ALKANES AND CYCLOALKANES
1/83
Earn XP
Description and Tags
2ND SHIFTING - ORGCHEM LEC
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
Reaction Mechanisms
- subtype of chemical kinetics
- overall progress of chemical reaction
-stepwise chemical reaction (or the sequence of elementary steps that lead to product formation)
Types of Chemical Kinetics
reaction rate and reaction mechanism
General Organic Chemistry Reactions
Addition, Elimination, Substitution, Rearrangement
Addition is also known as
Combination, Synthesis, Direct Union
Addition
A + B -> AB
Elimination is also known as
Decomposition, Analysis
Elimination
AB -> A + B
Substitution is also known as
Displacement
Types of Substitution
Single, Double
Single Displacement
AB + X -> AX + B
Double Displacement is also known as
Metathesis, Exchanges
Double Displacement
AB + CD -> AC + BD
Rearrangement is also known as
Cis/Trans Interconversion
Example of Rearrangement
Keto-Enol Tautomerization
Common General Reaction Mechanisms
Polar and Radical
Polar
results from a heterolytic bond cleavage/formation (e- pair move together)
interaction between Nucleophile (Nu) and Electrophile (e+)
Nucleophile (Nu)
neutral/negatively charged atom
e- rich species
e- pair donor
Examples of Nucleophiles
HO-, H2O
Electrophiles are also known as
Lewis Acids
Electrophile (e+)
neutral/positively charged atom
e- poor species
e- pair acceptor
Examples of Electrophile
C=O, R-X
Radical Mechanism
results from a homolytic cleavage/formation
e- pair move independently -> radical formation (Reactive Oxygen Species)
common reaction mechanism for alkanes/cycloalkanes in which a radical is formed at high temperature (△) or irradiation (hv)
Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)
can damage cells/tissues
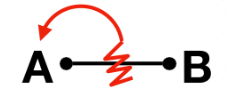
Polar Mechanism results to
(A-) Nucleophile/Nu
(B+) Electrophile/e+
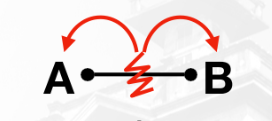
Radical Mechanism results to
(A.) Free Radical
(B.) Free Radical
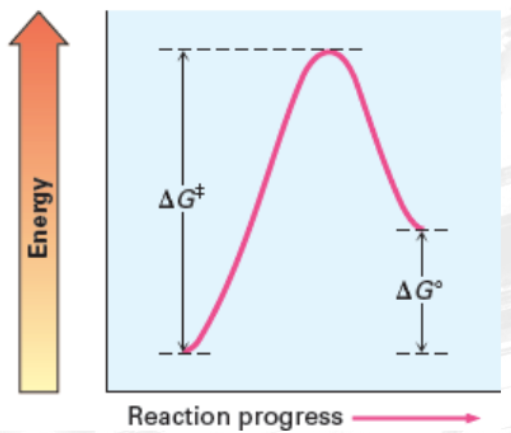
Terms to Remember When Describing a Reaction Energy Diagram
Activation Energy, Transition State, Delta G naught prime, Fast/Slow, Exergonic reaction, Endergonic reaction
Activation Energy (Ea)
minimum energy required to reach the transition state
Transition State (Ts)
state of peak free energy and where reactants start to form
Transition State is also known as
Activated Complex, Intermediate Products (unstable species)
Delta G naught prime (△G°)
free energy change of a reaction in standard condition
change in Gibbs free energy
Fast/Slow
amount of Ea to reach Ts
inversely proportional with Ea
Ea = molecular collisions = Ts formation = _ reaxtion rate
low, high, high, high
Exergonic (Exothermic) Reaction
reactions that releases energy (hot surroundings)
has a negative △G° (△G° < 0)
Endergonic (Endothermic) Reaction
reactions that absorbs energy (cold surrounding)
has a positive △G° (△G° > 0)
Fast and Exergonic with a negative △G°
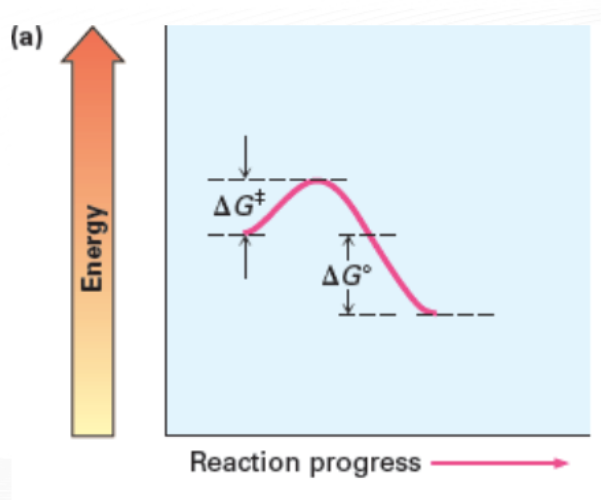
Slow and Exergonic with a negative △G°
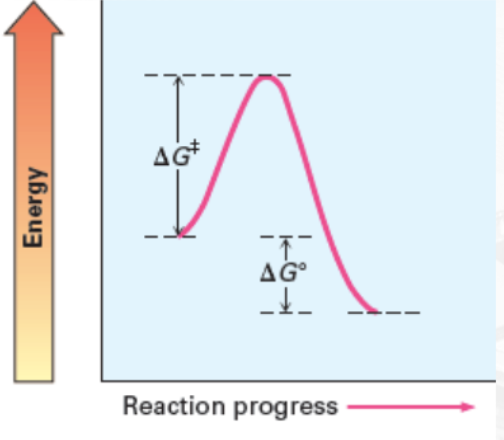
Fast and Endergonic with a positive △G°
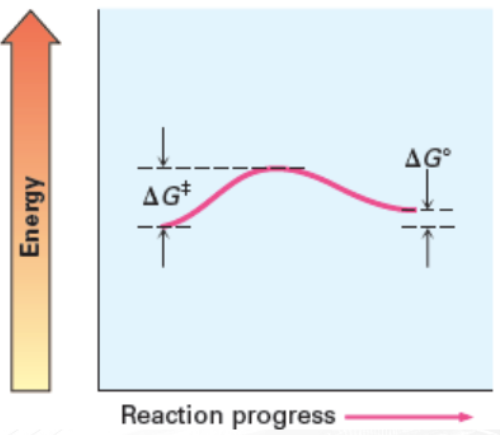
Slow and Endergonic with a positive △G°
First Transition State
a=
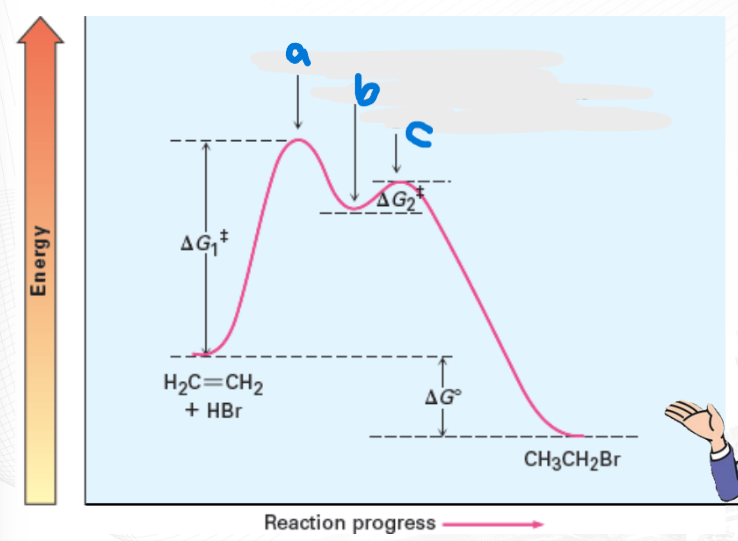
Carbocation Intermediate
b=
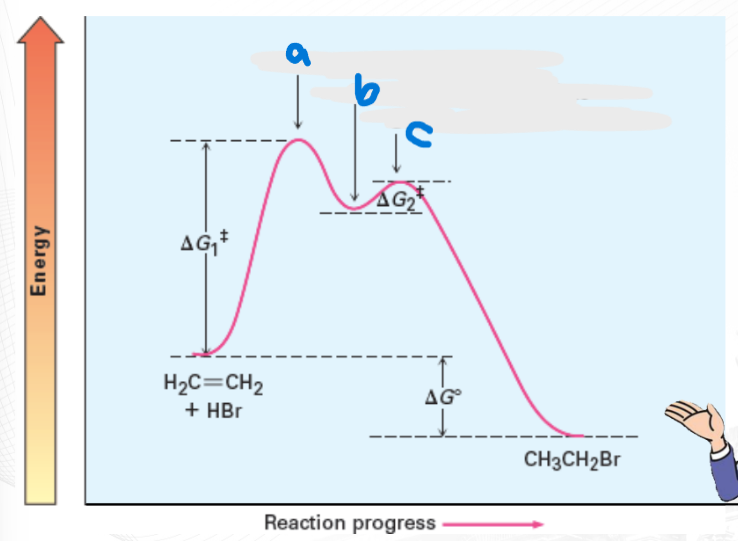
Second Transition State
c=
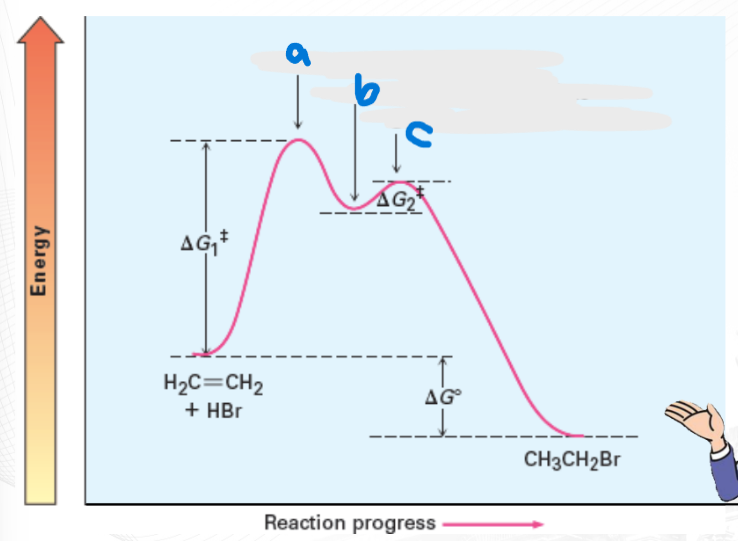
Carbocation Intermediate
In cases of 2-step reaction, a ______ is formed in between 2 transition states (Ts).
Carbocation Intermediate
require energy for activation in order to progress thru the reaction.
CnH2n+2
General Formula of Alkanes
Alkanes
saturated hydrocarbons made up of completely single bonds
Petroleum and Natural Gas
sources of alkanes and a mixture of hydrocarbons
Kinds of Alkanes
Linear-chain/Normal
Branched-chain
CnH2n
General Formula of Cycloalkanes
Cycloalkanes
saturated hydrocarbons (HC) but has 2 fewer hydrogens compared to normal alkanes
Cycloalkanes
have their terminal carbons connected to created an enclosed cyclic system
can be substituted with different atoms or functional groups similar to a normal alkane.
insoluble in water
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF ALKANES AND CYCLOALKANES:
Both of them exhibits London dispersion forces which is a non-polar IMF and is not soluble in polar molecule such as water.
lower densities than water
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF ALKANES AND CYCLOALKANES:
They will not dissolve in water and furthermore they will even float.
BP increases = carbon chain increases in length or size
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF ALKANES AND CYCLOALKANES:
As the carbon chain increases, the number of IMF also increases which is required to be broken for a material to boil.
least
Alkanes and Cycloalkanes are the ____ reactive of all organic compounds but are not completely unreactive.
Combustion
CHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF ALKANES AND CYCLOALKANES:
reaction between a substance and O2 that produces CO2 and H2O, resulting in the production of large amounts of heat and light; less dangerous to environment
CO2, H2O, Heat and Light Energy
Result of Combustion
Cracking
CHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF ALKANES AND CYCLOALKANES:
chemical process where large hydrocarbon molecules (like long-chain alkanes or cycloalkanes) are broken down into smaller, more useful molecules like alkenes and shorter alkanes with the aid of heat and/or Al2O3 catalyst
Heat/Al2O3
Catalyst of Cracking
smaller/shorter alkanes
Result of Cracking
Types of Cracking
Thermal, Catalytic
Oil refining
use of cracking wherein crude petroleum is distilled to separate it into usable fractions that differ in BP
increases
Stability _____ from primary to quaternary, primarily because the R-groups provides support on stability when a carbocation is formed.
Primary carbon / 1○
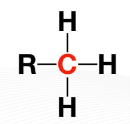
Secondary carbon / 2○
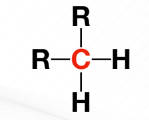
Tertiary carbon / 3○
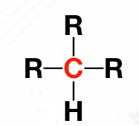
Quaternary carbon / 4○
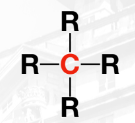
substitution-type reaction
Alkanes and Cycloalkanes will only react under specific conditions of
temperature and irradiation following a _______.
Substitution reactions
chemical reaction in which part of a small reacting molecule replaces an atom or a group of atoms on a hydrocarbon or hydrocarbon derivative.
Halogenation
chemical reaction between a substance and a halogen in which one or more halogen atoms are incorporated into molecules of the substance
follows a radical mechanism
R-H (alkane/cycloalkane) demonstrates the -H atom that will be replaced by one incoming -X atom.
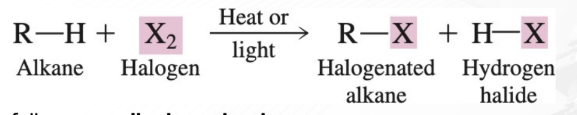
R-X (halogenated alkanes / haloalkanes)
Primary Product of Halogenation
H-X
By-Product of Halogenation
Initiation Phase/Radical Production
High temperature/light (irradiation) is required to break the bonds X-X bonds. This results into the formation of X• radical.
Radical/Free radical is an atom with an unpaired electron; on the product side
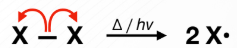
Propagation Phase
The Cl• radical initiate the homolytic cleavage of one C-H bonds by attracting an electron to itself.
It results in the formation of a HCl and a new •CH3 (methyl radical).
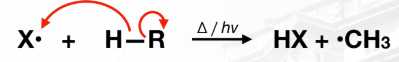
Termination Phase/Non-Radical Production
Combination of 2 radicals causes that reaction to undergo R• the termination phase. It decreases the available radicals for propagation.
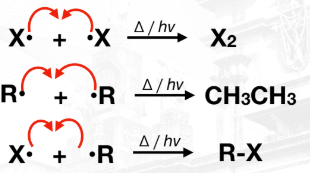
mono-, di-, or poly- substituted products
Radical substitution (SR) of alkanes can form __________ because halogenated alkane can continuously react with halogens resulting to polyhalogenated products.
excess (x’ss) amount of alkane
To maximize monohalogenation and prevent continuous propagation of
radical species, __________ is used.
Reactivity-Selectivity Principle
In situation, where there are multiple carbons that can undergo
halogenation, the _______ is applied.
Reactivity-Selectivity Principle
states that the greater the reactivity of the species, the less selective it will be
aids in determining the most common halogenation product that can be formed
5.0x
Relative reactivity of alkyl radical formation by a Cl• at RT: 3°
3.8x
Relative reactivity of alkyl radical formation by a Cl• at RT: 2°
1.0x
Relative reactivity of alkyl radical formation by a Cl• at RT: 1°
1600x
Relative reactivity of alkyl radical formation by a Br• at 125°C: 3°
82x
Relative reactivity of alkyl radical formation by a Br• at 125°C: 2°
1.0x
Relative reactivity of alkyl radical formation by a Br• at 125°C: 1°