7. Community Ecology (Predation, Biocontrol, Disease, and Dominant and Keystone Species)
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
Facilitation (interaction)
( + / + ) or ( + / 0 )
one species benefits from the presence of another, which positively impacts its growth, survival, or reproduction
Lotka-Volterra Predator Prey Equations
(pic)

prey distribution =>
search behavior, interference among predaotrs, aggregation of prey
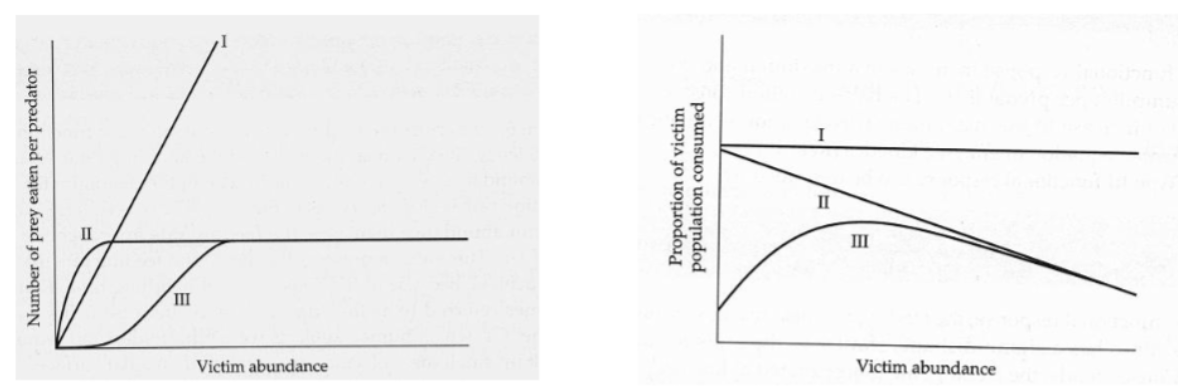
3 types of functional response
Type I function response: linear: predator consumption rate is is constant; a constant proportion of the prey population is removed per unit time
TypeII function response: capture rates rise at a continually decreasing rate until an asymptote is reached
predator hadling time is incorporates into the functional response
type III functional response: the attack rates lag initially at low prey densities and then increase with increase in prey densities and eventually decrease similar to the Type II response. the sresponse is sigmodi (s-shaped)
predator learning, predator switching behaviors or fixed and variable costs associated with foraging are being modeled
aposematic coloration
animals with effective h=chemical defense often exhibit bright warning colors
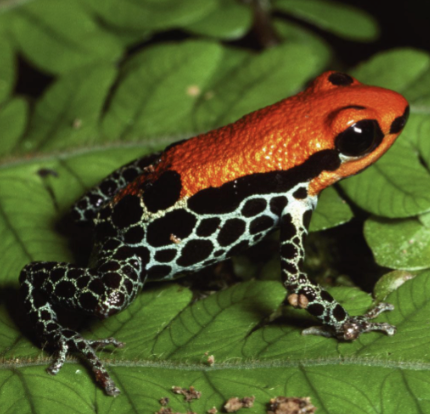

batesian mimicry
a palatble or harmless species mimics an unpalatable or harmful model
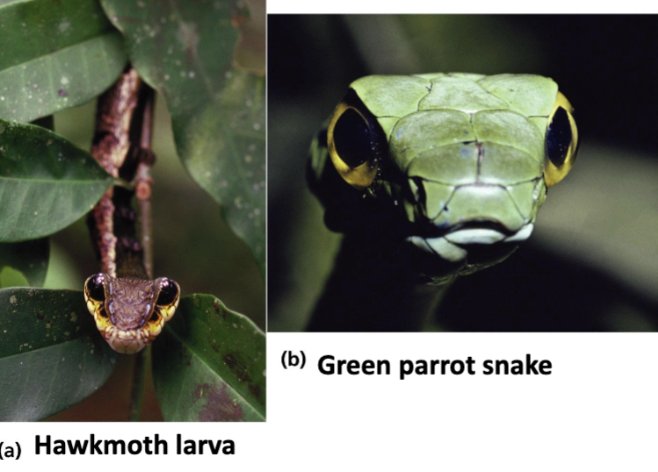

Müllerian mimicry
two or more unpalatable species resemble each other

herbivory
an interaction in which herbivores eats parts of a plant or alga
does not necessarily kill the victim
problems with chemical control:
some insecticides also reduce the pop of predators
biomagnification
insecticide resistance
cost
biological control
use predators or parasites to reduce pest population below some threshold level
pathogens
disease-causing microorganisms
dominant species
those that are most abundant or have the highest biomass
keystone species
exert strong control on a community by their ecological roles, or niches
ex. filed studies of sea stars exhibit their role as a keystone species in intertidal communities