HBS 1.1.6 Bone Remodeling and Repair
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
1
New cards
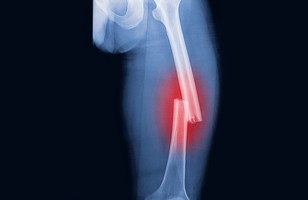
fracture
A crack or break in a bone.
2
New cards
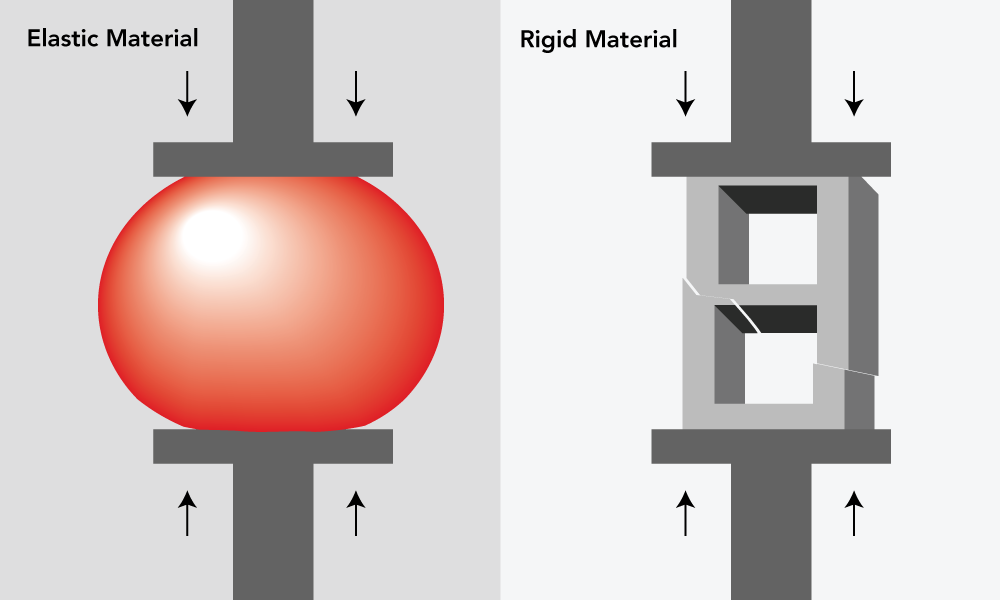
compression force
Compression force (or compressive force) occurs when a physical force presses inward on an object, causing it to become compacted.
3
New cards
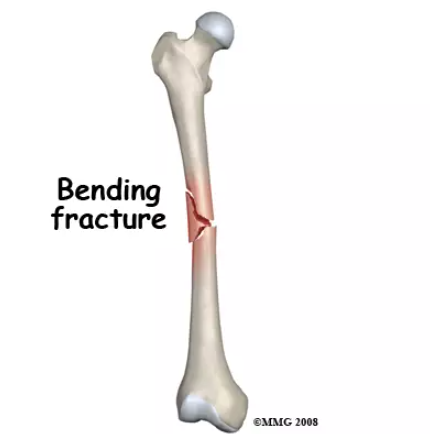
bending / transverse fracture
A bending fracture, also known as a flexural or tension fracture, occurs when a force is applied perpendicular to the long axis of a bone. This force causes the bone to bend, and if the stress is too great, it may result in a break.
4
New cards
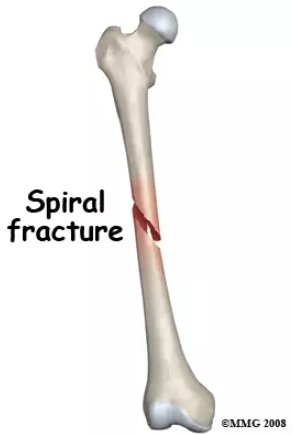
twisting / spiral fracture
A twisting fracture, also called a torsion or spiral fracture, occurs when a bone is subjected to a twisting or torsional force. This type of fracture results in a spiraling break along the bone's length, often seen in sports-related injuries or accidents.
5
New cards
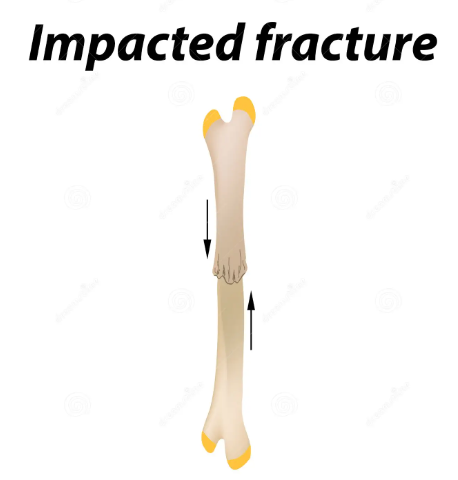
impact / comminuted fracture
An impact fracture occurs when a sudden and intense force is applied directly to a bone, causing it to break. This type of fracture is often the result of a high-impact collision or fall, such as in car accidents or sports injuries.
6
New cards
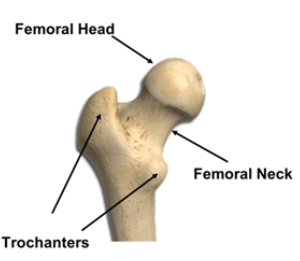
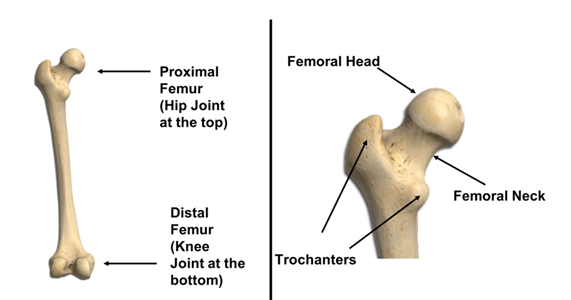
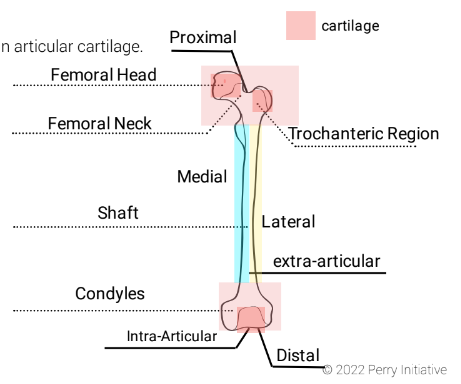
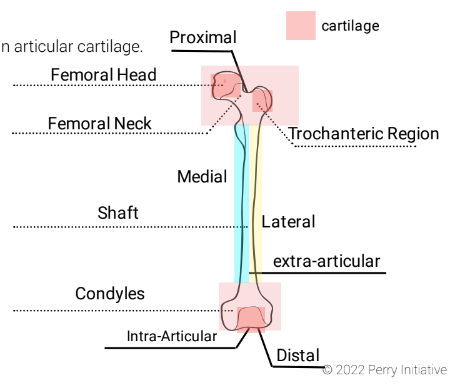
femoral head
Location: Rounded end of the thigh bone (femur) at the hip joint.
7
New cards
femoral neck
Location: Narrow section connecting the femoral head to the femur shaft.
8
New cards
trochanteric region
Location: Bony protrusions on the upper femur; includes greater and lesser trochanters.
9
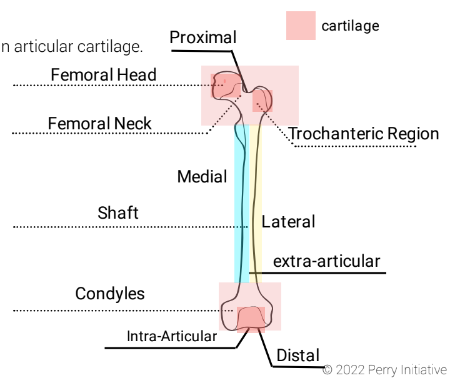
New cards
shaft
Location: Long, central part of a long bone.
10
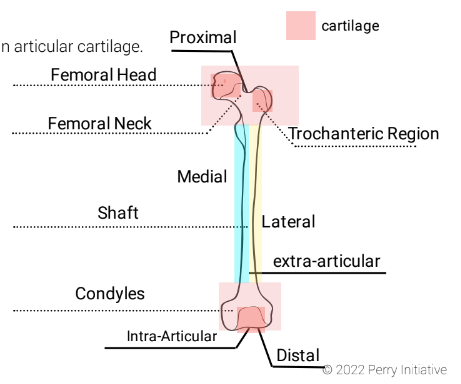
New cards
extra-articular
Location: Outside a joint; not involving the joint's interior.
11
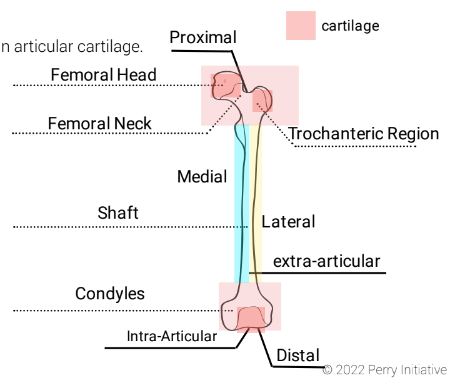
New cards
lateral condyle
Location: Rounded projection on the outer lower end of the femur, forming part of the knee joint.
12
New cards
medial condyle
Location: Rounded projection on the inner lower end of the femur, also part of the knee joint.
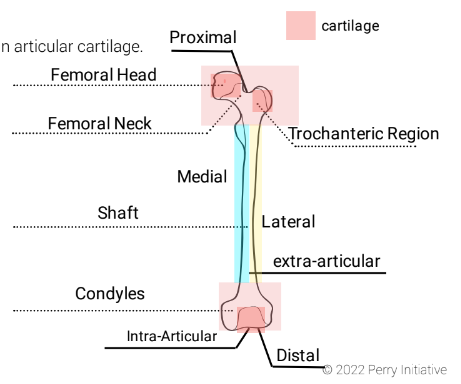
13
New cards
intra-articular
Location: Within a joint; affecting the joint's interior.
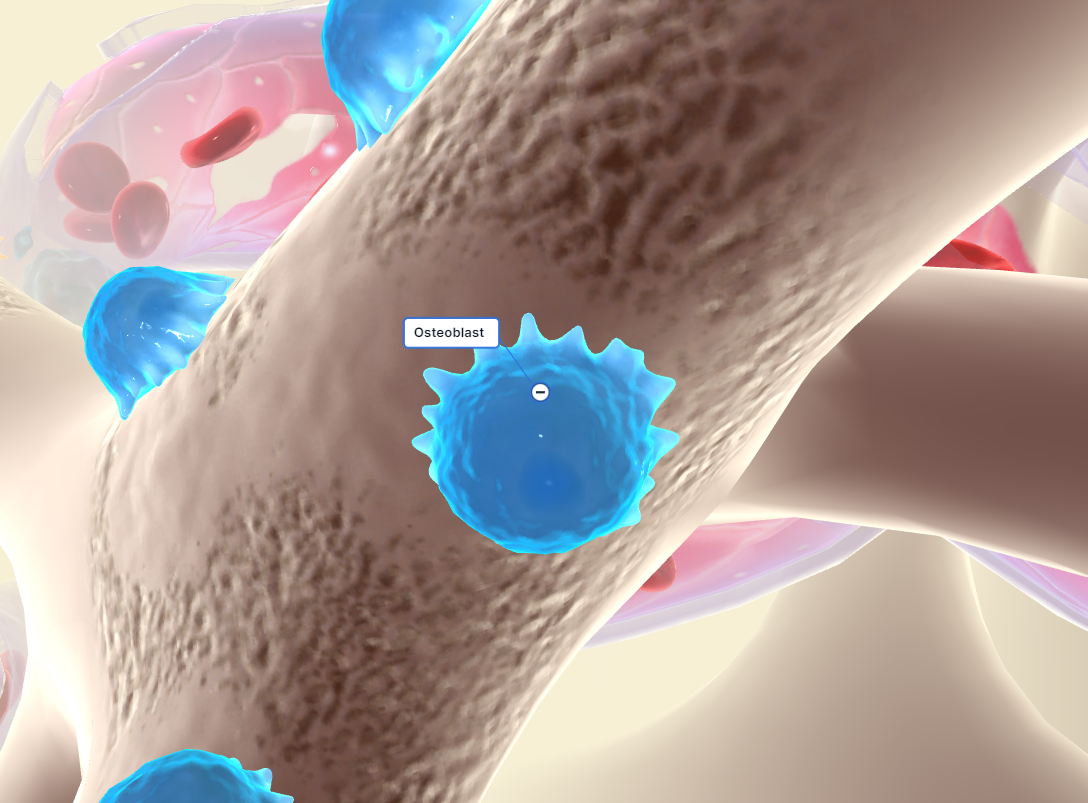
14
New cards
osteoblast
A bone-forming cell.
\
Function: Osteoblasts are bone-forming cells responsible for synthesizing and secreting the organic matrix of bone tissue, primarily composed of collagen. They play a crucial role in bone formation and mineralization, helping to build and strengthen bones.
\
Function: Osteoblasts are bone-forming cells responsible for synthesizing and secreting the organic matrix of bone tissue, primarily composed of collagen. They play a crucial role in bone formation and mineralization, helping to build and strengthen bones.
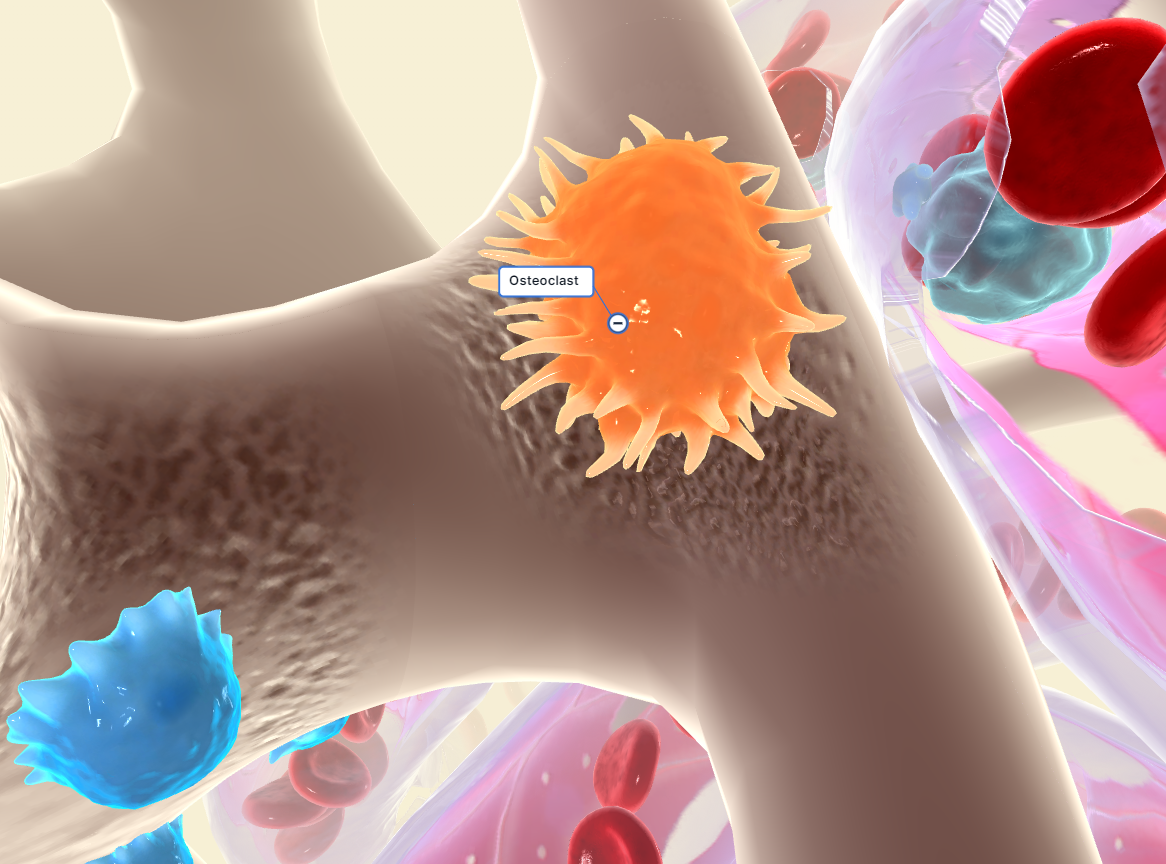
15
New cards
osteoclast
Any of the large multinucleate cells closely associated with areas of bone resorption (as in a fracture that is healing).
\
Function: Osteoclasts are bone-resorbing cells responsible for breaking down and remodeling bone tissue. They help regulate calcium and phosphate levels in the body by resorbing old or damaged bone, making space for new bone formation, and maintaining bone health through a dynamic process called bone remodeling.
\
Function: Osteoclasts are bone-resorbing cells responsible for breaking down and remodeling bone tissue. They help regulate calcium and phosphate levels in the body by resorbing old or damaged bone, making space for new bone formation, and maintaining bone health through a dynamic process called bone remodeling.
16
New cards
stages of fracture healing
1) hematoma formation
2) fibrocartilage callus formation
3) bony callus formation
4) bone remodeling
2) fibrocartilage callus formation
3) bony callus formation
4) bone remodeling
17
New cards
hematoma formation
Blood vessels that are ruptured during the break swell to form a mass called a hematoma. This mass forms between the broken bones. This clotting reduces the blood supply to many of the cells in the area of injury, and as a result, these cells die.
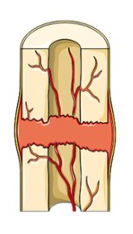
18
New cards
fibrocartilage callus formation
New capillaries begin to form into the clotted blood in the damaged area. Connective tissues cells form a mass of repair tissue called a fibrocartilage callus. This callus contains some cartilage, some bone, and collagen fibers. The combined mass closes the gap between the broken bones.
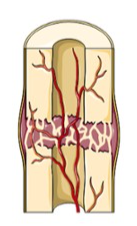
19
New cards
bony callus formation
The fibrocartilage callus is gradually replaced by one made of spongy bone. This new mass is referred to as the bony callus. Osteoclasts and osteoblasts move to the area and multiply.
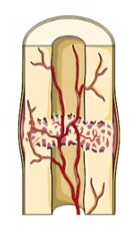
20
New cards
bone remodeling
Over the weeks and months to come, the callus is remodeled with the help of osteoclasts and osteoblasts. The shape of the bones will gradually return to normal, and there will eventually be little evidence of the fracture.
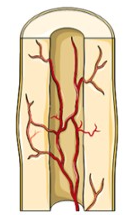
21
New cards
x-ray
X-ray scans provide a two-dimensional image of the interior of the body. X-rays are often used to provide images of the chest or broken bones.
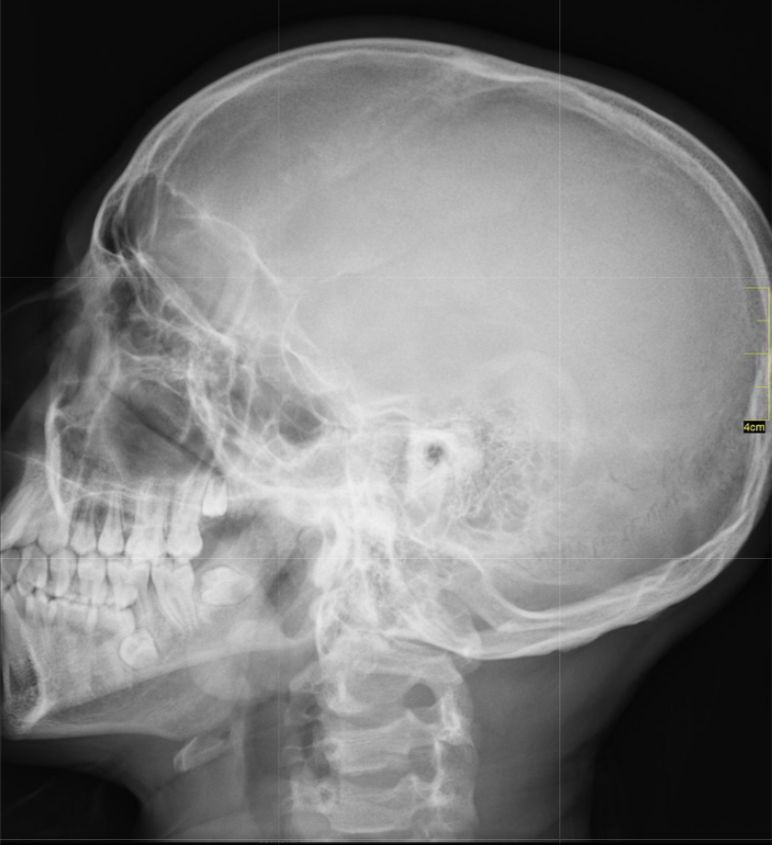
22
New cards
magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
MRIs do not use radiation and can provide detail of very fine soft tissue. In an MRI machine, the patient lies down in a cylinder that has a very large magnet. MRI machines create images of the body using a large magnet and radio waves.
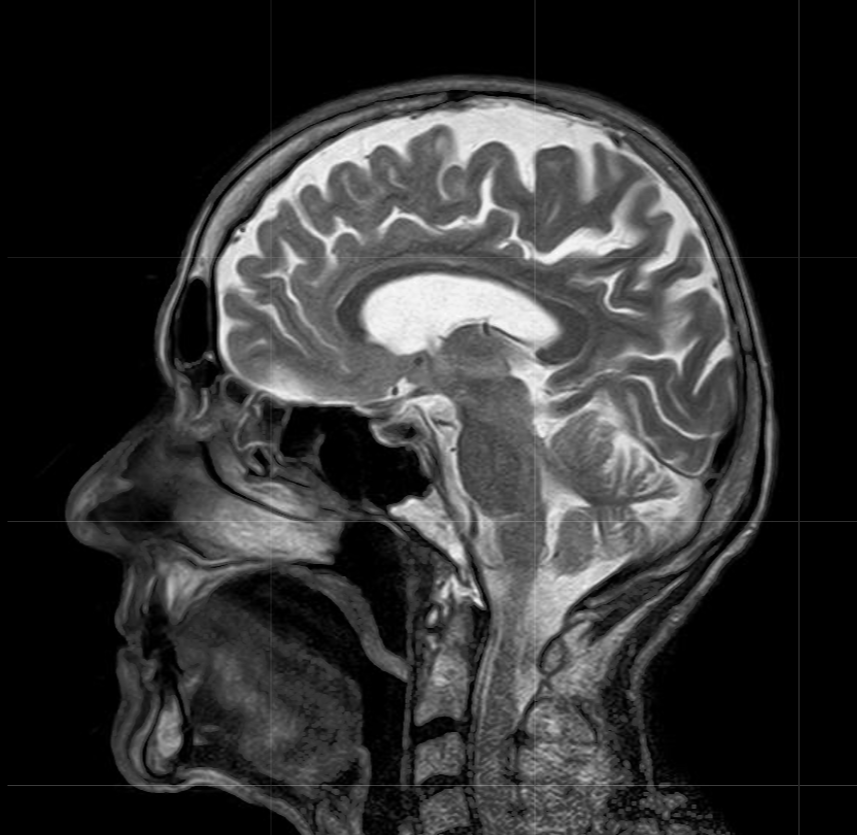
23
New cards
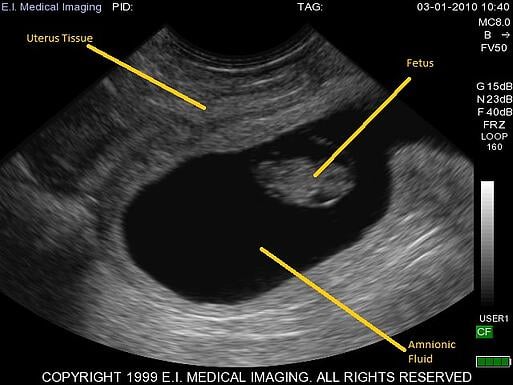
ultrasound imaging
Ultrasounds create an image of internal body structures such as tendons, muscles, joints, blood vessels, and internal organs. The ultrasound pulses echo off tissues with different reflection properties and are returned to the probe, which records and displays them as an image. Ultrasounds are one of the few diagnostic imaging techniques that capture motion.