Isomerism of Sugars (Sumakabilang Mukha???)
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What is the configuration of the monosaccharide if the OH group on the penultimate carbon is oriented to the left?
L-Configuration
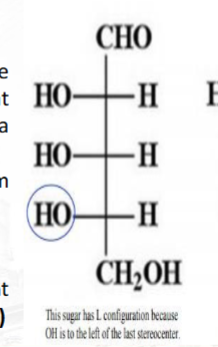
What is a point in a molecule where swapping any two groups creates a different stereoisomer, which can be an atom with three or four groups, including double bonds?
Stereocenter
What is a type of stereocenter that is specifically a carbon atom bonded to four different single-bonded groups, leading to non-superimposable mirror images (enantiomers)
Chiral Center
What is the configuration of the monosaccharide if the OH group on the penultimate carbon is oriented to the right?
D-configuration
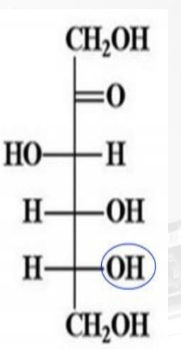
A term used to describe the rotation of the plane of polarized light
to the right (+)
Dextro-rotatory
A term used to describe the rotation of the plane of polarized light
to the left(-)
Levorotatory
Term used to describe molecules that have the Same molecular formula but differ from each other by having different structures.
Structural Isomerism
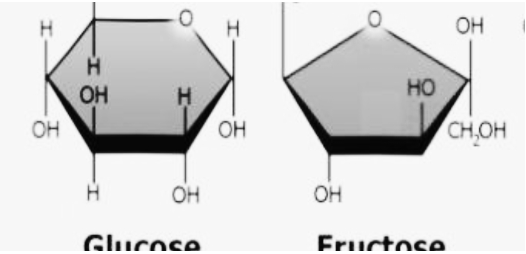
Determine the type of isomerism:
Structural Isomerism
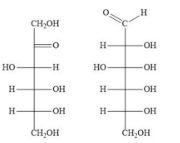
Determine the type of isomerism:
Structural isomerism
Determine the type of isomerism:
Same molecular formula and same structure, but they
differ in configuration
Stereoisomerism


Determine the type of isomerism:
stereoisomers that are mirror images but not superimposable
Enantiomers (Eh-non-tiomers)
Determine the type of isomerism:
stereoisomers that are non-superimposable, non-mirror images
Diastereomers
Determine the type of isomerism:
diastereomers that differ from each other in configuration at only one chiral carbon (other than the anomeric) atom
Epimers
Determine the type of isomerism:
These are isomers obtained from the change of position of hydroxyl group attached to the anomeric carbon
Anomerism
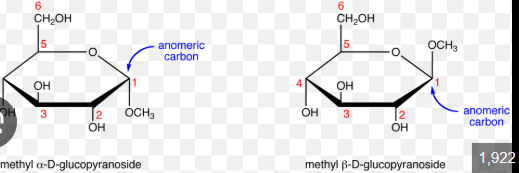
a carbon that, in the acyclic form, is not a stereocenter, but once it takes on the cyclic form, it becomes a stereocenter
Anomeric Carbon
Determine the type of isomerism:
Occurs when two similar groups are attached to the same or opposite sides of a double bond (in open-chain form) or across a ring structure (in cyclic form).
Cis-Trans Isomerism
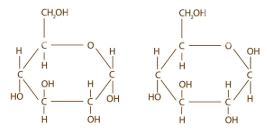
Determine the type of isomerism:
AB or cis-trans
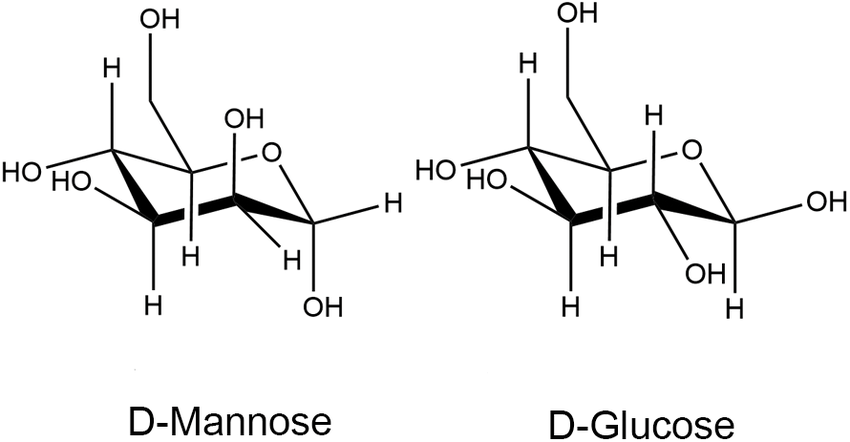
Determine the type of isomerism:
Epimers (C2)
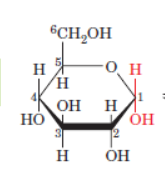
Alpha or beta; Cis or trans?
Alpha, Trans
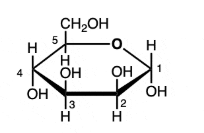
Alpha or Beta; Cis or trans?
Alpha, Trans
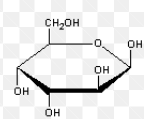
Alpha or Beta; Cis or trans?
Beta, Cis
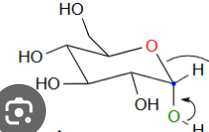
Alpha or Beta; Cis or trans?
Alpha, Trans
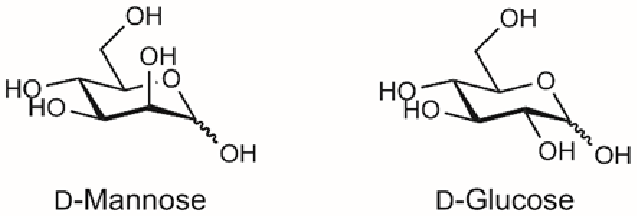
Determine the type of isomerism:
Diastereomer (Epimer)
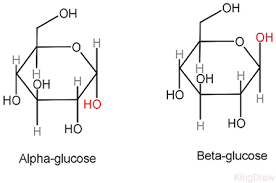
Determine the type of isomerism:
Anomer (alpha beta)
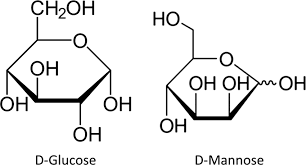
Determine the type of isomerism:
Epimers
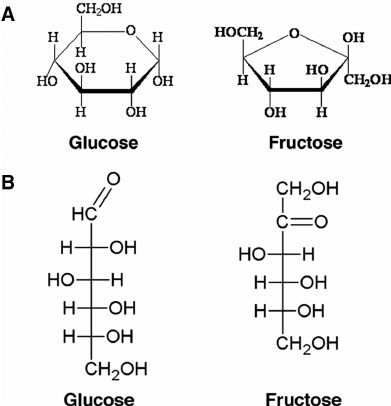
Determine the type of isomerism:
Structural Isomers
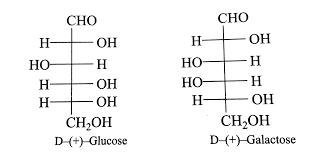
Determine the type of isomerism:
Diastereomer (Specifically an Epimer)
They differ at one or more chiral centers but are not mirror images