ECG Interpretation: Fundamentals, Leads, and Paper
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
What is the fundamental principle regarding the heart's electrical activity and its detection on an EKG?
The heart produces an electrical field in which currents flow in repetitive patterns with each cardiac cycle; the arms and legs are linear extensions of this electrical field; electrical activity can be detected at the extremities by placing electrodes of opposite polarity on the skin at opposite poles of the heart’s electrical field.
In short, the heart's electrical pulse flows through the entire body, and we use the arms and legs as convenient places to attach sensors to "listen" to this signal.
How is a lead defined in the context of an EKG setup?
A lead is composed of two electrodes of opposite polarity (bipolar) or one electrode and a reference point (unipolar).
What is the EKG (ECG)?
The EKG (ECG) is a recording of the cardiac electrical cycle.
What causes an upward deflection on the EKG tracing?
Electrical depolarization coming toward a positive electrode will cause an upward deflection on the EKG.
What causes a negative deflection on the EKG tracing?
Electrical depolarization moving away from a positive electrode will cause a negative deflection on the EKG.
Describe the proper placement location for precordial lead V1.
V1 is placed in the right fourth intercostal space; counting four intercostal spaces along the right sternal border.
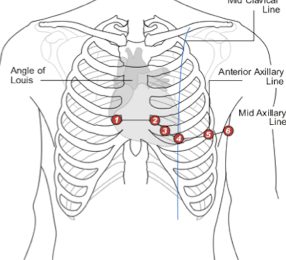
Describe the proper placement location for precordial lead V2.
V2 is placed the left fourth intercostal space along the left sternal border.

Describe the proper placement location for precordial lead V4.
V4 is placed in the midclavicular line in the fifth intercostal space.

Describe the proper placement location for precordial lead V3.
V3 is placed halfway between V2 and V4.

Describe the proper placement location for precordial lead V5.
V5 is placed in the anterior axillary line in the fifth intercostal space.

Describe the proper placement location for precordial lead V6.
V6 is placed in the midaxillary line in the fifth intercostal space.

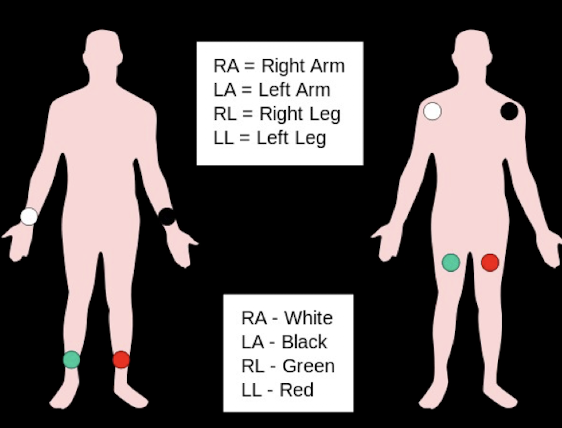
What is a useful mnemonic for proper electrode placement (regarding White and Smoke)?
White on the Right (right arm) and Smoke (left arm) Over Fire (left leg)
What view of myocyte electrical activity do the Limb leads (I; II; III; aVR; aVL; aVF) provide?
Limb leads provide view of myocyte electrical activity in a frontal plane; viewing electrical forces that move up and down and left and right.
What view of myocyte electrical activity do the Precordial Leads (V1-V6) provide?
Precordial Leads provide a view of myocyte electrical activity in a horizontal plane; viewing electrical forces that move anteriorly and posteriorly.
What type of limb leads are I; II; and III?
Bipolar (Standard) Limb Leads.

What are the Unipolar Augmented Limb Leads?
aVR aVL aVF

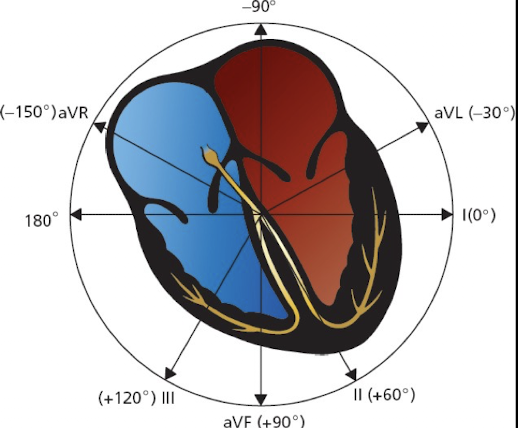
What are the characteristics (plane; polarity; angle) of Bipolar Limb Lead I?
Frontal Plane; Left arm Positive and Right arm Negative; Angle of orientation 0 degrees.
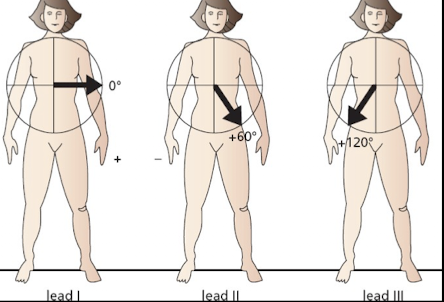
What are the characteristics (polarity; angle) of Bipolar Limb Lead II?
Both legs positive and Right arm Negative; Angle of orientation 60 degrees.

What are the characteristics (polarity; angle) of Bipolar Limb Lead III?
Both legs positive and left arm negative; Angle of orientation 120 degrees.

How is the negative electrode (common ground) established for Unipolar Augmented Limb Leads?
A single lead is chosen to be positive; all others made negative (their average serves as the negative electrode or common ground).
Why are the unipolar limb leads referred to as "Augmented"?
Augmented because the EKG machine must amplify the tracings to get adequate recording.
What is the positive polarity and angle of orientation for Augmented Limb Lead aVL?
Left arm positive; Angle of orientation -30 degrees.
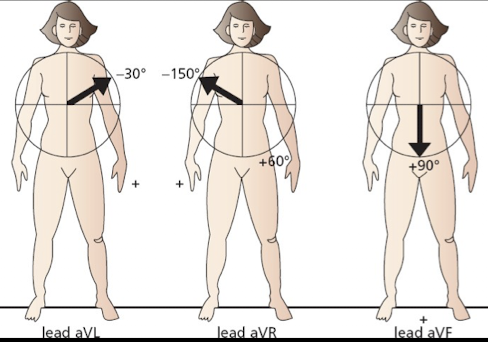
What is the positive polarity and angle of orientation for Augmented Limb Lead aVR?
Right arm positive; Angle of orientation -150 degrees.

What is the positive polarity and angle of orientation for Augmented Limb Lead aVF?
Both legs positive; Angle of orientation +90 degrees.

What are the leads assocuated with each angle?
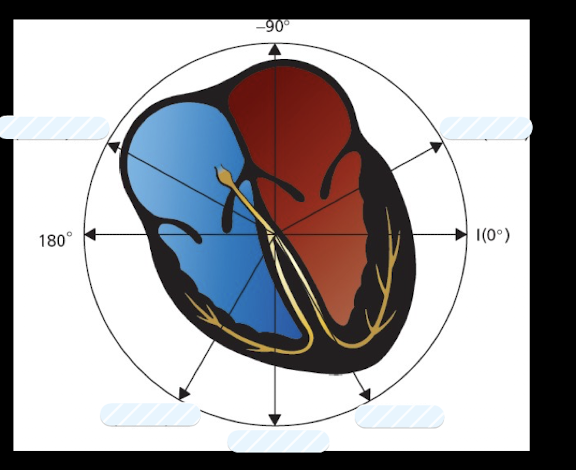
What is the polarity of each precordial lead (V1-V6) and what acts as the common ground?
Each precordial lead has a positive polarity; The whole body functions as a common ground
Which precordial lead lies directly over the right ventricle?
Lead V1 lies directly over the right ventricle.
Which precordial leads lie over the interventricular septum?
Leads V2 and V3 lie over the interventricular septum.
Which precordial lead lies over the apex of the left ventricle?
Lead V4 lies over the apex of the left ventricle.
Which precordial leads lie over the lateral left ventricle?
Lead V5 and V6 lie over the lateral left ventricle.
Which lead group is classified as "Anterior"?
V2, V3, V4.
Which lead group is classified as "Left lateral"?
I, aVL, V5, V6.
Which lead group is classified as "Inferior"?
II, III, aVF.
Which lead group is classified as "Right ventricular"?
aVR, V1.
How many electrodes are typically placed on the patient to obtain a standard 12-Lead EKG?
10 electrodes are placed on the patient (one for each arm and leg and then 6 across the chest).
How many leads does the EKG machine produce from the electrodes?
The EKG machine measures the voltage difference between specific electrodes to produce 12 Leads on the EKG.
Describe the sequence in which the EKG machine records the 12 leads.
Leads I, II, and III are recorded first. Followed by aVR, aVL, and aVF after 2.5 seconds. Then V1, V2, and V3 after another 2.5 seconds; and finally V4, V5, and V6 for the final 2.5 seconds.
What is the standard sweep speed for EKG paper?
The most common speed is 25 mm/sec which is roughly 1 inch per second.
How many milliseconds are equal to 0.1 seconds?
100 milliseconds.
What do the light lines on EKG paper represent?
Light lines make up small squares of 1x1 mm.
What do the dark lines on EKG paper represent?
Dark lines make up large squares of 5x5 mm.
On the EKG paper, what axis measures time, and how much time does one small square represent?
Horizontal. One small square represents 0.04 seconds
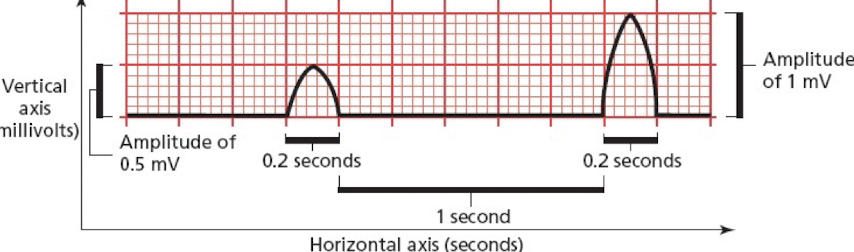
On the EKG paper what axis measures voltage, and how much voltage does one small square represent?
Vertical One small square represents 0.1 mv

What measurements can be determined using the horizontal axis of the EKG?
Measurements along the horizontal axis indicate the overall heart rate, regularity, and give time intervals during electrical activation that move from one part of the heart to another.
What does the voltage measured on the vertical axis of the EKG represent?
This voltage represents the "summation" of the electrical activation of all of the cardiac cells.
A practitioner suspects an inferior wall myocardial infarction based on clinical symptoms; which group of EKG leads must be closely monitored for changes such as ST elevation?
Leads II III and aVF; as these are classified as the Inferior lead group.
During an EKG setup; the PA places an electrode in the anterior axillary line in the fifth intercostal space; which precordial lead is correctly placed at this specific location?
V5 is correctly placed in the anterior axillary line in the fifth intercostal space.