Unit 5 Chapter 10 AP Hug
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/66
Last updated 3:05 AM on 2/16/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
1
New cards
Agribusiness
commercial agriculture characterized by integration of different steps in the food processing industry, usually through ownership by large corporations
2
New cards
Agricultural origins
Humans were primarily nomadic hunters and gatherers, moving to find new food sources
3
New cards
Animal domestication
the adaptation of a plant or animal from a wild or natural state to life in close association with humans
4
New cards
Biotechnology
A form of technology that uses living organisms (usually genes) to modify or make plants and animals, or to develop other microorganisms for specific purposes
5
New cards
Cereal grain
A grass yielding grain for food
Examples: Oats, Wheat, Rye, Barley
Examples: Oats, Wheat, Rye, Barley
6
New cards
Combine
a machine that reaps, threshes, and cleans grain while moving over a field
7
New cards
Commercial agriculture
The farming of products for sale off the farm
8
New cards
Crop
Grain or fruit gathered from a field as a harvest during a particular season
9
New cards
Crop rotation - purpose
* The practice of rotating use of different fields from crop to crop each year
* To avoid exhausting the soil and improve soil nutrients
* To avoid exhausting the soil and improve soil nutrients
10
New cards
Dairying
An agricultural activity involving the raising of livestock, most commonly cows and goats, for dairy products
11
New cards
\#1 milk producing nation
India
12
New cards
Double cropping
harvesting twice a year from the same field
13
New cards
Farming
deliberate effort to change a portion of Earth's surface through the cultivation of crops and the raising of livestock for sustenance or economic gain
14
New cards
Grain
* Seed of a cereal grass
* staple grains: maize, wheat, rice (most produced grains worldwide)
* staple grains: maize, wheat, rice (most produced grains worldwide)
15
New cards
Green Revolution
a period of increased agricultural productivity that occurred in the mid-20th century, primarily in developing countries
16
New cards
Horticulture
The growing of fruits, vegetables, and flowers
17
New cards
Hunting and gathering
The first way humans obtained food
18
New cards
Aquaculture
the cultivation of aquatic organisms (such as fish or shellfish) especially for food
19
New cards
intensive subsistence
* form of subsistence agriculture
* farmers must put in a lot of effort to produce the maximum possible yield from a piece of land
* farmers must put in a lot of effort to produce the maximum possible yield from a piece of land
20
New cards
livestock ranching
the raising of domesticated animals for the production of meat and other products
21
New cards
luxury crops
a crop that is grown to serve some purpose other than sustaining human life
22
New cards
mediterranean agriculture
agriculture practiced in areas with mediterranean climate, mostly horticulture
23
New cards
metallurgy
art and science of extracting metals from their ores and modifying the metals for use
24
New cards
pastoral nomadism
a form of subsistence agriculture based on herding domestic animals
25
New cards
pasture
grass or other plants grown for feeding grazing animals, and land used for grazing animals
26
New cards
plantation agriculture
a single person or company owns a big farm and grows a single crop
* ex: corn, cotton, wheat
* ex: corn, cotton, wheat
27
New cards
Common locations today for plantation agriculture -
tropical areas of Latin America, Asia and Africa
28
New cards
plant domestication
wild plants are cultivated into productive crops, often with more desirable traits
29
New cards
prime agriculture land
* most productive farmland
* pastureland, cropland, forestland
* pastureland, cropland, forestland
30
New cards
slash-and-burn agriculture
method of cultivation in which forests are burned and cleared for planting
31
New cards
shifting cultivation
land being farmed for 2-3 years before moving on to other areas
32
New cards
subsistence farming
Agriculture primarily to provide food for consumption by the farmer and the farmer's family
33
New cards
Early human activities
* Primary Economic Activities
* Secondary Economic Activities
* Tertiary Economic Activities
* Quaternary Economic Activities
* Secondary Economic Activities
* Tertiary Economic Activities
* Quaternary Economic Activities
34
New cards
Primary
* harvesting
* mining raw materials
* fishing and farming
* mining raw materials
* fishing and farming
35
New cards
Secondary
* processing
* refining natural resources
* factory work
* timber into furniture
* refining natural resources
* factory work
* timber into furniture
36
New cards
Tertiary
* sale
* exchange of goods
* retail
* real estate
* exchange of goods
* retail
* real estate
37
New cards
Quaternary
* generation of knowledge
* sharing of research
* teaching
* medical service
* sharing of research
* teaching
* medical service
38
New cards
First Neolithic Agricultural Revolution
* 12,000 years ago, occurred first in Mesopotamia
* transition from hunting and gathering to planting and sustaining
* transition from hunting and gathering to planting and sustaining
39
New cards
Second Agricultural Revolution
* increased technology
* increased farm productivity through mechanization
* increased farm productivity through mechanization
40
New cards
Third (green) Agricultural Revolution
* animal/plant breading with another
* genetic engineering of products
* increased use of pesticides and fertilizers
* genetic engineering of products
* increased use of pesticides and fertilizers
41
New cards
Peripheral Agriculture vs Core Agriculture activities around the world
* core countries exploit peripheral for labor and raw materials
* peripheral countries are dependent on core countries for capital and have an underdeveloped industry
* peripheral countries are dependent on core countries for capital and have an underdeveloped industry
42
New cards
Distribution of agricultural activities in the US and Worldwide (Whittlesey Map)
Regions according to the map:
* Southeast Asia ( Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines)
* West Africa
* Sri Lanka
* Central USA (North Dakota, South Dakota, Nebraska)
* Central America
* Southeast Asia ( Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines)
* West Africa
* Sri Lanka
* Central USA (North Dakota, South Dakota, Nebraska)
* Central America
43
New cards
Where did agriculture originate
The Fertile Crescent
* ex: (Lebanon, Syria, Jordan, Israel, parts of modern day Iraq)
* ex: (Lebanon, Syria, Jordan, Israel, parts of modern day Iraq)
44
New cards
Von Thunen Model
\
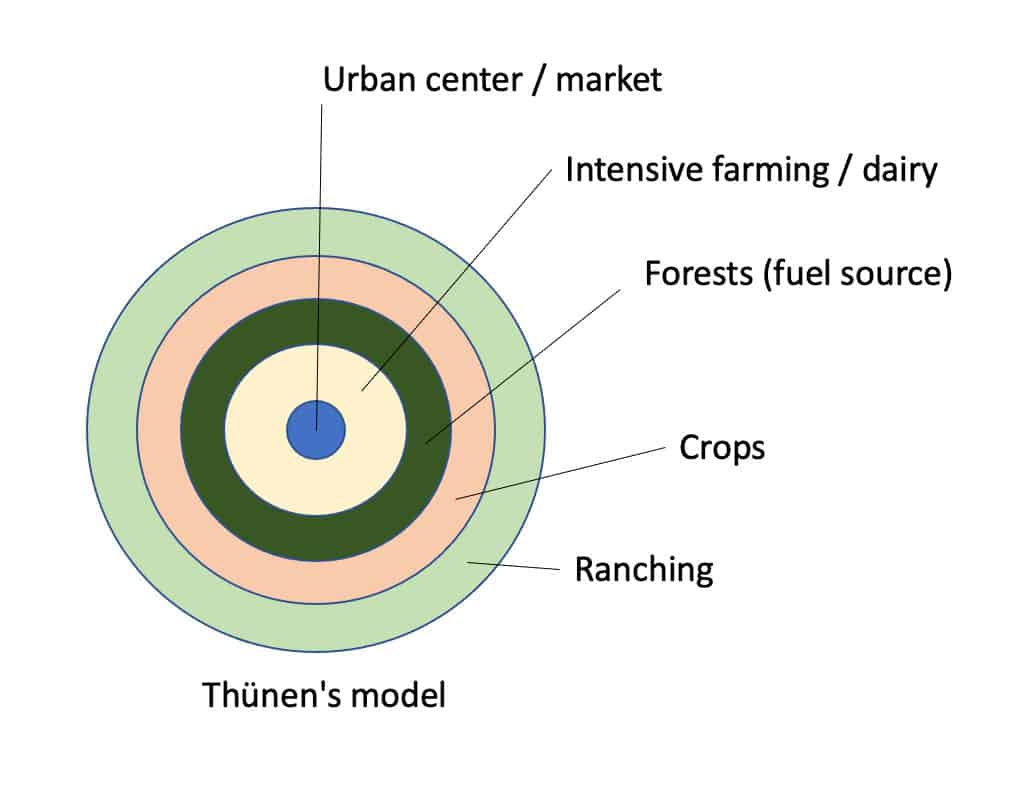
45
New cards
Center Position (1)
Market - where the business occurs
46
New cards
2nd position
* Labor Intensive crops
* farming and dairying
* produce of berries, lettuce, or tomatoes
* farming and dairying
* produce of berries, lettuce, or tomatoes
47
New cards
3rd position
* managed forests
* timber and firewood used for heating, cooking, building
* weight makes transporting expensive
* timber and firewood used for heating, cooking, building
* weight makes transporting expensive
48
New cards
4th position
* Labor Extensive crops
* devotion to grains and cereal crops (rye, wheat, barley)
* Less likely to go bad quickly and not too bulky
* devotion to grains and cereal crops (rye, wheat, barley)
* Less likely to go bad quickly and not too bulky
49
New cards
5th position
* grazing
* livestock production
* livestock production
50
New cards
Risks of single crop economies
high use of fertilizers, pests, biodiversity, environmental pollution
51
New cards
Aquaculture vs Commercial Fishing
* farming of aquatic organisms under controlled conditions for human consumption
vs
* catching fish and other seafood for commercial profit
vs
* catching fish and other seafood for commercial profit
52
New cards
Where is the Corn Belt
From the panhandle of Texas up to North Dakota and east to Ohio
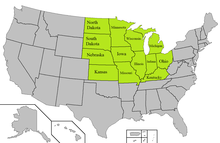
53
New cards
Places where Rice is the leading energy source
* Asia
* Sub-Saharan Africa
* South America
* Sub-Saharan Africa
* South America
54
New cards
Where is wheat?
Temperate areas of the Northern Hemisphere
55
New cards
Description of an Extractive industry
made up of mining, quarning, oil and gas industries
56
New cards
Place of first domestication of many animals
Middle East
57
New cards
Major forms of subsistence
* shifting cultivation
* pastoral nomadism
* intensive subsistence: wet rice dominant
* Plantation farming
* pastoral nomadism
* intensive subsistence: wet rice dominant
* Plantation farming
58
New cards
Major forms of commercial agriculture
* Dairy farming
* Mixed crop and livestock
* Grain farming
* Livestock ranching
* Mediterranean agriculture
* Commercial gardening and fruit farming
* Mixed crop and livestock
* Grain farming
* Livestock ranching
* Mediterranean agriculture
* Commercial gardening and fruit farming
59
New cards
Malnourished vs undernourished (where would we see the most?)
when your diet doesn't contain the right amount of nutrients (South Asia)
vs
specifically not getting enough nutrients (Yemen)
vs
specifically not getting enough nutrients (Yemen)
60
New cards
Practices in rice farming
1. Field Preparation
2. Flooding and Seeding
3. Maturation of Rice
4. Harvest
5. Milling and Storage
61
New cards
Reasons for planting drug crops in LDCs
* a vital source of economic and physical security for poor
62
New cards
Strategies for increasing food supply
* Reduce food waste
* Grow different crops
* Capitalize on Urban Farming
* irrigation
* Grow different crops
* Capitalize on Urban Farming
* irrigation
63
New cards
Common crops of mixed crop and livestock areas and reasons for their use
* beef
* milk (promotes growth and energy)
* eggs (Sources of protein for animals and plant growth)
* corn (animals feed: cows get thicccer)
* root crops (human food, animal feed)
* soybeans (animal feed: high of protein)
* milk (promotes growth and energy)
* eggs (Sources of protein for animals and plant growth)
* corn (animals feed: cows get thicccer)
* root crops (human food, animal feed)
* soybeans (animal feed: high of protein)
64
New cards
Describe truck farming and where it is practiced
* production of crops of some vegetables on a larger scale
* California, Texas, Florida
* California, Texas, Florida
65
New cards
Sustainable yields
* the harvest of a specific resource
* Keeping the stock at the level producing maximum growth
* Keeping the stock at the level producing maximum growth
66
New cards
Most common commercial agriculture in Europe
Mixed Crop and Livestock
67
New cards
Long Lot Plot System
long rectangular plots of farmland to give equal access to the river