unit 4 sensation and perception
1/102
Earn XP
Description and Tags
11th ap psychology
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
sensation
process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive stimulus energies (information) from our environment
transduction
process of converting stimulus energy into neural activity (retina, cochlea, cilia)
adaptation
constant level of stimulus results in decreased response over time (impacts transduction)
perception
- process of selecting and identifying information from the environment
- organizing and interpreting sensory information so we can identify its meaning
bottom up processing
- using sensory receptors that works up to the brain's integration of sensory info
- ex: smelling popcorn, stubbing toe
top down processing
- using experience and expectations (higher-level mental processes) to process information
- ex: filling in gaps based on what we sense, green eggs and ham
psychophysics
study of the relationship between physical characteristics of stimuli and our psychological experience with them
human factors and engineering psychology
- use of scientific research to improve products
- goal: better understand what people expect and how people interact with products to create safer, more effective, and more reliable systems
- ex: cars, phones
absolute threshold
- the minimum stimulation needed to detect a stimulus 50% of the time
- ex: the least amount of basil one can taste in pasta
signal detection theory
- how and when we detect the presence of a faint stimulus in a background
- depends on person's experience, expectations, motivations, and level of fatigue
just noticeable difference
- the minimum difference between two stimuli required for detection 50% of the time
- ex: how much the volume have to increase/decrease before you can tell the music is louder/softer
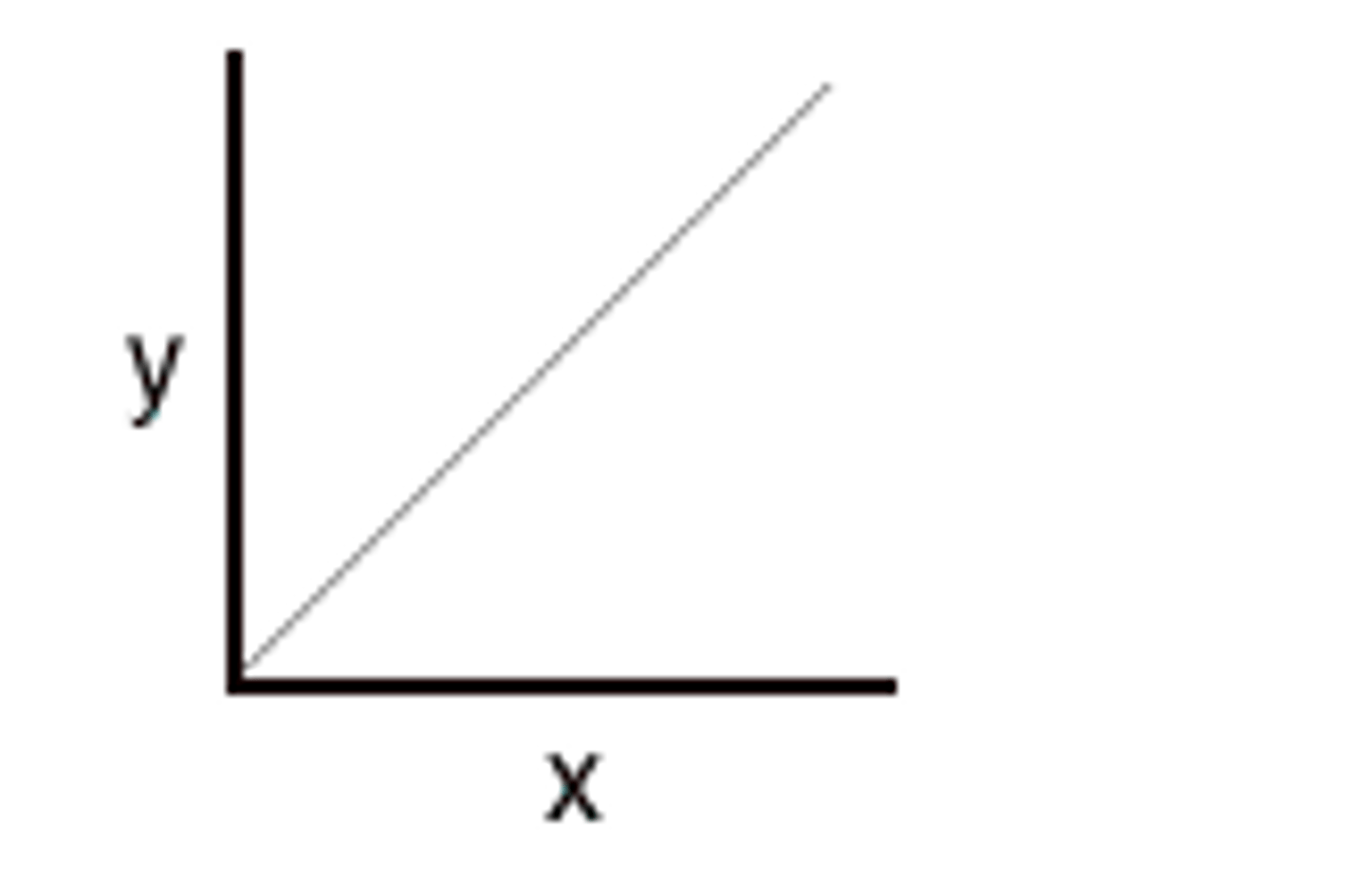
weber's law
- two stimuli must differ by a constant proportion for the difference to be noticeable
- fixed ratio based on original stimulus
- ex: if you go from 1 to 2, then you must go from 2 to 4, then 3 to 6 to notice same difference
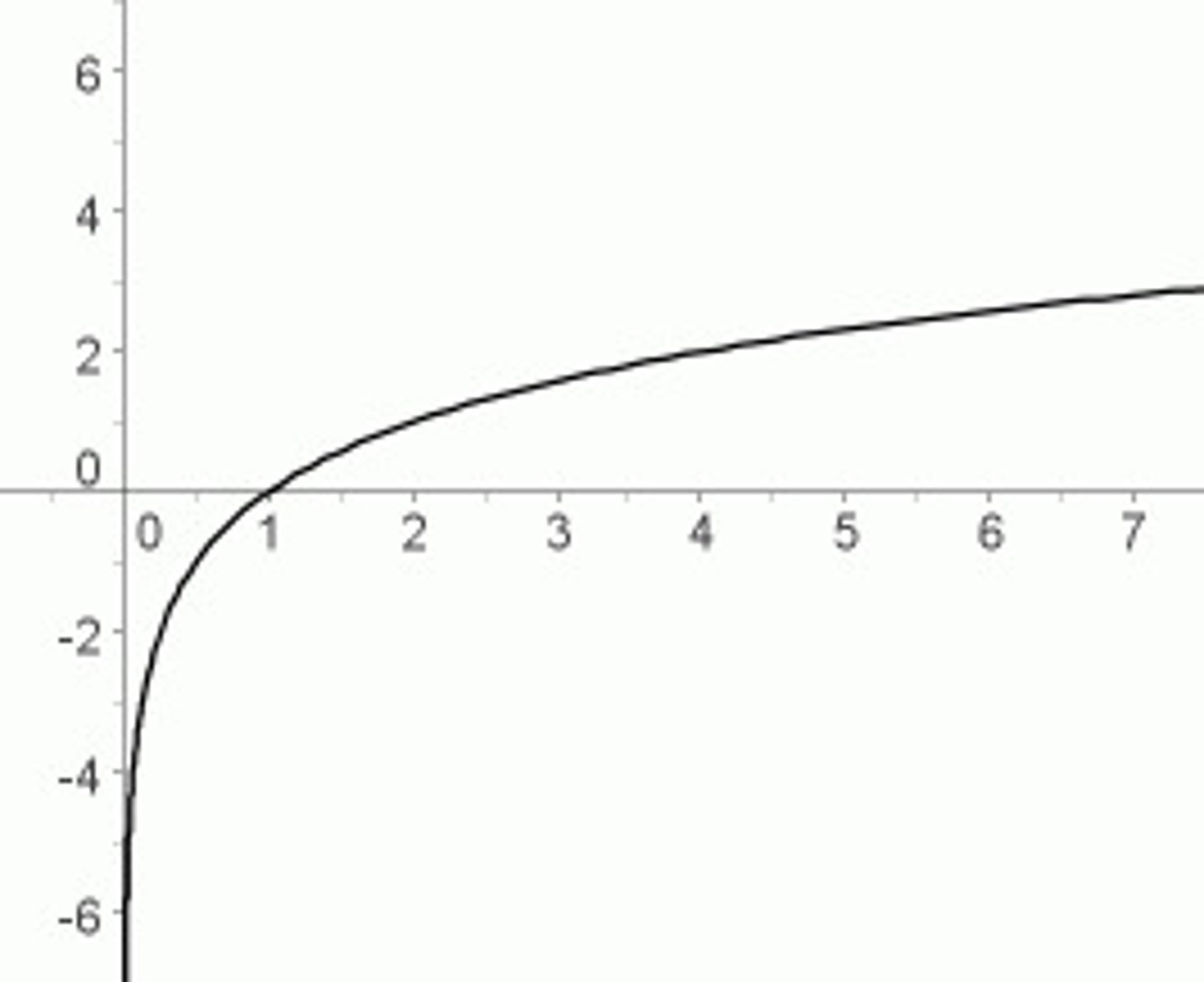
fechner's law
- continuous increase/decrease in physical energy will result in smaller increases in perceived magnitude
- not a true ratio
- eventually we reach a point where physical energy starts to level off and we no longer notice difference
- ex: concerts need a larger change to hear a difference
subliminal stimulation
stimuli below one's absolute threshold of conscious awareness (underlying messages)
cornea
- protects eye
- bends light towards central focal point to provide focus
pupil
- controls the amount of light that is able to enter the eye
- bright conditions: iris expands → pupil smaller
- dark conditions: iris contracts → pupil larger
lens
focuses image on back of the eye
retina
- converts light into electric impulses that are sent through the optic nerve
- transduction
- cones and rods
macula
large collection of photoreceptors that influence clarity in our visual processes
photoreceptors
cones and rods
fovea
- middle of macula
- bundle of cones
optic nerve
- sends visual information to the thalamus then the occipital lobes
- blind spot
cones
- 6 million
- center of retina (fovea)
- color sensitive
- clarity
rods
- 120 million
- edge of retina (periphery)
- night vision
feature detectors
- nerve cells that responds to shape, angle, and movement
- located in the visual cortex (brain cells)
parallel processing
the processing of several aspects of a stimulus simultaneously (color, depth, form, movement)
trichromatic theory
- hermann von helmholtz and thomas young
- retina contains 3 different color receptors
- can produce the perception of any color when stimulated in combination
dichromatic color vision
- individual lacks one of the 3 color receptors
- color blindness, usually the red or green receptor
opponent processing theory
- opposing retinal processes enable color vision
- red & green
- yellow & blue
- black & white
pinna
cartilage that channels sound waves into the external auditory canal
cochlea
converts stimulus from outside environment into nerve impulses for transmission to the brain (transduction)
tympanic membrane/eardrum
- conducts sound to the inner ear
- transmits vibrations to the ossicles (hammer, anvil, stirrup)
vestibular apparatus
maintains balance and has nothing to do with hearing
place theory
location in cochlea that is stimulated by pitch
frequency theory
how often a hair cell is stimulated
conduction hearing loss
- sound vibrations cannot be passed from the eardrum to cochlea due to damage in the middle ear
- ex: punctured or ruptured ear
sensorineural hearing loss
- also called nerve deafness
- caused by damage to the cochlea's receptor cells or to the auditory nerves
- cochlear implant
vestibular (somasthetic sense)
- tells us where our body is orientated in space (balance)
- located in the semicircular canals in ears
selective attention
the focusing of conscious awareness on a particular stimulus to the exclusion of others
cocktail party effect
- form of selective attention
- focus on a single talker among a mixture of conversations and background noises, ignoring other conversations
inattentional blindness
failing to see visible objects when our attention is directed elsewhere
change blindness
- form of inattentional blindness
- individuals don't notice a change after a brief visual interruption
change deafness
failure to notice a change in voice and/or speaking
choice blindness
- form of inattentional blindness
- people are "blind" to their own choices and preferences
visual capture
phenomena when vision competes with other senses, vision almost always win
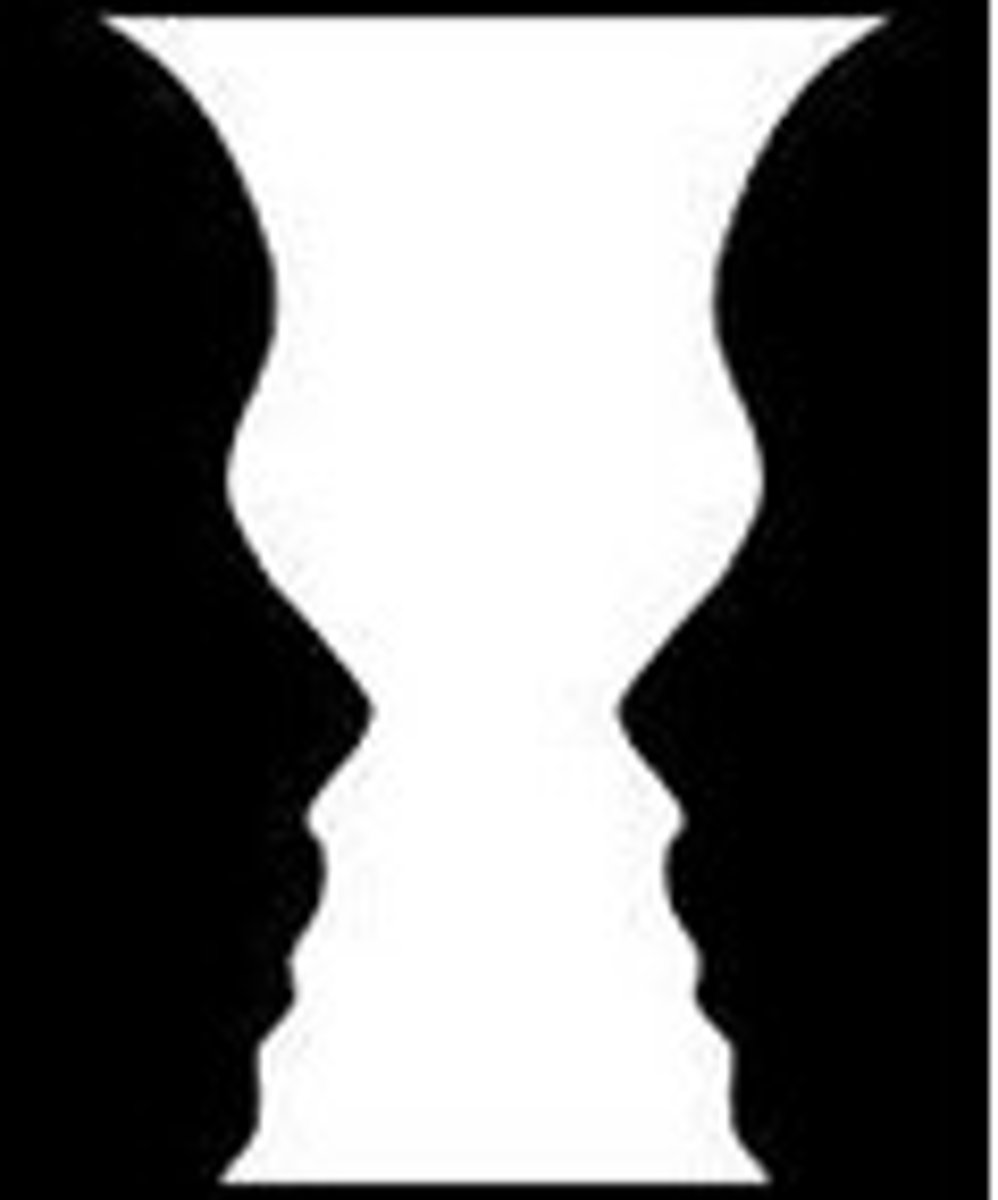
figure-ground (gestalt principle)
the perceptual tendency to organize stimuli into objects that stand out from their surrounding
figure (gestalt principle)
- object stands out
- foreground
ground (gestalt principle)
- surrounding visual field
- background
visual (gestalt principle)

auditory (gestalt principle)
a singer (foreground) and their band (background)
gustatory (gestalt principle)
hotdog (background) with lots of onions (foreground)
olfactory (gestalt principle)
using a candle (foreground) to cover other smells (background)
grouping (gestalt principle)
perceptual tendency to organize stimuli into understandable groups
similarity (gestalt principle)
objects look similar to each other
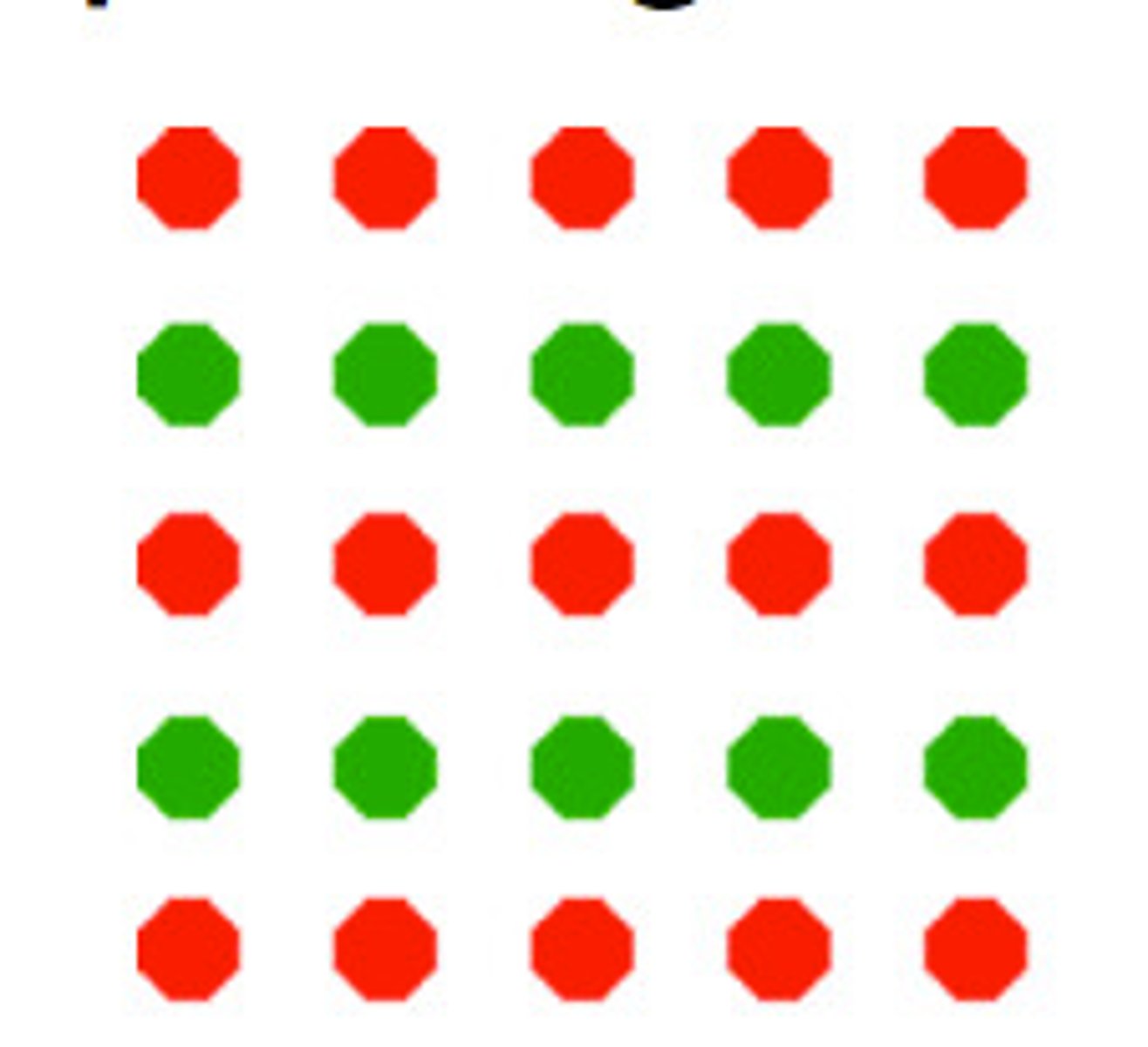
proximity (gestalt principle)
how close objects are to each other
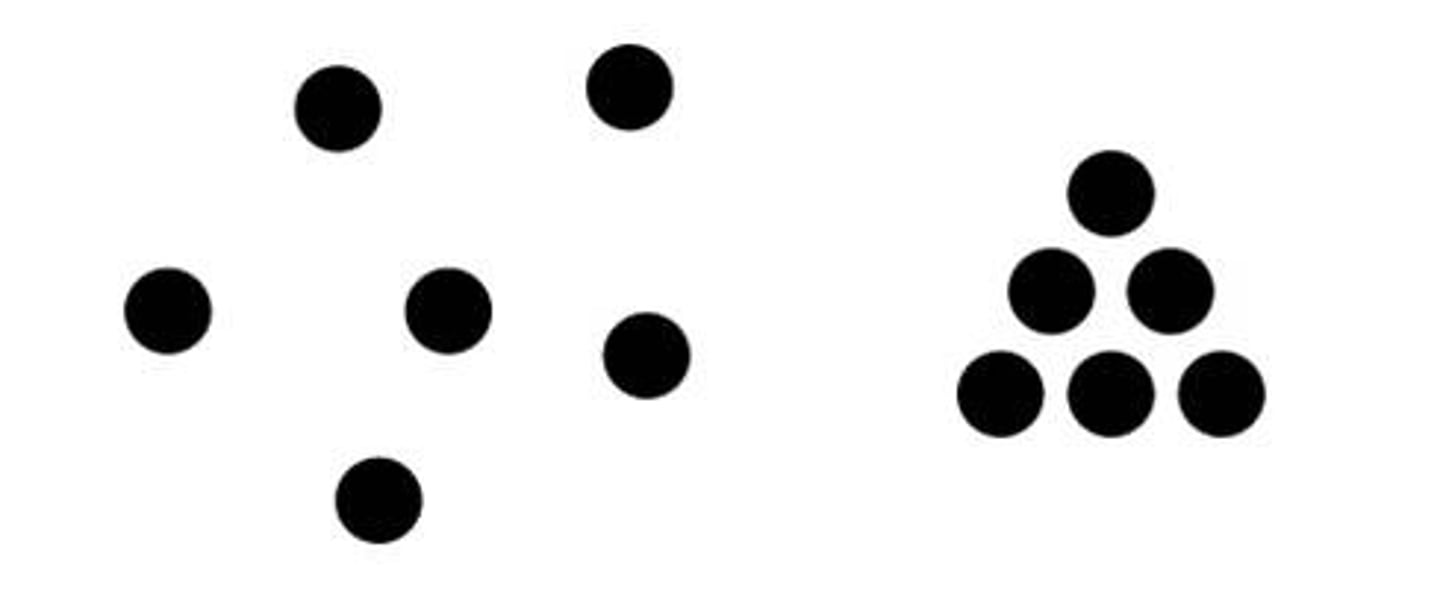
closure (gestalt principle)
filling in gaps
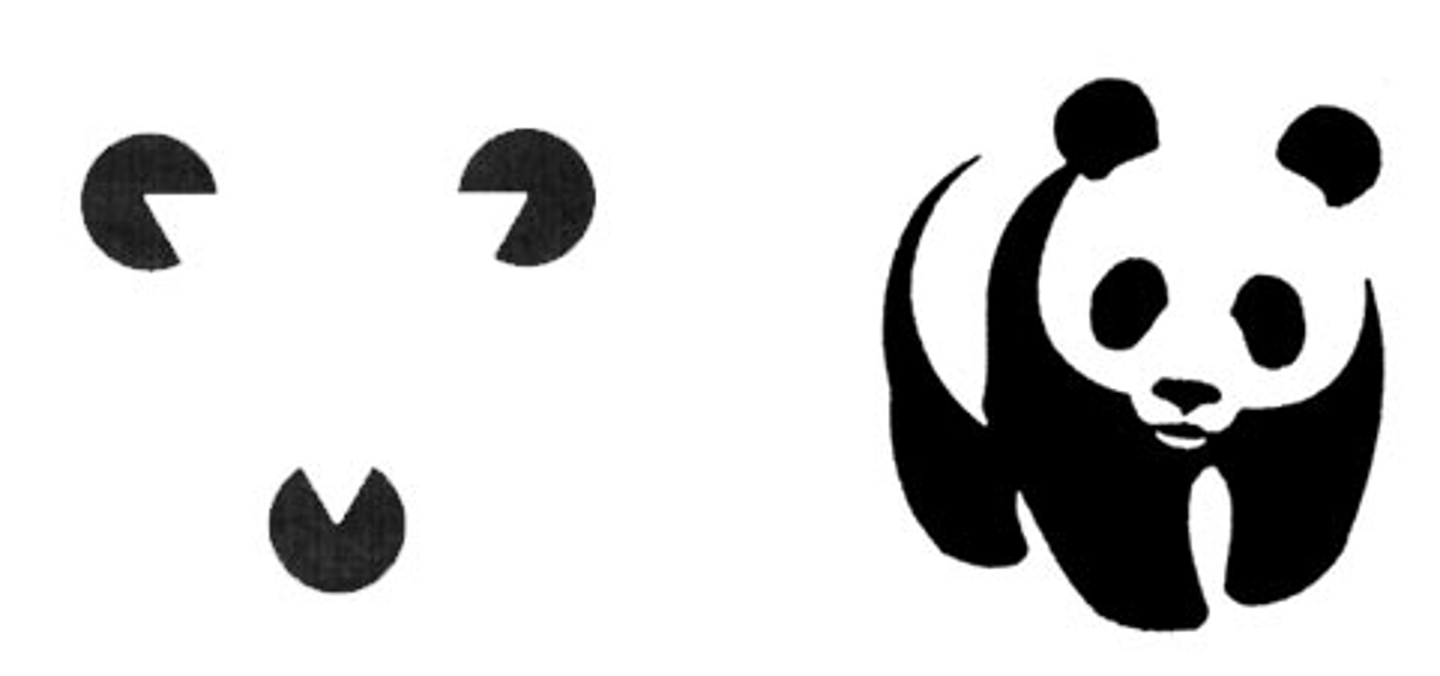
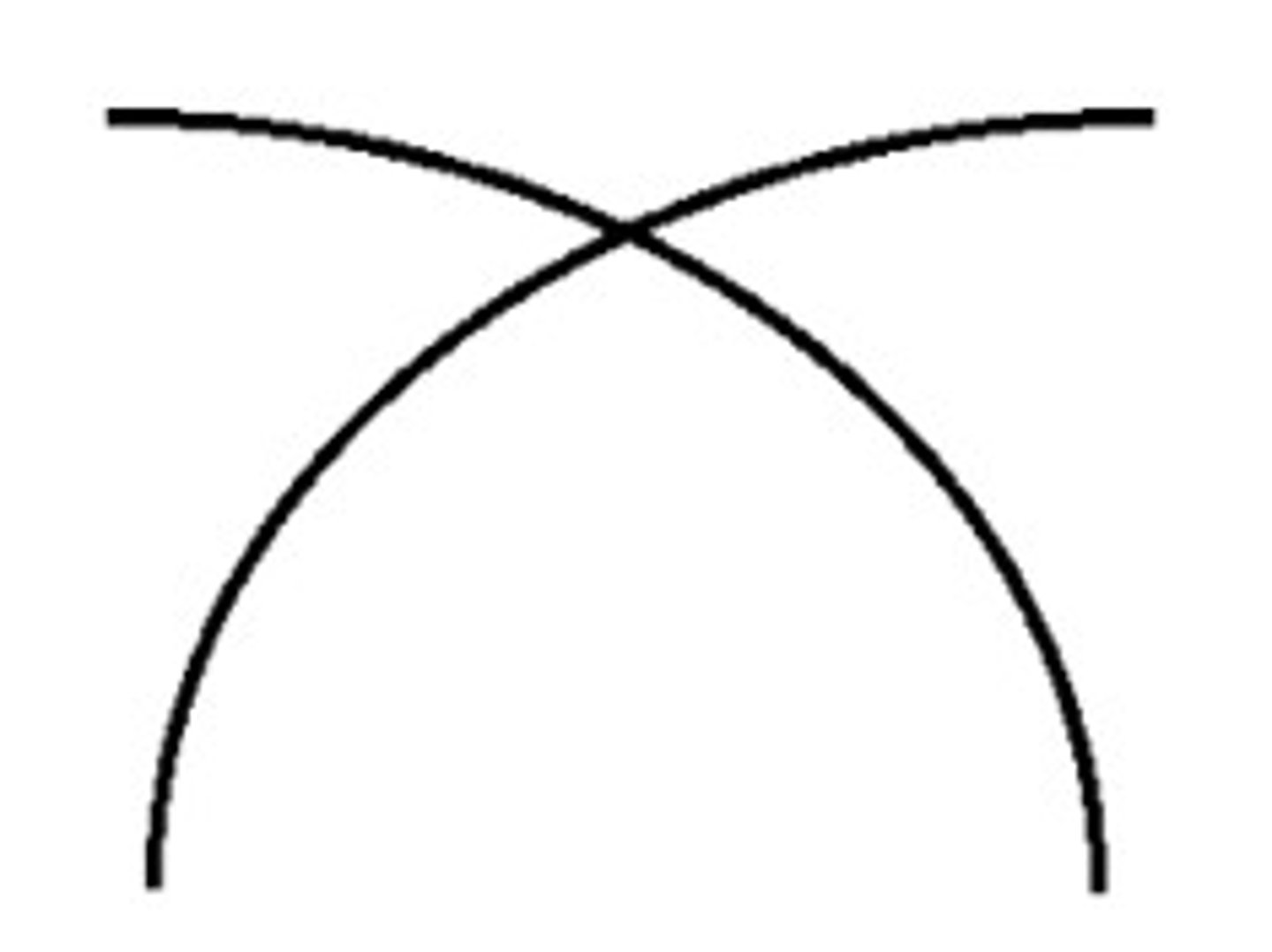
continuity (gestalt principle)
smooth, continuous patterns
depth perception
- the ability to see objects in 3 dimensions allowing us to judge distance, despite the fact that our retinas take in only 2 dimensions
- binocular cues
- monocular cues
visual cliffe
laboratory device for testing depth perception in infants and young animals
binocular cues
- retinal disparity
- convergence
- use of two eyes
retinal disparity
- comparing images from each eyes
- greater the difference = greater the object
- judges distance
convergence
- eyes turn inward as objects get nearer
- judges distance
monocular cues
- requires only one eye
- relative size
- relative height
- relative clarity
- relative motion
- interposition
- linear perspective
- light & shadow
- texture gradient
relative size
- using the perceived size of familiar object to determine depth/distance
- larger objects = closer
relative height
objects higher in our field of vision are farther away
relative clarity
hazy objects are farther away than sharp, clear objects
relation motion/motion parallax
- using a distant object to determine depth while in motion
- closer objects = faster
interposition
when one object partially blocks a view, we perceive it as closer
linear perspective
parallel lines appear to converge as they move farther into the distance
light and shadow
- nearby objects reflect more light
- dimmer objects = farther away
texture gradient
textured surfaces appear smoother and finer as distance increases
cilia
receptor cells that collect molecules of odor
olfactory bulb
- receives an electrical signal and generates a "code" that is sent to the brain for interpretation
- has sensory receptors part of the brain that influences memory
sensory interaction
- one sensory process influencing another
- ex: smell and taste; hold nose to lessen taste
papilla
bumps on the tongue's surface
taste buds
located in walls and grooves of the papilla, roof of mouth, and throat
tastes we can detect
- sweet
- sour
- salty
- bitter
- umami (savory/protein)
epidermis
waterproof, protective layer (melanin to protect from sun)
dermis
hair follicles, sweat glands, and touch receptors
hypodermis
fat and connective issues
mechanoreceptors
pressure, vibrations, texture
thermoreceptors
temperature of objects
nocireceptors
pain receptors
proprioceptors
position and movement (muscles, joints, tendons)
gate control theory
an area in the spinal cord that acts like a "gate" and either inhibit pain messages or transmit them to the brain
kinesthetic
- tells us where our body parts are in spatial/relational sense
- receptors located in muscle, joints, and tendons
stroboscopic motion
- illusion of motion by the rapid project of slightly changing images
- ex: film animations
phi phenomenon
- illusion of motion when fixed lights are turned on and off in a sequence
- ex: christmas lights
perceptual constancy
- understanding the object is not changing, even as the retinal image changes
- ex: a swinging door
size constancy
tendency to interpret object as always being the same size despite its distance
shape constancy
understanding that object's shape remains the same even though angle may change its shape on retina
light constancy
ability to see object as having constant level of lightness on matter how the lighting conditions change
perceptual adaptation
the ability to adjust to a new perception, but not perceived as the "new normal"
perceptual set
a mental predisposition to perceive one thing and not another that is based on experiences, assumptions, and expectations
parapsychology
- study of paranormal phenomena
- lacks replicable scientific evidence
- telepathy, clairvoyance, precognition
telepathy
mind to mind communication
clairvoyance
perceiving remote events
precognition
perceiving future events
nearsightedness
- eyeball too long
- image focused in front of the retina
- also called myopia
farsightedness
- eyeball too short, lens has incorrect curvature, cornea is flat
- image focused behind the retina
- also called hyperopia