AP Psychology - Unit 3: Developmental Psychology
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
Conception
The action of conceiving a child
Zygote
Fertilized egg
embryonic stage
Developing human organisms 2 weeks to 2nd month
Tetratogens
agents, such as chemicals and viruses, that can reach the embryo or fetus during prenatal development and cause harm
Ex) radiation, toxic, alcohol
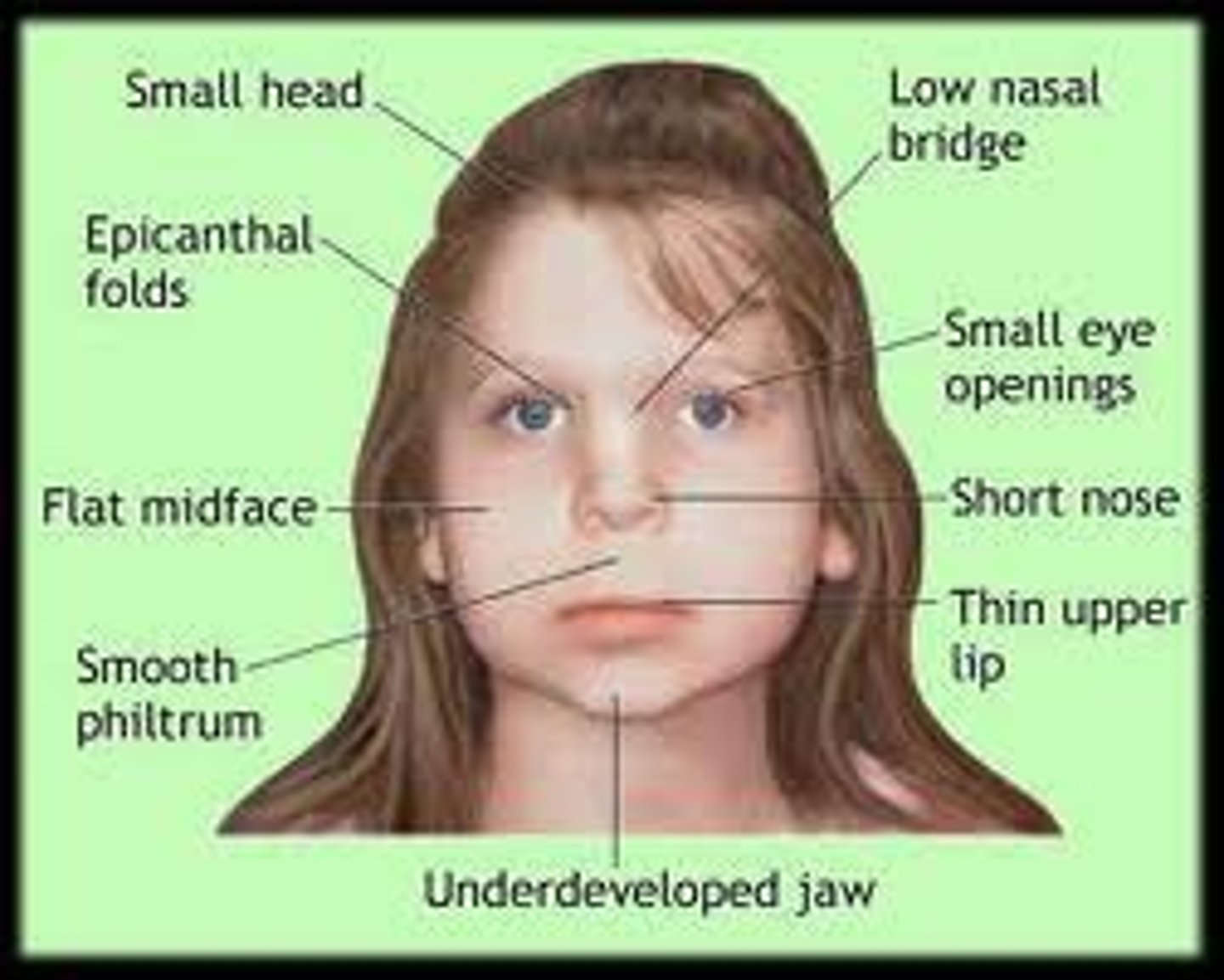
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome
a medical condition in which body deformation or facial development or mental ability of a fetus is impaired because the mother drank alcohol while pregnant
Reflexes
Responses ideally suited for our survival
Rooting Reflex
Baby's basic survival instinct - helps baby find + latch onto bottle or nipple
Habituation in infants
As infants gain familiarity with repeated exposure to a visual stimulus, their interest wanes and they look away sooner.
Visual cliff
A research method used to study depth perception in infants + animals
motor development
The growth in the ability of children to use their bodies and physical skills
Fine motor
small muscle movements Ex) holding a pencil and writing
Gross motor
Use of larger muscles
Ex) waving your arm
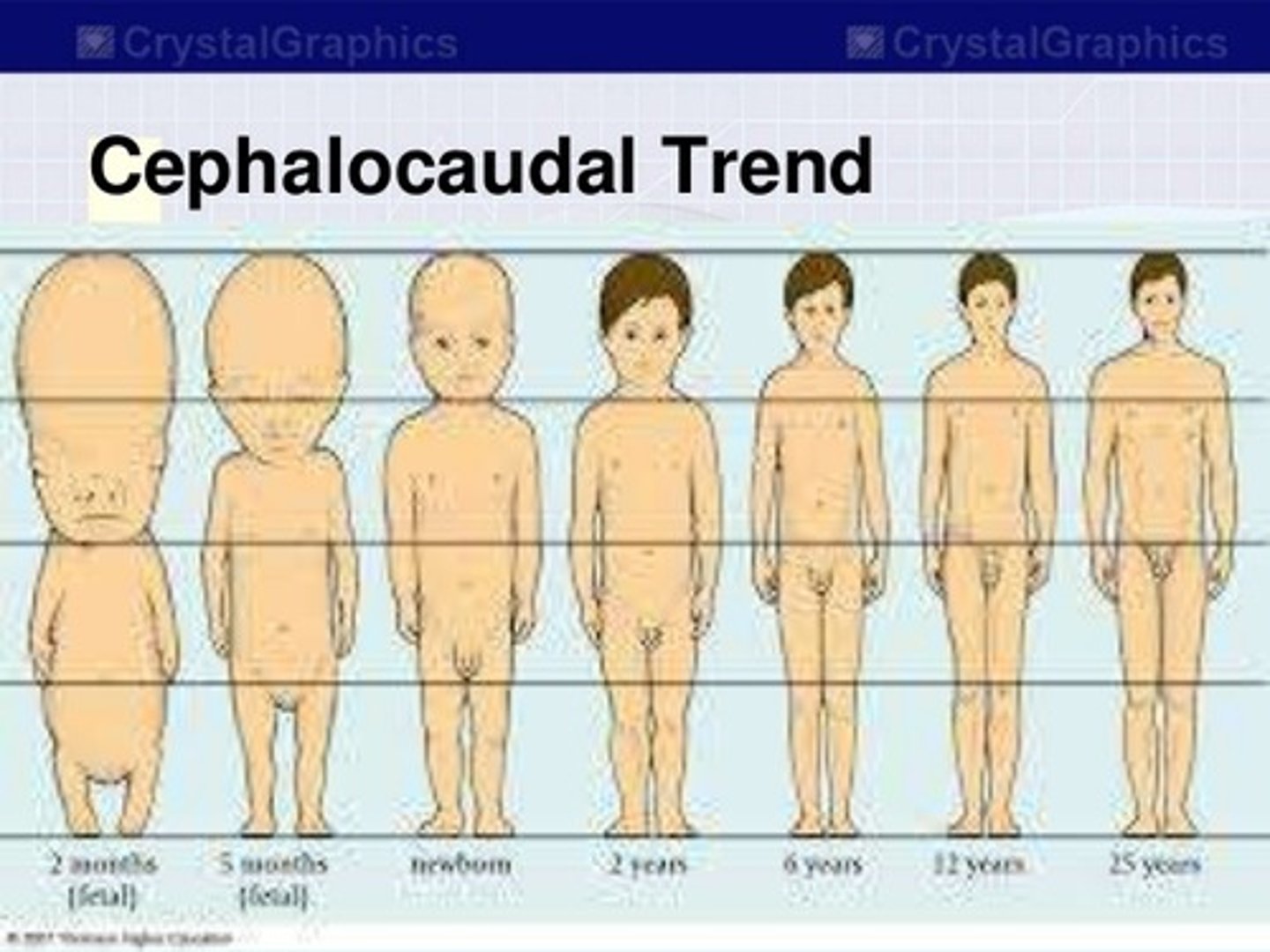
cephalocaudal trend
the head-to-foot direction of motor development
Proximodistal Trend
Gross motor to fine motor development
infantile amnesia
the inability to remember events from early childhood
Cognition
All the mental activities associated with thinking, knowing, remembering and communicating
Jean Piaget
Known for his theory of cognitive development in children
4 stages of development
Schema
How we see the world
Assimilation
interpreting our new experiences in terms of our existing schemas
Accommodation
adapting one's current understandings (schemas) to incorporate new information
Sensorimotor stage
The stage where infants know the world mostly in terms of their sensory impressions + motor activities
object permanence
the awareness that things continue to exist even when not perceived
Preoperational stage
The stage during which a child learns to use language but does not yet comprehend the mental operations of concrete logic
Conservation
properties such as mass, volume, and number remain the same despite changes in the forms of objects
Pretend play & imaginary audience
A type of play where children use their imagination to create scenarios and act out different roles and events
mental symbols
Internal cognitive symbols/structures that stand for objects, events or concepts in the mind
Animism
Belief that objects that are non living have feelings/thoughts
Egocentrism
the inability to see the world through anyone else's eyes
Theory of Mind
people's ideas about their own and others' mental states—about their feelings, perceptions, and thoughts, and the behaviors these might predict.
Empathy
the ability to understand and share the feelings of another
concrete operational stage
Stage where children gain the mental operations that enable them to think logically about concrete events
Formal operational stage
Stage where children begin to think logically about abstract concepts
Critical thinking
Thinking that examines assumptions, evidence, assesses conclusion
Ex) decision making
abstract thinking
ability to think beyond concrete literal ideas Ex) imagination
Hypothetical thinking
Being able to consider possibilities, probabilities and alternatives
Lev Vygotsky
Studied how children think and learn
child's mind grows thru interaction w/ the social environment
Zone of proximal development
the difference between what children can do with assistance and what they can do alone
MKO
more knowledgeable other - anyone who has a better understanding or higher ability level than the learner
Parenting styles
The overall approach or strategy that parents use to raise and interact with their children
Authoritarian Parenting
When parents impose rules and restrictions while expecting obedience (controlling)
Authoritative parenting
Parents are nurturing, responsive, and supportive, yet set firm boundaries
Permissive parenting
Parents view themselves as more of a friend than a parent and don't set strict rules
Separation Anxiety
the distress displayed by infants when a customary care provider departs
Attachment
an emotional tie with another person
Harry Harlow's Experiment on Attachment
Examined the importance of contact comfort in monkeys - concluded that infants feel an attachment toward their caregiver
Contact comfort
The physical + emotional comfort that an infant receives from being in physical contact with its mother/primary caregiver
Critical period for attachment
an optimal period early in the life of an organism when exposure to certain stimuli or experiences produces normal development
Secure attachment
Infants feel distress when caregiver leaves and finds comfort in the caregiver's return
Insecure attachment
Infants feel distress when caregiver leaves and does not feel comfort in the caregiver's return
Avoidant attachment
infants who seem unresponsive to the parent when they are present, are usually not distressed when she leaves, and avoid the parent when they return
anxious attachment
demonstrated by babies who seem constantly afraid of potential separation from the caregiver
Disorganized attachment
a type of attachment that is marked by an infant's inconsistent reactions to the caregiver's departure and return
Adverse childhood experiences
Potentially traumatic events that occur in childhood (physical abuse, neglect)
Konrad Lorenz
Some infant animals become attached on individuals or even objects they see
Imprinting
the process by which certain animals form attachments during a critical period very early in life
Child temperament
A child's characteristic emotional reactivity and intensity
self-concept
All our thoughts and feelings about ourselves in answer to the question "who am I"
Possible selves
A potential self derived from self knowledge, past experiences, social interactions and cultural context
Enriched environment
an environment that offers a person many chances to learn
Impoverished environment
An environment that fails to provide opportunities for a lot of growth and development
Peer influence
The impact that peers have on an individual's thoughts, attitudes and behaviors
Puberty
The period of sexual maturation, during which a person becomes capable of reproducing
Primary sex characteristics
the body structures (ovaries, testes, and external genitalia) that make sexual reproduction possible
secondary sex characteristics
nonreproductive sexual characteristics, such as female breasts
Menarche
the first menstrual period
Spermarche
first ejaculation
Social identity
The idea that individuals derive a sense of self and their identity from the groups they belong to
James Marcia's 4 stages of identity development
Identity diffusion
identity foreclosure
identity moratorium
identity achievement
Identity diffusion
A state where you lack a clear sense of self and have not made commitments to any particular identity
Identity foreclosure
commitment in the absence of exploration
Identity moratorium
exploration without having reached commitment
ex) gap year
identity achievement
commitment to values, beliefs, and goals following a period of exploration
Occupational identity
Describes an individual's sense of self and identity based on their chosen occupation or profession
Familial identity
the sense of self as always connected to family and others
Sexual orientation
a person's romantic and emotional attraction to another person
Fluid intelligence
Ability to learn, assess and navigate new situations
crystallized intelligence
Accumulated knowledge you can recall as needed
Generativity
Desire to nurture and guide the next generation
Stagnation
Individuals becomes self-absorbed and lacks sense of contribution to world
Social clock
the culturally preferred timing of social events such as marriage, parenthood, and retirement
Mid life crisis
a dramatic period of self-doubt caused by the passing of youth and the move into later adulthood.
Ego integrity
Sense of acceptance and satisfaction with one's life
Ego despair
The feeling of regret, failure
Empty nest syndrome
alleged period of depression in mothers following the departure of their grown children from the home
Elizabeth Kubler-Ross 5 stages of grief
1. Denial
2. Anger
3. Bargaining
4. Depression
5. Acceptance
Language
A complex system of communication that involves the use of words, symbols, or signs to express ideas
Phonemes
in language, the smallest distinctive sound unit
Morphemes
The smallest units of meaning in a language.
Semantics
Meaning of words and sentences
Syntax
The ordering of words when making a sentence
telegraphic speech
early speech stage in which a child speaks like a telegram—"go car"—using mostly nouns and verbs.
Cooing stage
at about 2 months the infant begins to make vowel-like sounds
babbling stage
The uttering articulate sounds but can't pronounce words
Linguistic determinism
language determines the way we think
Linguistic relativity
the hypothesis that one's language determines the nature of one's thought