Maternal Health and Mortality in Public Health
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
Maternal Mortality
Death from pregnancy-related causes during pregnancy or postpartum.
Leading Causes of Maternal Mortality
Hemorrhage, hypertension, and sepsis are primary causes.

Spontaneous Abortion
Natural termination of pregnancy before viability.
Induced Abortion
Medical or surgical termination of pregnancy.
Stages of Labor
Three phases: dilation, expulsion, and placental.
Skilled Birth Attendant
Trained professional providing childbirth assistance.
Traditional Birth Attendant
Untrained individual assisting in childbirth.
Maternal Mortality Ratio
Number of maternal deaths per 100,000 live births.
Postpartum Hemorrhage
Severe bleeding after childbirth, often preventable.
Active Management of Third Stage of Labor
Intervention to prevent postpartum hemorrhage.
Preeclampsia
Elevated blood pressure during pregnancy, can be dangerous.
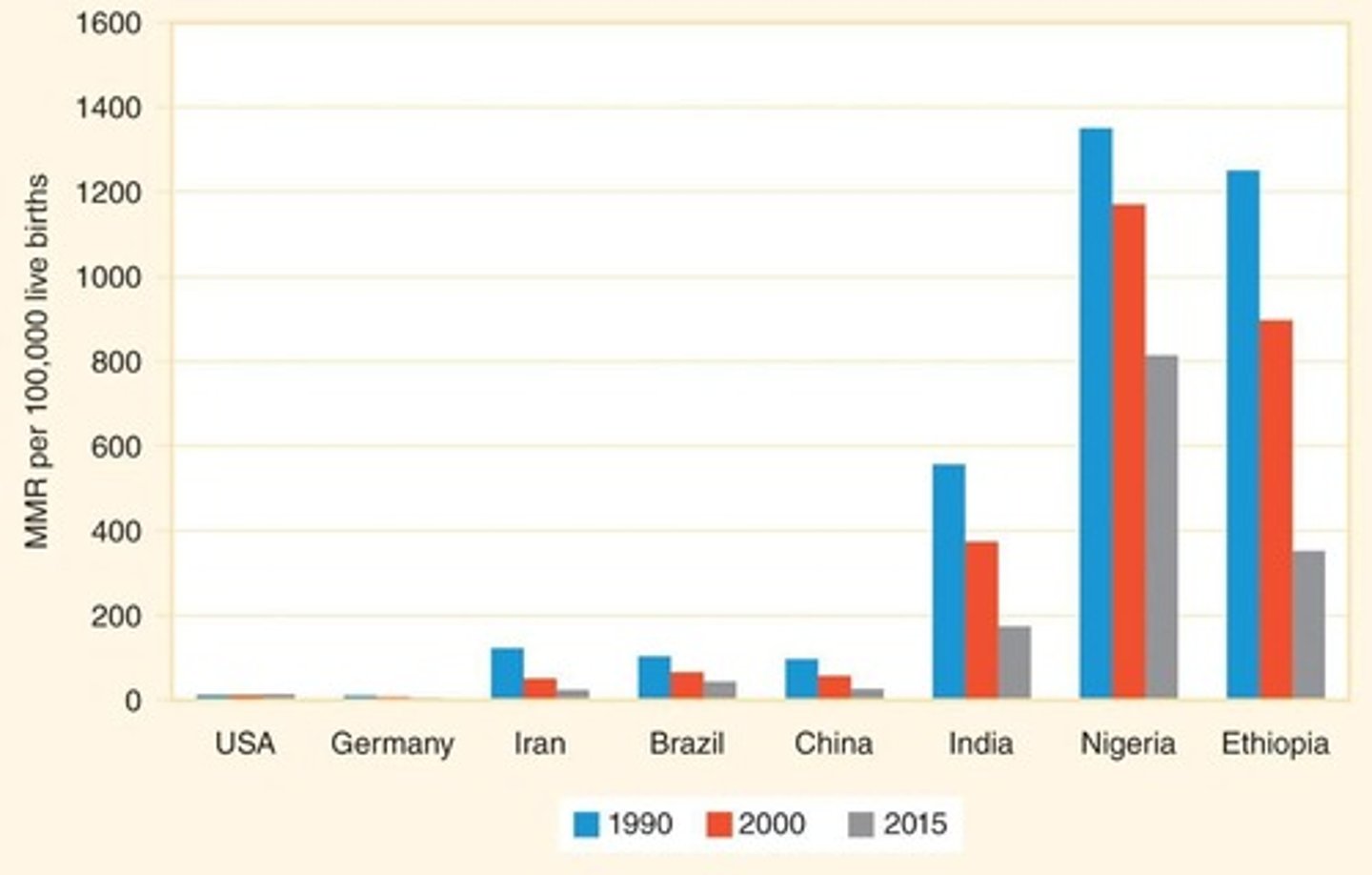
Global Disparity in Maternal Mortality
Higher rates in low-income countries compared to wealthy.
Preventable Maternal Deaths
Deaths that could be avoided with better healthcare access.
Millennium Development Goals
International targets to improve global health, including maternal health.
Sepsis
Blood poisoning from infection, leading to organ failure.
Maternal Deaths in 2015
Approximately 300,000 women died from maternal causes.
Maternal Deaths in 1990
About 500,000 women died from pregnancy-related causes.
Obstetric Care
Medical care focused on pregnancy and childbirth.
Contraception Access
Availability of birth control methods to prevent pregnancy.
Malnutrition
Lack of proper nutrition, contributing to maternal health issues.
Hypertension in Pregnancy
Dangerously elevated blood pressure during pregnancy.
Childbirth Complications
Health issues arising during or after childbirth.
Preeclampsia
Hypertension and protein in urine during pregnancy.
Obstructed Labor
Baby wedged in birth canal, cutting off blood flow.
Obstetric Fistula
Hole between vagina and rectum or bladder.
Maternal Mortality
Death of a woman during pregnancy or childbirth.
Family Planning
Informed decisions on childbearing and spacing.
Birth Spacing
Waiting at least 2 years between pregnancies.
Abstinence
Refraining from sexual intercourse and genital contact.
Condom
Barrier preventing sperm from contacting an egg.
Contraception
Intentional prevention of pregnancy.
Oral Contraceptives
Pills preventing ovulation when taken as prescribed.
IUDs
Devices creating unfavorable uterine environment for sperm.
Sterilization
Surgical procedures making reproduction difficult or impossible.
Spontaneous Abortions
Natural termination of pregnancy before 20 weeks.
Induced Abortions
Medical or surgical termination of pregnancy.
Skilled Birth Attendants
Trained professionals assisting in childbirth.
Traditional Birth Attendants
Non-professionals assisting in childbirth.
Complications of Labor
Issues arising during the three stages of labor.
Leading Causes of Maternal Mortality
Three main reasons for maternal deaths globally.
Health Risks of Preterm Deliveries
Potential complications for babies born early.
Permanent Disabilities from Complications
Long-term health issues post-pregnancy complications.
STI Prevention Methods
Only abstinence and condoms prevent sexually transmitted infections.
Informed Decisions in Family Planning
Understanding reproductive options and implications.
Abortion
Termination of pregnancy, either spontaneous or induced.
Spontaneous abortion
Natural loss of a pregnancy, commonly known as miscarriage.
Induced abortion
Surgical or chemical termination of a pregnancy.
Family planning
Methods to control the number and timing of children.
Skilled birth attendant (SBA)
Trained professional assisting during childbirth.
Traditional birth attendant (TBA)
Lay midwife trained through apprenticeship.
Three stages of labor
Labor, delivery, and delivery of the placenta.
Stage 1 of labor
Contractions dilate cervix to 10 centimeters.
Stage 2 of labor
Delivery of the neonate.
Stage 3 of labor
Delivery of the placenta (afterbirth).
Access to contraception
Availability of family planning methods to individuals.
SDG 3.7.1
Goal to satisfy family planning needs globally.
Complications in childbirth
Potential issues arising during any labor stage.
Contraception
Methods to prevent unplanned pregnancies.
Healthcare providers
Professionals delivering family planning services.
Reproductive-age women
Women aged 15-49, often targeted for family planning.
Unplanned pregnancies
Pregnancies that occur without prior family planning.
Lay midwife
Non-professional assisting with childbirth without formal training.
Obstetrician
Physician specializing in pregnancy and childbirth.
Nurse midwife
Nurse trained in midwifery and childbirth care.
Sub-Saharan Africa births
Half occur without skilled birth attendants.