Biol 1020 Exam 4 ch. 23-Ecology
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
113 Terms
Hardy-Weinberg theorem
p²+2pq+q²
In the Hardy-Weinberg Theorem p represents
frequency of dominate allele
In the Hardy-Weinberg Theorem q represents
frequency of occurrence of recessive allele
In the Hardy-Weinberg Theorem p² represents
frequency of homozygous dominant genotypes
In the Hardy-Weinberg Theorem 2pq represents
frequency of heterozygous genotype
In the Hardy-Weinberg Theorem q² represents
frequency of homozygous recessive genotypes
What are the assumptions of the Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium
large population size
no migration or gene flow
no mutations
random mating
no natural selection
Genetic drift
change in gene frequencies of populations due to small population size
Gene flow
caused by migrating individuals carrying their allele with them and usually results in changes in allele frequencies
Fitness
relative ability of a genotype to contribute to future generations
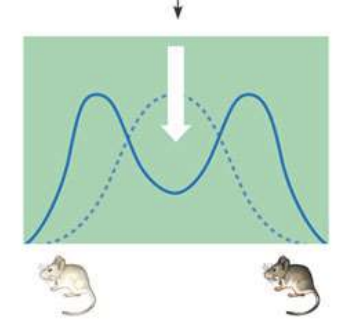
Directional selection
species adapt to environmental change by favoring selection of one extreme over the other
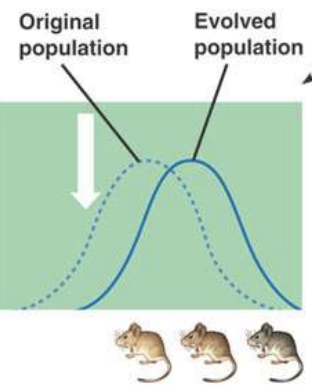
Stabilizing selection
When populations are well adapted to their environments, selecting against phenotypic extremes
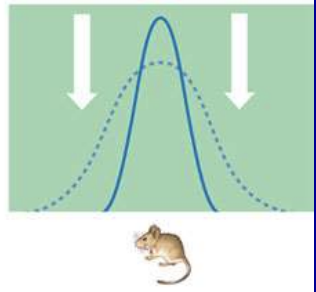
Disruptive selection
when more than one extreme phenotype is favored over intermediate phenotypes
Macroevolution
formation of new species and the accompanying events
Species biological concept
one or more populations whose members are capable of interbreeding, able to reproduce fertile offspring, and reproductively isolated from other such groups
reproductive isolation
mechanism that prevents gene flow between two species
Prezygotic barriers
prevent fertilization (zygote formation) between gametes from two species
Postzygotic barriers
reproductive isolation after fertilization has occurred
Habitat isolation
Form of prezygotic barrier; similar species reproduce in different habitats
Temporal isolation
Form of prezygotic barrier; similar species reproduce at different times
Behavioral isolation
Form of prezygotic barrier; similar species have distinctive courtship behaviors
Mechanical isolation
Form of prezygotic barrier; similar species have structural differences in their reproductive organs
Gametic isolation
Form of prezygotic barrier; Gametes of similar species are chemically incompatible
Hybrid inviability
Form of postzygotic barrier; interspecific hybrid dies at early stage of embryonic development
Hybrid sterility
Form of postzygotic barrier; Interspecific hybrid survies to adulthood but is unable to reproduce successfully
Ex: mule
Hybrid breakdown
Form of postzygotic barrier; offspring of interspecific hybrid have problems reproducing
anagenic speciation
gradual change of one species not a new form with the new form replacing the old form
cladogenic speciation
when two or more species are present where only one had existed before; species share a common ancestor
Allopatric speciation
one population becomes geographically separated from the rest of the species
sympatric speciation
a species becomes reproductively isolated and evolves in the same geographic location as ancestral species
Adaptive radiation
the rapid production of many species from a common ancestor
Darwin’s Gradualism Model
suggests that evolution occurs gradually
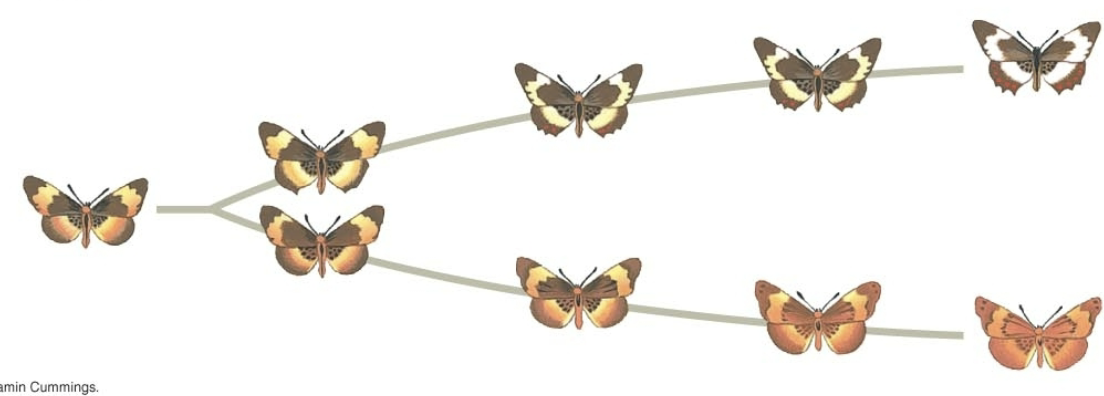
Punctuated equilibrium
Evolution occurs quickly compared to gradual

How old is the earth?
4.6 billion years old
Earth’s early atmosphere was lacking in what gas
O2
What are the four requirements for forming life on Earth
1) little or no free oxygen
2) abundant energy sources
3) Chemical building blocks of water, dissolved mineral ions, and atmospheric gases
4) time
Polymers
spontaneous formations from monomer building blocks on sand, clay, or rock surfaces
Prebiotic broth hypothesis for how life on Earth began
life began from an ‘organic soup’ in the oceans
bubble hypothesis for how life on Earth began
‘oily bubbles’ from an organic soup interacted with land surfaces at shallow seas or seashores
iron-sulfur world hypothesis for how life on Earth began
life began from an ‘organic soup’ interacting with mineral surfaces at hyper thermal vents in the ocean floor; with abundant iron and sulfur there impacting the early metabolism that developed
deep-hot biosphere hypothesis for how life on Earth began
life began in an ‘organic soup’ deep within the earth
exogenesis explanation for how life on Earth began
an extraterrestrial source put life on Earth
RNA world hypothesis
RNA is believed to be the component of the first cells with DNA coming along later
In vitro evolution
How RNA has evolved and this supports the RNA world hypothesis
microfossils of prokaryotic cells
first evidence of cells
Stromatolites
rocklike structures made up of layers of bacteria and sediment
The first cells were likely…
anaerobic heterotrophs
The first photosynthetic organisms were likely…
Cyanobacteria
Stromatolites containing cyanobacteria have been found to date as far back as
3.5 bya
Banded iron formations
date back about 2.5 by a and indicate the massive release of O2 into the oceans
About how long ago did eukaryotes first appear in the fossil record
2 bya
Precambrian time
from 4.6 by a to 542 million years ago; possibly a snowball earth and ended with the Ediacaran Period
Paleozoic Era
542-251 mya; contains the Cambrian period, Ordovician period, Silurian period, Devonian period, Carboniferous period, Permian period
Ended with the largest mass extinction event
Cambrian period
542-488 mya; Biggest expansion in diversity with the Cambrian explosion of multicellular organisms
Ordovician period
488-444 mya; species include trilobites, brachiopods, mollusks; first coral reefs and terrestrial plants
Ended with the first mass extinction event that was likely due to an ice age
Silurian period
444-416 mya; first vascular plants and first true terrestrial animals
Devonian period
416-359 mya; Age of fishes with jawed fishes diversifying and dominating seas; amphibians and insects first appear & vascular plants diversify
Ended with 2nd mass extinction event
Carboniferous period
359-299 mya; reptiles appear and amphibians diversify and dominate terrestrial carnivores making this the age of amphibians
Permian period
299-251 mya; by the end of this period the continents have merged as the Pangaea super continent
Ended with the 3rd mass extinction event
Mesozoic era
251-65 mya; age of reptiles/ dinosaurs
contains the triassic, jurassic, and cretaceous periods
Triassic period
251-200 mya
dinosaurs and mammals first appear; gymnosperms are dominant land plants
Ended with the 4th mass extinction event that paved the way for dinosaurs
Jurassic period
200-146 mya
Dinosaurs dominate the land and birds evolve from dinosaurs
Cretaceous period
146-65 mya
Flowering plants evolved and diversified; many animals coevolved with flowering plants
Ended with 5th mass extinction event that killed the dinosaurs and gymnosperms
Iridium layers worldwide, deposits from tsunamis around the Gulf of Mexico, and a large crater site in the Yucatan Peninsula of Mexico provide evidence for…
the 5th mass extinction being caused by impact of a large extraterrestrial body
Cenozoic Era
65 mya - present
Age of Mammals along with diversification of birds, insects, and flowering plants
Contains the Paleogene and neogene periods
Neogene period
The rise of humans
Has many ice ages and mass extinctions and will result in the 6th mass extinction
Ecology
Scientific study of interactions between organisms and the environment
Biotic factors
living organisms that shape the environment
Ex: aquatic plants and fish
Abiotic factors
Non-living components of the ecosystem that shape the environment
Ex: mountain
Climate
long term prevailing weather conditions at a given place
Abiotic factors of climate
land formations and bodies of water (by heating and cooling air masses)
How do mountains effect climate
influence air flow and the amount of sunlight that reaches an area & the higher the elevation the more cold and less oxygen available
Equinox
start of spring and fall
Solstice
start of summer and winter
biomes
classified by the species that live in a certain area (major life zones)
What causes the seasons
tilt of the earth
Lakes
One of the major aquatic biomes; standing fresh water with littoral (shallow) and limnetic (deeper) zones
Wetlands
One of the major aquatic biomes; water-saturated soil and sometimes standing water
Streams & rivers
One of the major aquatic biomes; fresh water with a current
Estuaries
One of the major aquatic biomes; river/sea transition, salt/fresh water content varies, influenced by tide and slow flow of water
Intertidal zone
One of the major aquatic biomes; exposed and covered up daily by the tides
Ocean pelagic zone
One of the major aquatic biomes; open ocean with currents and deep photic zone
Coral reefs
One of the major aquatic biomes; photic zone with calcium carbonate substrate, very diverse
Marine benthic zone
One of the major aquatic biomes; the sea floor
photic zone
zone of water biome where light reaches
aphotic zone
zone of water biome where no light reaches
benthic zone
bottom of water biome
Turnover in lakes
Process driven by temperature changes when nutrient-rich bottom waters turnover with oxygen-rich top waters
Help keep life alive by keeping the entire lake oxygenated
Eutrophication
nutrient-rich water has algal blooms and then lots of detritus; both deplete oxygen
Tropical forest
One of the major terrestrial biomes; rainy with thick forest/closed canopy, diverse
Desert
One of the major terrestrial biomes; monsoons, fluctuates between tempurature extremes, scattered vegetation, dry
mostly near 30 degrees latitude
Savanna
One of the major terrestrial biomes; warm all year, wet and dry seasons, grasses scattered with thorny trees, has adaptations to fire and dryness
chaparral
One of the major terrestrial biomes; near coast, cool and wet winters, long dry summers, shrubs and small trees, fire-adapted
temperate grassland
One of the major terrestrial biomes: dry, cold winter; wet, hot summer; grass-dominated; where most of human food is grown
Taiga (coniferous forest)
One of the major terrestrial biomes: largest biome; cold, long winters; conical trees (snow adaptation)
temperate broadleaf forest
One of the major terrestrial biomes: winters near freezing; hot, humid summers; moderate to high rainfall; vertical flora layers
Tundra
One of the major terrestrial biomes: high wind; long, cold winters; short, cool summers; permafrost; moss, lichens, some grasses, dwarf trees
Makes up 20% of land
Climograph
graph of temperature vs. precipitation
Ecotone
biome transition zone
Population ecology
study of populations in relation to their environment