Chapters 10, 11, and 12 Exam Review
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
116 Terms
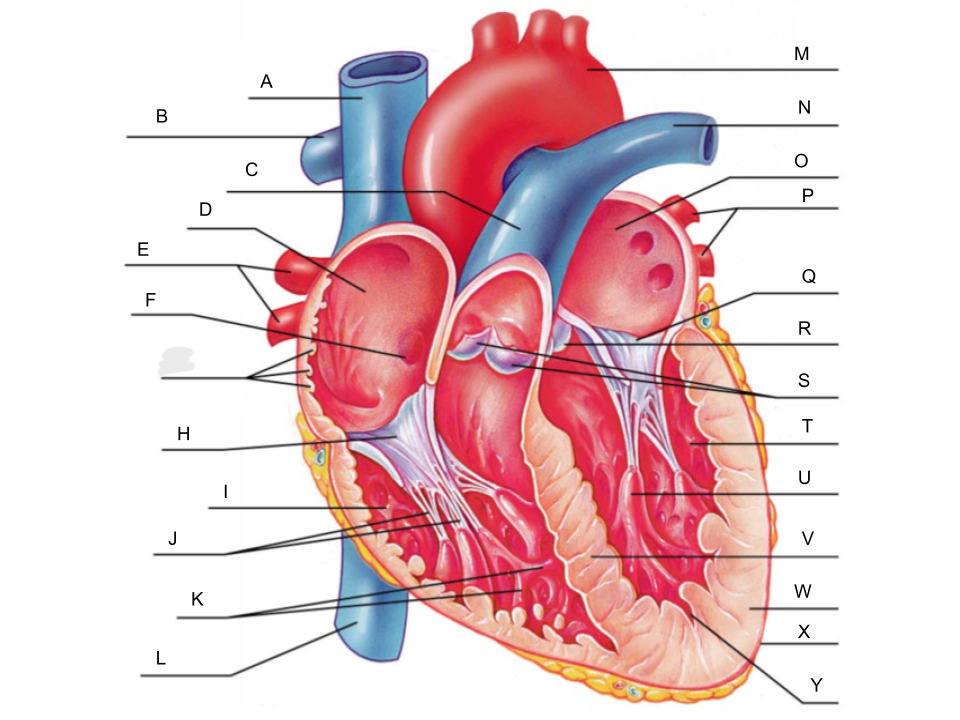
What is A?
superior vena cava
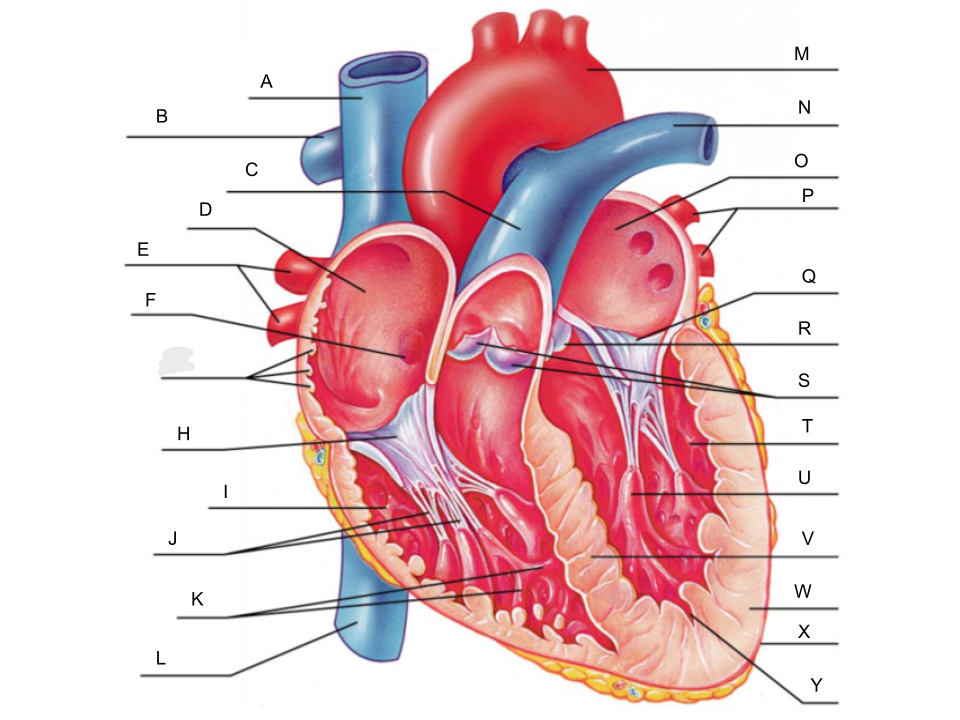
What is B?
right pulmonary artery
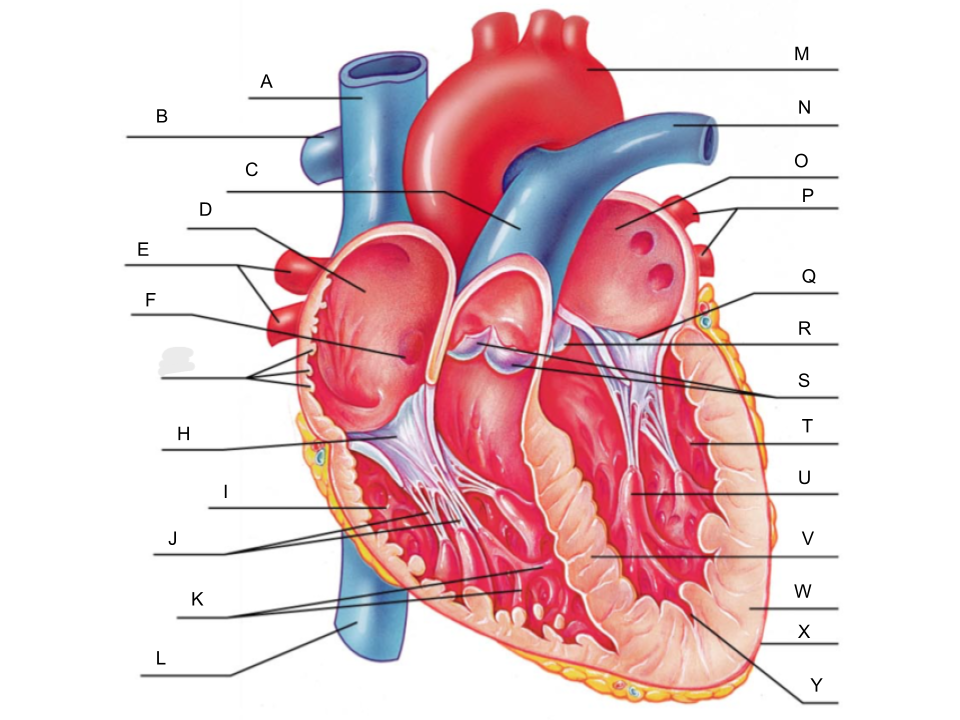
What is C?
pulmonary trunk
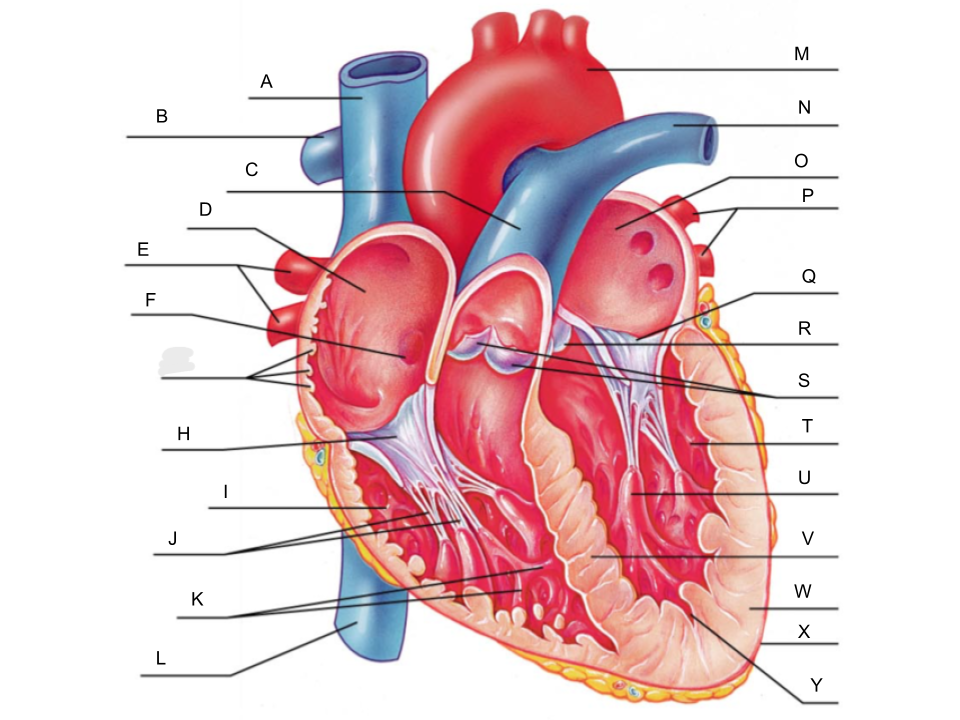
What is D?
right atrium
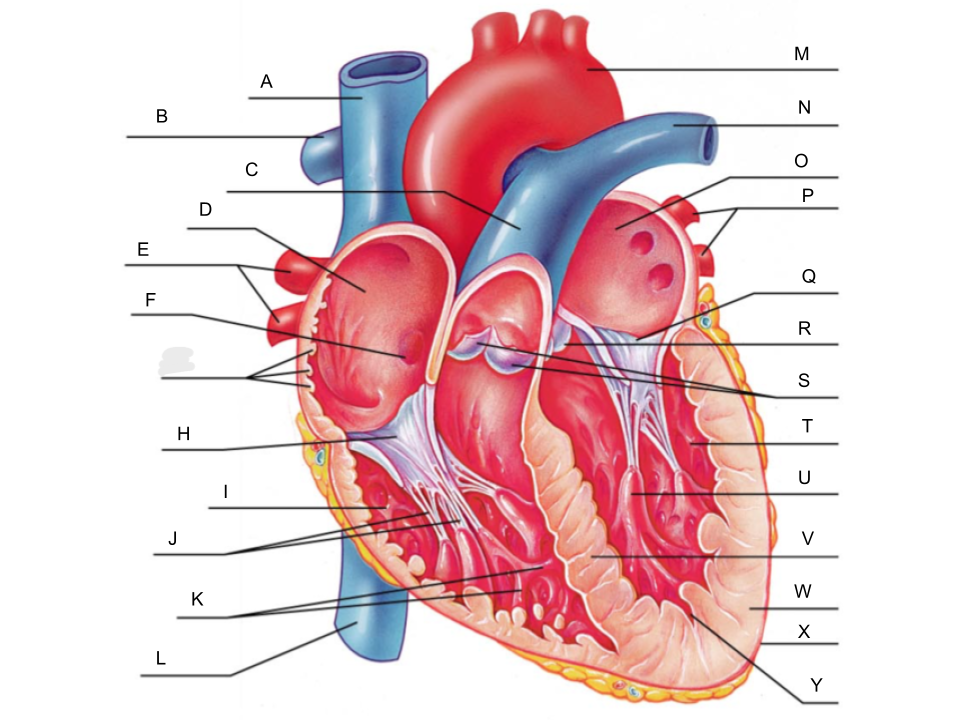
What is E?
right pulmonary veins
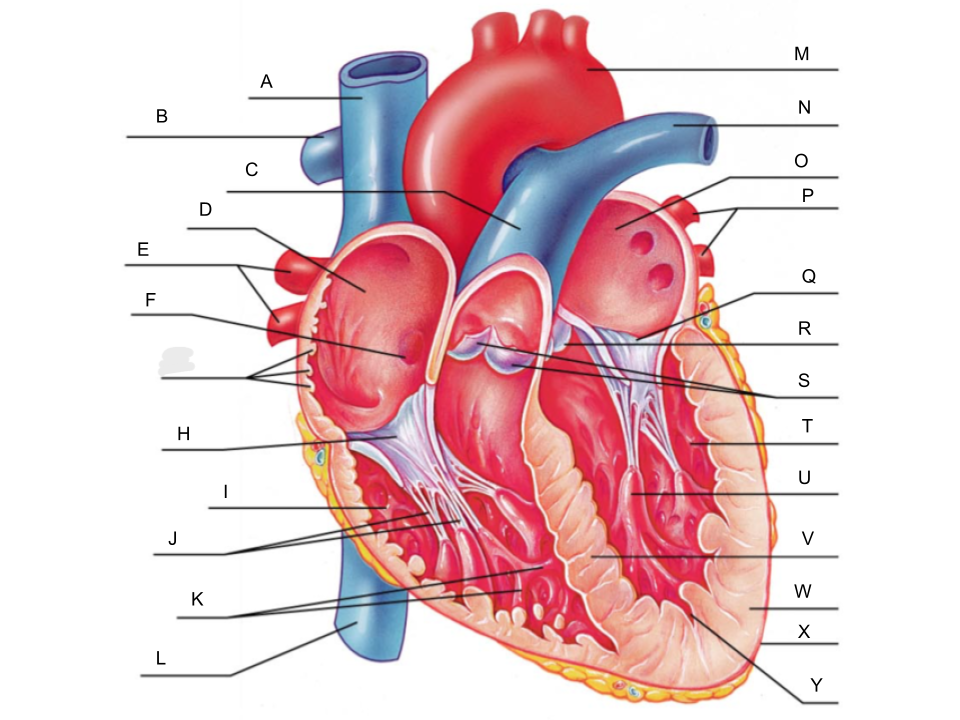
What is F?
fossa ovalis
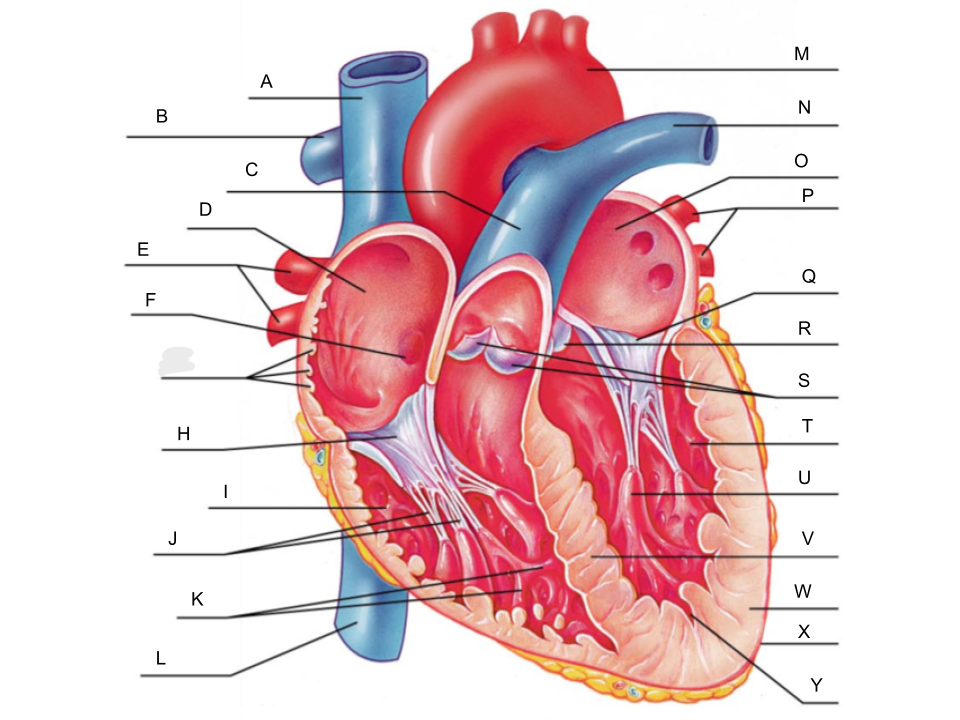
What is G?
pectinate muscles
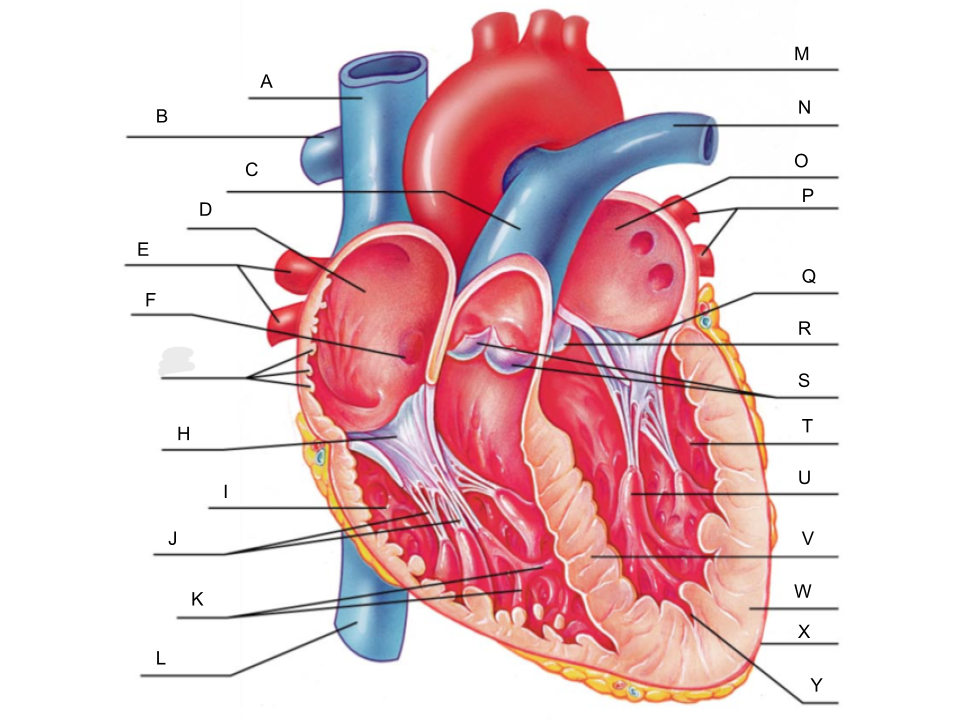
What is H?
tricuspid valve
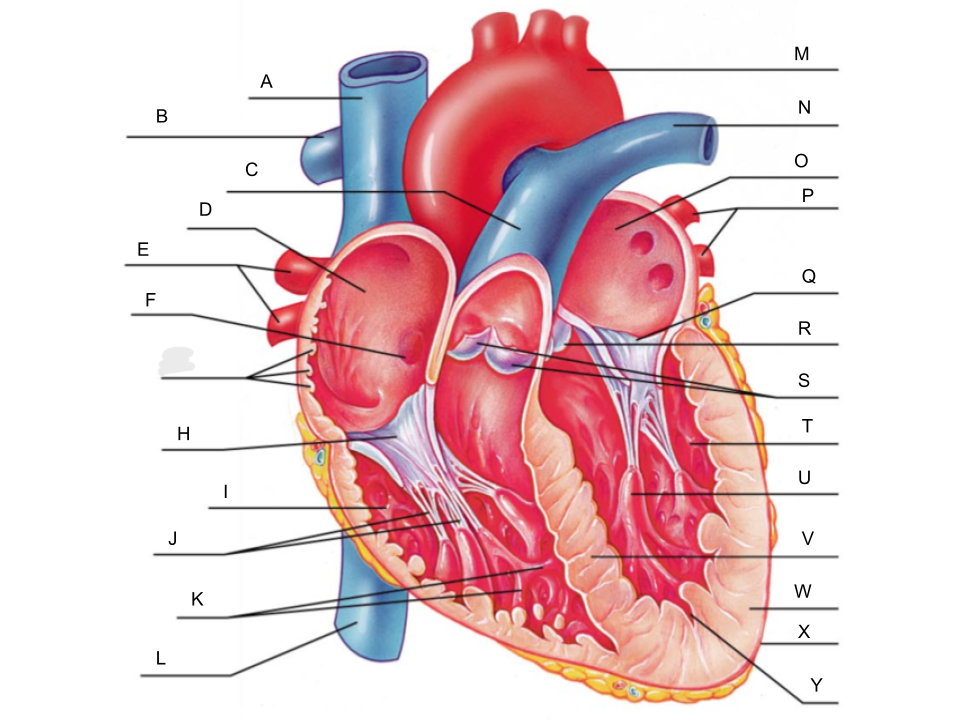
What is I?
right ventricle
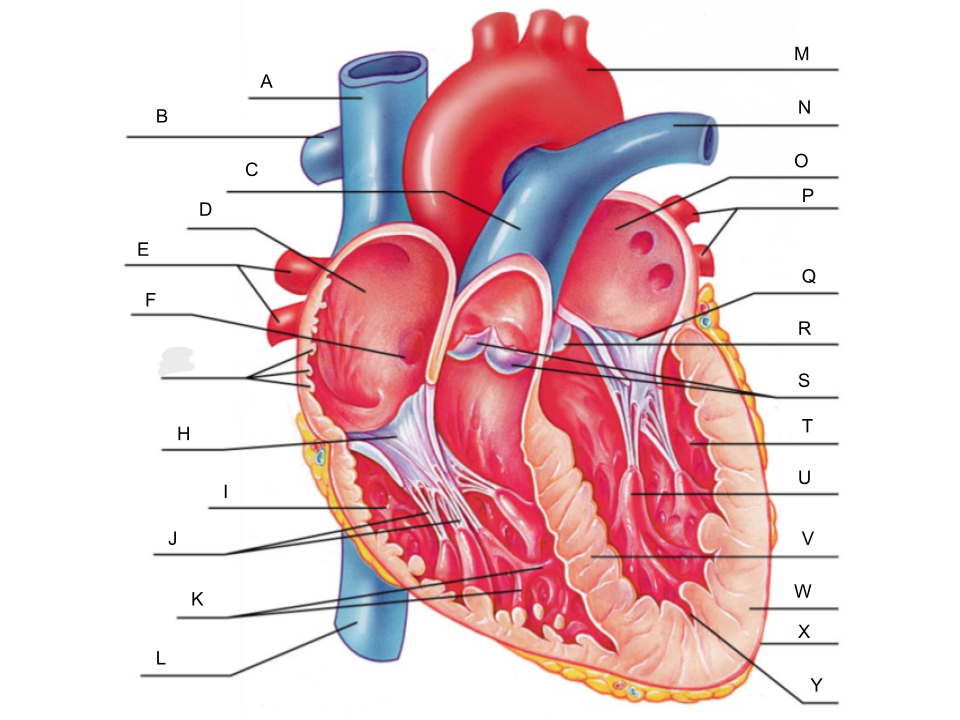
What is J?
chordae tendineae
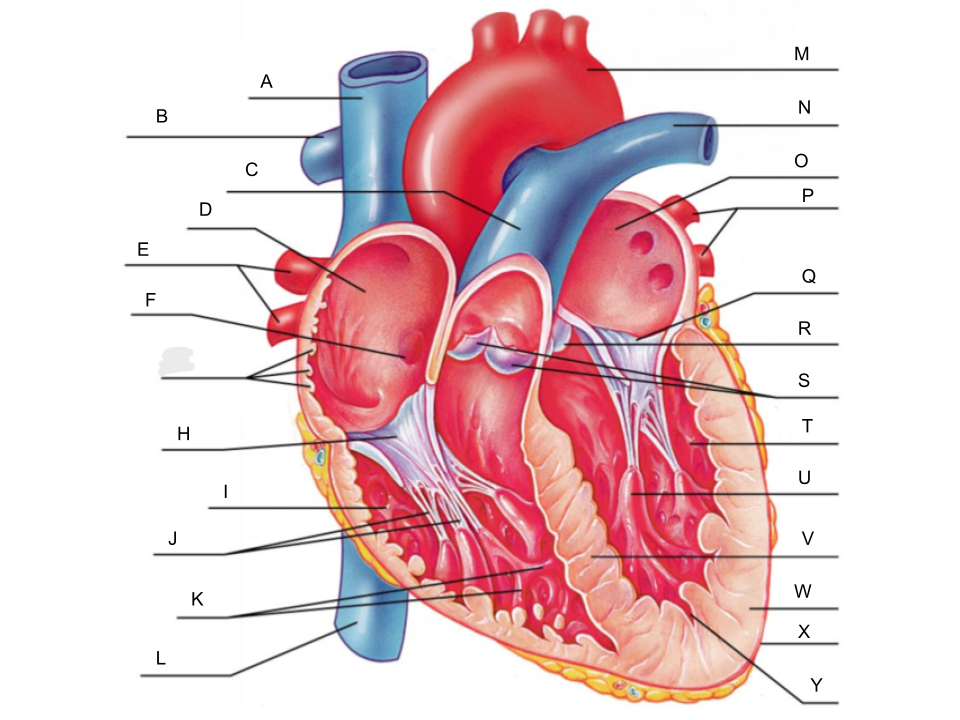
What is K?
trabeculae carneae
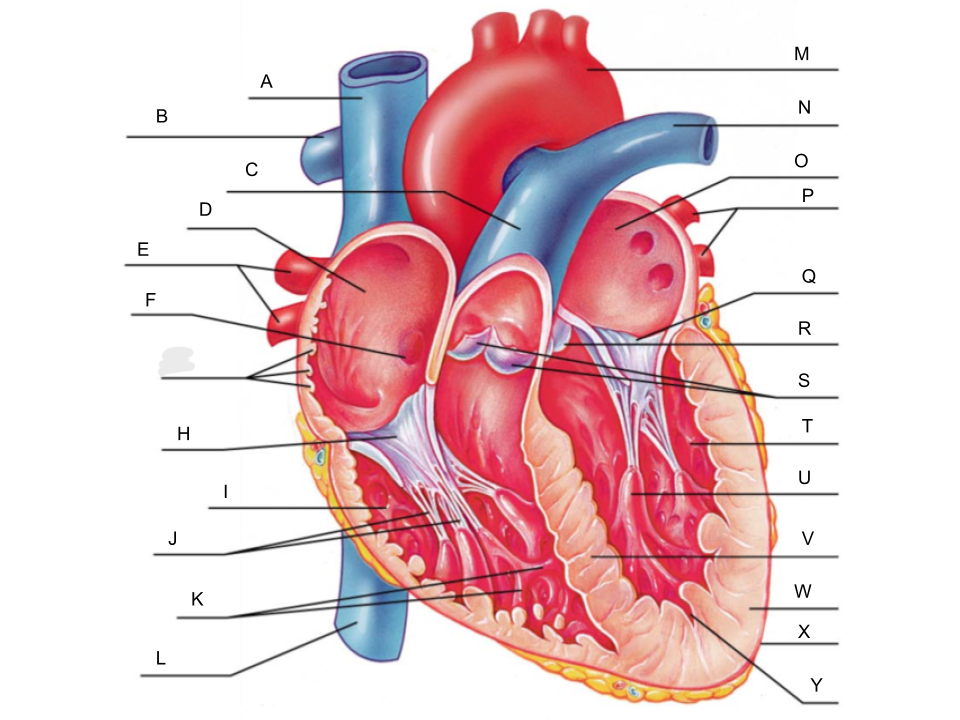
What is L?
inferior vena cava
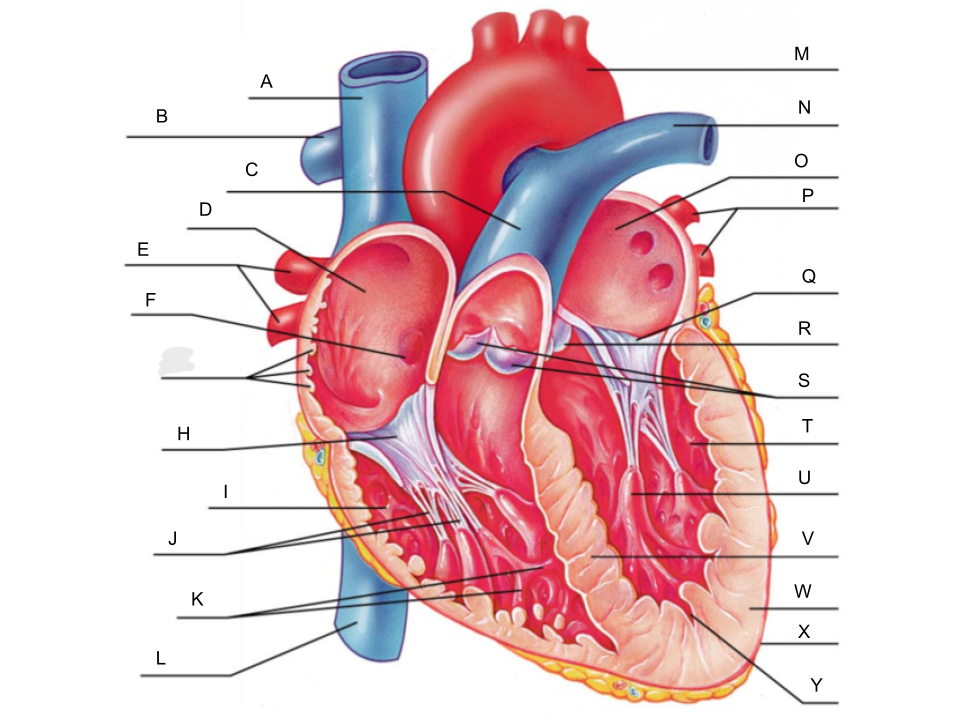
What is M?
aorta
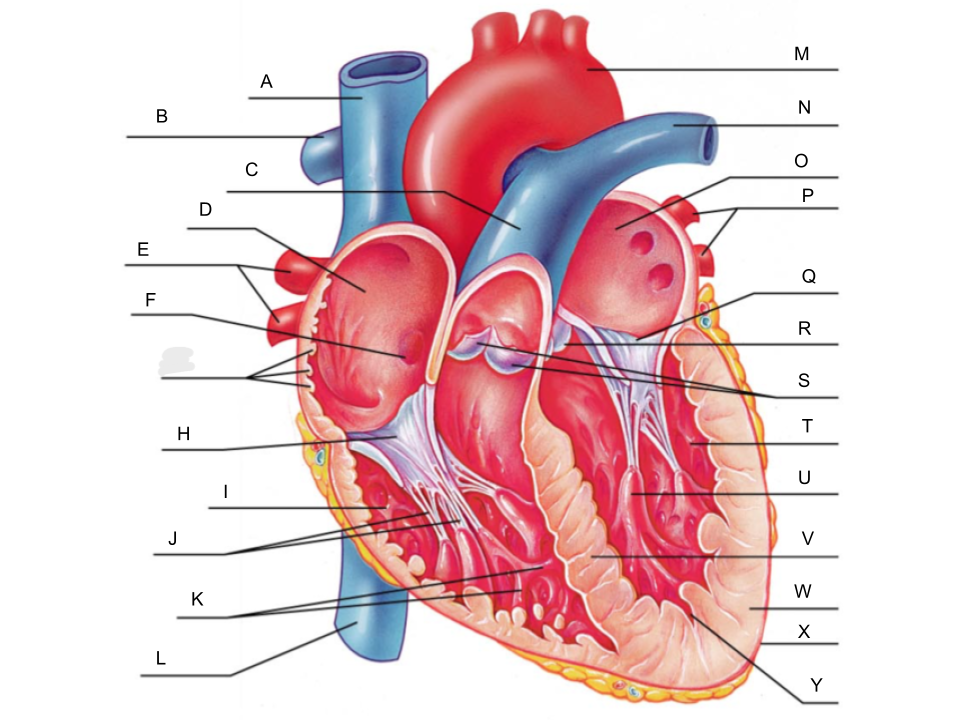
What is N?
left pulmonary artery
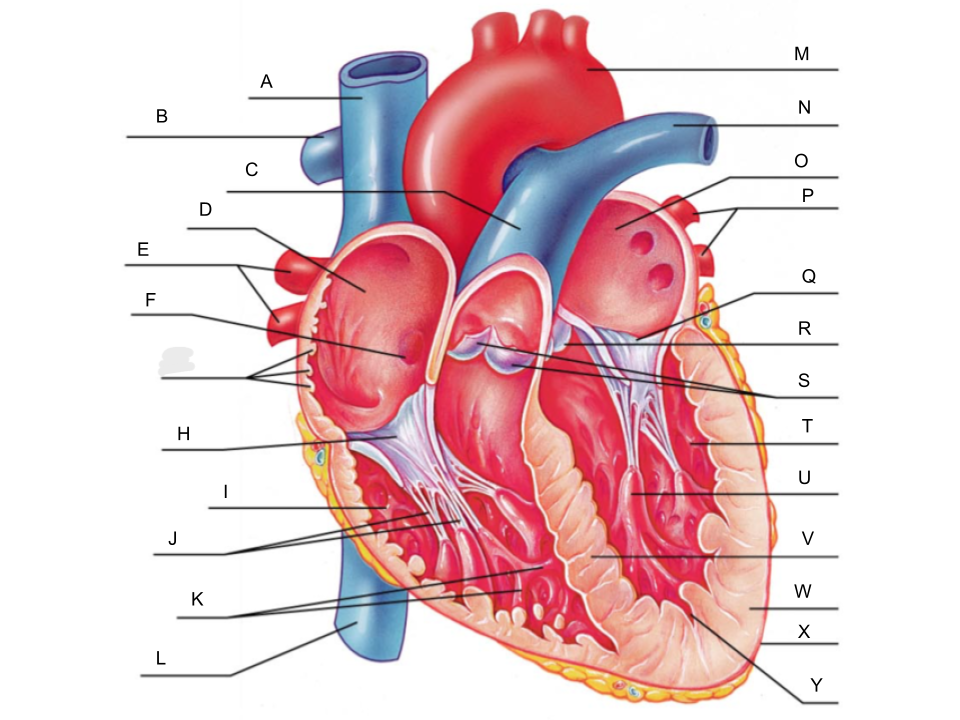
What is O?
left atrium
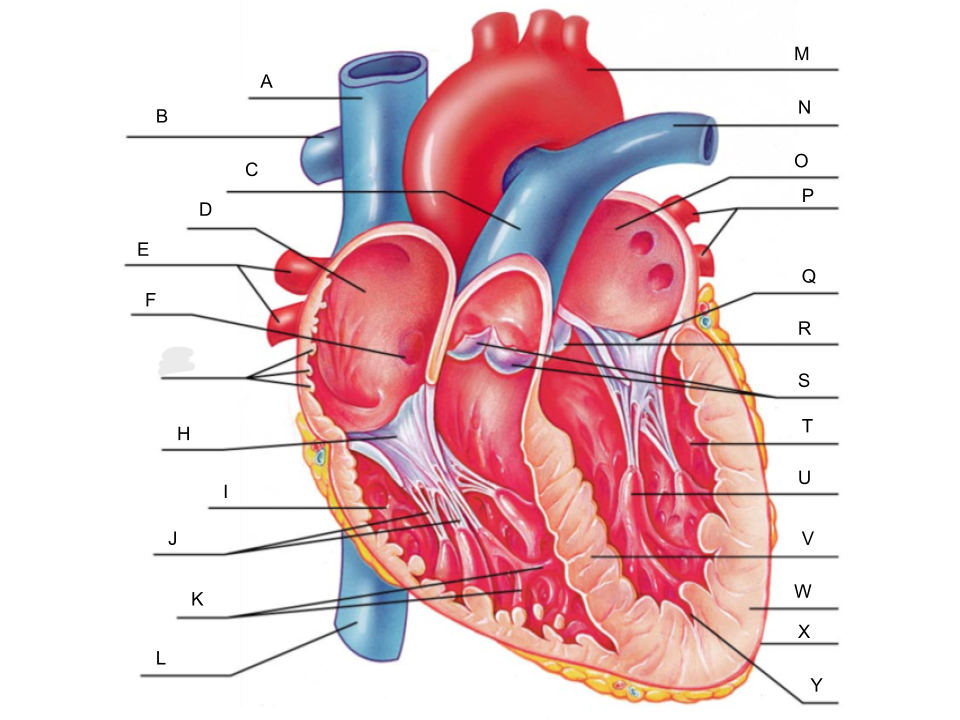
What is P?
left pulmonary veins
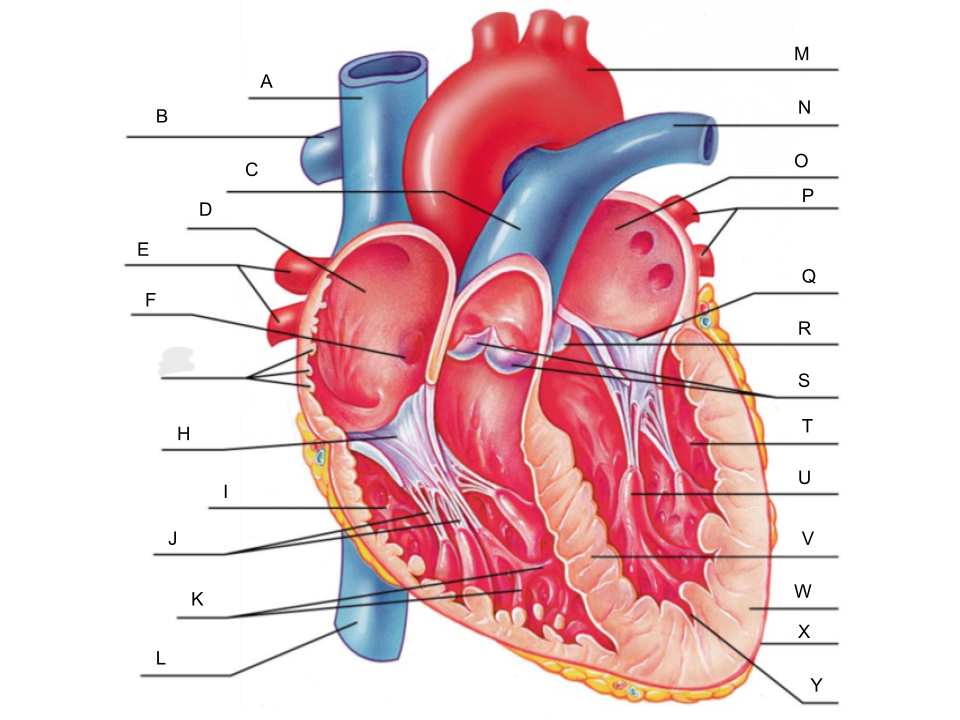
What is Q?
bicuspid valve
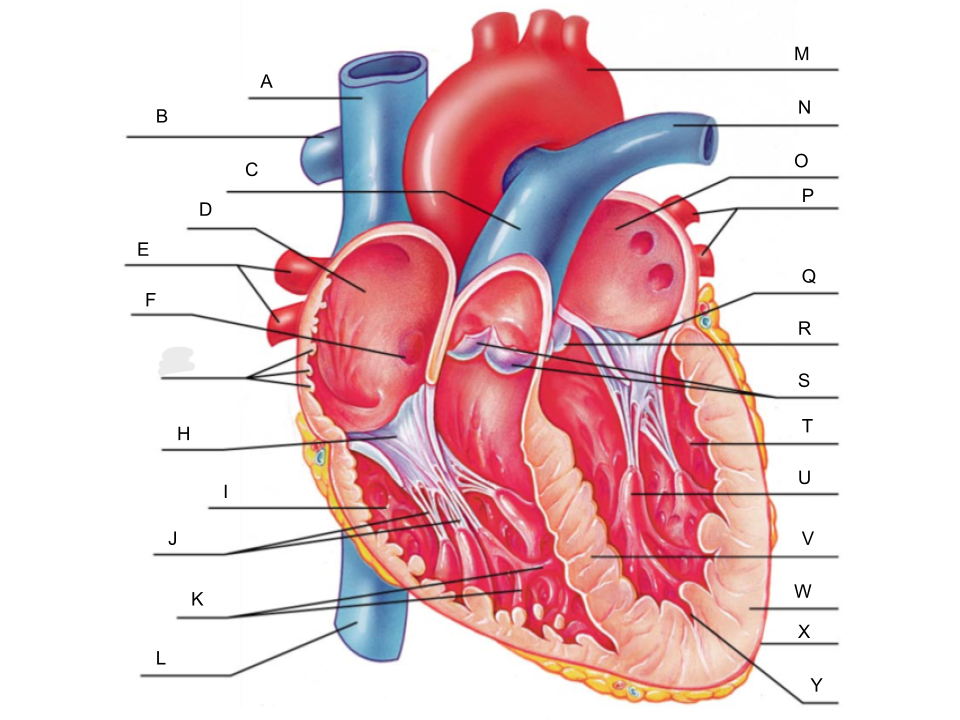
What is R?
aortic valve
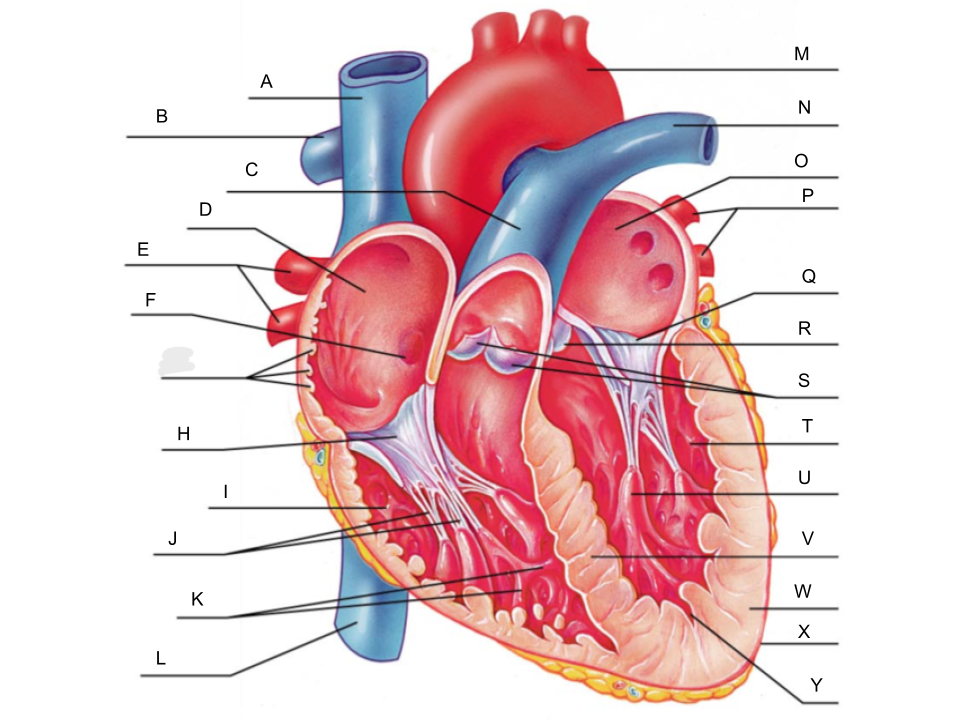
What is S?
pulmonary valve
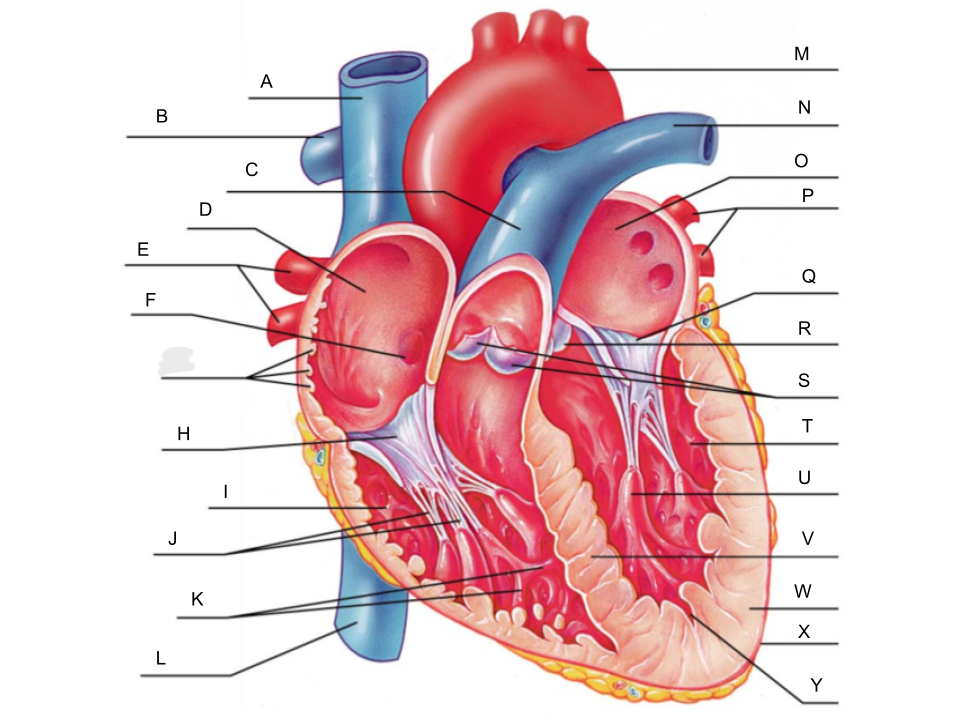
What is T?
left ventricle
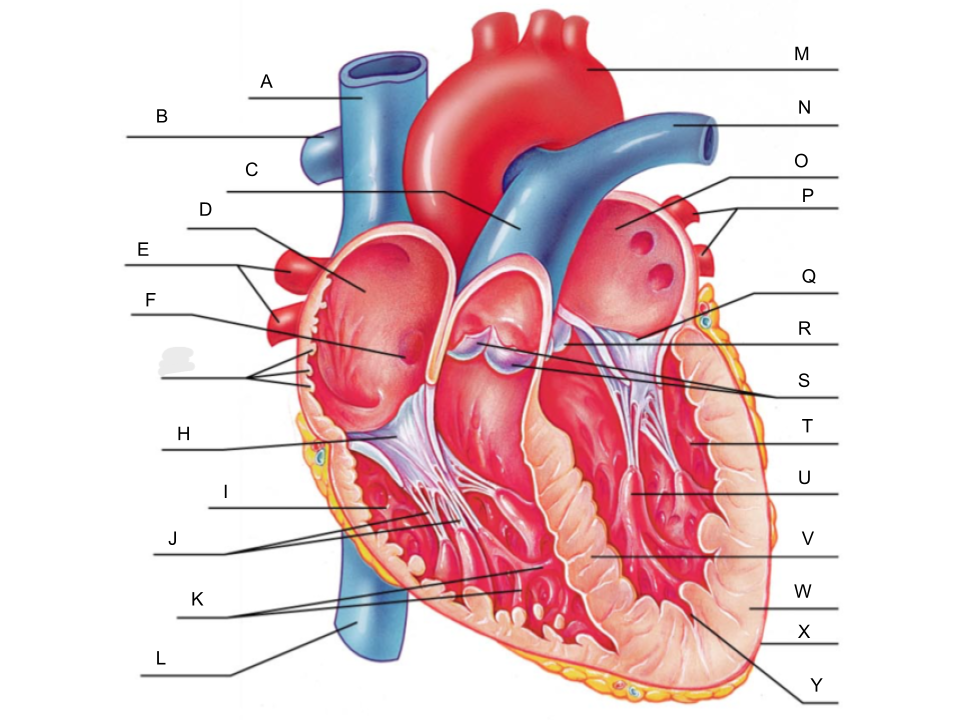
What is U?
papillary muscle
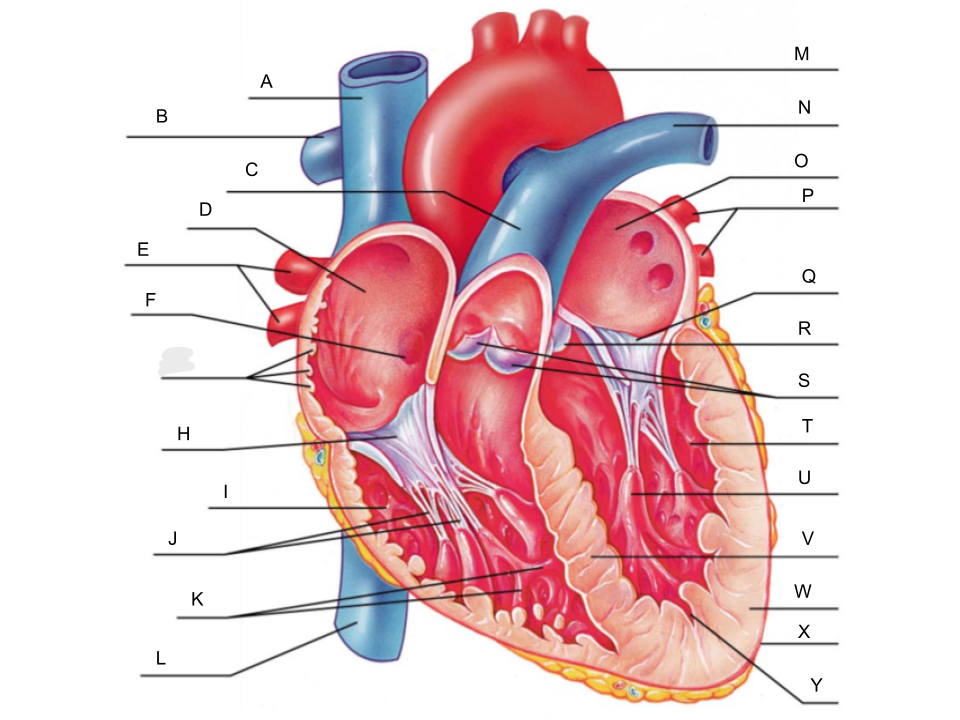
What is V?
interventricular septum
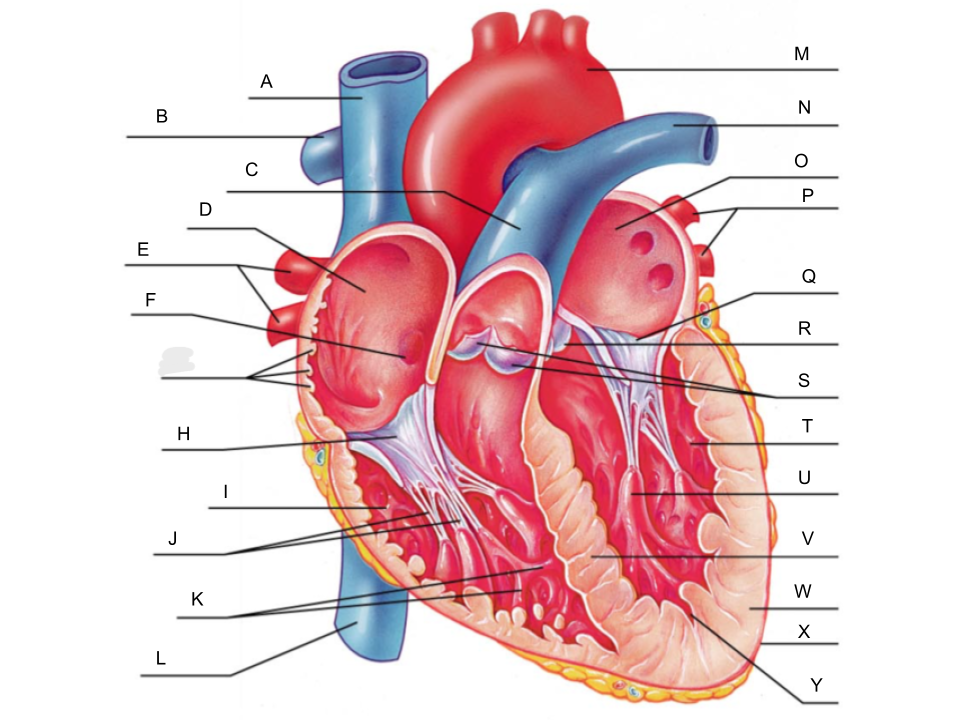
What is W?
myocardium
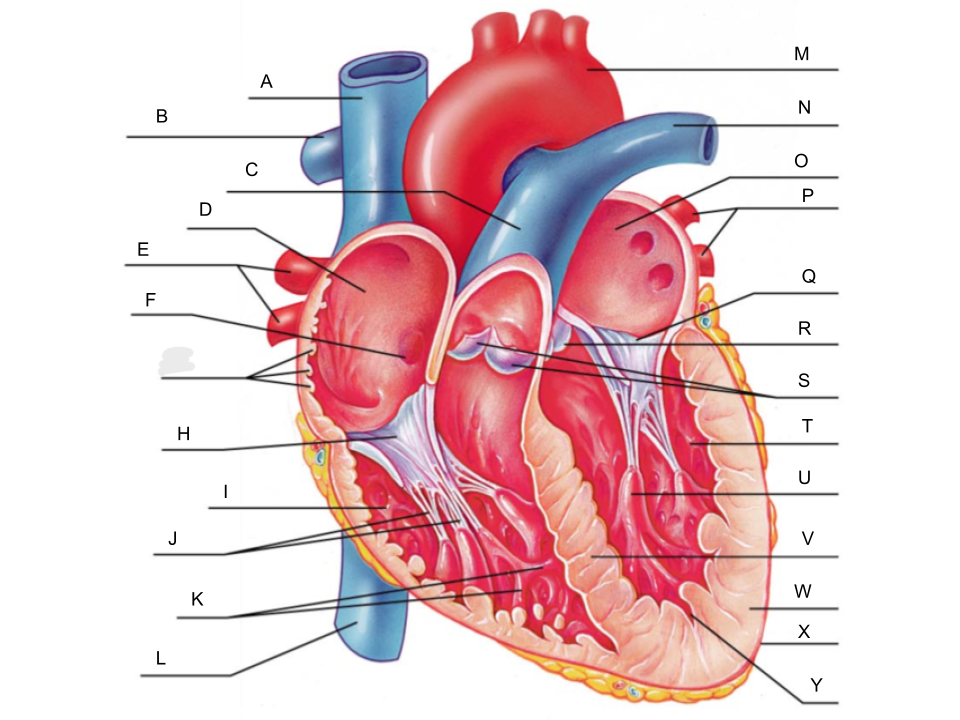
What is X?
pericardium
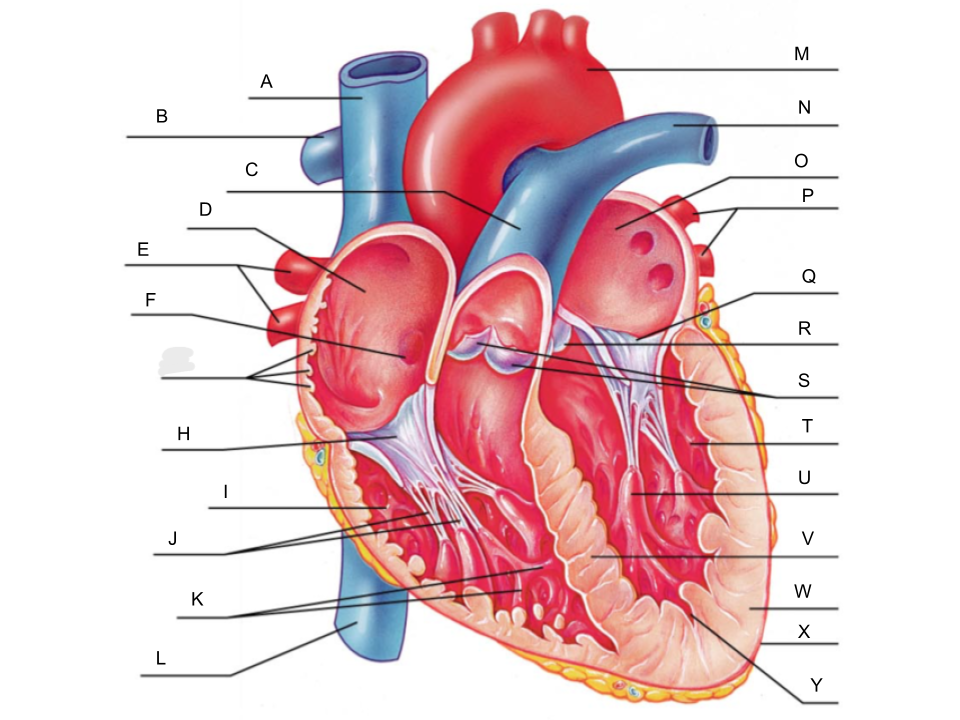
What is Y?
endocardium
What are the glands of the endocrine system?
hypothalamus, pituitary posterior, pituitary anterior, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenals, pancreas, gonads, thymus, pineal, kidneys, placenta
What hormone(s) does the hypothalamus release?
thyroid releasing hormone
What hormone(s) does the pituitary posterior release?
oxytocin, ADH
What hormone(s) does the pituitary anterior release?
growth hormone, TSH, ACTH, gonadotropins, prolactin, MSH
What hormone(s) does the thyroid release?
thyroid hormone, calcitonin
What hormone(s) does the parathyroid release?
parathyroid hormone
What hormone(s) do the adrenals release?
epinephrine, glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids
What hormone(s) does the pancreas release?
androgens, insulin
What hormone(s) do the gonads release?
glucagon, testosterone, estrogen/progesterone, LH/FSH
What hormone(s) does the thymus release?
thymosin
What hormone(s) does the pineal release?
melatonin
What hormone(s) do the kidneys release?
erythropoietin
What hormone(s) does the placenta release?
HCG
What is the function of the thyroid releasing hormone?
causes other hormones to be released
What is the function of oxytocin?
stimulates milk release
What is the function of ADH?
increases water reabsorption by kidneys (increased blood pressure)
What is the function of the growth hormone?
increases bone and tissue growth
What is the function of TSH?
causes thyroid hormones to be released
What is the function of ACTH?
increases cortisol from adrenals
What is the function of gonadotropins?
bind gonads and increase LH and FSH
What is the function of prolactin?
stimulates milk production
What is the function of MSH?
increases melanin production (darker skin)
What is the function of the thyroid hormone?
regulates metabolism
What is the function of calcitonin?
reduces Ca2+ in blood
What is the function of the parathyroid hormone?
increases Ca2+ in blood
What is the function of epinephrine?
stimulates increased heart rate, respiration, etc.
What is the function of glucocorticoids?
increases breakdown of fats/proteins
What is the function of mineralocorticoids?
retains water + Na, K (increased blood pressure)
What is the function of androgens?
affects sexual characteristics
What is the function of insulin?
decreases blood glucose
What is the function of glucagon?
increases blood glucose
What is the function of testosterone?
development of reproductive structure
What is the function of estrogen/progesterone?
menstruation?
What is the function of LH/FSH?
affects secretion of test./estr/prog.
What is the function of thymosin?
training T cells
What is the function of melatonin?
affects sleep
What is the function of erythropoietin?
increased red blood cells
What is the function of HCG?
maintains pregnancy
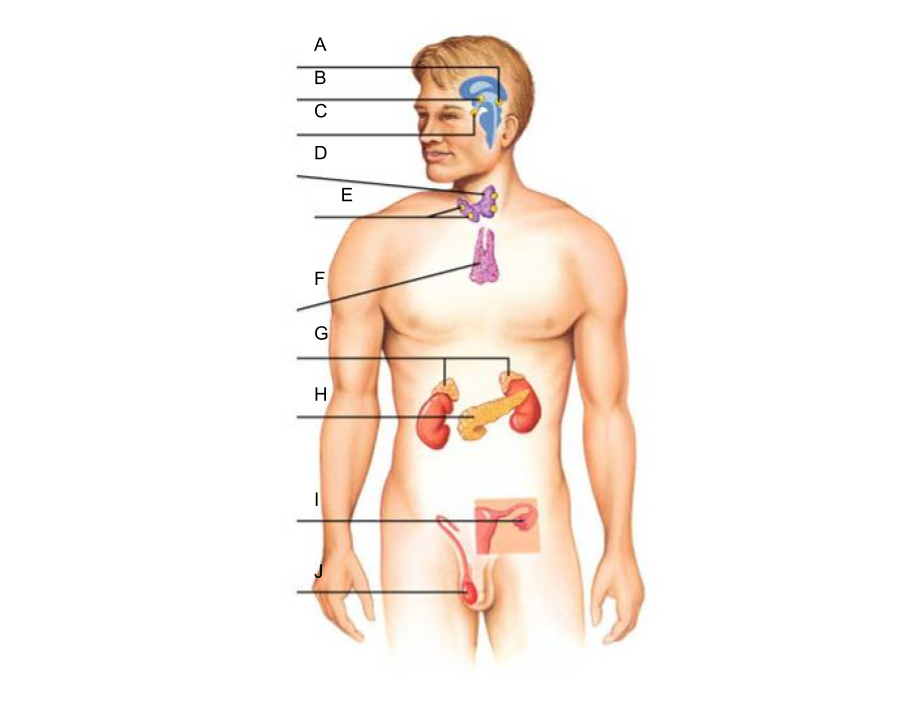
What is A?
pineal gland?
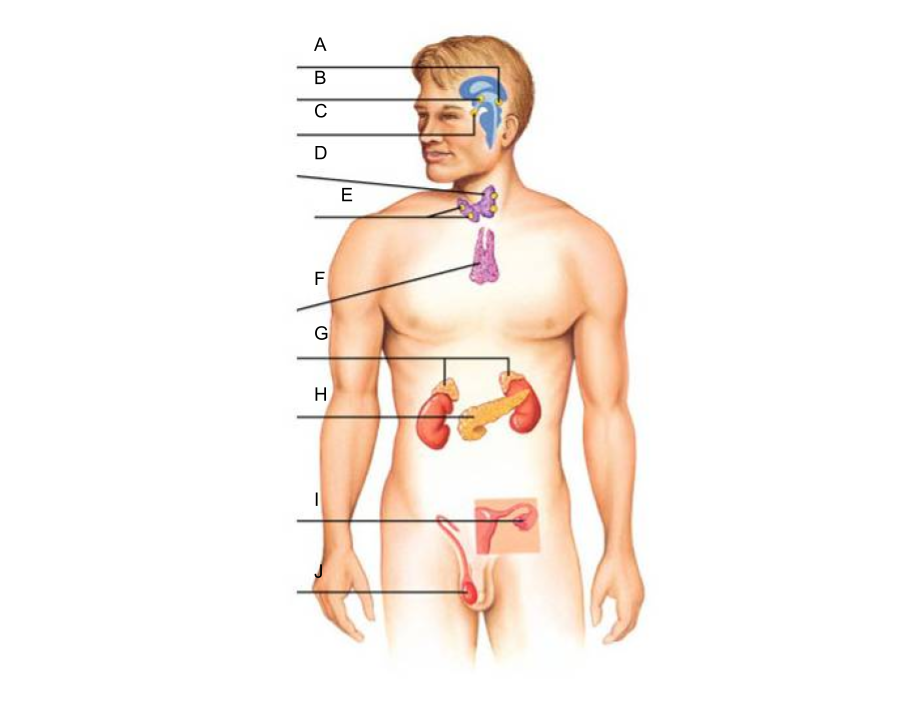
What is B?
hypothalamus
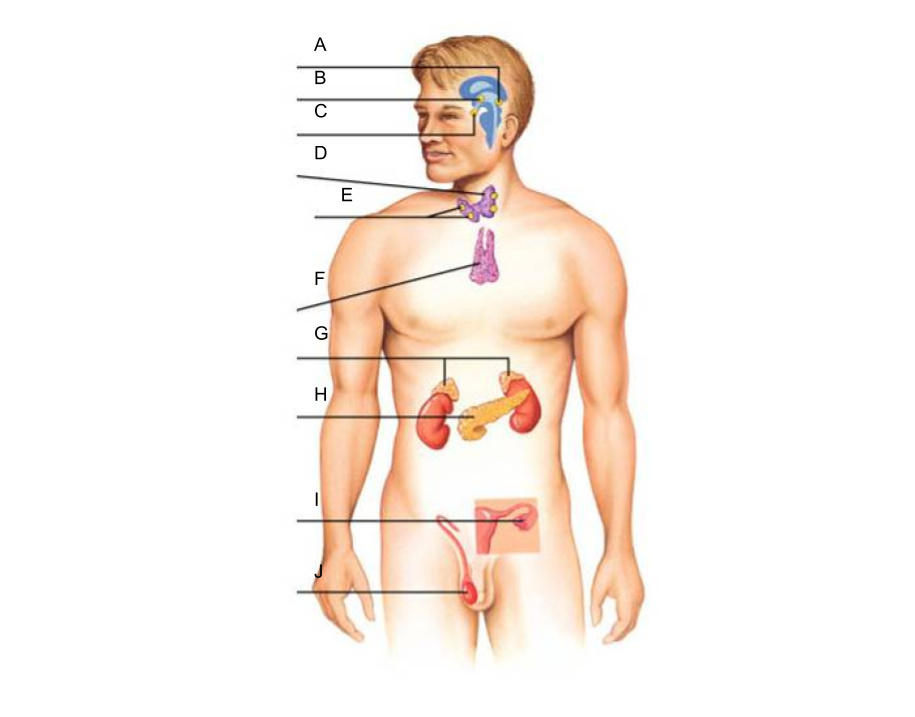
What is C?
pituitary gland
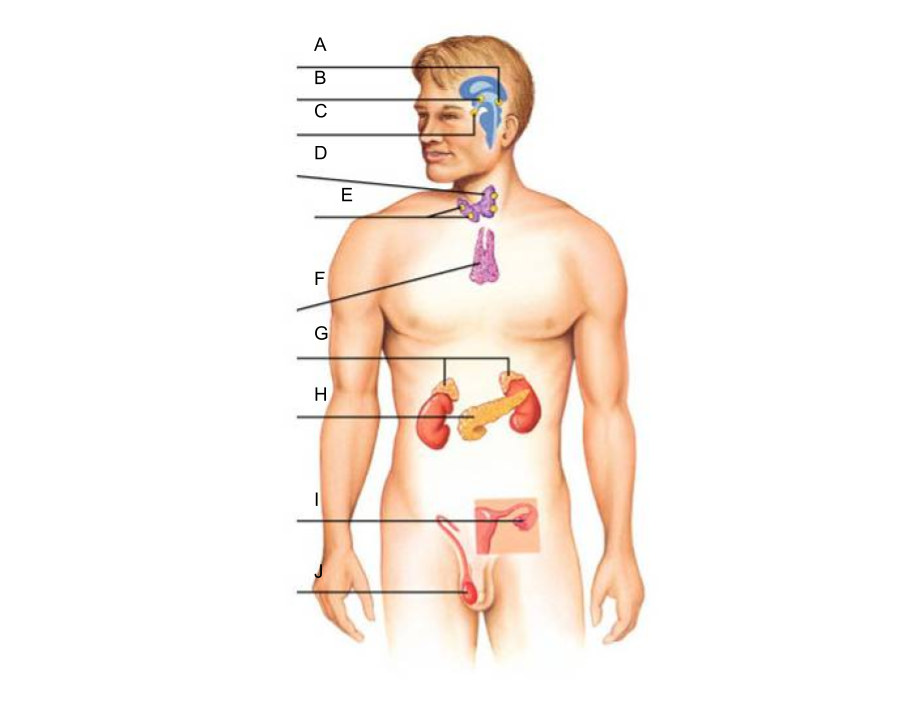
What is D?
thyroid gland
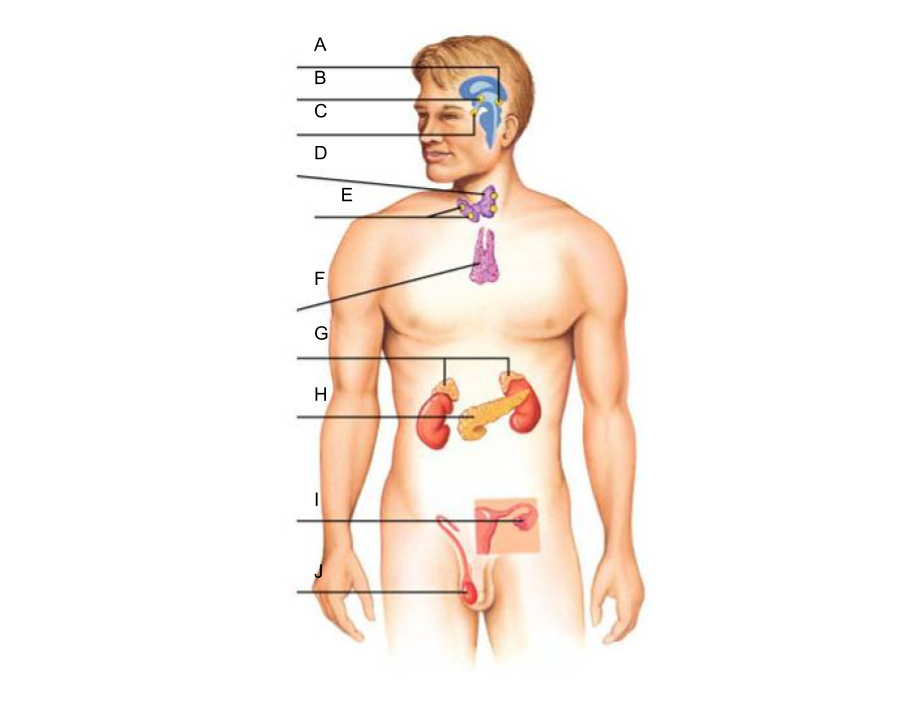
What is E?
parathyroid glands
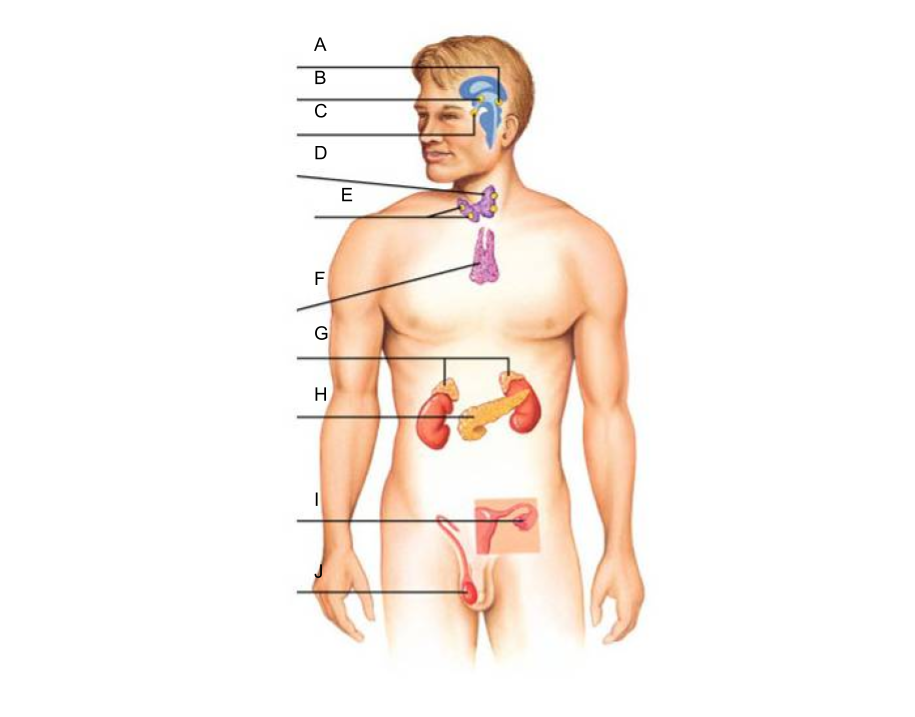
What is F?
thymus gland
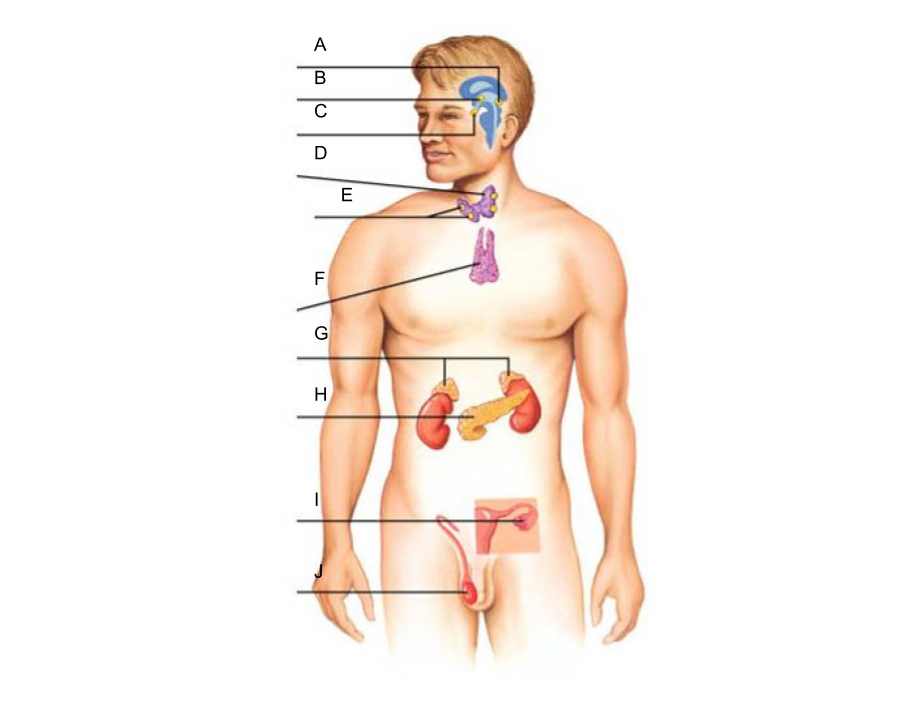
What is G?
adrenal glands
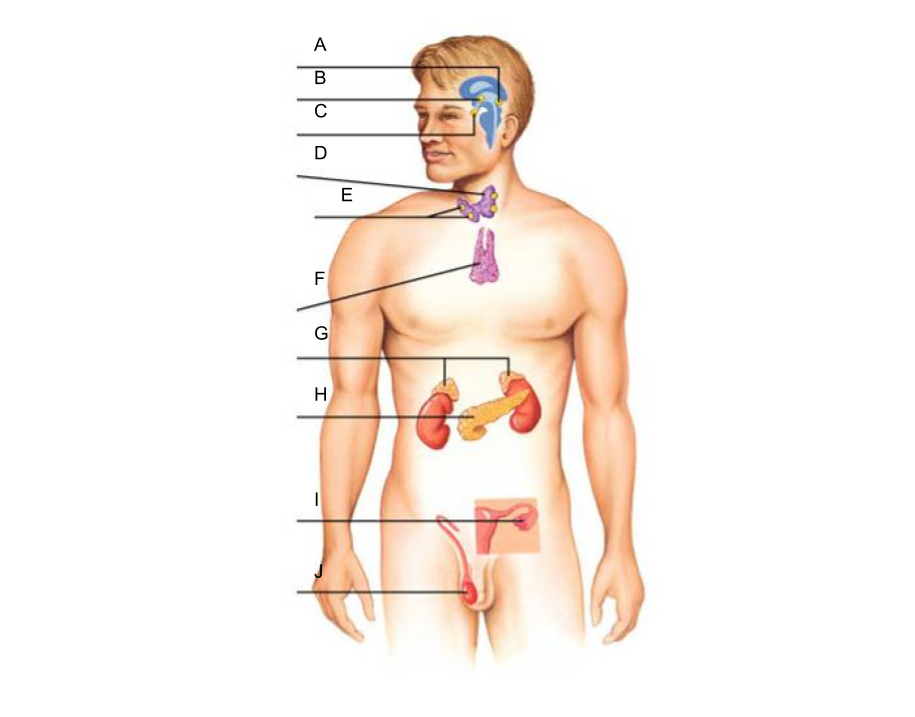
What is H?
pancreas
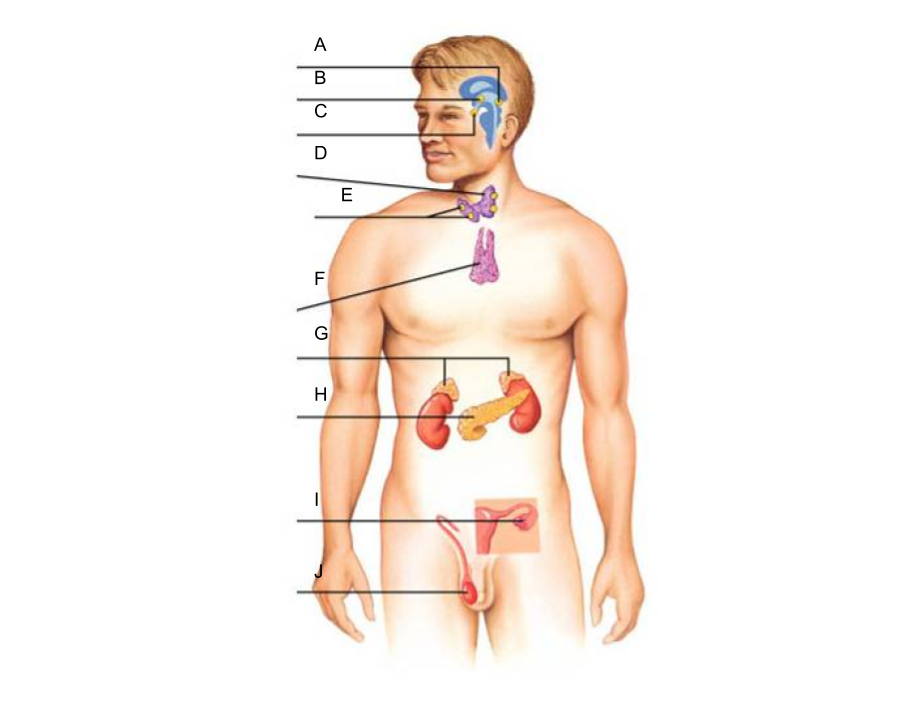
What is I?
ovaries (female)
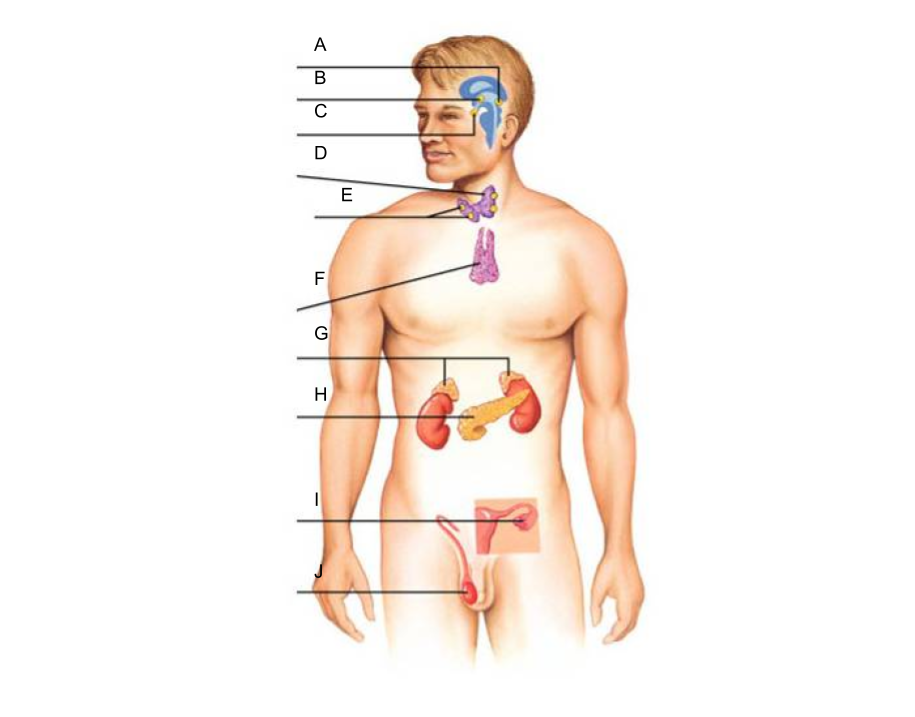
What is J?
testes (male)
What are the four blood types?
A, B, AB, O
What is the genotype for blood type A?
IAIA or IAi
What is the genotype for blood type B?
IBIB or IBi
What is the genotype for blood type AB?
IAIB
What is the genotype for blood type O?
ii
What are the main components of blood?
granulocytes, agranulocytes
What are the subunits of granulocytes?
neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils
What are the subunits of agranulocytes?
lymphocytes, monocytes → macrophages
What is hemoglobin?
a protein found in red blood cells that carries oxygen through the body
What are the parts of hemoglobin?
globin, heme
What is globin?
protein
What is heme?
contains iron, binds oxygen
Where is an intracellular signal?
within a cell
Where is an intercellular signal?
between cells
What is an autocrine signal?
between cells of same tissue
What is a paracrine signal?
between cells of different tissue
Where does a hormone signal travel?
glands→blood→cells
Where does a neurohormone signal travel?
neurons→blood→cells
Where do neurotransmitters/modulators travel?
neurons→synapse→postsynaptic cell
Pheromones are:
secreted into environment (effect on another organism)
What is cardiac output?
the quantity of blood pumped by the heart in a given period of time, typically measured in liters per minute
What is an intrinsic mechanism?
a process or response that originates from within a system or organism itself
What is the first place blood flows through the heart?
superior vena cava
What is the second place blood flows through the heart?
right atrium
What is the third place blood flows through the heart?
right ventricle
What is the fourth place blood flows through the heart?
pulmonary valve
What is the fifth place blood flows through the heart?
right ventricle