CCRN Questions
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
A patient has had a large anterior myocardial infarction last month and developed a ventricular aneurysm. He now has episodes of ventricular tachycardia that are not prevented or converted with antidysrhythmic agents. An implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) is implanted. Four days after surgery he develops ventricular tachycardia. The ICD has delivered three shocks but has not converted the rhythm. He is pulseless and apneic. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation is in progress. What is the priority action now?
A.
Administer epinephrine IV.
B.
Administer amiodarone.
C.
Defibrillate.
D.
Reset the ICD.
Defibrillate
A 28-year-old woman is admitted to the critical care unit from the emergency department with a diagnosis of asthma. Her initial arterial blood gases on a 28% Venturi mask are as follows:
pH 7.48
PaCO2 30 mm Hg
HCO3 24 mEq/L
PaO2 64 mm Hg
Which of the following repeat arterial blood gases on 40% oxygen indicate that the patient's condition is worsening?
A.
pH 7.48, PaCO2 30 mm Hg, PaO2 68 mm Hg
B.
pH 7.46, PaCO2 32 mm Hg, PaO2 61 mm Hg
C.
pH 7.40, PaCO2 40 mm Hg, PaO2 62 mm Hg
D.
pH 7.39, PaCO2 30 mm Hg, PaO2 60 mm Hg
C.
pH 7.40, PaCO2 40 mm Hg, PaO2 62 mm Hg
The case study shows stage II asthma. Option c shows stage III asthma. The patient is still breathing at a fast rate, but carbon dioxide is starting to be retained as evidenced by the increase of the PaCO2 into normal range. Options a and b are still stage II. Option d shows a respiratory alkalosis with a metabolic acidosis because you would have expected the pH to be in an alkalotic range with the PaCO2 of 30.
A patient experiencing alcohol withdrawal syndrome describes the swirls in the wallpaper as being worms. This is an example of which of the following?
A.
Delusion
B.
Hallucination
C.
Illusion
D.
Visual impairment
C.
Illusion
An illusion is a misperception or misinterpretation of an actual external stimulus. Illusions and hallucinations (a perception that has no actual external stimulus) are common during alcohol withdrawal syndrome.
A patient arrives in the emergency department with multiple gunshot wounds. He requires massive transfusion for blood loss from chest and abdominal wounds. The electrocardiogram should be observed closely for changes indicative of which of the following?
A.
Atrioventricular block
B.
Hyperkalemia
C.
Hypercalcemia
D.
Hypomagnesemia
Hyperkalemia
Banked blood is high in potassium because of hemolysis. Look for tall, peaked T waves and widening of the QRS complex. Other considerations with massive transfusion of banked blood are hypocalcemia, hypothermia, and decreased tissue oxygen delivery caused by decreased levels of 2,3-diphosphoglycerate.
A 65-year-old woman reports severe dyspnea 2 days after abdominal surgery. She is transferred to the critical care unit. On 5 L of oxygen by nasal cannula, her arterial blood gases are as follows:
pH 7.39
PaCO2 35 mm Hg
HCO3 19 mEq/L
PaO2 40 mm Hg
Arterial oxygen saturation 75%
Why does this patient have hypoxemia without hypercapnia?
A.
Because carbon dioxide is more diffusible than oxygen
B.
Because carbon dioxide has more driving pressure
C.
Because carbon dioxide is less diffusible than oxygen
D.
Because carbon dioxide excretion by the kidney is increased
Because carbon dioxide is more diffusible than oxygen
Carbon dioxide is 20 times more diffusible than oxygen. In conditions that affect diffusion but do not affect ventilation, expect the PaO2 to be decreased and the PaCO2 to be normal (or decreased in hyperventilation, as in this patient). If ventilation were affected, such as if this patient were fatiguing, the PaCO2 then would increase. Driving pressure is the fraction of the gas in inspired air multiplied by the barometric pressure. Because carbon dioxide is ~0.5% of inspired air, the driving pressure would be very low. The kidney eliminates bicarbonate and hydrogen ions, but the lungs eliminate carbon dioxide.
A 55-year-old patient has headache, nuchal rigidity, photophobia, and positive Kernig's and Brudzinski's signs. These are consistent with which of the following?
A.
Intracranial hemorrhage
B.
Subarachnoid hemorrhage
C.
Epidural hemorrhage
D.
Subdural hemorrhage
Subarachnoid hemorrhage
When there is bleeding from an aneurysm, that blood irritates the meninges. The clinical presentation is very similar to meningitis. This clinical presentation is not consistent with intracranial, epidural, or subdural bleeding because the blood is not in contact with the meninges in those situations.
An extra heart sound preceding S1 is most likely an S4 if the stethoscope's:
A.
diaphragm is over the apex.
B.
bell is over the aortic area.
C.
diaphragm is over the aortic area.
D.
bell is over the apex.
bell is over the apex.
S3 and S4 are low pitched, so choose options with the bell being used. S3 and S4 are heard at the mitral area (i.e., apex) unless the right ventricular is affected, and then they are heard in the tricuspid area.
Low-Pitched is best heard with Bell
The charge nurse on the 7 pm to 7 am shift was asked to assist a group of nurses to resolve their conflict so that their two opposing goals are discarded and new goals are adopted. This is an example of which of the following?
A.
Smoothing of conflict
B.
Facilitating collaboration
C.
Encouraging compromise
D.
Democratic approach
Facilitating collaboration
This is an example of facilitating collaboration. The nurse is, in essence, acting as mediator to assist these two groups in developing common goals. In smoothing, you would try to reduce the emotional stress of the conflict, but the conflict really would not get resolved. In compromising, each group would give up something that it wants. In a democratic approach, majority rules.
Which of the following are the most clinically significant intracranial pressure (ICP) waveforms that require immediate intervention?
A.
A waves
B.
B waves
C.
C waves
D.
D waves
A waves, or plateau waves, are spontaneous, rapid increases in pressure between 50 and 200 mm Hg that last 5 minutes or more. A waves cause cerebral ischemia and are the most clinically significant ICP waveforms. Immediate intervention is necessary to prevent further brain injury and herniation.
A waves are Awful
Which of the following diagnostic tests would provide definitive evidence of a pneumothorax?
A.
Arterial blood gases
B.
Chest x-ray film
C.
Pulmonary function studies
D.
Spiral computed tomography
Chest x-ray film
(Which is not really true.. but the test says so..
Which of the following does not shift the oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve to the left or the right?
A.
Blood pH
B.
2,3-diphosphoglycerate (2,3-DPG) levels
C.
Body temperature
D.
Cardiac output
Cardiac output
Body temperature, body pH, PaCO2 levels, and 2,3-DPG levels affect the oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve. Cardiac output does not directly affect the curve.
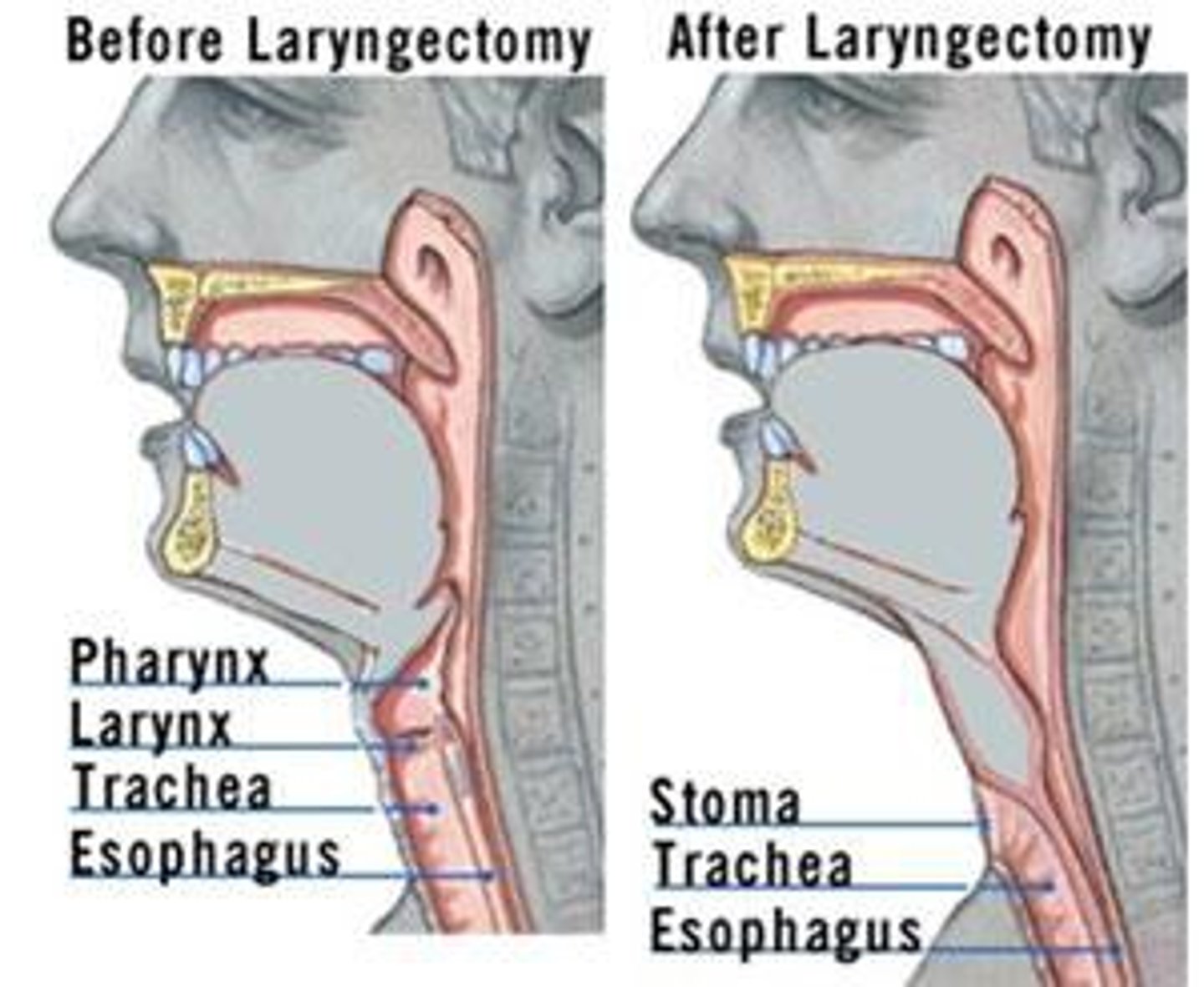
Which of the following is the primary difference between a tracheostomy tube and a laryngectomy tube?
A.
The laryngectomy tube is longer.
B.
The laryngectomy tube does not have a cuff.
C.
Only the tracheostomy tube has an inner cannula.
D.
The tracheostomy tube has a larger lumen.
The laryngectomy tube does not have a cuff.
A cuff is not necessary because food and fluid from the mouth can go only to the esophagus and the stomach, and air going into the laryngectomy tube can go only into the lungs. The only way this patient can aspirate is if a fistula develops because the anatomy has been surgically altered by removal of the larynx.
The mean QRS axis of ventricular tachycardia is most likely to be:
A.
normal or left axis deviation.
B.
right axis deviation or indeterminate axis.
C.
right axis deviation or left axis deviation.
D.
left axis deviation or indeterminate axis.
left axis deviation or indeterminate axis.
Ventricular tachycardia is most likely to be left axis deviation of −30 or greater or indeterminate axis, whereas aberrancy is more likely to be normal axis or right axis deviation.
A 58-year-old man is admitted to the critical care unit with upper gastrointestinal bleeding. He has a history of chronic renal failure. When one is administering antacids, it is important to remember to avoid:
A.
magnesium-containing antacids.
B.
phosphate-binding antacids.
C.
calcium-containing antacids.
D.
histamine2 receptor antagonists.
magnesium-containing antacids.
Magnesium-containing antacids can lead to magnesium intoxication in the patient with renal failure.
A patient is complaining of dull, diffuse abdominal pain. Of the following possible causes, which is most likely to be the cause?
A.
Appendicitis
B.
Cholecystitis
C.
Ulcerative colitis
D.
Large intestinal obstruction
Large intestinal obstruction
The rest are sharp pain
Vt for extubation
5ml/kg
A 30-year-old man is in the surgical intensive care unit after exploratory laparotomy performed after he sustained a gunshot wound to the abdomen. He now has developed a pancreatic fistula. Which acid-base imbalance is this patient at risk for developing?
A.
Respiratory acidosis
B.
Metabolic acidosis
C.
Respiratory alkalosis
D.
Metabolic alkalosis
Metabolic acidosis
The stomach is acidic, but the gastrointestinal tract below the stomach is alkaline. Pancreatic secretions are rich in bicarbonate, and these losses would cause metabolic acidosis.
A 65-year-old man was admitted 2 hours ago after coronary artery bypass grafting. He has had the following vital sign changes:
Admission 2 Hours Later
Blood pressure (mm Hg) 110/80 96/76
Heart rate (per minute) 85 100
Right atrial pressure (RAP; mm Hg) 6 2
Pulmonary artery pressure (PAP; mm Hg) 24/12 18/6
Pulmonary artery occlusive pressure (PAOP; mm Hg) 10 5
Cardiac output (L/min) 6 4
Cardiac index (L/min/m2) 3.5 2.5
Systemic vascular resistance index (SVRI; dynes/sec/cm−5) 1920 2590
What is the most likely cause of these changes?
A.
Stunned myocardium
B.
Blood loss
C.
Cardiac tamponade
D.
Intraoperative myocardial infarction
Blood loss
Note that all of the volume indicators (RAP, PAP, PAOP) have decreased. The increase in SVRI is compensatory and is caused by sympathetic nervous system stimulation. Stunned myocardium and intraoperative myocardial infarction more likely would cause an increase in PAOP because of heart failure. Cardiac tamponade would cause an increase in RAP, PAP, and PAOP.
Provision of adequate nutrition in a malnourished patient may cause severe deficiency of which of the following electrolytes?
A.
Potassium
B.
Magnesium
C.
Calcium
D.
Phosphate
Phosphate
This often is called refeeding syndrome. Nutritional support allows the cells to begin making more adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and phosphate supplies are depleted. The same thing happens in diabetic ketoacidosis with treatment when insulin allows glucose to move into the cell increasing production of ATP and depletion of phosphate.
Which of the following would be a contraindication to the use of fibrinolytic drugs, such as recombinant tissue plasminogen activator?
A.
Hypotension
B.
Heart block
C.
Uncontrolled hypertension
D.
Pain lasting more than 6 hours
Uncontrolled hypertension
Pain of more than 6 hours duration is no longer a contraindication to the use of fibrinolytic drugs, although we certainly want to give fibrinolytic drugs as early as possible. Consider that pain indicates the presence of lactic acid and anaerobic metabolism. If the myocardial infarction is completed, there is no pain because dead myocardium does not metabolize aerobically or anaerobically. As long as there is pain, there is salvageable myocardium. Hypotension and heart block are not contraindications to fibrinolytic drugs, and they may improve with reperfusion of the myocardium. Uncontrolled hypertension increases the risk of hemorrhagic stroke.
A 72-year-old woman arrives at the emergency department after becoming unresponsive while watching television with her husband. The nurse observes paralysis of her right extremities, aphasia, and lethargy. The patient receives fibrinolytic therapy. After the patient is stabilized, a diet is offered. The nurse knows that before the patient eats, it is crucial to check which of the following cranial nerves?
A.
IX, X
B.
I, II
C.
III, VI
D.
VIII, XI
IX, X
Cranial nerves IX and X control the gag and swallow response. These must be intact bilaterally to protect the patient's airway.
glossopharngeal and vagus
A 23-year-old man is admitted via the emergency department after a motorcycle collision. His Glasgow Coma Scale score was 12 in the emergency department, and it is still 12 upon his admission to the neurologic intensive care unit. Both eyes are ecchymotic and swollen shut, and he has multiple abrasions on his face. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A.
Linear skull fracture
B.
Basal skull fracture
C.
Orbital fracture
D.
Mandibular fracture
Basal skull fracture
Which leads are most helpful in differentiating ventricular tachycardia from a supraventricular tachycardia with aberrancy?
A.
Leads II and III
B.
Leads V1 and V6
C.
Leads I and aVL
D.
Leads V3 and V4
Leads V1 and V6
Looking at the heart from either side helps to identify whether the impulse originated in one ventricle or the other. Inferior, lateral, and anterior leads have a predominantly positive QRS complex because the wave of depolarization through the heart is downward and to the left. Lead V1 is the single most helpful lead to differentiate ventricular ectopy from aberrancy. Leads V1 and V6 together are the two most helpful leads.
Which of the following describes the primary role of a case manager?
A.
Educator
B.
Evaluator
C.
Facilitator
D.
Advocate
Advocate
A patient develops carpopedal spasm and neuromuscular irritability manifested by Chvostek's and Trousseau's signs. Which electrolyte imbalance should you suspect?
A.
Hyperkalemia
B.
Hypercalcemia
C.
Hypermagnesemia
D.
Hyperphosphatemia
Hyperphosphatemia
The patient's signs/symptoms are associated with hypocalcemia and its reciprocal condition, hyperphosphatemia. The same signs/symptoms also are seen in hypomagnesemia.
A patient with which of these conditions would have a normal serum lactate?
A.
Ventricular fibrillation
B.
Cardiogenic shock
C.
Severe anemia
D.
Renal failure
Renal failure
All of these will cause metabolic acidosis, but in renal failure the acidosis is related to accumulation of nonvolatile acids (e.g., urea and uric acid). Ventricular fibrillation, cardiogenic shock, and severe anemia would decrease tissue oxygen delivery, resulting in the conversion of metabolism from aerobic to anaerobic and the buildup of lactic acid. Lactic acidosis is reflected as an increase in serum lactate level.
A patient has a diagnosis of pulmonary embolism made by pulmonary arteriography. He now is receiving 100% oxygen via a non-rebreathing mask for 24 hours. The nurse is concerned about the possibility of oxygen toxicity. What is a common, early sign of oxygen toxicity?
A.
Cyanosis
B.
Hypercapnia
C.
Substernal chest pain
D.
Moist, productive cough
Substernal chest pain
Early indications of oxygen toxicity are substernal distress, paresthesias in extremities, and gastrointestinal symptoms (e.g., anorexia, nausea, vomiting, fatigue, malaise, dyspnea, and restlessness). Late indications are hypercapnia, cyanosis, decreasing compliance, increasing A:a gradient, and pulmonary edema.
While hyperventilation therapy was used routinely in the past for patients with neurological injury, it is now reserved for indications of acute herniation. What is the physiologic rationale for this restriction?
A.
The resultant vasodilation increases cerebral blood flow but increases intracranial volume and pressure.
B.
The resultant hypervolemia increases cerebral blood flow but increases intracranial volume and pressure.
C.
The resultant hypovolemia decreases intracranial volume and pressure but causes cerebral ischemia.
D.
The resultant vasoconstriction decreases intracranial volume and pressure but causes cerebral ischemia.
The resultant vasoconstriction decreases intracranial volume and pressure but causes cerebral ischemia.
Hyperventilation causes respiratory alkalosis which causes vasoconstriction which decreases intracranial volume and pressure. However, this vasoconstriction potentially causes cerebral ischemia.
A decrease in static compliance would occur in which of the following?
A.
Pneumothorax
B.
Flail chest
C.
Bronchospasm
D.
Mucous plug
Pneumothorax
Static compliance is the compliance of the lung when no air is moving, so it reflects the compliance of the lung and the chest wall. Dynamic compliance is the compliance of the lung when air is moving, so it reflects the compliance of the lung and chest wall plus airway resistance. Pneumothorax causes a sudden decrease in static compliance, whereas acute respiratory syndrome causes a gradual decrease in static compliance. Bronchospasm or mucous plug causes a decrease in dynamic compliance because it affects airway resistance. Flail chest actually would increase the static compliance because of the loss of intactness of the bony thorax.
A 46-year-old woman is admitted to the critical care unit with acute respiratory failure as a result of pneumonia.
Vital Signs
Blood pressure 140/88 mm Hg
Heart rate 108 beats/min
Respiratory rate 26 breaths/min
Temperature 39.8° C (103.8° F)
Arterial Blood Gases
pH 7.29
PaCO2 54 mm Hg
HCO3 24 mEq/L
PaO2 60 mm Hg
What effect would these alterations have on the oxyhemoglobin curve and oxygen saturation?
A.
A shift to the right and arterial oxygen saturation (SaO2) greater than 90% for the PaO2 of 60 mm Hg
B.
A shift to the left and SaO2 greater than 90% for the PaO2 of 60 mm Hg
C.
A shift to the left and SaO2 less than 90% for the PaO2 of 60 mm Hg
D.
A shift to the right and SaO2 less than 90% for the PaO2 of 60 mm Hg
This patient has hyperthermia and acidosis. Both of these cause a shift in the oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve to the right. Shift to the right causes a lower saturation for a given PaO2 because of a lower affinity between oxygen and hemoglobin. Though a PaO2 of 60 mm Hg usually is associated with an oxygen saturation of 90%, this patient would have a saturation of less than 90% for the PaO2 of 60 mm Hg. When the curve is shifted to the right, affinity is decreased. This means that the pickup of oxygen at the lung level is impaired but drop-off at the tissue level is improved. A shift of the curve to the left improves pickup of oxygen at the lung level but impairs drop-off at the tissue level.
A 70-kg male patient with acute respiratory failure is being weaned from mechanical ventilation using the intermittent mandatory ventilation (IMV) method. Ventilator settings and current arterial blood gas results are as follows:
Ventilator Settings Arterial Blood Gases
Fraction of inspired oxygen, 0.35 pH, 7.29
Tidal volume, 700 mL HCO3, 22 mEq/L
IMV, 4 breaths/min PaCO2, 52 mm Hg
PaO2, 96 mm Hg
The patient has copious secretions. Before suctioning the patient's endotracheal tube, the nurse should adjust the vacuum pressure so that it is:
A.
as high as necessary.
B.
100 mm Hg of vacuum.
C.
60 mm Hg of vacuum.
D.
10 mm Hg below the systolic blood pressure.
100 mm Hg of vacuum.
Using a suction level as high as necessary certainly could increase trauma to the tracheobronchial tree. Pressure as low as 60 mm Hg would be unlikely to clear copious secretions. This pressure has nothing to do with systolic blood pressure.
A 24-year-old woman is admitted with a closed head injury after a fall from a cliff. She is less responsive and has a nonreactive dilated right pupil. These signs suggest pressure in which area of the brain?
A.
Right hemisphere
B.
Left hemisphere
C.
Cerebellum
D.
Hypothalamus
Right hemisphere
CN III controls pupil constriction. Hemispheric pressure on this nerve will result in a dilated pupil on the same side as the pressure.
A 29-year-old woman has been a patient in the critical care unit for 2 weeks with acute tubular necrosis (ATN) as a result of crush injuries experienced in a motor vehicle collision. She was normotensive on admission. Which electrolyte imbalances are likely to result from ATN?
A.
Hypomagnesemia, hypocalcemia, hypokalemia
B.
Hypomagnesemia, hypercalcemia, hypokalemia
C.
Hypermagnesemia, hypercalcemia, hyperkalemia
D.
Hypermagnesemia, hypocalcemia, hyperkalemia
Hypermagnesemia, hypocalcemia, hyperkalemia
Hypermagnesemia and hyperkalemia result from the inability of the kidneys to excrete these electrolytes. Hypocalcemia is the result of the inability of the kidneys to produce the active component of vitamin D, 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol and the change in calcium as a result of the hyperphosphatemia that is seen in ATN.
The physician has prescribed mannitol (Osmitrol) for a patient with intracranial hypertension. Which of the following is an important consideration when administering mannitol (Osmitrol)?
A.
The drug must be protected from light.
B.
The drug must be administered through an in-line filter.
C.
The drug must be administered into a central venous catheter.
D.
The drug must be refrigerated.
The drug must be administered through an in-line filter.
Mannitol may crystallize out of solution if exposed to low temperatures. If crystals are observed, the solution should be warmed to dissolve them and then the solution should be returned to room temperature prior to use. Because there is rarely time for this process in neurologic patients in crisis, another bottle should be requested. Also, a filter needle should be used to draw up mannitol from a vial, and mannitol solution must be given through an in-line filter because there are likely crystals that cannot be seen.
A patient admitted with a gunshot wound and open pneumothorax has had her chest tube dislodged. What would be the most appropriate action?
A.
Reinsert the tube and chart it.
B.
Leave the dressing off and call the physician.
C.
Cover the wound with a petroleum jelly dressing and call the physician.
D.
Cover the wound with a gauze dressing taped on three sides and call the physician.
Cover the wound with a gauze dressing taped on three sides and call the physician.
You want to avoid impairing the movement of air out of the chest because a tension pneumothorax might occur. However, you do want to impede the movement of air into the chest. You would never reinsert a contaminated chest tube back into the chest.
Which aspect of assessment is the most important in a patient with a platelet count of 10,000/mm3?
A.
Skin assessment for petechiae and ecchymosis
B.
Level of consciousness
C.
Blood pressure
D.
Urine output
Level of consciousness
Monitor for cerebral hemorrhage
In patients predisposed to stress ulcer, the goal of therapy is to keep gastric pH:
A.
Less than 3
B.
Between 3.5 and 5
C.
Between 5 and 6.5
D.
Above 7
Between 3.5 and 5
Hydrochloric acid has a pH of 1.0 to 3.0. Making the gastric secretions less acidic by using histamine2 receptor antagonists (e.g., ranitidine), proton-pump inhibitors (e.g., pantoprazole), and antacids decreases the caustic nature of the secretions and decreases the risk of stress ulcer. True alkalinization (pH greater than 7) is not desirable because it would allow proliferation of bacteria. The desirable gastric pH in prevention of stress ulcer is between 3.5 to 5.
Which of the following is the most common form of bifascicular block?
A.
Left bundle branch block
B.
Right bundle branch block and left anterior hemiblock
C.
Right bundle branch block and left posterior hemiblock
D.
Left anterior and left posterior hemiblocks
Right bundle branch block and left anterior hemiblock
The three fascicles of the intraventricular conduction system are the right bundle branch, the left anterior branch of the left bundle branch, and the left posterior branch of the left bundle branch. The left anterior branch of the left bundle is long and thin and is blocked more often than the left posterior branch. A right bundle branch block along with a block of the left anterior branch of the left bundle branch (called a left anterior hemiblock) is the most common form of bifascicular block.
Which of the following is the most common cause of heart failure?
A.
Aging
B.
Diabetes mellitus
C.
Coronary artery disease
D.
Hereditary factors
Coronary artery disease
Which of the following assessment findings is specific to hemothorax rather than pneumothorax?
A.
Chest or shoulder pain
B.
Diminished or absent breath sounds
C.
Tachypnea
D.
Dullness to percussion
Dullness to percussion
Pneumothorax is hyperresonant or even tympanic to percussion, and hemothorax is dull to flat. Options a, b, and c would be seen in both.
What electrolyte abnormalities put you at risk for Torsades?
Hypocalcemia and hypomagnesemia
Which of the following drugs stabilizes epithelial mast cells, thereby reducing the release of histamine?
A.
Triamcinolone (Azmacort)
B.
Ipratropium bromide (Atrovent)
C.
Cromolyn sodium (Intal)
D.
Metaproterenol (Alupent)
Cromolyn sodium (Intal)
If a patient is breathing room air and his PaCO2 level is elevated, must his PaO2 be reduced?
A.
Yes, because of Fick's law of diffusion
B.
Yes, because of Dalton's law of partial pressures
C.
No, because of the driving pressure of oxygen
D.
No, because PaCO2 is a reflection of ventilation, not oxygenation
Yes, because of Dalton's law of partial pressures
If the patient is breathing room air and the PaCO2 is elevated, the PaO2 must be reduced because of Dalton's law, which basically says that all the partial pressures cannot add up to more than atmospheric pressure. So if we have only 760 mm Hg maximum, and PaCO2 takes more than its fair share, there is less "room" for oxygen, and the PaO2 will be decreased. Fick's law of diffusion says that the rate of transfer of a gas through a sheet of tissue is proportional to the tissue area, so it is not pertinent to this situation. The driving pressure is the concentration of the gas times the pressure of the gas, so the driving pressure of oxygen is not affected by PaCO2. PaCO2 is a reflection of ventilation, but impaired ventilation and an increase in PaCO2 can limit how high the PaO2 can be because of Dalton's law. However, if the patient is breathing supplemental oxygen, he can have an elevated PaCO2 and a normal PaO2. This is why pulse oximetry does not tell you that your patient is ventilating adequately. He can have a normal pulse oximetry but be significantly hypercapnic if he is breathing supplemental oxygen because the driving pressure of oxygen is increased by increasing the concentration of oxygen.
what does radiolucent vs radiopaque mean in a chest radiograph?
radiolucent - is dark as the normal lung of radiograph. This is most likely to be free air
radiopaque- is bright white on radiograph. Meaning particularly dense - could be bone, consolidations, nodules..
A patient was admitted with a diagnosis of left lower lobe pneumonia. He is coughing up large amounts of rust-colored sputum. Which of the following is the most likely organism?
A.
Pseudomonas
B.
Klebsiella
C.
Streptococcus
D.
Staphylococcus
Streptococcus causes rust-colored sputum. Staphylococcus is likely to cause sputum to be pinkish. Pseudomonas is likely to cause sputum to be greenish. Klebsiella is likely to cause sputum to be currant-colored.
What effect does oxygen have on pulmonary vasculature? What efect does hypoxemia have??
o2 is a potent vasodilator
hypoxemia will cause vasoconstriction
How to you calculate do2??
The DO2I is calculated as CaO2 (that is, SaO2 × Hgb × 1.34) × (CI × 10),
What heart sound is anssociated with angina
s4 (associated with decreased LV compliance - hypertrophy, ischemia)
What is an s3 heart sound
sound of rapid ventricle filling in an alrady fluid overloaded LV. (heart failure)
Which vessel is used as a graft when the minimally invasive direct coronary artery bypass grafting (MIDCABG) procedure is performed?
The internal thoracic (also called the internal mammary) artery is used for a MIDCABG.
A 55-year-old patient has headache, nuchal rigidity, photophobia, and positive Kernig's and Brudzinski's signs. These are consistent with which of the following?
When there is bleeding from an aneurysm, that blood irritates the meninges. The clinical presentation is very similar to meningitis. This clinical presentation is not consistent with intracranial, epidural, or subdural bleeding because the blood is not in contact with the meninges in those situations. (pick the bleed that touches the meninges.
What often precipitates a worsening in guillan barre syndrome>
viral illness - demylenates axons
An S4 is an expected physical finding in which of the following?
A.
Acute myocardial infarction
B.
Left ventricular failure
C.
Pericarditis
D.
Bundle branch block
remember that s4 is heard in a noncompliant ventricle. Noncompliance is caused by ischemia, infarction, hypertrophy, cardiac tamponade, constrictive pericarditis, or restrictive cardiomyopathy. Left ventricular failure would cause an S3. Pericarditis would cause a pericardial friction rub. Bundle branch blocks cause splits (left bundle branch block causes a paradoxical split of S2, and right bundle branch block causes a split of S1 and increased splitting of S2 during inspiration).
What would be the best laboratory test to evaluate this patient's glomerular filtration rate (GFR)?
urine creatinine clearance
A patient is diagnosed with acute kidney injury (ARF) and is placed on fluid restrictions. The patient's total output for yesterday was 600 mL. Which of the following fluid volumes would be allowed for today?
A.
300 mL
B.
600 mL
C.
1100 mL
D.
1500 mL
Fluid allowances for the patient with ARF are usually 500 mL for insensible loss added to the previous day's urine output.
SOOO 1100.
Which of the following would indicate right ventricular failure as a complication of inferior MI?
A.
Reflex tachycardia with an irregular pulse
B.
Diffuse crackles with shortness of breath
C.
ST elevation in right precordial leads, especially V4R
D.
Reduced central venous pressure
Because one third of all patients with inferior MI will have concurrent right ventricular infarction, ST elevation in leads V4R to V6R should be sought. The fact that this patient responded positively to a fluid challenge along with the presence of inferior MI increases this index of suspicion. Diffuse crackles with shortness of breath would not be treated with fluids but with fluid restriction, diuretics, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, and possibly venous vasodilators. Fluids should increase central venous pressure. Reflex tachycardia is related to vasodilation and vasodilators.
C
All of the following have immunosuppressive effects except:
A.
malnutrition.
B.
noise.
C.
anesthetic agents.
D.
diuretics.
DIURETICS
NOISE CAUSES STRESS WHICH HAS A DETRIMENTAL EFFECT ON THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
A patient is admitted with left lower lobe pneumonia. To optimize oxygenation, how should the patient with pneumonia be positioned?
A.
On his left side
B.
On his right side
C.
On his back
D.
Prone
In any unilateral lung condition (except pneumonectomy), the patient should be positioned preferentially on the side of the good lung (i.e., right lung in this case).
B
Which of the following are two significant adverse effects of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors (e.g., captopril [Capoten])?
A.
Heart failure and hypokalemia
B.
Proteinuria and hyperkalemia
C.
Thrombocytopenia and hepatotoxicity
D.
Dysrhythmias and hyponatremia
B
Focus on physiology. ACE inhibitors prevent angiotensin II from being activated and aldosterone from being secreted. Aldosterone causes sodium and water retention and potassium excretion, so blocking that effect potentially would cause hyperkalemia. Choose option b.
A 22-year-old man is admitted to the intensive care unit after a motor vehicle collision. There are lacerations on his face and head. The nurse observes a steady drip of clear fluid coming from his left ear. Which of the following is an appropriate action to contain the drainage of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)?
A.
Applying sterile ear packing
B.
Connecting low suction to the ear
C.
Applying loose sterile dressing
D.
Leaving ear uncovered
It is important not to obstruct CSF flow because this could increase intracranial pressure. Introducing suction could cause bleeding, infection, or further structural damage.
A 52-year-old woman developed an epidural hematoma after being in a motor vehicle collision. She has had a craniotomy to evacuate the clot, and an intraventricular catheter was placed during surgery. Which of the following is important in caring for the patient with an intracranial pressure (ICP) monitoring system?
A.
Use heparin to maintain integrity of the line.
B.
Use preservative-free isotonic saline.
C.
Use a flush system.
D.
Use a pressure bag.
ICP monitoring systems are closed systems. A flush system with heparin and a pressure bag with an intermittent flush device is appropriate for vascular pressure monitoring (e.g., arterial catheters and pulmonary artery catheters) but not for intracranial pressure monitoring systems. Preservatives in saline vials can cause meningeal irritation or brain tissue necrosis. Only preservative-free saline should be used to prime the system.
What part of the electrocardiographic waveform represents conduction through the atrioventricular node?
A.
P wave
B.
PR interval
C.
PR segment
D.
QRS interval
The PR interval represents the time from the beginning of atrial depolarization to the beginning of ventricular depolarization. The PR segment is the time between the P wave and the QRS complex and represents the delay in the atrioventricular (AV) node.
Which of the following drugs are used for first-line therapy for chronic management of hypertension?
Diuretics and beta blockers
Which of the following tests are used to differentiate the cause of jaundice?
An increase in direct bilirubin is associated with biliary obstruction because direct bilirubin is conjugated. An increase in indirect bilirubin is associated with hepatic disease or excessive hemolysis because indirect bilirubin is unconjugated.
what is the action of potassium in motility?
hyper= hypermotility
hypo=risk for ileus/hypomotility
Describe causes of
Guillan Barre
Myesthenia gravis
Guillan barre - demylenating
MG - autoimmune versus acetocholine receptors
Which of the following is the major advantage of minimally invasive direct coronary artery bypass grafting (MIDCABG)?
A.
Decreased cost
B.
Decreased length of stay
C.
Avoidance of cardiopulmonary bypass
D.
Less patient pain
C - avoidance of cardiopulmonary bypass
Brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) is secreted in response to which of the following?
stretch of the ventricular wall
Which clinical or laboratory feature would indicate a significant adverse effect of clopidogrel (Plavix)?
A.
Elevated blood urea nitrogen and creatinine
B.
Petechiae
C.
S3 at the apex
D.
Dyspnea
B
Which of the following increases oxygen consumption?
A.
Anxiety
B.
Hypothermia
C.
Sepsis
D.
Sedation
You may have thought of sepsis because you associate it with infection, fever, and hypermetabolism. Remember, however, that sepsis causes a decrease in the ability of the tissues to extract and use oxygen.
Answer A
Which of the following is the most common side effect of nesiritide (Natrecor) therapy in heart failure?
Hypotension
absorptive atelectasis. What is the cause of this complication of oxygen therapy?
Nitrogen washout
Absorptive atelectasis is caused by the elimination of nitrogen from the alveoli. Normally inspired air is approximately 21% oxygen and 79% nitrogen. This nitrogen is an unabsorbed gas that, along with the effect of surfactant, holds the alveoli partially open at the end of expiration. When 100% of the inspired gas is oxygen (an absorbable gas), the nitrogen is not present in the alveoli (described as nitrogen washout) to keep the alveoli open, and atelectasis occurs.
Over the past 2 hours, a patient admitted with severe acute heart failure has the following changes in assessment parameters:
Admission 2 Hours Later
Heart sounds S1, S2 S1, S2, S3 audible at apex
Blood pressure 118/60 mm Hg 98/54 mm Hg
Heart rate 105 beats/min 126 beats/min
Respiratory rate 30 breaths/min 36 breaths/min
Which of the following combinations of drugs are indicated for the achievement of the therapeutic goals of this patient?
A.
Nitroprusside (Nipride) and furosemide (Lasix)
B.
Dobutamine (Dobutrex) and furosemide (Lasix)
C.
Dobutamine (Dobutrex) and nitroprusside (Nipride)
D.
Morphine sulfate and furosemide (Lasix)
B - The answer would not be C, because nipride would to severely lower SVR and MAP
Positioning for infratentorial carniotomy
HOB flat!
Which of the following best describes multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS)?
A.
Progressive insufficiency of two or more organ systems
B.
Cessation of function of two or more organ systems
C.
Sepsis involving two or more organ systems
D.
Loss of function of two or more components of the same organ system
A
The definition does not require complete dysfunction, but more than 1 organ system needs to be involved.
A 68-year-old woman is admitted with ischemic stroke. When the bottom of her foot is stroked, the great toe moves upward and the other toes fan out. This finding indicates which of the following?
A.
Upper motor neuron lesion
B.
Lower motor neuron lesion
C.
Brainstem lesion
D.
Normal finding
A
Upper do to stroke, and the babinski reflex is an UMN lesion always
Your patient is in hepatic failure caused by chronic liver disease. She has ascites and severe peripheral edema. She is anorectic and vomiting and has developed metabolic alkalosis and hypokalemia. Which of the following would not be included in this patient's management?
A.
Diuretics
B.
Potassium supplements
C.
Antiemetics
D.
Diet high in protein
Diuretics would worsen the metabloc alkolis and hypokalemia. The patient with liver failure does not have the appropriate proteins to pull water from the tissues into the vascular bed, thus diuretics would lose their effect in this situation. A diet high in protein would only be contraindicated if the patient had a decrease in mental status from the liver failure ( H ammonia levels)
A 34-year-old man admitted with Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia asks the nurse what protective measures he should use at home to prevent transmission of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) to family members. The best response would include which of the following?
A.
Wear a mask to protect the family members.
B.
Use plastic eating utensils and paper plates.
C.
Launder clothing and linens separately.
D.
Clean up body secretion spills with a weak chlorine bleach solution.
D - throw out the extremes and remember than body secretions are the concern. I weak chlorine bleach will kill HIV
RA, RV, PA, and PAOP pressure normals?
What is a pressure for an optimally stretched wedge?
SVC/RA = 0-6 mmHg (at this point inflate balloon with 1.5 mL of air)
RV = 25/0 mmHg
PA = 15-30/5-15 mmHg
PAOP = 2-10 mmHg at 40-50 cm distance (if SCV/ IJ insertion)
somewhere in the ballpark of 12-20 mmHg
Which of the following accurately describes the normal difference between the pulmonary artery diastolic pressure (PAd) and the pulmonary artery occlusive pressure (PAOP)?
PAd should be 0-5mmHg higher than the PAOP.
This to monitor in ethanol poisioning
ethanol can cause hypoglycemia - as well as monitor ethanol levels.
How does heparin inhibit clotting
by neutralizing circulating thrombin
Describe the difference between the s3 and s4 heart sounds
s3 is the sound of rapid filling into an already distended ventricle
s4 is sound of atrial squeeze into a non-compliant ventricle (this non-compliance is caused by ischemia)
Which of the following drugs is an alpha- and noncardioselective beta-blocker?
A.
Propranolol (Inderal)
B.
Esmolol (Brevibloc)
C.
Carvedilol (Coreg)
D.
Metoprolol (Lopressor)
cavedilol
describe the dolls eyes reflex
The presence of dolls eyes is a good thing. when the heard is turned from side to side the brainstem has the ability to mantain the eyes looking forward regardless of spine rotation. The absence of dolls eyes is a BAD thing. The eyes stay midline following the head as it is turned.
What is Prinzmetal's angina
There is ST segmant elevation during periods of pain, but absence of EKG changes otherwise
A patient had a nephrectomy yesterday. She is being monitored closely for indications of hypoventilation and atelectasis. Which of the following would be the most appropriate treatment for this patient's hypoventilation?
A.
Suctioning of airway as needed
B.
Analgesics
C.
Bronchodilators
D.
Antibiotics
Flank, thoracic, and high abdominal incisions often are related to atelectasis because deep breathing is painful. Adequate analgesia allows the patient to take deep breaths and perform incentive spirometry with less discomfort.
B
What is the earliest sign of hepatic failure
hypoglycemia -
What is systems thinking
An example of this is when units are able to collaborate with one another to facilitate care and increase efficiency. DO NOT CONFUSE SYSTEMS THINKING WITH COLLABORATION, THEY WILL TRICK YOU.
Things to remember prior to testing
Read the answers through and then read the question. Read carefully as to not miss the do NOT and the DO questions.
A 42-year-old woman is admitted with "the worst headache I've ever had." Computed tomography reveals an aneurysm in the circle of Willis. Vasospasm may be treated with which of the following?
A.
Fluid administration
B.
Loop diuretics (e.g., furosemide)
C.
Antifibrinolytic (aminocaproic acid [Amicar])
D.
Osmotic diuretics (e.g., mannitol [Osmitrol])
Give fluids for treatment. Diuretics such as mannitol/lasix will excacerbate the problem with a hypovolemic state. antifibrin may cause re-bleeding and is not indicated for the treatment of vasospasm.
A patient with which of these conditions would have a normal serum lactate? Why?
A.
Ventricular fibrillation
B.
Cardiogenic shock
C.
Severe anemia
D.
Renal failure
Renal failure.
Do not confuse metabolic acidosis to always having an elevated serum lactate. All 4 of these conditions will cause metabolic acidosis, however, renal failure acidosis will be caused by urea build up. A, B, and C metabolic acidosis will be caused by a decreased 02 delivery, a conversion of aerobic to anaerobic metabolism, and a rising serum lactate.