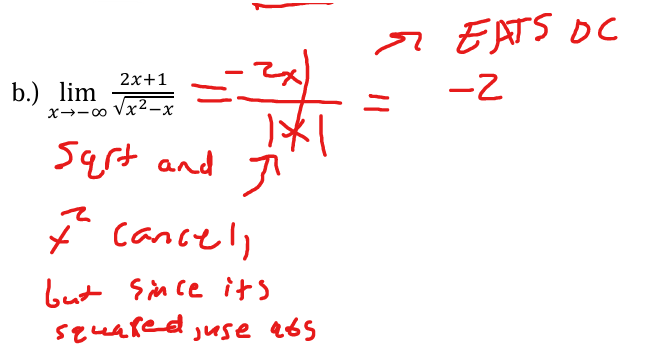AP Calculus AB Unit 1
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms

Conclusion Statement:
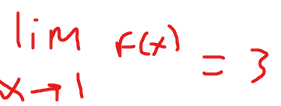
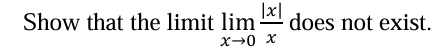
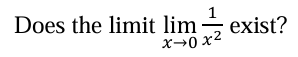
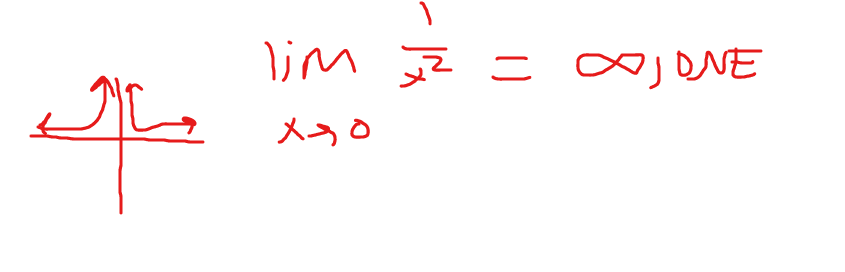
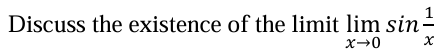
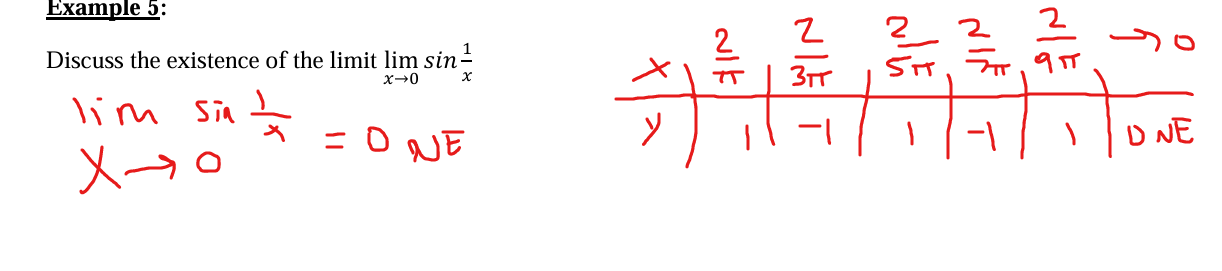
ln(e) = ?
1
ln(1)
0
ln(0)
undefined
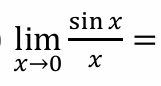
1
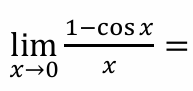
0
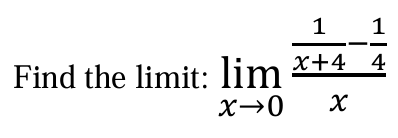
-1/16
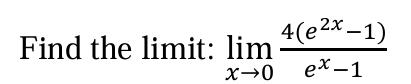
8
Three continuous conditions
f(c) is defined
lim f(x) as x approaches c exists
lim f(x) as x approaches c equals f(c)
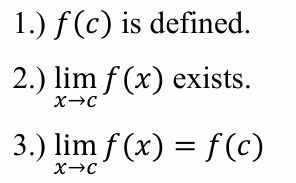
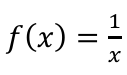
Continuity of this function:
can’t divide by 0, so (-∞,0) U (0,∞)
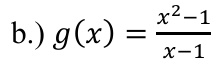
Continuity of this function:
hole at x=1, so (-∞,1) U (1,∞)
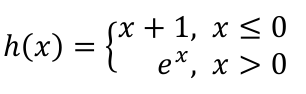
Continuity of this function:
(-∞,∞)
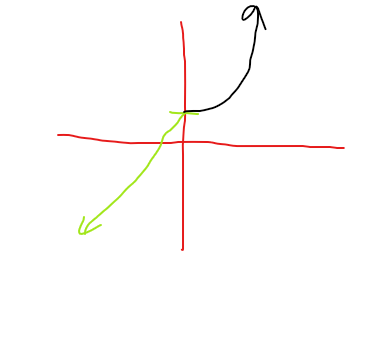
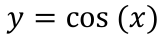
Continuity of this function:
(-∞,∞)
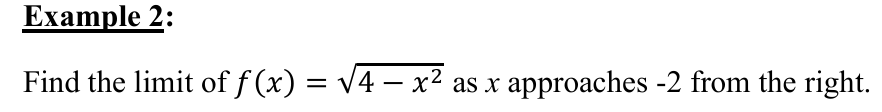
0
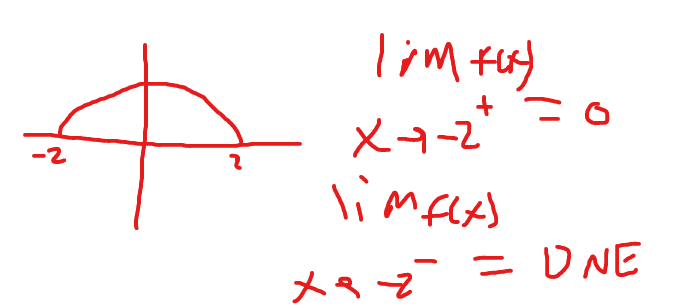
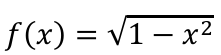
Discuss the continuity of this function:
f(x) is cont. on [-1,1]
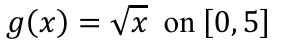
Discuss the continuity of this function:
g(x) is cont. on [0,5]
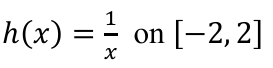
h(x) is cont. on [-2,0) U (0,2]
if f and g are continuous on (-∞,∞), then
fg is continuous (-∞,∞)
f±g is continuous (-∞,∞)
f/g is continuous (-∞,∞), given that the denominator is not 0
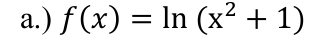
where is composite function continuous
y=x²+1 is cont. on (-∞,∞) and y=ln (x) is cont. on (0,∞), therefore f(x) is cont. on (0,∞)
IVT Theorem states that
If f is continuous on the closed interval [a,b], f(a) ≠ f(b), and k is any number between f(a) and f(b), then there is at least on number c in [a,b] such that f(c) = k
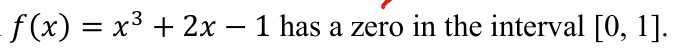
Prove that this function is continuous using IVT
f(x) is cont. on [0,1], since f(0) =1 and f(1) = 2 and -1 < 0 < 2, then by IVT, there is at least one c in [0,1] such that f(c) = 0
in order to give the IVT justification for a table, the question must state that
the function is continuous
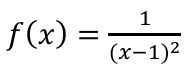
Determine the limit as x approaches 1 from the left and right
∞, DNE
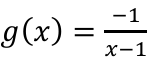
Determine the limit as x approaches 1 from the left and right
DNE
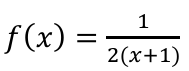
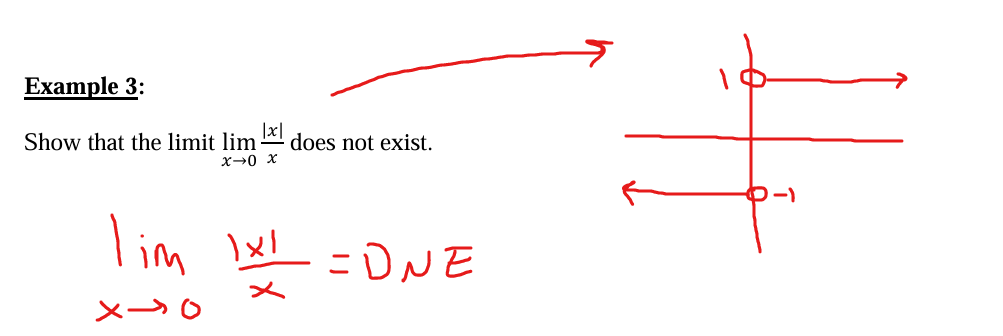
Determine the limit as x approaches -1 from the left and right
DNE
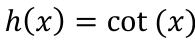
Find the VAs
pi(k)
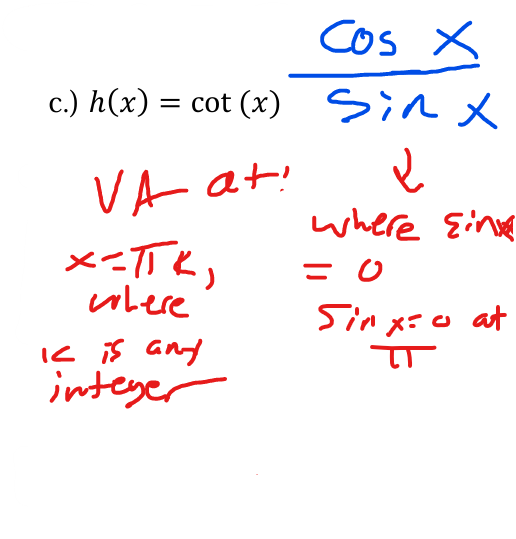
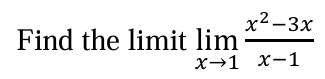
DNE
if you can’t find lim of a function through direct substitution, factoring, or conjugates, and you get b/0, then
solve for the lim as x approaches from both sides (±), the answer should be either ±∞, DNE or DNE
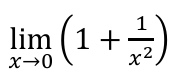
∞
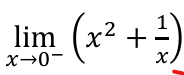
-∞
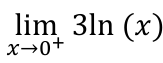
-∞
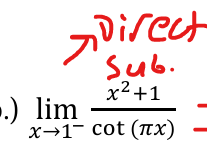
0
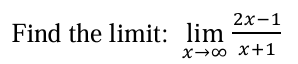
2
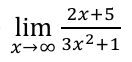
0
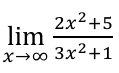
2/3
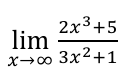
∞
For BOBO and EATS DC you get numbers for answers, but for BOTN you get
either ±∞
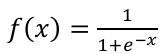
Find both of the horizontal asymptotes
1 and 0
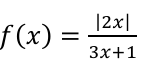
Show that f has different horizontal asymptotes from the left and right
2/3 and 0
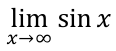
find the limit
DNE
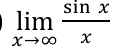
find the limit
0
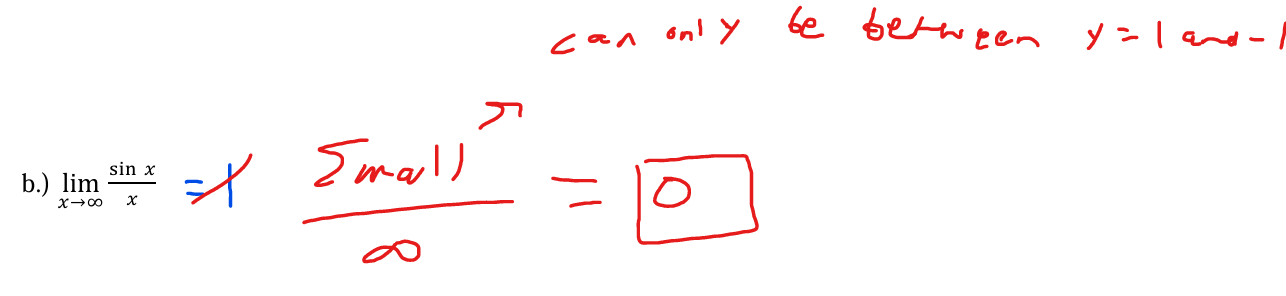
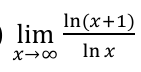
find the limit
1
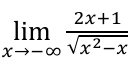
-2