AP Economics Unit 3 Review
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
What is the value of GDP?
Answer: c. $750
What is the value of disposable income?
Answer: b. $650
The $750 of wages, profit, interest, and rent… illustrates which GDP calculation approach?
Answer: d. income
What is the value of GDP?
Answer: c. $14,100
What is the value of net exports?
Answer: e. –$500
Which of the following refers to a loan in the form of an IOU that pays interest?
Answer: b. bond
Investment spending includes spending on which of the following?
Answer: b. physical capital
Which of the following is included in the calculation of GDP?
Answer: e. domestically produced capital goods
Which of the following is true for the current year if real GDP is greater than nominal GDP?
Answer: a. The price level has decreased since the base year.
A country’s labor force is equal to which of the following?
Answer: c. the number of people employed plus the number unemployed
The number of people who are considered unemployed is equal to the number of people who
Answer: e. are actively seeking work.
The unemployment rate is the number of people unemployed divided by the number
Answer: c. in the labor force.
The number of people counted as unemployed includes which of the following types of workers?
Answer: b. aspiring workers seeking their first job
A worker who is not working while engaged in a job search after moving to a new city is considered to be which of the following?
Answer: a. frictionally unemployed
A worker who is not working because his or her skills are no longer demanded in the labor market is considered to be which of the following?
Answer: b. structurally unemployed
The normal unemployment rate around which the actual unemployment rate fluctuates is known as which of the following?
Answer: d. natural rate of unemployment
Which of the following is true if the real wage rate is equal to the nominal wage rate?
Answer: b. The price level for the current year is the same as the price level in the base year.
A worker who is unemployed due to fluctuations in the business cycle is considered to be which of the following?
Answer: c. cyclically unemployed
When inflation makes money a less reliable unit of measurement, the economy is experiencing which of the following costs of inflation?
Answer: a. unit-of-account
Bringing down the inflation rate is known as
Answer: d. disinflation
The real interest rate is equal to the nominal interest rate
Answer: a. minus the inflation rate.
Who loses from unanticipated inflation?
Answer: e. people on fixed incomes
Assume a country has a population of 1,000. If 400 people are employed and 100 people are unemployed, what is the country’s unemployment rate?
Answer: d. 20%
Which of the following changes will result in an increase in the natural rate of unemployment?
Answer: b. The government increases the time during which an unemployed worker can receive benefits.
If the consumer price index rises from 120 to 132, what is the inflation rate?
Answer: b. 10%
1. Circular Flow Diagram (7 points)
a.
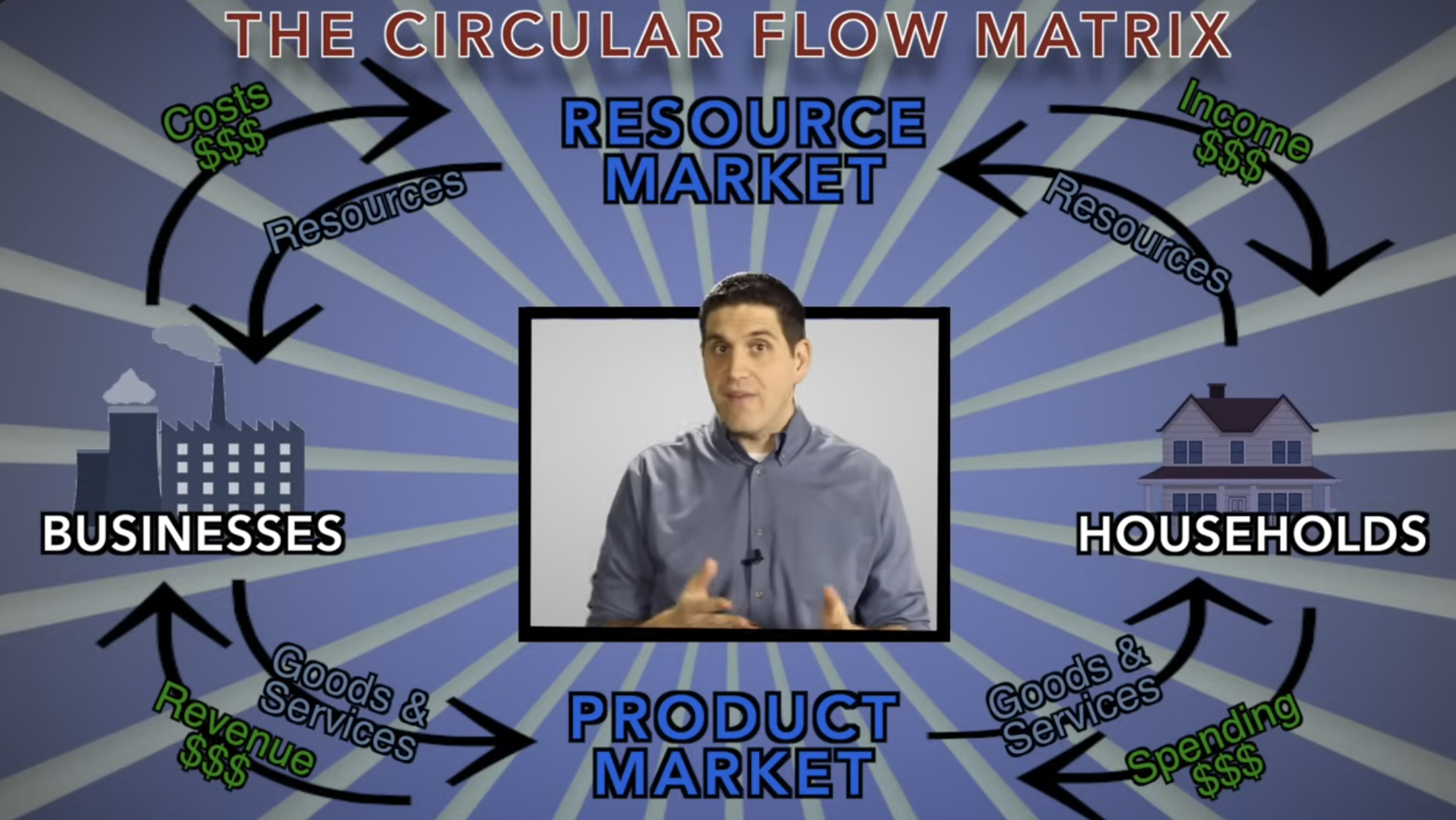
1. Circular Flow Diagram (7 points)
b.
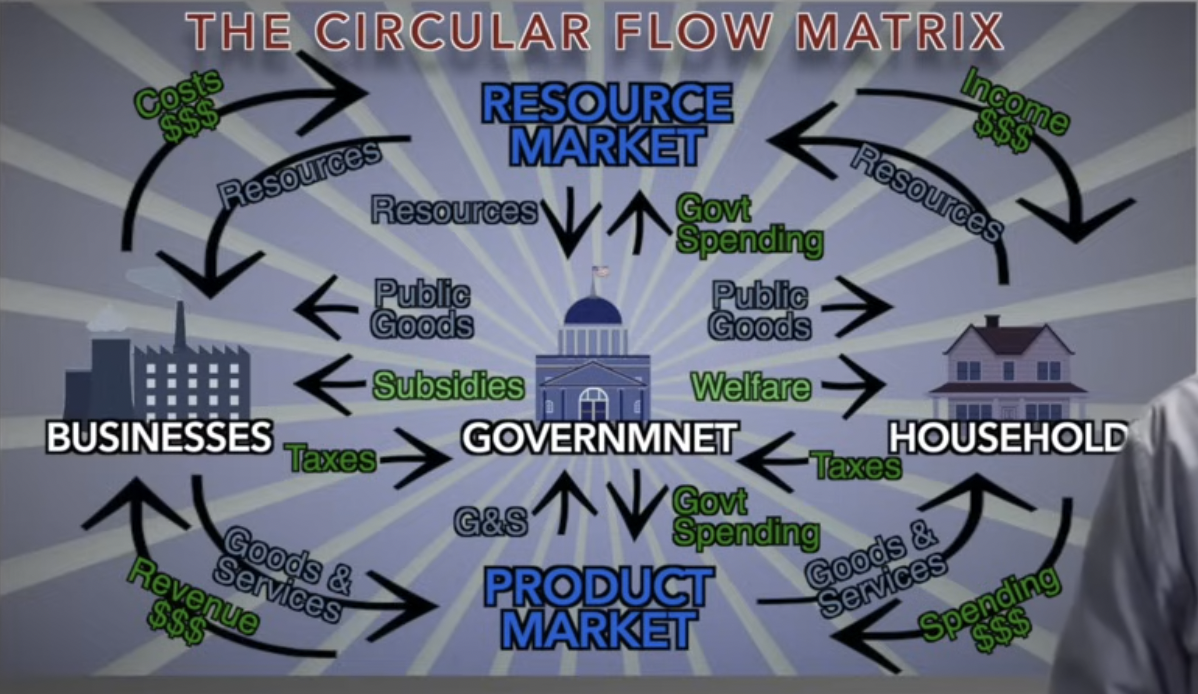
2. Technologia’s Unemployment Scenario ( 2. Assume the country of Technologia invests in an online application that efficiently matches job-seekers with employers and significantly reduces the time required for job searches.) (6 points)
a. Which type of unemployment is affected?
b. Will unemployment increase or decrease?
c. Effect on the natural rate of unemployment?
d. What will happen to real GDP? Explain.
a. Frictional unemployment
b. Decrease, because job matching is faster.
c. Decrease, because frictional unemployment is part of the natural rate. Explanation: Better job matching reduces the time workers are between jobs.
d. Increase Explanation: More people working = higher output, better resource use.
3. Price Level and Inflation (5 points)
Given:
Year | Price Level |
1 | $400 |
2 | $800 (Base Year) |
3 | $1,000 |
4 | $800 |
a. Calculate the price index for Year 1 and Year 2 (base year = 2):
b. Calculate inflation rate between Year 1 and Year 2:
c. Economy experienced deflation between which years? Explain.
d. Economy experienced disinflation between which years? Explain.
a. Price Index (Year 1) = (400 / 800) × 100 = 50 Price Index (Year 2) = (800 / 800) × 100 = 100
b. Inflation Rate = ((800 – 400) / 400) × 100 = 100%
c. Between Year 3 and Year 4: Price level fell from 1,000 to 800 Explanation: Deflation is a decrease in overall price level.
d. Between Year 2 and Year 3: Year 1 to 2 = 100% inflation Year 2 to 3 = ((1000 – 800)/800) × 100 = 25% Explanation: Inflation rate slowed down — that’s disinflation.