Water and wastewater treatment
1/225
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Part 1 of Industrial Waste Management and Control
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
226 Terms
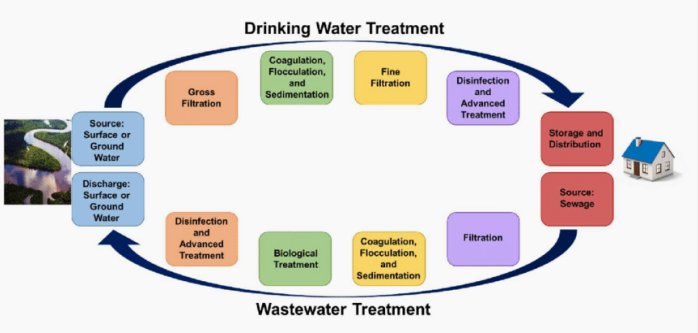
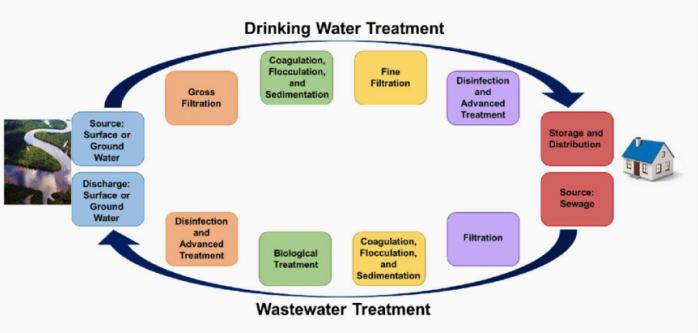
Water treatment plant (WTP)
It generally takes water from ground, surface, or rainwater sources, makes it drinkable and distributes it to water storage tanks or directly to people.
Wastewater treatment plant (WWTP)
It generally collects sewage from your house and other wastewater (and in some cases, stormwater) from various sites, cleans it, and releases it back into the environment at a safe level for humans, fish, and plants to be around.
Water treatment plant
WATER VS WASTEWATER TREATMENT. Determine whether it is a function of a water or wastewater treatment plant.
Generally smaller operations
Wastewater treatment plant
WATER VS WASTEWATER TREATMENT. Determine whether it is a function of a water or wastewater treatment plant.
Generates residual solids that are rich in nutrients (can be applied to farm lands as a fertilizer)
Wastewater treatment plant
WATER VS WASTEWATER TREATMENT. Determine whether it is a function of a water or wastewater treatment plant.
Product water is disinfected and released back into a nearby waterway or recycled.
Water treatment plant
WATER VS WASTEWATER TREATMENT. Determine whether it is a function of a water or wastewater treatment plant.
Better raw water quality (from rivers, lakes, or wells)—generally clean and just needs a bit of treatment and disinfection
Wastewater treatment plant
WATER VS WASTEWATER TREATMENT. Determine whether it is a function of a water or wastewater treatment plant.
Removes wide range of pollutants
Water treatment plant
WATER VS WASTEWATER TREATMENT. Determine whether it is a function of a water or wastewater treatment plant.
Small amounts of pollutants (ex.: turbidity) are removed
Water treatment plant
WATER VS WASTEWATER TREATMENT. Determine whether it is a function of a water or wastewater treatment plant.
Product water is fit for human consumption.
Wastewater treatment plant
WATER VS WASTEWATER TREATMENT. Determine whether it is a function of a water or wastewater treatment plant.
Much larger and more elaborate operations
Wastewater treatment plant
WATER VS WASTEWATER TREATMENT. Determine whether it is a function of a water or wastewater treatment plant.
Take sewage water from residential, commercial, and/or industrial sources
FAMILIARIZE.
FAMILIARIZE.
Chemical properties
Biological properties
Physical properties
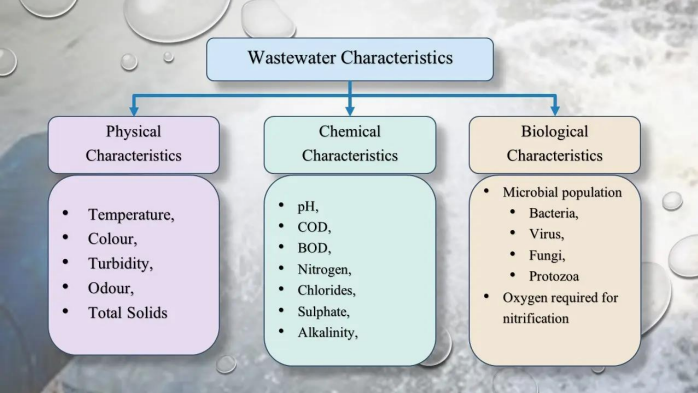
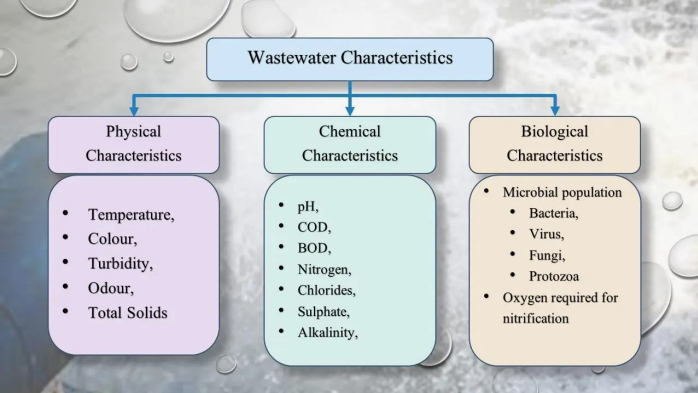
Enumerate the three (3) properties of water quality.
Chemical properties
PROPERTIES OF WATER QUALITY. Determine what property is being described below.
Includes gases (oxygen, etc.), metals (iron, etc.), nutrients (nitrogen, etc.), pesticides, and other organic compounds
Biological properties
PROPERTIES OF WATER QUALITY. Determine what property is being described below.
Includes bacteria, viruses, protozoans, phytoplankton, zooplankton, insect, plant, fish, etc.
Physical properties
PROPERTIES OF WATER QUALITY. Determine what property is being described below.
Includes color, smell, temperature, taste, turbidity, etc.
FAMILIARIZE.
FAMILIARIZE.
Priority pollutants
Organics
Dissolved oxygen (DO)
Inorganics
pH and alkalinity
Temperature
Solids
Nutrients and eutrophication
Whole effluent toxicity (WET)
Oil and grease
Enumerate the 10 industrial wastewater characteristics.
Priority pollutants
(ADDITIONAL: All priority pollutants are toxic. Most are organic, but biodegradable despite their toxicity.)
INDUSTRIAL WASTEWATER CHARACTERISTICS. Determine which is being described below.
It is treated on an individual-substance basis for regulatory control.
Organics
INDUSTRIAL WASTEWATER CHARACTERISTICS. Determine which is being described below.
Includes proteins, carbohydrates, fats and oils, petrochemicals, solvents, pharmaceutical, small and large molecules, solids and liquids
True
(ADDITIONAL: A typical industry produces many diverse waste streams.)
TRUE OR FALSE. Organic composition of industrial wastes varies widely due to different raw materials used by each specific industry.
Oxygen
It is a critical environment resource in receiving water streams and lakes.
Dissolved oxygen (DO)
INDUSTRIAL WASTEWATER CHARACTERISTICS. Determine which is being described below.
It is a poorly soluble gas in water.
False
(EXPLANATION: As temperature increases and pressure decreases, solubility of oxygen decreases.)
TRUE OR FALSE. As temperature increases and pressure decreases, solubility of oxygen increases.
True
TRUE OR FALSE. Warm wastewater discharges aggravate DO situation in receiving waters.
True
TRUE OR FALSE. Lowering temperature increases DO saturation levels and decreases biological metabolism rate.
True
TRUE OR FALSE. DO is minimum when BOD is maximum.
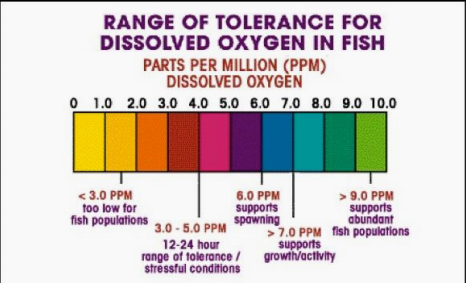
5 mg/L
INDUSTRIAL WASTEWATER CHARACTERISTICS. Determine which is being described below.
EPA has set minimum stream DO levels at ___ in summer (when the rate of biological metabolism is maximum).
FAMILIARIZE.
FAMILIARIZE.
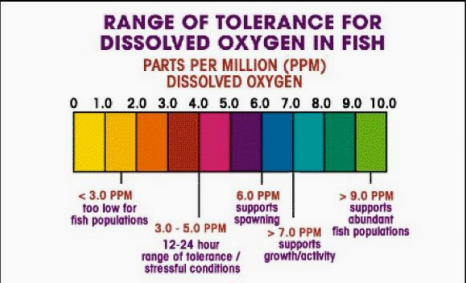
Maximum BOD levels and minimum oxygen-demanding components
INDUSTRIAL WASTEWATER CHARACTERISTICS. Determine which is being described below.
To maintain DO level at >5 mg/L, WW must have ___ and ___ when discharged.
Biochemical oxygen demand (BOD)
INDUSTRIAL WASTEWATER CHARACTERISTICS. Determine which is being described below.
It is an important measure of the waste organic strength.
Biochemical oxygen demand
INDUSTRIAL WASTEWATER CHARACTERISTICS. Determine which is being described below.
It measures the amount of oxygen that microorganisms require to break down organic matter present in a water sample.
Biochemical oxygen demand
INDUSTRIAL WASTEWATER CHARACTERISTICS. Determine which is being described below.
It is a primary parameter in determining the strength and effects of a pollutant.
BOD5 test
TESTS RELATED TO BIOCHEMICAL OXYGEN DEMAND. Determine which is being described below.
It determines the oxygen demand of a waste exposed to biological organisms (controlled seed) for an incubation period of 5 days.
BOD5 Test
TESTS RELATED TO BIOCHEMICAL OXYGEN DEMAND. Determine which is being described below.
It measures the decrease in DO concentrations in 5 days, which is then related to the sample strength.
Oxygen demand
It is usually caused by degradation of organic according to the equation:
Organic waste + O2 (DO) ——> CO2 +H2O
Safe to drink
TESTS RELATED TO BIOCHEMICAL OXYGEN DEMAND. Determine which is being described below.
If BOD5 = 1-2 mg/L, water is ___.
Moderately clean
TESTS RELATED TO BIOCHEMICAL OXYGEN DEMAND. Determine which is being described below.
If BOD5 = 2-5 mg/L, water is ___.
Near polllution source
TESTS RELATED TO BIOCHEMICAL OXYGEN DEMAND. Determine which is being described below.
If BOD5 > 5 mg/L, water is ___.
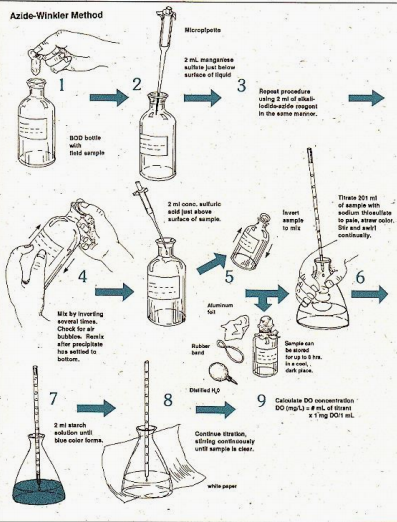
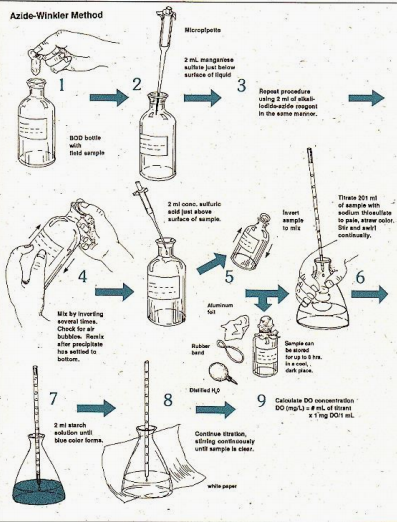
Fill two standard 300 mL BOD bottles with the sample wastewater. Seal the bottles properly.
Immediately determine the dissolved oxygen content of one of the samples using Winkler’s method.
Incubate the second bottle at 20°C for 5 days in complete darkness.
Determine the DO levels after 5 days.
TESTS RELATED TO BIOCHEMICAL OXYGEN DEMAND. Determine which is being described below.
How is the BOD5 test being conducted?
Winkler’s method
TESTS RELATED TO BIOCHEMICAL OXYGEN DEMAND. Determine which is being described below.
What method is commonly used to determine the dissolved oxygen content of a water sample?
FAMILIARIZE.
FAMILIARIZE.
BOD5
TESTS RELATED TO BIOCHEMICAL OXYGEN DEMAND. Determine which is being described below.
It measures the 5-day carbonaceous oxygen demand by aerobic bacteria, representing the readily biodegradable organic matter in wastewater.
BOD20
TESTS RELATED TO BIOCHEMICAL OXYGEN DEMAND. Determine which is being described below.
It indicates the total BOD, including slower-acting substances like grease and cellulose, after 20 days.
BODu (ultimate BOD)
TESTS RELATED TO BIOCHEMICAL OXYGEN DEMAND. Determine which is being described below.
It signifies the total oxygen required for the complete breakdown of all organic matter.
BOD20
TESTS RELATED TO BIOCHEMICAL OXYGEN DEMAND. Determine which is being described below.
BODu can be estimated by ___.
Chemical oxygen demand (COD)
TESTS RELATED TO BIOCHEMICAL OXYGEN DEMAND. Determine which is being described below.
It is a measure of the oxygen consumed by chemical oxidation of all organic compounds (biodegradable and non-biodegradable) and serves as a faster (<3 hours) alternative to BOD tests for monitoring pollution.
Total organic carbon (TOC)
TESTS RELATED TO BIOCHEMICAL OXYGEN DEMAND. Determine which is being described below.
It is a more rapid measurement of the organic content of wastes and may be correlated with BOD and COD for specific wastes.
Inorganics
INDUSTRIAL WASTEWATER CHARACTERISTICS. Determine which is being described below.
It is the direct result of inorganic compounds in the carriage water in industrial wastes.
True
TRUE OR FALSE. Softwater sources have lower inorganics than hardwater or saltwater.
Sodium
Many food processing wastewaters are high in ___.
True
TRUE OR FALSE. Domestic wastewaters have a balance in organics and inorganics.
True
TRUE OR FALSE. Process wastewaters are deficient in specific inorganic compounds.
between 6 and 9
INDUSTRIAL WASTEWATER CHARACTERISTICS. Determine which is being described below.
Wastewater should have pH values between ___ and ___ for minimum impact on the environment.
Corrosive
INDUSTRIAL WASTEWATER CHARACTERISTICS. Determine which is being described below.
If pH < 6, wastewater tend to be ___.
Metal ions
INDUSTRIAL WASTEWATER CHARACTERISTICS. Determine which is being described below.
If pH > 9 , precipitation of ___ as carbonates or hydroxides occur.
True
(ADDITIONAL: Adequate alkalinity neutralizes the acid waste components and those formed by partial metabolism of organics.)
TRUE OR FALSE. Alkalinity keeps pH values at the right level.
Neutral organics (ex.: carbohydrates, aldehydes, ketones, alcohols)
INDUSTRIAL WASTEWATER CHARACTERISTICS. Determine which is being described below.
These are biodegraded through organic acids, which must be neutralized by the available alkalinity.
Bicarbonate alkalinity
INDUSTRIAL WASTEWATER CHARACTERISTICS. Determine which is being described below.
It is considered as the primary buffer in wastewater.
Sodium carbonate
(ADDITIONAL: Sodium carbonate is better to be added than lime, which tends to be hard to control accurately, resulting in high pH levels and precipitation of Ca that forms part of the alkalinity.)
INDUSTRIAL WASTEWATER CHARACTERISTICS. Determine which is being described below.
If alkalinity is inadequate, what compound is added?
10°C and 30°C
INDUSTRIAL WASTEWATER CHARACTERISTICS. Determine which is being described below.
Operating temperatures are generally kept between ___.
True
TRUE OR FALSE. Most industrial wastes tend to be on the warm side.
Thermophilic biological WW treatment systems
INDUSTRIAL WASTEWATER CHARACTERISTICS. Determine which is being described below.
These can be operated up to 65°C with acclimated microbes.
True
(ADDITIONAL: Increased viscosity at low temperatures makes solid separation more difficult.)
TRUE OR FALSE. Low-temperature operations result in slow reaction rates for both biological and chemical WW treatment systems.
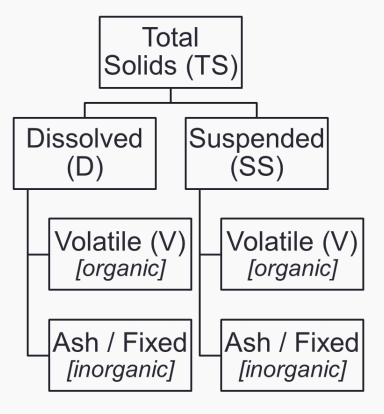
Total solids (TS)
INDUSTRIAL WASTEWATER CHARACTERISTICS. Determine which is being described below.
These are residues remaining from wastewater dried at 103 to 105°C.
Settleable solids
INDUSTRIAL WASTEWATER CHARACTERISTICS. Determine which is being described below.
These are solids that settle in an Imhoff cone in an hour.
FAMILIARIZE.
FAMILIARIZE.
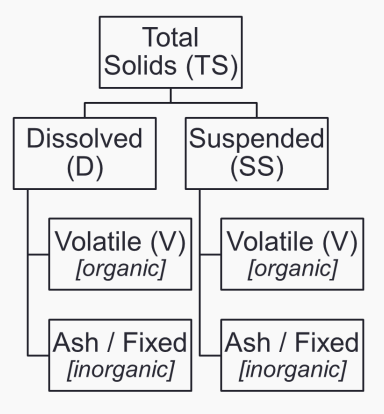
First separation
INDUSTRIAL WASTEWATER CHARACTERISTICS. Determine which is being described below.
In measuring settleable solids, it refers to the portion that passes through a 2-μm filter (dissolved) and the solids captured on the filter (suspended).
Succeeding separation
INDUSTRIAL WASTEWATER CHARACTERISTICS. Determine which is being described below.
In measuring settleable solids, it refers to the technique using combustion at 500°C which further separates the solids into volatile and ash (fixed), without distinguishing organic from inorganic solids.
True
TRUE OR FALSE. Inorganics are mostly lost during combustion.
True
TRUE OR FALSE. Volatile fraction approximates the organics present.
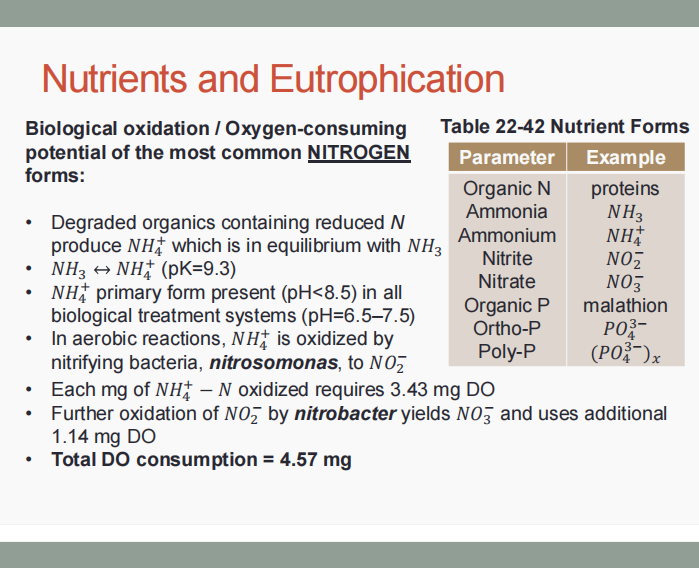
Nitrogen and phosphorous
INDUSTRIAL WASTEWATER CHARACTERISTICS. Determine which is being described below.
These cause the increase in aquatic biological productivity, resulting in low DO and eutrophication.
FAMILIARIZE.
FAMILIARIZE.
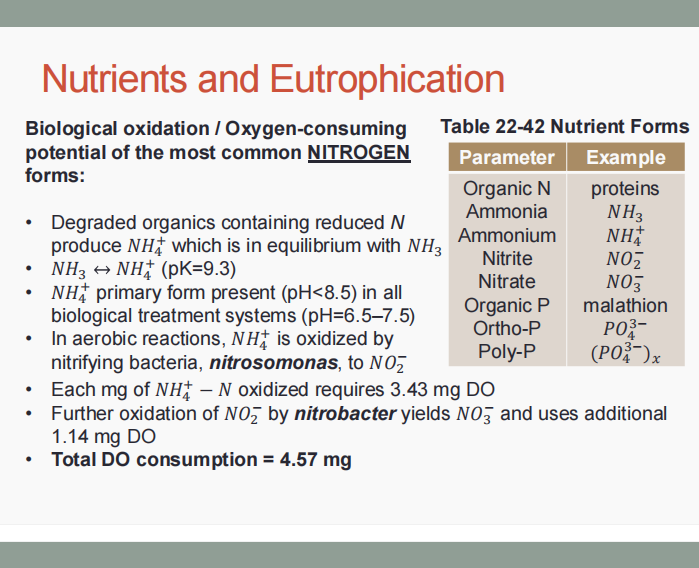
Nitrogenous BOD (NBOD)
INDUSTRIAL WASTEWATER CHARACTERISTICS. Determine which is being described below.
It refers to the BOD exerted by organic and ammonium N in the water environment.
Carbonaceous BOD (CBOD)
INDUSTRIAL WASTEWATER CHARACTERISTICS. Determine which is being described below.
It refers to organic BOD.
Total oxygen demand (TOD)
(ADDITIONAL: TKN refers to the total Kjedahl N.
INDUSTRIAL WASTEWATER CHARACTERISTICS. Determine which is being described below.
It must be satisfied in treatment of wastewaters with organics and ammonium, in accordance with the approximate formula:
TOD = 1.5(BOD5) + 4.5TKN
Organic N + NH4+ - N
INDUSTRIAL WASTEWATER CHARACTERISTICS. Determine which is being described below.
Total Kjeldahl N is equal to the summation of ___.
Phosphorous
INDUSTRIAL WASTEWATER CHARACTERISTICS. Determine which is being described below.
It is not oxidized or reduced biologically, but ortho-P may be formed from organic and poly-P.
Ortho-P
INDUSTRIAL WASTEWATER CHARACTERISTICS. Determine which is being described below.
This may be removed by chemical precipitation or biologically with sludges.
READ.
Many industrial wastes are very low in N and P, which must be added if biologically-based treatment is used.
Others contain very high levels of N (ex.: paint production wastes) and P (ex.: detergent production wastes), which must be treated in areas where eutrophication is a problem.
READ.
Many industrial wastes are very low in N and P, which must be added if biologically-based treatment is used.
Others contain very high levels of N (ex.: paint production wastes) and P (ex.: detergent production wastes), which must be treated in areas where eutrophication is a problem.
Whole effluent toxicity (WET)
INDUSTRIAL WASTEWATER CHARACTERISTICS. Determine which is being described below.
It is a term used to describe the toxic effects imposed on a species or population of aquatic organisms caused by exposure to an effluent.
Whole effluent toxicity
INDUSTRIAL WASTEWATER CHARACTERISTICS. Determine which is being described below.
It is determined analytically by exposing sensitive indigenous organisms to effluents using WET test protocols by EPA.
17
INDUSTRIAL WASTEWATER CHARACTERISTICS. Determine which is being described below.
How many analytical methods were established by the EPA for testing acute and chronic toxicity of point sources and their impact on surface water environments?
Whole effluent toxicity (WET)
INDUSTRIAL WASTEWATER CHARACTERISTICS. Determine which is being described below.
It reports on the general acute and chronic toxicity of all constituents in a complex effluent, and not the toxicity of specific chemicals.
Oil and grease
INDUSTRIAL WASTEWATER CHARACTERISTICS. Determine which is being described below.
These are substances found in many industrial wastes (Ex.: meat packing, petrochemical, soap production).
Oil and grease
INDUSTRIAL WASTEWATER CHARACTERISTICS. Determine which is being described below.
These tend to float on the water surface, blocking oxygen transfer, interfering with recreation, and producing an aesthetically poor appearance in the water.
Fats - solid at room temperature
Oils - liquid at room temperature
Grease - turns to liquid during cooking, but solidifies when cooled
INDUSTRIAL WASTEWATER CHARACTERISTICS. Determine which is being described below.
What is the difference between fats, oil, and grease?
Solvent-extraction
INDUSTRIAL WASTEWATER CHARACTERISTICS. Determine which is being described below.
Measurement of oil and grease is by a ___ procedure.
True
TRUE OR FALSE. Oil and grease must be removed as part of the initial stages of treatment.
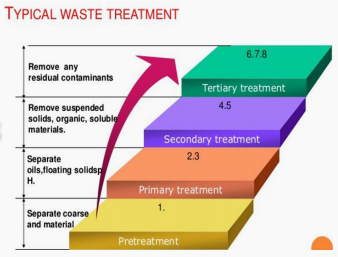
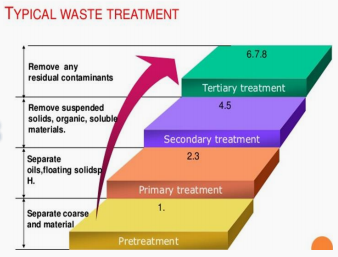
Pretreatment
Primary treatment
Secondary treatment
Physical-chemical treatment
Enumerate the four (4) kinds of wastewater treatment.
FAMILIARIZE.
FAMILIARIZE.
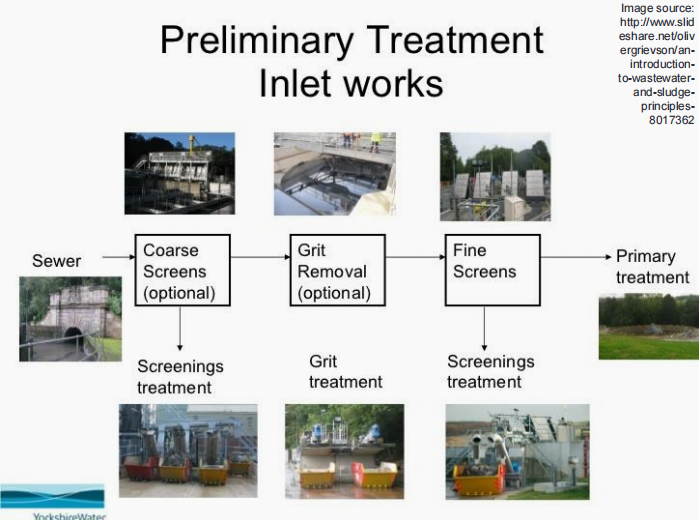
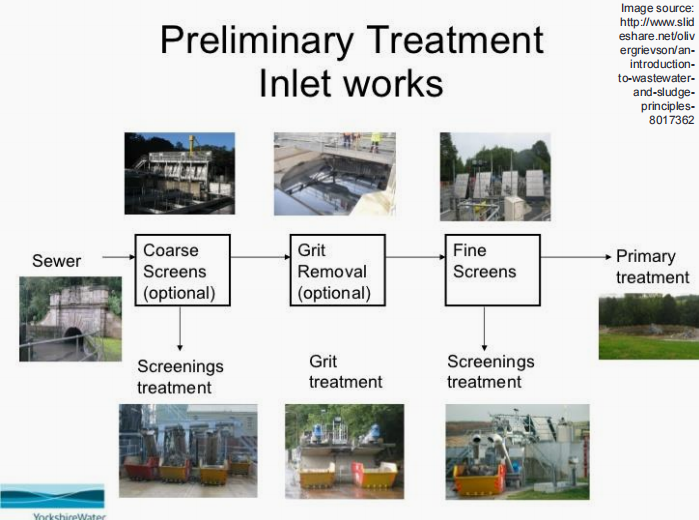
Pretreatment
WASTEWATER TREATMENT. Determine which is being described below.
This may include single or multiple unit processes, aimed to reduce the overall toxicity and adverse impact of the waste stream on the total treatment system.
Equalization
Neutralization
Grease and oil removal
Toxic substances
WASTEWATER PRE-TREATMENT. Determine which is being described below.
Pretreatment includes (4):
FAMILIARIZE.
FAMILIARIZE.
Equalization
WASTEWATER PRE-TREATMENT. Determine which is being described below.
It is one of the most important pretreatment devices and is best suited for batch discharge of concentrated wastes.
Equalization
WASTEWATER PRE-TREATMENT. Determine which is being described below.
It is important to equalize WW flows and/or concentrations.
Flow equalization
WASTEWATER PRE-TREATMENT. Determine which is being described below.
It tends to level out the hydraulic loads in treatment units.
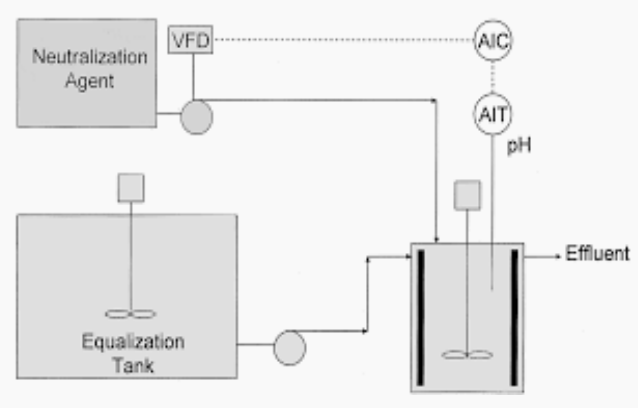
READ.
In flow equalization,
Periodic WW discharges tend to overload treatment units.
May or may not level out concentration variations, depending upon the extent of mixing within the equalization basin
READ.
In flow equalization,
Periodic WW discharges tend to overload treatment units.
May or may not level out concentration variations, depending upon the extent of mixing within the equalization basin
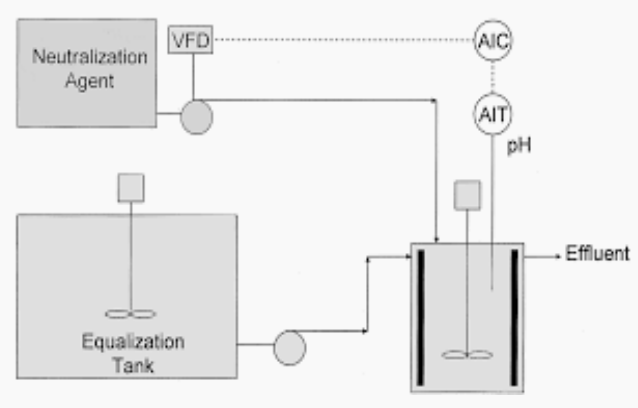
Mechanical mixing
WASTEWATER PRE-TREATMENT. Determine which is being described below.
For equalization, this may be adequate if the wastes are purely chemical in their reactivity.
Aeration mixing
WASTEWATER PRE-TREATMENT. Determine which is being described below.
For equalization, this is required for biodegradable wastes so that the microbes are kept aerobic and nuisance odors are prevented.