Comprehensive Final BIOL2311
1/631
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
632 Terms
sensory
What is the functional classification for neurons that carry information from peripheral receptors to the central nervous system?
motor
What is the functional classification for neurons that carry information from the central nervous system to peripheral effector organs?
ganglia
What are clusters of neuronal cell bodies in the peripheral nervous system called?
astrocyte
What type of glial cell is responsible for supporting neurons and maintaining the blood/brain barrier?
axon
What do we call neuronal processes that transmit membrane potentials away from the neuronal cell body?
dendrites
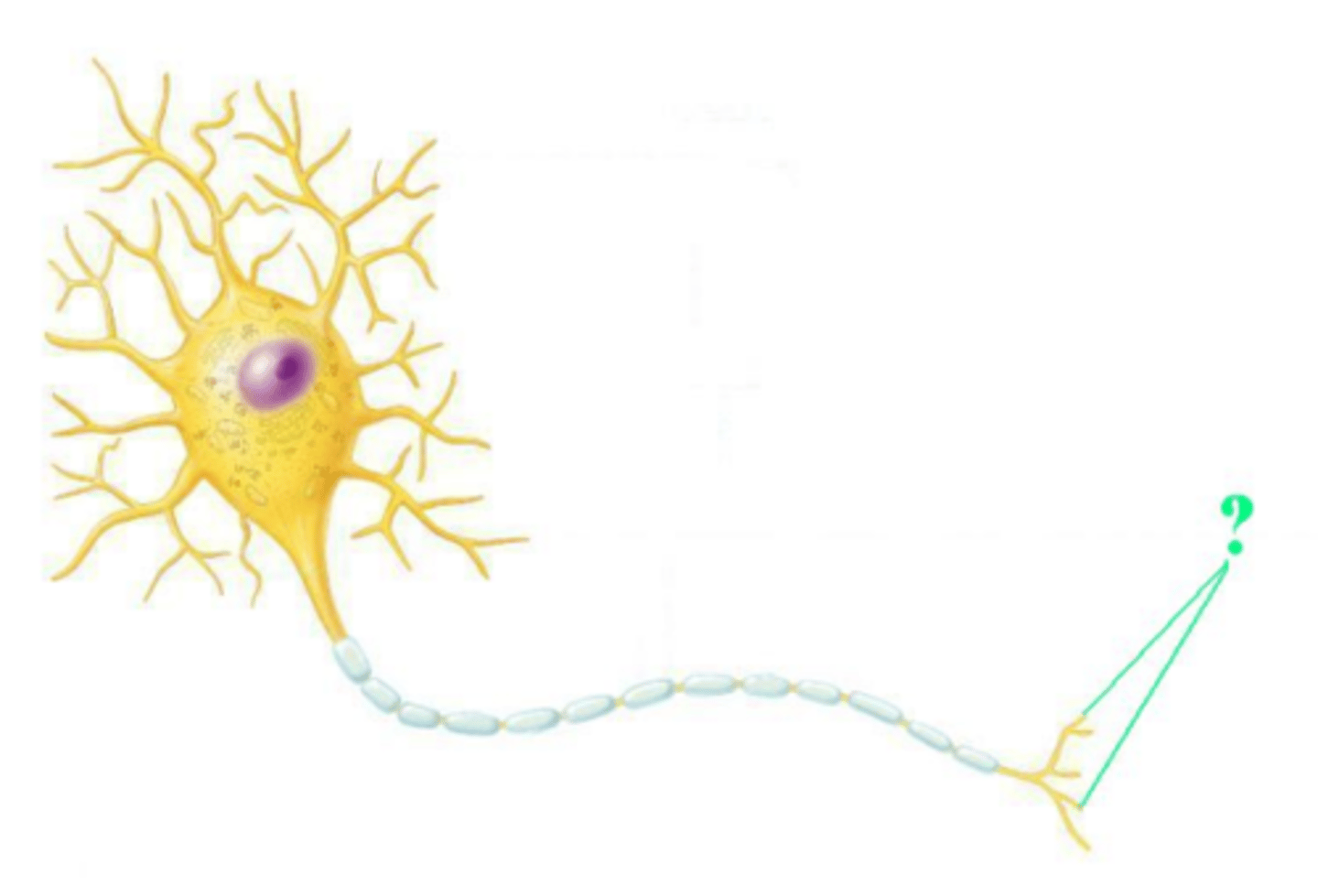
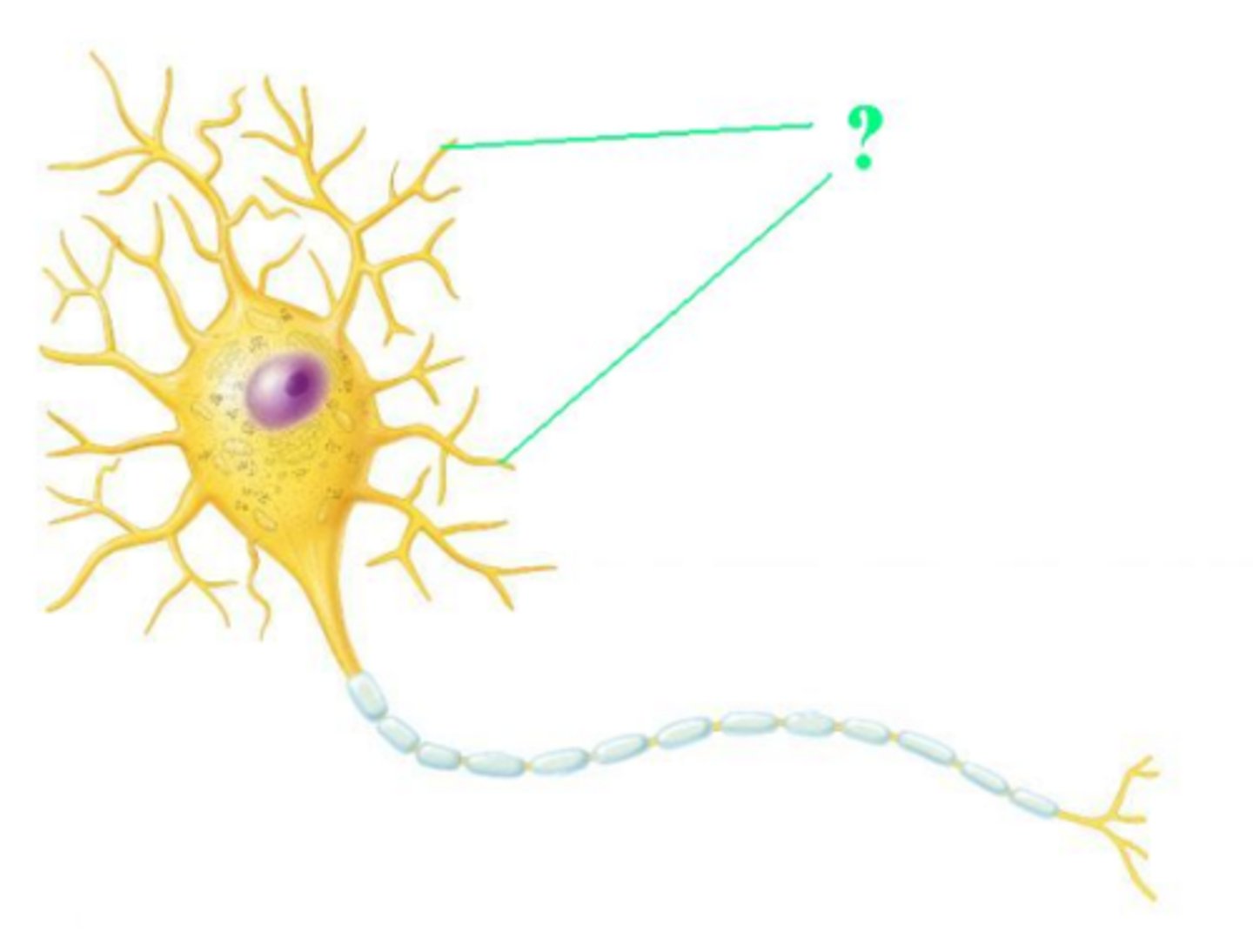
What do we call neuronal processes that carry receptors for neurotransmitters and that transmit membrane potentials toward the neuronal cell body?
nuclei
What are clusters of neuronal cell bodies in the central nervous system called?
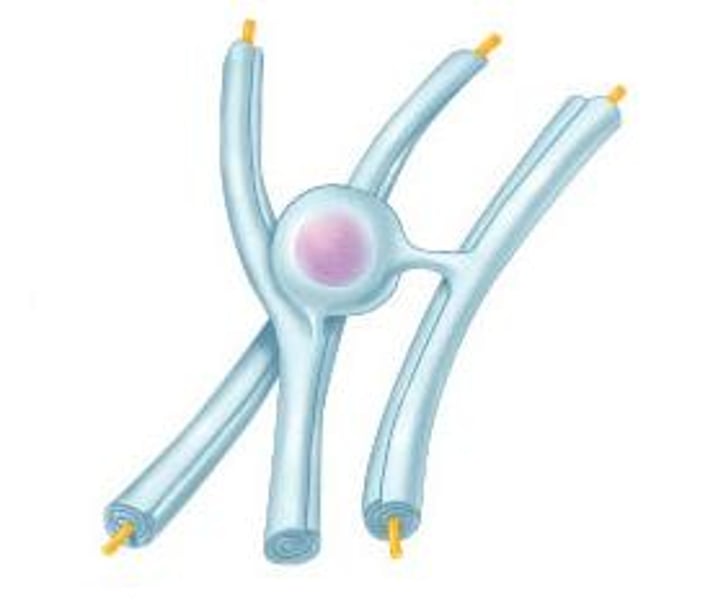
schwann cell
What type of glial cell is responsible for myelinating axons in the peripheral nervous system?
oligodendrocyte
What type of glial cell is responsible for myelinating axons in the central nervous system?
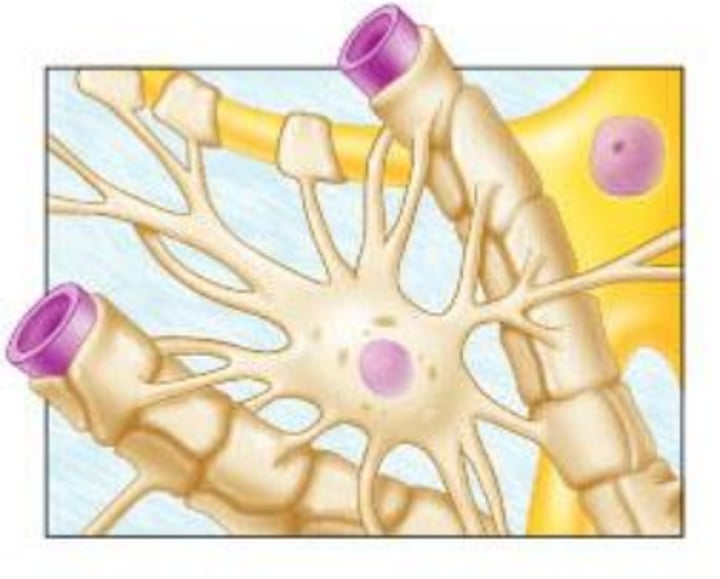
microglia
What type of glial cell is responsible for acting as phagocytic cells in the central nervous system?
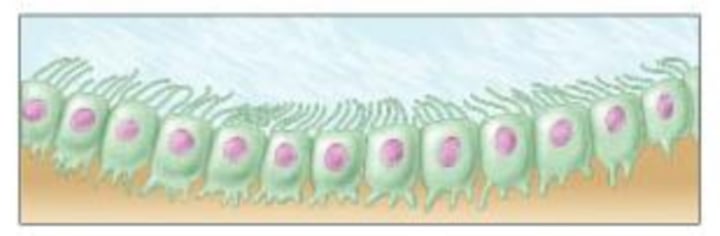
ependymal cell
schwann cell

oligodendrocyte
astrocyte
microglia
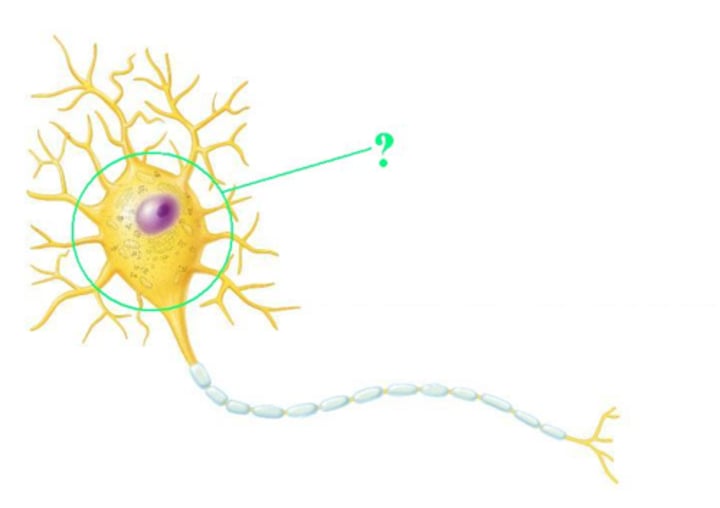
Soma
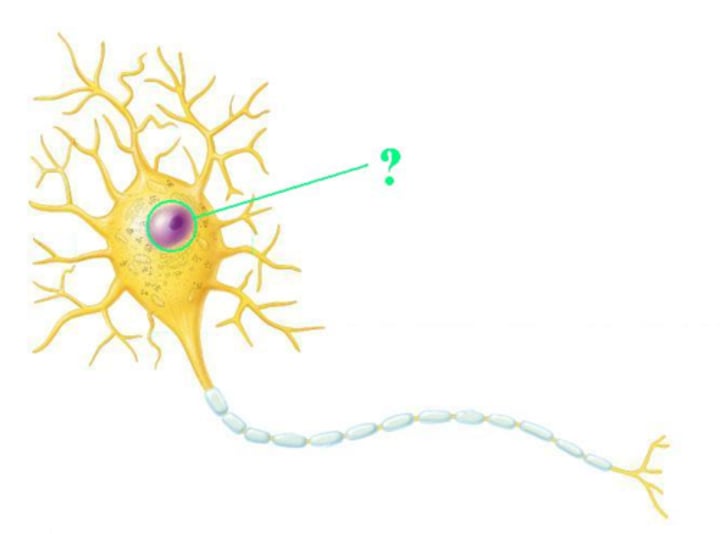
nucleus
schwann cell
axon hillock
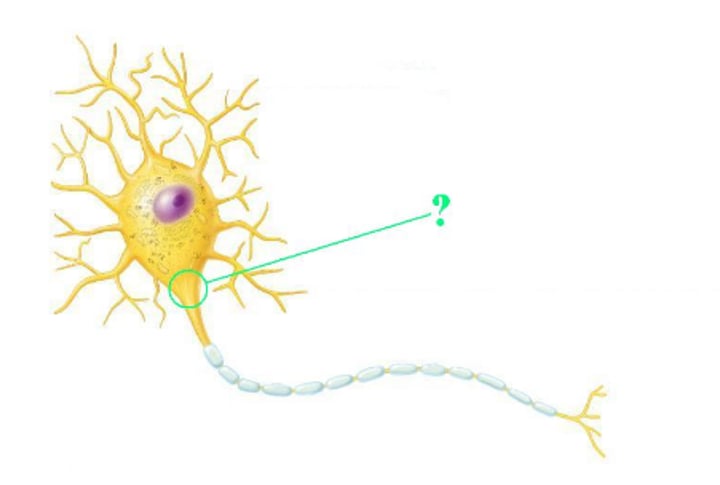
axon
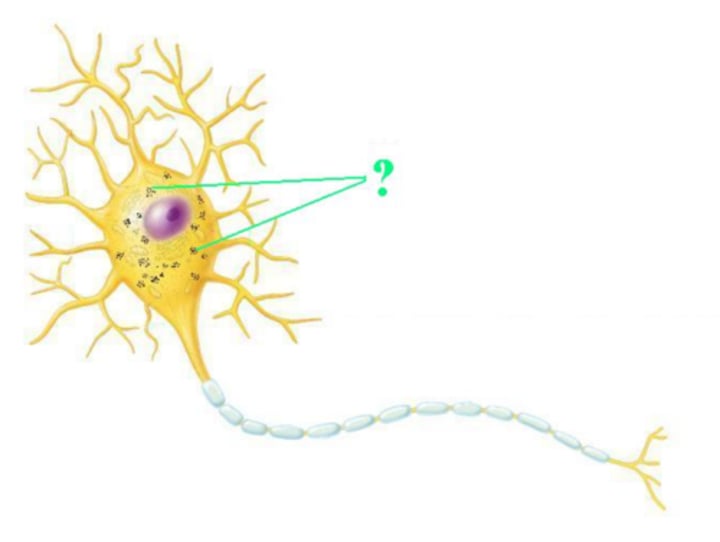
nissl bodies
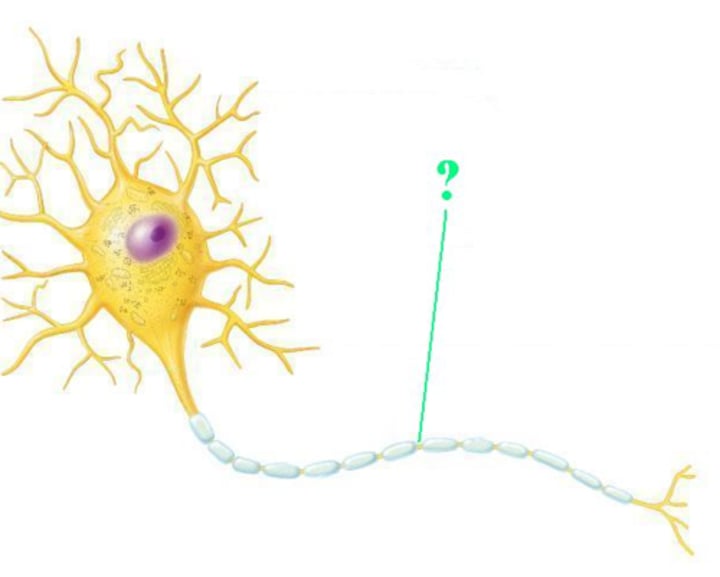
myelin sheath gap
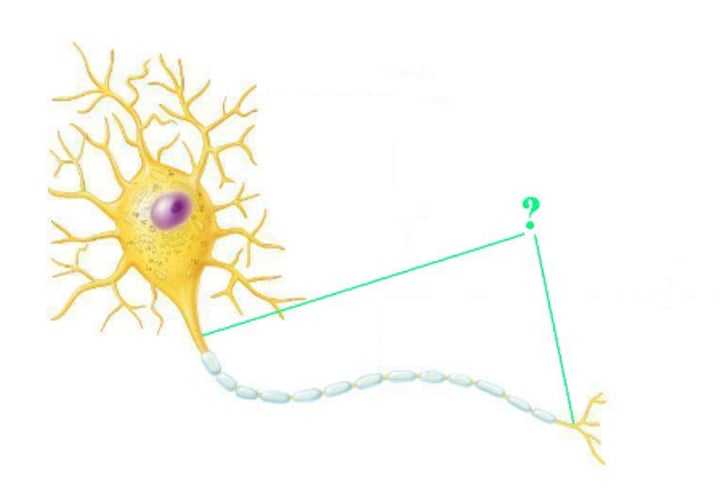
axon terminals
dendrites
presynaptic membrane
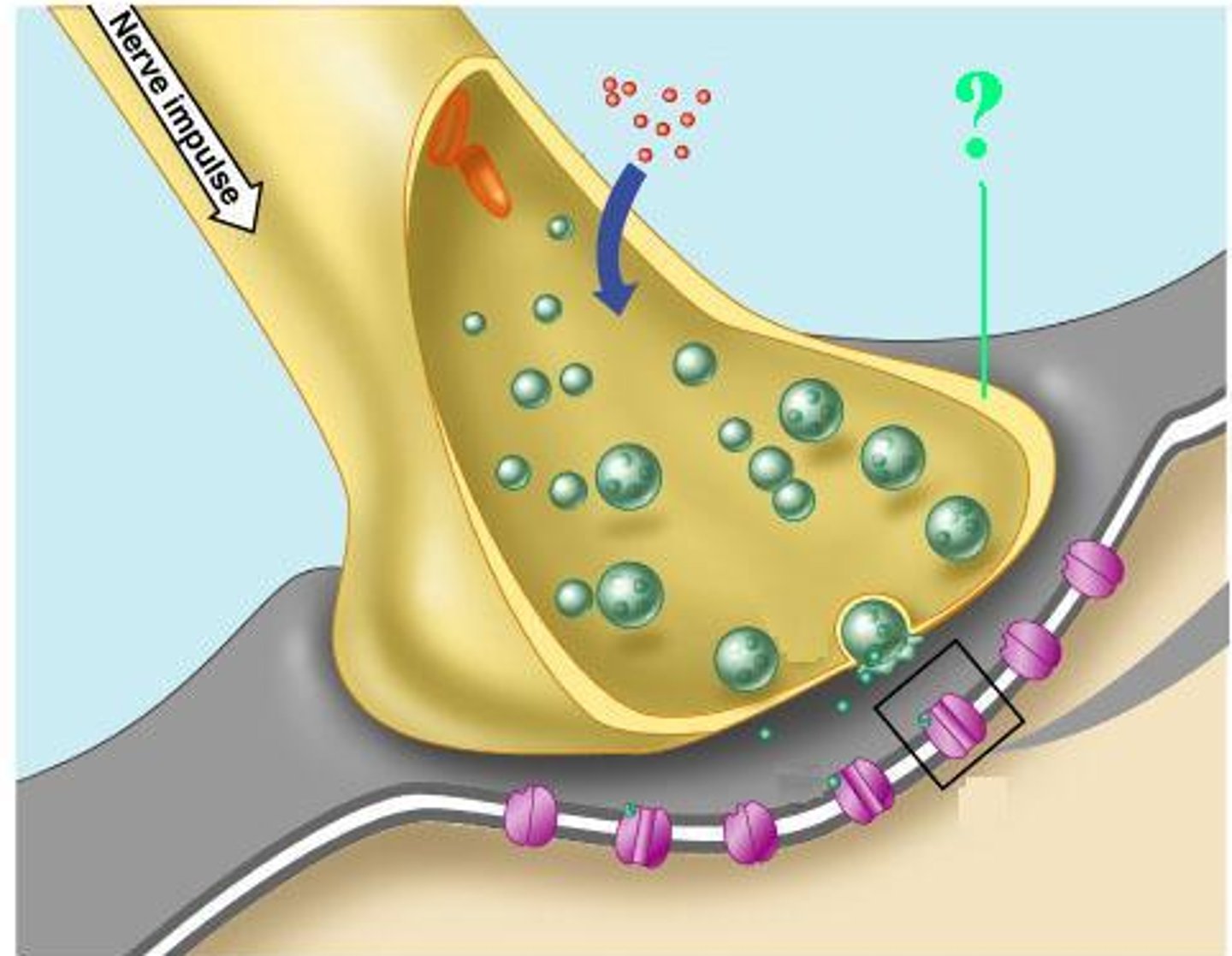
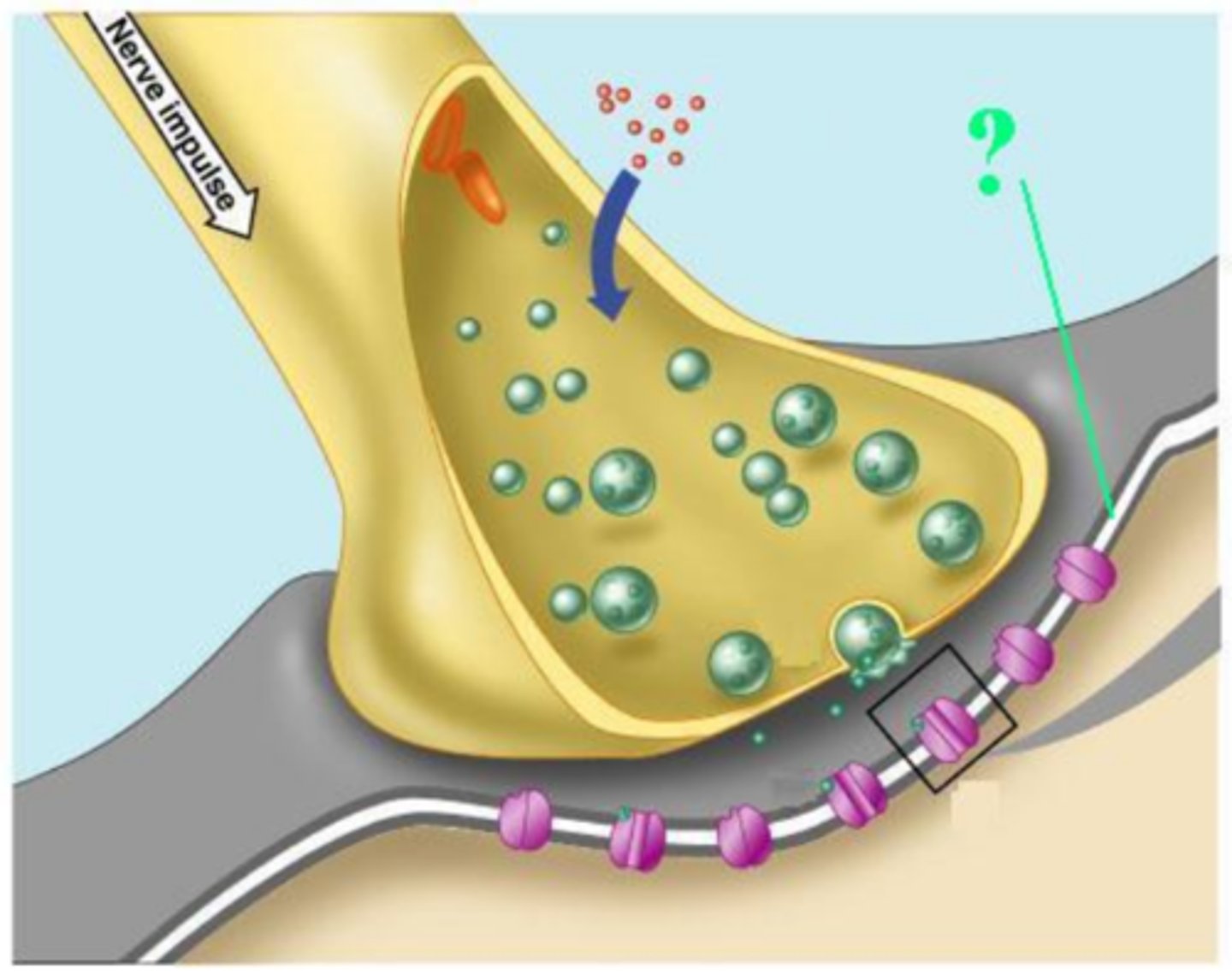
postsynaptic membrane
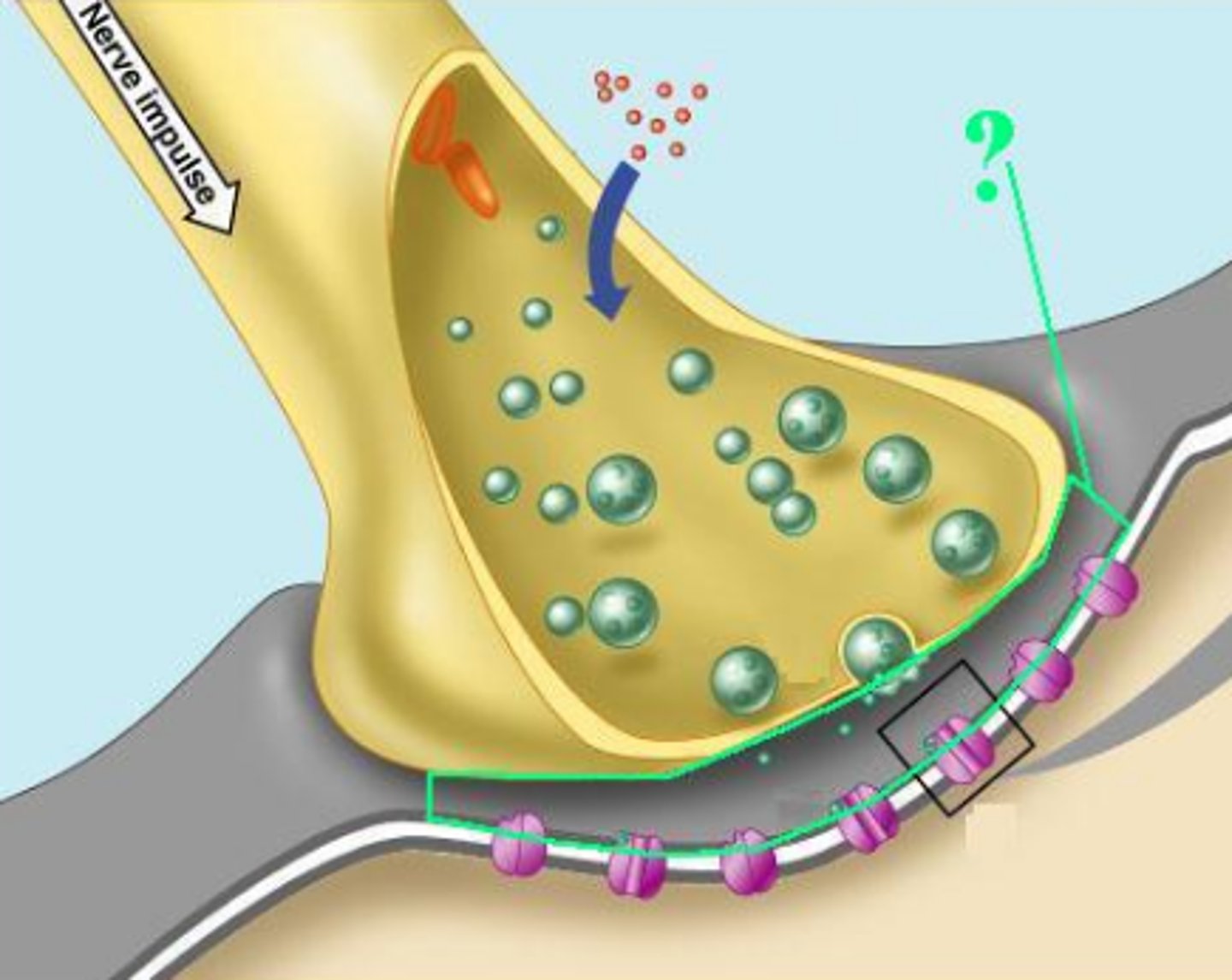
synaptic vesicles
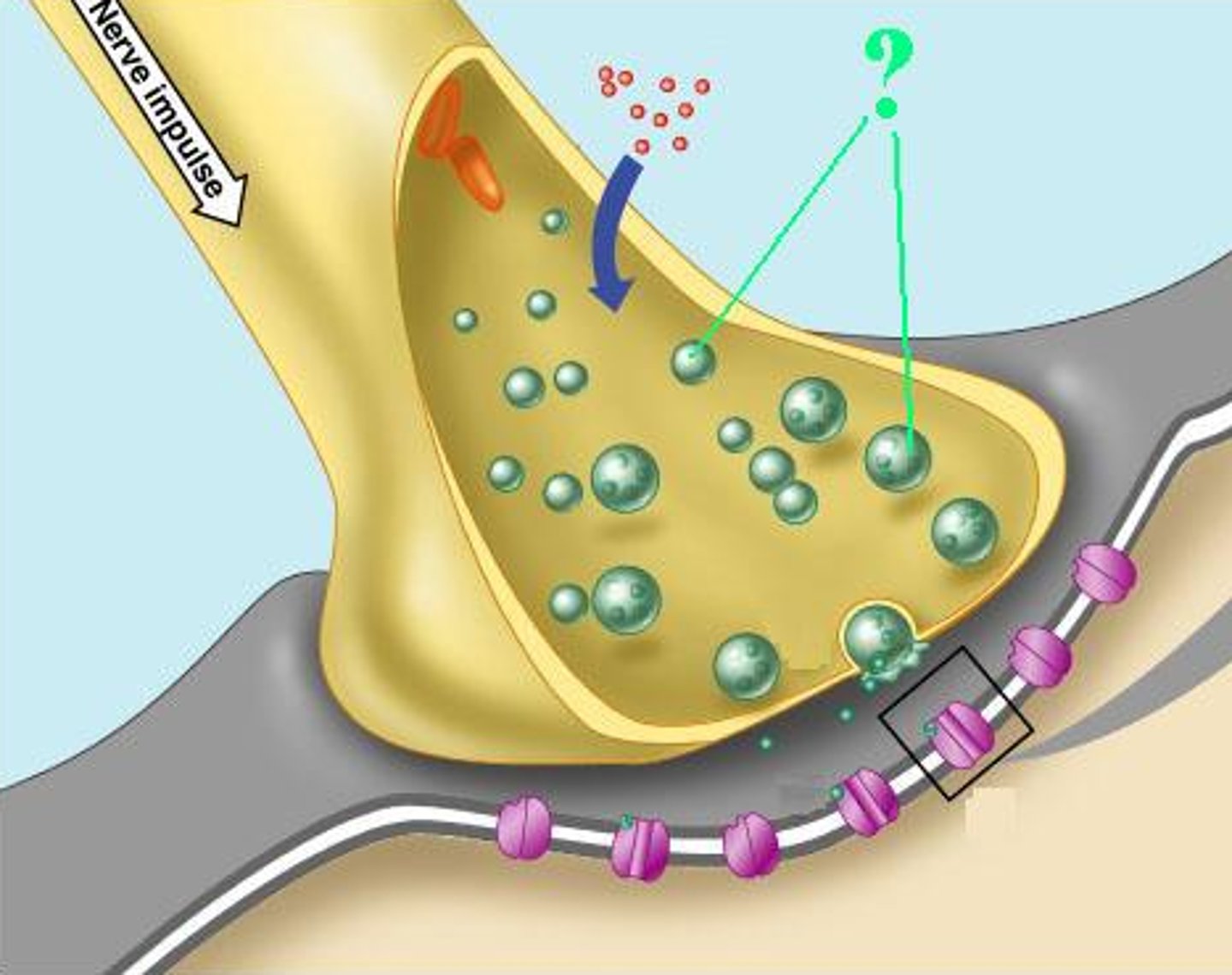
synaptic cleft
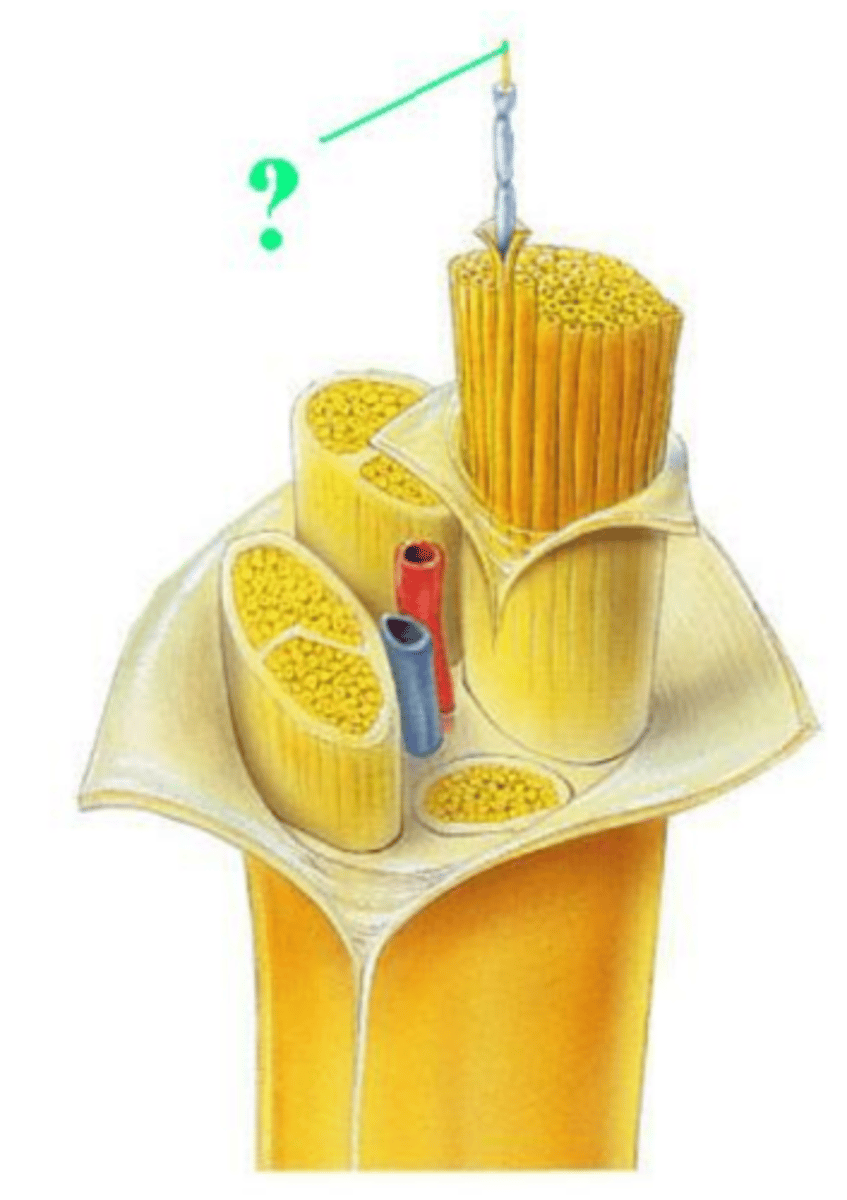
epineurium
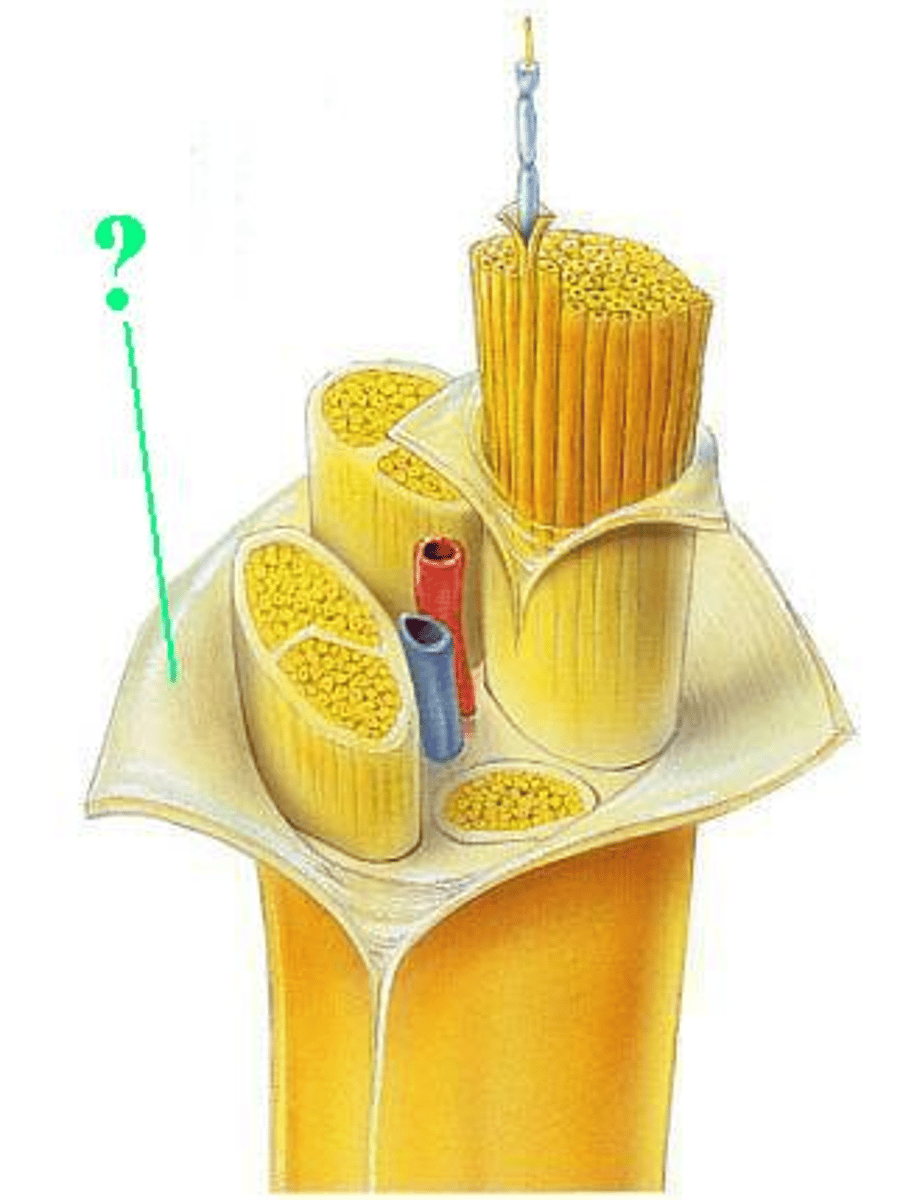
fascicle
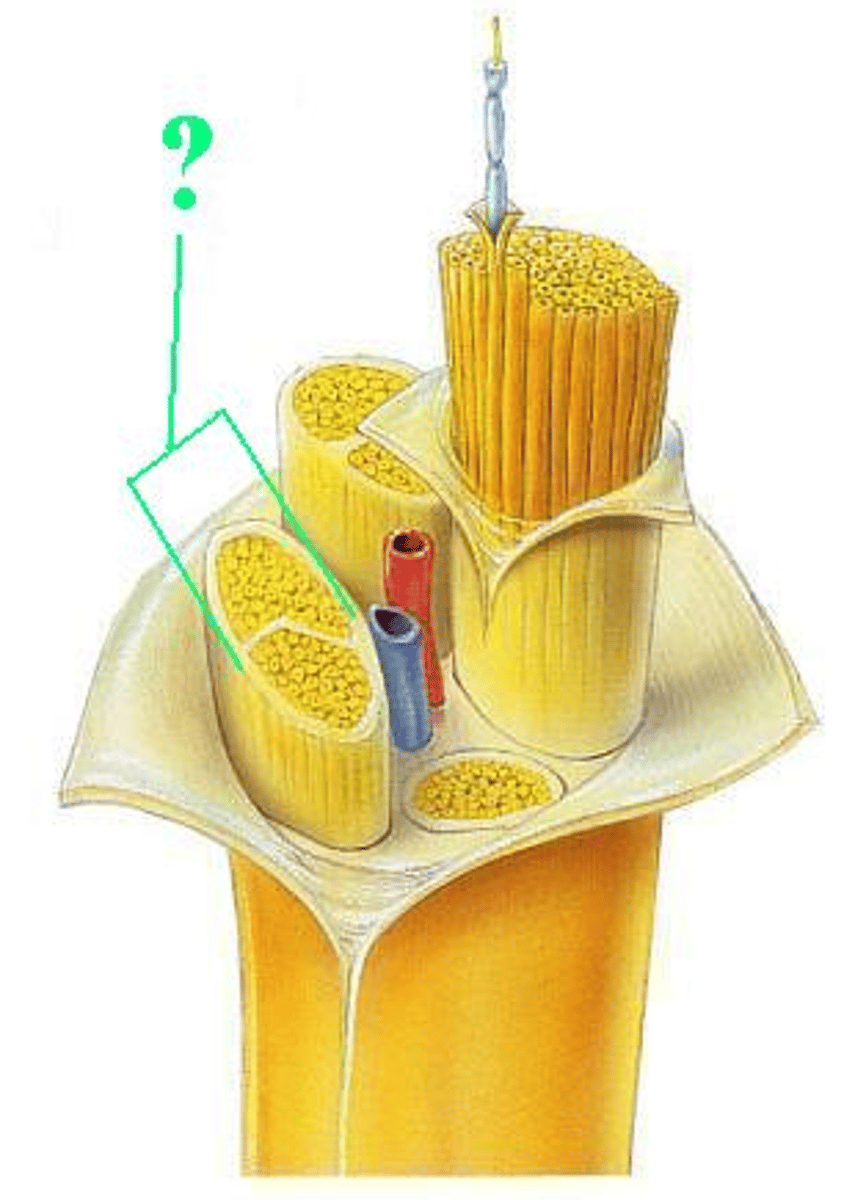
blood vessels
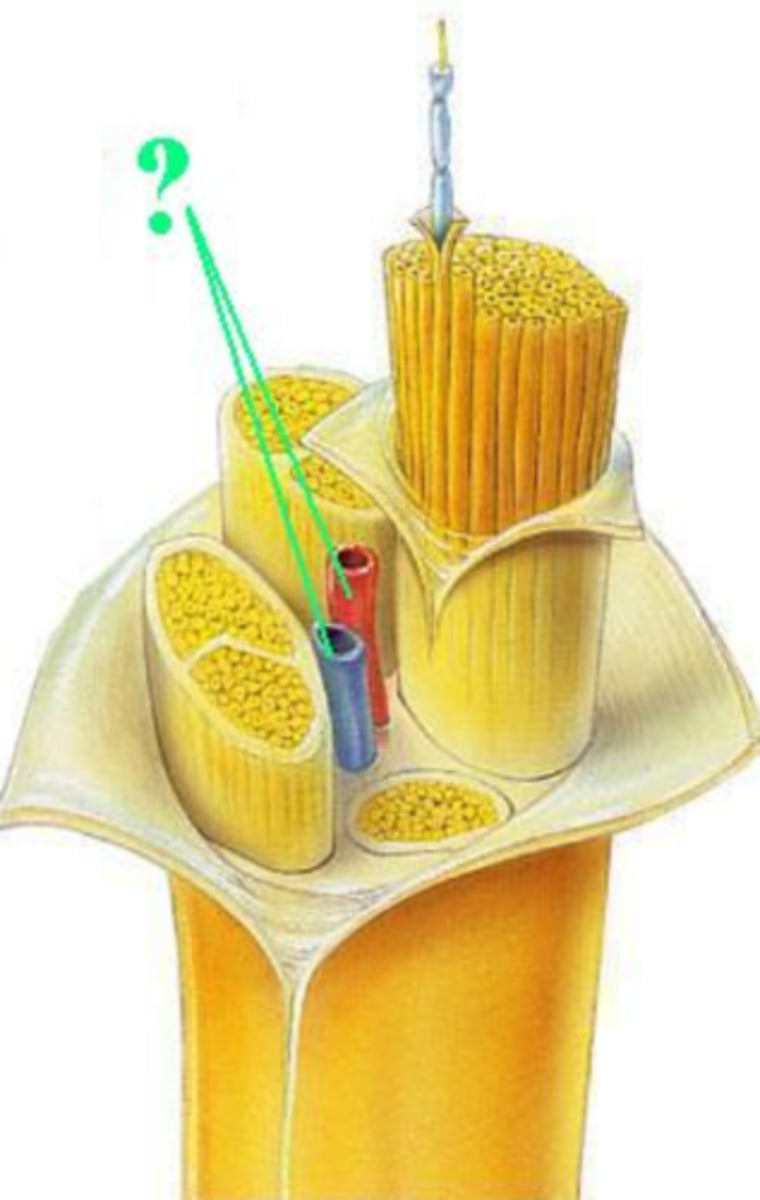
myelin sheath
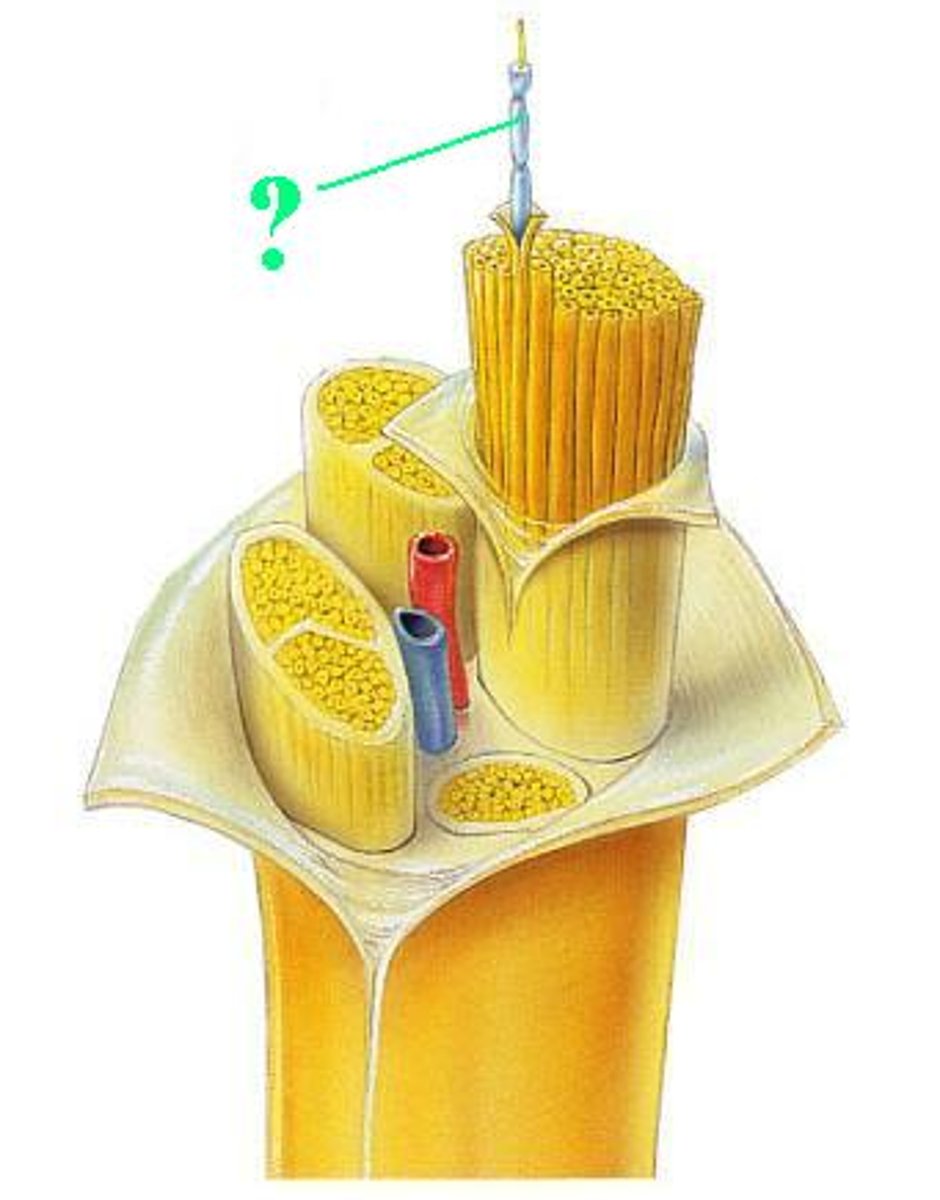
perineurium
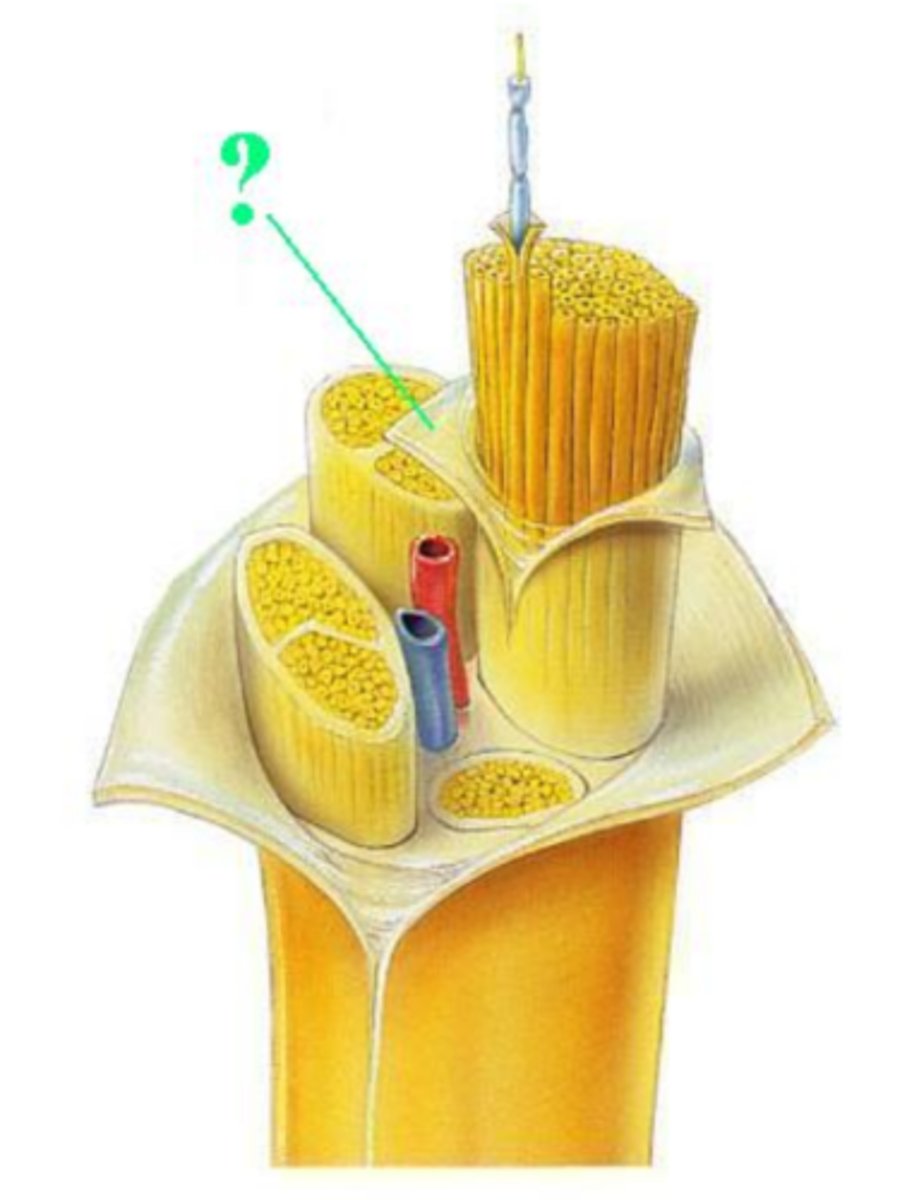
axon
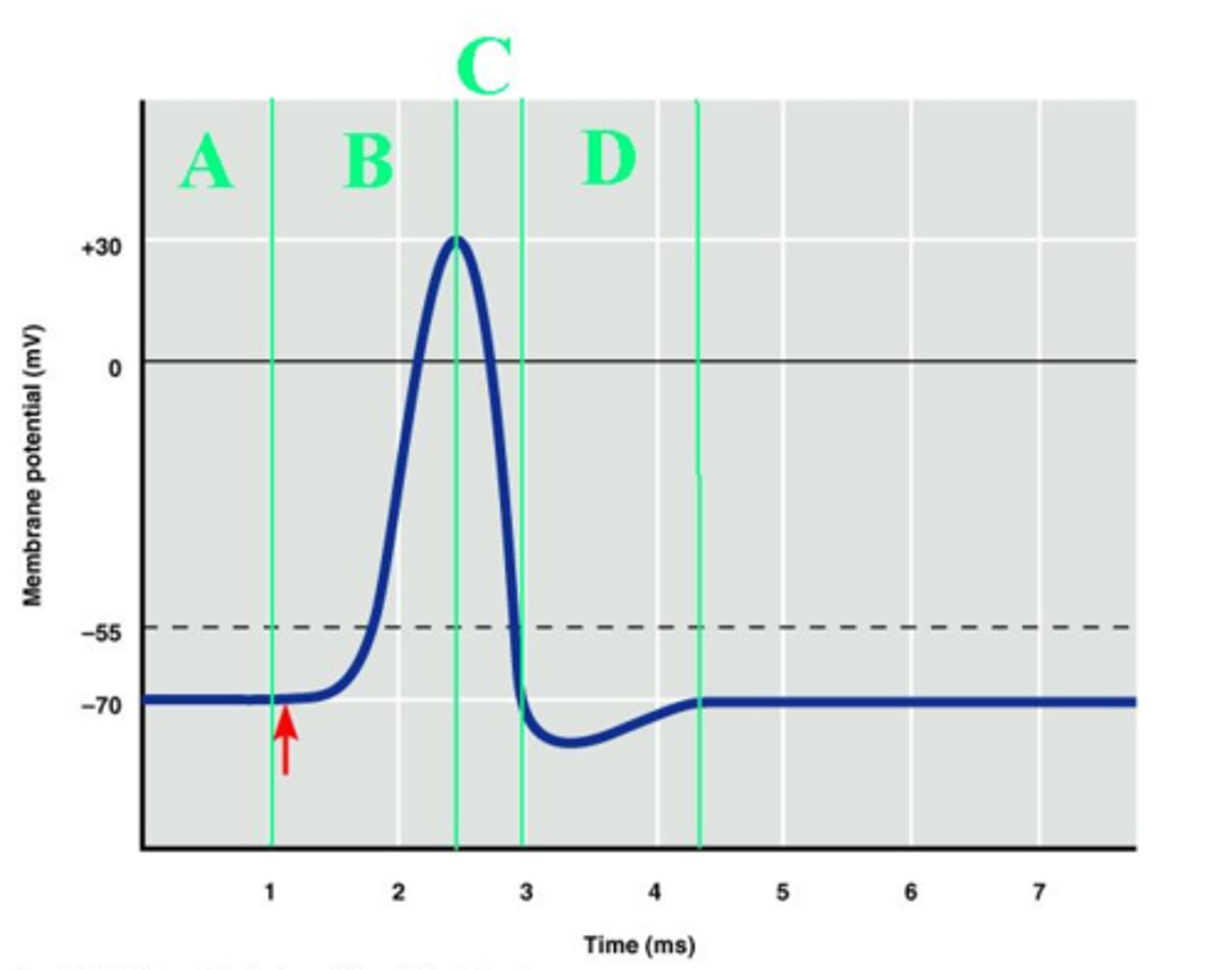
A
Which labeled portion of the diagram corresponds to the resting potential of the axon?
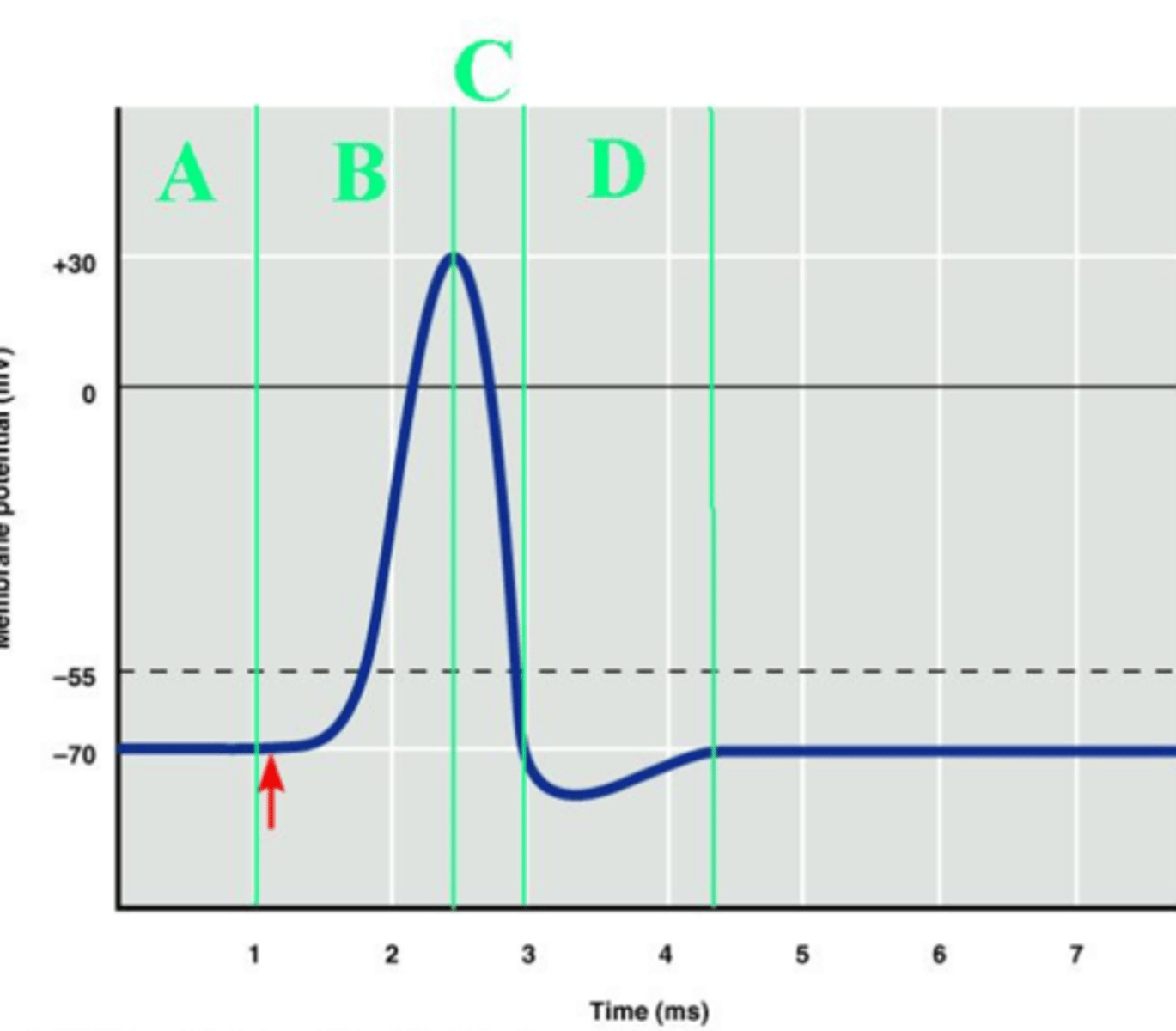
B
Which labeled portion of the diagram corresponds to the depolarization of the axon?
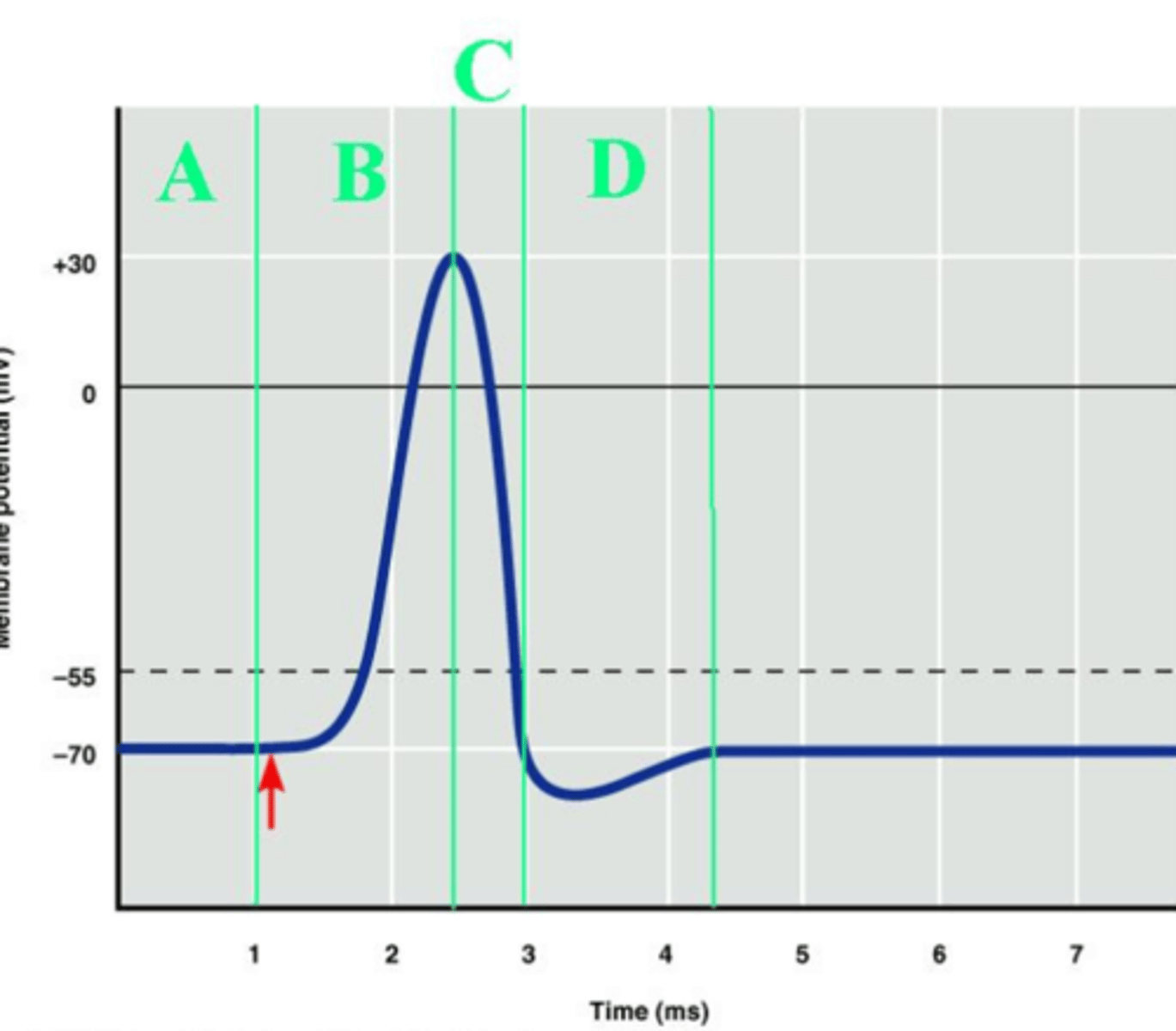
C
Which labeled portion of the diagram corresponds to the repolarization of the axon?
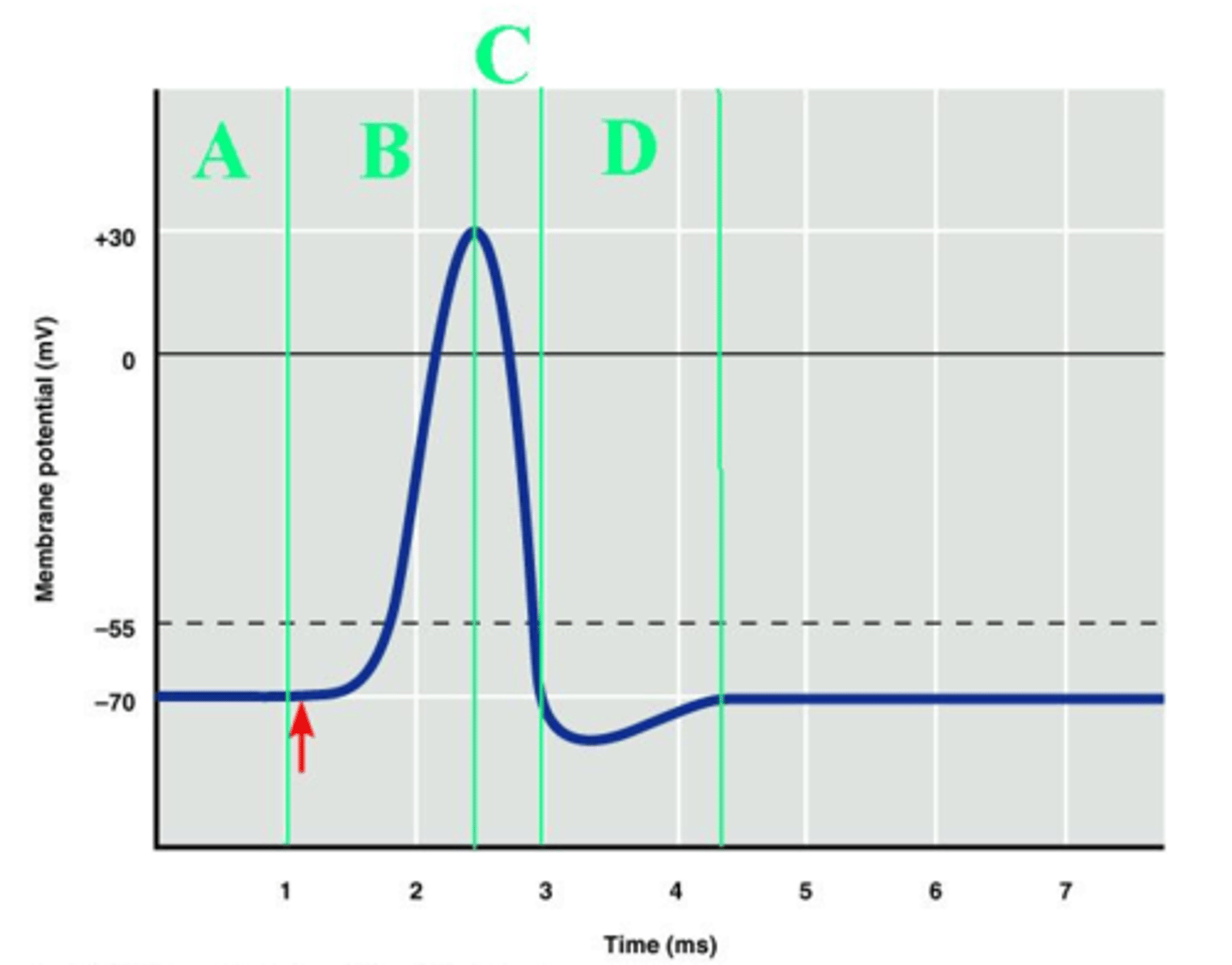
D
Which labeled portion of the diagram corresponds to the hyperpolarization of the axon?
threshold
What is the smallest stimulus that is capable of initiating an action potential called?
relative refractory period
What do we call the period during which initiation of an action potential requires a higher than normal threshold stimulus?
absolute refractory period
What do we call the period during which an action potential cannot be initiated, regardless of the strength of the stimulus?
sodium
Depolarization is the result of the rapid entry of which ion into the cell?
potassium
Hyperpolarization is the result of the excessive exit of which ion from the cell?
inhibition
In the PhysioEx exercise, what was the effect of curare on the nerve?
inhibition
In the PhysioEx exercise, what was the effect of ether on the nerve?
thalamus
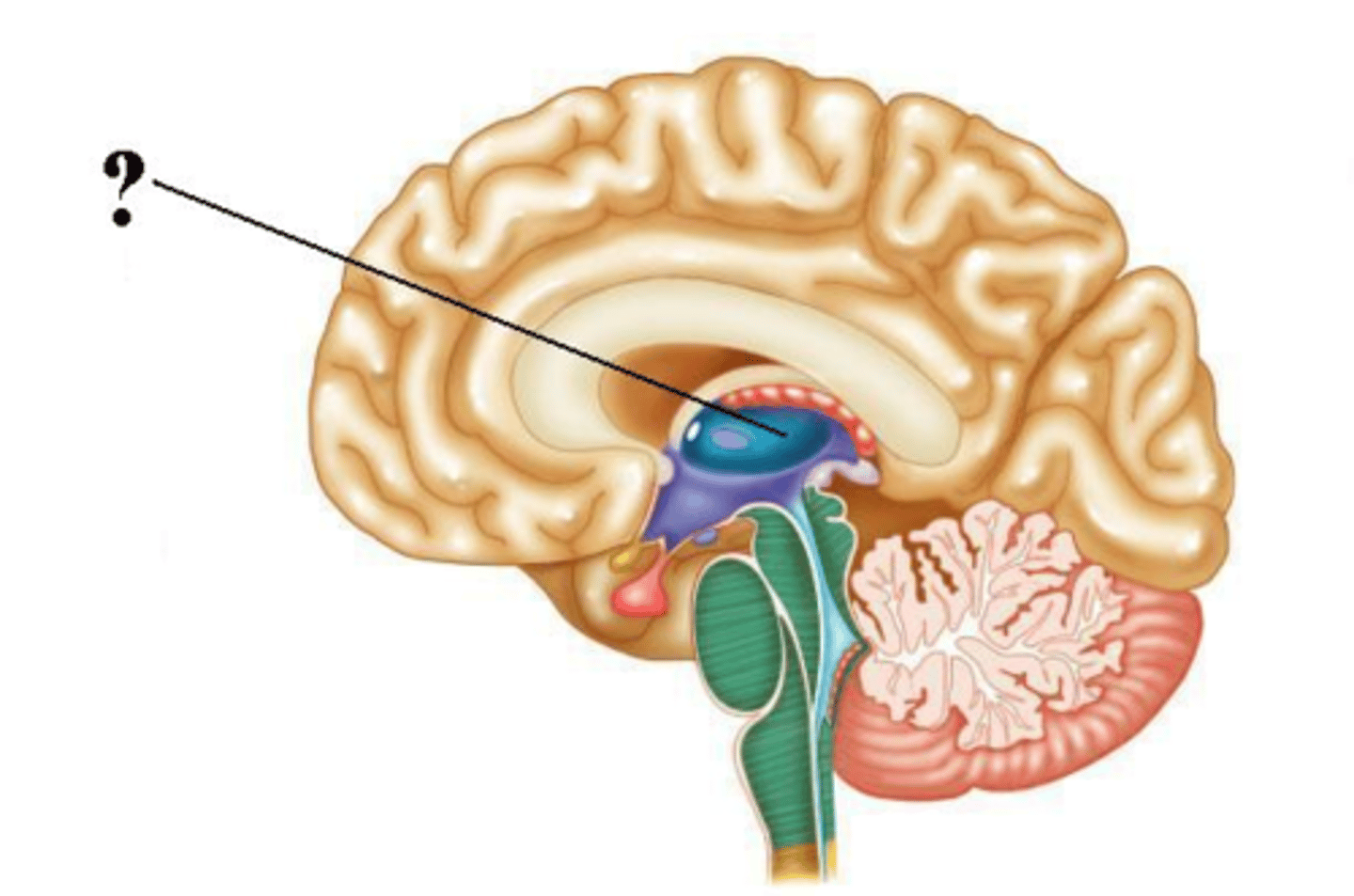
cerebral aqueduct
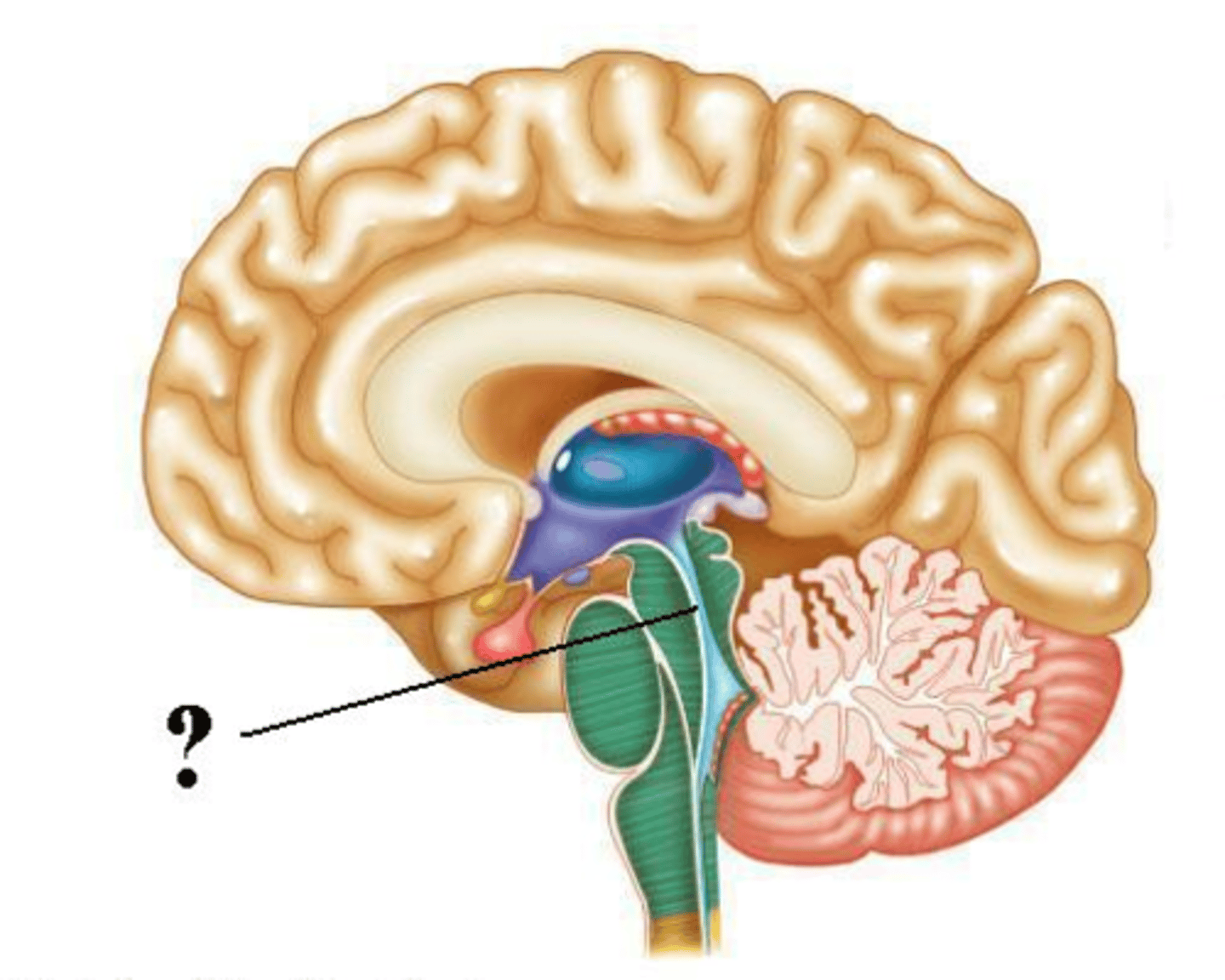
septum pellucidum
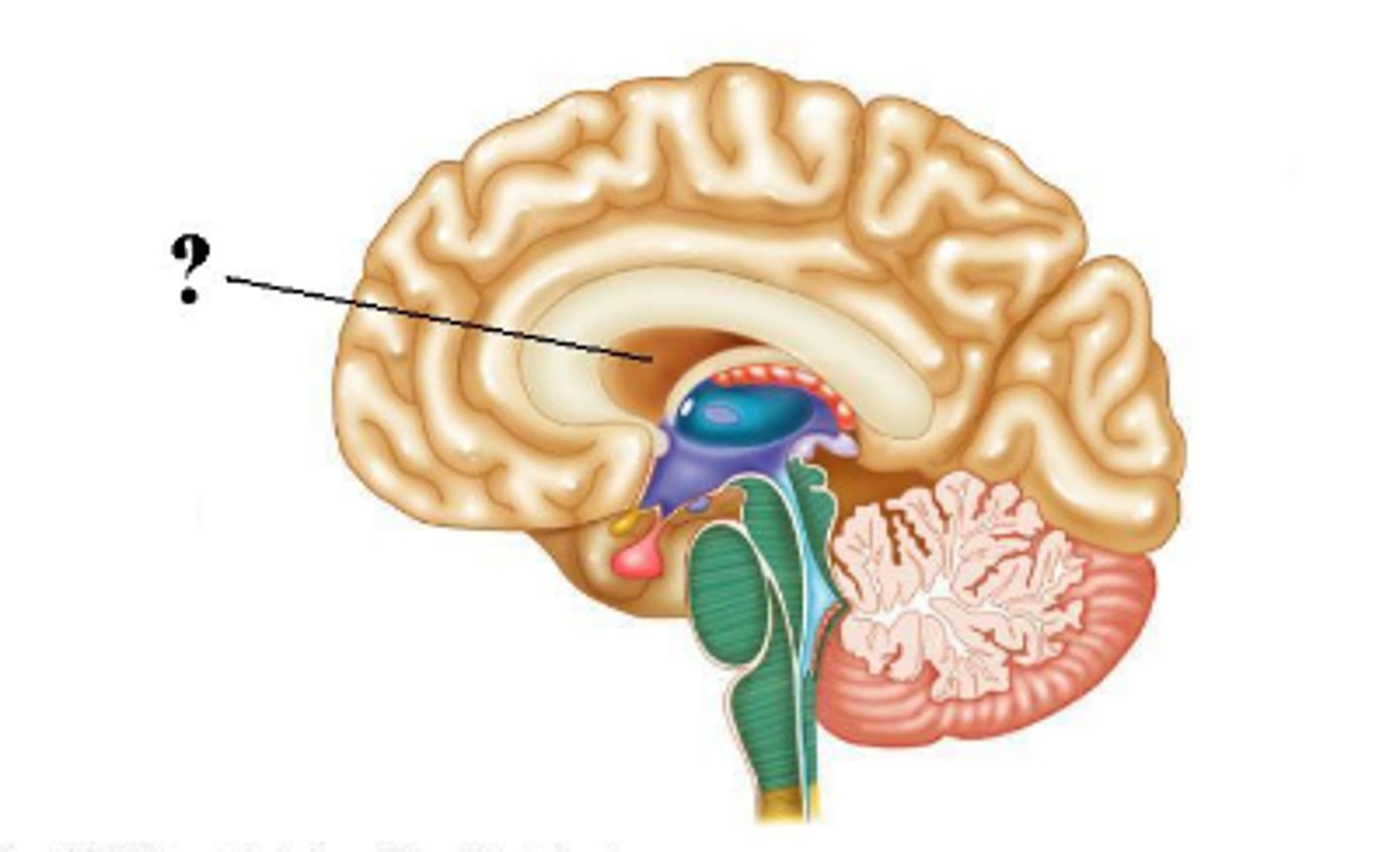
corpus callosum
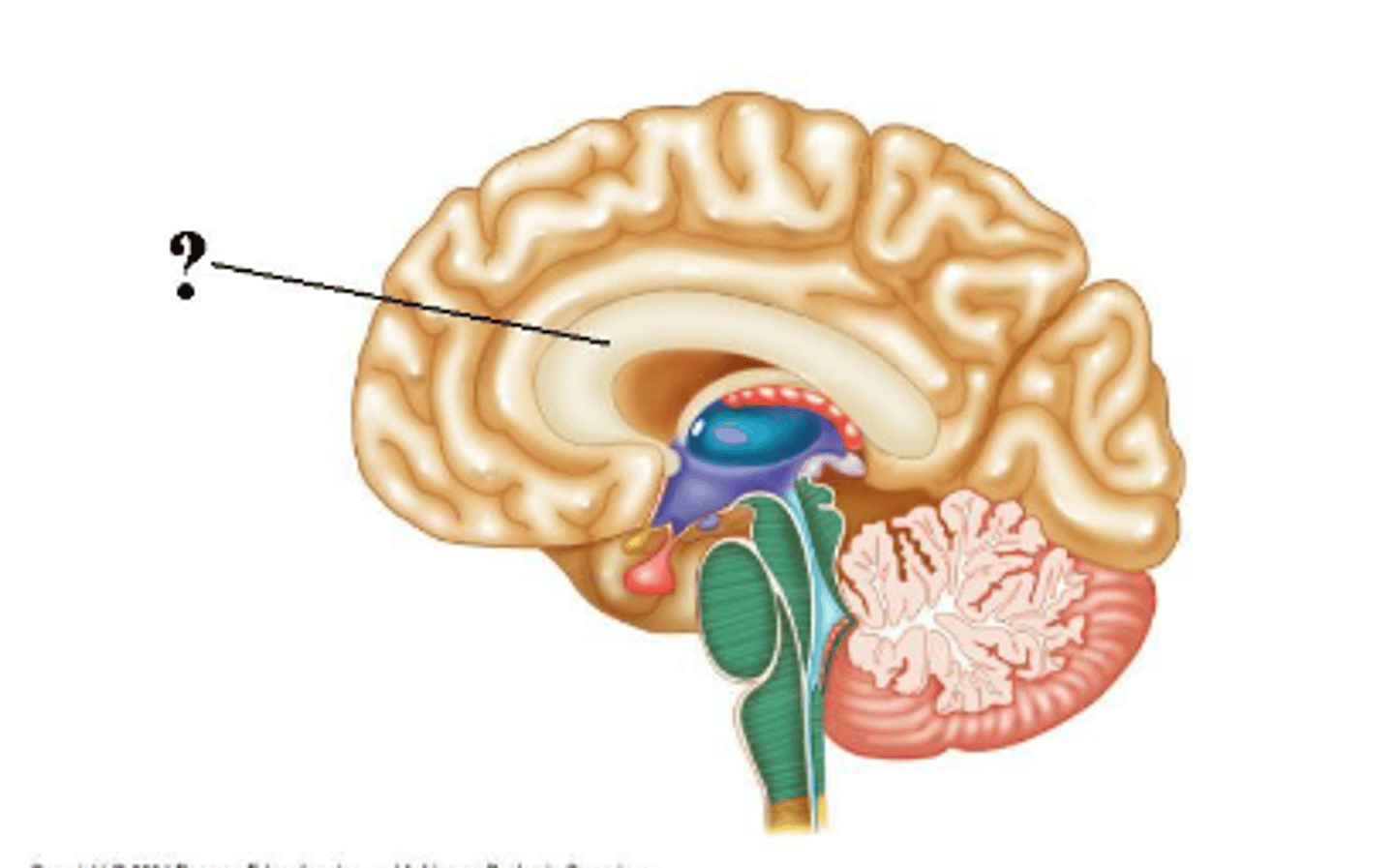
corpora quadrigemina
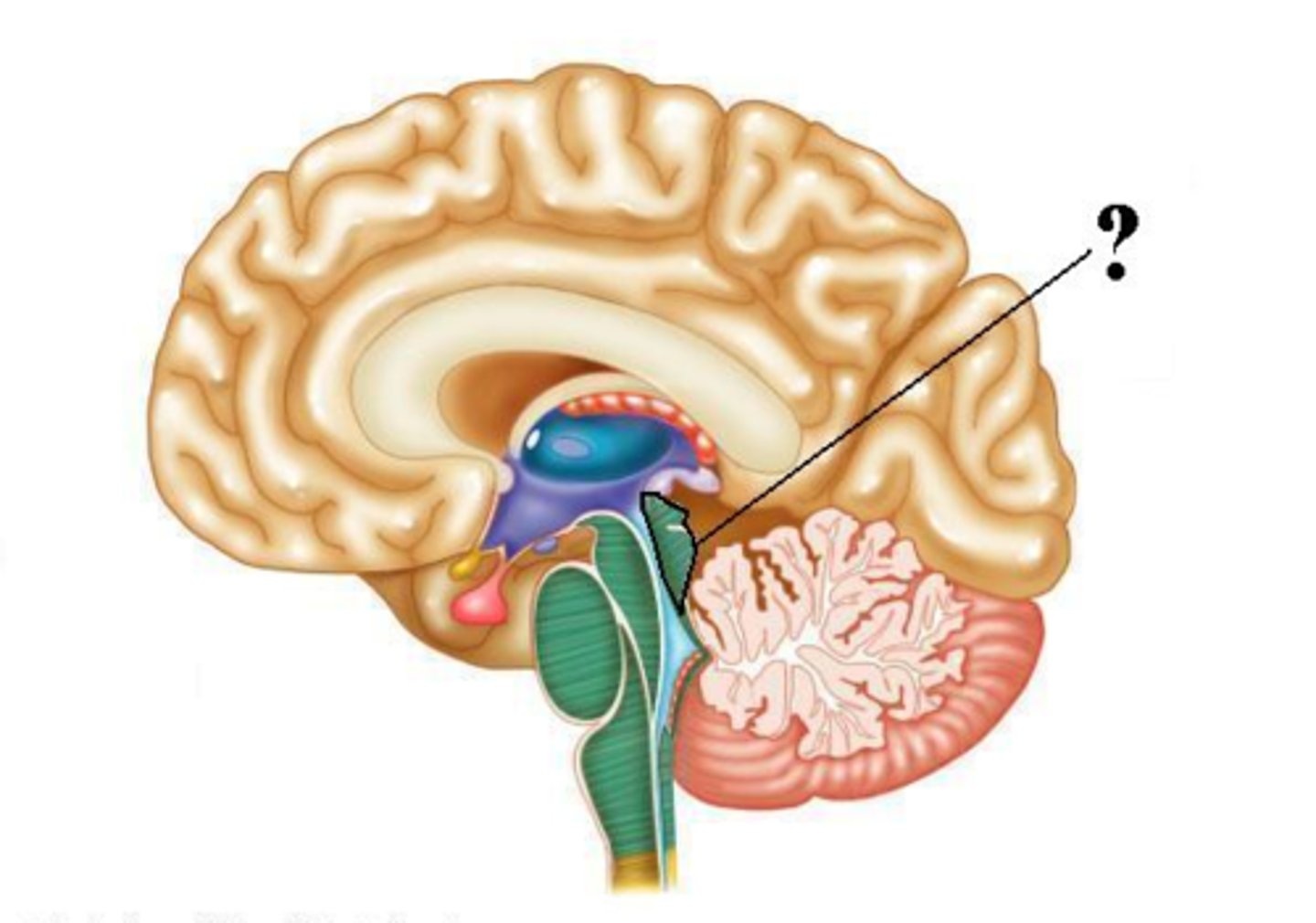
arbor vitae
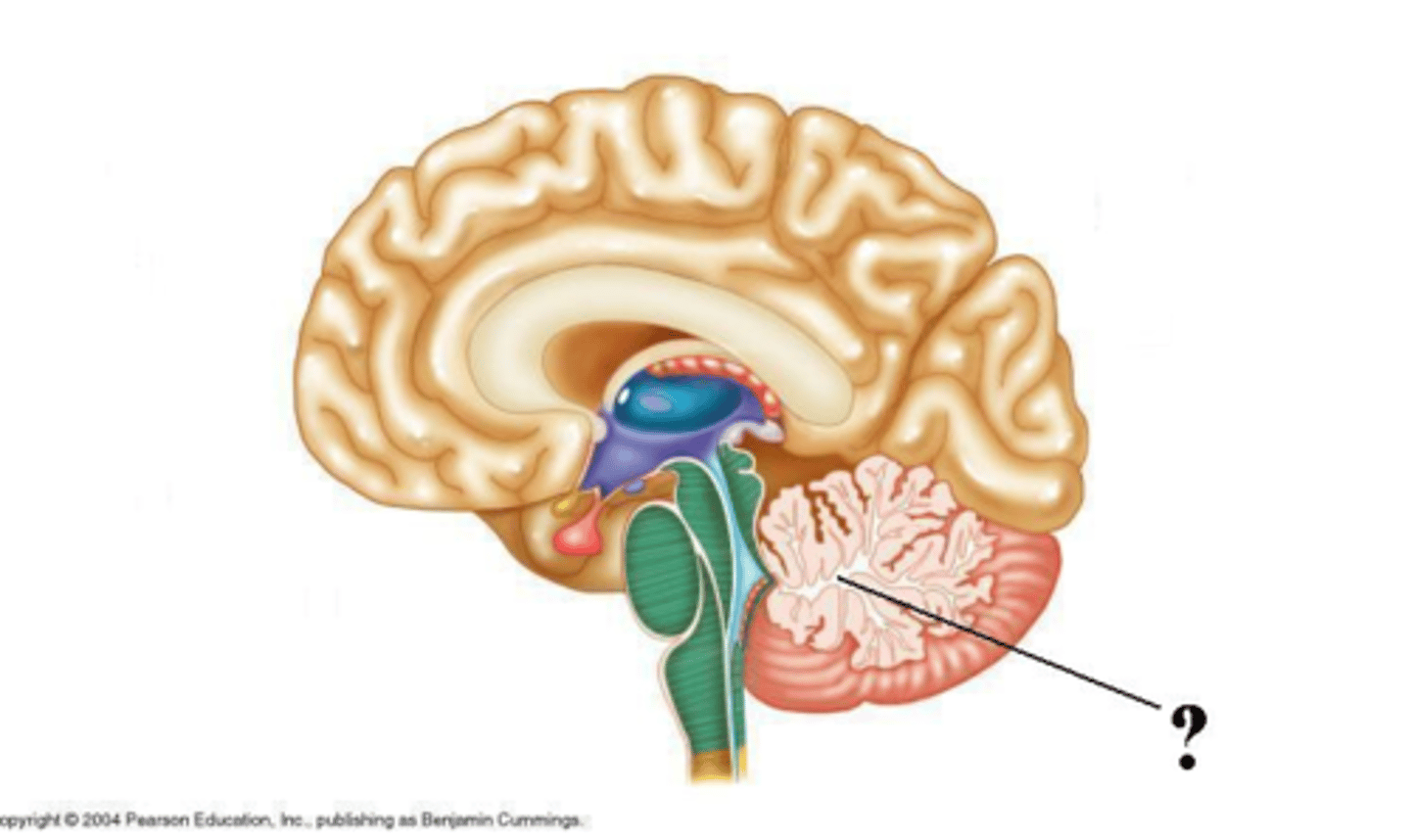
interventricular foramen
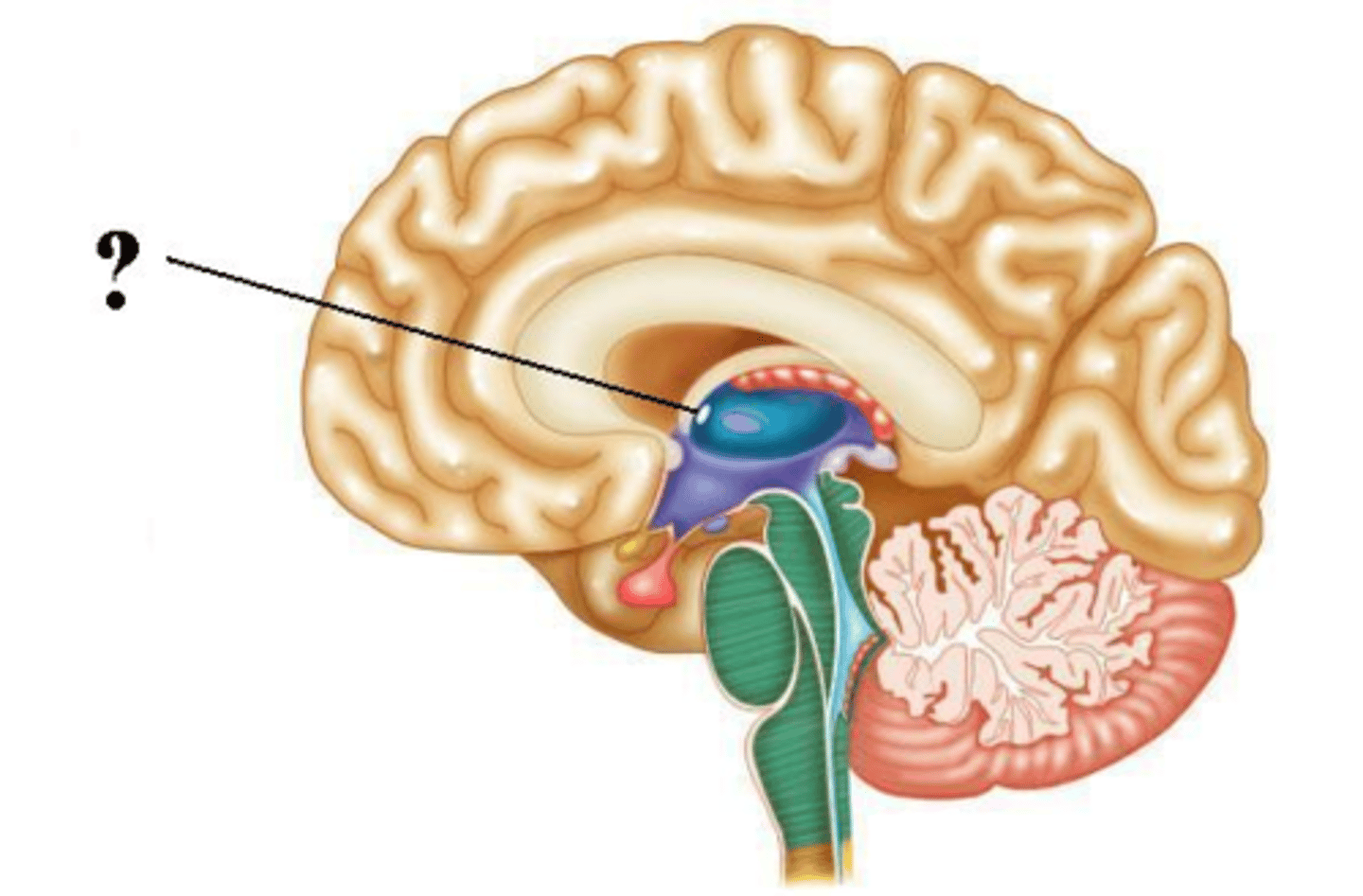
pineal gland
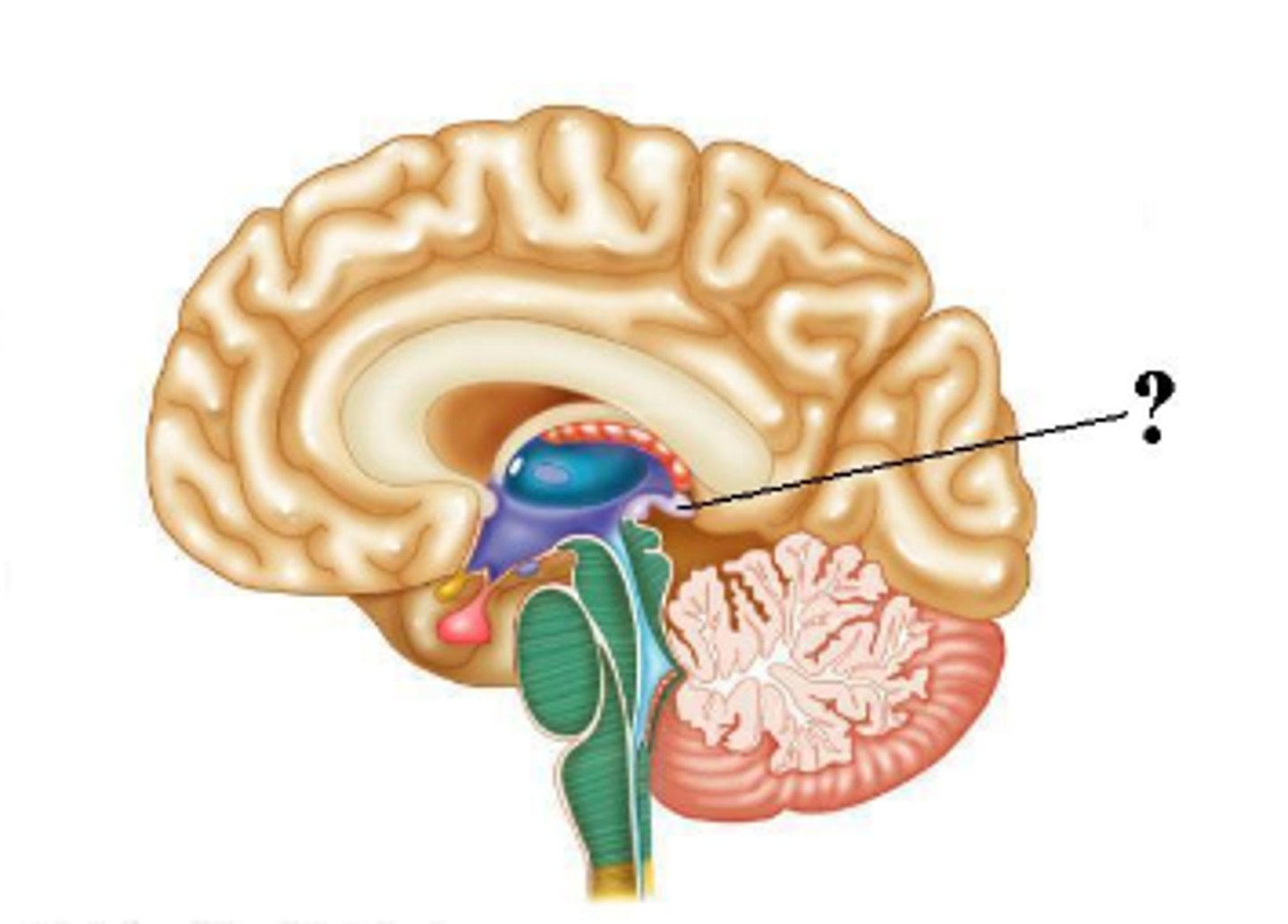
hypothalamus
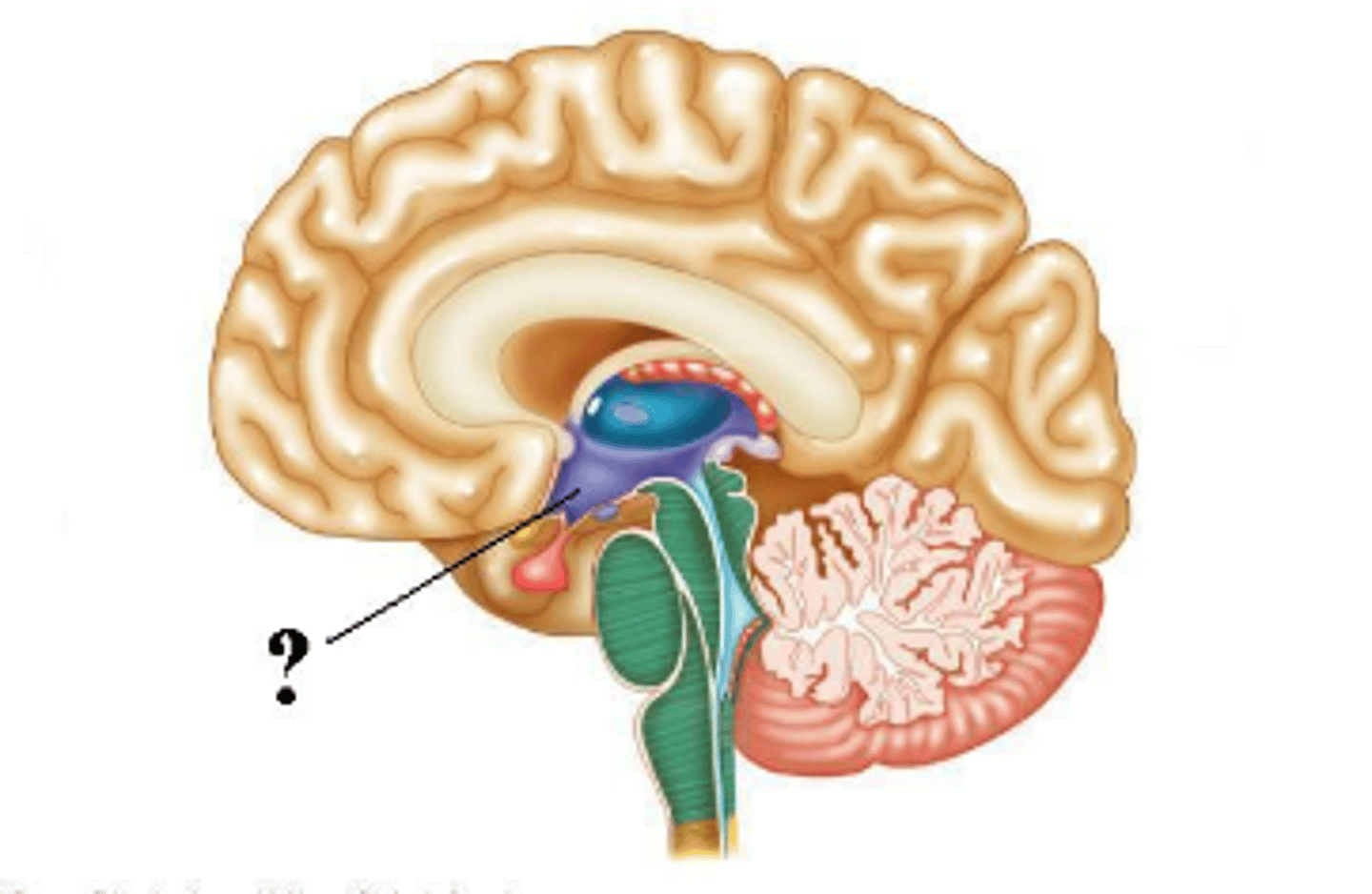
third ventricle
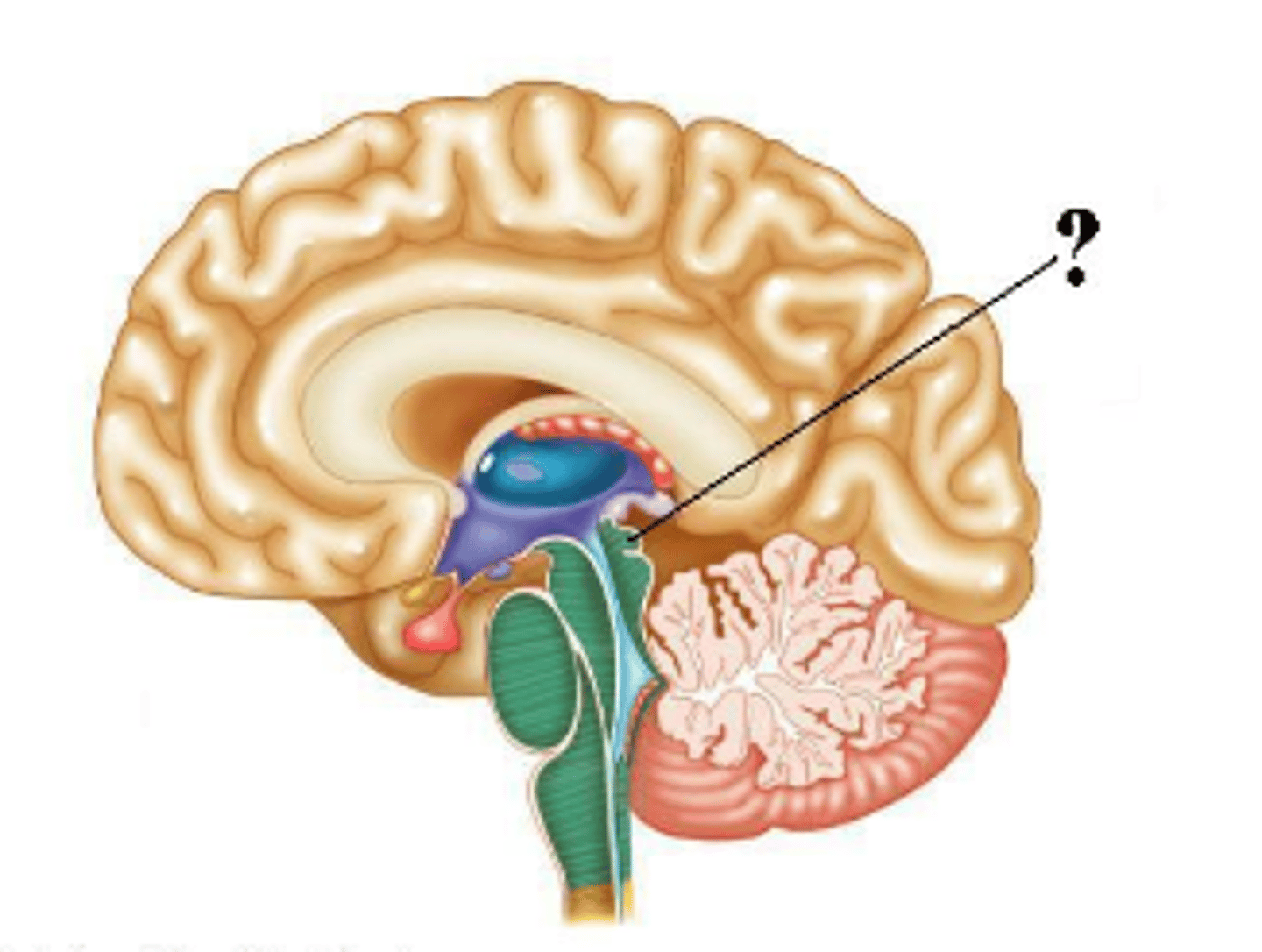
superior collicullus
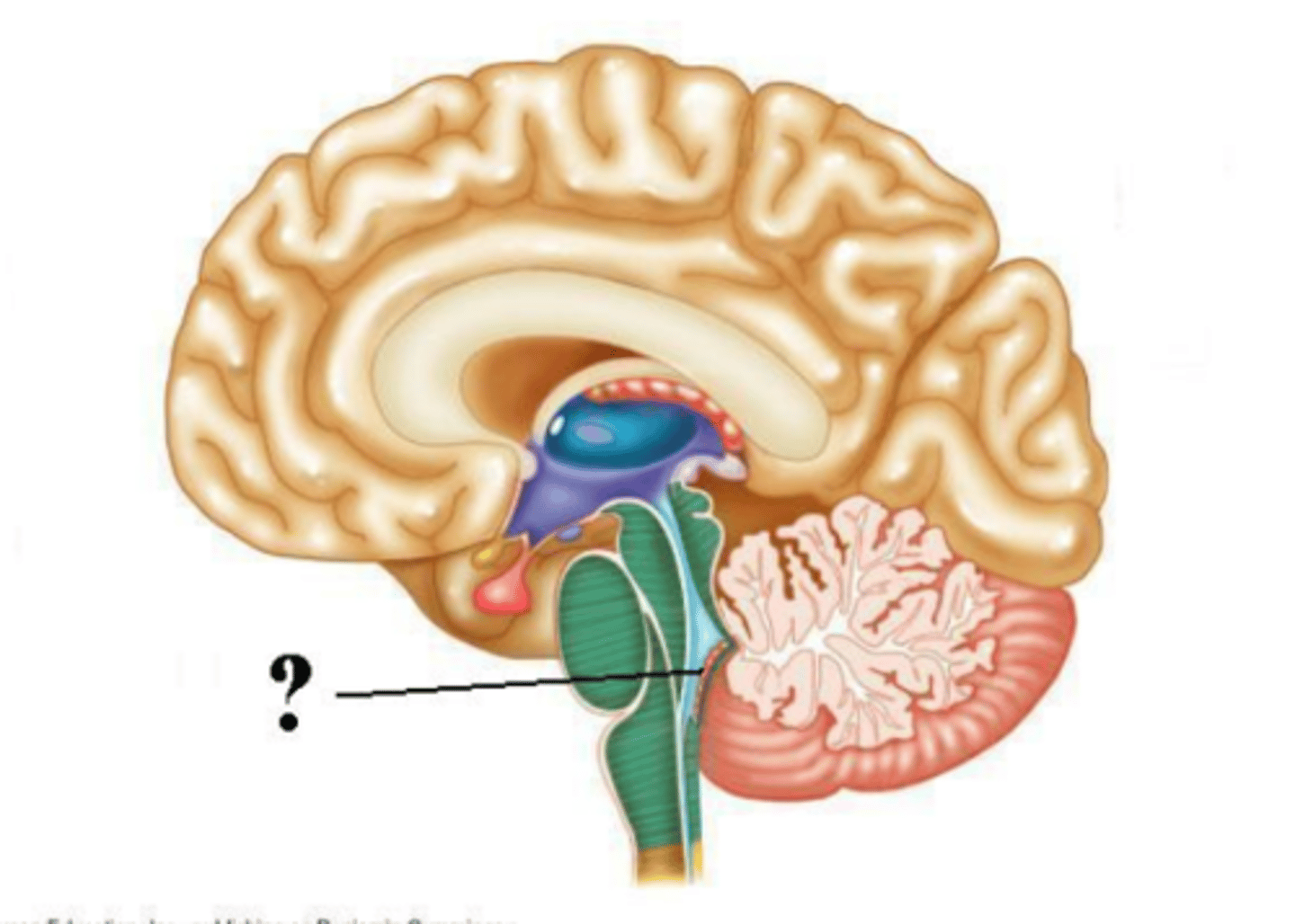
choroid plexus of the fourth ventricle
fourth ventricle
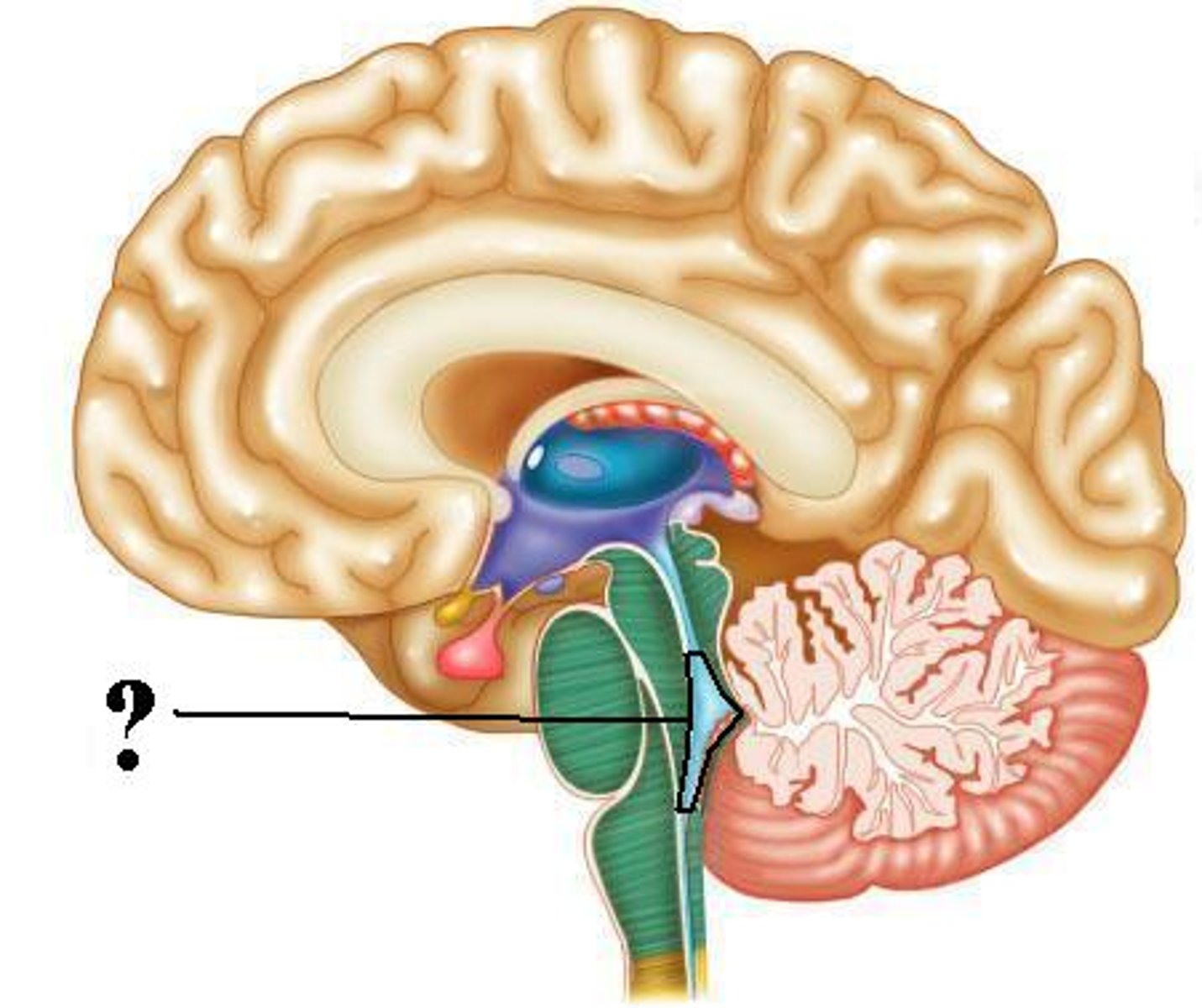
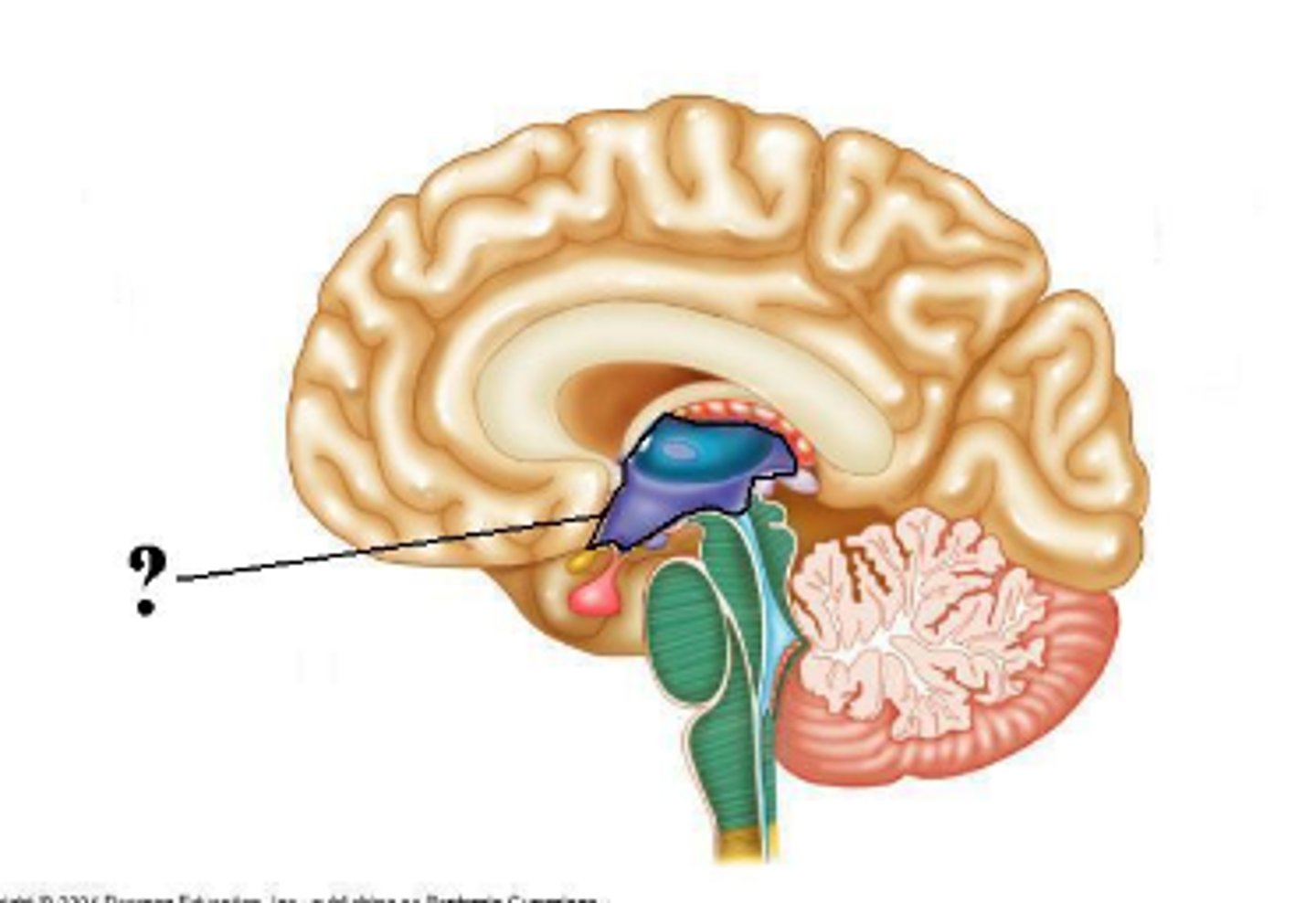
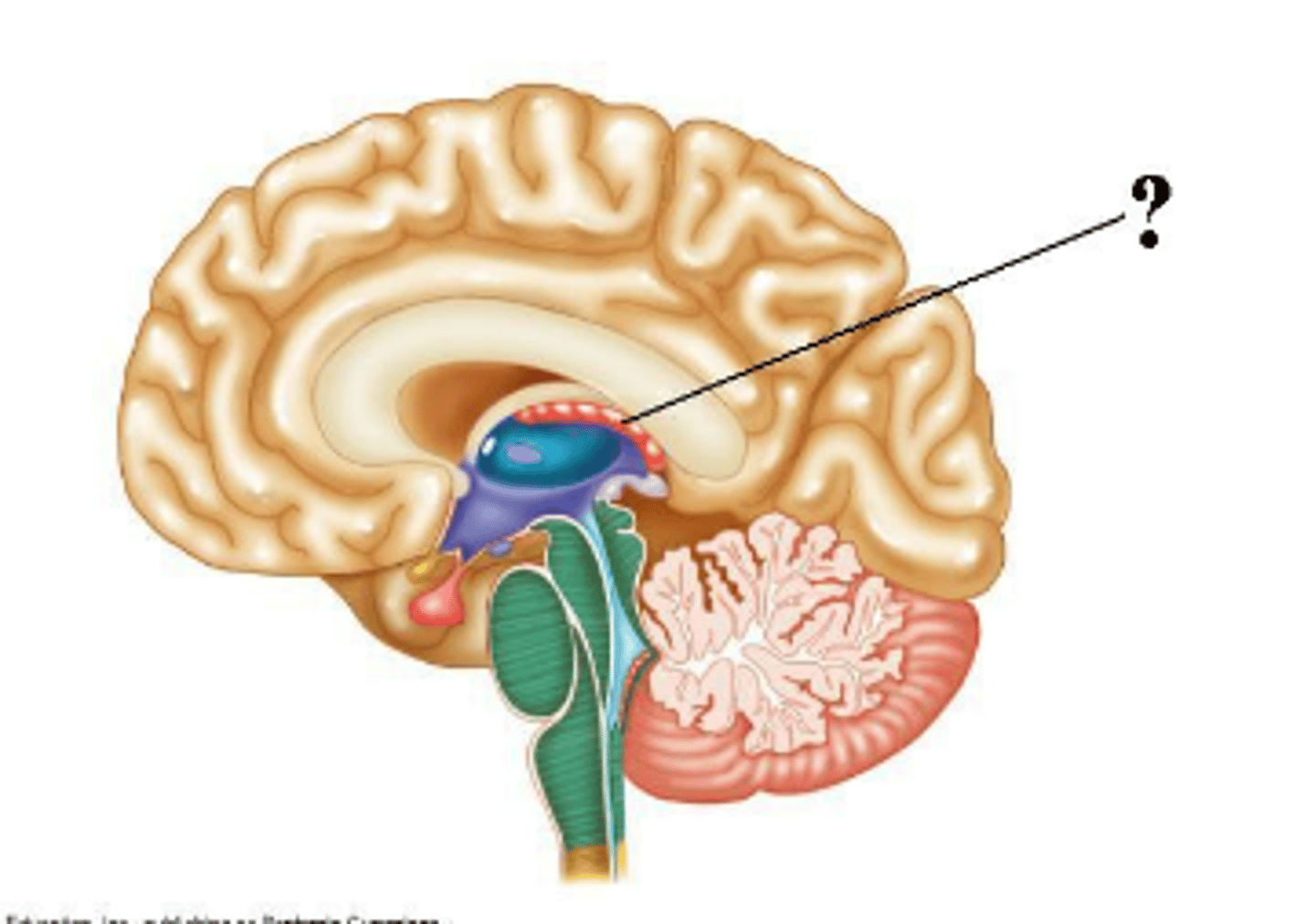
choroid plexus of the third ventricle
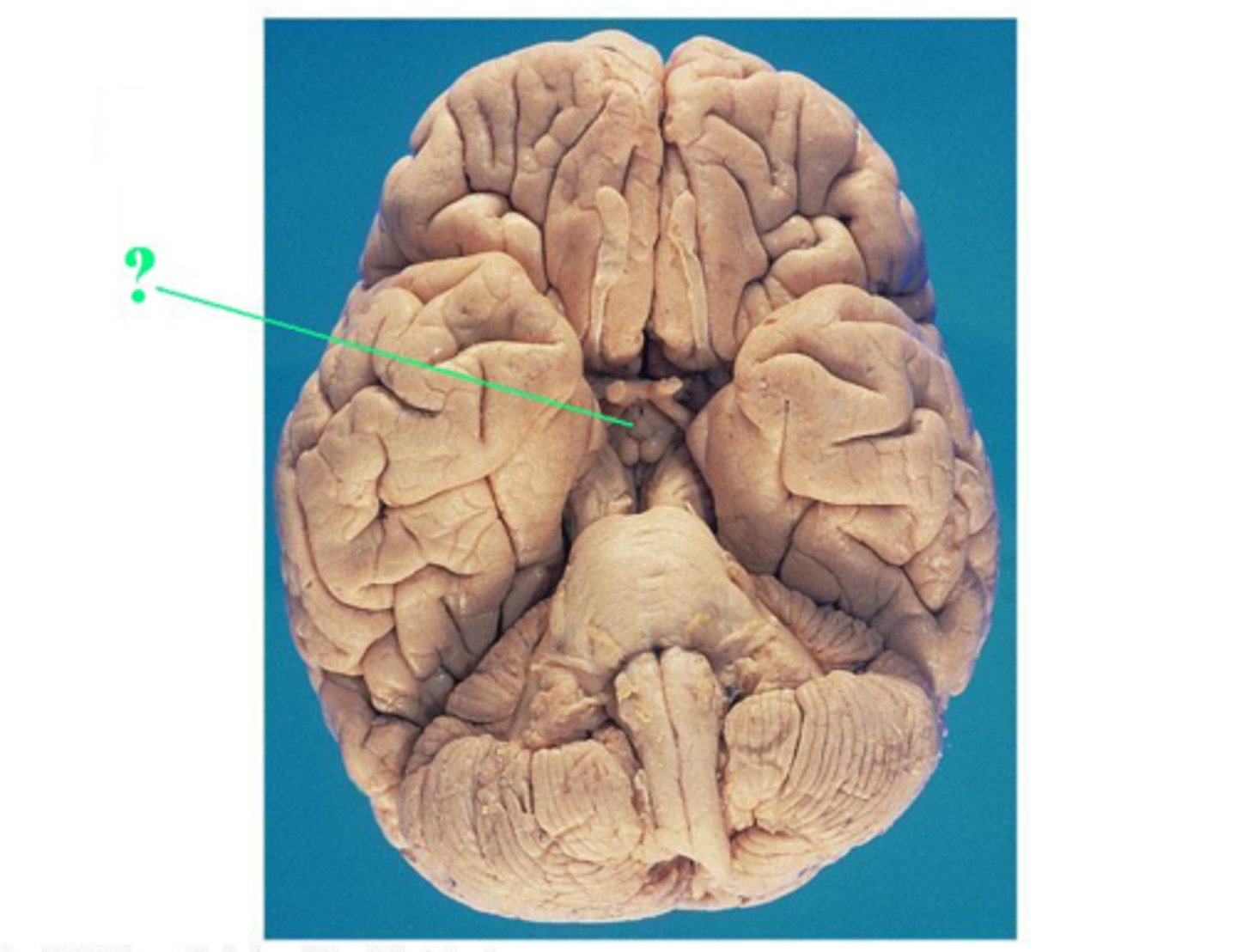
infundibulum
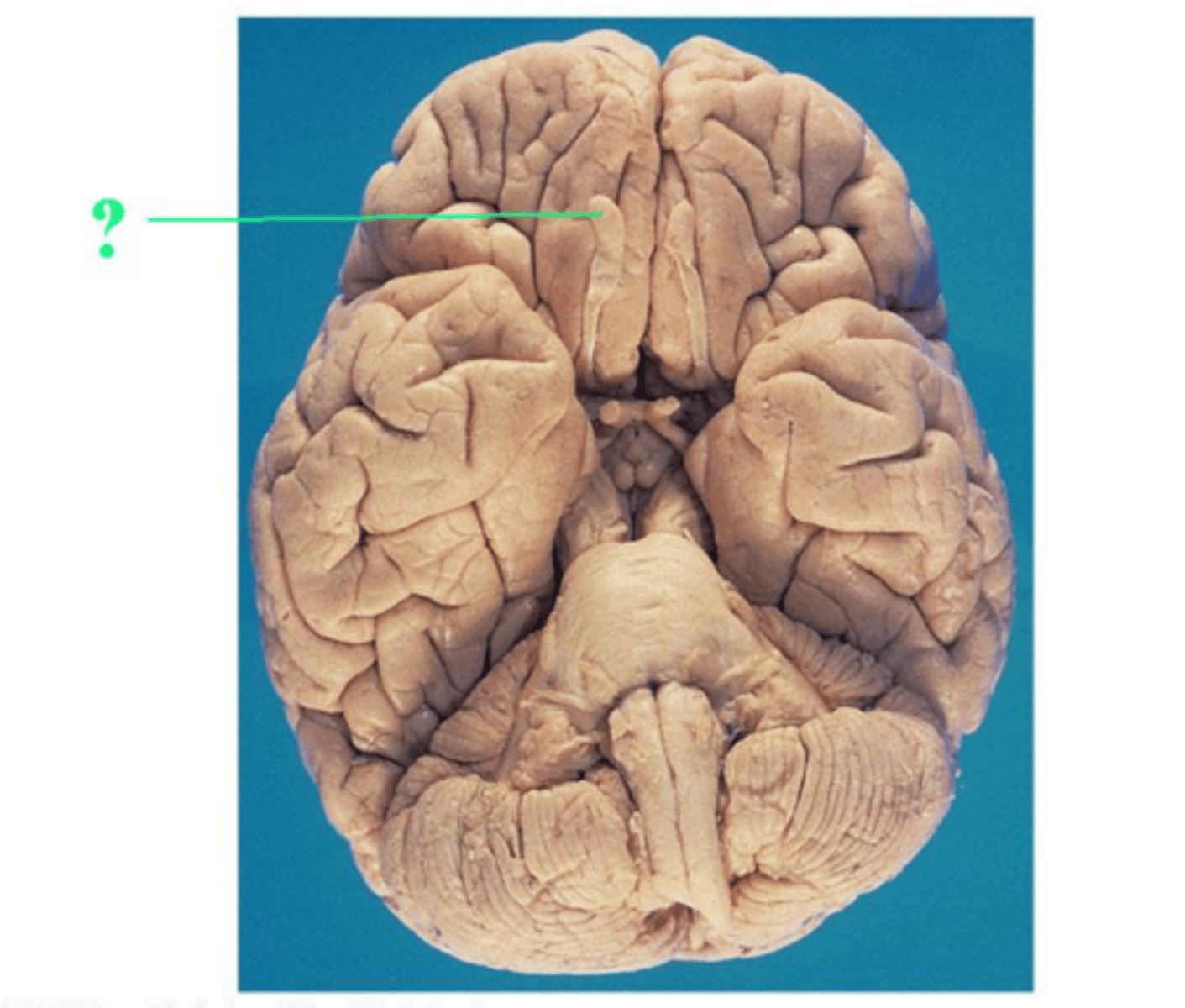
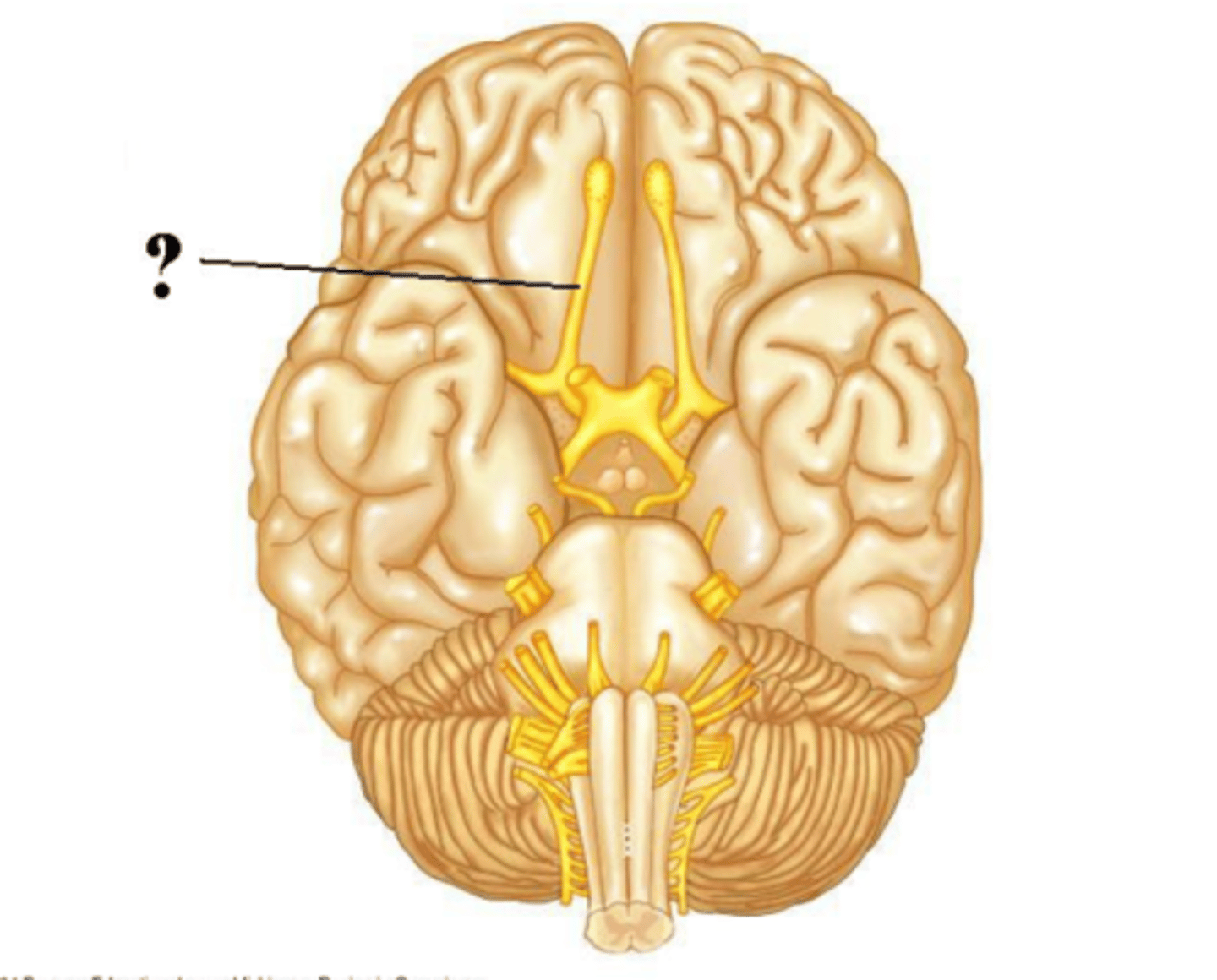
olfactory bulb
mammilary bodies
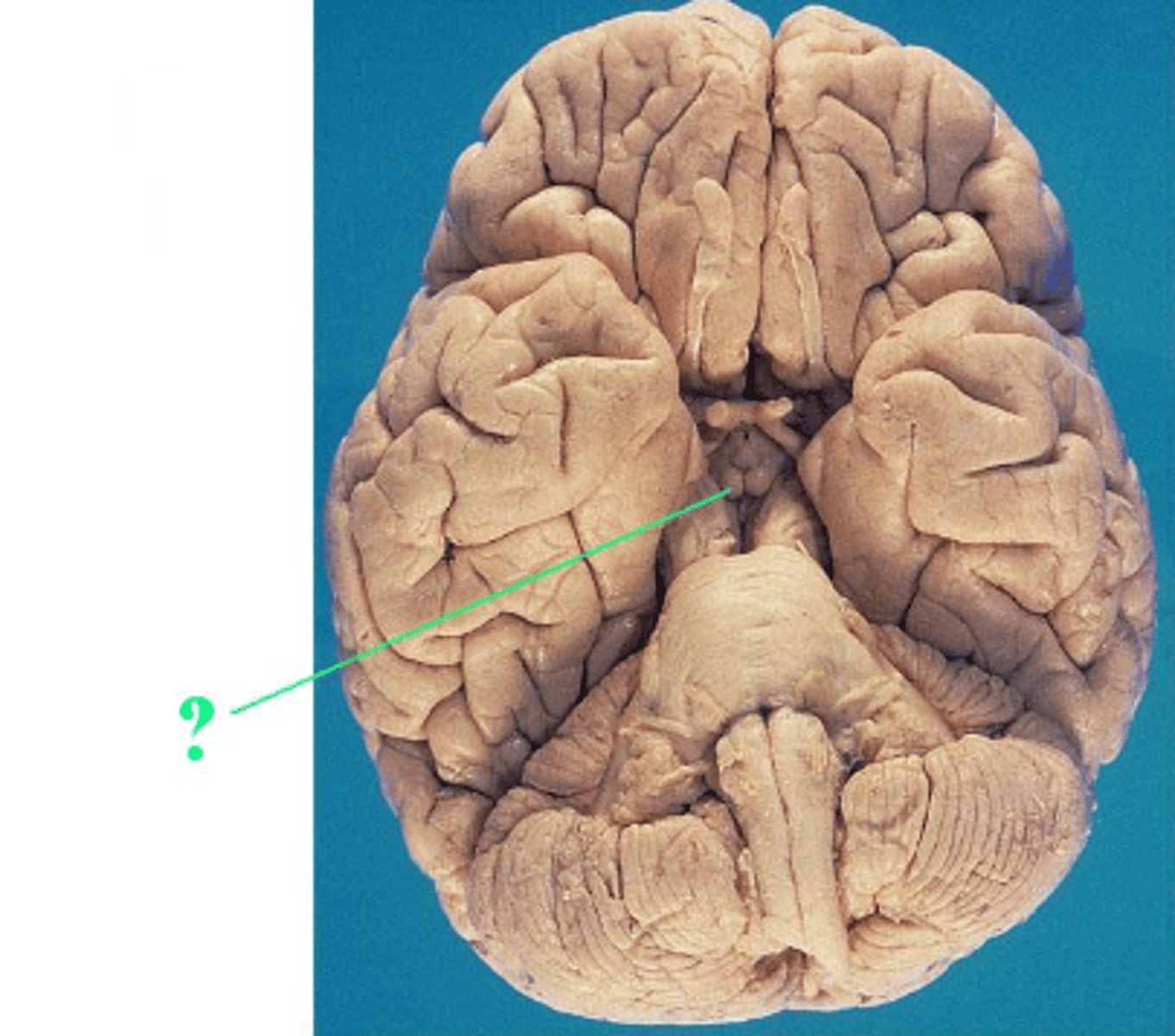
longitudinal fissure
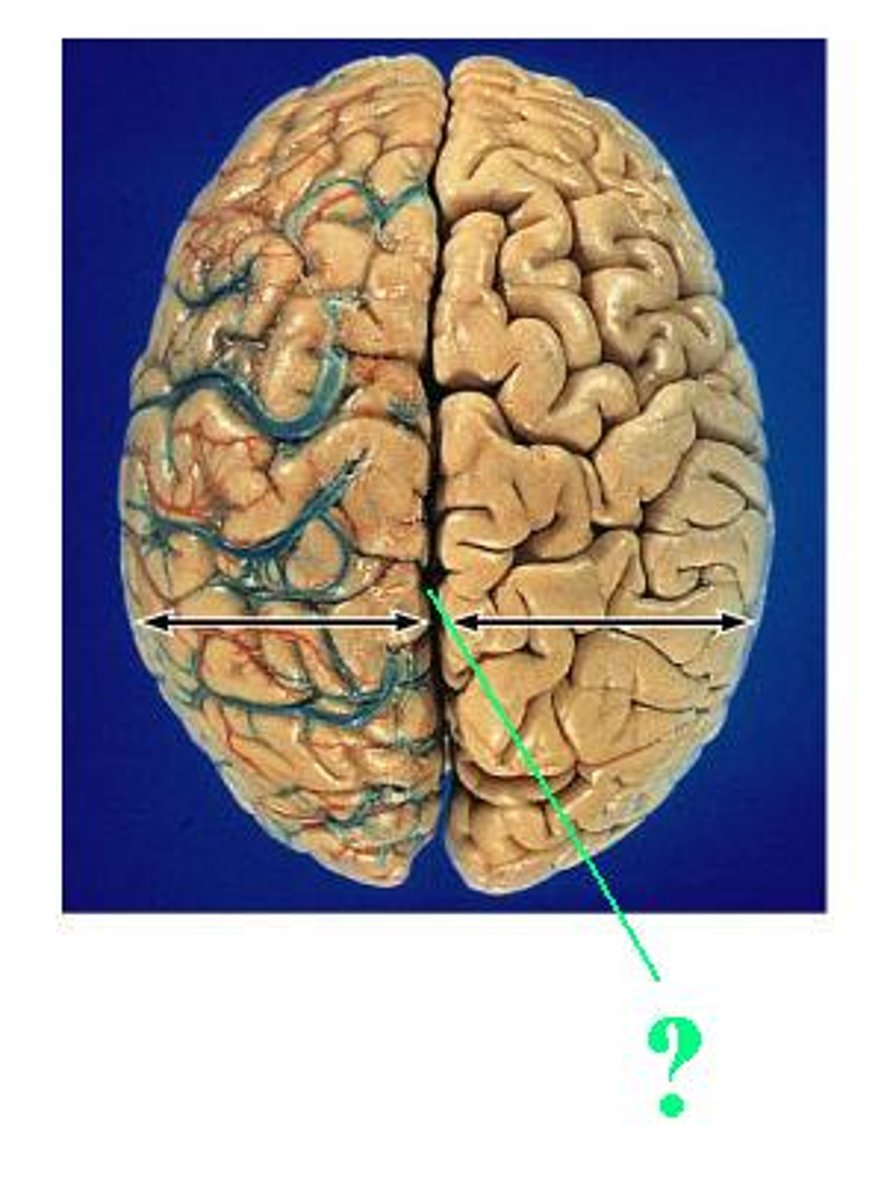
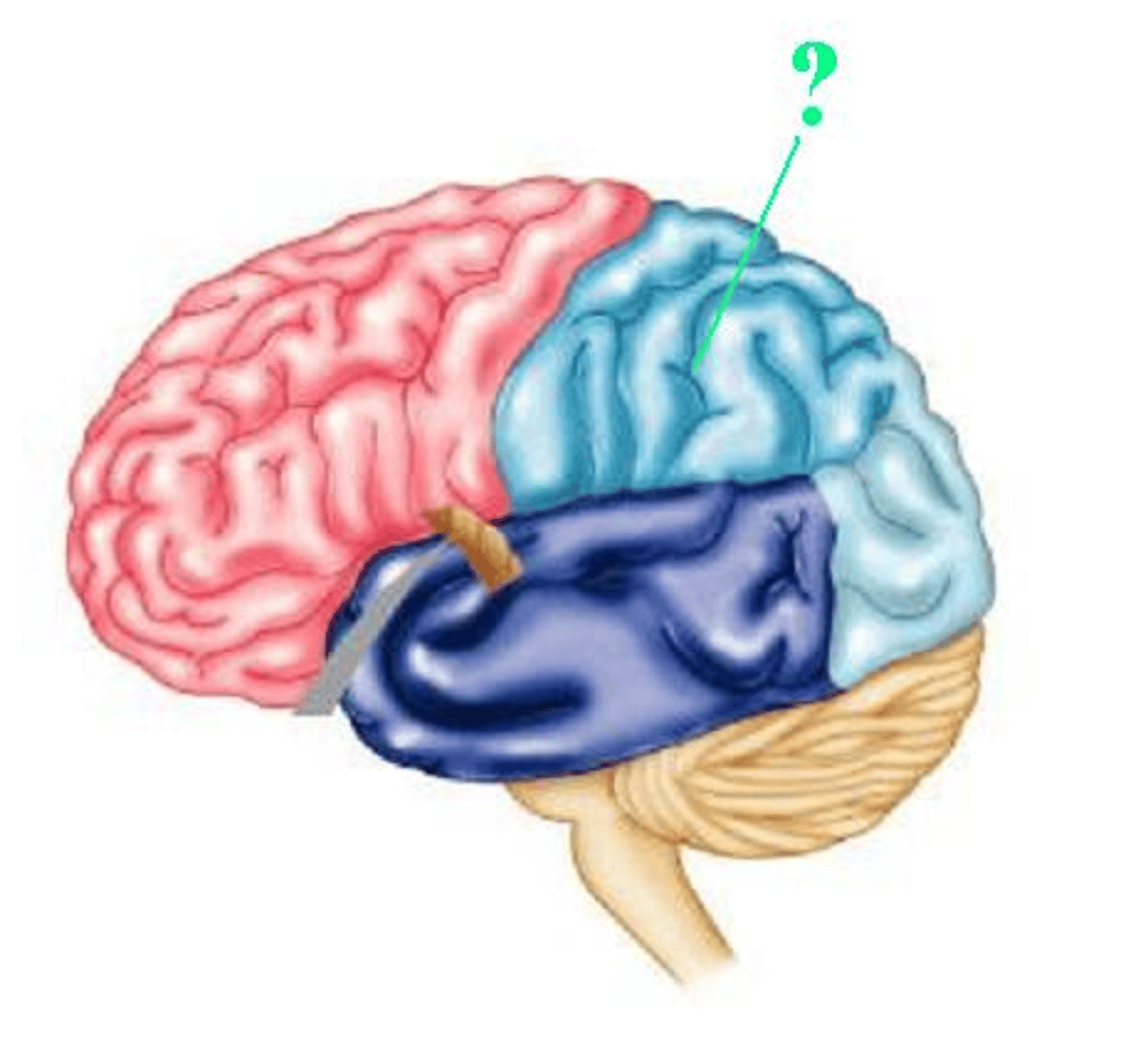
parietal lobe
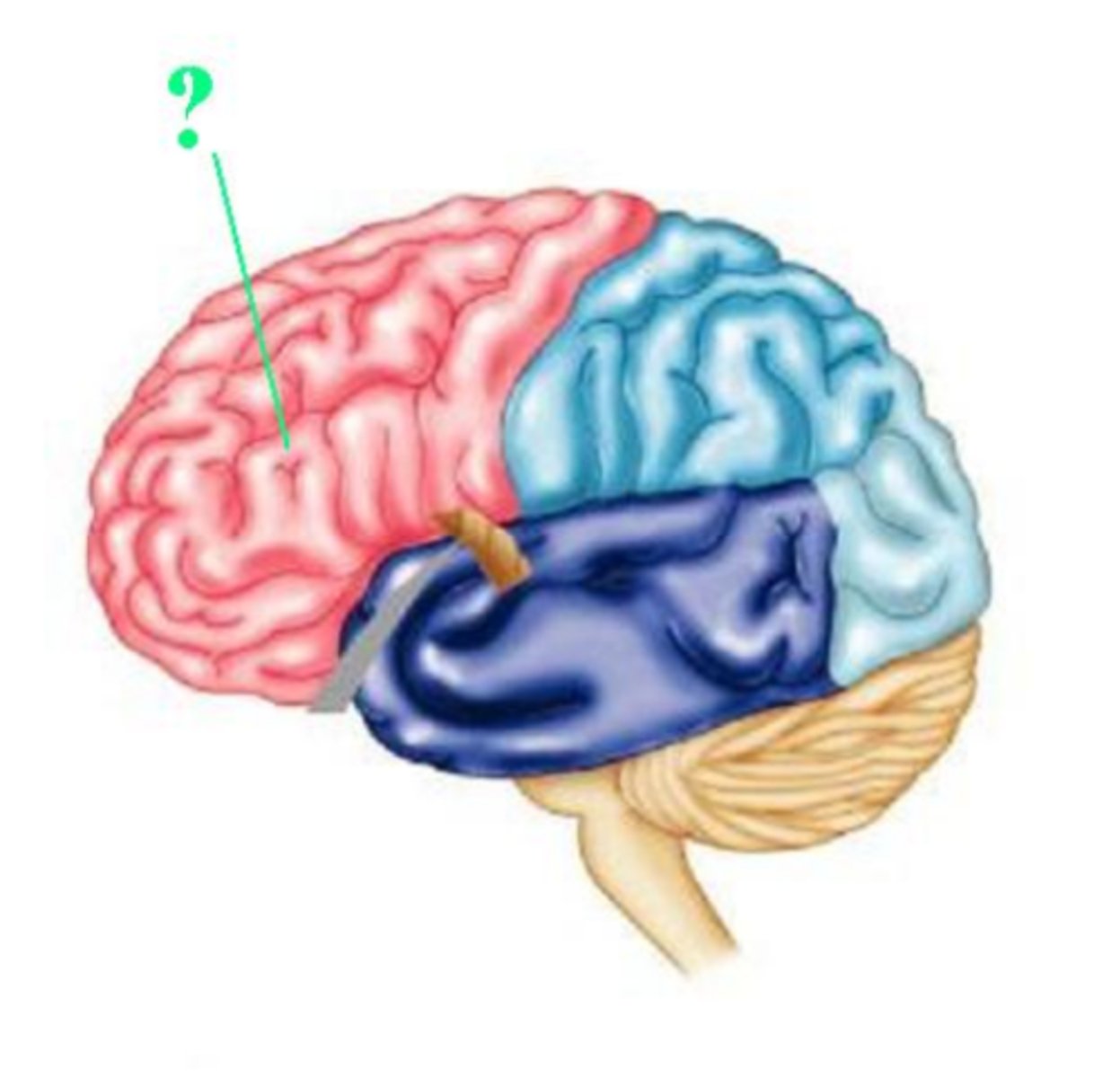
frontal lobe
lateral sulcus
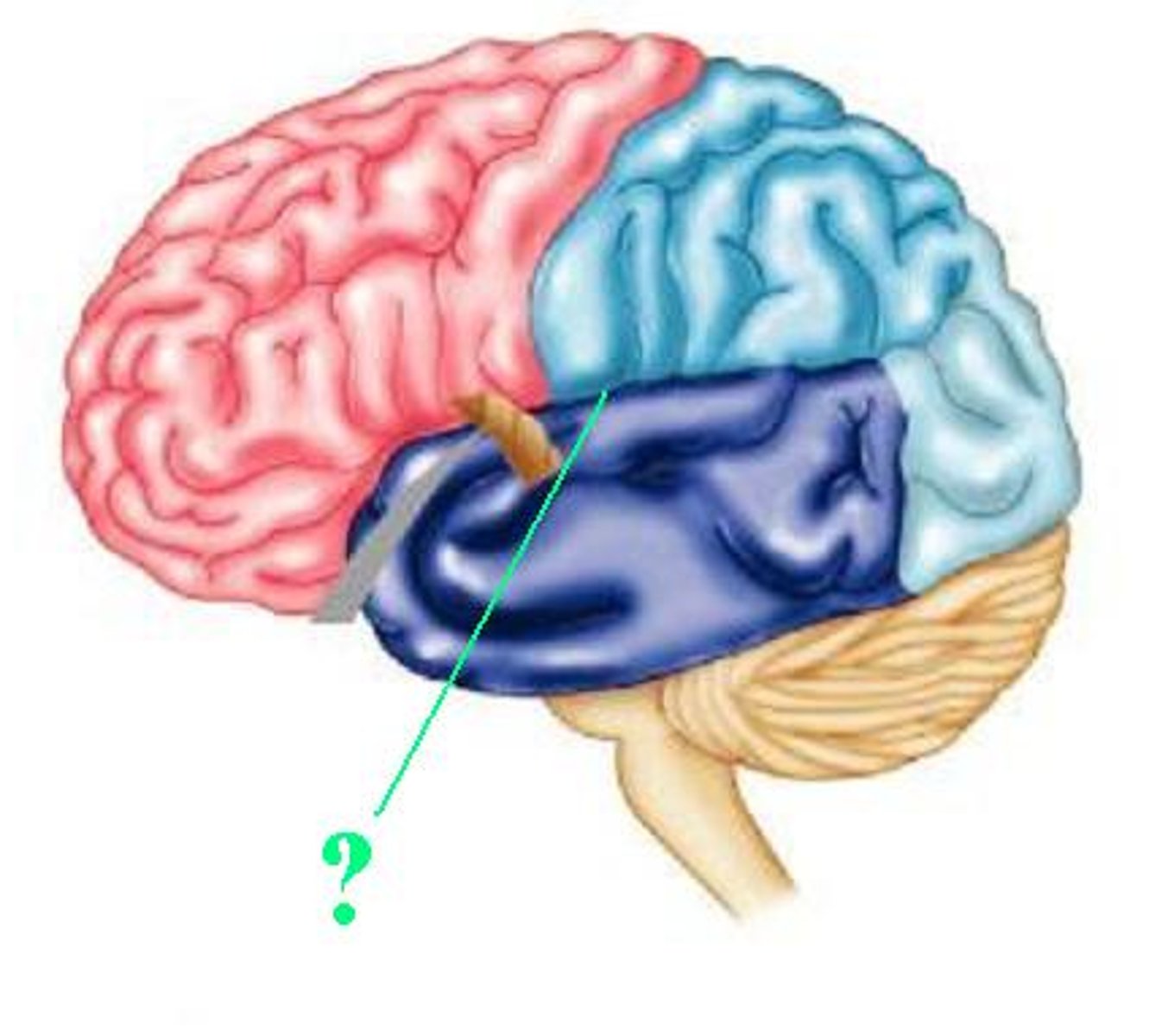
transverse cerebral fissure
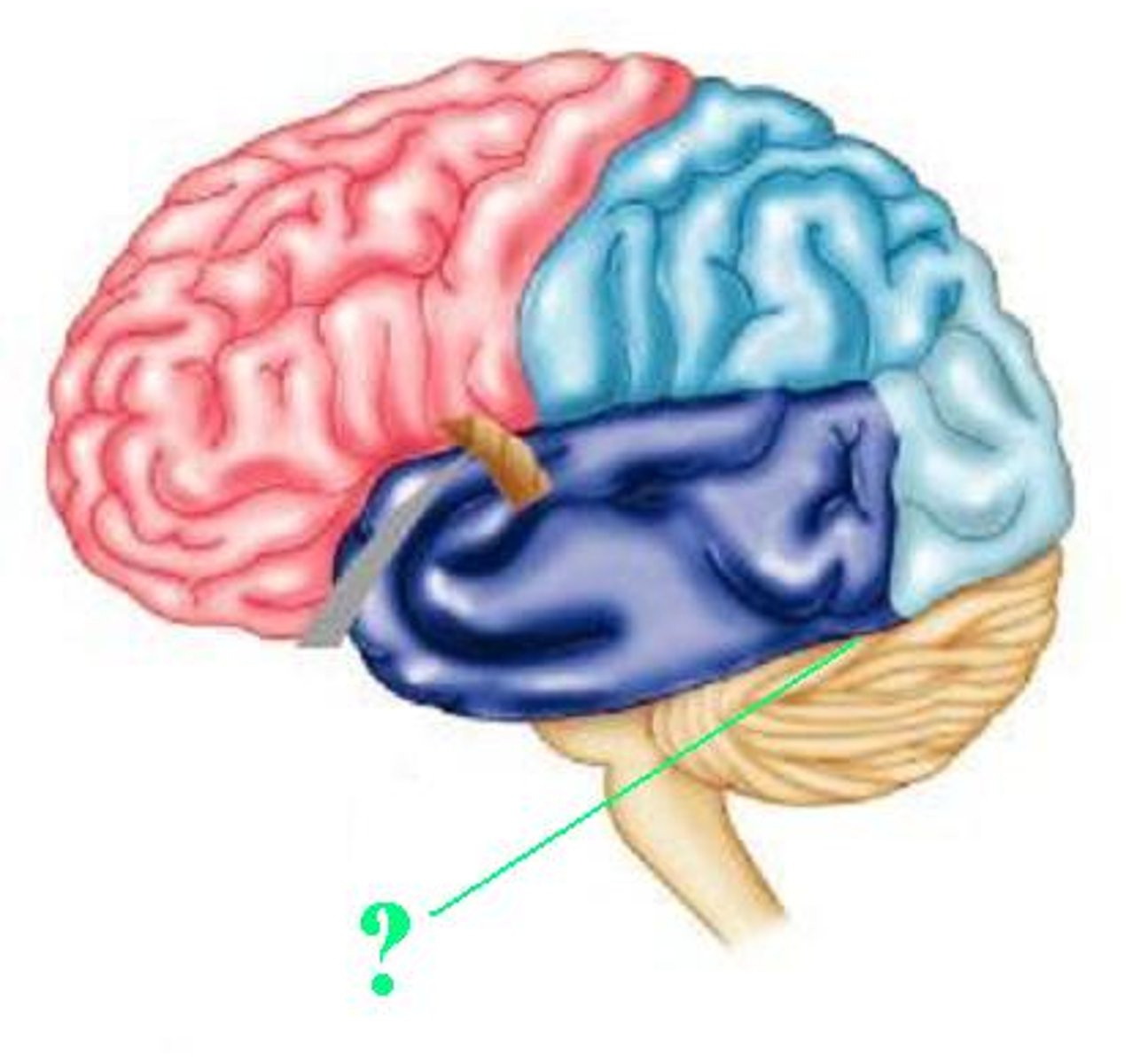
cerebellum
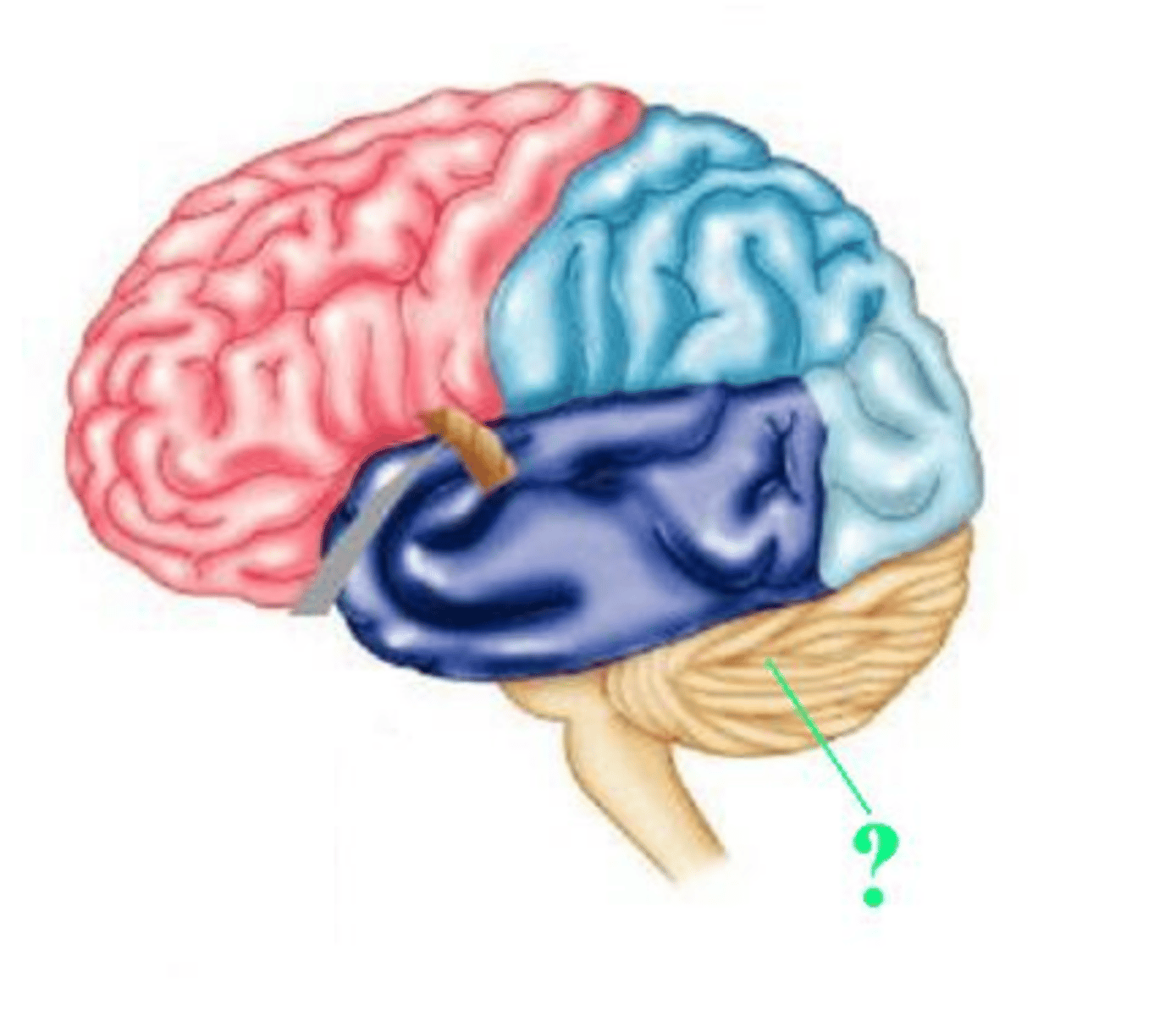
occipital lobe
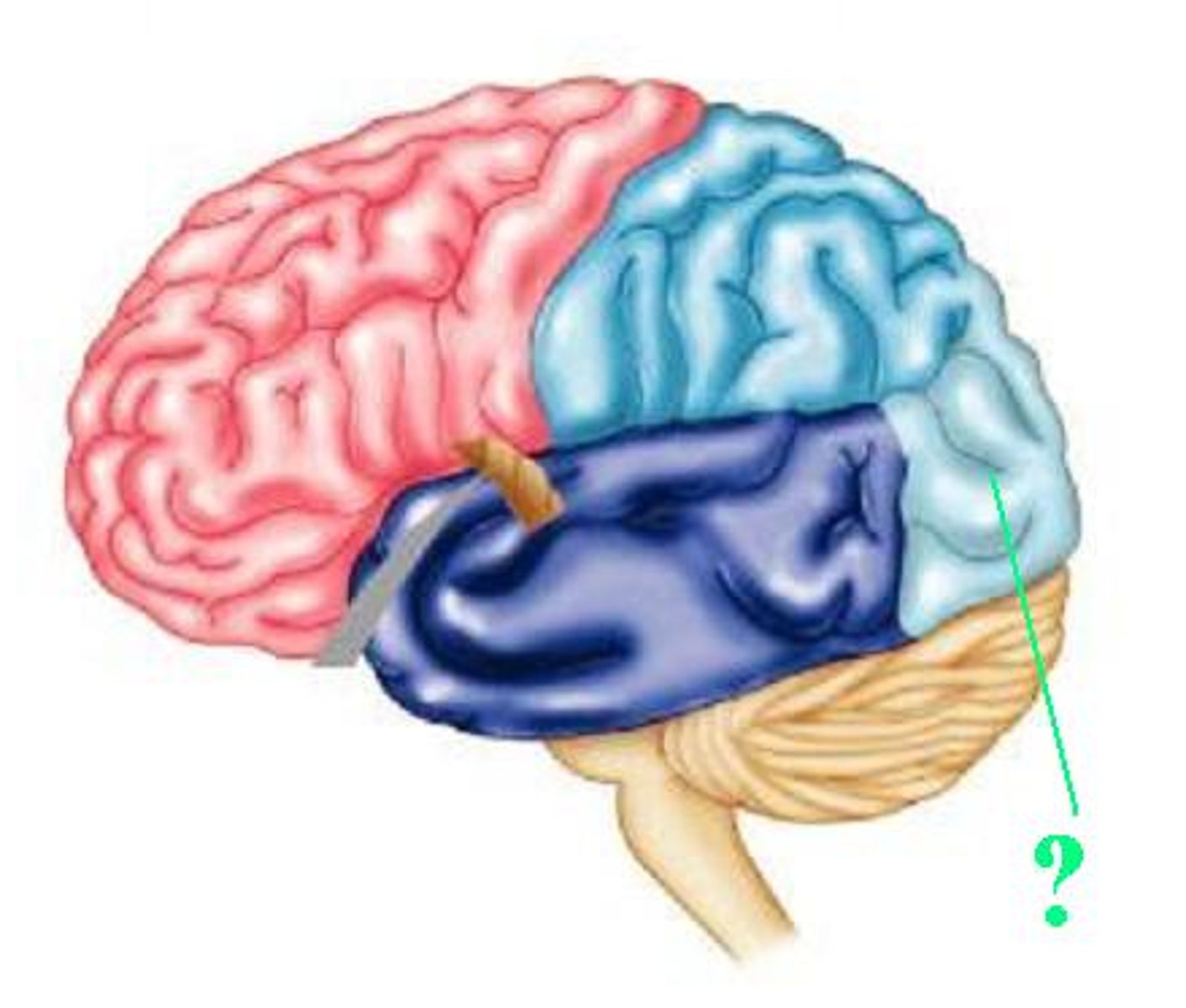
precentral gyrus
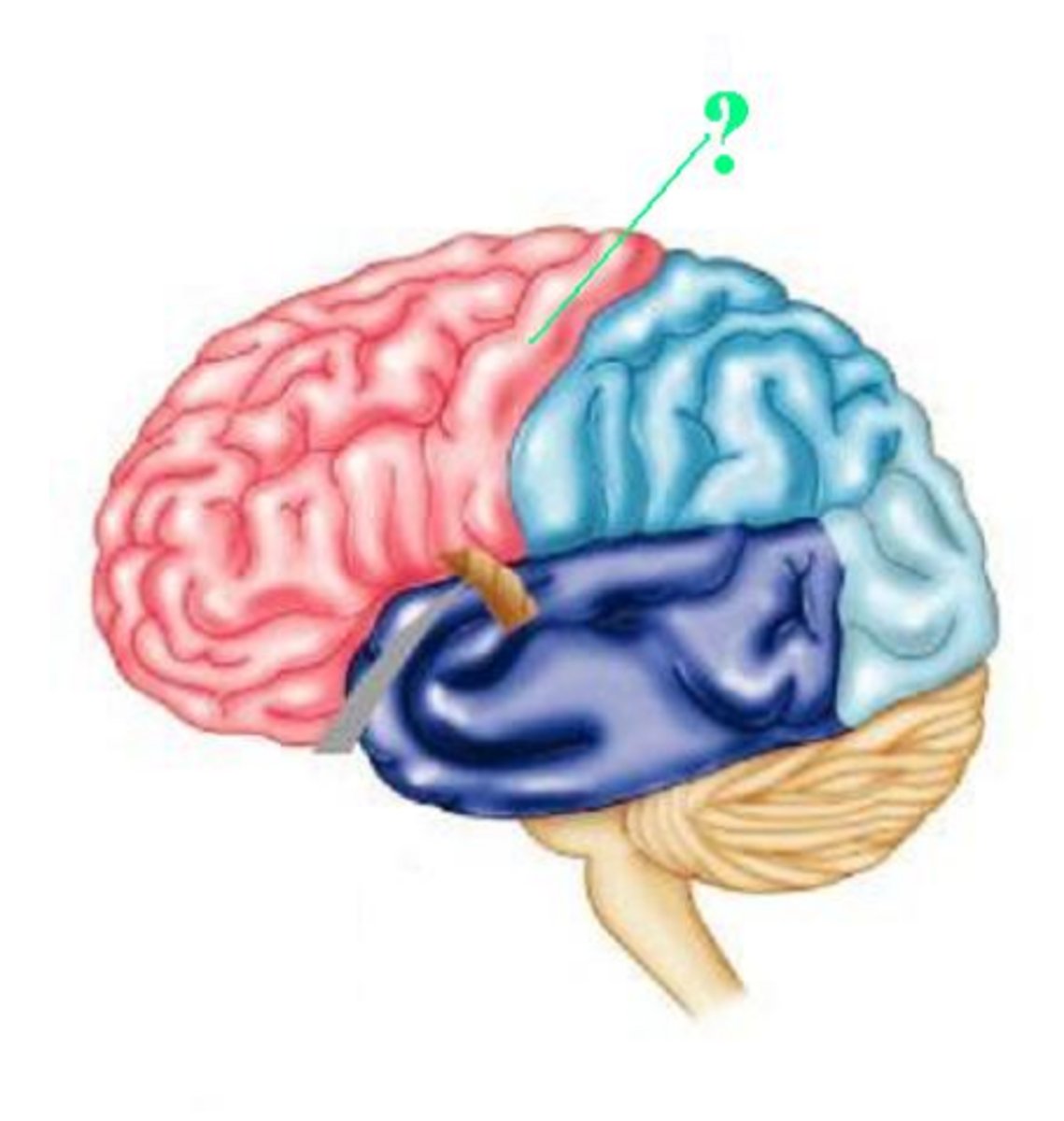
Lateral sulcus
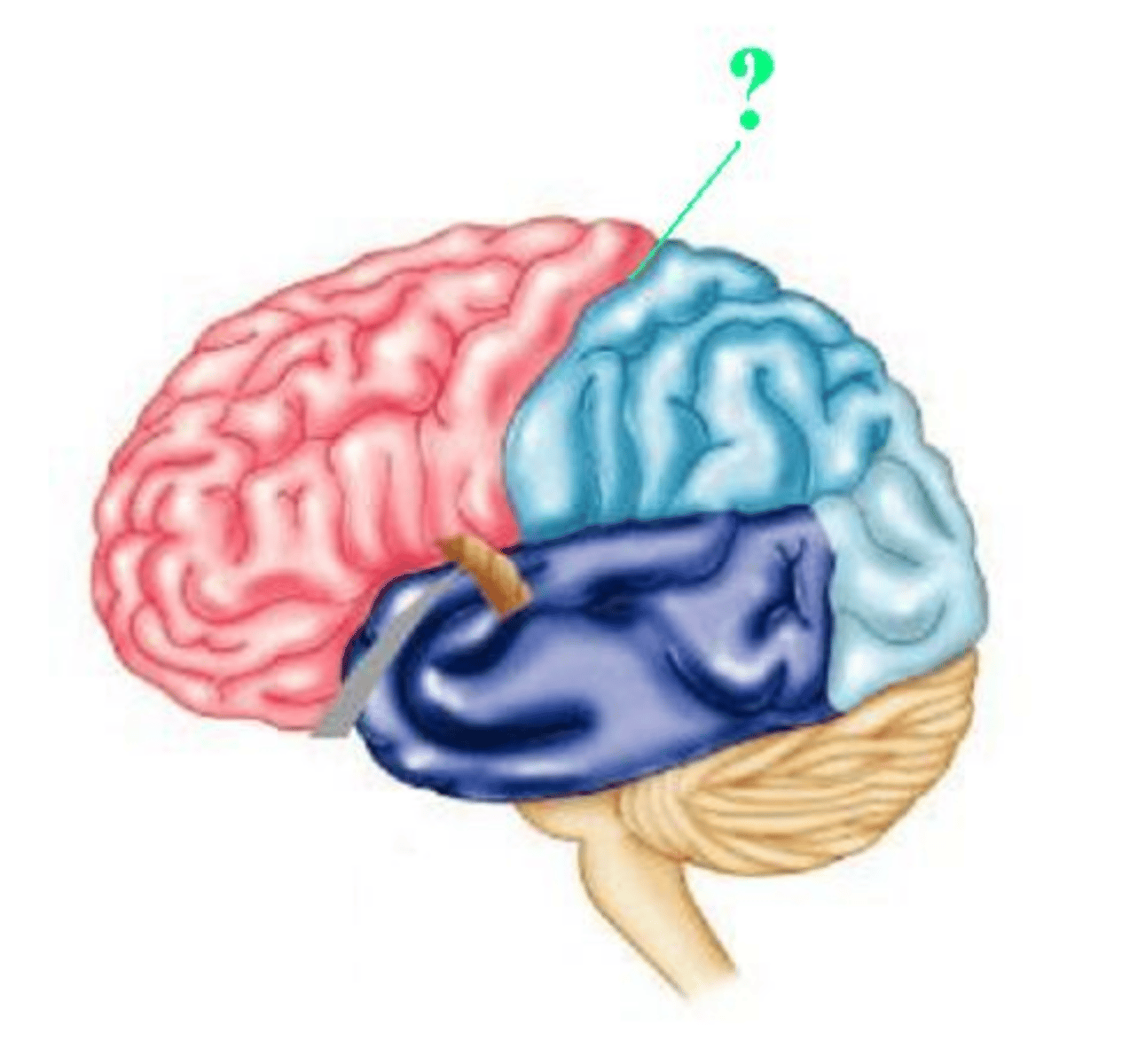
central sulcus
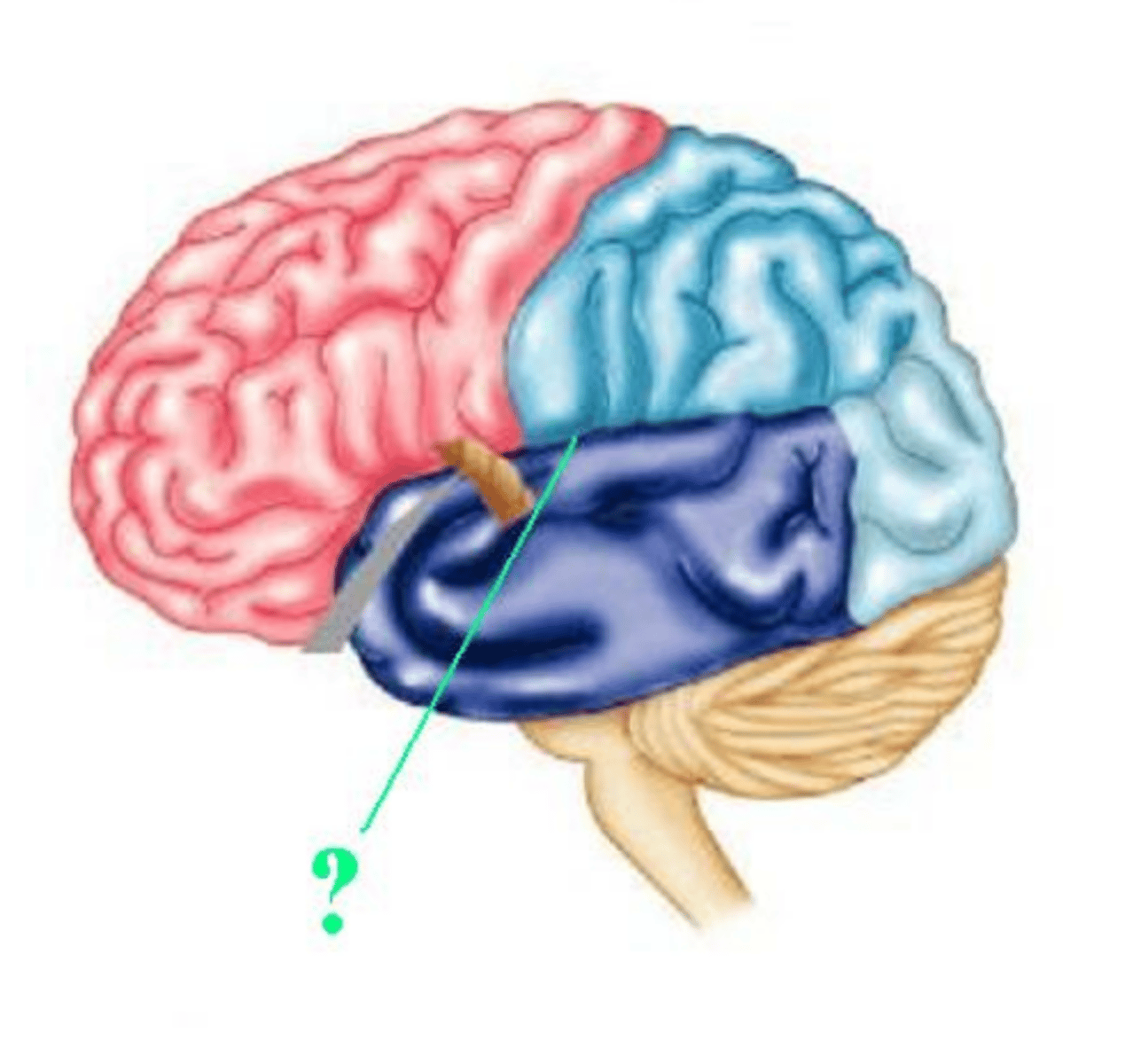
pons
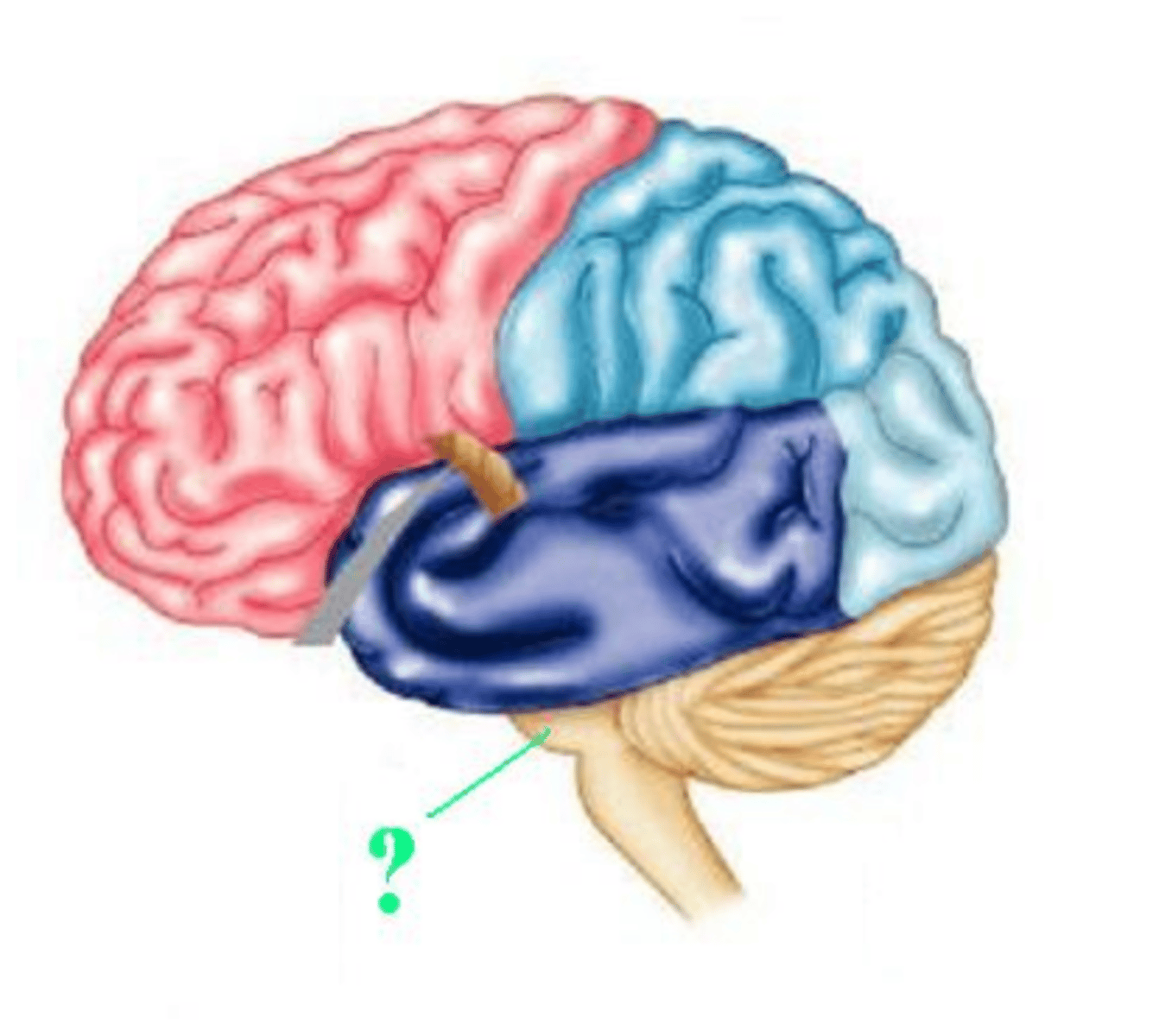
temporal lobe
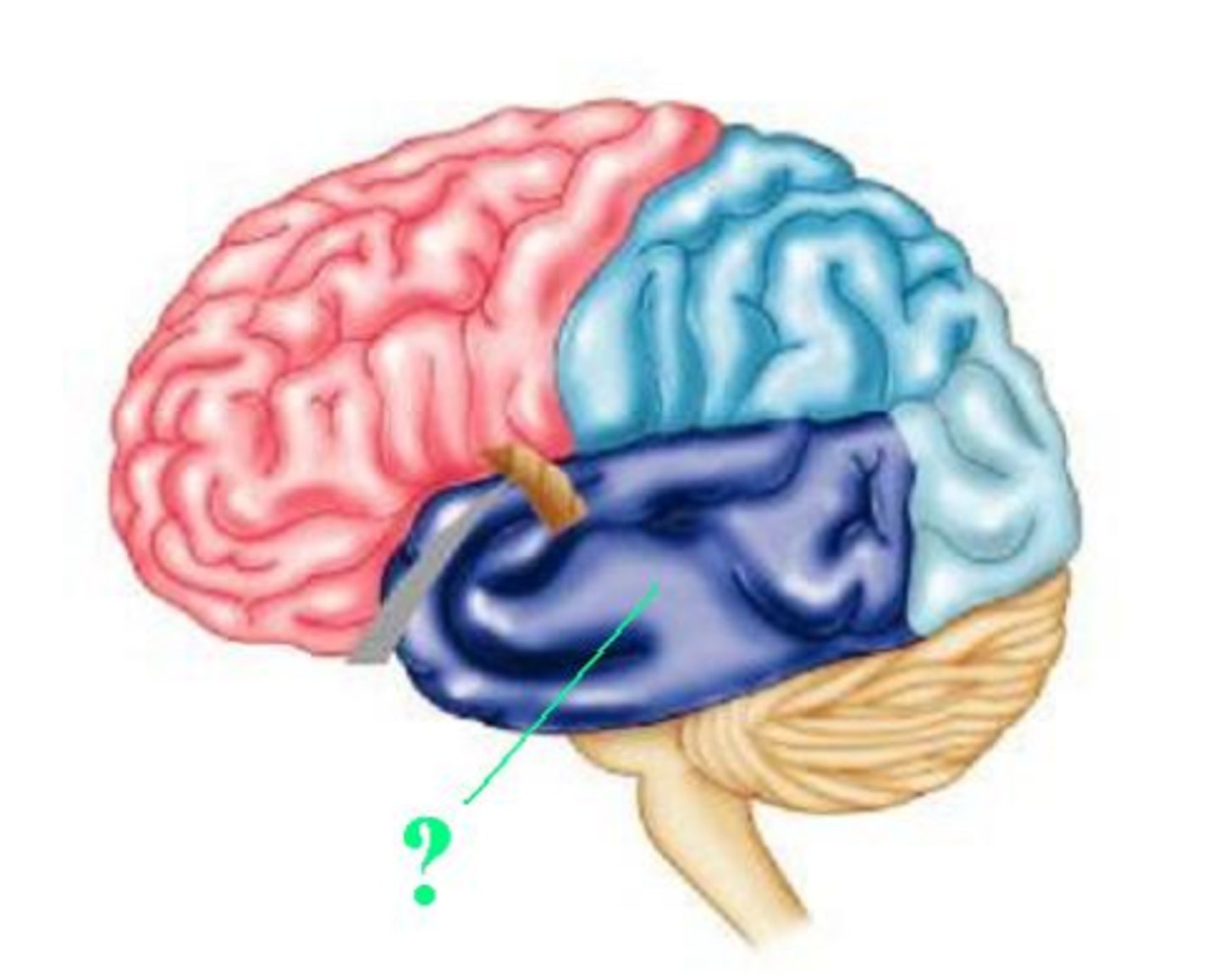
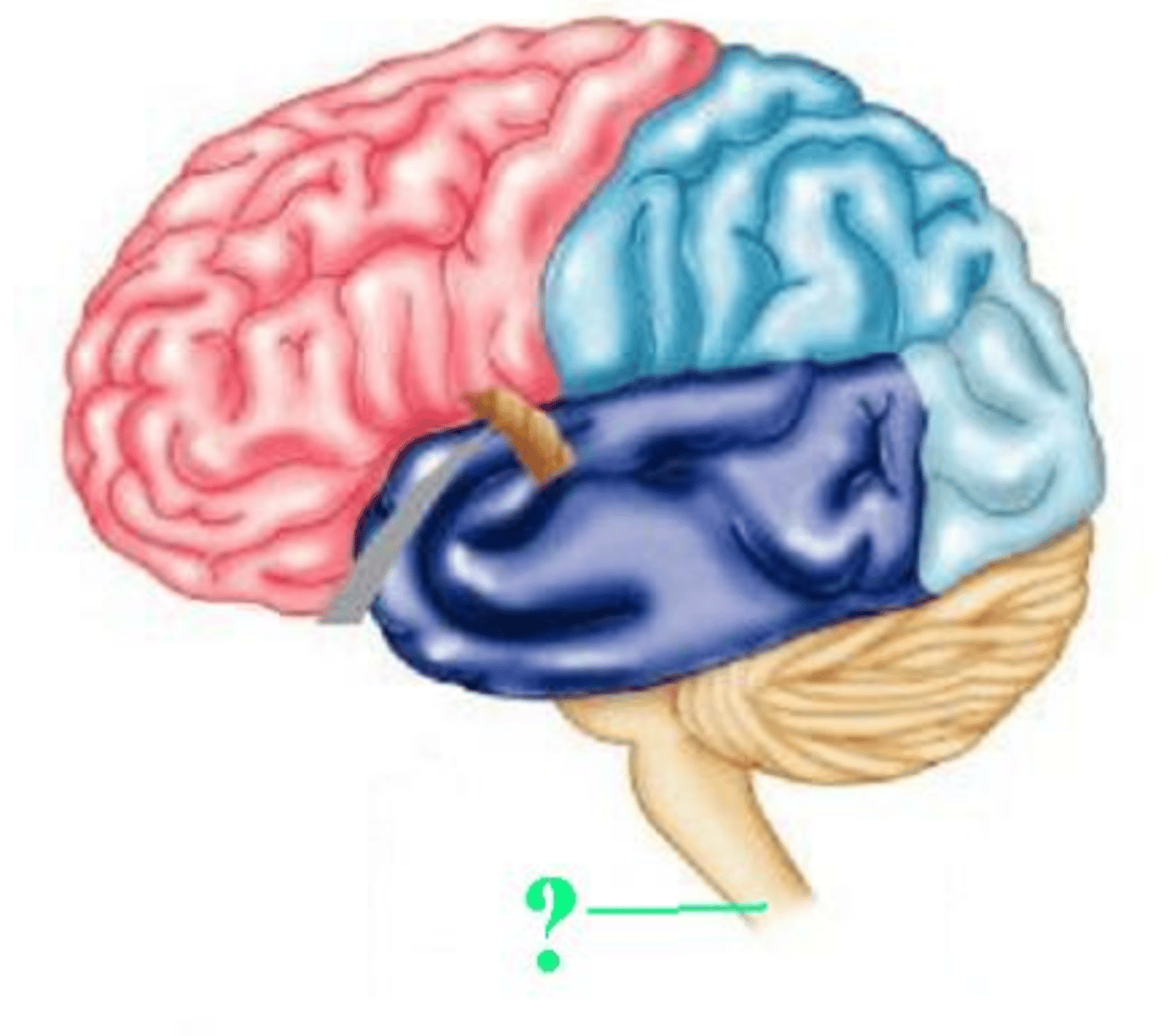
spinal cord
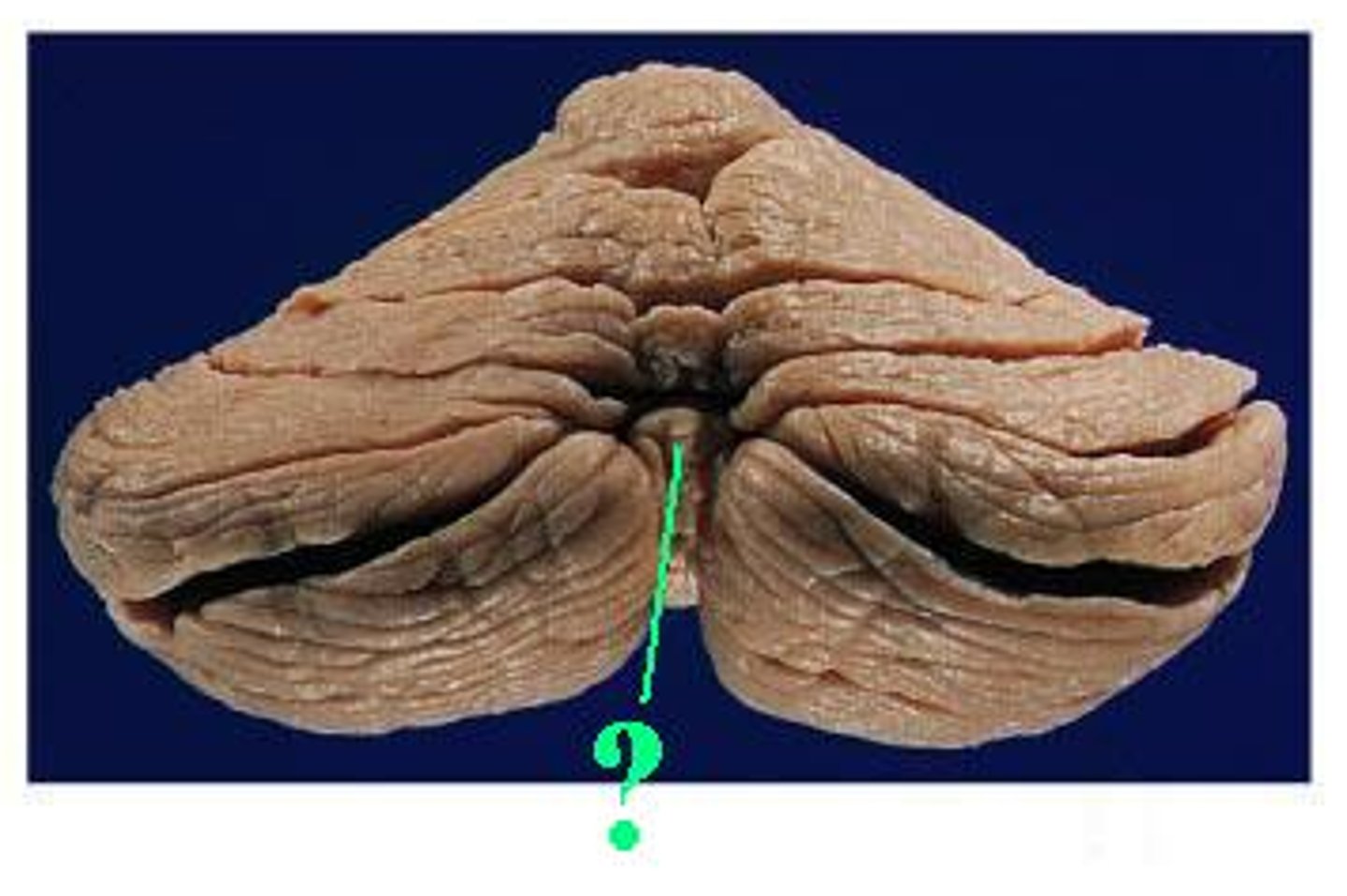
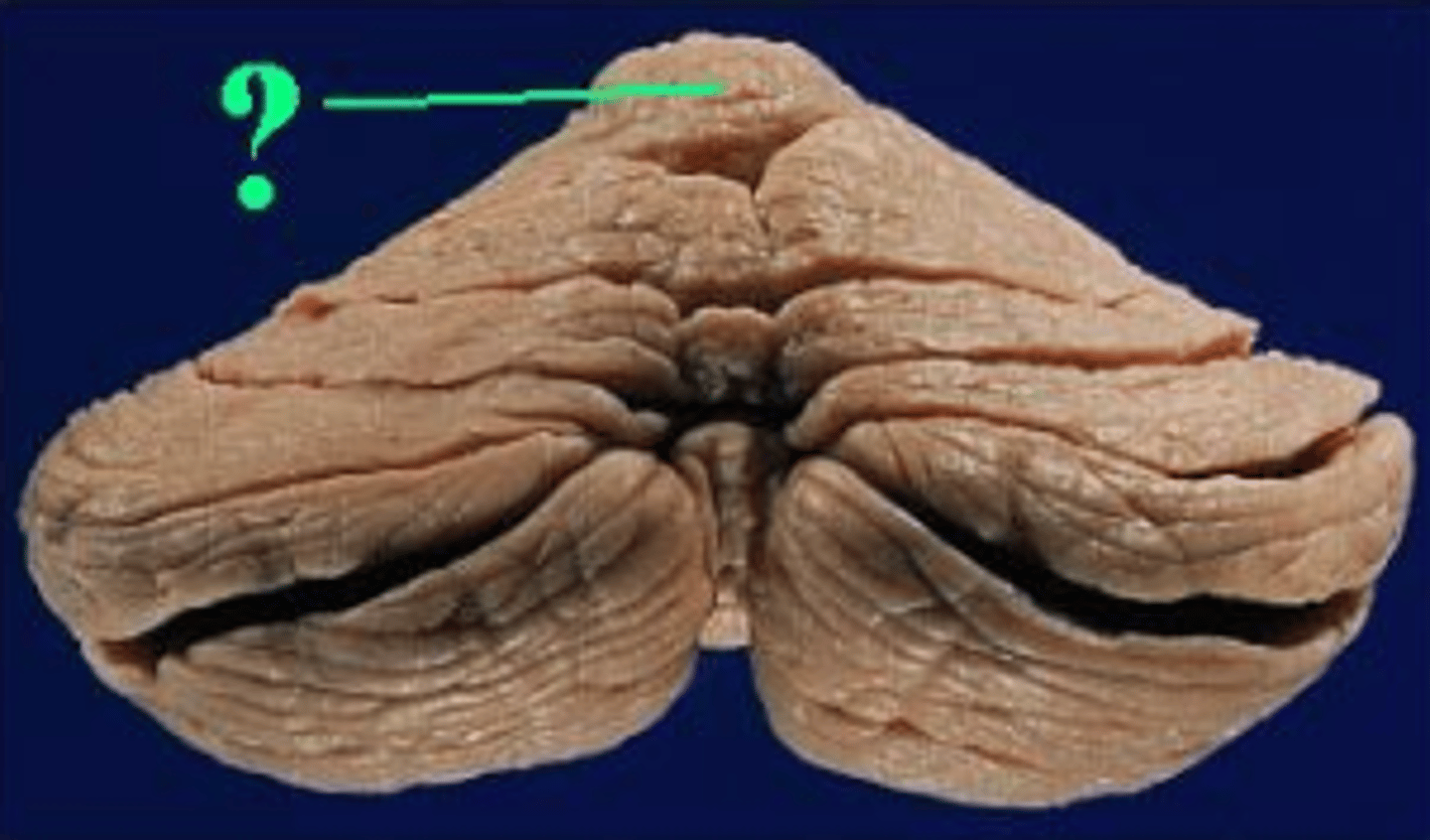
vermis
anterior lobe
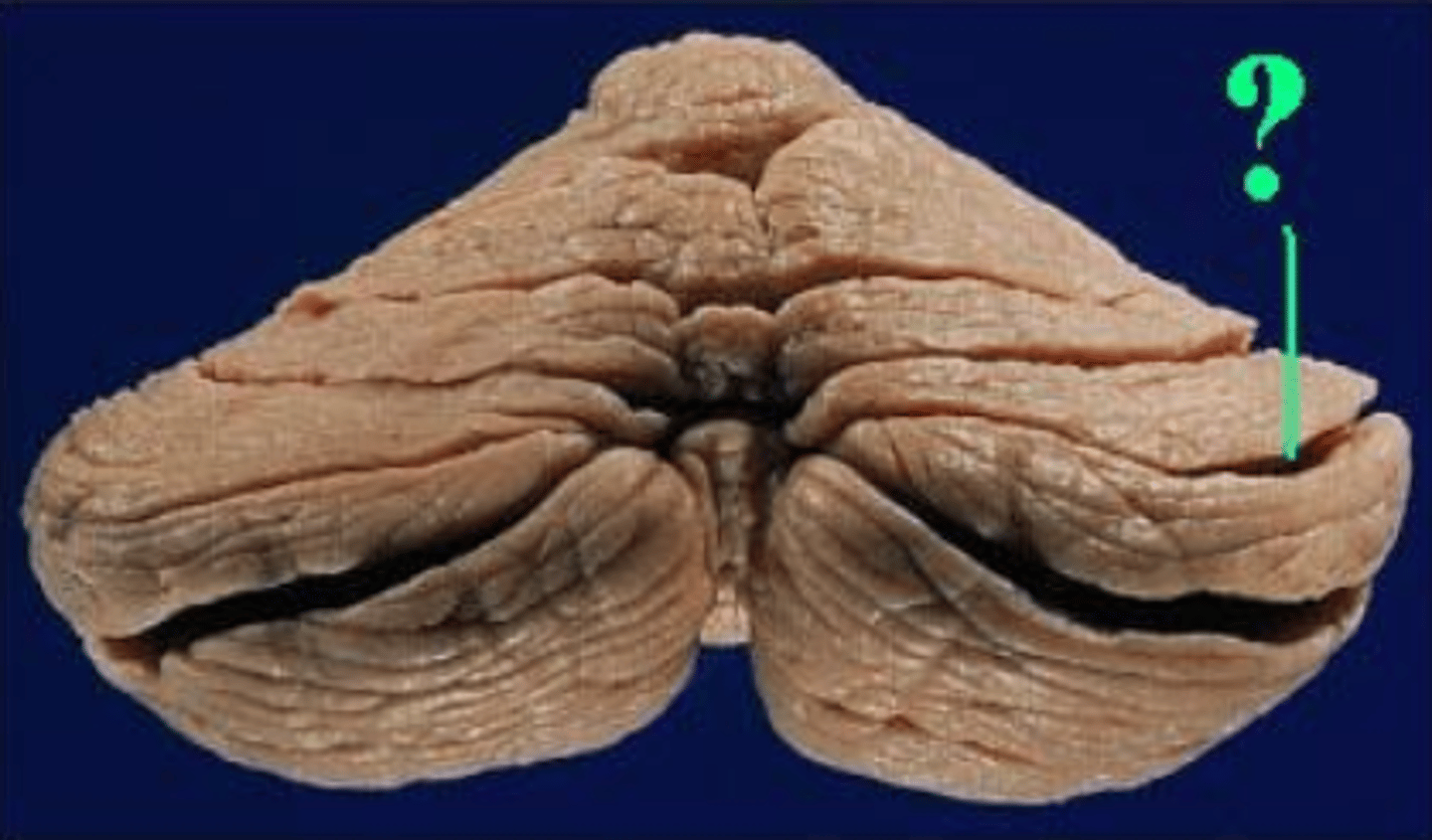
horizontal fissure
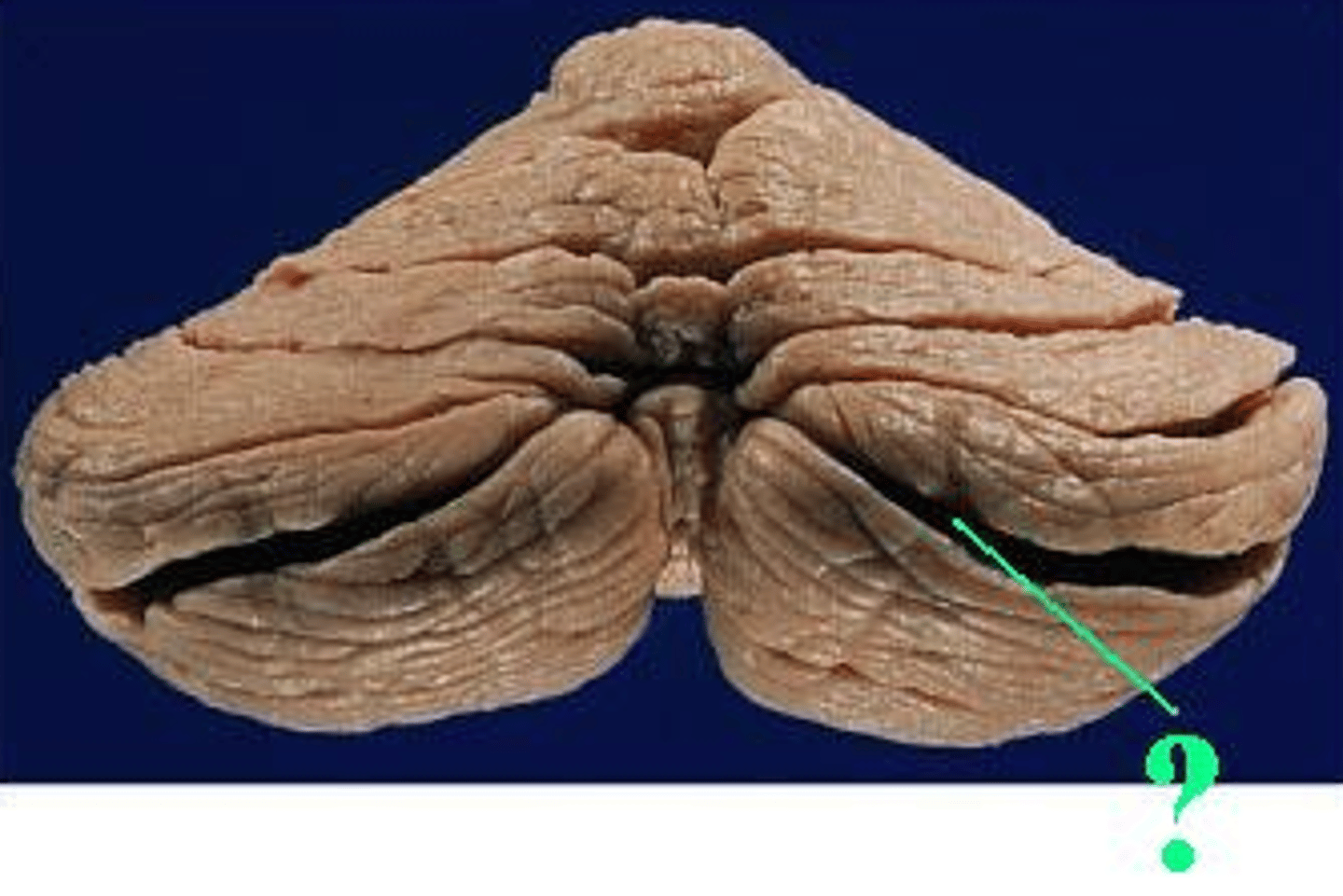
posterior lobe
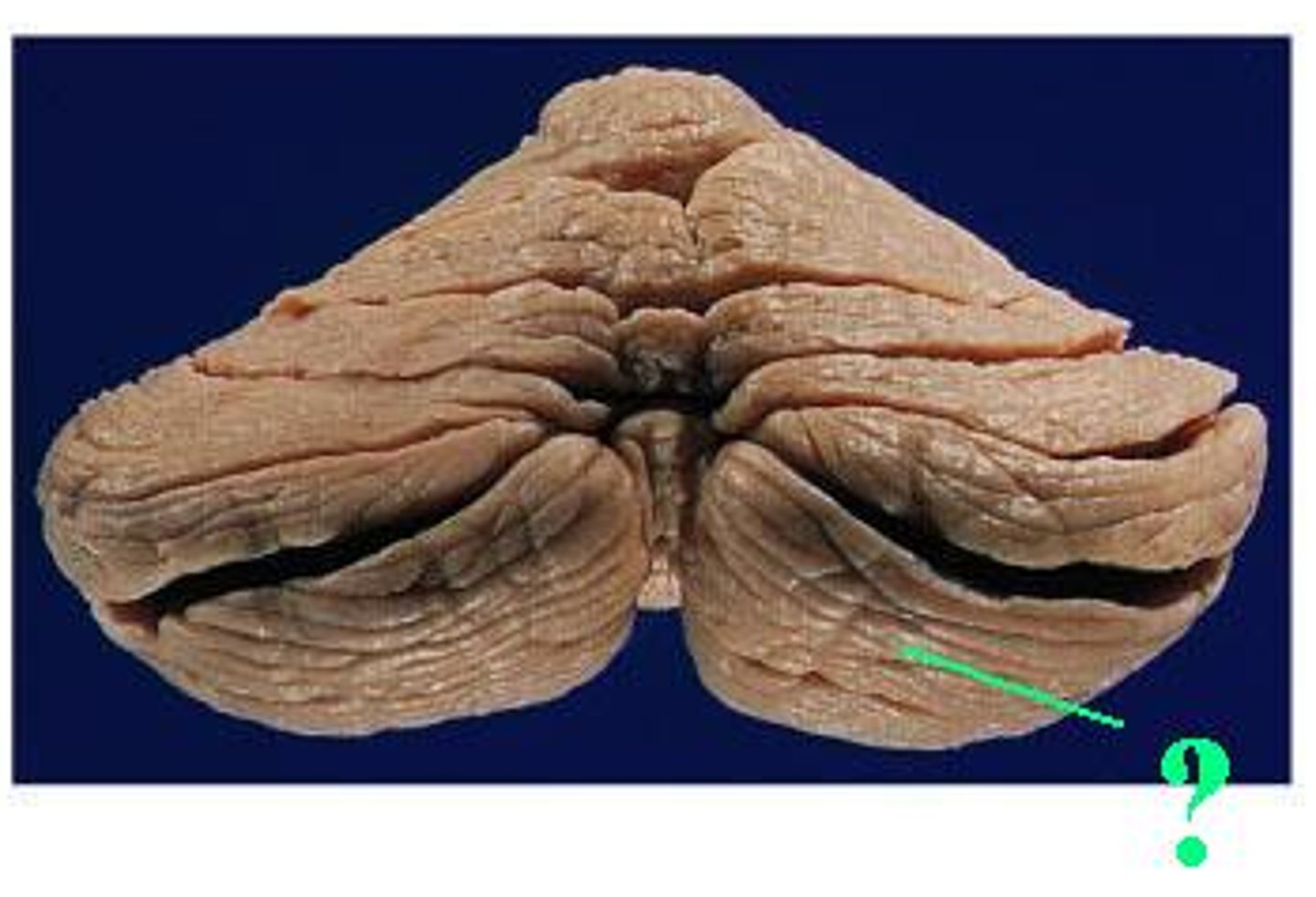
primary fissure
deep cerebellar nucleus
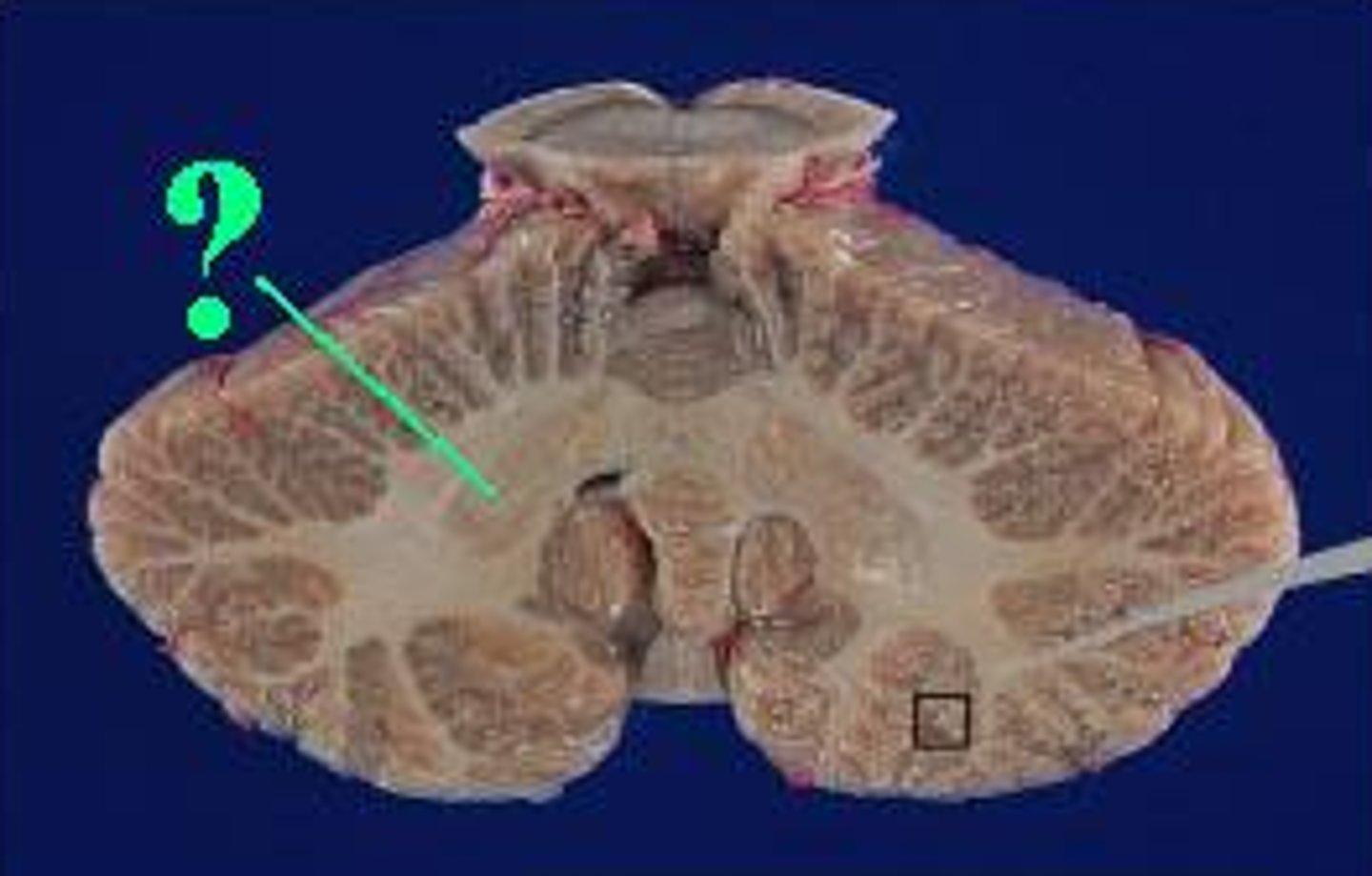
white matter
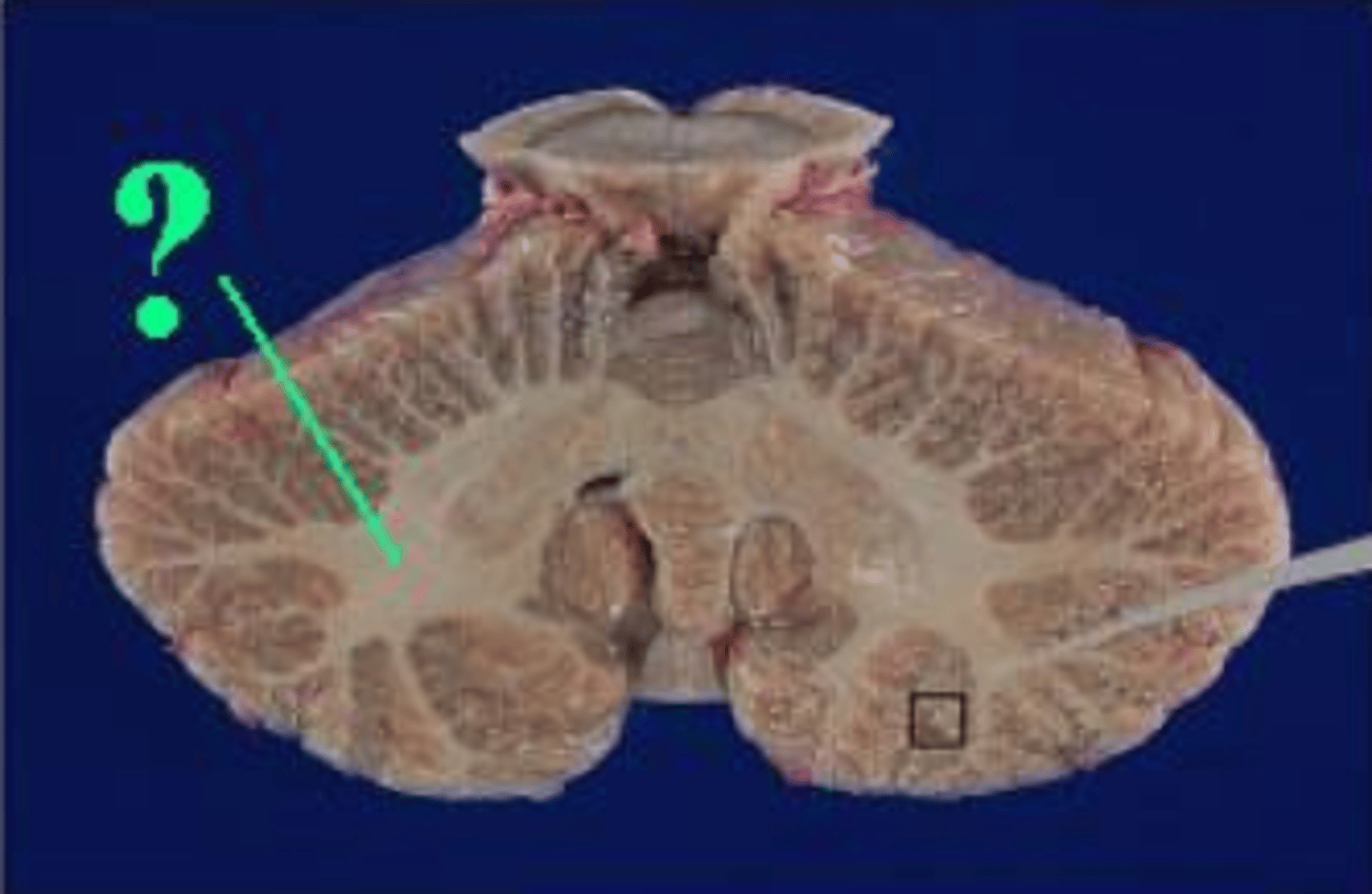
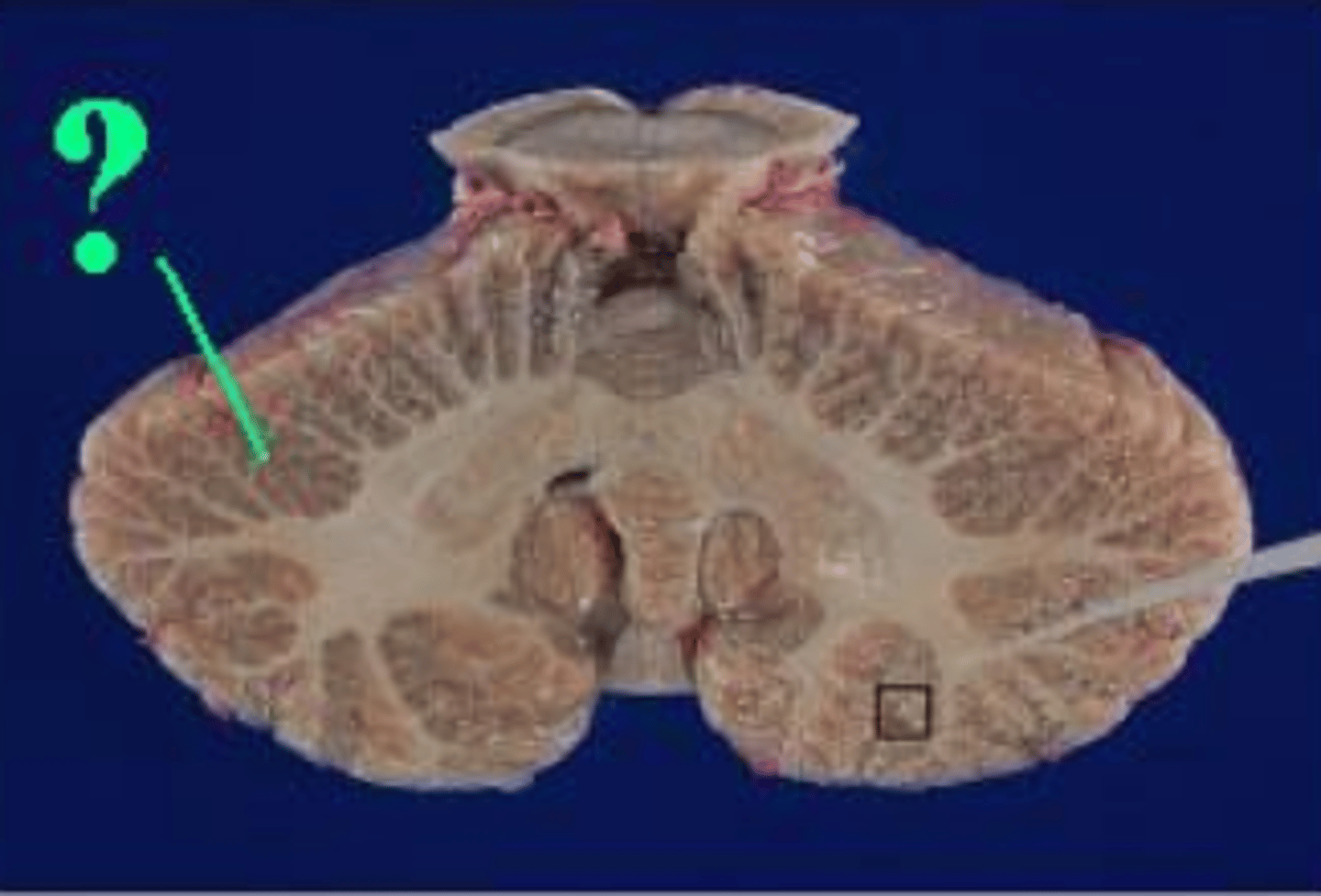
cerebellar cortex
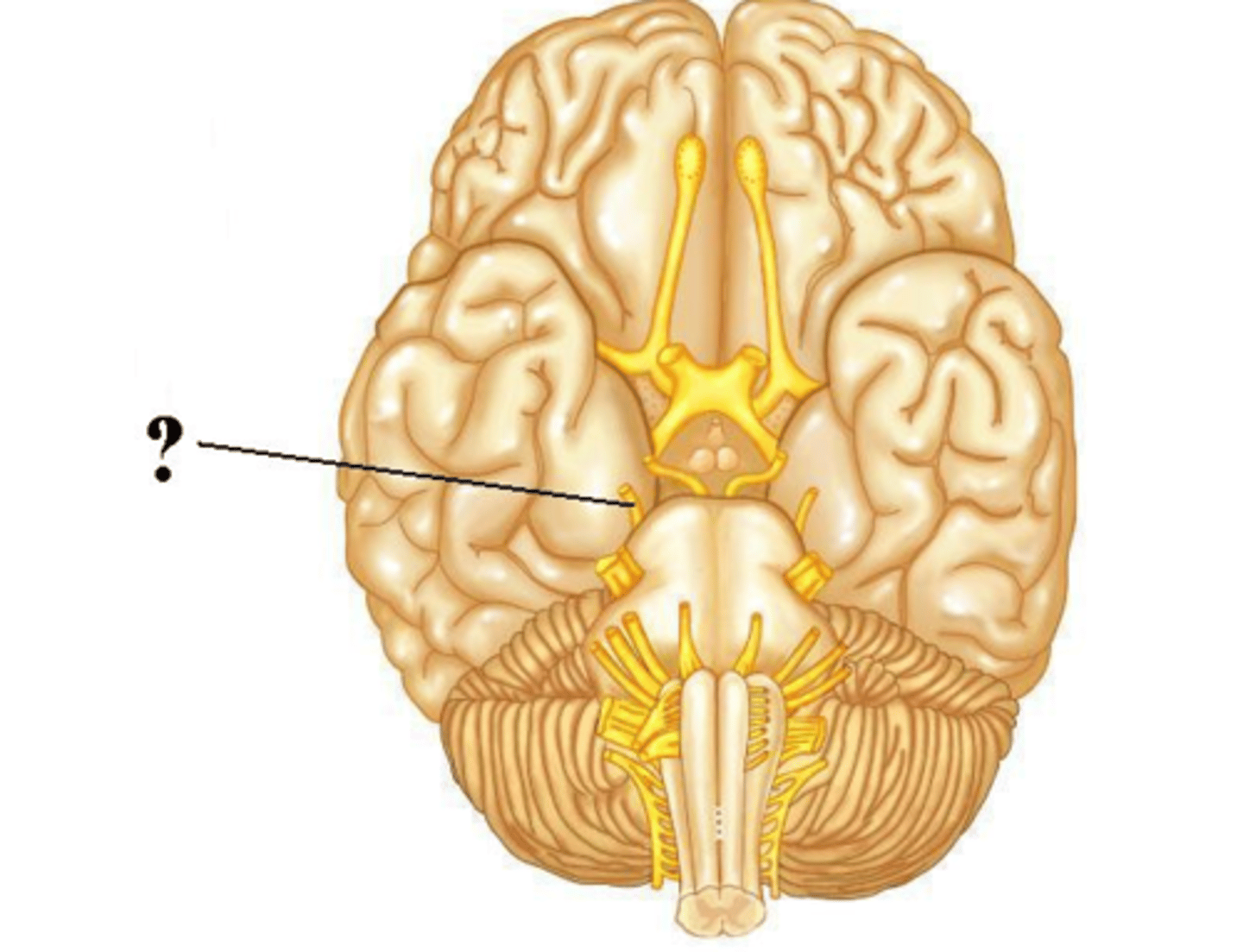
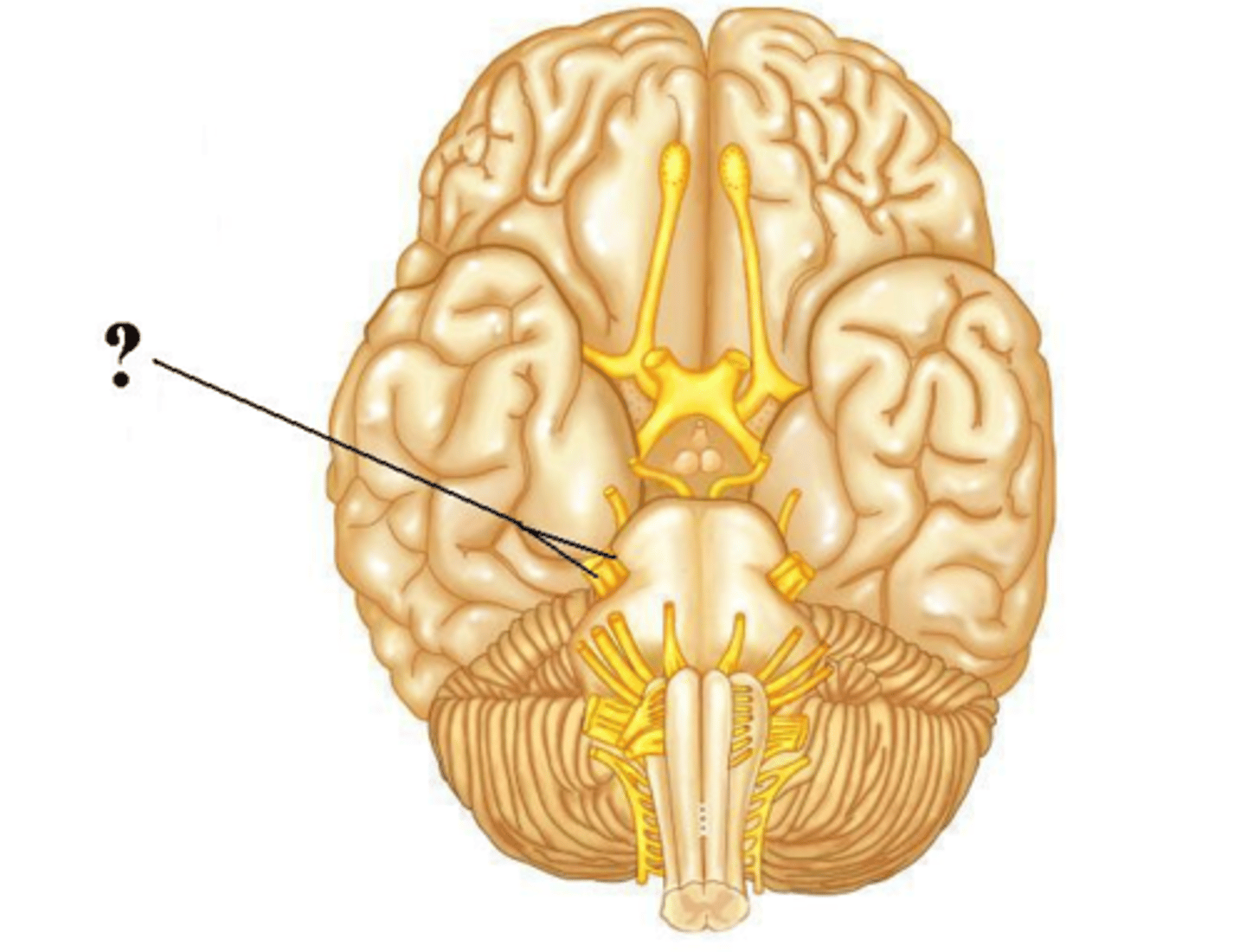
trochlear
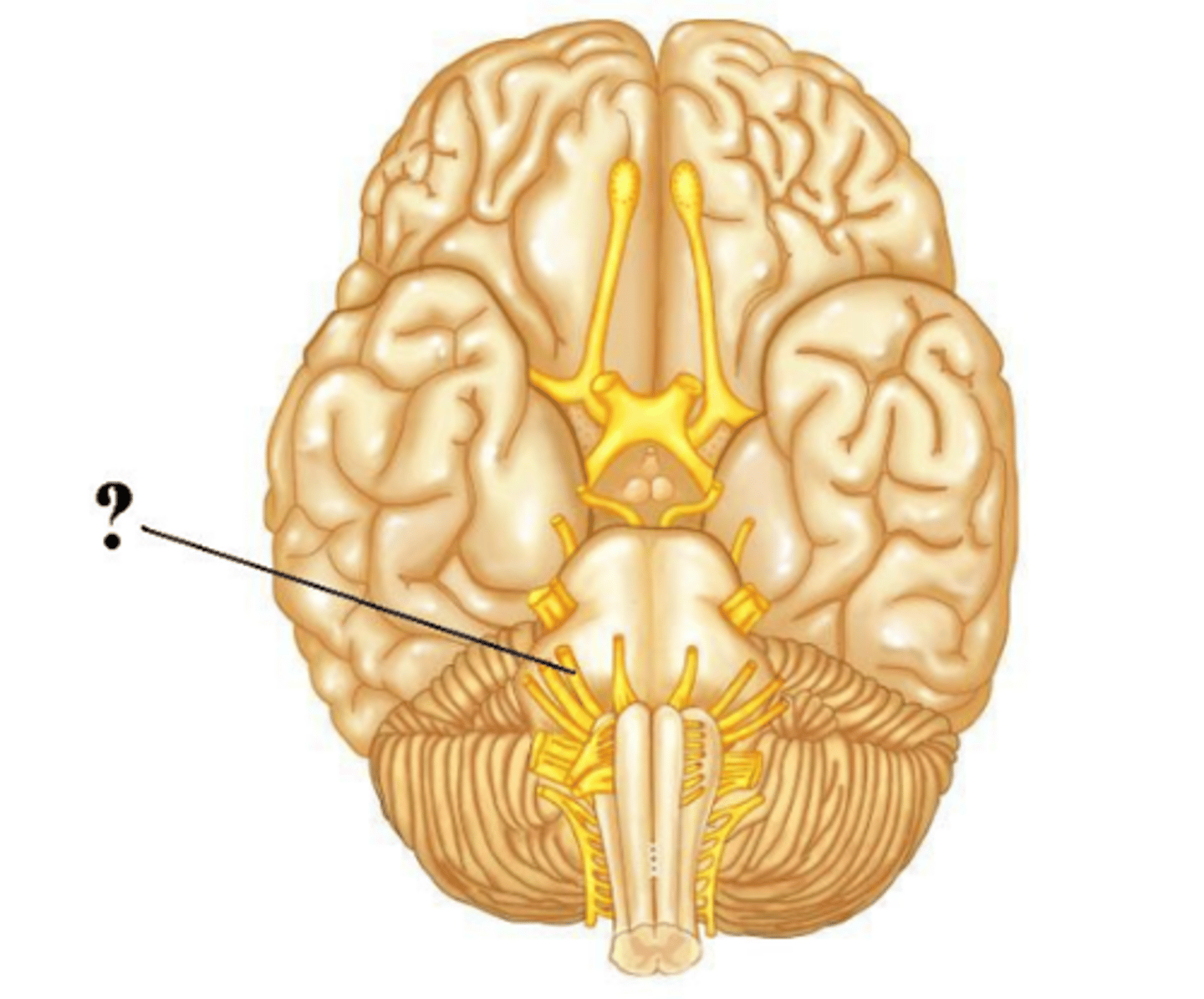
facial
optic tract
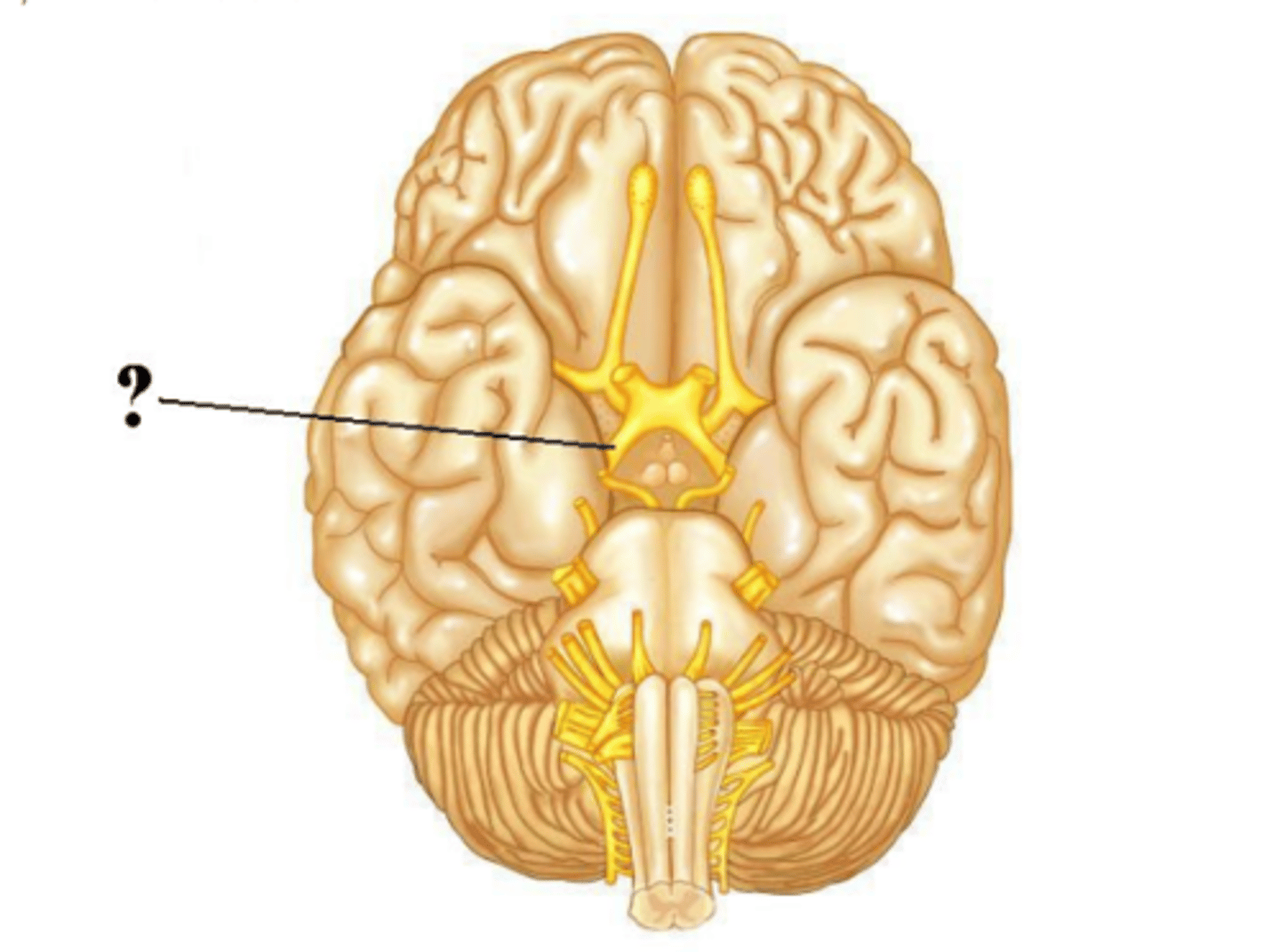
trigeminal
olfactory tract
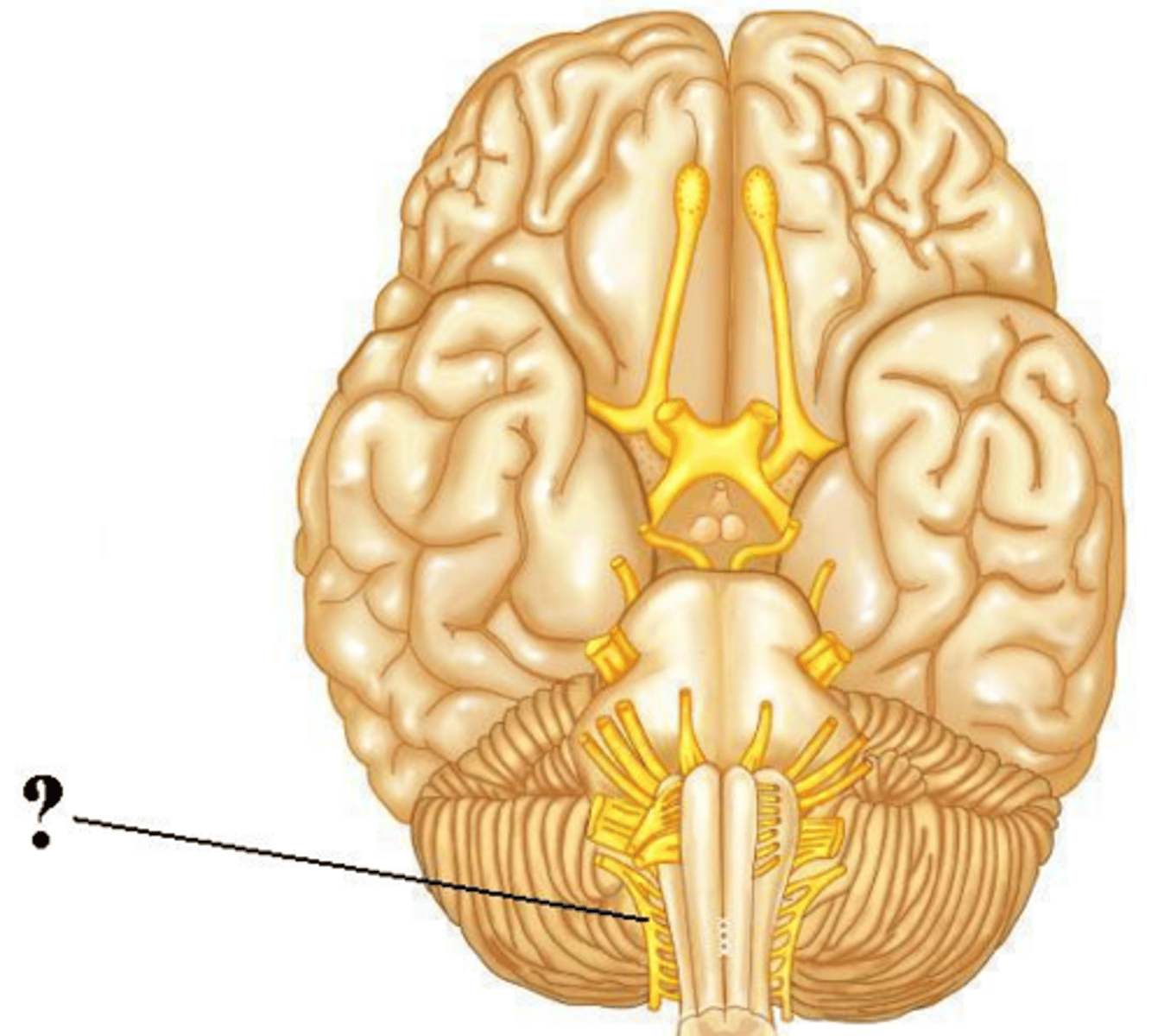
accessory
optic chiasm
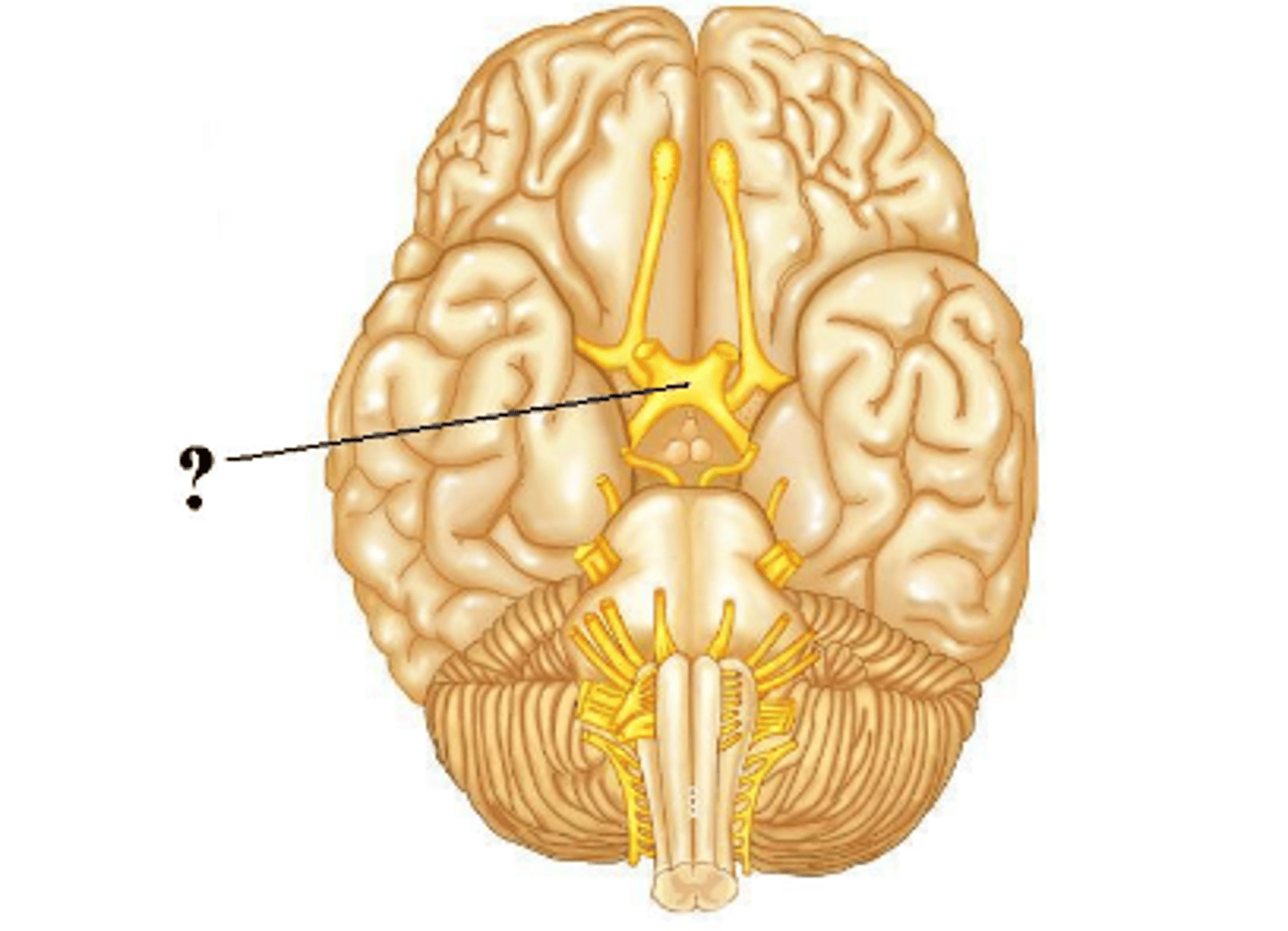
optic nerve
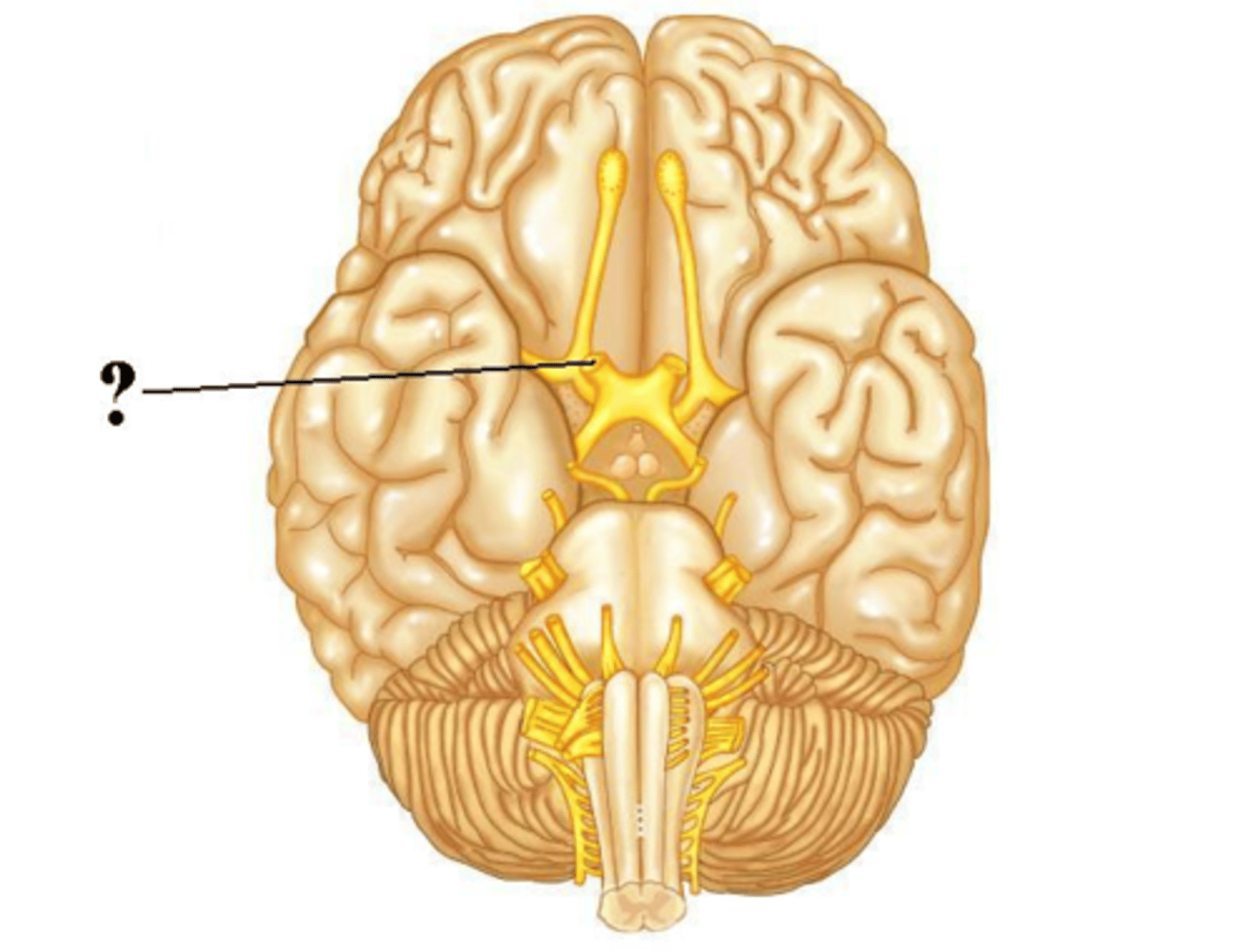
vagus
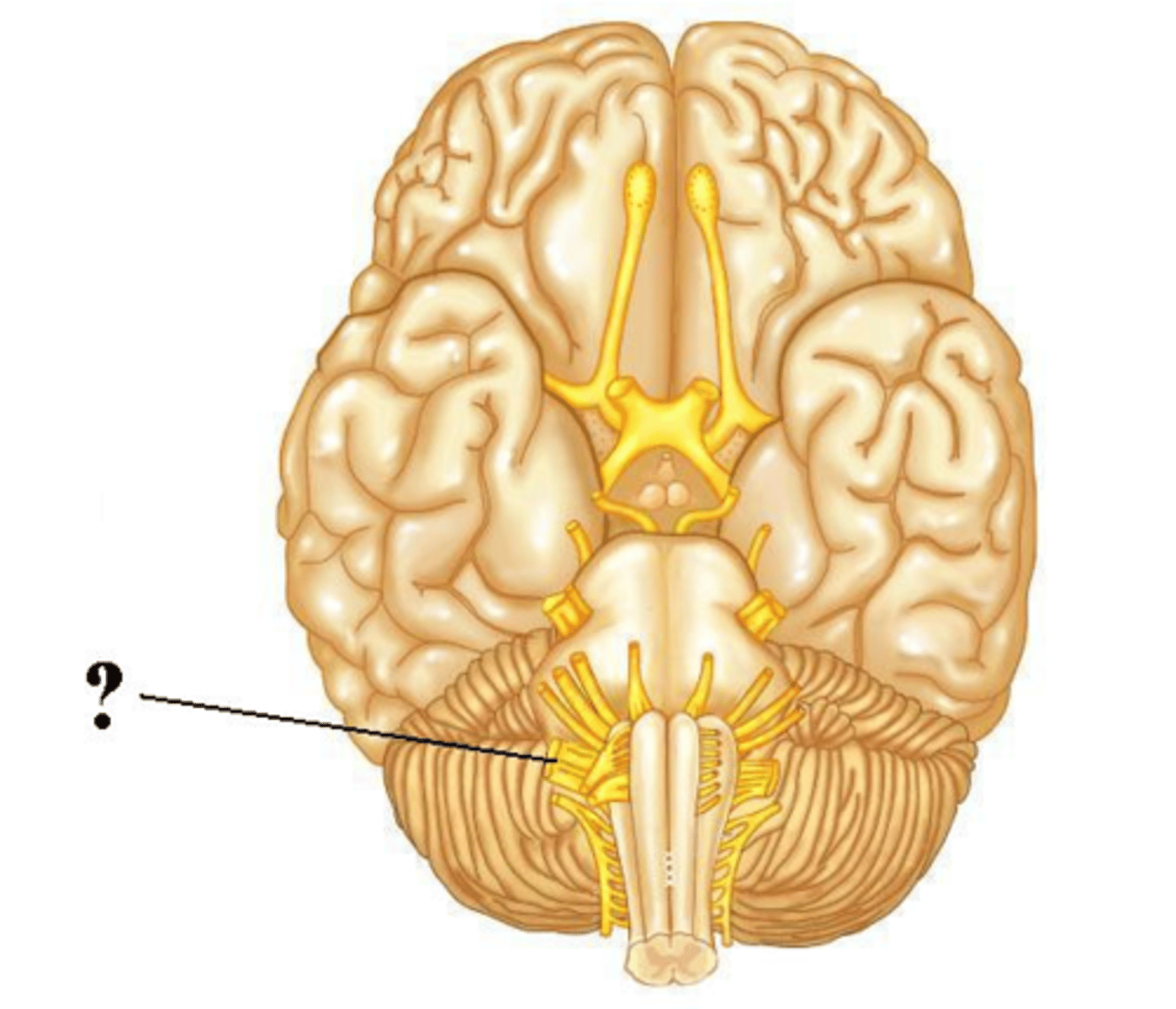
glossopharyngeal
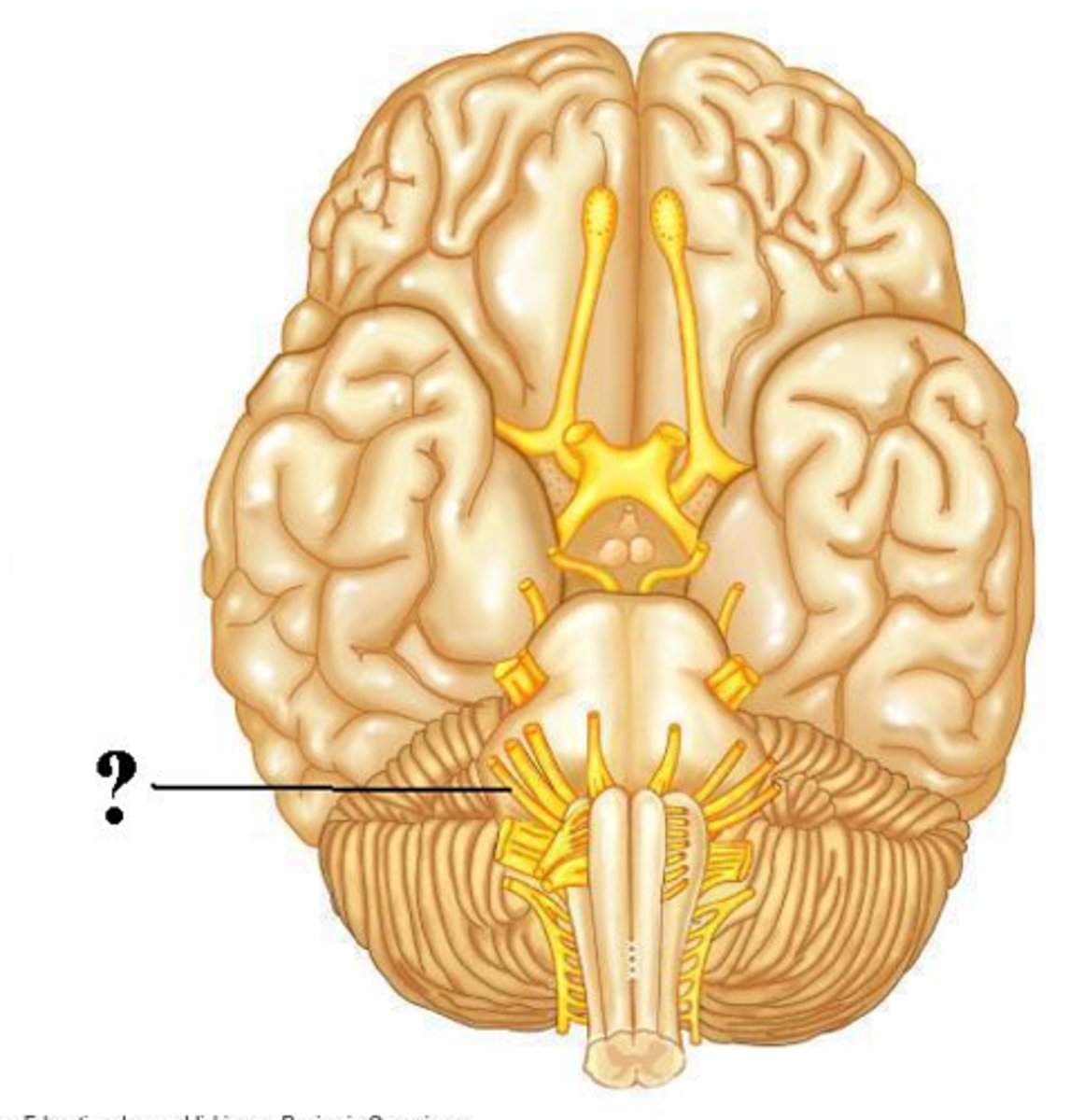
vestibulocochlear
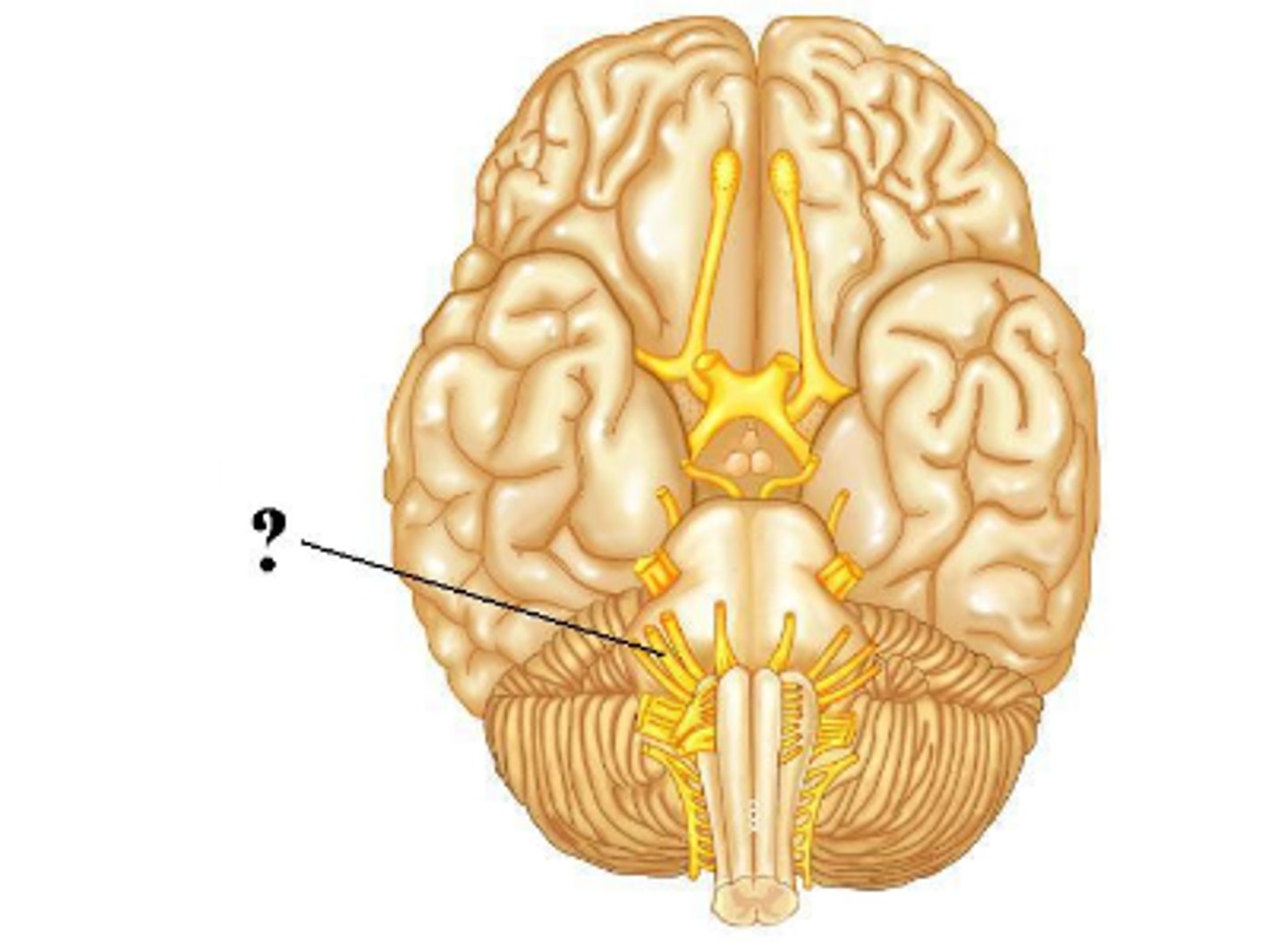
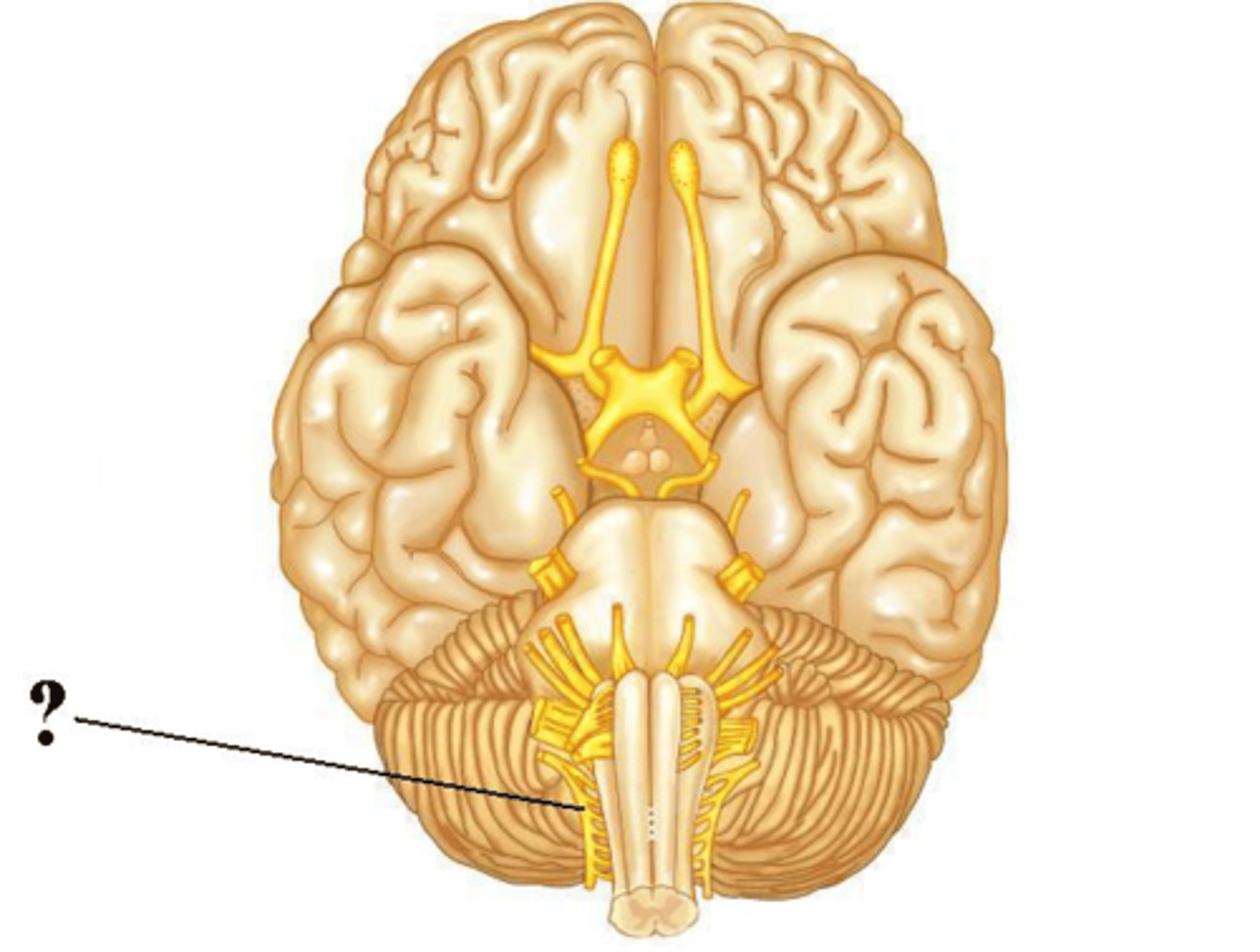
hypoglossal
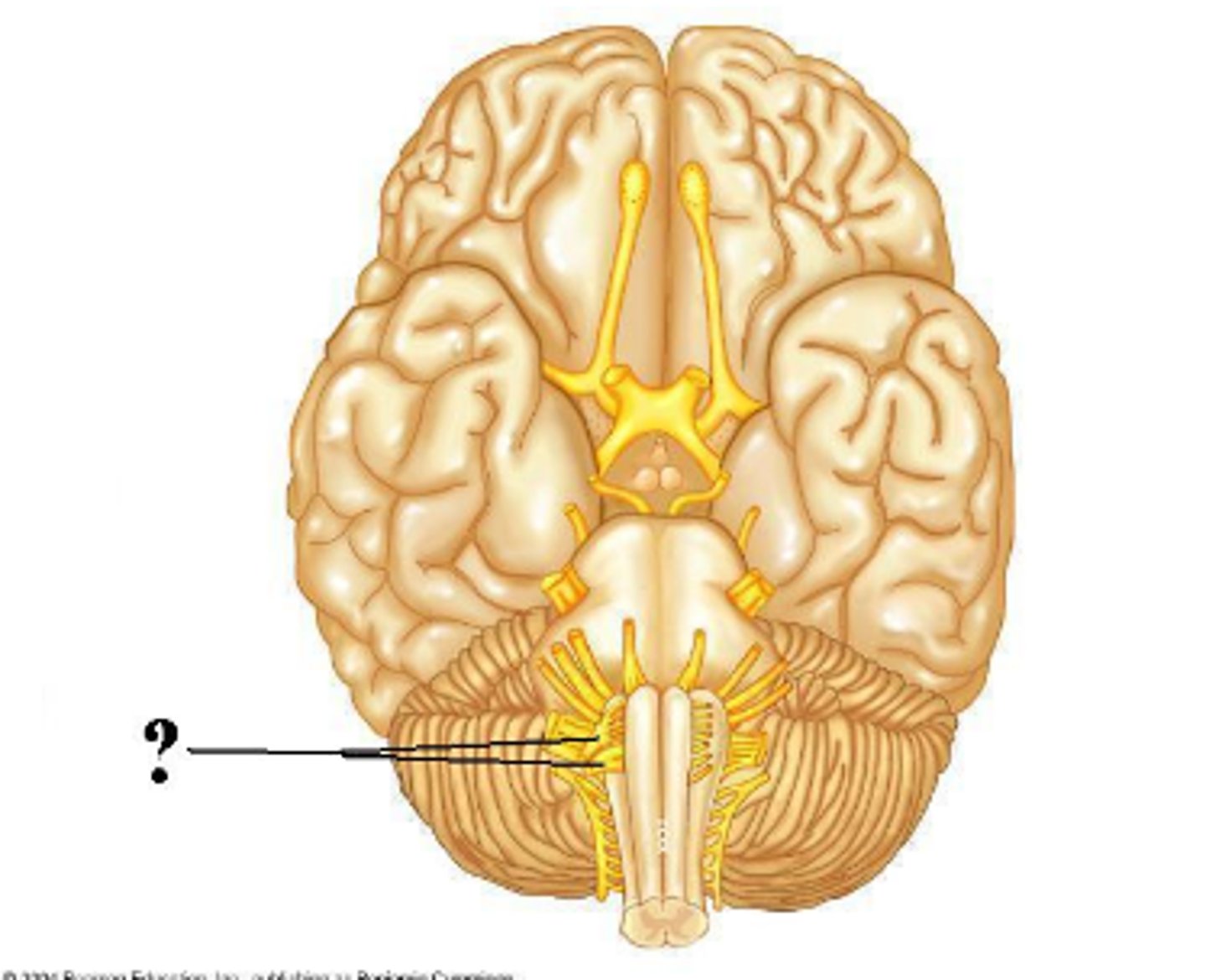
abducens
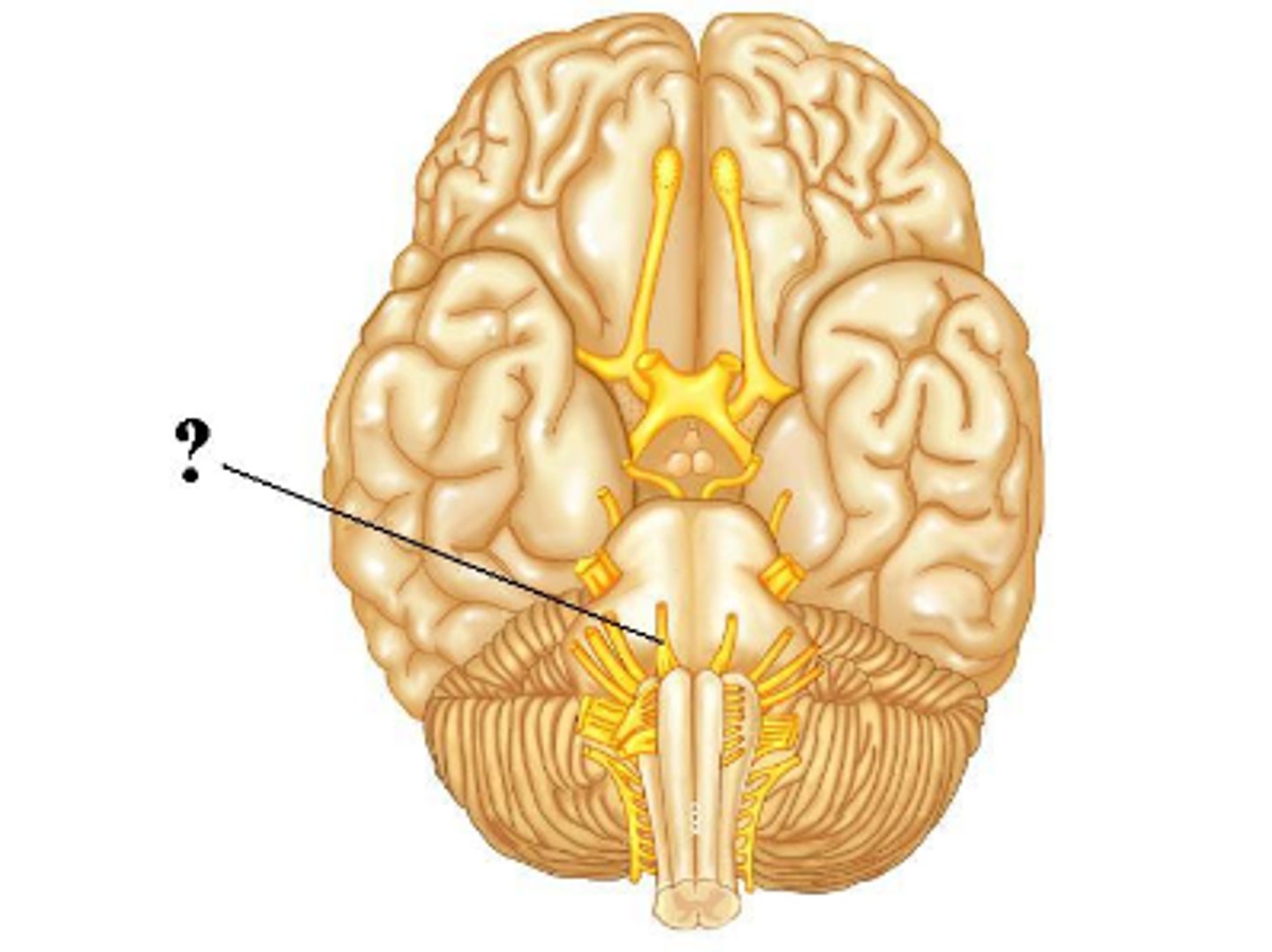
both
Is the indicated cranial nerve sensory only, motor only, or both sensory and motor?
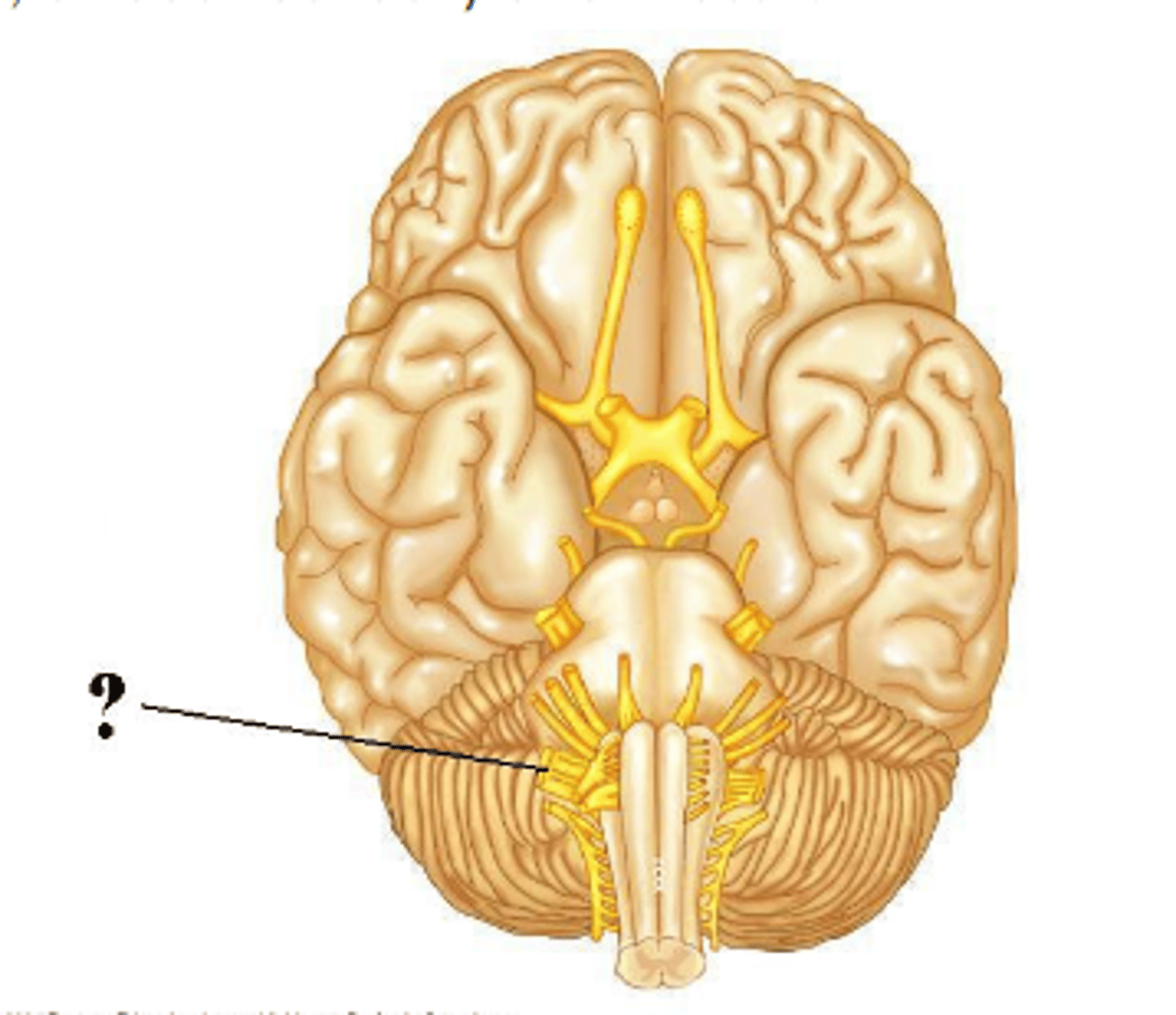
both
Is the indicated cranial nerve sensory only, motor only, or both sensory and motor?
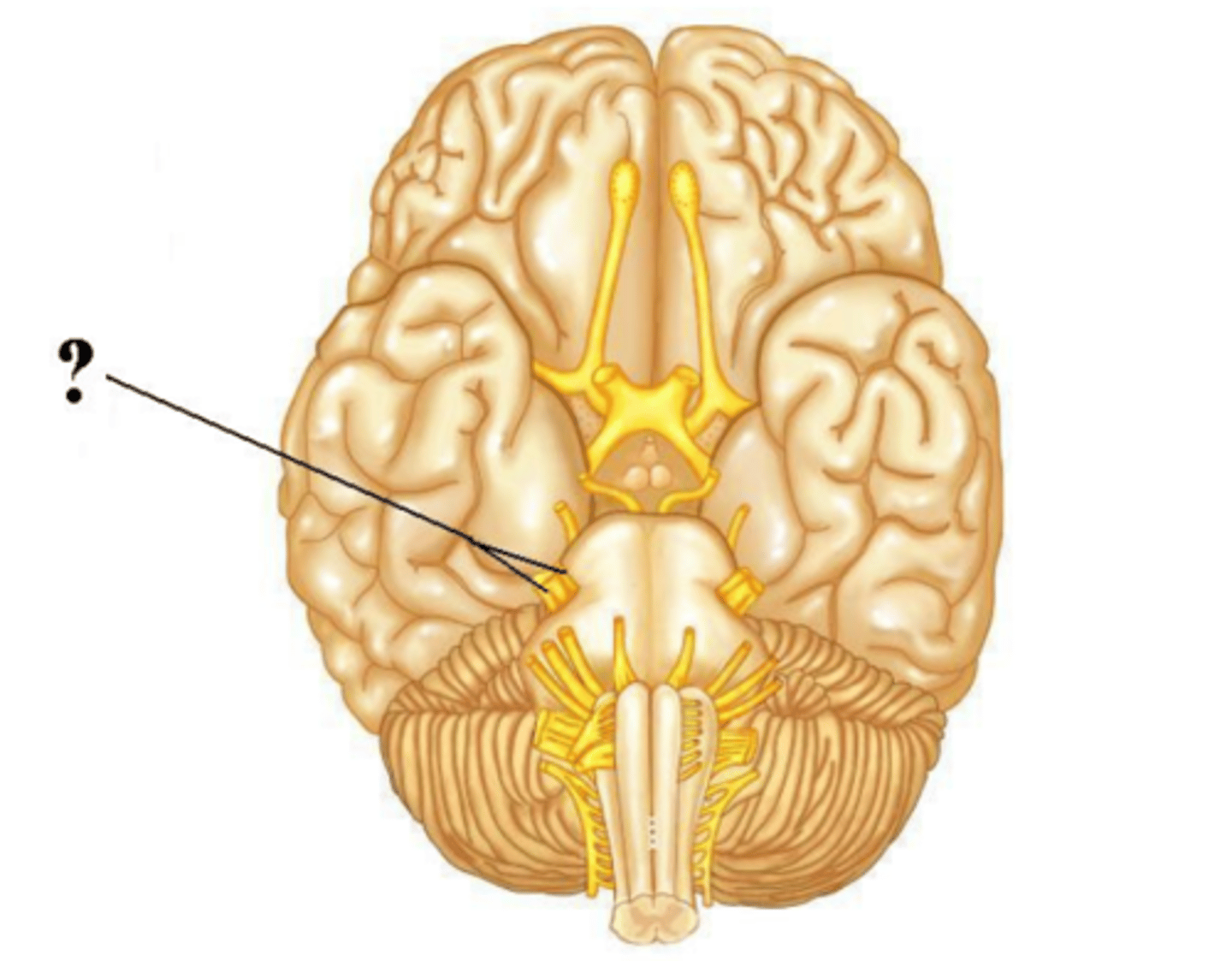
both
Is the indicated cranial nerve sensory only, motor only, or both sensory and motor?
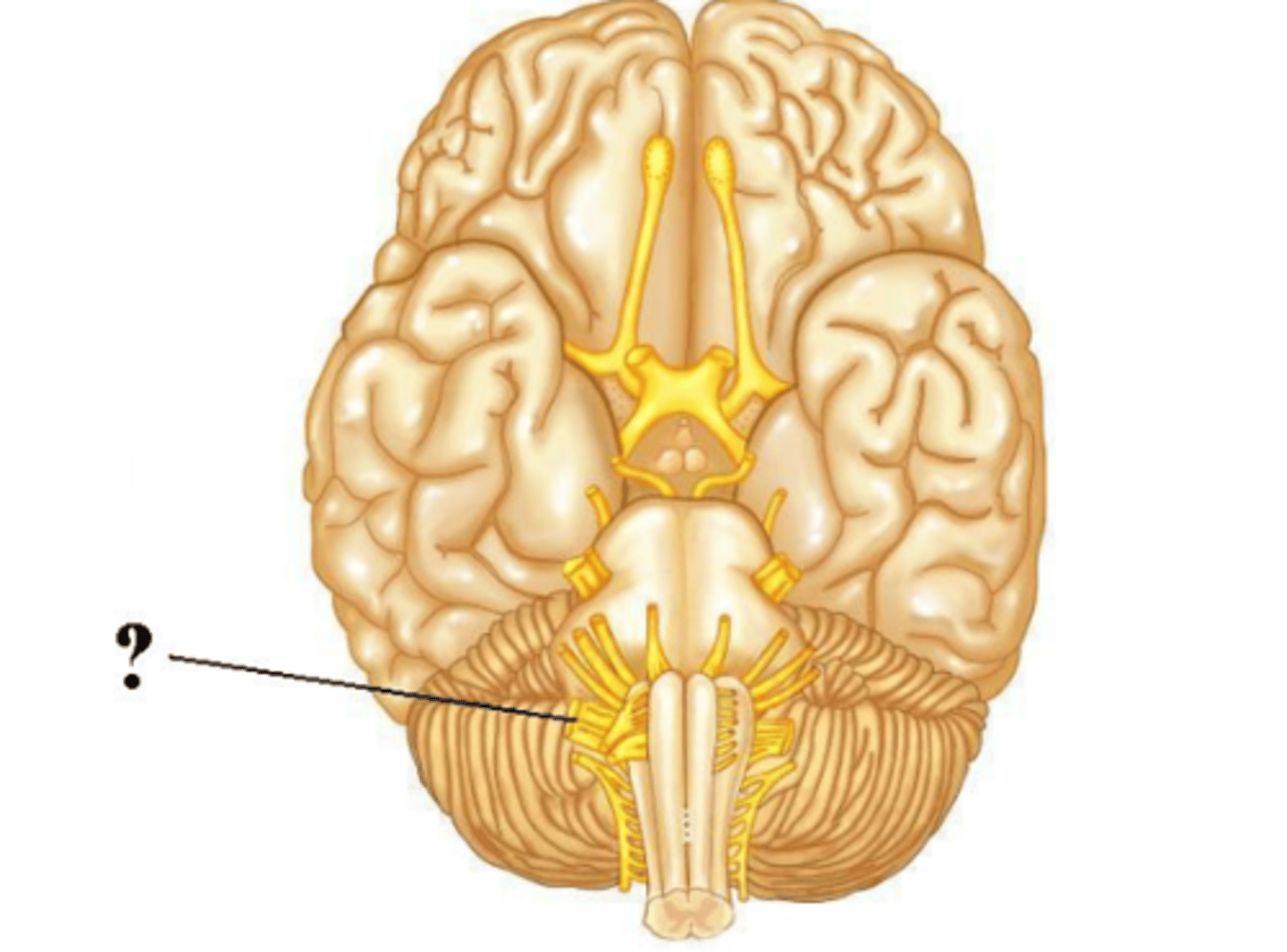
both
Is the indicated cranial nerve sensory only, motor only, or both sensory and motor?