Chemical Properties and Reactions of Lipids
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What is hydrogenation of fats and oils?
A chemical process that adds hydrogen atoms to unsaturated fatty acids, converting them into saturated fats, often catalyzed by metals like nickel.
What is the purpose of hydrogenation?
To change the consistency of oils, increase shelf life, and improve stability and texture of food products.
What are partially hydrogenated oils (PHOs)?
Oils commonly used in processed foods that have been linked to negative health effects, particularly trans fats.
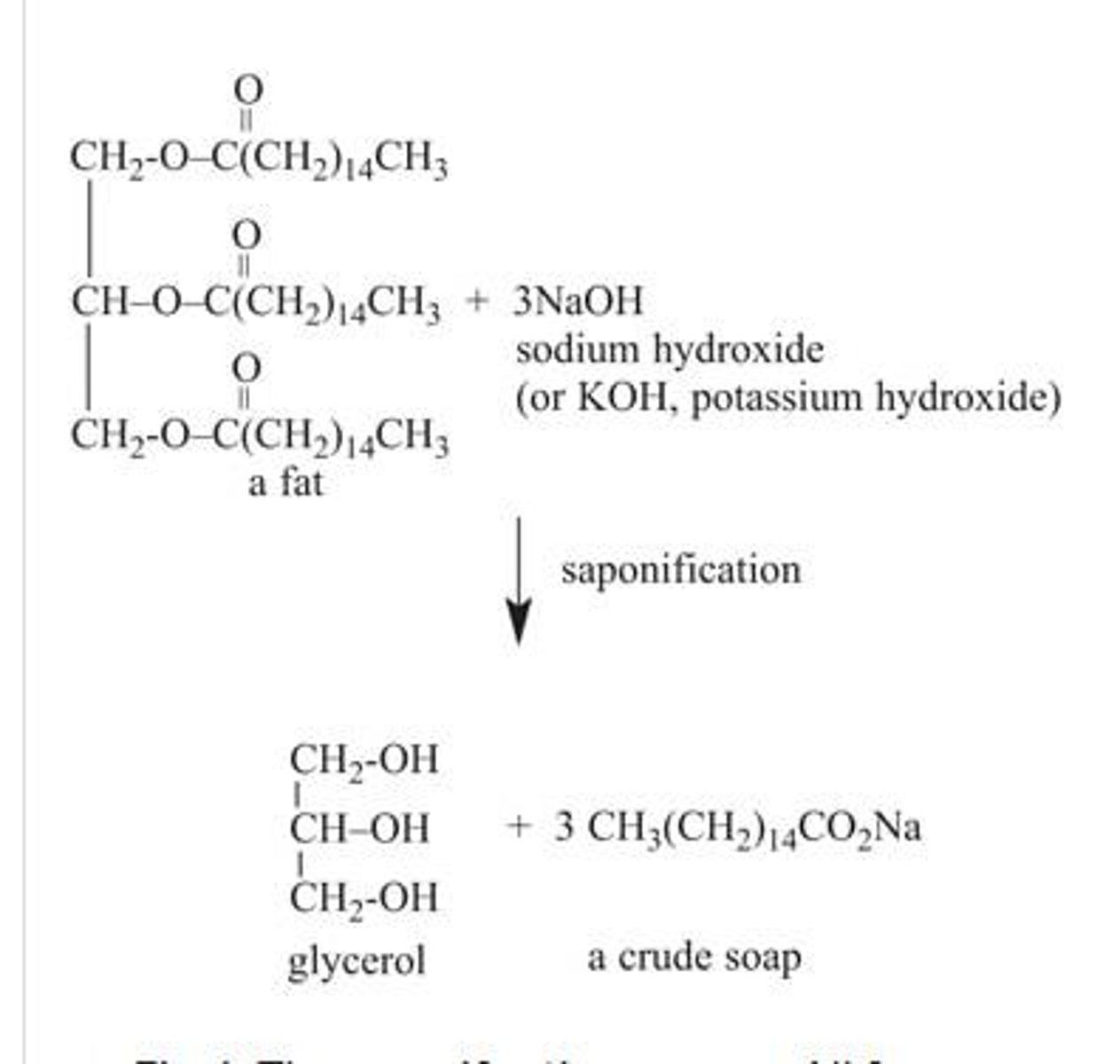
What is saponification?
The chemical process of making soap by reacting fats or oils (triglycerides) with a strong base like sodium hydroxide.
What are the products of saponification?
Glycerol and fatty acid salts, which are the main components of soap.
How is saponification used beyond soap production?
It is used to extract fat-soluble vitamins and pigments from plants.
What is rancidity?
The process by which fats and oils in food degrade, resulting in off-odor, flavor, taste, and texture due to oxidation of unsaturated fatty acids.
What factors accelerate rancidity?
Exposure to light, heat, and air.
What is emulsification?
The process of creating a stable mixture of two normally immiscible liquids, such as oil and water.
What are the two types of emulsions?
1. Water dispersed in fat/oil (e.g., butter, margarine); 2. Oil/fat dispersed in water (e.g., milk, mayonnaise).
What is hydrolysis in the context of lipids?
The process by which triglycerides are broken down into glycerol and fatty acids through the addition of water.
How is hydrolysis related to saponification?
Hydrolysis in the presence of a base is called saponification, converting fatty acids into their salt form (soap).
What is the chemical equation for saponification?
Triglyceride + NaOH → Glycerol + 3 Fatty acid salts (soap).
What is the role of bile salts in digestion?
Bile salts emulsify fats, allowing enzymes to efficiently break them down.
What is the effect of hydrogenation on the melting point of oils?
It increases the melting point of oils, solidifying liquid oils.
Why are solid fats preferred in food applications?
They are more stable and suitable for spreading and baking.
What is the significance of trans fatty acids in hydrogenation?
They are a byproduct of partial hydrogenation, which has raised health concerns.
What are fully hydrogenated oils?
Oils like coconut oil and palm oil that are mostly saturated and still used in food production.
What happens to the texture of foods during hydrogenation?
Hydrogenation can alter the texture, making foods more desirable for consumers.
What are unsaponifiable fractions?
Fat-soluble vitamins and pigments separated from the saponified mixture.
What is the main component of soap produced through saponification?
Fatty acid salts.
What is the relationship between triglycerides and fatty acids?
Triglycerides are esters formed by a glycerol bonded to three fatty acids.
What is a common strong base used in saponification?
Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) or potassium hydroxide.