Section B: The Changing Economic World
1/86
Earn XP
Description and Tags
all from megabook
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
1.1: How can different parts of the world be classified according to their level of economic development and quality of life?
HICs have higher gross national incomes than LICs
UK's (HIC) GNI/head is $55k, Brazil (LIC and NEE) US$17k
Quality of life is hard to measure. Involves shelter, safety and access to sufficient food and fresh water
Poorest countries, like in sub-Saharan Africa, quality of life is reduced by lack of sufficient food and fresh water, linked to having lower GNI per head
1.2: List the measurements of development
Gross national income (GNI) per head
Birth and death rate
infant mortality rate
life expectancy
people per doctor
literacy rate
access to safe water
human development index
1.2: Can you explain measures of development?
Gross national income (GNI) per head
Birth and death rate
Gross national income (GNI) per head: total value of goods and services produced by country + money earned from, and paid to, other countries. Per head or capita of the pop. higher = more developed country
Birth rate: number of births in a country, per year per 1k people
Death rate: number of deaths in a country, per year per 1k people
1.2: Why is BR and DR in UK the way it is? Comparing more to less developed countries?
BR 11 DR 10 = natural pop increase because BR is higher than DR
More developed countries, women have to better access to education and pursue a career = more likely to marry later and have less children as a result
Less developed countries, medical care is more basic and more people die from diseases = DR is higher as a result
1.2: Can you explain measures of development?
Infant mortality rate
Life expectancy
Literacy rate
Infant mortality rate: Number of babies who die, per 1,000 live births per year. UK - 4, Brazil - 12
Life expectancy: Average number of years people live to in a country. UK - 80, Brazil - 73
Literacy rate: % who can read and write in a country. UK - 99%, Brazil - 94%
1.2: Can you explain measures of development?
Access to safe water
Human Development Index (HDI)
Access to safe water: % of people with access to safe drinking water in a country. UK - 100%, Brazil - 98%. Nigeria - 70%
Human Development Index (HDI): Combined measure of development, providing a number 0-1 from 3 indicators: Life expectancy, Number of years of education, GNI per head
UK 0.929, Brazil 0.76, Nigeria 0.535
1.3: Can you give some limitations of economic and social measures of development?
Economic measures of development (GNI per head) only give average figure for country, not whole picture. Wealth may be concentrated in a few powerful people. GNI can become out of date
Social measures of development (infant mortality rate) may be unreliable if true level is mis-reported by the country. Some govs are corrupt and report false info
2.1: Can you explain the Demographic Transition Model (DTM)?
purpose
graph to show how changing BR/DR affect country's pop over time. A lot of countries have similar patterns of pop change over time, so Geographers made the DTM to explain this.
Blue line = birth rate
Red line = death rate
Black line = total population
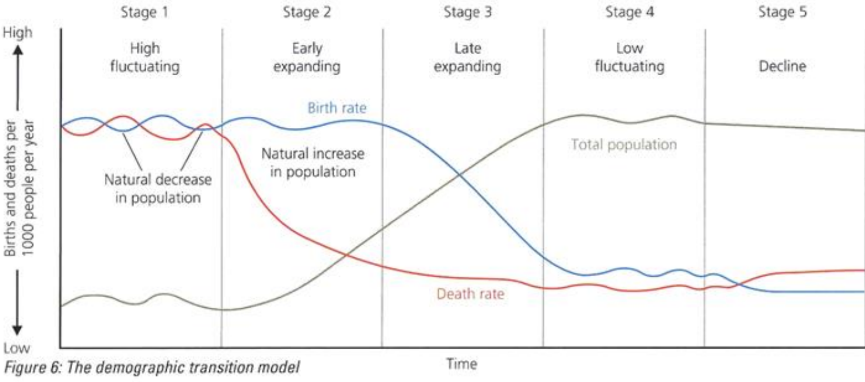
2.2: Can you explain the link between DTM stage and the level of development in a country?
stage 1 e.g
Rainforest tribes. In places like Amazon, small groups like Kayapo Tribe live separately with little contact with outside world. High BR and DR due to lack of contraception and little medical care
2.2: Can you explain the link between DTM stage and the level of development in a country?
stage 2 e.g
Afghanistan. BR is 36, DR 7. 73% live in rural areas, many working on the land. Need children to support them on farms and tending livestock
2.2: Can you explain the link between DTM stage and the level of development in a country?
stage 3 e.g
Brazil. BR fairly high (13) but is an NEE (newly emerging economy) experiencing economic growth
BR is falling as 87% live in urban areas like Rio and Sao Paulo where there’s good access to contraception. DR - 8
2.2: Can you explain the link between DTM stage and the level of development in a country?
stage 4 e.g
UK. Good quality health care = DR low (10). Women have small families, study and follow careers before having family = low BR (11)
BR slightly higher than death rate, = small rate of natural pop growth
Also boosted by immigration
2.2: Can you explain the link between DTM stage and the level of development in a country?
stage 5 e.g
Germany - well developed, population decline as DR exceeds BR. BR (9), one of lowest in world. Many women have careers and delay children, and have only 1 or 2 if they do start a family.
Ageing pop, DR (12) is set to rise
3.1: Can you explain some physical causes of uneven development?
Tough farming conditions: difficult for subsistence farmers to grow food to survive from poor soils or insufficient rain (aims to grow enough for family)
Natural resource availability: abundance of natural resources, Saudi Arabia -largest stocks of oil. Other countries have few
Natural disasters and extreme weather: Tropical storms, floods, droughts, earthquakes hold development as damage repair is costly
Climate-related disease: Tropical Africa, South America and Asia have more of these and pests than cooler parts. Mosquitos spread malaria, disease that stops people from work
Landlocked countries: only bordered by land, no access to seas, cut off from ocean trade (important for economic growth). Africa has the most
3.1: Can you explain some economical causes of uneven development?
Unfair trade: North America, Europe dominate world trade. Asia trading importance grows due to China, India. Mostly between rich countries. Pay little as possible for raw materials/minerals, many from LICs. More supply than demand = low prices. TNCs hold unfair power in trade. Many NEEs (Brazil) are developing manufacturing industries to boost export earnings
Few crops: Poor countries rely on selling 1 or 2 cash crops (or primary products) to others, like bananas, cocoa beans and coffee beans. Risky as prices fluctuate and yields can be low.
3.1: Can you explain some historical causes of uneven development?
Colonisation: forced taking over of another country for its people and/or resources. Started 1400, European explorers set to control new territories, seeking mineral wealth (gold)
1650-1900, 10+ mill transported from Africa to N.America, work as slaves on plantations. Almost all wealth produced went to European powers
End of 19th century Africa and parts of S.America and Asia, divided up between European superpowers
Countries like UK, Germany, Spain and France had powerful empires and colonies.
Since 1950 former European colonies have gained independence.
3.2: Can you explain consequences of uneven development?
Disparities in wealth and health: most developed countries = greatest wealth. 2014 fastest growth was in N.America, holds 35% of total global wealth and is the most important 'economic engine of growth'
Africa holds 1%. LICs are unable to invest in good-quality health care = Malaria/ other infectious diseases more common =More children under 15 die
International migration: move from one country to another to improve quality of their life.
Last few years hundreds of thousands of refugees fled home in Syria, Afghanistan and Iraq for a better life in Europe. Germany, Italy, France and UK have long histories of receiving them
4.1: Can you explain investment to reduce the development gap?
Many TNCs and countries invest money/expertise in LICs to boost their profits. (China and USA have several business and trading links with Africa)
China is Africa’s most important trading partner. 2k+ Chinese companies invested in energy, mining, construction and manufacturing
Led to new roads, bridges, stadiums and other projects all over Africa. Helped build biggest shopping mall in sub-Saharan Africa (Nairobi, capital of Kenya), and train lines across east Africa.
End of 2018, invested $60 bill
Many benefits, but maybe exploiting resources to benefit China's own economy OR aiming to shift its labour-intensive industries to Africa
4.1: Can you explain industrial development to reduce the development gap?
building factories = employment, higher incomes and opportunities to invest in housing, education and infrastructure.
Countries like Brazil focussed on industrial development, like automotive industry, to boost overall development level. Investment and industrial development can bring about multiplier effect
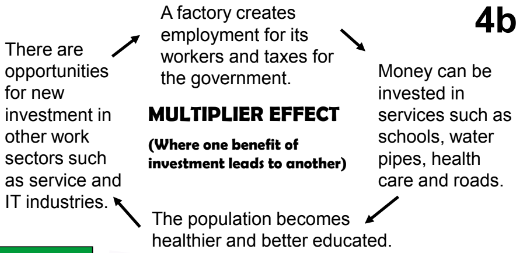
4.1: Can you explain aid to reduce the development gap?
Country or NGO (oxfam) donates resources to country to develop or improve lives. E.g Money, emergency supplies (tent), tech (tools) and skills (special skills like doctors and engineers)
Lets countries invest in development projects like roads, electricity and water management = long-term benefits
4.1: Types of Aid
Short-term aid: emergency response, e.g natural disaster
Long-term aid: improve quality of life over time, e.g helping build schools, improving water supplies, help with farming
Tied aid: money given with conditions, e.g recipient must spend it on donor countries products
Bilateral aid: from one country to another, often tied
Multilateral aid: involving several countries. Richer govs give money to international organisation like United Nations or World Bank, which help poorer countries
Voluntary aid: money donated by general public, usually in richer countries, then donated by NGOs like Oxfam
4.1: Aid from the UK
UK gov, target every year to give 0.7% of GNI as foreign aid
2015, £2 bill. 40%+ of budget went to multilateral organisations, like UN, who fund disaster relief
Remaining 60% directly to developing countries
UK's Department for International Development says biggest regional beneficiary is Africa, £2.54bn in 2016.
Ethiopia, Sierra Leone, South Sudan and Syria, each given £200m+.
Pakistan £374m 2015, more than any of the country. Mainly went to social welfare, education and healthcare
Syria £258m 2015 to support "humanitarian and development responses to conflict"
4.1: Goat aid from oxfam
Project to help families in Africa e.g Malawi. Money donated is used to buy a family a goat
Food, milk, butter and meat source, manure = crop fertiliser
Milk sold as income to pay for food and education
Goats bred easily and kids sold at market or given to other families
Improves quality of life and raises development
4.1: Can you explain intermediate technology to reduce the development gap?
Small-scale, sustainable aid projects suitable for needs and skills of a local pop in a LIC
Involves agriculture (farming), water or health
Ethiopia - dam project helped village of Adis Nifas. 15m high built to make reservoir close to farming fields.
Appropriate machinery provided by NGO and villagers provided labour.
Local stone and sand used to build. Water from reservoir used to irrigate (water) farm crops = therefore boost local food supplies.
4.1: Can you explain fair trade to reduce the development gap?
International movement - Fair Trade logo = farmer in LIC gets more money from sale of their crops
Improves quality of life for ordinary farmers that will have money to spend on housing and education for their kids.
In return must farm in environmentally-friendly ways.
Common products are bananas, coffee beans, tea bags, and chocolate bars from cocoa beans
4.1: Can you explain debt relief to reduce the development gap?
Many of poorest countries built up debts to rich ones since 70s. Money was borrowed to develop industry and infrastructure
Led to debt crisis with worst affected countries called HIPCs (highly indebted poor countries). Most in Africa
2005, G8 group of world's richest countries cancelled debts if the poorer spent saved debt money on education and health care projects
Despite this, African countries still have debts of over $300 bill
4.1: Can you explain microfinance loans to reduce the development gap?
Microfinance = small-scale loans from banks to help poor communities
Let individuals/families start small business, and be self-sufficient.
Many borrowers are women. E.g, Grameen Bank in Bangladesh lends $200 to village women to buy a phone.
Villagers pay to use phones. Loan is repaid and borrower make small profit.
Phones help people check prices before taking crops to market, keep in touch with relatives that moved to the city, and receive health advice
4.2: CASE STUDY: Can you give details on how the growth of tourism in Jamaica, a LIC, helps to reduce the development gap?
Island in Caribbean. Pop 2.8 mill. Sunny. Tourists visit Kingston (capital) in SE. Famous beaches; Montego Bay and Ocho Rios on N coast, Negril on W coast.
Birth place of reggae music legend Bob Marley in 'Nine Mile' near centre. Bob Marley museum in Kingston.
Near Ocho Rios, popular attraction Dunn's River Falls waterfall, and Mystic Mountain forest has a bobsled ride.
Tourism is 30% of GDP (per capita $6k), provides 1/3 of jobs = reduces development gap towards being a HIC. Other industries: mining, crops (sugar), making rum
3.3 million tourists 2022, 1+ mil from cruise ships, earned $3.7 bill, they spent $130/day on average.
Multiplier effect: Gov has more tax revenue’s for schools, hospitals, and key infrastructure like roads
People have more money to improve quality of life. Most development on north coast, wealthy Jamaicans enjoy high living standard.
4.2: CASE STUDY: Issues and solutions in Jamaica?
Many live in low-quality housing + Mass tourism led to environmental problems
New water treatment plant at Logwood in west reduces waste water pollution from hotels heading into sea.
Negril Marine Nature Park maintains biodiversity
Small-scale 'ecotourism' guest houses, employing local guides, promote low-impact ecotourism and provide more income for locals.
5.1: Brazil is a LIC and NEE. Can you explain the location and importance of Brazil regionally and globally?
5th biggest country and biggest country in South America. Capital is Brasilia.
South America has 12 countries, Brazil shares border with 10.
Brazil’s Eastern coastline is next to Atlantic Ocean.
Sao Paulo is most populous city in western and Southern Hemisphere and largest Portuguese-speaking city in world. 12 mill = megacity
Rio de Janeiro - second largest city in Brazil, 7 mill.
Brazil hosted men’s FIFA World Cup 2014 and 1950, has won 5 times, more than any country. Brazil is only team to have played in every event since it started in 1930.
Brazil hosted Summer Olympics 2016.
Amazon Rainforest is largest in world at 5,500,000 square km. 60% in Brazil
5.2: Can you explain the wider political context within which Brazil is placed?
South America's most influential country, rising economic power and one of the biggest democracies. BRICS (Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa), group of 5 major emerging national economies.
5.2: Can you explain the wider social context within which Brazil is placed?
Large population of 215 mill = fifth most populated country. Portuguese language as Portugal colonised Brazil 1500. Diverse pop, indigenous Americans and descendants of African slaves and European settlers. Last few years it made strides in efforts to raise mills out of poverty, although gap between rich/poor remains wide.
5.2: Can you explain the wider cultural context within which Brazil is placed?
World's most successful country at FIFA World Cup. Rio Carnival is the biggest street carnival, 2 million people per day for 6 days every year in Feb or March. 2012, Rio was named a World Heritage Site by Unesco for its blend of urban, coastal and mountainous landscapes.
5.2: Can you explain the wider environmental context within which Brazil is placed?
Exploitation of Amazon is a concern as this vast it absorbs CO2. "The Lungs of the Earth". Helps with 2015 Paris Agreement on climate change to try ensure global warming doesn’t increase over 2C since 1850 (pre-industrial times)
5.3: Different sectors and definitions, % in UK from AQA Textbook
Primary (2%) - taking things from land and sea. E.g. farmer, forest worker, fisherman
Secondary (15%) - manufacturing or building things, often using raw materials from primary sector. E.g: furniture, cars.
Tertiary (74%) - providing a service for others. E.g: teacher, dentist, hairdresser
Quaternary (9%) - high-level research. E.g: new medicines and tech
5.3: Can you explain the changing balance between different sectors of the economy in Brazil? (the changing industrial structure)
Brazil %
Primary (10%) - Agriculture historically key part of economy. Largest exporter of coffee, soya beans, beef and crop-based ethanol
Secondary (21%) - Diverse manufacturing industries; automobiles, steel, petrochemicals, computers, aircraft. VolksWagen - German TNC makes cars
Tertiary (60%) - Sao Paolo known for banking, considered financial capital of Brazil. Brazil is a major tourist destination -2017, 6.6 mill = 5th most popular country to visit in the Americas after USA, Mexico, Canada and Argentina.
Quaternary (no data) - Oil TNC Petrobras has HQ in Rio. Extracting oil from under sea is a primary industry, but researching the tech behind this is a high-tech quaternary industry.
THIS MEANS THAT: Fewer doing primary, more doing tertiary, compared to past. Both Brazil and UK, more than half pop has tertiary job
6.1: How has manufacturing stimulated economic development in Brazil?
21% jobs are in secondary sector, making products in factories
7th largest automotive producer and regional leader in S.America
Vehicle TNCs take advantage of large labour force, available space for factories, and good transport links to import parts and export vehicles via Atlantic Ocean ports
215 mill = large local market to sell cars to (biggest pop of SA)
South America has an estimated pop 420 mill = large regional market for car sales
Car TNCs manufacturing in Brazil are VW and Toyota. 2016, 2+ mill vehicles produced.
Most cars for Brazilian market run on petrol or ethanol fuel made from fermented sugar cane ('flex' cars)
6.1: How has manufacturing stimulated economic development in Brazil?
THIS MEANS THAT...
Economic development is stimulated because manufacturing provides tens of thousands of jobs.
Workers spend wages = trickle-down effect, spreading money through the Brazilian economy.
Sales taxes are taken by the gov, as it has more money it can spend more on schools, hospitals and infrastructure projects like roads, water pipes and power stations.
6.2: TNC (Trans national companies) definition
Large corporation or company which operates in several countries.
Usually has headquarters in 1 country with production plants in several others
Locate in foreign countries to take advantages of factors like: cheaper labour, access to a wider market, tax incentives.
6.2: What is the role of transnational corporations (TNCs) in relation to industrial development in Brazil?
2 e.g
Vale:
Mining company, HQ in Rio, one of biggest producers of iron ore, used to make steel.
Operates Carajas iron ore mine in Amazonia = deforestation of Amazon
Although primary operations are in Brazil, has operations in 30 countries.
Brazilian TNC = much of money earned abroad can return to Brazil. Profitable as there’s great worldwide demand for iron to make steel
Petrobras:
Brazilian TNC - oil and natural gas industry. HQ in Rio.
Controls significant oil and energy reserves in 16 countries in Africa, N+S.America, Europe, and Asia.
Brazil represented 92% of Petrobras worldwide production in 2014
Employs 68k and is partly owned by Brazilian gov. Profitable as there’s great worldwide demand for oil
6.3: What are the advantages of foreign TNCs operating in Brazil as the host country?
Employment, develop new skills among pop
More people employed = more money spent in economy = more tax revenue for gov = gov can invest in more schools, hospitals, better infrastructure like roads, bridges, railways and power stations.
Case of VW, majority cars are sold in Brazil
Other local companies benefit from more money in economy
Valuable export revenues earned by host country
6.3: What are the disadvantages of foreign TNCs operating in Brazil as the host country?
Management jobs often go to foreign employees brought in by the TNC
Much of profit may go abroad to TNC's home country
Local workers poorly paid and perhaps exploited
Working conditions may be hard
Work may be tedious, e.g working on an assembly line
6.3: VW in Brazil
Volkswagen first looked to produce vehicles outside home nation after WW2
German TNC chose automotive hub around Sao Paulo
1959 first VW factory built, Anchieta. Today, remains biggest car factory in Brazil, 1.6 mill square metres. VW's biggest factory outside Germany.
Site is close to Port of Santos, to ship in parts. Steady supply of technical staff from local uns.
12k staff can produce 1.6k cars/day on the current 3 shifts - Produces several models including Polo
made 20+ mill vehicles, 3 mill of which have been exported, this output driven by production at Anchieta
7.1: What are the changing political relationships between Brazil and the wider world?
Inter-gov relations:
BRICS countries, economy of growing importance. Significant natural resources, and large pop (215 mill), = continued economic development, 9th largest GDP (UN data)
Founding member of UN, among top 20 contributors to its peacekeeping operations, and likely to remain key figure.
Member of G20 - annual meeting of govs from 19 countries, EU and AU, the largest advanced and emerging economies. Discusses policies to promote international financial stability
7.1: What are the changing trading relationships between Brazil and the wider world?
Top exporter of beef, oranges and orange juice = profitable trading relationship with world.
Exports growing - 2017, value $6.2 bill, 1.3 million tonnes of beef to Hong Kong, China, EU, Iran and Egypt
Sao Paulo - largest exporter of beef, several cattle ranches in Amazonia on deforested land
World's pop 9 bill 2050 = rising demand for food. Brazil's meatpackers see opportunity to keep exports growing and be one of the biggest food producers
1/3 oranges in the world is grown in a relatively small area in states of Sao Paulo and Minas Gerais
95% produce shipped abroad, mainly orange juice
Brazil relies on external markets but exchange rate of real (R$) fluctuates = orange juice price go up/down
Farmers concerned that orange juice demand is falling, in Europe many prefer drinks with less natural sugar
7.2: What types of international aid does Brazil benefit from and what are the impacts on Brazil as the receiving country?
Bilateral aid from UK, 2017 gave €80 mill - Surprising as Brazil has 9th largest GDP
Chancellor Philip Hammond (Conservative) said money was to reduce poverty (favelas), and boost economic development
Also benefit’s UK as it leads to more trade and investment between them
Critics said it's wrong to give aid to richer developing countries like Brazil
7.3: Can you explain some environmental impacts of economic development in Brazil?
deforestation
Deforestation of Amazon hit highest rate in decade, from official data
7,900 square km of largest rainforest destroyed August 2017-July 2018. 5x London
Other reports suggest rate of deforestation is slowing compared to past, thanks to environment agency 'forest police' Ibama
Top cause of deforestation remains cattle ranching for beef
7.3: Can you explain some environmental impacts of economic development in Brazil?
HEP
Belo Monte hydro-electric power dam is latest to be built in Amazon, one of the biggest civil engineering projects, $18bn
When 18 turbines are fully operational, electricity-generating capacity will make it fourth largest dam
Tribal groups and river dwellers against it
Brazil's huge rivers = potential for 100 more HEP dam projects
7.3: Can you explain some environmental impacts of economic development in Brazil?
Mining
Mines in Brazil cater for growing demand for metals like steel = huge amounts of toxic waste produced
Cheapest way to dispose is dumping-grounds, sealed with dam
Jan 2019, one dam collapsed - hundreds dead and missing in Brumadinho town
7.3: Can you explain some environmental impacts of economic development in Brazil?
Air pollution
Cubatao (city in Sao Paulo state) had some of the worst air pollution from over 20 heavy industries
Acid rain caused locals to have skin complaints
Situation improved thanks to better filters on factory emissions
Air quality remains poor - Sao Paulo and Rio due high traffic levels
7.3: Can you explain some environmental impacts of economic development in Brazil?
Urban air and water pollution
Rio hosted 2016 Olympic Games = attention to severe water pollution in Guanabara Bay
Water teeming with dangerous viruses/bacteria, threatening athletes (sailors)
Rio - image of rich, beautiful, but crowded hospitals show nightmare of its sanitation for people who live with urban pollution every day
1/3 of 10+ mill inhabitants of greater metropolitan area live in places with no connection to sewage system
Half of city's waste is treated before entering waterways and eventually ocean
Many rivers flowing through Rio's urban areas into Guanabara Bay were found biologically dead by scientists years ago and tonnes of raw sewage pour into sea every day
7.4: Can you explain the effects of economic development on quality of life in Brazil?
inequalities in cities and amazon rainforest
Great inequalities in society - Millions in crowded favelas, leads to high crime rate in cities like Sao Paulo
Sao Paulo 400+ private helicopters transport super-rich people above the congestion below
Ka'apor tribe live under siege from illegal loggers in Amazon - Confrontations led to deaths of 6 tribe members since 2008
7.4: Is Brazil a developed country - arguements?
Largest economy in S.America (bigger than Argentina) and any countries in Central America (Mexico)
GDP is $1.9 trillion. Life expectancy 73
But…
GDP per capita ($9k) fairly low, less than $12k threshold to be HIC
Low living standards for many in thousands of favelas
High infant mortality rate (lack of access to clean water and health care for many)
Life expectancy less than 80, the HIC avg
8.1: What are the current employment sector percentages in the UK?
UK e.g of all sectors
Primary (2%) - Extracting crude oil, natural gas from North Sea, Crop farming, Livestock, Fishing in North Sea, English Channel and Atlantic Ocean, Timber extraction at Kielder Forest (man-made in England)
Secondary (15%) - mini car (owned by BMW) made at Cowley, near Oxford. Nissan has major factory in Sunderland, N England. Swiss TNC Nestle Kit-Kats at York factory
Tertiary (74%) - Selling in shops (Westfield), Banking (Square Mile), Teacher, dentist, hairdresser
Quaternary (9%) - Uni of Cambridge/Southampton Science Park. One of top countries for:
Aerospace: research, design, manufacturing of air/spacecraft. British TNC, BAE Systems is key player
Pharmaceuticals: medical drugs
8.1: Factories in the UK decreasing?
Many factories closed due to more products being made overseas
We import most clothes and textiles = largely “post-industrial landscape”
Manufacturing that left UK was labour-intensive - needed lots of people, so wage bills were high
8.2: Can you list causes of economic change in the UK?
De-industrialisation and the decline of traditional industrial base
Globalisation
Government policies
8.2: Can you explain these causes of economic change in the UK?
De-industrialisation and the decline of traditional industrial base
For decades, UK de-industrialisation = decline in manufacturing (secondary) industry and subsequent growth in services (tertiary) and research (quaternary) employment
Machines and robots replaced people in modern industries, like car production.
LICs like China and Indonesia produce goods cheaper as labour is cheap
Many think there’s a lack of investment in manufacturing UK
Coal mining, engineering, manufacturing have declined
UK is now a world centre for financial services, media, research and creative industries like fashion design, architecture and performing arts
8.2: Can you explain these causes of economic change in the UK?
Globalisation
Globalisation means how world has become more interconnected
Boosted by developments in transport (planes, container ships) and communications (internet)
Boosted world trade, easier to import goods from abroad = contributed to decline in UK manufacturing
Helped the quaternary (research) sector to grow in UK, many people working on global brands and products
8.2: Can you explain these causes of economic change in the UK?
Gov policies
45-79: Gov money helped unprofitable industries continue. Government created state-run industries (British Steel Corporation, National Coal Board, British Rail)
79-2010: State-run industries sold off to private shareholders = “privatisation”. Many older industries lost jobs (coal mining). New private companies brought change, e.g London Docklands transformed into Canary Wharf business district
2010+: Gov aiming to rebalance economy so there’s less focus on services and more manufacturing again
8.3: List how is the UK moving towards a post-industrial economy? What is a post-industrial economy?
Information technology development
Service industries
Finance
Research
Post-industrial economy - manufacturing (secondary) industry declined and replaced by growth in services (tertiary) and research (quaternary) sector. Happened in UK from 70s - UK 74% work in tertiary
8.3: List how is the UK moving towards a post-industrial economy?
Information technology development
1.3+ mill work in IT
UK is one of top leading digital economies, as people work with high-speed broadband connections
IT jobs - computer software design, phone app development
Internet access allows many to work from home
8.3: List how is the UK moving towards a post-industrial economy?
Service industry
Individuals in tertiary sector provide services
Sector grown rapidly since 70s
Makes 79% of UK economic output compared to 46% in 48’
8.3: List how is the UK moving towards a post-industrial economy?
Finance
Finance and banking are important parts of services sector
UK is top leading country for financial services (accounting, banking, insurance)
Key centre in “Square Mile”
Financial services sector is 10% of UK's GNI, employs 2+ mill
8.3: List how is the UK moving towards a post-industrial economy?
Research
Quaternary, 60k+ highly-skilled people, estimated $3+ bill to UK economy, likely area of continued growth
Done by British unis (Cambridge, Manchester, Southampton)
Organisations: Pharmaceutical companies, Cancer Research UK, Ministry of Defence, British Antarctic Survey (BAS)
BAS, 500+ highly-skilled people based in Cambridge
Researchers live on bases in polar regions (Halley Station, Antarctica)
Halley Station can be moved around Antarctica to stay on stable ice
Areas of research are; effects of climate change, like sea level rise
What is a science and business park? Give examples
Science park: group of scientific and technical knowledge-based businesses on a single site (quaternary sector). 100+ in UK, about 75k working in them. Most are linked to unis
University of Southampton Science Park
Business park: Area where several businesses cluster together. Often on edge of urban area where land is cheaper and better access to main roads
Cobalt Business Park, Newcastle-upon-Tyne
8.4: Facts about University of Southampton Science Park
100 science and innovation businesses, use high-speed broadband internet
Close to M3 and Southampton International Airport. Near the Uni = research facilities and graduates to employ
Attractive landscaped location, green areas and woodland. Helps with 'blue sky' thinking in their research
Fibrecore makes optical fibres, many uses (computer networking). PhotonStar makes high-tech lightning products
8.4: Facts about Cobalt Business Park, Newcastle-upon-Tyne
Biggest in UK. Has offices, retail outlets, fitness centre and cycle paths
NE England has suffered from economic decline as traditional businesses closed down, so businesses here qualify for gov assistance
Newcastle pop of 300k = large local workforce
Close to main A1 road and 20 mins from Newcastle International Airport
Businesses: Santander, IBM, Siemens, Proctor & Gamble
9.1: Can you give examples of how UK industry impacts on the physical environment?
Mining operations lead to huge waste tips piling up on edges of mining settlements
UK has several quarries - sites for extracting rocks and gravel for the building industry, that cut chasms (huge holes) into countryside landscape
Waste products from manufacturing are added to landfill sites which can pollute ground water and soil
9.2: Can you explain examples of how modern industrial development in the UK can be more environmentally sustainable?
Tech can reduce harmful emissions from heavy industry and power stations
E.g, projects in process to capture CO2 from coal power stations = reduce greenhouse gas emissions
Desulphurisation removes harmful gases (sulphur dioxide) from power station chimneys
Heavy fines issued when industrial pollution incidents happen
Careful design can reduce visual impact of industries
9.2: CASE STUDY: Torr Quarry is an example of a modern industrial development aiming to be more environmental sustainable
Key facts
In Somerset, Limestone quarry run by Aggregate Industries. 100+ people, site covers 2.5 square km
Quarrying began in 40s. Produces 5 mill tonnes of limestone/year
Nationally important source of construction materials like rock chippings, used to build roads
Most rock is transported by rail, to building projects in SE England
9.2: CASE STUDY: Torr Quarry is an example of a modem industrial development aiming to be more environmental sustainable.
Sustainability
200 acres of land re-landscaped with plants and trees = helps site blend into the landscape
Lakes created to encourage wildlife and to act as water supply reservoirs
Rail transport used to take limestone away = minimises impact on local roads and villages
Regular monitoring of noise, vibration, dust and water quality
Aggregate Industries has permission to continue deepening it until 2040s = less visual impact than it spreading out
9.3: Outer Hebrides rural area: how is population decline causing social and economic changes?
Outer Hebrides islands of Scotland - 27,400 people, most on isle of Lewis, one of the chain of 65 islands, decline of 50%+ since 1901 when 46k lived here
Social effects:
School closures due to less students. Less people of working age
Ageing pop with less youth to support them.
Economic effects:
Essential services (ferry to mainland), needs financial help, economy struggling, businesses closing (post offices)
Fishing: 48’, 900+ registered fishing boats. 2013, just a few. Foreign ships dominate deep-sea fishing
Tourism: 27% increase in visitors 2007-2014, but industry growth stopped by lack of tourist infrastructure (hotels, food place)
Farming: based on sheep breeding on small farms (crofts). Most now only have work for 2 days/week
9.4: South Cambridgeshire rural area: how is population growth causing social and economic changes?
Rapid 150k (expected 180k, 2031) pop growth as people leave Cambridge/London and migrate in. Attractive countryside in commuting distance of London. 1000+ job opportunities in Cambridge.
Social effects:
Commuters spend most money in city work city, not rural living area
80% car ownership = more traffic, less public transport demand
Modern developments on village edge = sad original villagers
Young people can't afford housing = move away
Economic effects:
Farmers sell land for housing = less agricultural jobs (though more construction jobs), lack of affordable housing
More European migrants = pressure on services (doctor's surgeries, schools)
21% work in high-tech industries
10.1: What improvements and new developments in transport infrastructure are taking place in the UK?
List them
Road infrastructure
Rail infrastructure
Port capacity
Airport capacity
10.1: What improvements and new developments in transport infrastructure are taking place in the UK?
Road infrastructure
2014 gov announced £15 bill road investment strategy
100 new road schemes planned by 2020
1,300 new lane miles added to motorways and A roads to tackle congestion
'Smart motorways' installed
Project in process to widen the A303 'south-west super highway' so it's all dual carriageway
10.1: What improvements and new developments in transport infrastructure are taking place in the UK?
Rail infrastructure
HS2 - massive £70bn+ project to create high-speed rail links between London- major cities in East Midlands and North England
Aimed at cutting journey times, increasing capacity, create jobs and grow UK economy outside London
Faced delays and concerns over exact route and huge costs
Crossrail (Elizabeth Line) opened in 2022. £19bn railway across London to connect Reading and Heathrow (west), to other side of east London in Essex via central London
10.1: What improvements and new developments in transport infrastructure are taking place in the UK?
Port Capacity
UKs ports industry is largest in Europe - leading ports include Tilbury (east London).
Dover is main port for freight (lorries, cars)
Felixstowe is biggest port for container ships
Liverpool2 is a new £300mill container terminal, opened in 2016 - Doubles Liverpool's capacity to 1.5mill containers a year
10.1: What improvements and new developments in transport infrastructure are taking place in the UK?
Airport Capacity
Gov wants to add new runway in south east UK, most likely third runway at Heathrow Airport
Heathrow is one of the busiest airports
Third runway = jobs and boost economy, but add to air and noise pollution
10.2: What is meant by the 'north-south divide' in the UK, and what factors are behind this, and prove it?
"North-south divide" = cultural and economic differences between south and north England
Several factors behind divide - decline of 'heavy industries' like steel making and ship building in northern cities
North West average pay £25k, unemployment is 6.9%, life expectancy 1.4yrs less than average, South East £28k, 4.4%
London and south east have many jobs and fast-growing service industry sector, especially finance
10.2: What strategies are being used to help resolve such regional differences like the ‘north-south divide’?
2015 gov launched a new strategy for a 'Northern Powerhouse' to rebalance wealth and influence of London and south east
Money invested to improve transport links between north and south
Local Enterprise partnerships started and Enterprise Zones created = encourage new businesses where there were none previously
supported by superfast broadband provision
HS2 rail project might also boost economy of northern cities
10.3: Can you explain the place of the UK in the wider world?
list them
Trade links
Culture
Transport
Electronic communication
Economic and political links with the Commonwealth
Economic and political links with the G7
10.3: Can you explain the place of the UK in the wider world?
Trade links
Trade means movement of goods and services across world
Over 50% of UK trade is with EU
Although UK left EU 'single market' due to brexit, goods can be traded without tariffs, due to the “Trade and Co-operation Agreement”. But trade barriers are higher than before.
Key trading partners include USA - (UK earns most trade money with USA), China, Germany, France.
10.3: Can you explain the place of the UK in the wider world?
Culture
Traditions and creative industries
Books - Harry Potter series, sold worldwide
TV exports - Dr Who, Sherlock and Downton Abbey
Markets - English-speaking countries like Australia and USA
Migrants brought their own culture: Italian fashions, American music, Thai food, Caribbean festivals.
10.3: Can you explain the place of the UK in the wider world?
Transport
Heathrow is one of the busiest airports. It’s an important hub for transfer flights
The Channel Tunnel links UK to Europe
Southampton is a major cruise ship port
10.3: Can you explain the place of the UK in the wider world?
Electronic communication
UK is a key link for submarine cables that provide internet connectivity
New project “Arctic Fibre” is a submarine cable planned to connect Asia, Canada and Europe through the Arctic Ocean. It will link London and Tokyo
10.3: Can you explain the place of the UK in the wider world?
Economic and political links with the Commonwealth
53 countries, most were once British colonies
Home to 2.2 bill people, with important trading and cultural links
King Charles III is the figure-head
'Secretariat' works to help member countries achieve sustainable development
Commonwealth Games, called 'the friendly games', happens every 4 years
10.3: Can you explain the place of the UK in the wider world?
Economic and political links with the G7
US, Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, and UK
Meet yearly to discuss global economic issues
Strengthen the global economy