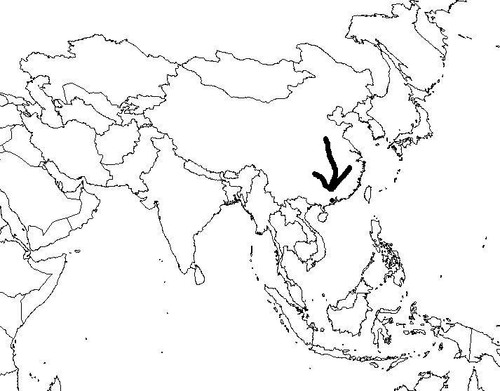
56
New cards
Malacca
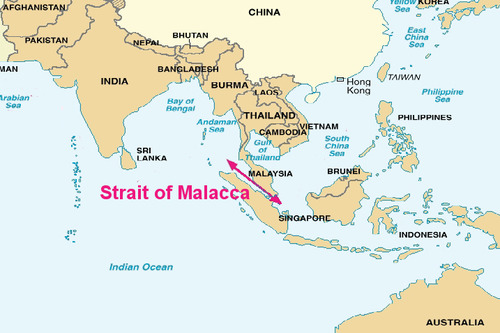
57
New cards
Manila
58
New cards
Mexico City
59
New cards
Mombasa
60
New cards
Moscow
61
New cards
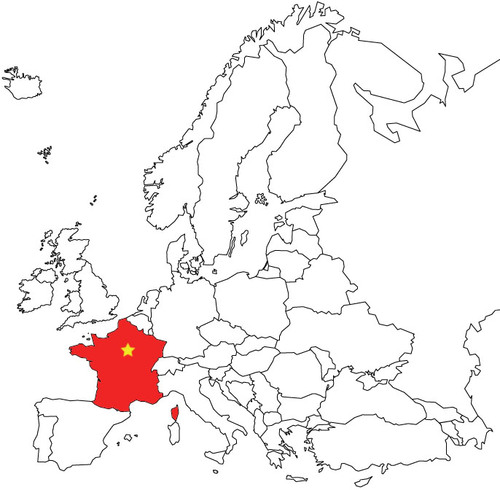
Paris
62
New cards
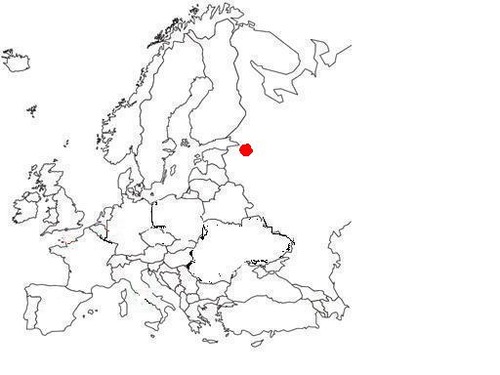
St. Petersburg
63
New cards
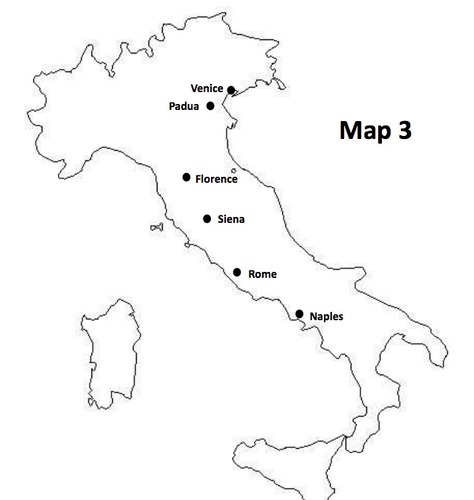
Venice
64
New cards
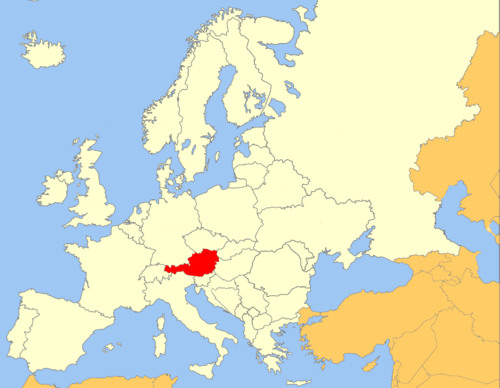
Vienna
65
New cards
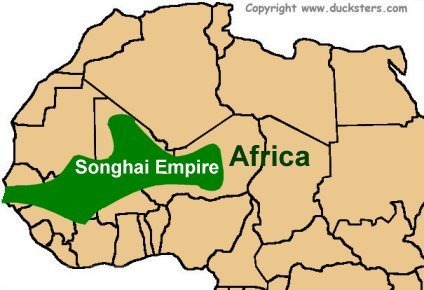
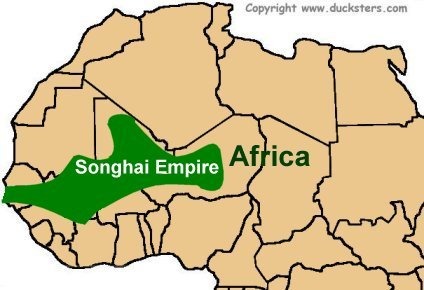
Songhai Empire
66
New cards
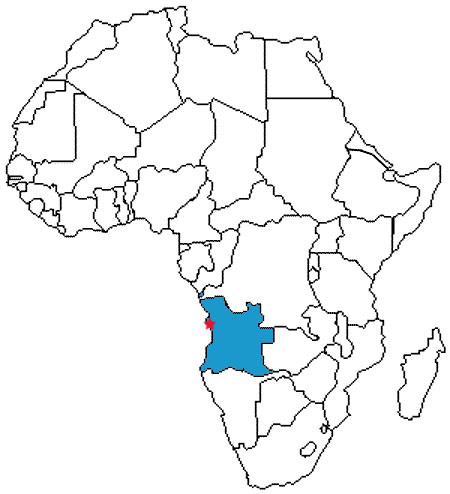
Kongo
67
New cards
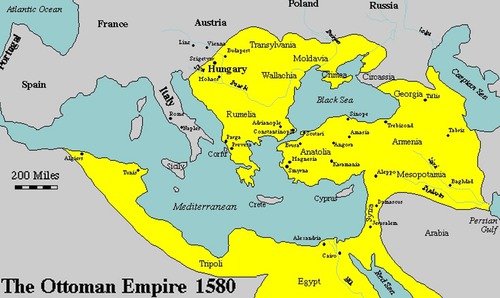
Ottoman Empire
68
New cards
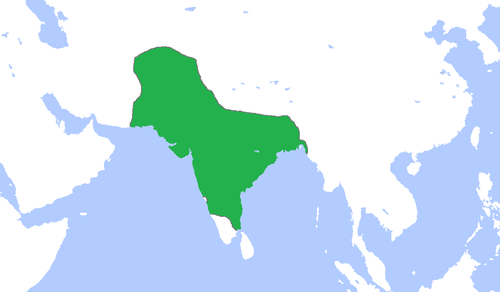
Mughal Empire
69
New cards
Russia
70
New cards
Dahomey
West African kingdom that became strong through its rulers' exploitation of the slave trade.
71
New cards
Ming dynasty
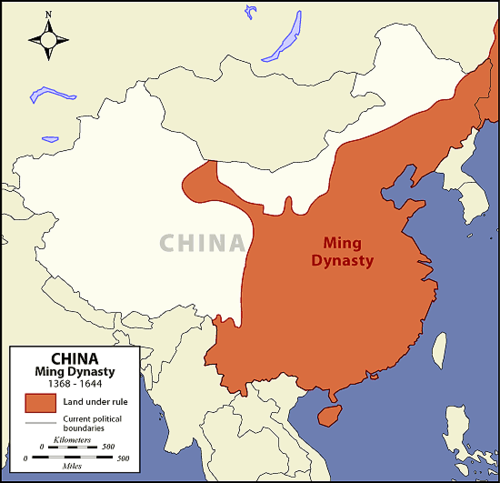
72
New cards
Qing dynasty
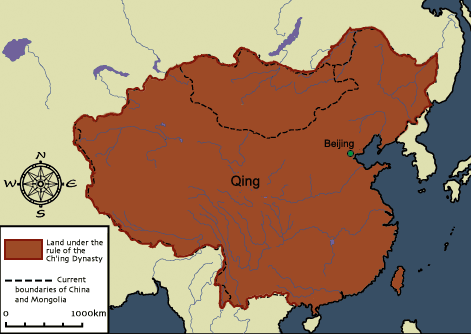
73
New cards
Tokugawa shogunate
74
New cards
African Diaspora
Name given to the spread of African peoples across the Atlantic via the slave trade.
75
New cards
Akbar
The most famous emperor of India's Mughal Empire (r. 1556-1605); his policies are noted for their efforts at religious tolerance and inclusion.
76
New cards
Aurangzeb
Mughal emperor (r. 1658-1707) who reversed his predecessors' policies of religious tolerance and attempted to impose Islamic supremacy.
77
New cards
Benin
West African kingdom (in what is now Nigeria) whose strong kings sharply limited engagement with the slave trade.
78
New cards
Bhakti
Hindu devotional movement that flourished in the early modern era, emphasizing music, dance, poetry, and rituals as means by which to achieve direct union with the divine.
79
New cards
cartaz
A pass that the Portuguese required of all merchant vessels attempting to trade in the Indian Ocean.
80
New cards
Catholic Counter-Reformation
An internal reform of the Catholic Church in the sixteenth century; thanks especially to the work of the Council of Trent (1545-1563), Catholic leaders clarified doctrine, corrected abuses and corruption, and put a new emphasis on education and accountability.
81
New cards
Columbian exchange
The massive transatlantic interaction and exchange between the Americas and Afro-Eurasia that began in the period of European exploration and colonization.
82
New cards
conquistadores
Spanish conquerors of the Native American lands, most notably the Aztec and Inca empires.
83
New cards
Council of Trent
The main instrument of the Catholic Counter- Reformation (1545-1563), at which the Catholic Church clarified doctrine and corrected abuses
84
New cards
creoles
Spaniards born in the Americas.
85
New cards
Dahomey
West African kingdom that became strong through its rulers' exploitation of the slave trade.
86
New cards
Daimyo
Feudal lords of Japan who ruled with virtual independence thanks to their bands of samurai warriors.
87
New cards
Darwin, Charles
Highly influential English biologist (1809-1882) whose theory of natural selection continues to be seen by many as a threat to revealed religious truth.
88
New cards
deism
Belief in a divine being who created the cosmos but who does not intervene directly in human affairs.
89
New cards
devshirme
The tribute of boy children that the Ottoman Turks levied from their Christian subjects in the Balkans; the Ottomans raised the boys for service in the civil administration or in the elite Janissary infantry corps.
90
New cards
Edict of Nantes
Issued by French king Henry IV that granted considerable religious toleration to French Protestants and ended the French Wars of Religion.
91
New cards
European Enlightenment
European intellectual movement of the eighteenth century that applied the lessons of the Scientific Revolution to human affairs and was noted for its commitment to open-mindedness and inquiry and the belief that knowledge could transform human society.
92
New cards
Freud, Sigmund
Austrian doctor and the father of modern psychoanalysis (1856-1939); his theories about the operation of the human mind and emotions remain influential today
93
New cards
Galilei, Galileo
Italian astronomer (1564-1642) who further developed the ideas of Copernicus and whose work was eventually suppressed by the Catholic Church.
94
New cards
Huguenots
The Protestant minority in France.
95
New cards
Jesuits in China
Series of missionaries in the late sixteenth and seventeenth centuries who, inspired by the work of Matteo Ricci, made extraordinary efforts to understand and become a part of Chinese culture in their efforts to convert the Chinese elite, although with limited success.
96
New cards
Little Ice Age
A period of cooling temperatures and harsh winters that lasted for much of the early modern era.
97
New cards
Luther, Martin
German priest and theologian (1483-1546) who inaugurated the Protestant Reformation movement in Europe
98
New cards
Manila
Capital of the Spanish Philippines and a major multicultural trade city that already had a population of more than 40,000 by 1600.
99
New cards
Marx, Karl
German philosopher (1818-1883) whose view of human history as a class struggle formed the basis of socialism.
100
New cards
mestizo
Literally, "mixed"; a term used to describe the mixed-race population of Spanish colonial societies in the Americas.