GEO 005 FINAL EXAM REVIEW
1/158
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
159 Terms
THUNDERSTORMS AND TORNADOES
What is humidity?
A measure of how much water vapor there is in the air
Where do clouds come from?
Hydrochloric Cycle
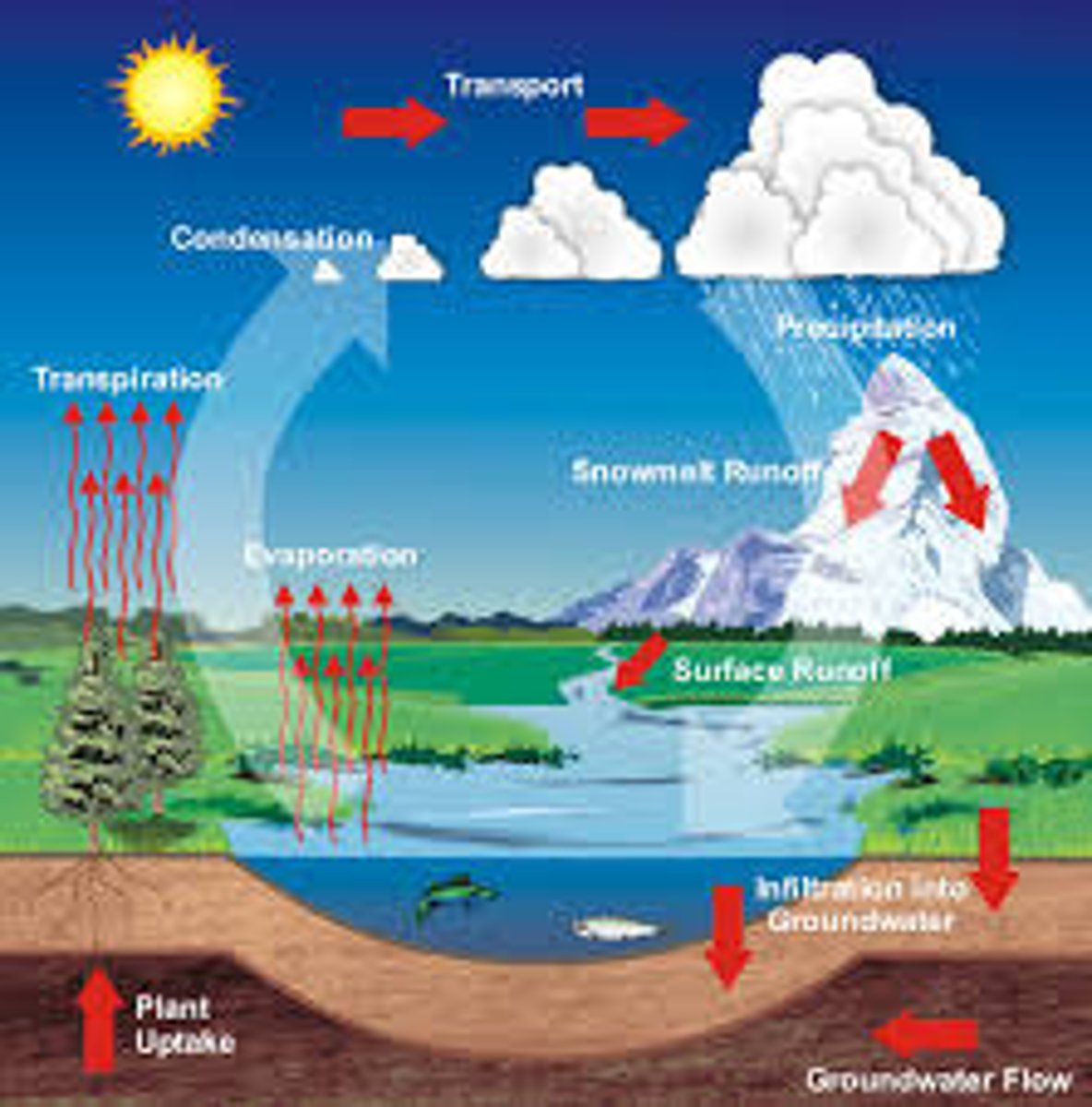
What happens to warm, moist air when it rises?
It cools, condenses and form clouds
What happens when a cold air mass collides with a warm, moist air mass?
Two air masses that come into contact push against each other along a line called a front. When cold air mass collides into warm air mass, the cool air slides under the warm air and pushes the warm air upwards. The warm air cools rapidly, creating a cold front.
What is heavier: dry air or moist air?
Dry air; Also meaning Cold air is heavier because cold air is drier
What causes lightning?
A strong separation of electric charge that builds up between clouds and the ground
What causes thunder?
The rapid expansion of super-heated air that results in a shock wave; that sound is thunder
What causes hail?
Hailstones are made from ice crystals that travel repeatedly above and below the freezing line, enabling additional water to freeze onto them until they become too heavy for the updrafts and fall to the ground.
What distinguishes supercells from all other thunderstorms?
A supercell as a thunderstorm with a deep rotating updraft (mesocyclone). In fact, the major difference between supercell and multicell storms is the element of rotation in supercells
What is wind shear?
Fast-moving winds that roll air below into a horizontal vortex-a spinning tube- above opposing surface winds
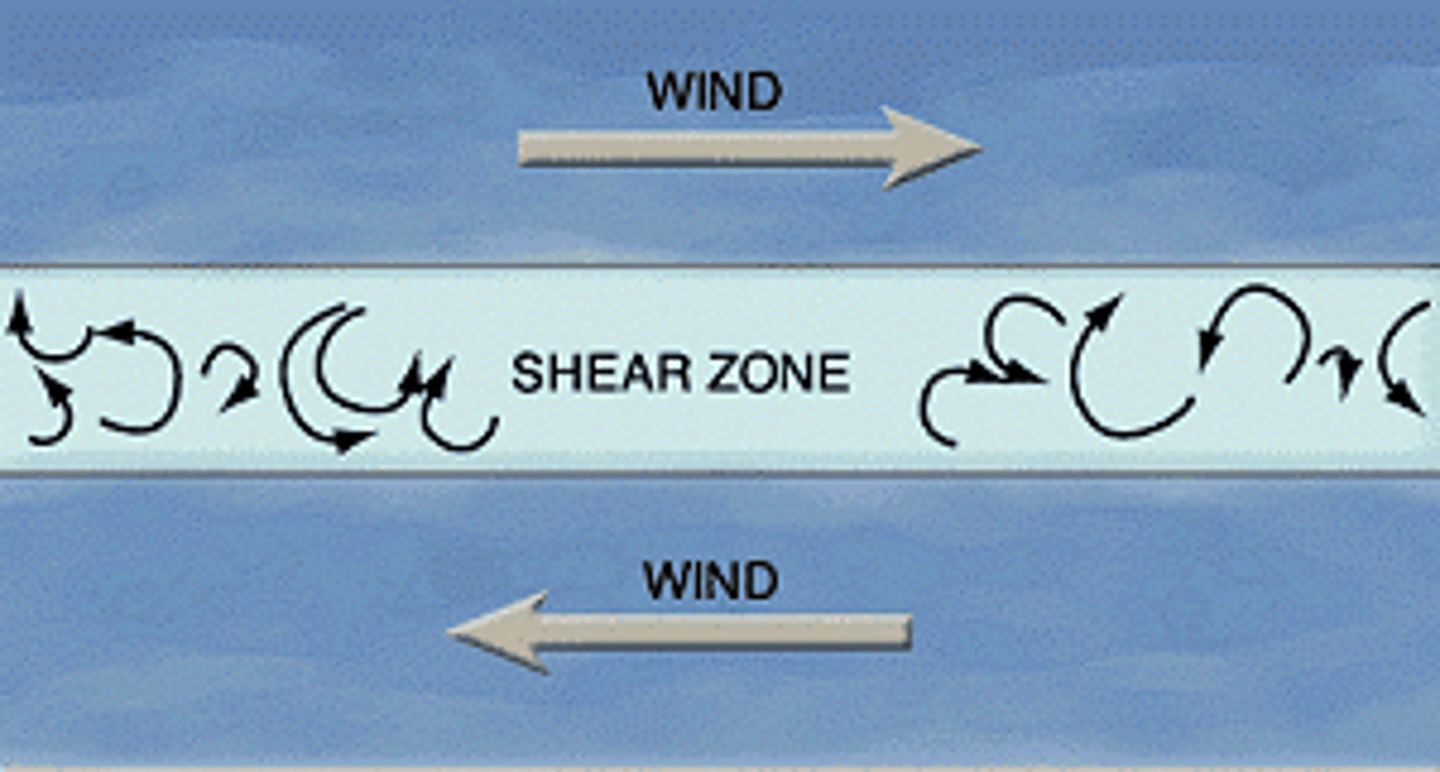
How do supercells develop?
A supercell forms when strong wind shears lead to a horizontal vortex that is them rotated into a vertical vortex
Supercell
Upper-level winds tilt the rotating updraft, called a mesocyclone. This allows the storm to keep growing, as warm air is sucked into the storm away from the cool downdraft
Why is hail often found in front of a tornado?
In most mature super-cell thunderstorms like this one, the incredible updrafts are lofting copious amounts of moisture thousands of feet into the air. ... So, if the tornado is moving toward the hail, then yes, you would experience hail followed by the destructive, twisting winds of the tornado.
Which way does the wind blow near a tornado?
What are the components that make the mid-west so productive for tornadoes?
- Cold, dry air from the north that collides with warm, moist air from the gulf to form cumulonimbus clouds
- Winds from the jet stream cause the clouds to experience horizontally shear (vortices parallel to the ground)
- Warm, dry air from the southwest lifts and rotates the vortices into a vertical orientation, generating a spinning supercell
How many tornadoes occur each year in the U.S.?
Approximately 1000
When is prime tornado season in the U.S.?
Peak tornado season in the U.S. occurs in the Spring, when waters from the Gulf of Mexico begin to warm, while cold air masses still descend from the North
How does the Enhanced Fujita scale rate tornadoes?
The EF scale uses the amount of damage to rate tornadoes; Damage is used to estimate wind speed
Classified EF-0 - EF-5
-ef0 65-85mph
-ef1 86-110 mph
-ef2 111-135 mph
-ef3 136-165 mph
-ef4 166-200 mph
-ef5 200+ mph
Can a fixed Doppler radar easily measure tornado wind speeds?
Tornado wind speeds are difficult to measure, and fixed Doppler radars can only measure wind speeds a few km above the ground. This is sufficient for supercells, but not tornadoes
Can tornadoes contain multiple vortices?
Tornadoes cannot split or join as this would disrupt the wind flow and destroy both, but multiple vortices are common with each rotating around a larger tornadic center
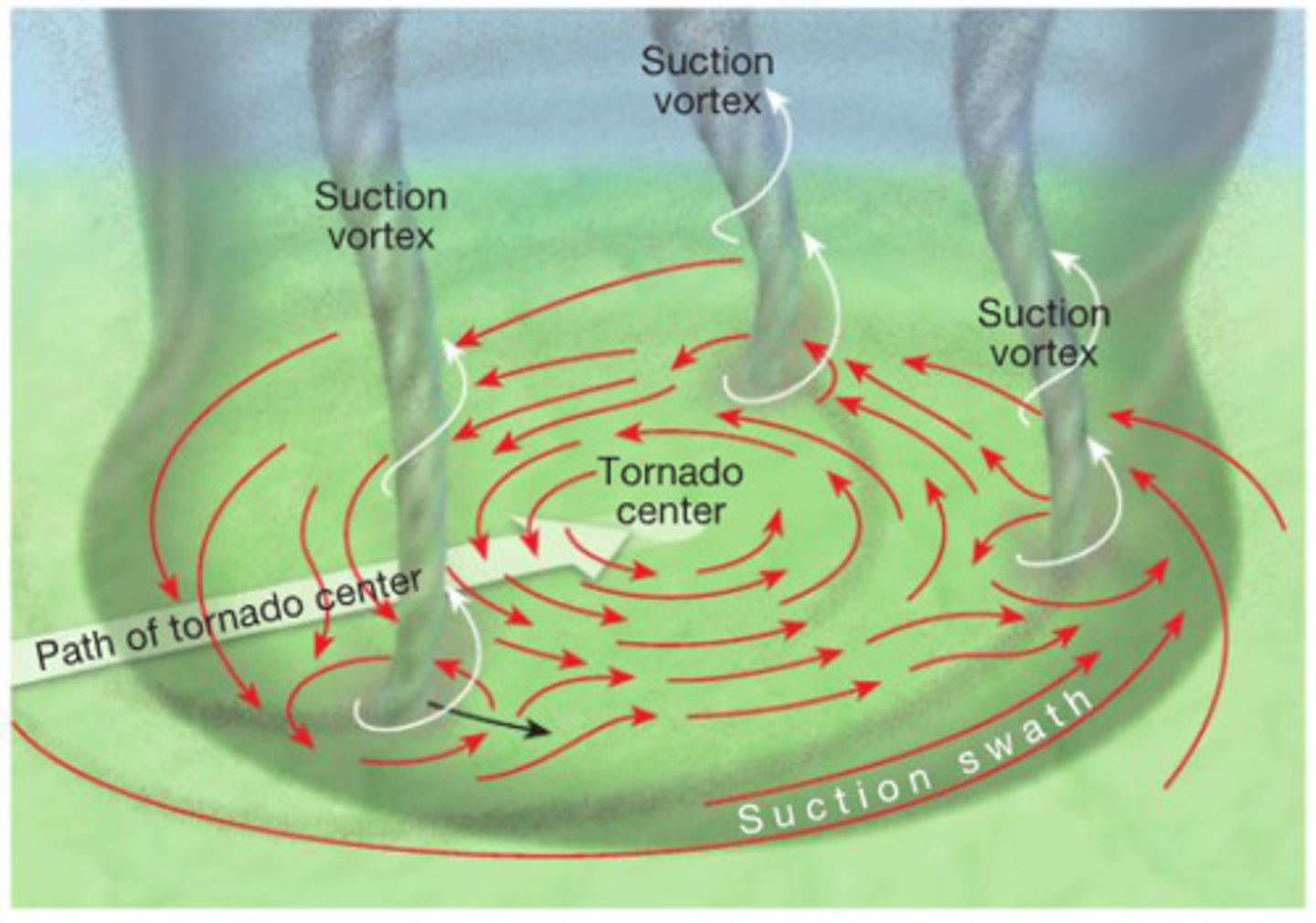
Where would one take shelter from a tornado?
The safest place is underground; if you have no underground, go to ground-level room with no windows
What is the biggest danger from tornadoes?
Flying debris and being tossed around; mainly debris
What type of front involves fast moving thunderstorms and severe weather?
Cold Front
Why do cold fronts give rise to strong thunderstorms?
Because they rapidly push warm, moist air high into the atmosphere; forming Cumulonimbus Clouds
What type of weather does Warm Fronts give rise to?
Gentle showers, as warm air gradually gains altitude. Forms Cumulus Clouds.
How are clouds classified?
Based on height - higher clouds carry winds and more rain (Thunderstorms)
Where are clouds made?
Troposhpere
Which type of severe thunderstorm generally spawn the largest tornadoes?
Supercell storms
HURRICANES
Which way do winds around a low pressure system in the Northern Hemisphere blow?
Counter-clockwise
Wind direction based on pressure and location?
Northern Hemisphere:
Low P. - Counter Clockwise
High P. - Clockwise
Southern Hemisphere:
Low P. - Clockwise
High P - Counter clockwise
Low Pressure System:
- lower pressure at its center
- winds blow towards low pressure
- air rises in the atmosphere
High Pressure System:
-higher pressure at its center
-Winds blow away from high pressure
- air sinks down to fill space
What is a hurricane?
A tropical cyclone; an organization of large number of thunderstorms originating in the tropics into a massive single rotating storm system
- is in an area of low atmospheric pressure
What is the difference between a hurricane, cyclone, and typhoon?
All are the same, but differ by location
- A hurricane is located in the Atlantic and East Pacidic
- A cyclone is located in Indian Ocean
- A typhoon is located in the Western Pacific Ocean
Why can't cyclones form on the equator?
Because the Coriolis Effect vanishes there
What is the difference between a tropical depression, a tropical storm, and a cyclone?
- Different levels of tropical cyclone development
- Order is: Tropical Disturbance weak and unorganized), Tropical Depression (<39 mph), Tropical Storm (39-74 mph), Hurricane/Cyclone (>75 mph)
What provides the energy for hurricanes?
Warm Tropical Waters provide energy
What happens when hurricanes venture over land?
once a hurricane ventures onto land, it'll lose energy and diminish rapidly
When is the primary North Atlantic hurricane season?
June 1st to November 30th, but peak is mid-August to late October
What are the conditions found in the "eye" of a hurricane?
- Calmest part of a hurricane
- Lowest winds
- Lowest pressure
What are the conditions found in the "eyewall" of a hurricane?
- Most intense wind and rainfall in a hurricane; high pressure
What is the Saffir-Simpson Intensity Scale based on?
- Saffir-Simpson Intensity Scale classifies hurricanes based on wind speed
- There are five categories
What occurs in each category of a hurricane?
1. 74-95 mph winds, 4-5 ft storm surges, minimal damage
2. 96-110 mph winds, 6-8 ft storm surges, moderate damage
3. 111-130 mph winds, 9-12 ft storm surges, extensive damage
4. 131-155 mph winds, 13-18 ft storm surges, extreme damage
5. >155 mph winds, >18 ft storm surge, catastrophic damage
- Pressure decreases each category
What is the main way the wind speed, pressure, and temperature of a hurricane are measured?
Dropsondes, instruments dropped from an aircraft into a hurricane, is most accurate way to measure wind speed, direction, humidity, temperature, and atmospheric pressure
What causes storm surges?
Hurricane winds can push water onshore, causing severe coastal flooding; mimics super high tides
What is the deadliest hazard associated with a hurricane?
In the case of hurricanes, storm surge by far causes the greatest damage and contributes to 90
percent of all hurricane-related fatalities
What causes nor'easters?
- Nor'easters are Extratropical cyclones, that occur far from the tropics
- Nor'easters form when cold arctic air collides with and lifts warm, moist air above the Gulf Stream
- Also referred to as Cold Core Storms
What are the similarities and differences between hurricanes and nor'easters?
Similarities:
- rotating storms
- both are just as destructive
- both rely on warm waters
Differences:
Nor'easters:
- requires cold front (cold core)
- Cold air underlies nor'easters
-Occurs in North Atlantic
- Brings in Snow
- Occurs in Winter
Hurricanes:
- Not associated with fronts (cold/warm)
- Warm air underlies hurricanes
- Occurs in Tropics
- Occurs in Summer
- Has distinct "eye"
What are the major components of the 1991 "Perfect Storm"?
The Perfect Storm contained a cold front, nor'easter, and hurricane Grace
What are good hurricane safety practices?
- Evacuate if mandatory or if you live in mobile home; go early as possible to avoid traffic
- Gather food, water, emergency supplies and medicine if at home and utilities go out
-Try to waterproof valuables and cover windows in a way to prevent shattering
Can a hurricane change into a typhoon?
Hurricanes and Typhoons are the same weather phenomenon: tropical cyclones. Only difference is where the storm is located
CLIMATE CHANGE AND GLOBAL WARMING
What describes climate rather than weather?
"The winters here are dry and warm."
How is the Earth's climate changing?
It is warming due to increased levels of CO2 in the atmosphere
What is the main reason why Earth's temperature changes over very long periods of time?
- Over the past 400,000 years, changes in the Earth's orbital parameters was the main reason why global temps. had varied so greatly
How have global temperatures changed over the last 800,000 years?
They have increased and decreased many times
Atmospheric temperature results from four factors:
- Solar energy - how much light is the earth getting from the sun
- Greenhouse gases - how much heat is being trapped by the atmosphere
- Aerosols - particles in the atmosphere that block light and thus cause cooling
- Albedo - how much light is being reflected (no heat added) or absorbed (heat added) by a surface
What best describes how greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere have changed in the last 2000 years?
Concentrations were mostly steady until ~1900 when they began to increase rapidly
What is unique about the current rise in global temperatures?
- Average global temperatures have risen more than 2 degrees f relative to the late 19th century
- Humans have added more greenhouse gases to the atmosphere; causes more heat to be trapped and temperatures to rise
How has the average amount of energy that the Earth received from the Sun changed over the past 50 years?
Over the last 50 years the amount of energy the earth has received from the sun has remained the same or decreased
How do greenhouse gases cause warming of the Earth's atmosphere?
- By trapping longwave radiation (infrared)
- The absorption of infrared radiation by the atmosphere
- Greenhouse gases absorb some of the energy radiating from earth's surface and as a result the lower atmosphere is much warmer than it would be
What would the Earth be like if there were no greenhouse gases?
Without the greenhouse effect, the Earth would have an average temperature of -18 °C and be covered in ice. Life as we know it would not be able to survive.
What is the approximate percentage of the atmosphere that comprises greenhouse gases?
Humans can have a significant influence on greenhouse gases like co2 because they account for only a tiny fraction of our atmosphere (.05%)
- Trace gases, including greenhouse gases, account for the remaining 0.1 percent. As of April 2016, carbon dioxide accounted for 0.04 percent of the atmosphere's chemical composition.
What is the current source of the most greenhouse gas emissions?
Anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions far outpace those from natural sources, with the most coming from burning fossil fuels
Which gas accounts for the majority (more than half) of the anthropogenic greenhouse effect?
Carbon dioxide
What are aerosols?
Very small liquid or solid particles that reflect sunlight
How do aerosols influence global warming?
Increasing aerosols in the atmosphere can cause global cooling
How do scientists measure the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere for dates prior to 1955?
From air bubbles in glacial ice from cores
What do ice cores tell about the relationship between global temperatures and greenhouse gas concentrations?
When one increases, the other usually increases as well
What do atmospheric numerical models conclude regarding the cause of the current significant rise in global temperatures?
They are primarily due to anthropogenic (man-made) increases in greenhouse gas emissions
What is the difference between "Global Warming" and "Climate Change"?
- Global warming refers to the ongoing rise in global average temperatures
-Climate change refers to the increasing changes in the measures of climate over a long period of time - including precipitation, temperature, and wind patterns
-changes in climate:hotter/cooler, wetter/dryer, frequency and severity of storms brought about from global warming
What are some problems associated with ice sheets melting?
- Melting ice sheets adds water to the ocean, raising sea level
- Melting ice sheets adds fresh water to the ocean, changing global ocean currents
- Some places rely on water from ice sheets to replenish their water supply
What is NOT a problem associated with ice sheets melting?
Melting glacial ice on the Atlantic Ocean will contribute most rising sea level due to its melting directly into the ocean
How can climate change influence the weather?
- Global warming causes changes in weather patterns
- Unusually warm weather in the arctic pushes unusually cold weather to the south
- Higher temperatures mean more water evaporates leading to more storms and flooding
What are the effects that climate change are already causing?
- Ocean temperatures are increasing
- Glaciers are melting
- Sea levels are rising
What is not evidence that the Earth is warming?
Earthquake activity is increasing
What is the approximate percentage of peer-reviewed scientific papers about the causes of global warming that conclude that humans are the cause?
97% of all peer-reviewed scientific papers dealing with climate change endorse the position that humans are causing global warming
What does confirmation bias refer to?
- The urge to believe ibky things that confirm what you already believe to be true
- Backfire effect: instead of embracing the truth, many believers double down on their beliefs after being presented with evidence that contradicts them
- Effective tipping point: "motivated reasoners" start to accept the hard truths after seeing enough claims debunked over and over
What are the areas where legitimate debate or uncertainty still exist in regards to climate change
Legitimate debate on climate change exists on three major fronts:
- How should be balance environmental and economic concerns?
- How much will the earth heat up?
- What are the best strategies to fight global warming?
If all of the Arctic sea ice completely melted, how much would sea levels rise?
- 5 cm
-However if land-based ice (Antarctic and Greenland) melted, the sea would rise 60m
WILDFIRES
What is a wildfire?
A wildfire is an uncontrolled fire in an area of combustible vegetation that occurs in a wilderness area, such as a forest or grassland
Are wildfires caused more often by lightning or humans?
85% of all wildfires in the US are human caused (the rest is by lightning)
Which burns more acres, fires caused by humans or lightning?
- Most wildfires are caused by humans , but fires started by lightning burn more acres
- Lightning burns more because they tend to be in more remote area
- They go longer before being noticed
- More difficult to fight
What are factors that strongly influence the potential for wildfires to start?
The potential for a wildfire to spread depends on the type of vegetation (some fuels burn more easily) topography (fire burns faster uphill) and weather (hotter and dryer means faster burn)
What us not an important indicator of whether a region is prone to wildfires?
Bedrock composition
What is not true about wildfires?
Early european settlers of North America brought the ability to use fire for heat, light, and cooking to Native Americans
What is required for a fire to burn?
Heat, fuel, and oxygen
What are surface fires?
spread of flaming front and burn leaf litter, fallen branches and other fuels located at ground level
What are ground fires?
burn organic matter in the soil beneath surface litter and are sustained by glowing (smoldering) combustion
What are crown fires?
Wildfire type that is dominated by fires moving along treetops
What are the three stages of a wildfire?
-Preignition - heat of fuels cause them to lose moisture, making them more combustible
-Combustion - hotter temperatures cause fuels to release gases that combine with oxygen in a chemical reaction to release more heat, leading to a chain reaction
-Extinction - fire is out
What happens during the preignition process in wildfire development?
Fuel is heated, it loses water and is ready to be ignited
What happens during the combustion phase of wildfires?
Fuel is ignited, leading to flames and smoldering
Types of Combustion:
- flaming combustion: (early stage) rapid, high temp conversion of fuel to thermal energy
- glowing or smoldering combustion: takes place at lower temperature
What was the largest wildfire that occurred in U.S. history?
Great fire of 1910; burned 3 million acres in the northwest for 2 days; 87 killed including 78 firefighters
What are the original policies of the U.S. Forest Service regarding fighting wildfires?
(After 1910 fire) Aggressively fight all fires, prevent and fight all fires.
The consequence was the lack of smaller fires, so there was more fuel for larger fires like the 1988 Yellowstone fire
What are the current policies of the U.S. Forest Service regarding fighting wildfires?
Around 1972, more policies were enacted, shifting the policy from suppression to mitigation and management.
- prescribed and controlled fires for fuel reduction and ecosystem improvement