Upper Respiratory System
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What are the 2 main components of the respiratory system?
Upper respiratory system
Lower respiratory system
What organs are in the upper respiratory system (5) #0097ff
Nose
Nasal cavity #fd8900
Nasopharnyx #ffce02
Larynx #00b837
Trachea #00d7ea
What are the organs in the lower respiratory system?
Bronchus
Bronchioles
Lungs
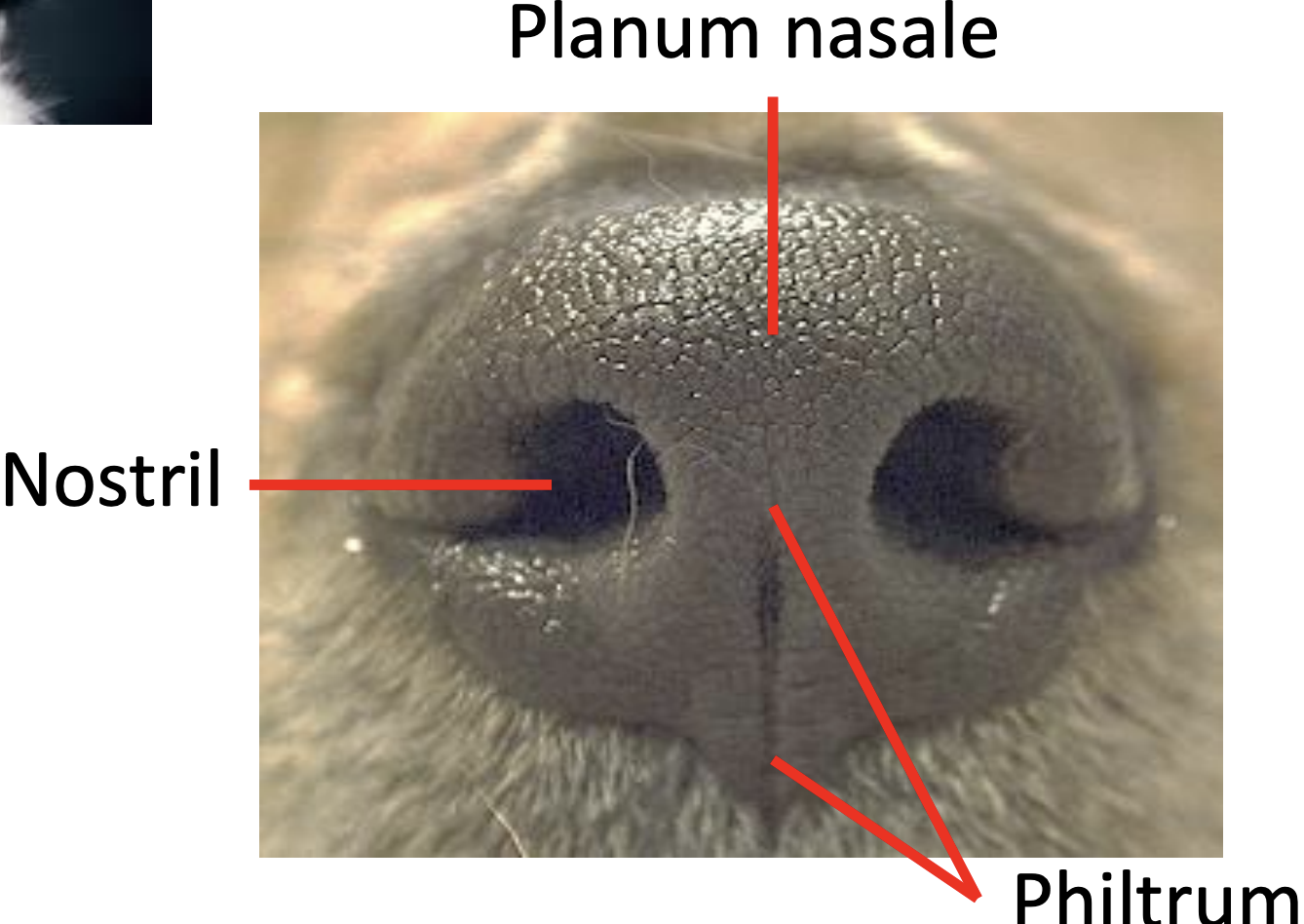
Nose
Location
What are nostrils
Lead to
What are the 2 parts of the muzzle (snout)
Each contain
Species difference
In cat, dog, sheep and goat, the planum nasale is separated by?
Location:
Rostral to eyes
Dorsal to oral regions
What are nostrils: External nares (openings) of respiratory tube
Lead to: Nasal passages
What are the 2 parts of the muzzle (snout):
Skin around nares with hairs
Contain: Sebaceous and eccrine sweat glands
Non-haired area
Contain: Eccrine sweat glands
Species difference:
Planum nasale: cat dog, sheep and goat
Planum rostrale: pig
Planum nasolabiale: cattle
In cat, dog, sheep and goat, the planum nasale is separated by: Philtrum
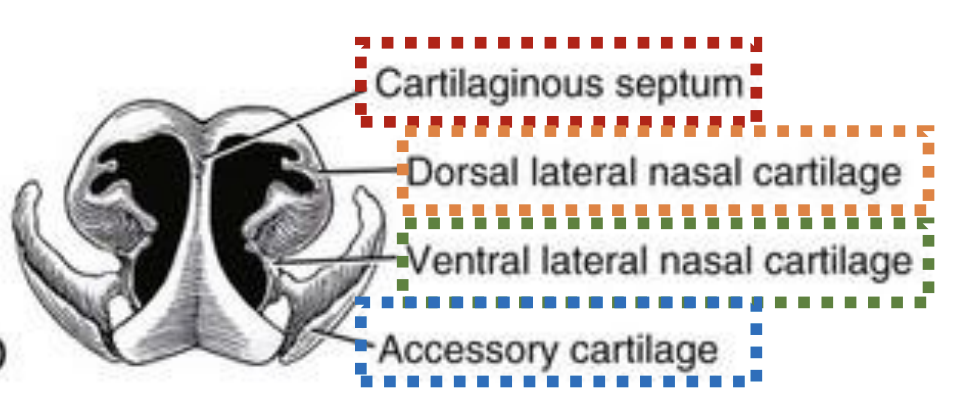
Nose: Bone & Cartilage
Lateral wall of bony portion is formed by
Roof is formed by
Bony nasal aperture forms
Bounded rostrally by
How is it the movable portion of nose
Movable part of nose ends in
What are 4 cartilages of the nose
Which is paired and which is not?
Lateral wall of bony portion is formed by:
Incisive bone
Maxillae bone
Roof is formed by: Paired nasal bones
Bony nasal aperture forms: Largest opening into skull
Bounded rostrally by: Nasal cartilages
How is it the movable portion of nose: Contains ligaments
Movable part of nose ends in: Truncated apex
What are 4 cartilages of the nose:
Paired:
Dorsal lateral nasal cartilage
Ventral lateral nasal cartilage
Accessory cartilages
Unpaired: Cartilaginous septum
Nasal Cavity #fd8900
Location
Location of choana
Marks the boundary between
Nasal cavity separated into
By
Which part of septum is cartilaginous
Caudal part is created in
How is it separated from nasal cavity
Location: Between nostrils and choana
Location of choana: Caudal end of hard palate
Marks the boundary between: Nasal cavity and nasopharynx
Nasal cavity separated into: Left and right cavities
By: Median nasal septum
Which part of septum is cartilaginous: Rostral part
Caudal part is created by: Osseus septum (plate of bone)
How is it separated from nasal cavity: By hard and soft palate
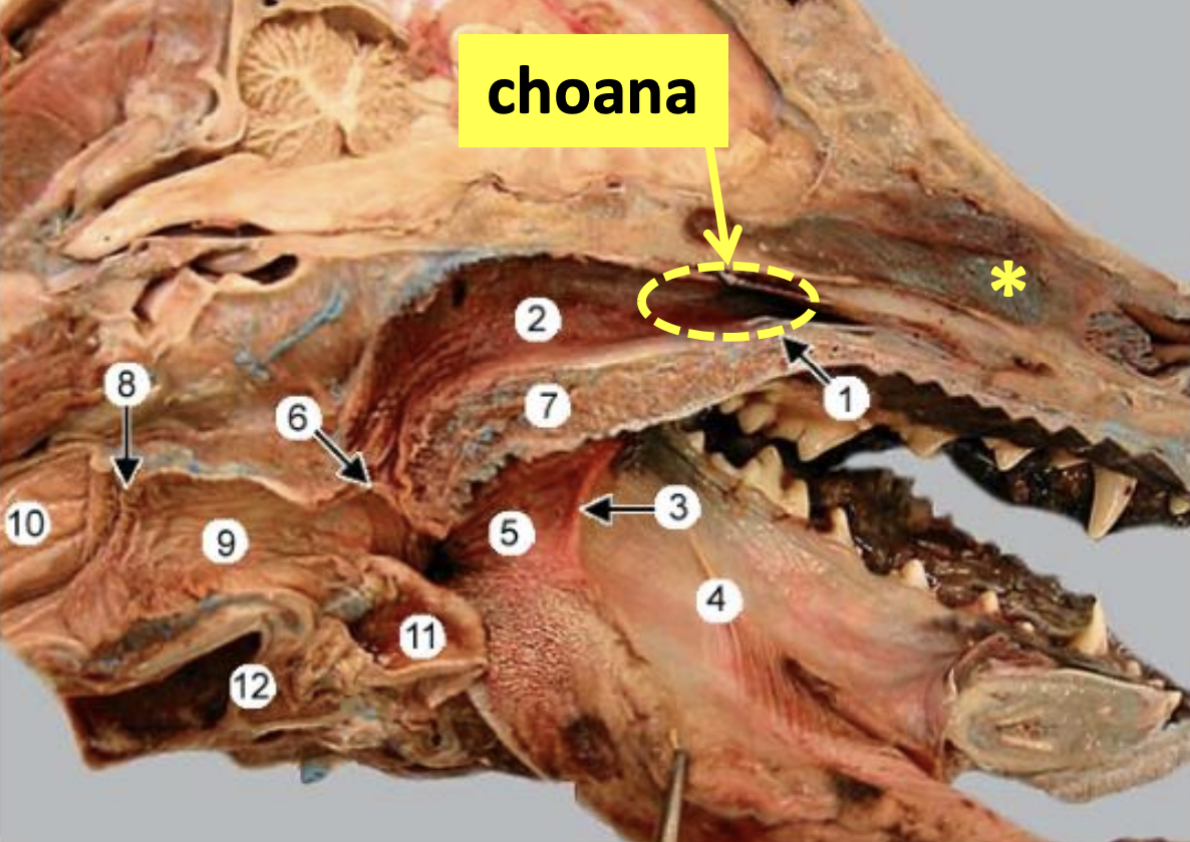
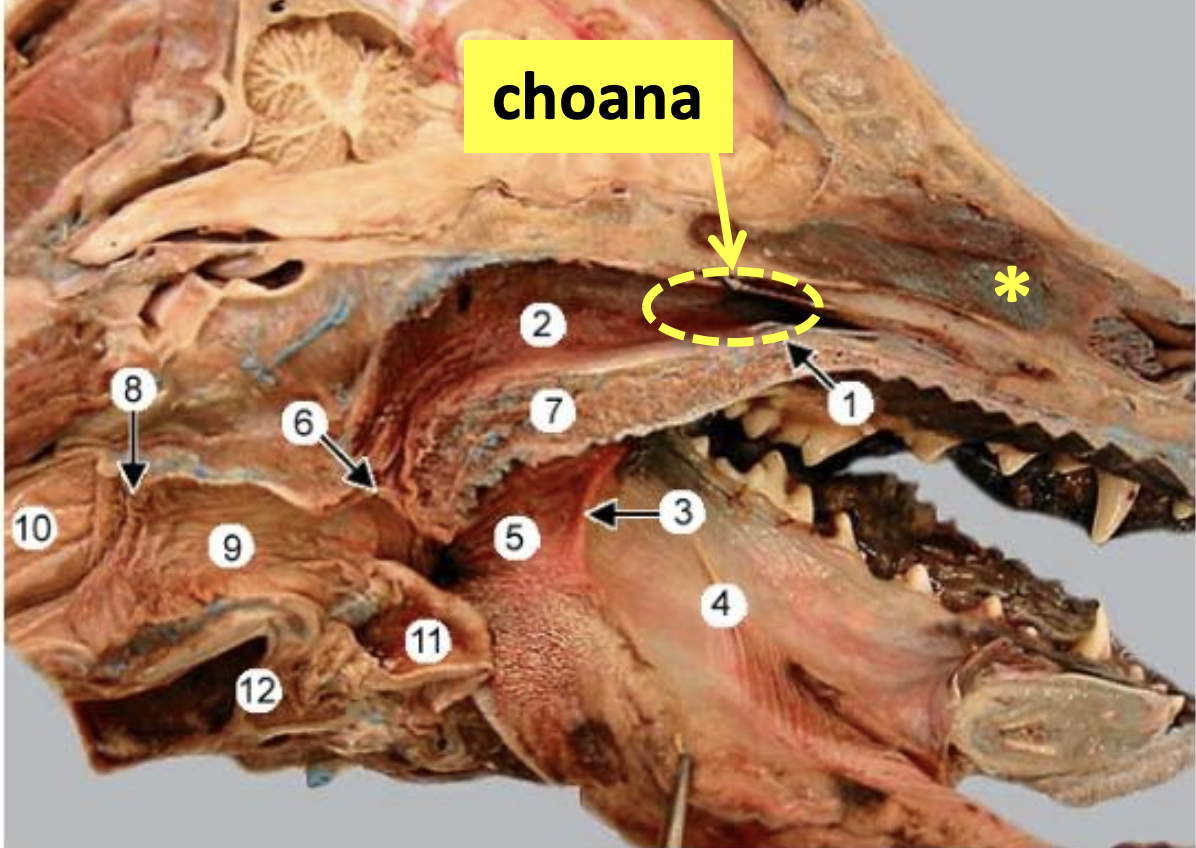
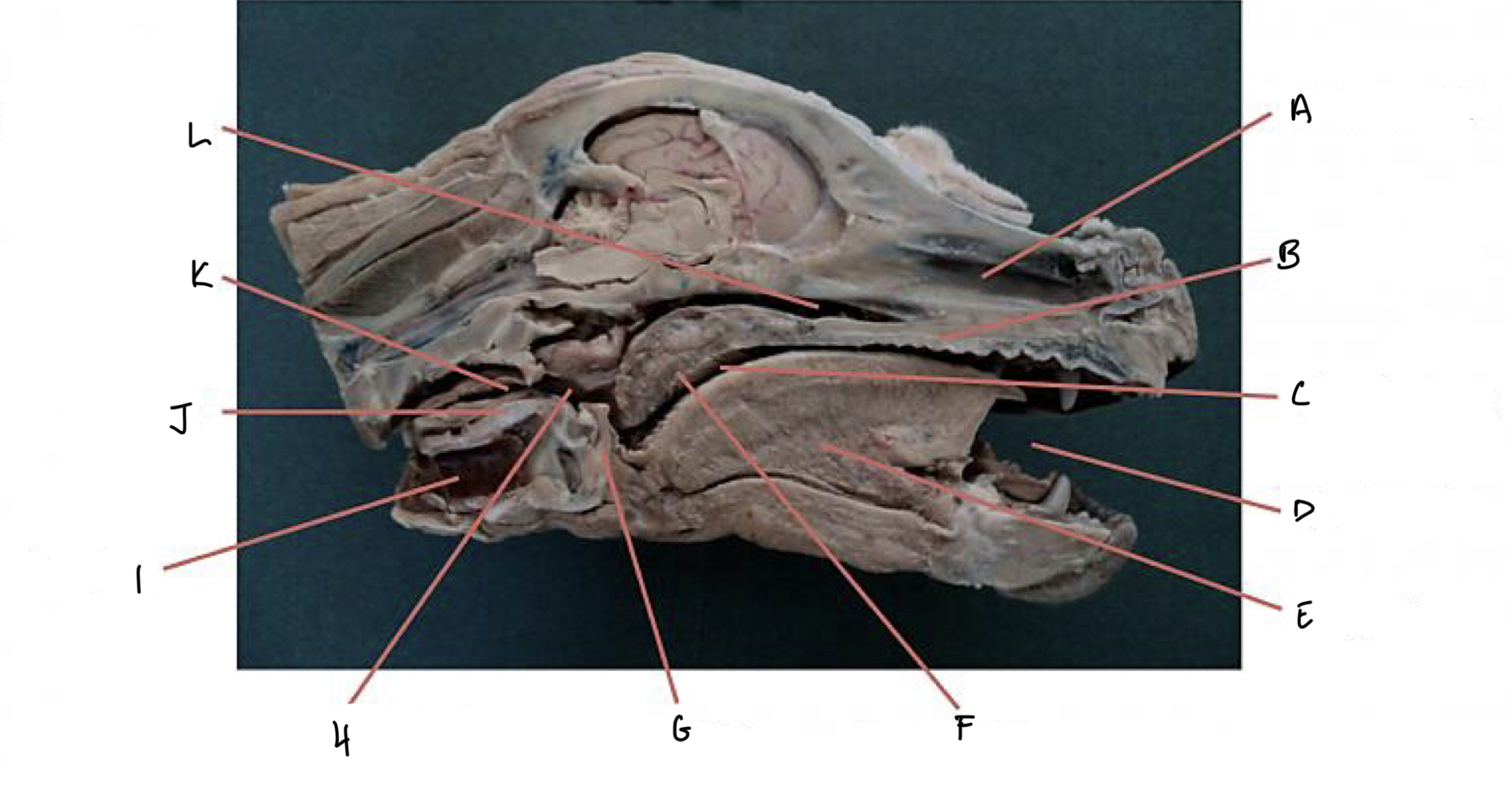
Nasal Cavity: Name the structures
What is *
What is 1
What is 2
What is 7
*: Choana
1: Hard palate
2: Nasopharynx
7: Soft palate
Nasal Cavity: Nasal Conchae #fd8900
What
Covered with
Function
Arises from
4 Types
Which fill the middle portion
Which fill the caudal parts
Which are the major two
Which one has the olfactory epithelium
Contains what
Function
What: Cartilaginous or ossified scrolls
Covered with: Vascular mucous membrane
Function: Warms and humidify inspired air
Arises from: Bones of lateral wall
4 Types:
Dorsal: middle portion
Ventral: middle portion
Middle: middle portion
Ethmoidal: caudal parts
Major 2 conchae: Dorsal and ventral
Which one has the olfactory epithelium: Ethmoidal conchae (pseudostratified columnar epithelium)
Contains what: Sensory endings of olfactory nerve (cranial nerve I)
Function: Mediates the sense of smell
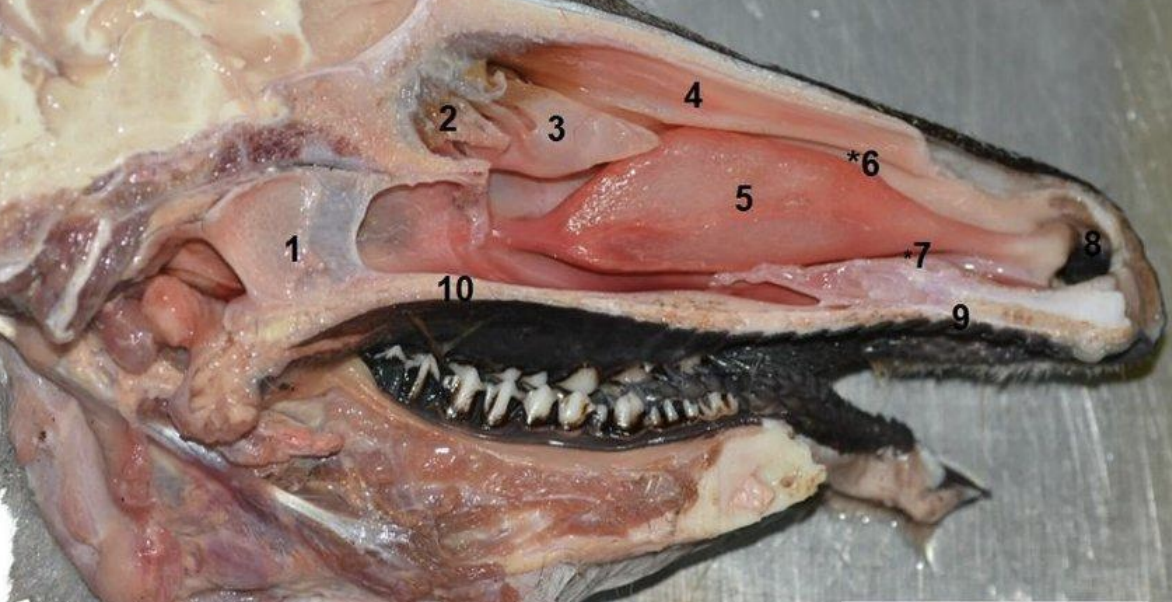
Nasal Cavity: Conchae
Label the diagram 1-10
1: Nasopharynx
2: Ethmoidal conchae
3: Middle nasal concha
4: Dorsal nasal concha
5: Ventral nasal concha
6: Middle meatus (passageways)
7: Ventral meatus (passageways)
8: Nostrils
9: Hard palate
10: Soft palate
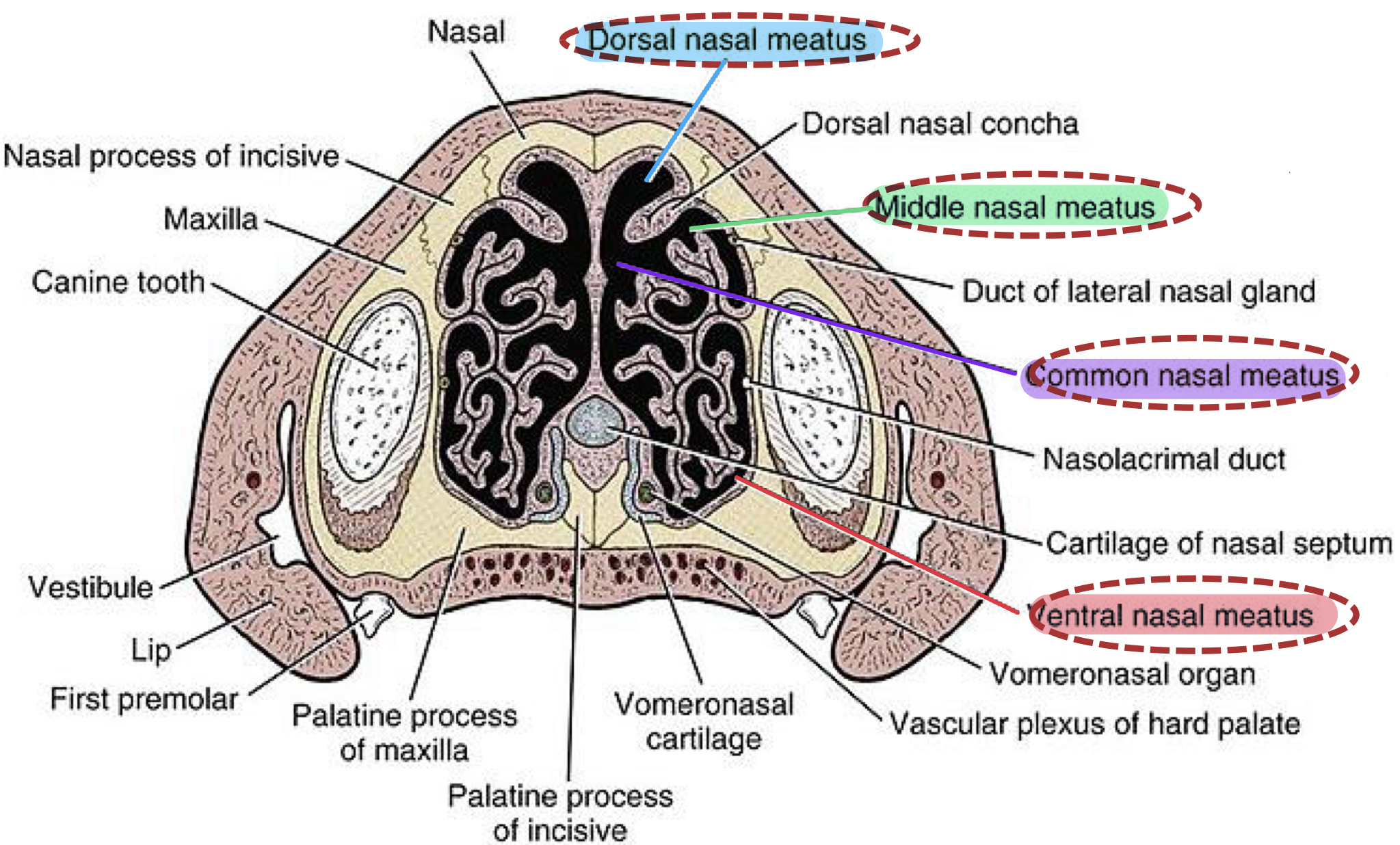
Nasal Cavity: Nasal Meatuses
What are the 4 nasal meatuses
Their locations
Dorsal Nasal Meatus:
Location: Between the dorsal conchae and roof of nasal cavity
Middle Nasal Meatus:
Location: Between dorsal and ventral conchae
Common Nasal Meatus: (communicates between the others)
Location: Adjacent to nasal spetum
Ventral Nasal Meatus:
Location: Between ventral conchae and floor of nasal cavity
Nasal Cavity: Paranasal Sinuses
What
Communicates with
Functions
What are the 6 paranasal sinues
What: Air-filled spaces lined with mucosa
Communicaties with: Nasal cavity
Functions:
Resonating (voice)
Insulation
Cooling of the brain
Light weight skull construction
6 paranasal sinuses:
Maxillary sinus #ffd100
Frontal sinus
Palatine sinus
Sphenoid sinus #00c52c
Lacrimal sinus
Dorsal conchal sinus #9000ff
Nasal Cavity: Paranasal Sinuses Absence
Which paranasal sinus is absent in carnivores and pigs
Which paranasal sinus is absent in dog and small ruminant
Which paranasal sinus is absent in carnivores and pigs: Palatine sinus
Which paranasal sinus is absent in dog and small ruminant: Sphenoid sinus
Nasal Cavity: Paranasal Sinuses Presence
Which 2 paranasal sinus is present in pig and ruminant
Which 2 paranasal sinus is present in pig and ruminant:
Lacrimal sinus
Dorsal conchal sinus
Nasal Cavity: Paranasal Sinuses
Which paranasal sinuse is present in all animals?
Frontal sinus
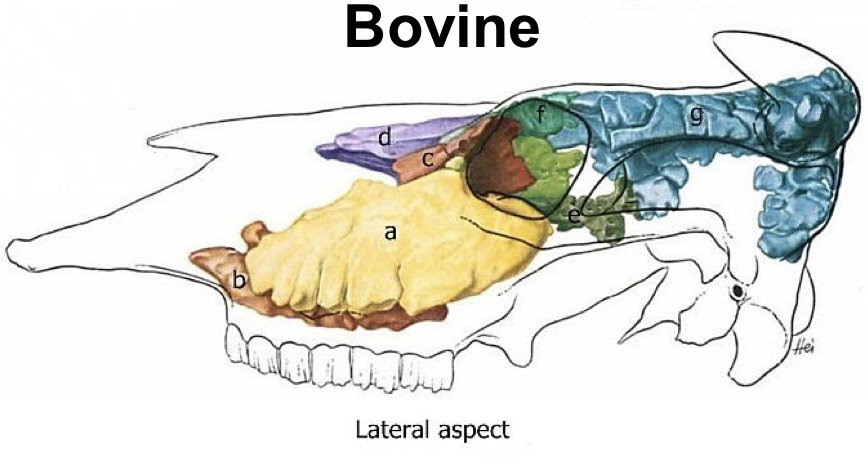
Nasal Cavity: Paranasal Sinuses
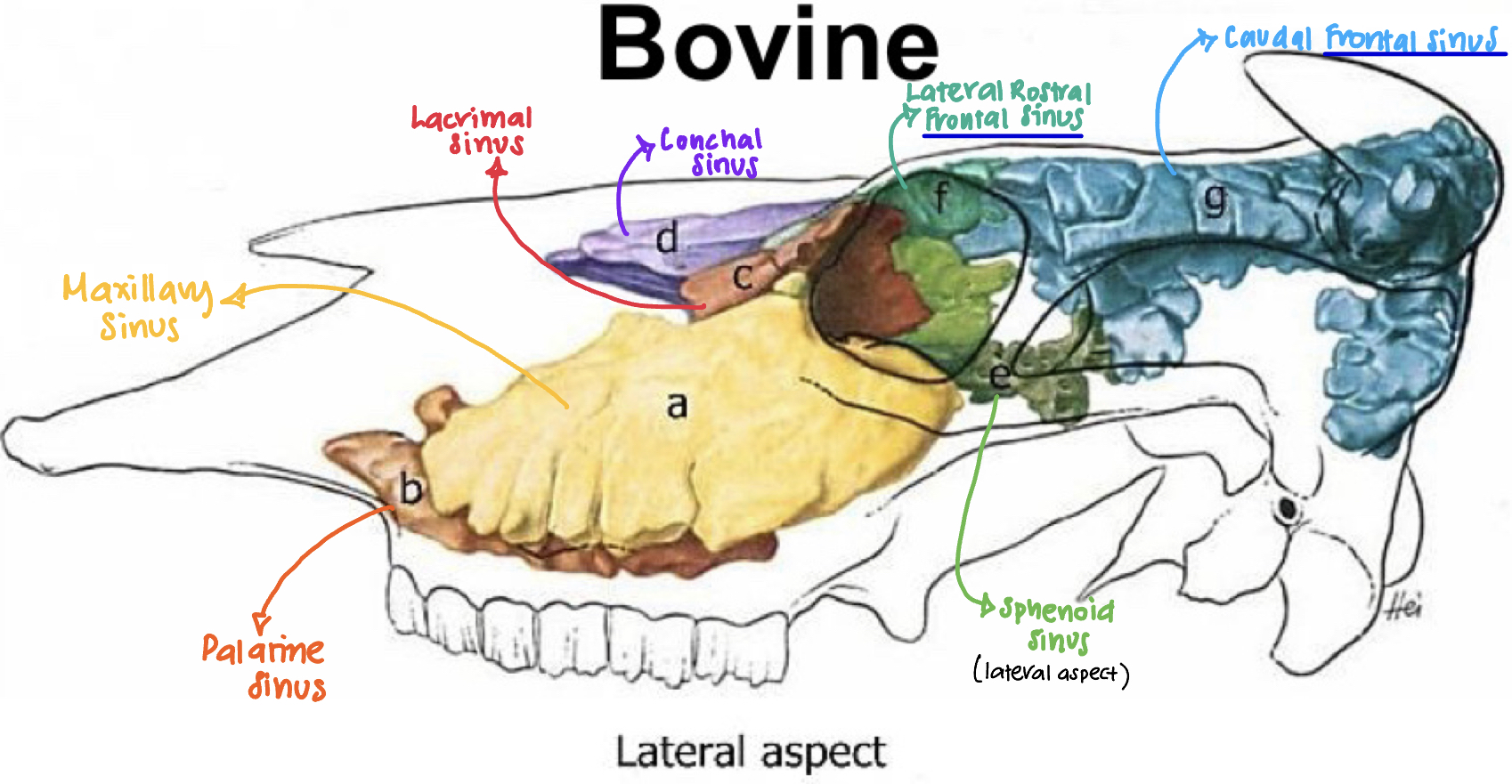
Label the diagram a-g
A: Maxillary sinus #ffd100
B: Palatine sinus
C: Lacrimal sinus
D: Conchal sinus #9000ff
E: Sphenoid sinus #00c52c
F: Lateral rosatral frontal sinus
G: Caudal frontal sinus
Nasal Cavity: Paranasal Sinuses
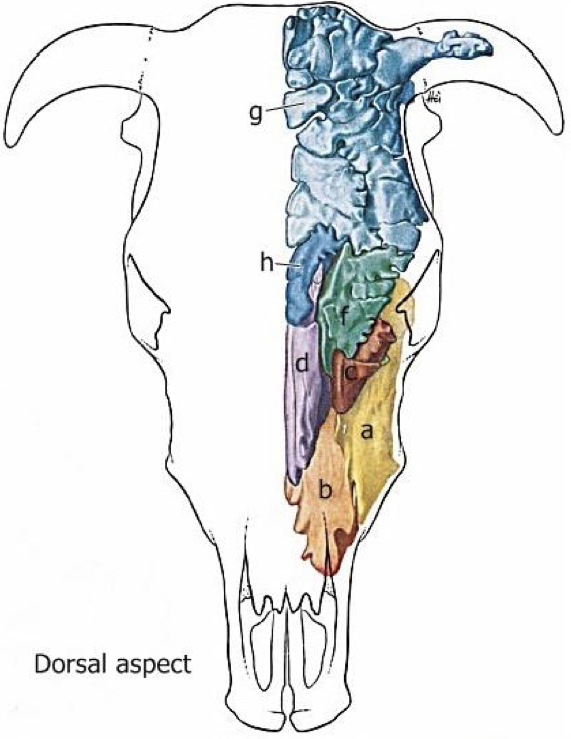
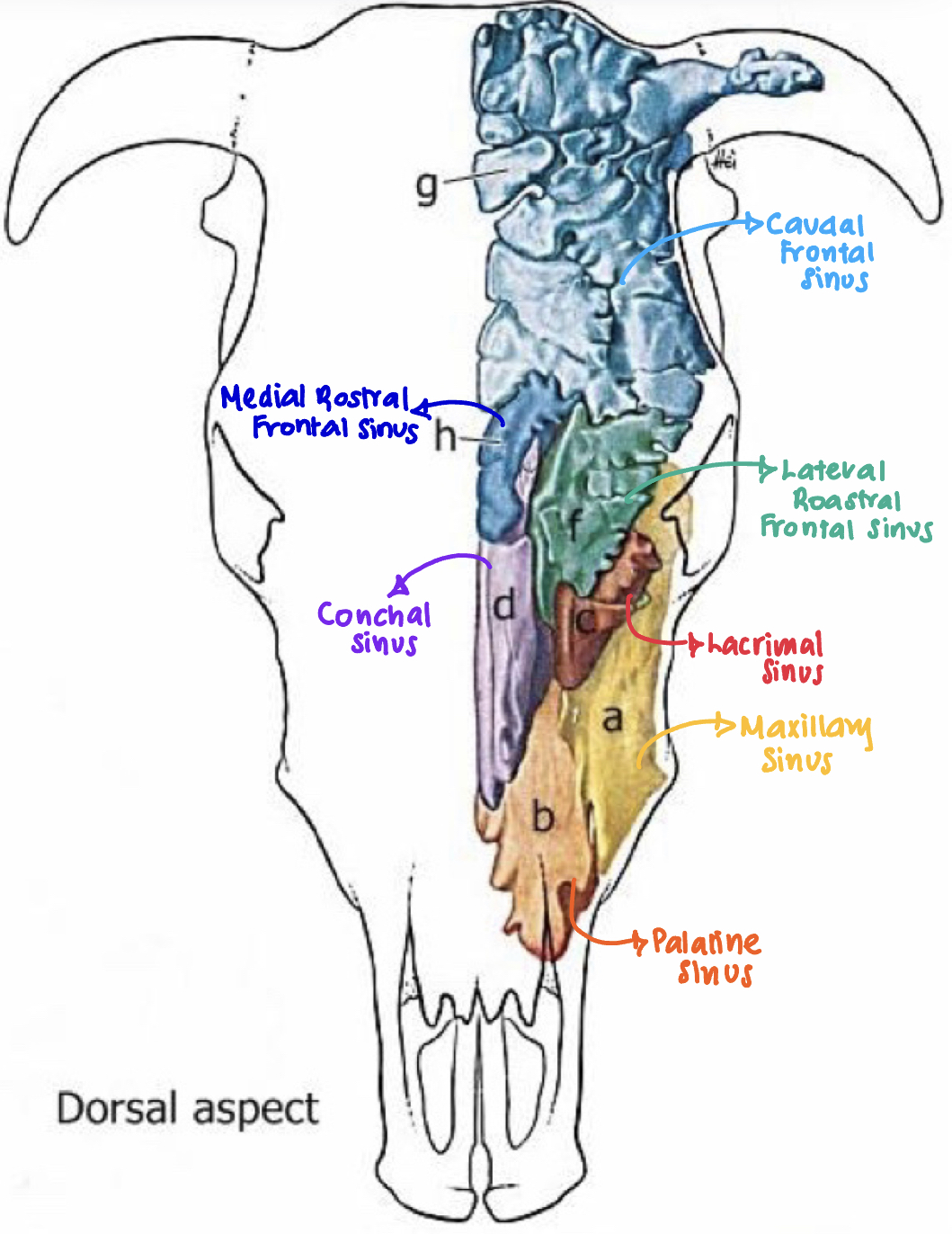
Label the diagram a-h
A: Maxillary sinus #ffd100
B: Palatine sinus
C: Lacrimal sinus
D: Conchal sinus #9000ff
E: Sphenoid sinus #00c52c
F: Lateral rostral frontal sinus
G: Caudal frontal sinus
H: Medial rostral frontal sinus
Pharynx #ffce02
What
Function
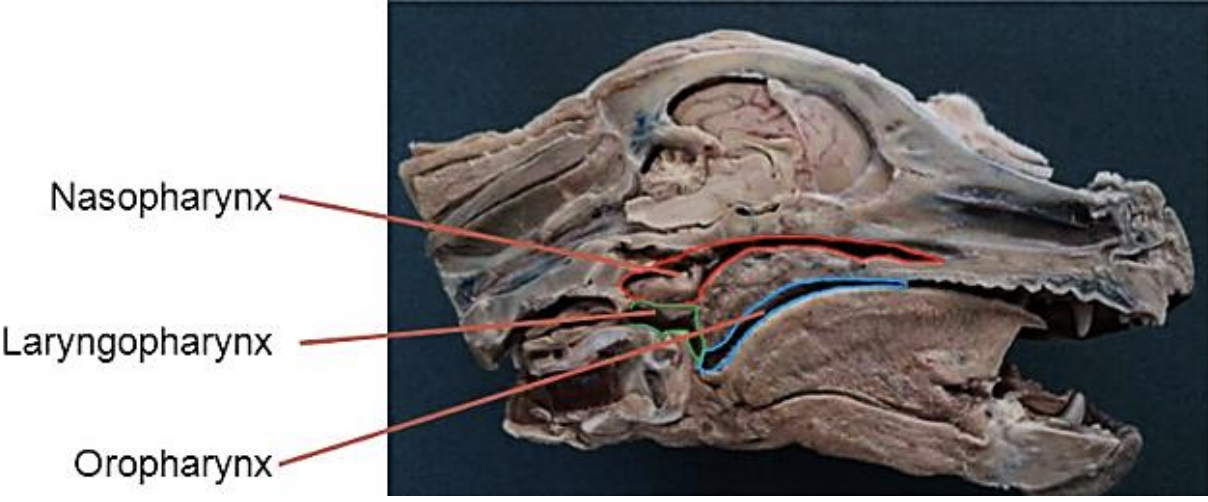
Divide into 3 regions
What: Muscular tube that connects the oral cavity to the trachea and esophagus
Function: Act as a passageway for air and food
Divide into 3 regions:
Nasopharynx
Laryngopharynx
Oropharynx
Pharynx: Nasopharynx #ffce02
Part of
Location
Extends from and to
Passage for
Shape of the roof of nasopharynx
Part of: Respiratory channel
Location: Lies dorsal to the soft palate
Extends: From the choana to the intrapharyngeal opening
Passage for: Air only
Shape of the roof of nasopharynx: Concave
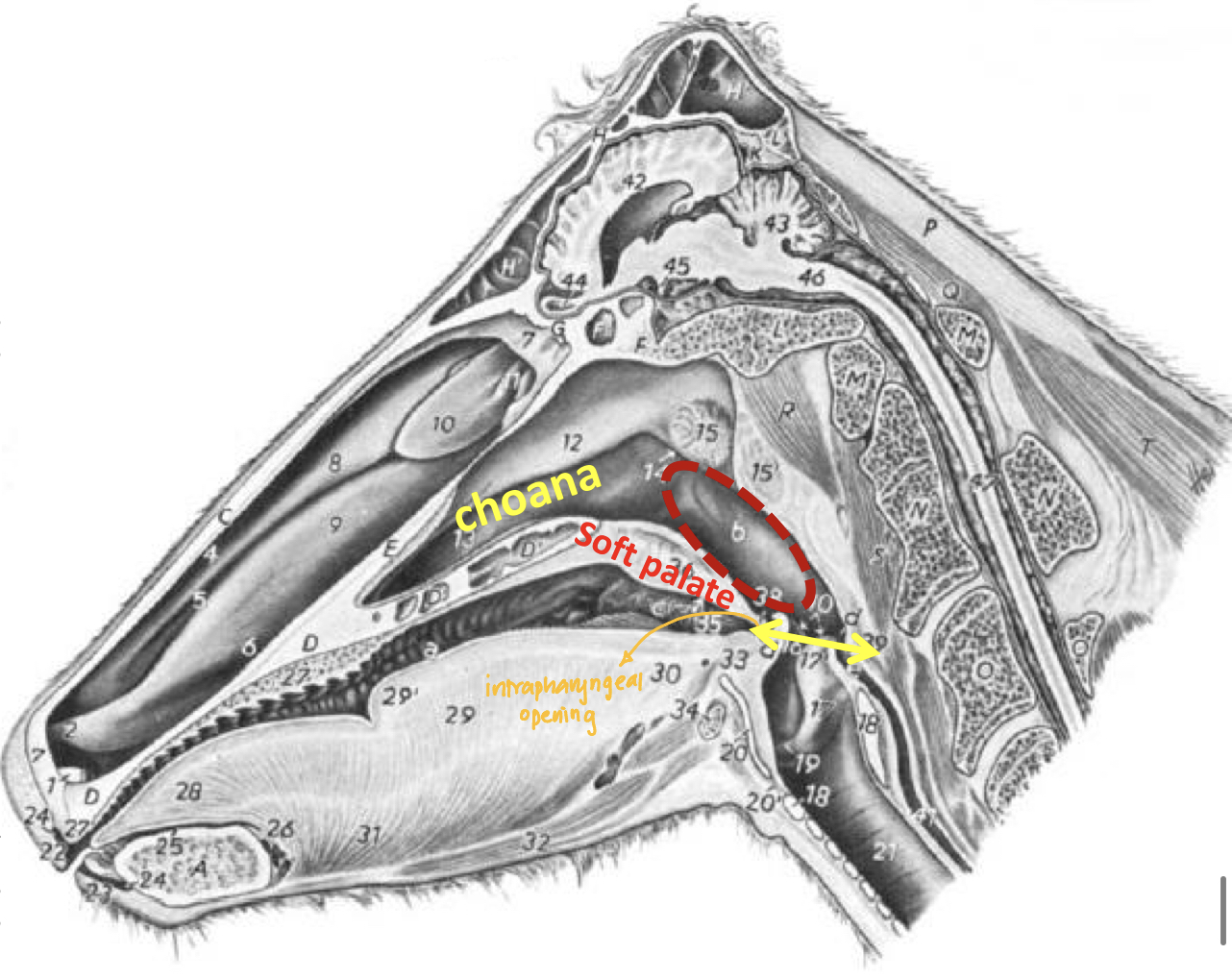
Pharynx: Laryngopharnx #ffce02
Passage for
What
Extends from and to
Becomes continuous with
Passage for: Air and food
What: Caudal continuation of oropharynx
Extends: From the base of epiglottis to the cricoid cartilage of larynx
Becomes continuous with: Esophagus
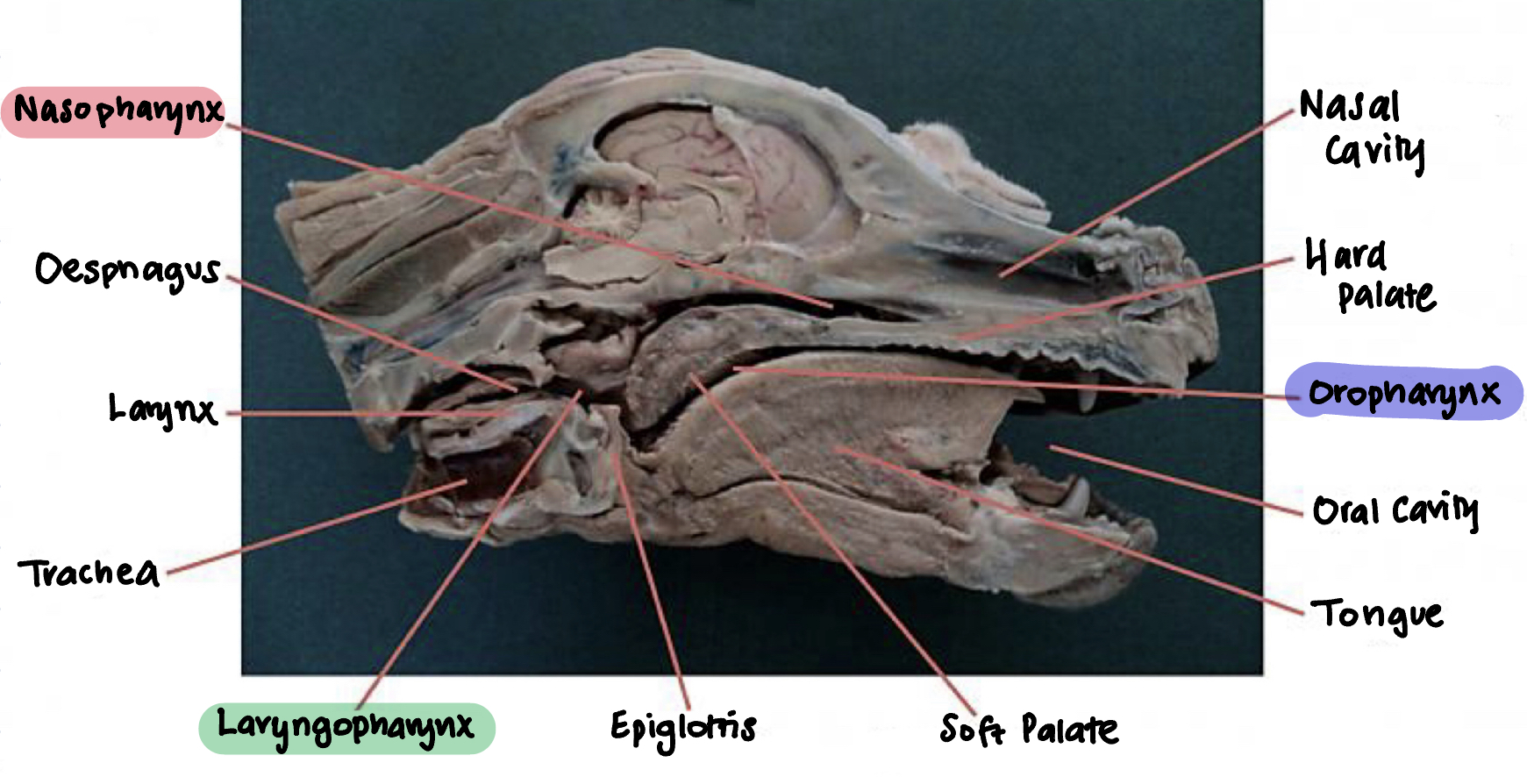
Pharynx:
Label the diagram A-L
A: Nasal cavity
B: Hard palate
C: Oropharynx
D: Oral cavity
E: Tongue
F: Soft palate
G: Epiglotiss
H: Laryngopharynx
I: Trachea
J: Larynx
K: Oesphagus
L: Nasopharynx
Larynx #00b837
What
Connects
Consist of
Lined with
How are the cartilages connected to each other, the hyoid bond and trachea
What are the 4 laryngeal cartilages
What: Short cartilaginous tube
Connects: Pharynx with trachea
Consist of: Several cartilages
Lined with: Mucous membrane (stratified squamous and pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium)
How are the cartilages connected to each other, the hyoid bond and trachea: By ligaments and muscles
4 laryngeal cartilages:
Epiglottic cartilage
Thyroid cartilage
Cricoid cartilage
Arytenoid cartilage (paired)
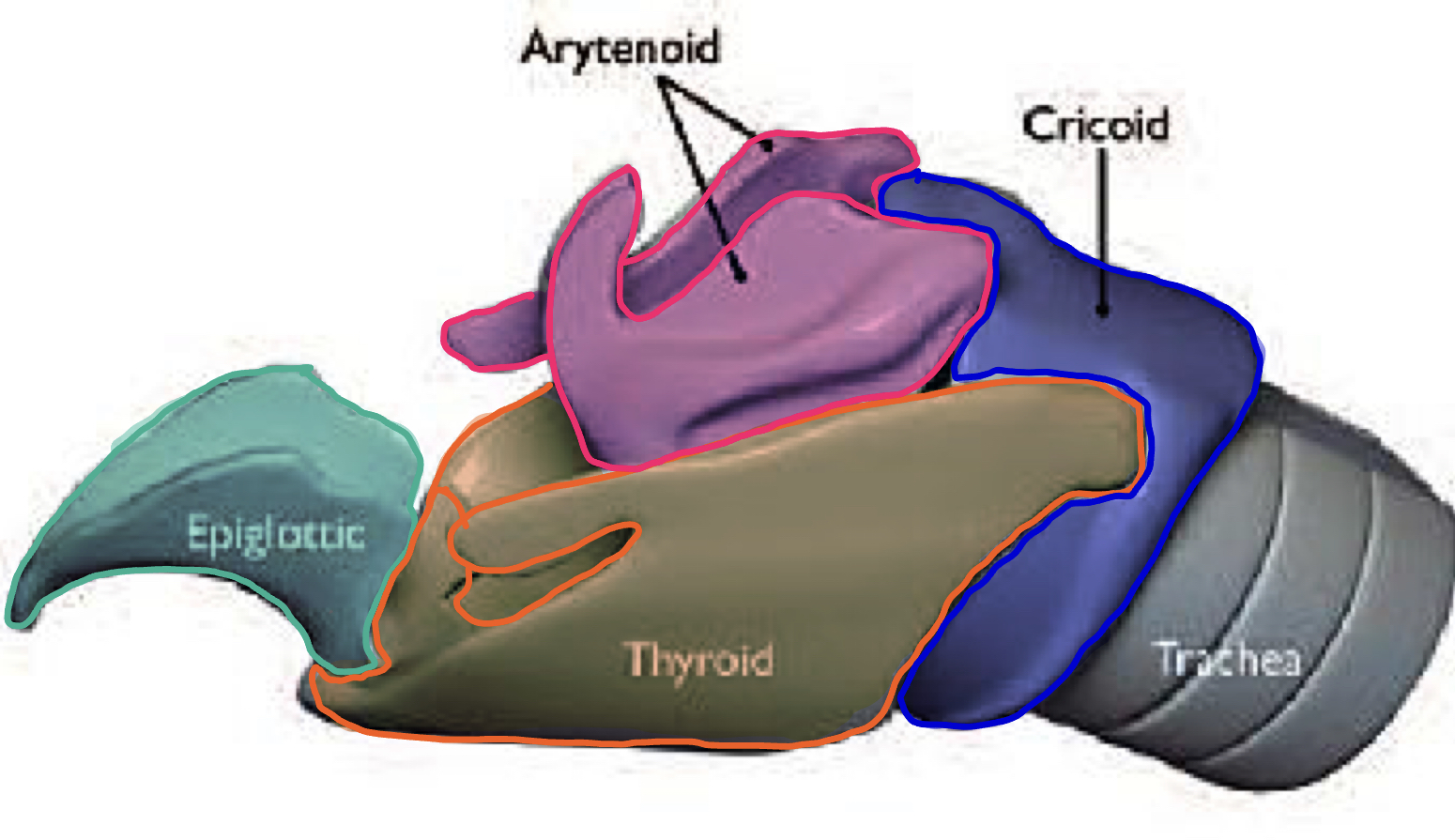
Larynx: Position during Breathing
Which end of the larynx is related to soft palate
During normal breathing, the larynx forms what
What happens to the oropharynx during nasal breathing
Where does the epiglottis project during nasal breathing
Which end of the larynx is related to soft palate: Rostral end
During normal breathing, the larynx forms what: Direct continuation of nasopharynx
What happens to the oropharynx during nasal breathing:
Nasopharynx is dilated
Soft palate lies against roof of tongue causing the oropharynx to close
Where does the epiglottis project during nasal breathing: Through the intrapharyngeal ostium into the nasopharynx
Trachea
Location
Consist of
Connected by
Which allows
Collapsible or non-collapsible
Tracheal cartilages are open
Dorsal surface is connected by
Covered with
Lined with
Location: Extends from the cricoid cartilage of larynx to its bifurcation
Consist of: C-shaped hyaline cartilages
Connected by: Annular ligaments
Which allows: Flexibility
Collapsible or non-collapsible: Non-collapsible
Tracheal cartilages are open: Dorsally
Dorsal surface is connected by: Transverse tracheal muscle
Covered with: Adventitia
Lined with: Mucous membrane
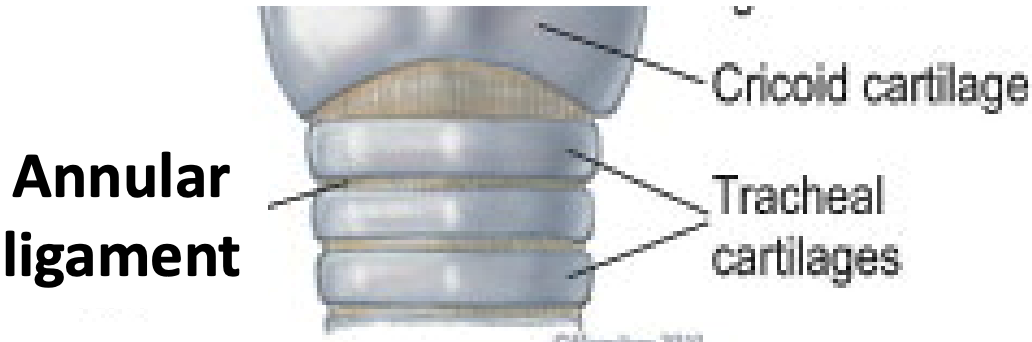
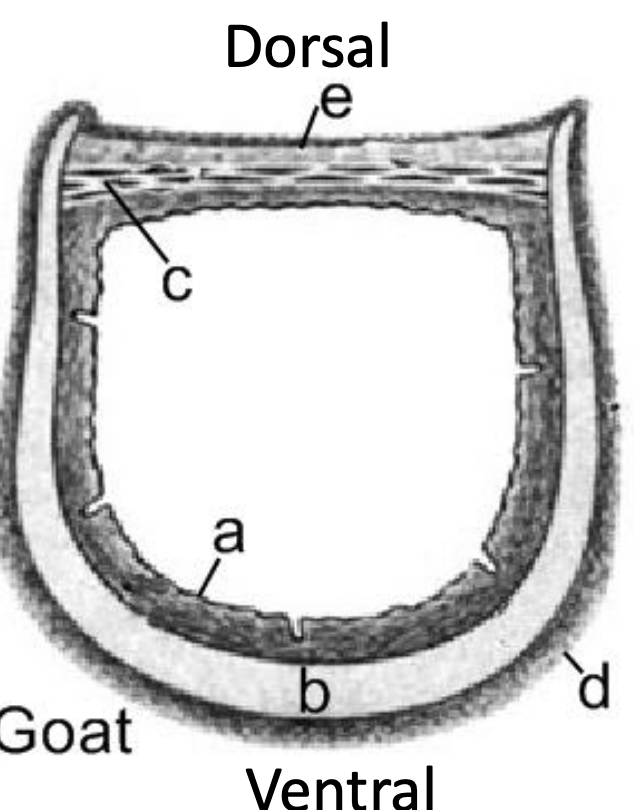
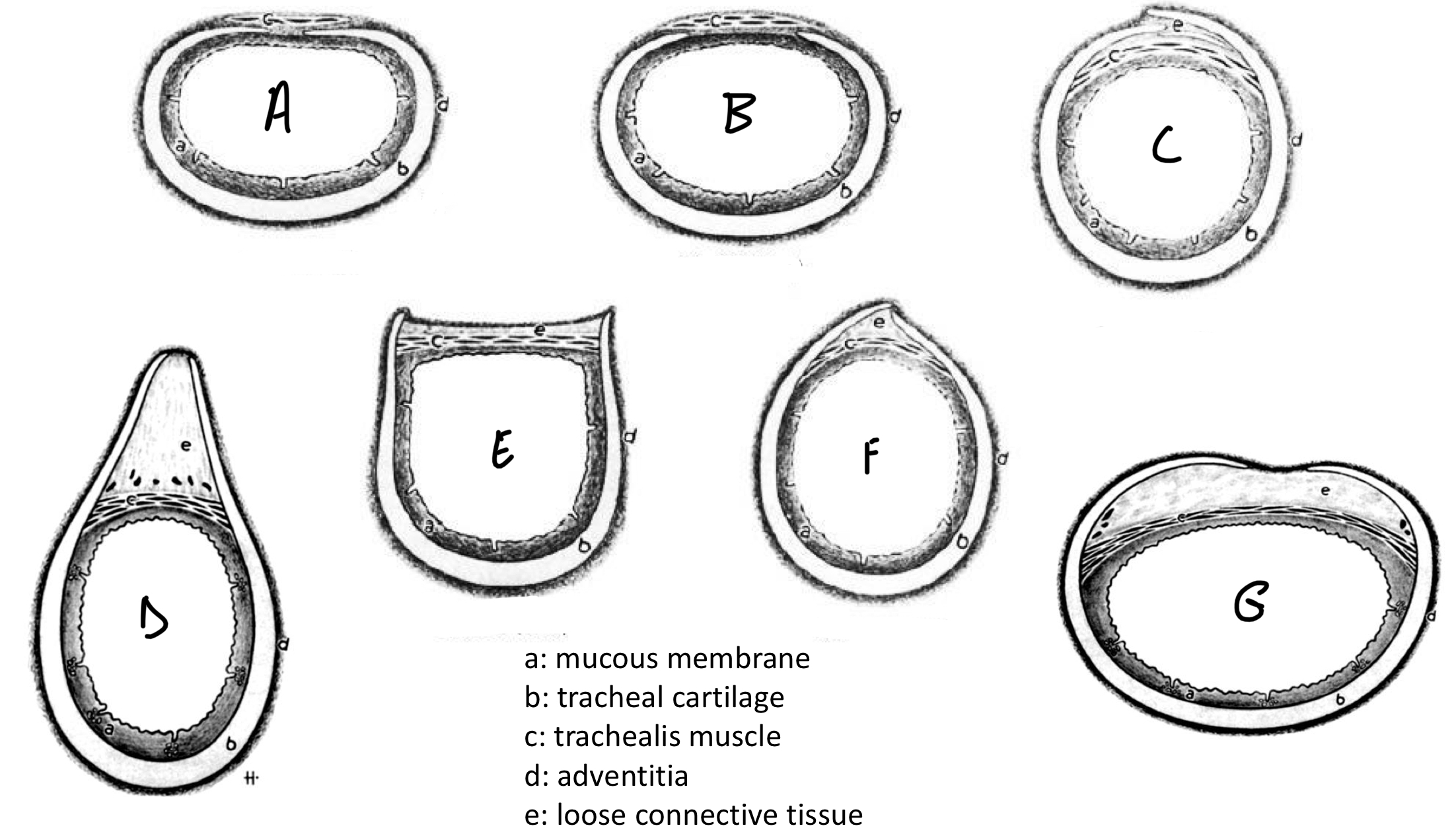
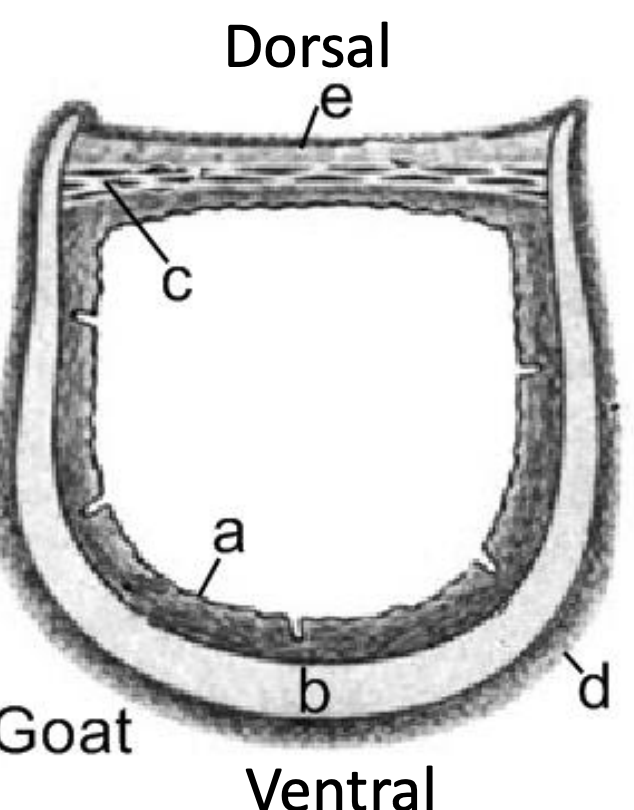
Trachea
Label a-e
A: Mucous membrane
B: Tracheal cartilage
C: Trachealis muscle
D: Adventitia
E: Loose connective tissue
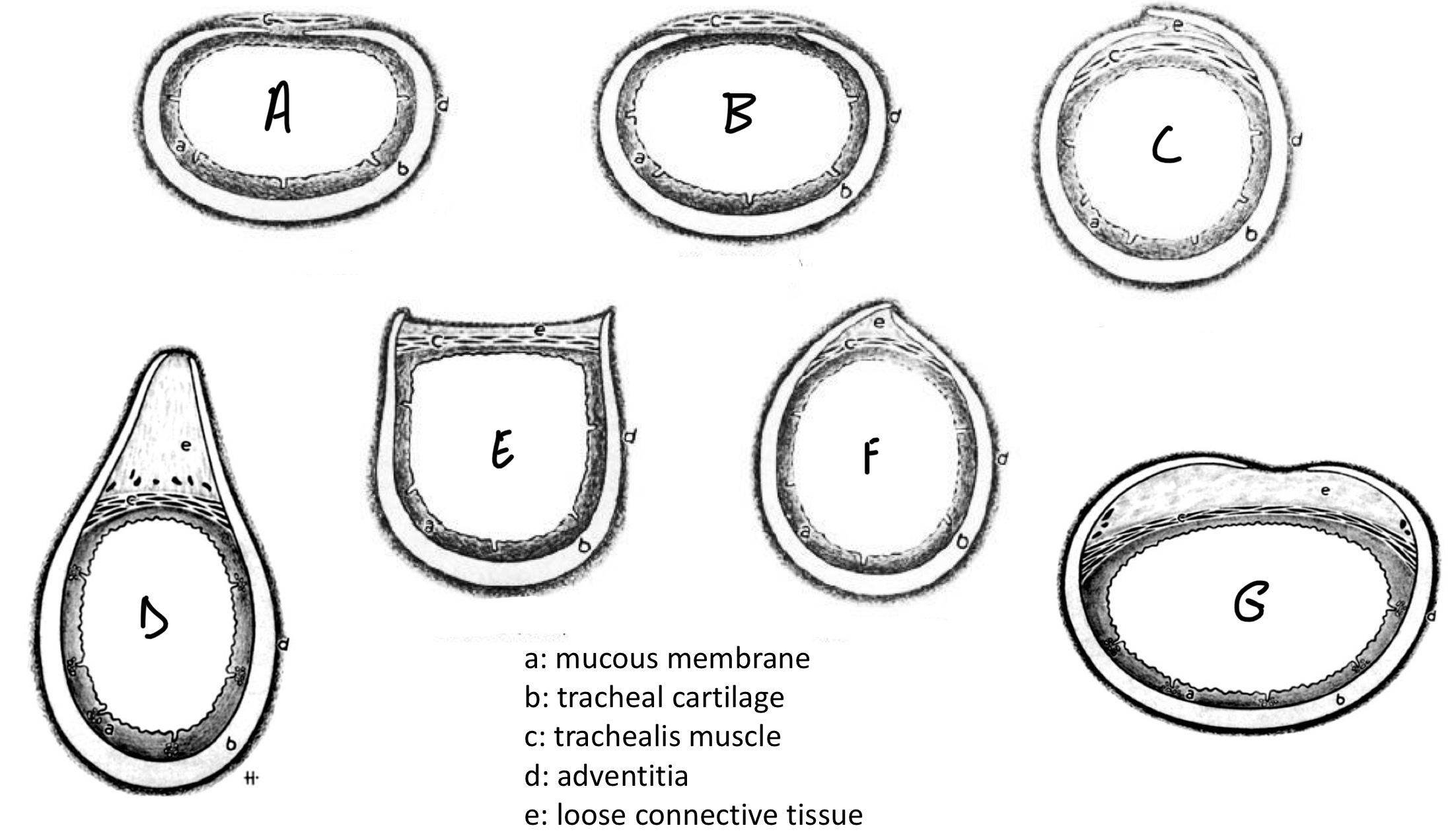
Trachea: Species Differences
Label the species a-g
A: Cat
B: Dog
C: Pig
D: Cattle
E: Goat
F: Sheep
G: Horse