Anatomy - Hair, Skin and Nails
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
3 types of hair
Downy hair: Fine, unpigmented that appears on fetus in the last 3 months of development.
Vellus hair: Fine and pale hair
Terminal hair: longer, coarser hair
Structure of hair
Shaft: hair above skin
Root: beneath skin
Medulla: core of loosely arranged cells and air spaces
Cortex: most of the bulk of hair
cuticle: Composed of multiple layers of scaly cells that overlap each other like roof shingles with their free edges
Follicle
Slender filament of keratinized cells that grow from an oblique tube in the skin
Arrector muscle
Bundle of smooth muscle cells extending from dermal collagen fibers to the connective tissue root sheath of the folic. It responds to cold, fear, or other stimuli. Makes hair stand (goose bumps)
Functions of hair
Receptors can prevent infection by parasites, insects, fleas
Retain heat (only on scalp)
Advertise species, age, sex, “individual factor” (style, color)
Guards entry into nose, ears, eyes
facial expressions
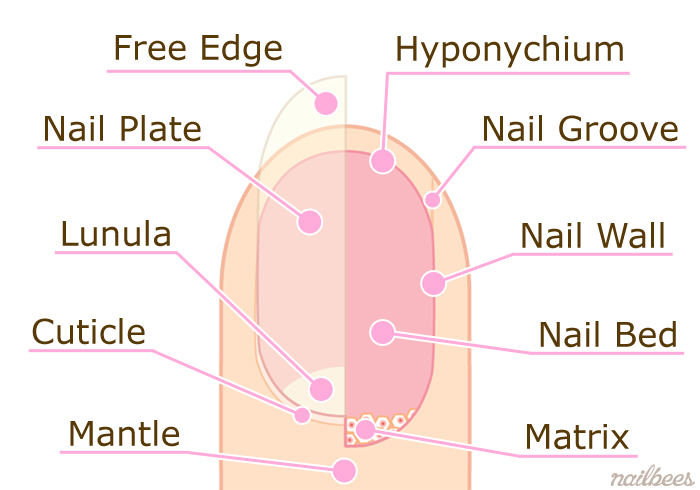
Structure of nail:
Nail: nail plate
Root: under skin
Free edge: top of nail
Body: the whole nail
Types of sweat glands
Sweat glands
Apocrine: ducts empty onto hair follicle/root = sex pheromones
Eccrine: Ducts that secrete sweat onto skin surface, cools skin, forehead, hands and feet.
Sebaceous gland: associated with hair root. secretes sebum onto hair root, keeps hair and skin mosit
Ceruminous gland: ear —> ear wax, traps dust
Mammary glands: produces milk, develop during pregnancy