ALL ABOUT BONES
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Matrix
The matrix is made up of collagen fibers embedded in protein and polysaccharides
Weight of bone
1/3 organic
Collagen (protein)
2/3 Inorganic salts
Calcium (ca)
Phosphorus (p)
Magnesium (mg)
Function of bones
Support
Protection
Leverage
Storage
Calcium (Blood cell formation)
Hematopoiesis
Osteoblasts
Cells that produce bone
Harden matrix through ossification
Once surrounded by bone osteoblasts are called osteocytes
Osteoclasts
Remodel/Remove bone
Volkmann Canals
Channels through bone matrix that contain blood vessels
Blood vessels in the Volkmann canals join with blood vessels in the Haversian system
Nutrient foramina
Channels in many large bones
Contain large blood vessels, lymph vessels, and nerves
Cancellous bone
Bone: Light and spongy
Red bone marrow
Compact bone
Dense and heavy
Cancellous bone
Tiny spicules of bone that appear randomly arranged
Spaces between the spicules contain bone marrow
Bone marrow
Fills the spaces within bones
2 types: Red bone marrow, Yellow bone marrow
Red bone marrow
Forms blood cells
Majority of the bone marrow of young animals
Only small portion in older animals
Yellow bone marrow
Consists primarily of adipose connective tissue
Most common in adult animals
Can revert to red bone marrow if needed
Compact bone
Shafts of long bones
Outside layer of all bones
Composed of Haversian systems that run lengthwise with the bone
Haversian system
Concentric layers of ossified bone matrix arranged around a central canal
Blood and lymph vessels and nerve
Long bones
Femur
Humerus
Short bone
Carpal
Tarsal bones
Flat bone
Scapula
Irregular bone
Sesamoid bones
Vertebrae
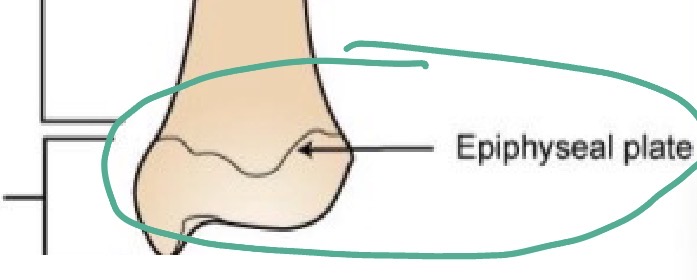
Epiphyseal plates
Cartilage located between diaphysis and epiphyses of bone
Sites where new bone develops to allow long bones to lengthen
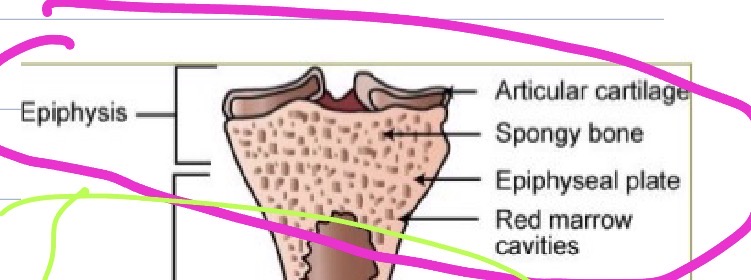
Epiphysis
Articular cartilage
Spongy bone
Epiphyseal plate
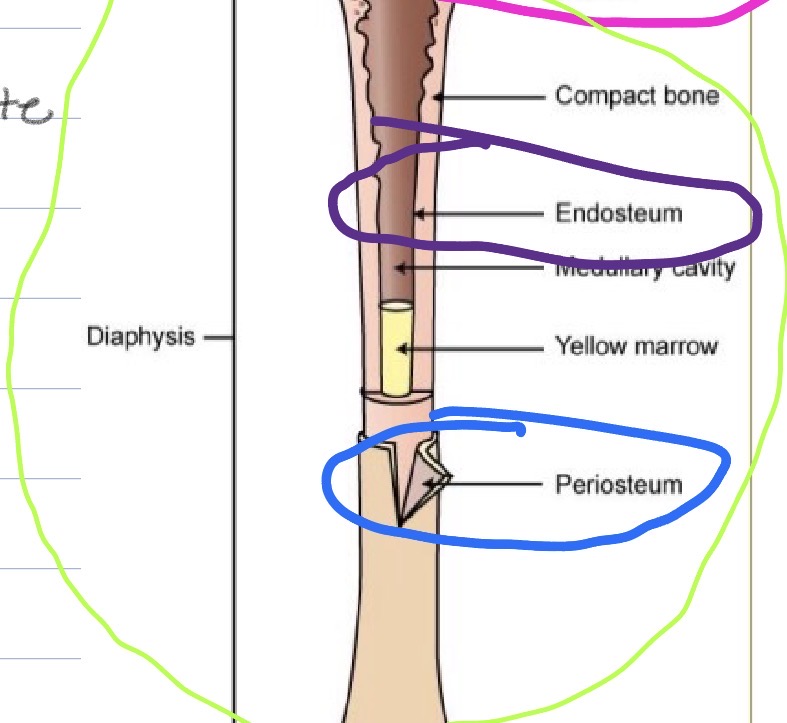
Diaphysis
Compact bone
Periosteum
Endosperm
Medullary cavity
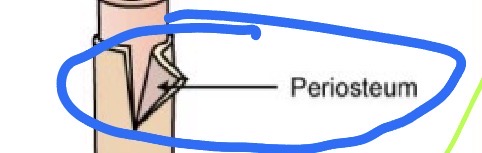
Periosteum
Membrane that covers outer surfaces of bones
Outer layer is composed of fibrous tissue
Inner layer contains osteoblasts
Not present on articular surfaces

Endosteum
Membrane that lines the hollow interior surfaces of bones
Also contains osteoblasts
Primary
Growth center: Bones develop in the diaphyses
Cartilage bone
Cartilage is removed as bone is created
Secondary
Growth centers: Develops in the epiphyses of the bone
Ossification
When the bone has reached its full size the Epiphyseal plates completely ossify
Condyle
Large round articular surface
Head
Spherical articular surface on the proximal end of a long bone
Joins with the shaft of the bone at the neck region
Facet
Flat articular surface
Projections
Off a bone surface
Foramen
Hole in a bone; may contain blood vessels, nerves
Fossa
Depressed areas on the surface of a bone
Axial skeleton
Bones of the head and trunk
Bones of the “the main body mass”
Appendicular
Bones of the limbs (extremities)
Axial skeleton
Skull
Hyoid bone
Spinal column
Ribs
Sternum
Appendicular skeleton
Thoracic limb (foreleg)
Pelvic limb (rear leg)
Thoracic limb (proximal to distal)
Scapula
Humerus
Radius
Ulna
Carpal bones (carpus)
Metacarpal bones
Phalanges
Skull
Usually consists of 37 or 38 separate bones
Sutures
Most of the skull bones
Mandible
Is connected to the skull by a synovial joint