CH 9.3 (psychopharm)
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Oral or transdermal
Route of administration: relatively slow absorption; slow drug availability to the brain
IV or inhalation
Route of administration: rapid drug entry into the brain and a fast onset of drug action; but shorter duration of action
produce the strongest euphoric effects as a result of rapid drug delivery to the brain
Route with fast drug action
Have the greatest addiction potential; produce strongest euphoric effects and shortest latency
Short latency
Between response and reinforcer lead to:
stronger and faster drug conditioning
Addiction is more likely
Positive reinforcers
Consuming the drug strengthens whatever preceding behavior was performed by the organism
eg. parking lot always smoked in
Drug reward
The positive subjective experience associated with the drug, euphoria or the high
Self administration tests
Drug reinforcement is studied using these tests
strong reinforcers in these tests have high addiction potential for humans (cocaine, heroin, and meth)
Fixed ration (FR) schedule
The typical dose response function is an inverted U shape curve
At higher doses
At what doses does the number of reinforcers decline?
due to satiation, aversive reactions, or behaviorally disruptive side effects
Progressive ration procedure
Animals are trained continuous reinforcement (CR) schedule then switched to a low FR schedule, increased until he animal stops responding (breakpoint)
Breakpoint
animal stops responding, tells us how addictive drugs is
Breakpoints can vary with dose
Reinstatement of drug seeking behavior
Relapse can be modeled by stopping drug delivery, then exposing animal to cue a cue previously paired with drug delivery
Stimuli effective in reinstatement
experimenter delivers a small dose of the drug (drug priming)
Subjecting the animal to stress
Exposing animal to environmental cues that were previously paired with drug delivery
Slide 52
Negative consequences
occur later of time, after a long period of use
Family breakups, job loss, health effects etc
Individual factors that contribute to addiction development
Personality traits, mental health status, childhood experiences, lifestyle, present life stressors
Place conditioning
Animals associates one compartment with rewarding effect of a drug. One compartment paired with drug, then how long animal spend in each compartment is measured in drug free state
IV: one compartment paired with drug w/o drug
DV: time spent in each compartment
Electrical self stimulation
Electro is inserted in the brain’s reward circuits on performing an operant response. The threshold is reduced for self stimulating reward centers when animals have been treated acutely with drug of abuse.
Drugs are reinforcing
When under the animals control (self admin)
Drugs MAY be aversive
When administered by the experimenter
Physical dependence
Withdrawal May play a key role in establishing and maintaining drug addiction
i want to do drugs to stop withdrawal symptoms
Withdrawal symptoms
Also called abstinence syndrome: motivates the user to take the drug again (negative reinforcement)
Agonist replacement therapy
Experimental results from heroin studies support the use of methadone or buprenorphine in the treatment of opioid dependence
help with withdrawal
Slide 57
Development of addiction
Drug taking behavior progresses from an impulsive stage to a compulsive stage
process due to gradual recruitment of antireward system in the brain (neuroadapted stage)
Impulse stage
An episode of binge drinking results in a pleasant state of intoxication.
Because of the repeated pairing of intoxication with environmental stimuli, a conditioning process causes those stimuli to trigger a renewed craving for the alcohol reward.
leading to more binging and intoxication
Compulsive stage
Individuals undergo periods of prolonged intoxication that bring relief from their depressed baseline mood state.
they are now alcohol dependent, abstinence leads to withdrawal symptoms that include even greater negative effect
Craving in this stage is related to relief from the state of withdrawal
Impulsive stage
What stage is this?
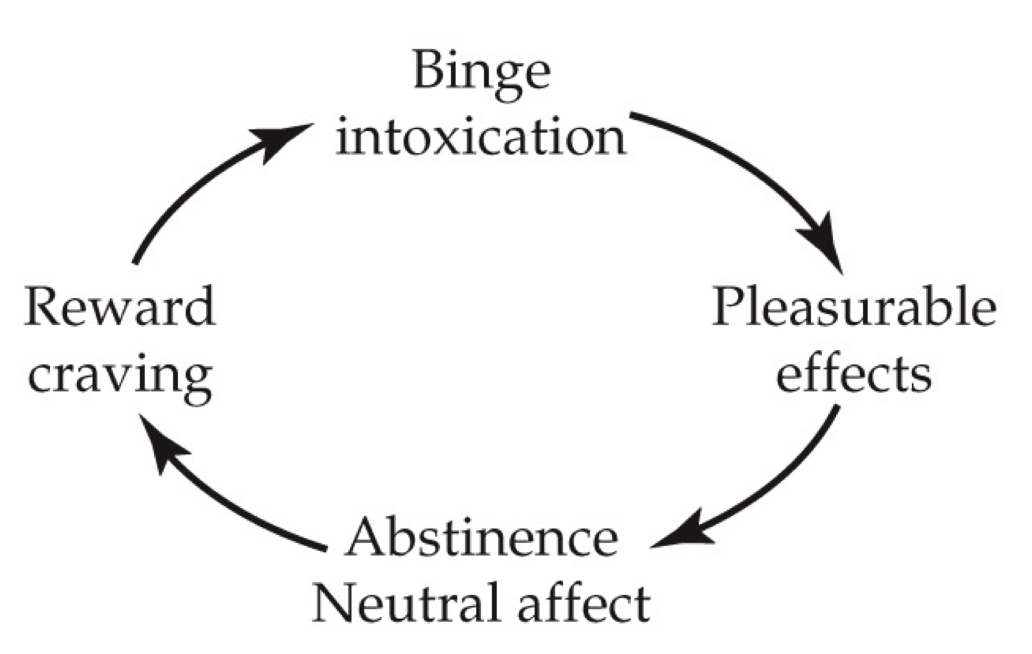
Compulsive stage
What stage is this?
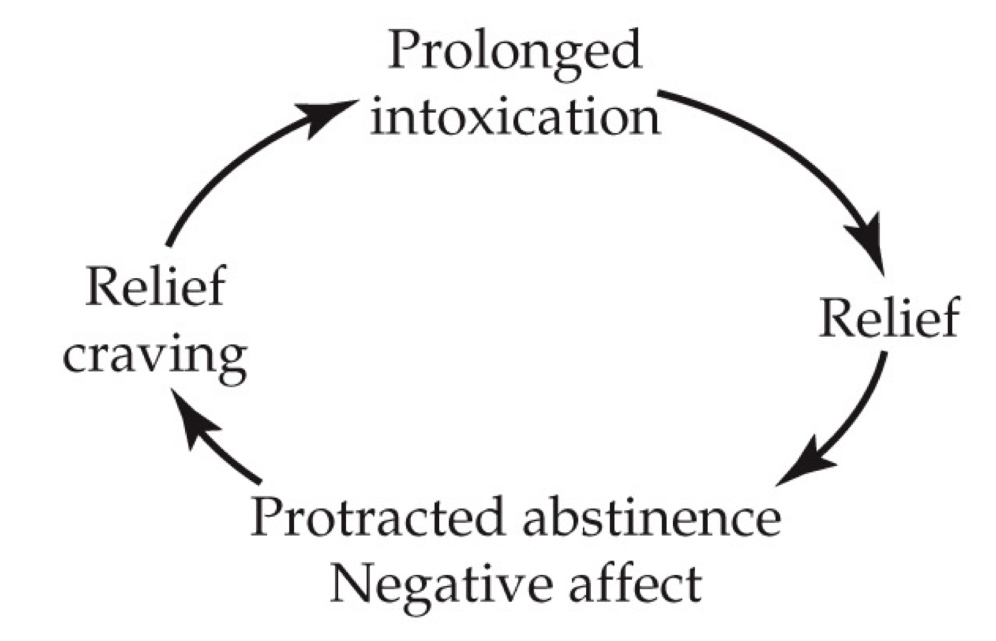
Episodes of withdrawal
The responses can become classically conditioned to the stimuli associated with the environment in where it occurs
symptoms, such as craving, can be triggered by exposure to the conditioned stimuli
Discriminative stimulus
Psychoactive drugs produce these effects in animals, thought to corrrespond to subjective effects produced by these compounds in human users.
willing to work harder to administer substances
Experienced users come to expect the subjective effects which contributes to the persistence of drug use
Genetic factors
Contribute to the risk for addiction, been assessed using family, adoption, and twin studies
Heritability
Of substance use disorders is in the range of 40% to 60%
some substances like cocaine show higher
Psychedelics show lower
Environmental influences
Remaining variability that contributes to risk for addiction
Adolescence increased risk
Of drug addiction is associated with younger age, less education, nonwhite racial background, lack of employment, and conduct problems in childhood
Psychosocial variables
Contribute to increased addiction risk
adolescents
Stress
Mental health comorbidity
Stress
Frequent and severity of stressful life events and an individuals ability to cope with such events
Comorbidity
Diagnosis of anxiety, mood, or personality disorders in addition to substance abuse disorder
Self medication hypothesis
Individuals suffering from elevated anxiety should prefer sedative anxiolytic drugs; depressed individuals should seek out stimulants drugs
Shared etiology
Certain factors (genetic or environmental) contribute to elevated risk of both addiction and other psychiatric disorders
Familial and sociocultural influences
Childhood maltreatment, violence in the family, inadequate parental monitoring
Social facilitation
Promote this, remove user from normal social roles and responsibilities, promote solidarity within a particular ethnic group or lead to association with a specific drug to subculture
Protective factors
Absence of risk factors
Factors protecting against initiation; family cohesion, parental warmth/monitoring
For people recovering; a support network, maintaining a stable lifestyle, sources of reinforcement
Men substance use misuse
Often begin in a social context
Women substance use misuse
begin in response to a negative life events and/or onset of depression or anxiety
Rapidly escalate substance use (telescoping)
More sensitive to drug related cues
Experience more severe drug craving
Sex differences in substance use
Linked to female reproductive hormones or to differences in stress responding
Natural recovery
Transitioning from substance misuse or addiction to non-problematic use or nonuse without assistance
facilitated by transitional life events or by negative consequences of drug use
Maintaining abstinence
Helped by avoiding drug associated cues, non drug sources of reinforcement, new social support networks, financial stabilit, and achieving a general structure in life
Bio psychosocial model of addiction
Includes the full range of pharmacological, biological, and psychological/sociocultural factors that influence addiction risk
promote the likelihood of substance misuse and addiction
Increases
Positive reinforcing effects of drug (Behavioral and neural mechanisms) INCREASES OR DECREASES compulsive drug seeking and drug use
Increases
Negative reinforcing effects of drug due to relief of withdrawal INCREASES OR DECREASES compulsive drug seeking and drug use
Increases
Discriminative subjective effects of drugs INCREASES OR DECREASES compulsive drug seeking and drug use
Increases
Stimuli conditioned to drug effects INCREASES OR DECREASES compulsive drug seeking and drug use
Decreases
Averse effects of drugs INCREASES OR DECREASES compulsive drug seeking and drug use?
Increases
Risk Factors (psychological, familial, sociocultural, and genetic) INCREASES OR DECREASES compulsive drug seeking and drug use
Decreases
Protective factors INCREASES OR DECREASES compulsive drug seeking and drug use