Kaarten: Ch1: The plurality of worlds | Quizlet
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
What were the main ideas of the Copernican Revolution and how did they change our view of the universe?
The Copernican Revolution marked a significant shift from the geocentric model of the cosmos, which positioned Earth at the center, to a heliocentric one with the Sun at the center. This was a fundamental change in astronomy, effectively launching modern scientific inquiry into the universe. The revolution began with Copernicus's propositions and was furthered by astronomers like Galileo and Kepler, who provided observational and mathematical evidence to support a sun-centered system.
Copernicus' heliocentric theory:
- The planetary orbit is a circle with epicycles
- The sun is approx. at the center of the orbit
- The speed of the planet in the main orbit is cte.
(sun and moon no longer planet)
Define a planet according to the International Astronomical Union (IAU).
A planet is a celestial body which
1) Is in orbit around its star
2) Has sufficient mass to assume hydrostatic equilibrium
3) Has "cleared the neighbourhood" around its orbit
=> If only 1) and 2) are fulfilled = dwarf planet
Why is the definition of a planet controversial, and how does this controversy impact the classification of celestial bodies?
The controversy over the definition of a planet centers on the third criterion of the IAU definition, which requires a planet to have "cleared the neighborhood" around its orbit. This criterion led to the reclassification of Pluto as a dwarf planet and has been a subject of debate among astronomers.
List the main bodies that comprise our Solar System and describe one unique property of each.
In order: ([So] My Very Educated Mother [Ann] Just Served us Nine [KTO’Z] (pizza's)
- Sun:
> G2
> Teff = 5770K
> 99.8% of mass solar system
> 8500 parsec from the galactic center
- Mercury:
> Terrestrial planet
> Tidally locked in 3:2 spin-orbit resonance
- Venus:
> Terrestrial planet
> Retrograde (rotates in opposite direction to its orbital motion around the Sun)
-Earth:
> Terrestrial planet
> exhibits intelectual life
- Mars:
> Terrestrial planet
> Red planet with thin CO2-dominated atmosphere
> Debate about life supporting qualities
- Asteroid belt:
> Between Mars and Jupiter
> Primarily rocky bodies
> boundary between inner terrestrial planets and outer gas giants
- Jupiter:
> Gas giant
> The largest planet in the solar system
- Saturn:
> Gas giant
> Has the most moons
> Has seven rings
- Uranus:
> Ice giant
> It is the only planet that rotates on its side
- Neptune:
> Ice giant
> Found because of deviation in Uranus' orbit
- Kuiper belt:
> Objects beyond Neptune around 30 to 50 Au
> around 10^9 bodies, majority being ice-rich
- The Trans-Neptunian objects:
> Objects where the orbit is greater than Neptune, this includes all objects in the Kuiper belt
- The oort cloud:
- Spherical shell surrounding the Sun
- Further than kuiper belt, between 10 000 and 50 000 AU
- Around 10^12 comets
- Quasi-isotropic distribution
-Source of the long-period comets
- The zodiacal cloud:
- between earth and mars
- It reflects sunlight
- causes zodiacal light to be seen on earth
- possibly due to dust storms on Mars
How are the asteroid and Kuiper belt alike?
Astronomers think the icy objects of the Kuiper Belt are remnants from the formation of the solar system. Similar to the relationship between the main asteroid belt and Jupiter, it's a region of objects that might have come together to form a planet had Neptune not been there. Instead, Neptune's gravity stirred up this region of space so much that the small, icy objects there weren't able to coalesce into a large planet.
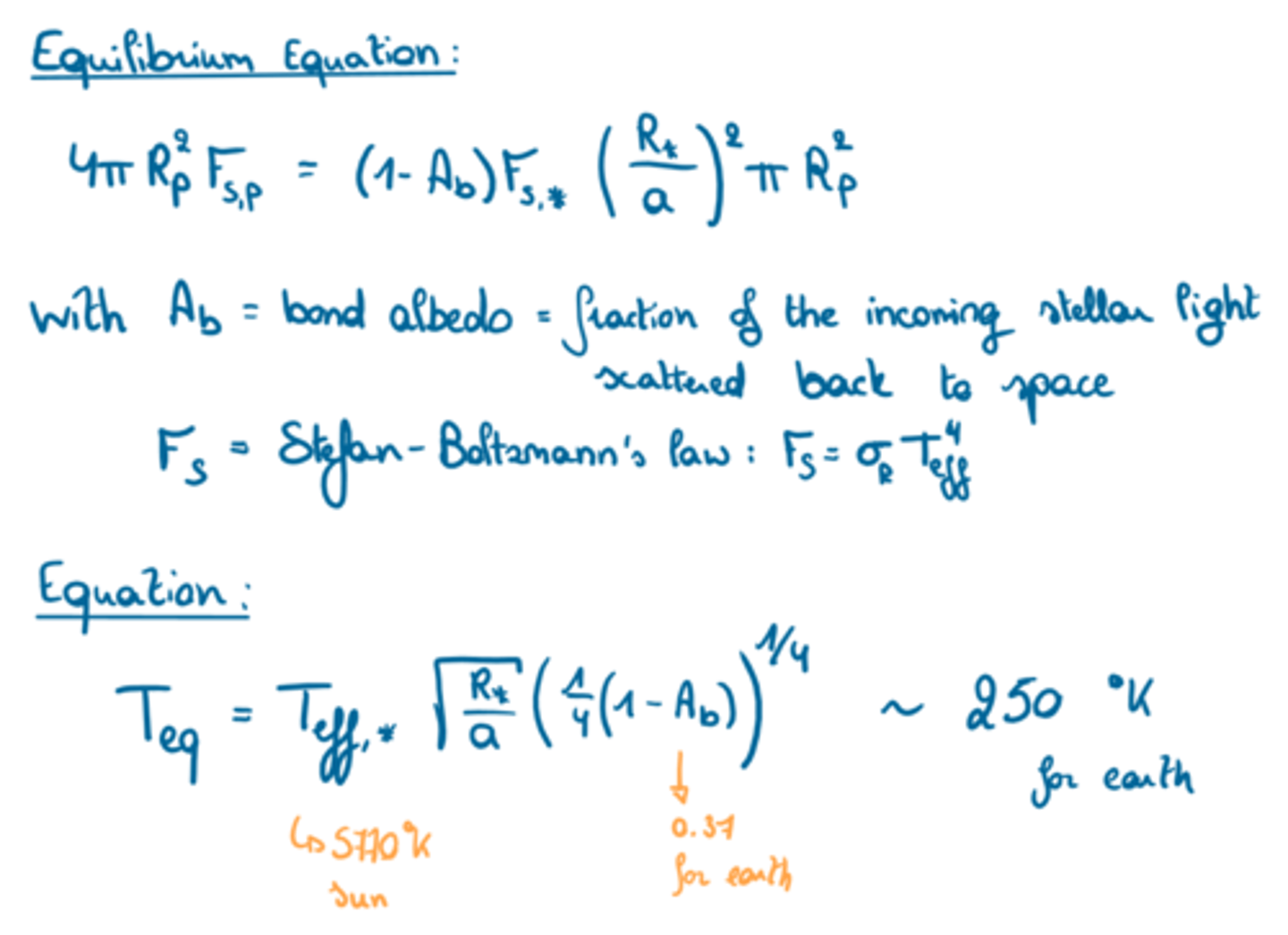
Explain the concept of equilibrium temperature and how it applies to a planet.
It is an estimate of the effective temperature of a planet if we neglect its own internal energy (luminosity).
It is the temperature at which a planet would be in equilibrium with the radiative energy from the host star, assuming it behaves like an isothermal body.
Formula:
T_eq = T_eff sqrt(R_s / a) (1/4*(1-Ab))^1/4
for earth this is around 250K
with Ab = bond albedo = fraction of the incoming stellar light scattered back to space
Discuss how the equilibrium temperature of a planet is influenced by its distance from the sun and its atmosphere.
The bond albedo will change
What is the effective temperature of a planet and how is it calculated?
It is the temperature of a black body emitting the same amount of radiative energy than the planet, i.e. having the same luminosity.
L= 4piR²sigma*Teff^4
Describe the habitable zone and why it is significant in the search for extraterrestrial life.
Circumstellar region in which a terrestrial-mass planet with a CO2-H2O-N2 atmosphere can sustain liquid water on its surface. (Zone is model dependant)
For the solar system this is between 0.95 to 1.67 AU.
Since the luminosity of main-sequence stars evolves over time so does the habitable zone.
What criteria are used to determine whether a celestial body belongs in the asteroid belt or the Kuiper belt?
The asteroid belt consists of rocky bodies and is located between Mars and Jupiter, while the Kuiper belt extends beyond Neptune's orbit and contains icy bodies. The composition and location of these belts offer clues about the formation and evolution of our Solar System.
An alien living on Proxima b is looking at the Solar System with his optical telescope, what does he see first around the Sun?
The zodiacal light
An alien living on Proxima b is looking at the Solar System with his radio telescope, what does he see first around the Sun?
The Kuiper belt
(The zodiacal light only sends out visible light and the radio signals of the Oort cloud are too weak)
How was the first exoplanet around a main-sequence star (51 Peg) discovered?
Radial velocity
What is the Copernican Revolution?
A sequence of events that proved the heliocentric model to be the correct model of the Solar System.
(The Earth and the other planets orbit the Sun)