CDC MODULE 1-4
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
FALSE
DNA generates messenger RNA through transcription and RNA generates DNA through translation.
True
False
TRUE
Nucleic acids can only be synthesized in vivo in the 5' to 3' direction.
True
False
B. Nucleotide
When a nitrogenous base, a 5 carbon sugar, and a phosphate group bond, they form a:
A. Nucleoside
B. Nucleotide
C. RNA
D. DNA
E. All of the above
When nucleotides form chains they can become:
A. Nucleic Acid
B. RNA
C. DNA
D. A Macromolecule
E. All of the Above
A. Hydrogen, Oxygen, Carbon, Nitrogen, Phosphorus
DNA is made up of these elements:
A. Hydrogen, Oxygen, Carbon, Nitrogen, Phosphorus
B. Hydrogen, Oxygen, Carbon, Nitrogen, Potassium
C. Hydrogen, Carbon, Phosphorus, Uracil, Sulfur
D. Halogen, Oxygen, Carbon, Nitrogen, Phosphorus
B. Cytosine pairs with Guanine
Which DNA nitrogenous bases pair to form a double DNA chain?
A. Adenine pairs with Guanine
B. Cytosine pairs with Guanine
C. Cytosine pairs with Uracil
D. Adenine pairs with Cytosine
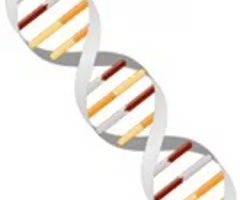

B.
Which of the following images is considered the best representation of the double-stranded DNA structure?
B. Helicase unwinds and separates the two complementary DNA chains
The first step in DNA replication occurs when:
A. RNA polymerase binds to DNA
B. Helicase unwinds and separates the two complementary DNA chains
C. DNA Primase enzymes break hydrogen-bonded base pairs.
D. Okazaki Fragments appear in DNA
A. DNA Polymerase III generates Okazaki Fragments on the lagging strand.
During DNA replication, the DNA Leading Strand is created by DNA Polymerase 3 in a continuous strand, while:
A. DNA Polymerase III generates Okazaki Fragments on the lagging strand.
B. DNA Ligasegenerates the lagging strand.
C. RNAse generates discontinuous fragments on the lagging strand.
D. Single Strand Binding proteins generate discontinuous fragments on the lagging strand
A. may be double stranded
RNA is usually single-stranded and
A. may be double stranded.
B. only occurs in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells.
C. is rarely associated with viruses.
D. is rarely used for molecular diagnostics
A. Hydrogen, Oxygen, Carbon, Phosphorus, Nitrogen
RNA is made up of these elements:
A. Hydrogen, Oxygen, Carbon, Phosphorus, Nitrogen
B. Hydrogen, Oxygen, Carbon, Potassium, Nitrogen
C. Hydrogen, Carbon, Phosphorus, Uracil, Sulfur
D. Halogen, Oxygen, Carbon, Phosphorus, Nitroge
B. DNA is a double strand more stable molecule than RNA.
The difference between RNA and DNA is:
A. DNA contains 2'-OH ribose sugar which makes it more stable.
B. DNA is a double strand more stable molecule than RNA.
C. DNA is used in diagnostics, while RNA is not used in genetic diagnosis.
D. RNA is a single strand of DNA with similar structure, composition, and stability.
B. mRNA - Messenger RNA
C. tRNA - Transfer RNA
D. rRNA - Ribosomal RNA
There are several types of RNA. (Select all that apply)
A. rRNA - Recumbent RNA
B. mRNA - Messenger RNA
C. tRNA - Transfer RNA
D. rRNA - Ribosomal RNA
D. Uracil
Like DNA, there are four nitrogenous bases that make up the RNA molecules. Of the following, which nitrogenous base is only found in RNA?
A. Adenine
B. Cytosine
C. Guanine
D. Uracil
False
Single strand is the only structural form of RNA.
True
False
C. Transcription
When DNA is used as a template to generate mRNA, the process is called:
A. Cell division
B. Replication
C. Transcription
D. Translation
True
In a molecular biology laboratory test setting, specimen processing area is defined as a "clean" area because no nucleic acid amplification has occurred in this area.
True
False
True
The fundamental objective of biosafety in a molecular biology laboratory is to contain potentially harmful biological agents.
True
False
B. Applies to facilities in which work is done with indigenous or exotic agents which may cause serious or potentially lethal disease after inhalation.
Which statement best describes only the characteristics of a BSL-3 laboratory?
A. Suitable for work involving agents of moderate potential hazards to personnel and the environment.
B. Applies to facilities in which work is done with indigenous or exotic agentswhich may cause serious or potentially lethal disease after inhalation.
C. Includes various bacteria, parasites and viruses that can cause severe to fatal disease for which preventive or therapeutic interventions are always available.
D. Includes bacteria and viruses that cause only mild diseases to humans.
A. Nucleic acid extraction area
B. PCR reagent mix preparation area
You are assigned to perform a new procedure. According to the SOP, this procedure must be done within "clean" areas in terms of excessive nucleic acid. Identify the work areas that you may choose to perform this procedure:
A. Nucleic acid extraction area
B. PCR reagent mix preparation area
C. PCR amplification area
D. Post-amplification area
A. PCR Reagent Mix Preparation, Nucleic Acid Extraction Area, PCR Amplification Area, Post-Amplification Area
To avoid contamination you must follow a specific workflow while transferring the lab materials. Choose the correct unidirectional workflow in a molecular diagnostic laboratory.
A. PCR Reagent Mix Preparation, Nucleic Acid Extraction Area, PCR Amplification Area, Post-Amplification Area
B. Nucleic Acid Extraction Area , PCR Reagent Mix Preparation, PCR Amplification Area, Post-Amplification Area
C. Amplification Area, Nucleic Acid Extraction Area, PCR Reagent Mix Preparation, Post-PCR Amplification Area
D. Nucleic Acid Extraction Area, PCR Reagent Mix Preparation, Amplification Area, Post-PCR Amplification Area
A. Decontaminate laboratory working surfaces between steps.
C. Have decontamination solutions freshly made in each area regardless of the laboratory setup.
D. Change your lab coat when moving from one working area to another.
From the items below, identify practices you should follow to prevent contamination.
A. Decontaminate laboratory working surfaces between steps.
B. Use the same set of pipettes throughout the assay in all areas to ensure reproducibility.
C. Have decontamination solutions freshly made in each area regardless of the laboratory setup.
D. Change your lab coat when moving from one working area to another
D. Inactivate RNase from glassware
A freshly prepared diethylpyrocarbonate (DEPC) solution may be used to:
A. Disinfect laboratory glassware when autoclave is not effective
B. Disinfect heat labile solutions
C. Remove nucleic acid contamination from glassware
D. Inactivate RNase from glassware
False
Nucleic acid template should be added to the reaction in the PCR master mix area.
True
False
A. Autoclaving if the contaminant is a virus.
B. Baking at 240°C or higher for at least 4 hours if the contaminant is RNase.
D. Treating with DEPC if the contaminant is RNase
When laboratory glassware is contaminated, the decontamination procedure may require:
A. Autoclaving if the contaminant is a virus.
B. Baking at 240°C or higher for at least 4 hours if the contaminant is RNase.
C. Rinsing with water if the contaminant is DNase.
D. Treating with DEPC if the contaminant is RNase.
A. Contamination can lead to false negative results.
Which of the following is correct about contamination and good practices in decontamination in molecular biology?
A. Contamination can lead to false negative results.
B. PPE should be kept only in the PCR reagent mix preparation area as this is the cleanest area.
C. Heating is the most effective way to completely eliminate RNase activity.
D. Don't perform decontamination until molecular testing is finished.
True
To extract cellular nucleic acid using liquid extraction method, cell lysis step is usually performed first.
True
False
C. The protocol may not be suitable since the source of DNA is different.
Your colleague uses a blood DNA extraction protocol to extract DNA from a small fatty tissue sample. What suggestion may you offer to the colleague?
A. The protocol is appropriate since it is for DNA extraction.
B. The protocol is appropriate only if the DNA from the fatty tissue will be used for PCR.
C. The protocol may not be suitable since the source of DNA is different.
D. Fatty tissue should be done in a high-throughput fashion.
B. Precipitate proteins by adding a concentrated salt solution.
Which of the following could remove cellular protein from nucleic acid in a cell lysate?
A. Add a detergent to keep proteins soluble in aqueous phase.
B. Precipitate proteins by adding a concentrated salt solution.
C. Centrifuge to separate two layers of liquid, salt layer and aqueous layer.
D. Precipitate protein by adding phenol.
A. Column clogging
B. Size of the target nucleic acid
C. Binding capacity of the column
D. PH of the buffer used to release the nucleic acid from the column
Which of the following may affect the result of a column-based nucleic acid extraction?
A. Column clogging
B. Size of the target nucleic acid
C. Binding capacity of the column
D. PH of the buffer used to release the nucleic acid from the column
B. Automation of the process is possible
In the magnetic bead-based nucleic acid extraction:
A. The magnetic beads are packed in a column
B. Automation of the process is possible
C. Matrix clogging is a major disadvantage
D. High salt solution is required to wash nucleic acid off the beads
C. Phenol
D. Chloroform
Which of the following chemicals are NOT used in nucleic acid precipitation step?
A. Ethanol
B. Isopropanol
C. Phenol
D. Chloroform
C. RNA concentration can be estimated by spectrophotometric measurement.
Which statement is correct for nucleic acid spectrophotometric measurement?
A. Use visible light instead of UV light to perform spectrophotometric measurement.
B. Spectrophotometric reading of nucleic acid is usually a negative number.
C. RNA concentration can be estimated by spectrophotometric measurement.
D. Size of the nucleic acid can be calculated based on A260 reading.
A. Other non-specific DNA contaminants can interfere with A260 measurement of you specific DNA.
B. Protein contamination in the extracted DNA can be monitored by A260 and A280 ratio.
Which statements are true about using spectrophotometric measurement to detect contamination in extracted DNA?
A. Other non-specific DNA contaminants can interfere with A260 measurement of you specific DNA.
B. Protein contamination in the extracted DNA can be monitored by A260 and A280 ratio.
C. RNA contamination in your DNA product can be identified by A260 reading.
D. RNA contamination in your DNA product can be identified by A280 reading.
A. You observe the intensity, position, and appearance of nucleic acid bands.
Which of the following is true about gel electrophoresis analysis of nucleic acid?
A. You observe the intensity, position, and appearance of nucleic acid bands.
B. Ethidium bromide should be replaced with SYBR Green for RNA staining.
C. Larger nucleic acid runs off agarose gel before smaller nucleic acid.
D. Nucleic acid samples are loaded on the positive electrode end of the gel.
B. Ethidium bromide can be used to stain DNA.
C. Gel electrophoresis is one way to observe DNA degradation.
D. SYBR Green can be used to stain DNA.
Which of the following are true about DNA agarose gel electrophoresis analysis?
A. DNAs of 20 kb and 200 kb migrate at the same speed on agarose gel.
B. Ethidium bromide can be used to stain DNA.
C. Gel electrophoresis is one way to observe DNA degradation.
D. SYBR Green can be used to stain DNA.
A. Bands of smaller DNA fragments on your stained electrophoresis gel.
Which could indicate that your purified large size DNA product is contaminated with smaller DNAs?
A. Bands of smaller DNA fragments on your stained electrophoresis gel.
B. Bands of smaller DNA fragments on your unstained electrophoresis gel.
C. High A260 reading.
D. High A280 reading.
D. Warm up the UV lamp and record the A280 reading.
Which is usually NOT considered a DNA quantification gel electrophoresis protocol step?
A. Check that the gel is placed in the correct orientation in the electric field.
B. Mix the nucleic acid sample with a sample loading dye.
C. Prepare DNA standards of known concentrations.
D. Warm up the UV lamp and record the A280 reading.
False
4°C is recommended for long-term RNA storage.
True
False
B. Your DNA has degraded
Which could be a cause of smeared band on your DNA electrophoresis gel?
A. Your DNA sample was not mixed by extensively vortexed before loading.
B. Your DNA has degraded.
C. EDTA in the gel running buffer activates DNase.
D. Tris (pH 8.5) was included in your DNA storage buffer.
D. 95°
At what temperature does denaturation occur?
A. 55°
B. 75°
C. 65°
D. 95°
B. DNA polymerase
To perform reverse transcriptase PCR analysis, you need:
A. RNA polymerase
B. DNA polymerase
C. dNTPs
D. EDTA
A. Denaturation
D. Annealing
Steps to perform PCR include (all that apply):
A. Denaturation
B. Expanding
C. Termination
D. Annealing
A. At each cycle in real-time
In Quantitative PCR (qPCR), at what point are PCR products detected?
A. At each cycle in real-time
B. After the last cycle at the end
C. After the first cycle at the beginning
D. After the last cycle at the beginning
False
TaqMan probes recognize all regions within the target DNA sequence.
True
False
True
SYBER® Green is a dye used for dye-based DNA detection.
True
False
A. Absolute quantification
D. Relative quantification
Determination of nucleic acid amount or quantification by real-time PCR can be done by (all that apply):
A. Absolute quantification
B. Positive quantification
C. Negative quantification
D. Relative quuantification
A. Fluorescent dye-based detection
B. Fluorescent probe-based detection
What are the most commonly used methods used to detect products in qPCR?
A. Fluorescent dye-based detection
B. Fluorescent probe-based detection
C. Fluorescent curve-based detection
D. Fluorescent hybrid-based detection
A. No template control
Which control would you use to identify nucleic acid contamination in reagents?
A. No template control
B. No reverse transcriptase control
C. No amplification control