Biology- Heredity Honors
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/115
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
116 Terms
1
New cards
genetics
study of heredity
2
New cards
Allele
a different version of a gene
3
New cards
Genotype
Genetic makeup
4
New cards
recessive
Must inherit 2 copies to produce phenotype
5
New cards
Homozygous
The same
6
New cards
Homozygous two other names
purebred, true-breeding
7
New cards
Heredity
the passing on of genetic characteristics,
8
New cards
Gene
Segment of DNA that codes a protein
9
New cards
phenotype
physical trait, not always visible
10
New cards
Homologous chromosomes
Where alleles are kept
11
New cards
Genome
collection of all organisms genes
12
New cards
Heterozygous/hybrid
two different alleles are inherited
13
New cards
linked genes
14
New cards
progeny
Offspring
15
New cards
What is a phenotypic ratio
Report resulting phenotypes of cross
16
New cards
What is a genotypic ratio
A way to report the resulting genotypes of a cross
17
New cards
How to show a genotypic ratio
\# hom dom: # hetero: # hom rec
18
New cards
how to show a phenotypic ratio
\#dom: # rec
19
New cards
In a plant called jimsonweed, flowers can be white or purp.e. A jimonsweed plant with white flowers is crossed with jimsonweed plant with purple flowers. All of the offspring have purple flowers. Based on the results, which of the following statments most likely describes the alleles for flower color in jimsonweed.
The allele for purple flowers is dominant to the allele for white flowers??
20
New cards
What describes a genotype
the allele/genetic makeup of an organism
21
New cards
Brown eyes: blue eyes 3:1 What is the ratio of phenotypes in a Punnett square
phenotypic ratio
22
New cards
What is the genotype for a pea plan homozygous for round seeds (R) and heterozygous for yellow seeds (Y)
RRYy
23
New cards
What is an example of a phenotype
Blue
24
New cards
True or false: a phonotype describes the physical expression of a gene, or how something looks
true
25
New cards
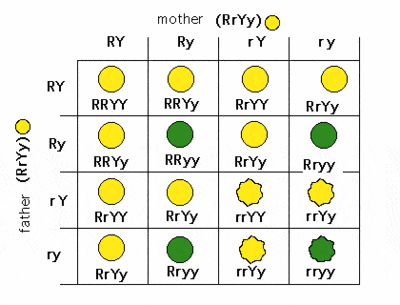
In peas, round is dominant to wrinkled and yellow is dominant to green. Based on this dihybrid cross, what fraction of the offspring will have wrinkled yellow seeds
3
26
New cards
There are multiple alleles for the ABO blood group Why are there only two of these alleles present in any one individual
Each parent contributes one allele
27
New cards
In pea plants Tall stems (T) are dominant to short stems (t) cross a homozygous tall plant with a homozygous recessive plant, what is the phenotypic ratio?
4:0
28
New cards
Which of the following is an example of a genotype
Bb
29
New cards
Which of the following is an example of a homozygous recessive genotype
rr
30
New cards
What are the possible gametes from AaBB
AB, AB, aB, aB
31
New cards
A male beetle has the genotype Ttbb. If this beetle mates with a female with genotype TTBb, what is the chance their offspring will have the genotype TtBb
4 /16
32
New cards
How many alleles does one have for each gene
2
33
New cards
Why is the gene for a disorder more likely to be found on the X chromosome than Y
The X chromosome has more genes
34
New cards
In guinea pigs, Black fur (B) is dominant to white (b), cross Bb x bb and determine genotypic ratio for offspring
0:2:2
35
New cards
A baby dragon recieves two dominant alleles which codes for dark green skin; however, they also receive two recessive alleles for skin pigment production and therefore are albino, none of teh dark green is able to show. The specific pattern of inheritance described is
recessive epistasis
36
New cards
What 3 alleles are responsible for the phenotypic expression of ABO blood types
IA, IB, I (recessive)
37
New cards
What type of inheritance is determined by multiple genes and there can be a septum of pho types
polygenic
38
New cards
Tomato plants usually have hairy stems. Hairless stems are present in tomato plants that are homozygous recessive for this trait. If the stem characteristics are determined by a single gene, what is the expected outcome of crossing two tomato plants that are heterozygous for hairy stems
75% hairy, 25% not
39
New cards
If a person has type B blood, the pho type is B. What can this genotype be
IBIB or IBi
40
New cards
In some carnations, flower color exhibits codominance. When crosses red (R) and white (r) flowers make speckled flowers (Rr) that show both colors. Complete a cross between 2 specked flowers and find the genotype ratio
1:2:1
41
New cards
H= normal blood clotting
H= hemophilia
XHXh x XHY
What is the probability that any of their offspring will have hemophilia
H= hemophilia
XHXh x XHY
What is the probability that any of their offspring will have hemophilia
1/4
42
New cards
The ratio of homozygous dominant to heterozygous to homozygous recessive offspring
genotypic ratio
43
New cards
What are the 4 possible phenotypes for human blood type based solely on the ABO blood group
Type O, A, B, AB
44
New cards
A father has type AB blood and the mother has type O. Which option matches the phenotypic probabilities for their offspring
A: 50% B: 50%
45
New cards
A man with type B blood is wondering if he is the father of a type A baby. the mother is type A. Could this man be the father?
Yes, could be heterozygous
46
New cards
In interaction where one gene masks another gene is called
Epistasis
\
\
47
New cards
In anadaluian fowls, black individuals (BB) and white individuals (bb) are homozygous. Heterozygous individuals are grey (Bb). Cross a black fowl with a white fowl. What is the photo pic ratio.
48
New cards
This pattern of inheritance results in heterozygotes with a mixed or blended phenotype
49
New cards
when crossing two parents who are heterozygous for two traits, what is the phenotypic ratio for the progeny?
50
New cards
A ___ is a segment of DNA that codes for a particular protein, which leads to a particular trait
gene
51
New cards
Genes/rains located close to each other on the same chromosome and therefore more likely to be passed on together are known as
Linked
52
New cards
Hemophilia is a recessive x-linked disorder. Which genotype represents a femele who is a carrier for hemophilia
XHXh
53
New cards
How many alleles do you get from each parent
1
54
New cards
the letters on the top and the side of a Punnett square represent
The possible alleles given before meiosis
55
New cards
Examples of this pattern of inheritance include eye color, hair color, skin tone and height
Polygenic
56
New cards
What pattern of non-Mendelian inheritance is shown by ABO blood group
multiple alleles
57
New cards
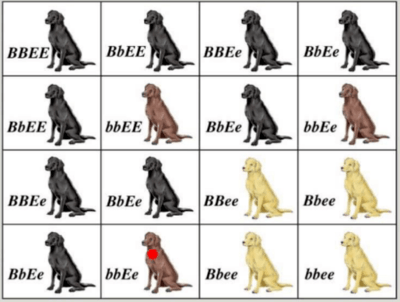
B=black, b= chocolate. Some labs inherit black or brown fur alleles but have light fur due to the effect of a different gene. This shows which pattern of inheritance
Epistasis
58
New cards
What is the probability that the offspring from the cross AaBB x Aabb will be heterozygous for both traits
1/2
59
New cards
Genes/traits located close to each other on the same chromosome and therefore more likely to be passed on together are known as
Linked
60
New cards
____ is the father of modern genetics
Gregor Mendel
61
New cards
Who was Mendel?
A monk in the 1800s that investigated the inheritance of physical traits of pea plants
62
New cards
We inherit two alleles for each gene because
chromosomes exist in homologous pairs
63
New cards
Mendel needed to describe the way that the alleles… he did so on his observations of traits in pea plants
interacted
64
New cards
alleles can be classified in two ways
dominant, recessive
65
New cards
Allele inhericance affects our
physical appearance
66
New cards
Genotype determines
phenotype
67
New cards
Mendel did experiments over ___ of pea plants
generations
68
New cards
3 steps of medals experiments
p gen, f1-gen, f2-gen
69
New cards
The F1 cross: 2 steps
first, p-gen crossed, then f1 gen: the cycle of mixing the parents gen
70
New cards
Teh f2 cross:
mixes the F1 plants, conches if they are hetero or homozygous
71
New cards
Go over F1, F2, and p-gen genotypes and phenotypes
72
New cards
The F1 gen
Self-pollinates
73
New cards
What is a test cross
Organism with dominant phenotype x organism with recessive
74
New cards
What is a dihybrid cross
Uses two traits in a Punnett square
75
New cards
Dihybrid experiments- mendels experiments , P-gen- YYRR x yyrr, f1 gen- 100% yellow round peas, f2=
9:3:3: yellow round, green round, yellow wrinkled: green wrinkled
76
New cards
We can predict _____ that would form from parent genotypes
Possible gametes
77
New cards
What are examples of gametes that could be made from HhRRNn
HRn, HRN, HRN, hRn
78
New cards
Incomplete dominance
both show up blended in a heterozygote
79
New cards
In incomplete dominance and codominance there is no true
dominant/recessive trait
80
New cards
Incomplete dominance with mendels experiment
p gen: red x white, f1: 100% pink flowers f2: 1/4 red, 1/2 pink, 1/4 white
81
New cards
Codominance:
two phenotypes appear in a pattern
82
New cards
in codominance, heterozygous have a ____ appearance
patterned
83
New cards
Punnett squares with codominance traits: use
superscripts to show heterozygous (codominance)
84
New cards
Codominance in mendels experiment: p- red x white flower
f1- 100% spotted f2- 25% red, 50% spotted, 25% white
85
New cards
linked genes
some alleles are not separated form each other during meiosis, too close to one another
86
New cards
Multiple alleles
2+ alleles for a gene exist
87
New cards
An organism with multiple alleles still only inherit…
2
88
New cards
What is a common example of multiple alleles/codominance
Blood type
89
New cards
Humans have ____ blood groups
ABO
90
New cards
Polygenic inheritance
a single trait is influenced by many (2+) genes
91
New cards
Some alleles in polygenic inheritance contribute an ____ on phenotype
additive effect
92
New cards
_____ have additive effect
certain alleles
93
New cards
What is an example of polygenic inheritance
producing more pigment in height, skin tone, hair color, and eye color
94
New cards
________ fall along a spectrum
Polygenic phenotypes
95
New cards
When determining polygenic phenotypes, look for where it fits on the
spectrum
96
New cards
What is epistatis
A form of polygenic interaction in which one gene masks or hides the phenotype produced another gene
97
New cards
What is recessive epistasis
Masking the gene requires two recessive alleles to hid the phenotype
98
New cards
dominant epistasis
masking the gene only requires one dominant allele to hid the phenotype
99
New cards
Two common examples of epistasis
Labs, albinism
100
New cards
In the Y-chromosome, there are ______ genes
Few