BIOL0510: Microbial Biotechnology
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
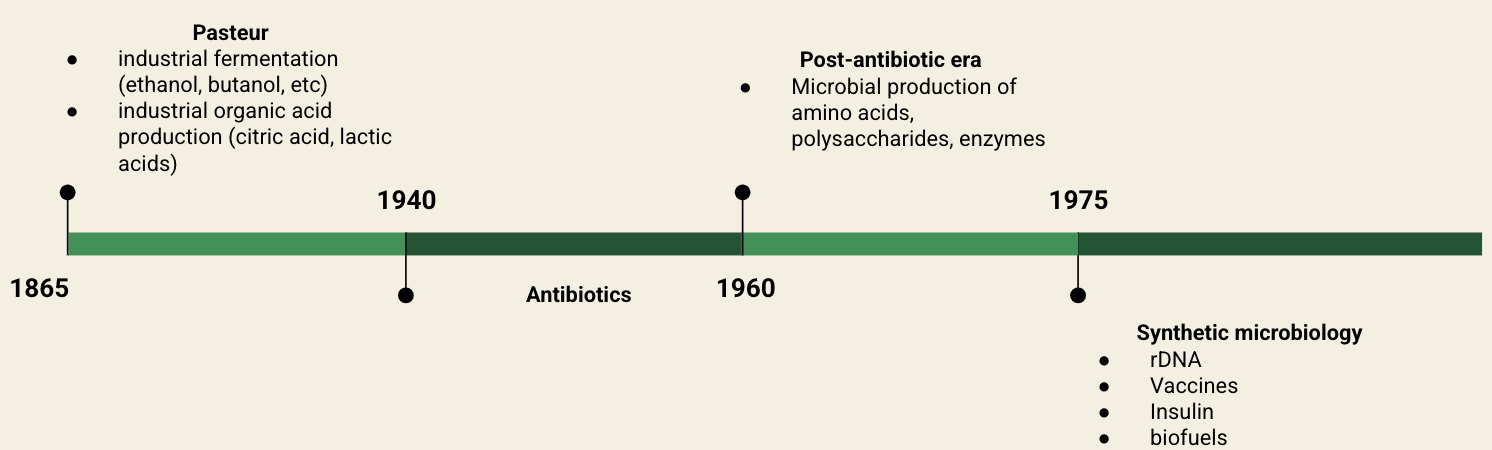
What is the biotechnology timeline?
pre-Pasteur (fermenting drinks/food)
Pasteur (industrial fermentation and organic acids)
antibiotics
post-antibiotics (producing amino acids, enzymes, etc)
synthetic microbio (vaccines, insulin, biofuels)
What is microbial biotechnology?
the use of microorganisms, cells, or cell components to make a product (ex. foods, vitamins, enzymes)
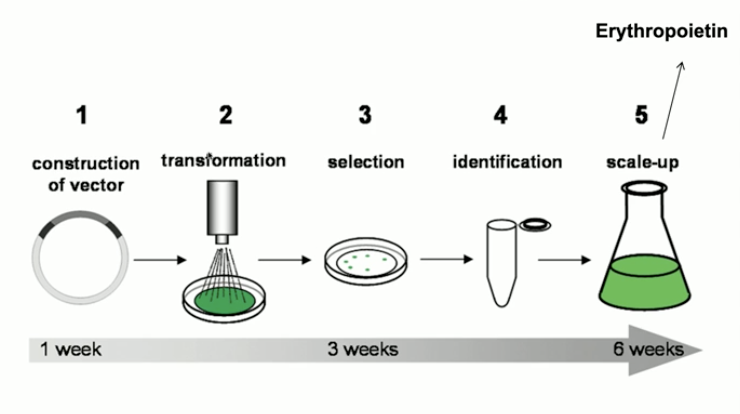
What is erythropioetin?
a protein/hormone that encourages the production of red blood cells
What is a vector?
a DNA molecule used as a vehicle to transfer genetic material (ex. a plasmid or virus)
What are shuttle vs expression vectors?
shuttle: usually plasmids that can propagate (spread) and facilitate gene transfer between two or more species
expression: transfer a gene and express the protein product of the gene
How do you make a shuttle vector?
introduce new DNA into existing organisms’ DNA to make recombinant DNA
introduce the recombined DNA into an animal to make them transgenic
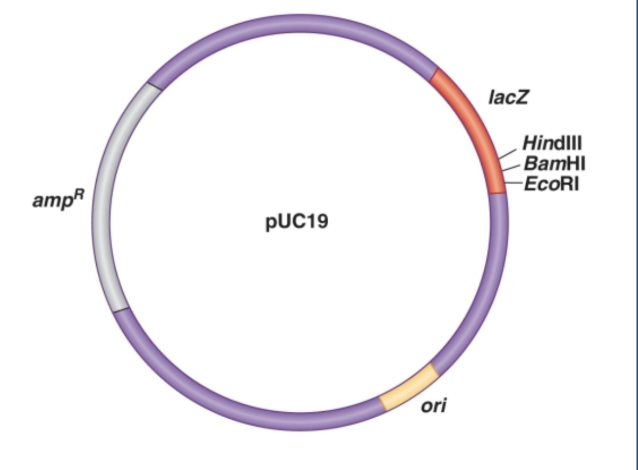
What is recombinant DNA?
DNA created by combining genetic material from different sources/species to produce a ‘recombined’ genome
What is a transgenic animal?
one whose genome has been altered by the introduction of a foreign gene from another species
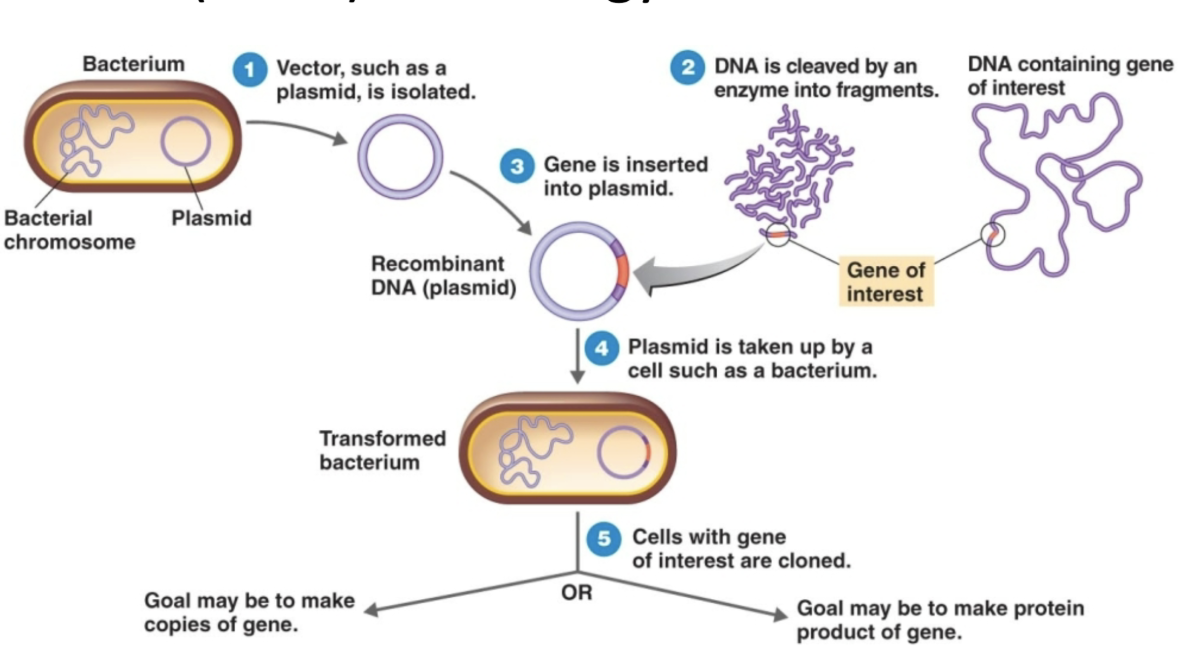
Describe the steps of genetic engineering using recombinant DNA technology
isolate a vector (ex. plasmid) from a bacterial cell
cleave your DNA segment of interest using enzymes
insert the gene of interest to the vector
introduce the vector to a bacterial cell for amplification
clone cells with the gene of interest to either produce copies of the gene or to produce proteins by that gene
What do we use to cut and paste a gene of interest into a plasmid?
restriction endonucleases: DNA cutting enzymes that cut at the ends of your gene of interest
ligases: link together gene fragments
What are the different ends you can make from cutting DNA?
sticky: cut pieces of DNA with an overhang
blunt ends: evenly cut ends
Why do bacteria have restriction endonucleases, aka what are their other functions?
they are antimicrobial against phages
they can degrade other bacteria that may infect them with their DNA
(defense strategies)
How do we get a new bacterial cell to take up a plasmid? 2 ways
transformation: forming pores in bacteria to induce plasmid uptake
CaCl2 + heat shock
Electroporation
Transduction: using bacteriophages that contain engineered plasmids to spread the plasmid via infection
How do we make sure that the bacteria received the plasmid? List 3 common selection markers
In a process called selection
common markers/strategies used to verify selection
antibiotics
fluorescent marker (GFP)
sequence the DNA
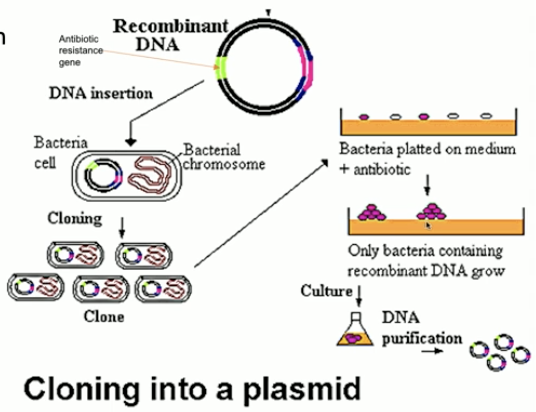
Describe the first step of selection used to verify that the correct plasmid (with ampR and LacZ disruption insertions) was uptaken
place transgenic bacteria in a plate with ampicillin; bacteria that took up the plasmid with the ampR insertion will continue to grow/display resistance to ampicillin
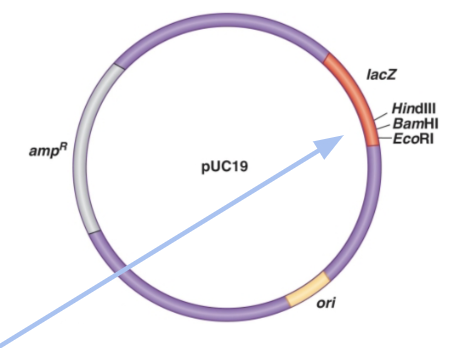
Describe the 2nd step of selection used to verify that the correct plasmid (with ampR and LacZ disruption insertions) was uptaken. Define lacZ and xgal, discuss the two possible outcomes, and explain why you would select for white colonies over blue.
lacZ: a gene that makes galactosidase
X gal: galactose with dye on media
outcomes:
X gal (on plate) + galactosidase (LacZ is functional) = blue colonies grow
X gal (on plate) + no galactosidase (LacZ is NOT functional) = white colonies grow
selection:
we want to select for and clone white colonies: white colonies are white because they disrupted LacZ activity (which is what we intended for the disruption insertion to do)
we don’t want to select for blue colonies: blue colonies are blue because the disruption insertion ended up inserting outside of the LacZ gene or not inserting at all
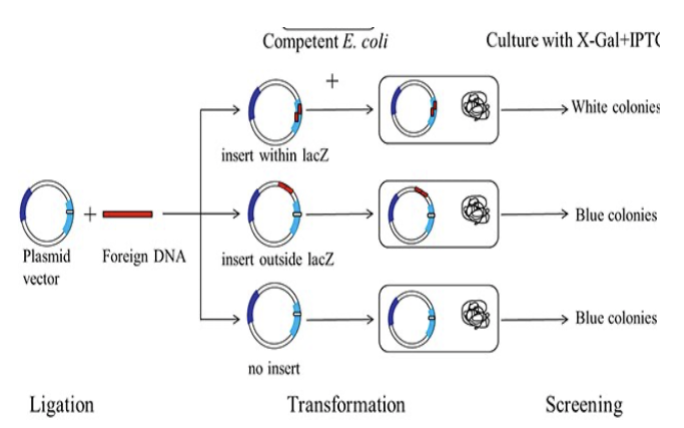
Why do both ampicillin resistance and lacZ screening need to be conducted in this example of gene editing?
ampicillin selection ensures you’re only working with cells that took up the plasmid
lacZ screening allows you to distinguish between cells with the original non-recombinant plasmid (blue colonies) and those with the recombinant plasmid (white colonies)
What do we do to the bacteria with recombinant DNA after selection? Define the step and how its conducted
purification: isolating the desired product (often a protein) from bacterial cells
How:
give them media and let them grow
Conduct high-performance liquid chromatography: a general process that detects for proteins of a certain size that match the desired protein product
List some drugs that are made via genetic engineering/cloning
insulin, human growth hormone, estrogen, steroids, epinephrine
How did diabetic people get insulin treatment before cloning?
received insulin injections produced by cow pancreases (14 cow pancreases/1 person/year)
How did people with stunted growth get human growth hormone before cloning? What is the risk associated with that method?
human cadavers; 18 cadavers were needed/person/year; risk: potential transmittance of human pathogens
List 2 pros to protein cloning
increased safety of supplemental drugs
come from reliable, affordable, and purified sources
What is gene therapy?
using DNA to treat diseases by
replacing defective/missing genes
removing genes
How does an adenovirus vaccine (ex. COVID vaccine) work?
the gene for a specific antigen is inserted into a non-pathogenic version of the target virus —> creates the vaccine
the vaccine is injected into a patient in vivo or a patient’s cells ex vivo
the virus part of the vaccine infects the patient’s cells so they can express the antigen on their surfaces
the patient’s immune system can now detect the virus and maintain immunity to it upon external exposure
What are the safety issues associated with recombinant DNA treatments/products?
avoid accidental release
GMO crops must be safe for consumption and for environment
lower diversity of plants
humans — revertant
few are approved
What does it mean for a vaccine to be revertant?
an attenuated virus used for gene therapy becomes pathogenic in the host
How is CRISPR used as a gene editing tool; use sickle cell gene editing as a case study
remove a sickle cell patients’s HSPCs
genetically modify them ex vivo
reintroduce them into the body