Gr.9 Science Test Static Electricity
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Objects that have like charges _________ each other
repel
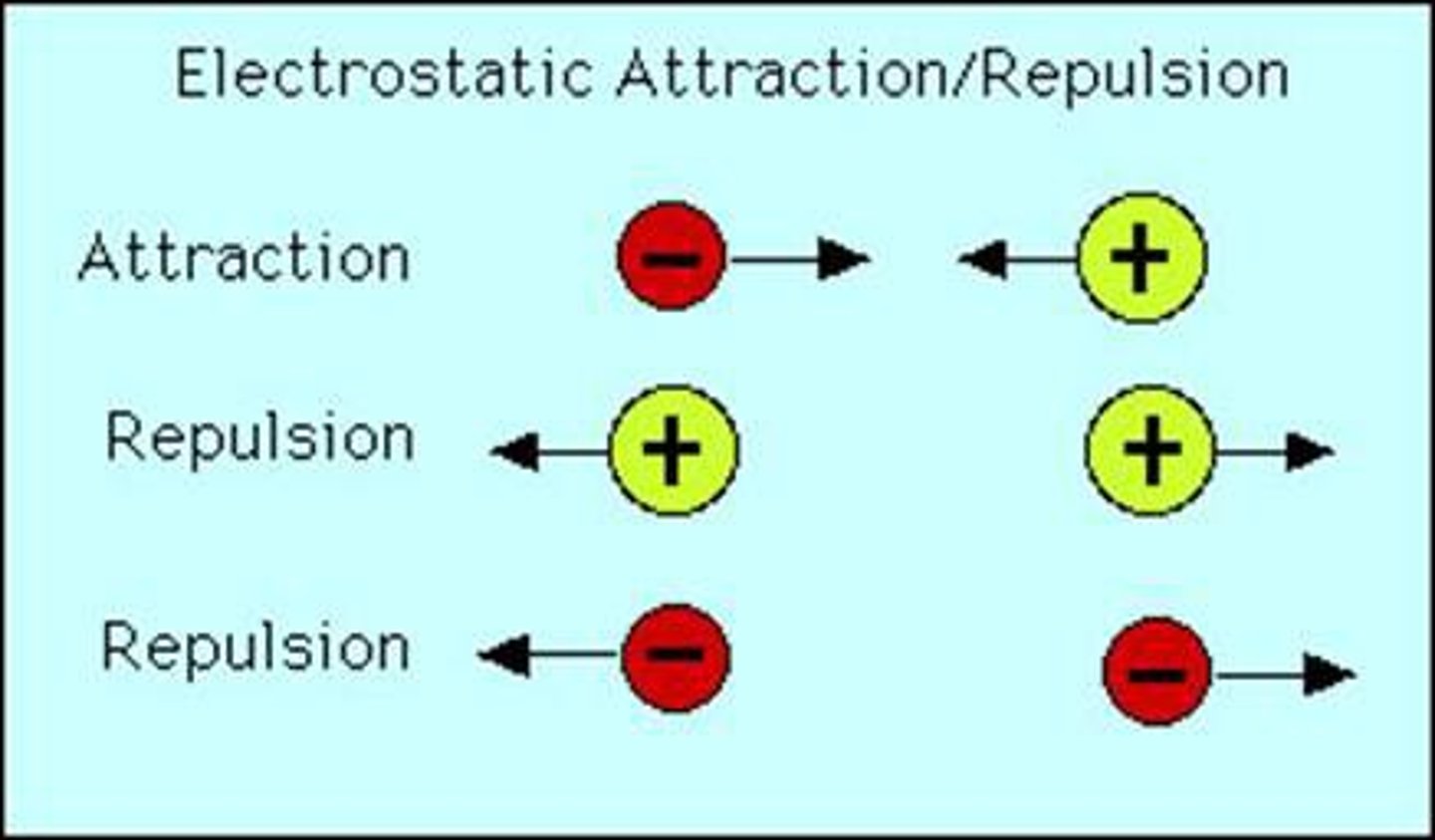
Objects that have opposite charges (p and n) __________ each other
attract
Neutral objects ____________ charged (p or n) objects
attract

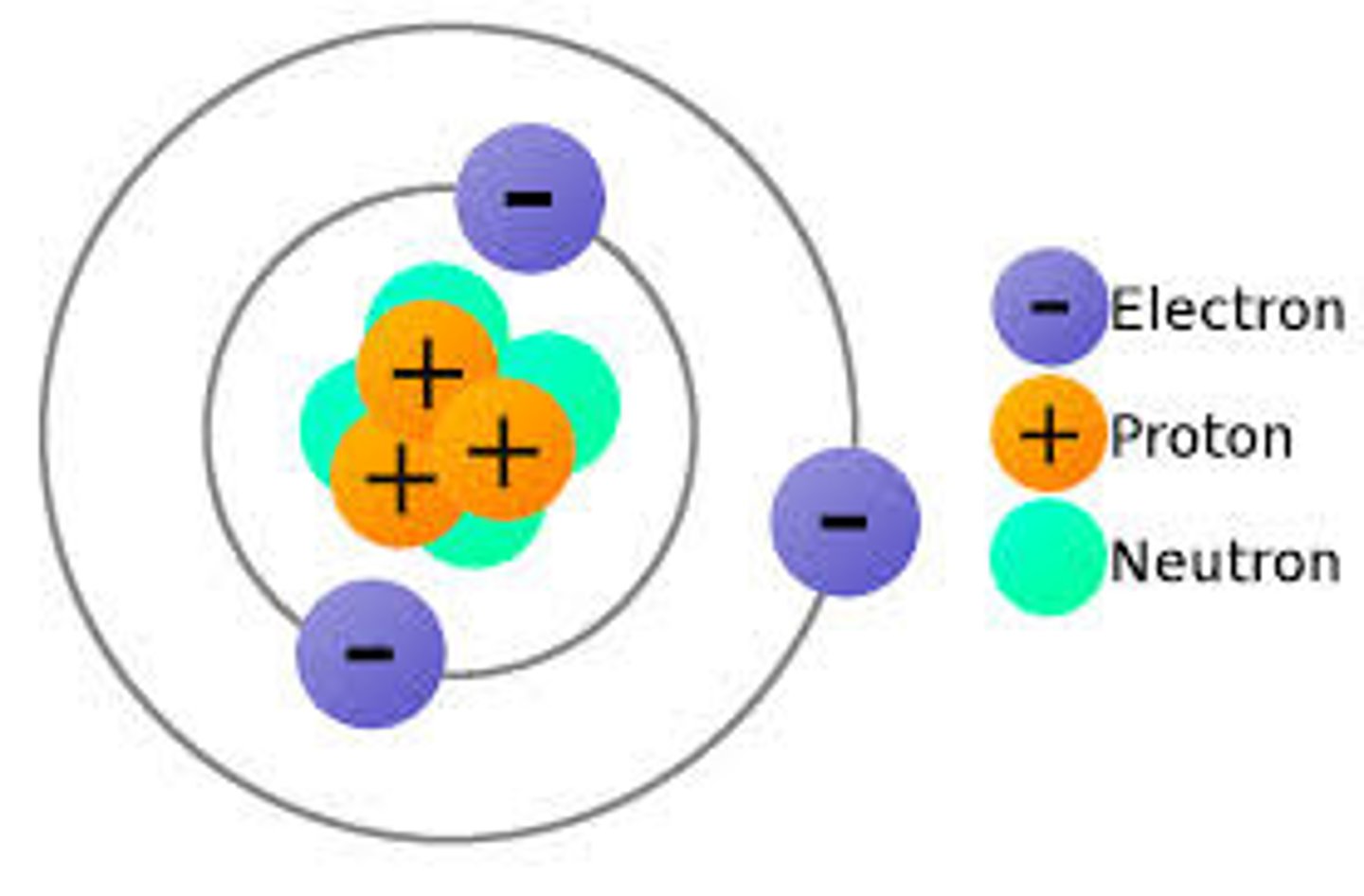
Where are protons found and what charge do they have?
Nucleus and positive
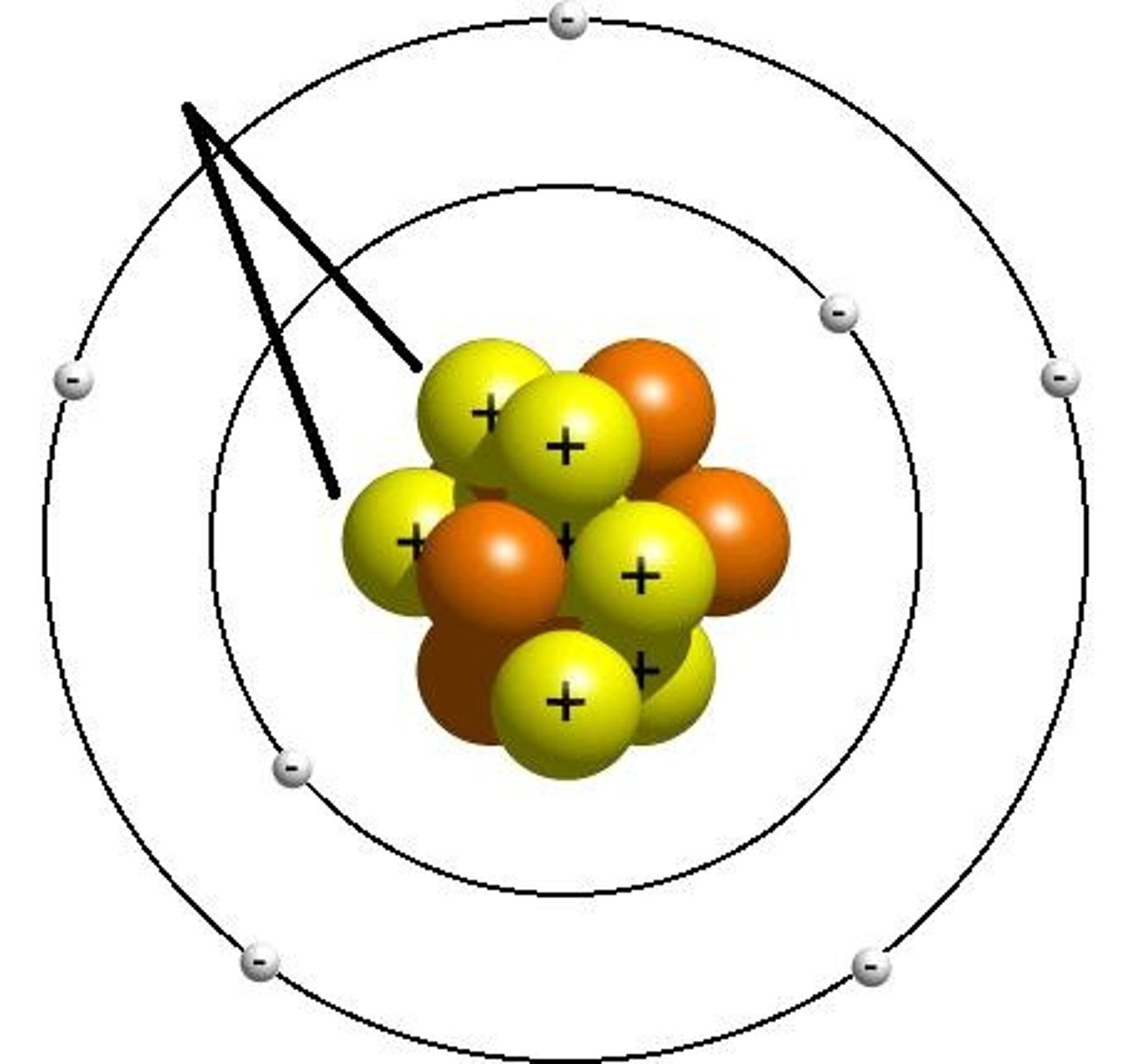
Where are electrons and what charge do they have?
The outside rings of the nucleus and negative charge
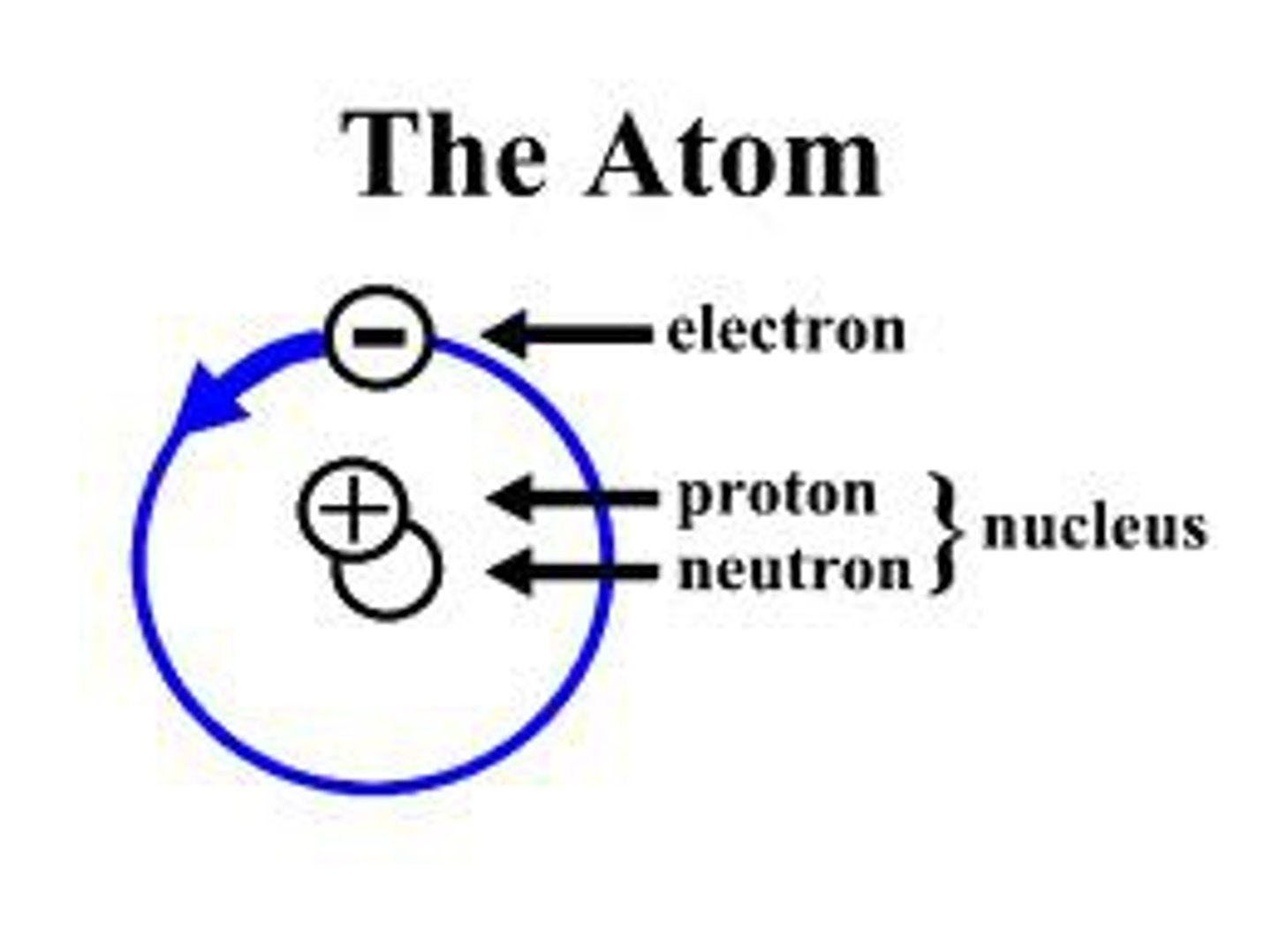
Where are neutrons found and what charge do they have?
The nucleus and neutral charge
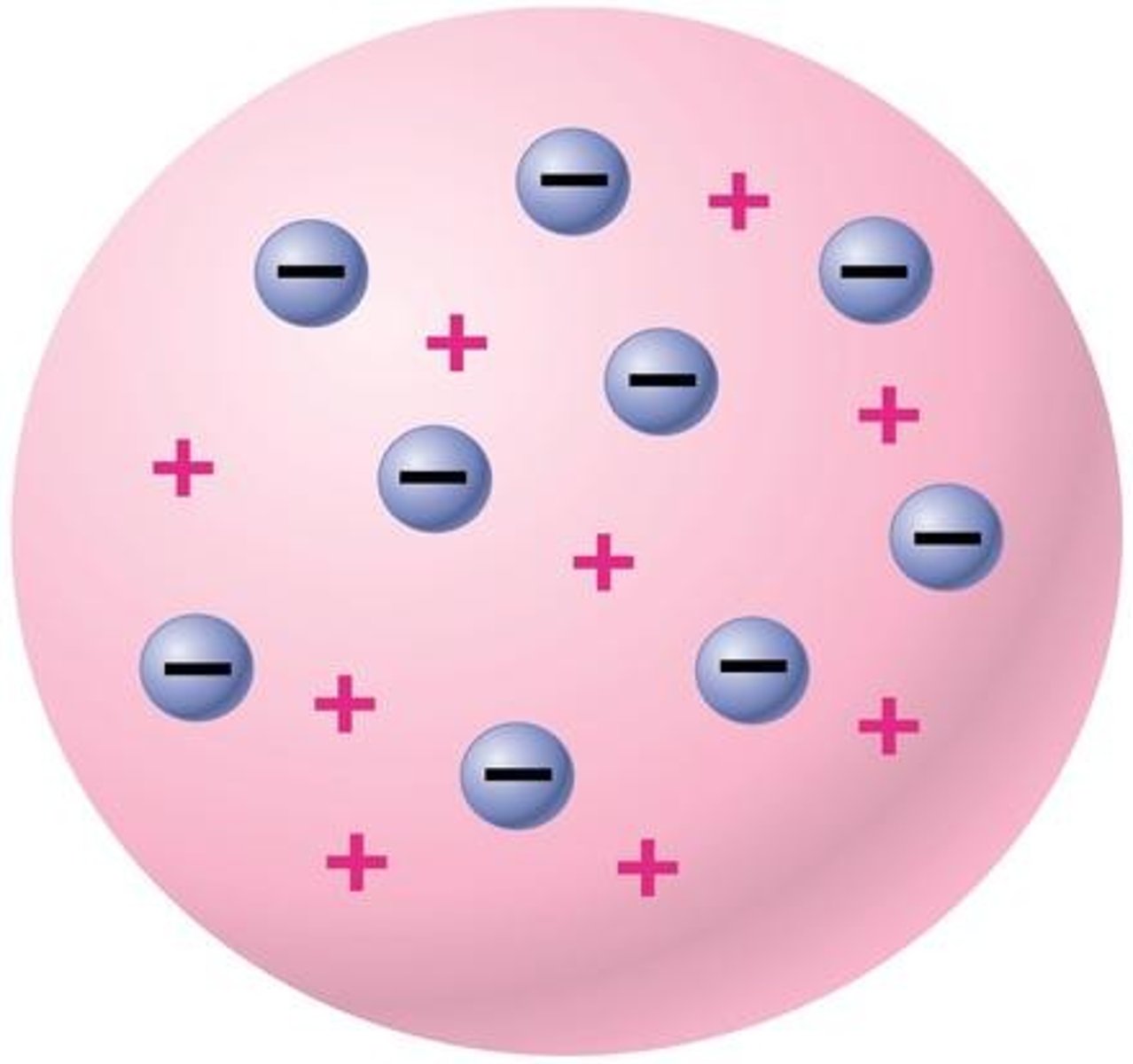
What is static electricity?
-The result of an imbalance between negative and positive charges in an object
-A stationary electric charged by friction
-A build-up of charge that stays in place
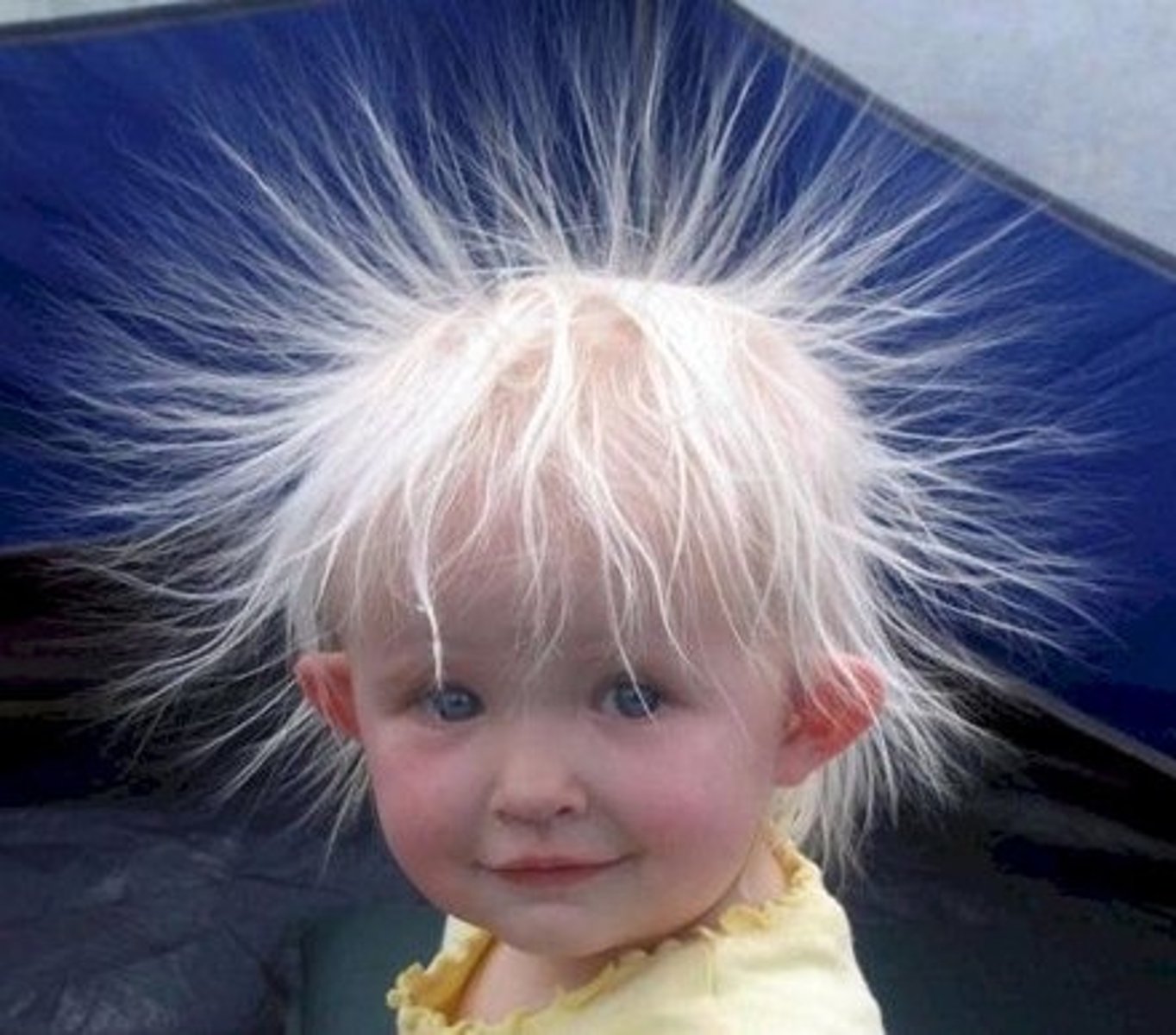

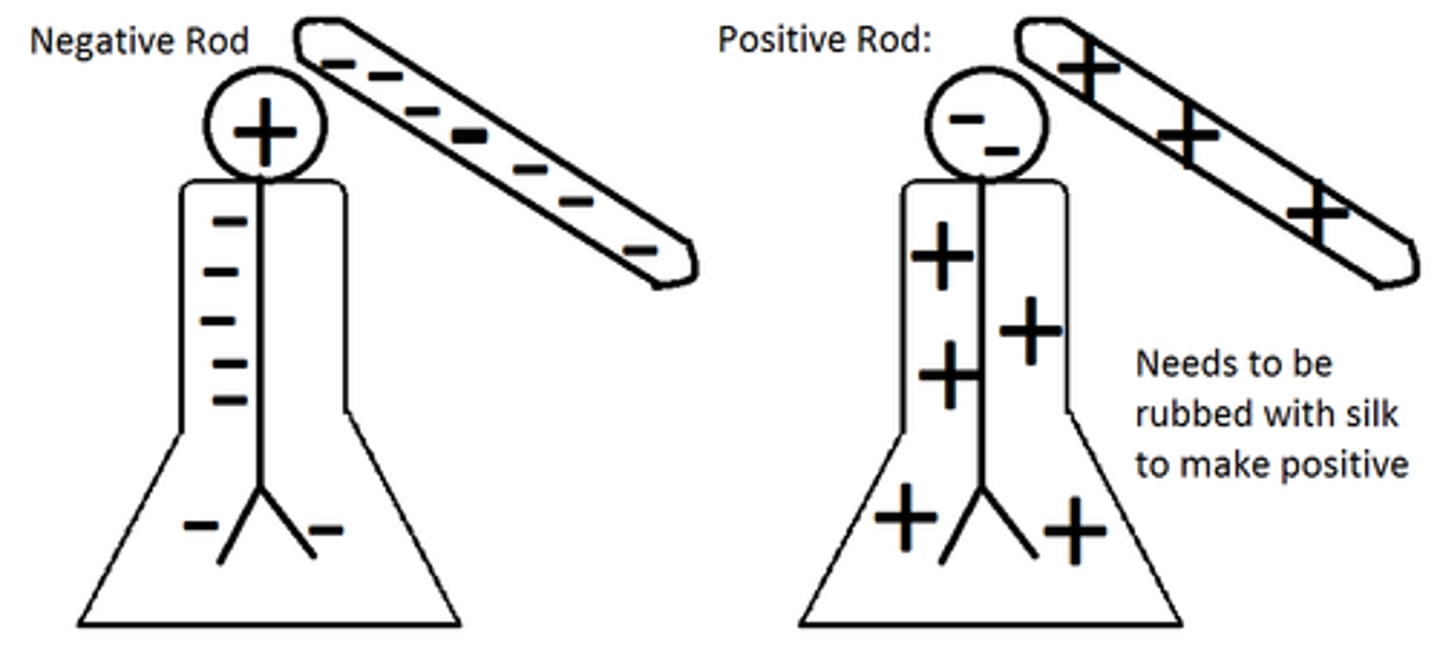
What happens when two neutral objects rub together?
One of the objects will give up its electrons to the other which will create one negative object and one positive
-The object with the lower electronegativity will give up the electrons
What happens when a charged object touches a neutral object?
If a negative object touches the neutral object it will become negative, if a positive object touches the neutral object it will become positive. This is called charging by contact.
What is charging by induction?
-Starts with one charged object (- or +) and one neutral object
-Charged object comes "close to" the neutral object, giving it a temporary charge
-+ object will charge leaves of neutral object + temporarily
- - object will charge leaves of neutral object - temporarily
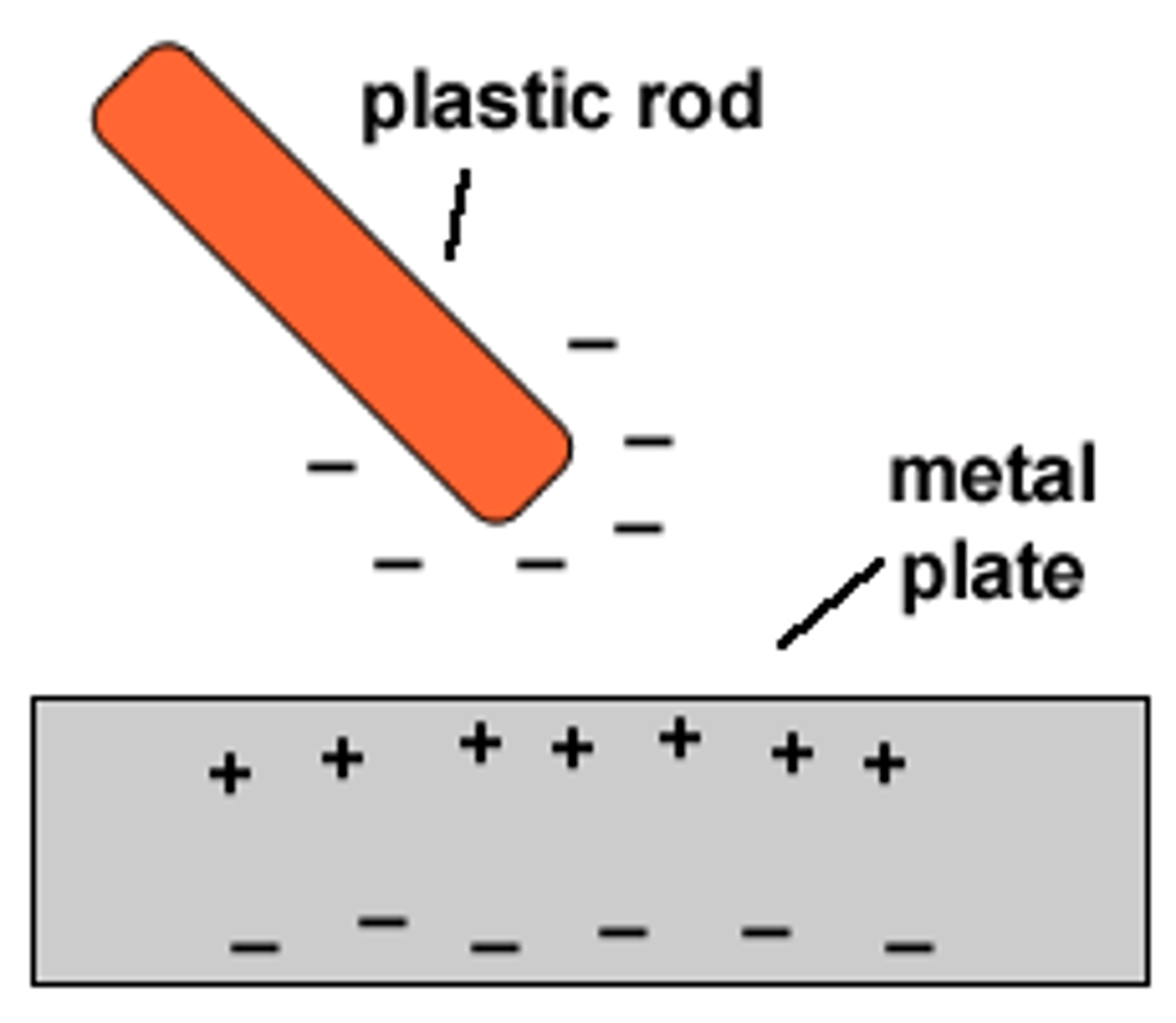
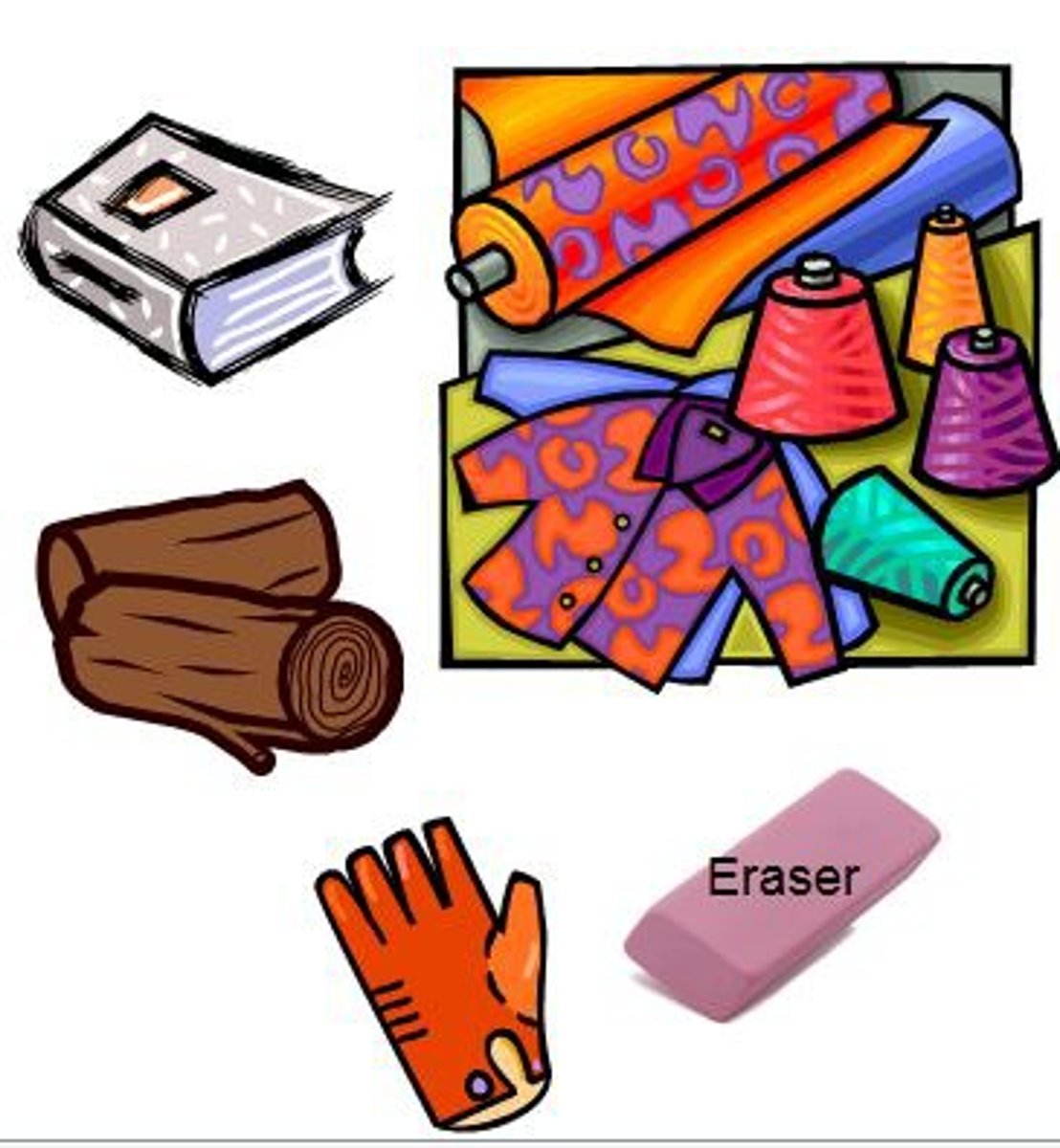
What is an insulator? What are some examples of an insulator?
Don't allow electrons to pass through
-Wood
-Plastic
-Rubber

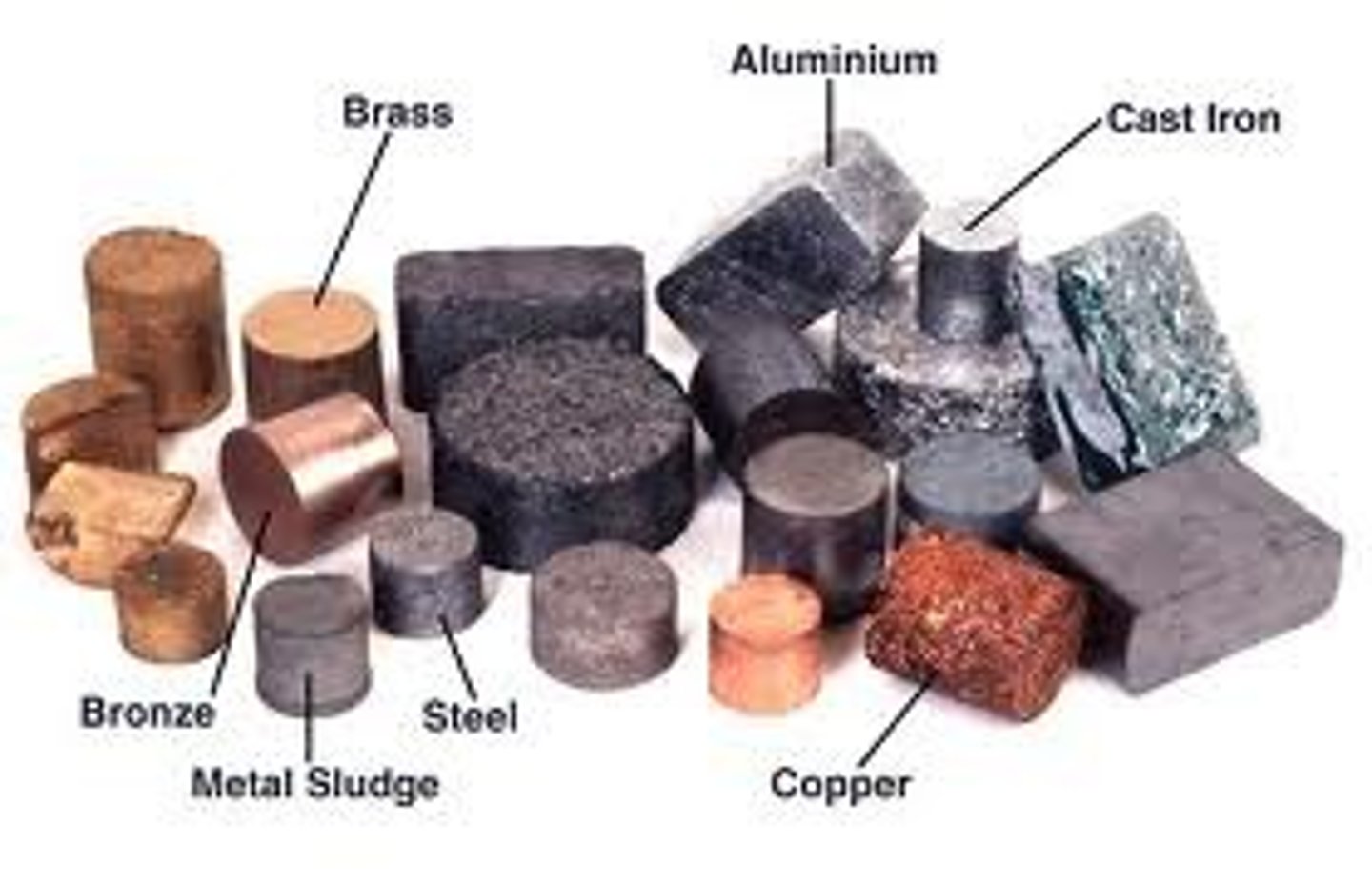
What is a conductor? Examples?
Allows electrons to move through easily
-Copper
-Aluminum
-Silver

What is grounding and what is an example of this?
Grounding is removing the charge from an object
-Using a conductor (metal, human, etc)

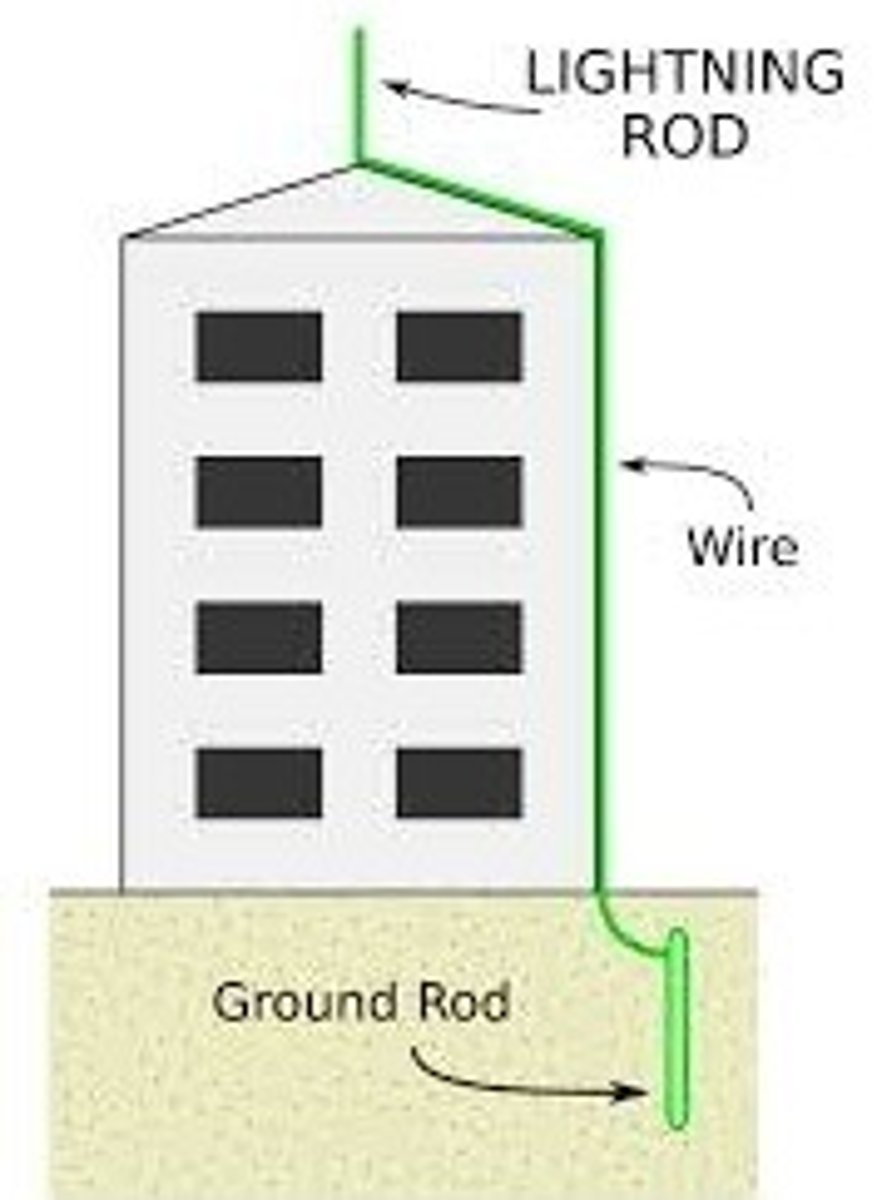
What is a lightning rod?
To protect a house or building from a direct lightning strike. It helps prevent fires.
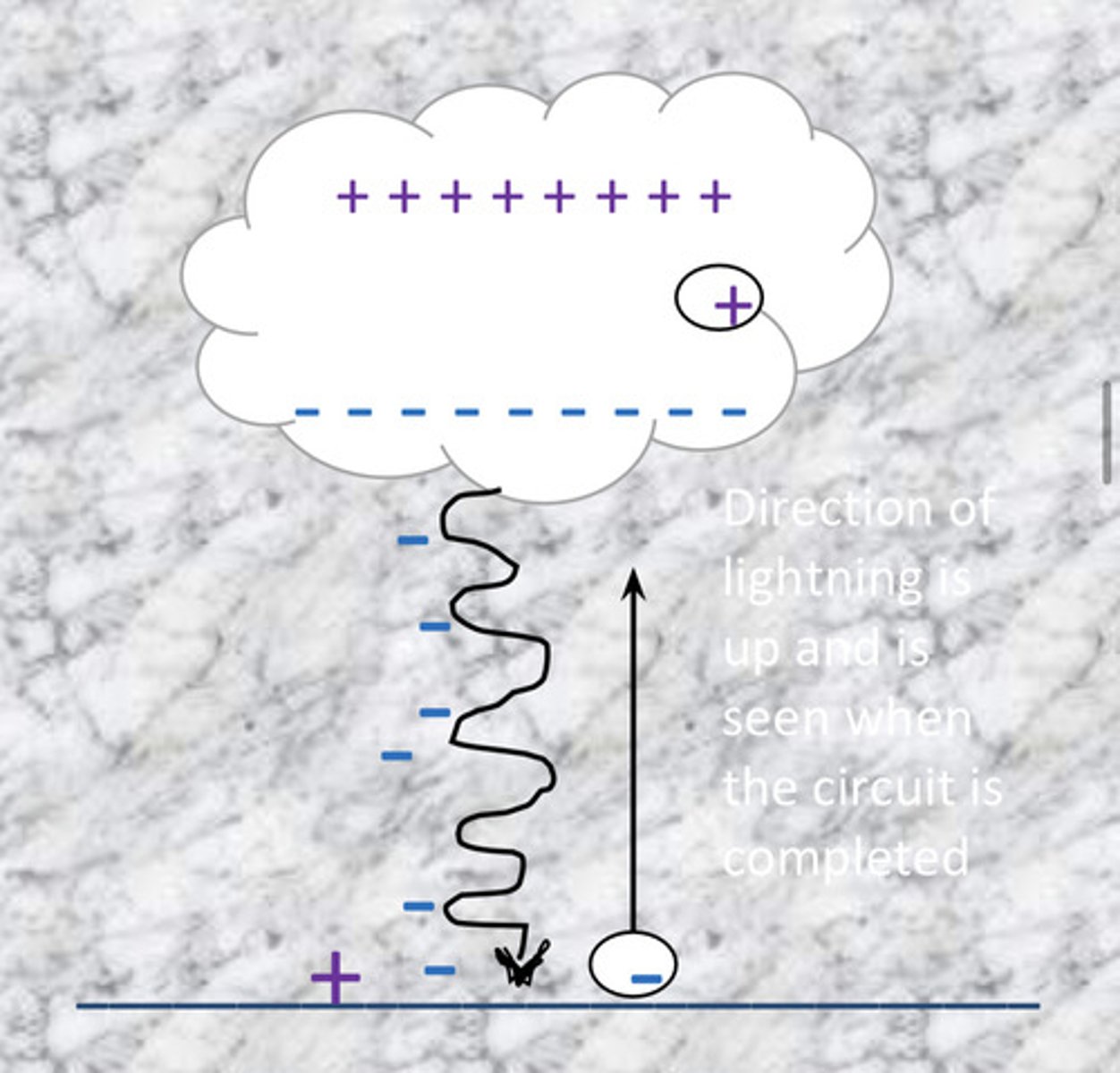
How is lightning formed?
Lightning is formed when the electrons in thunderclouds become attracted to the protons in the ground. Since there are lots of protons in the ground and plenty of electrons in the clouds, they become attracted to each other. Protons cannot move so the electrons strike the ground (lightning strike) to get closer to the protons.