Lecture 16: Repair and regeneration
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Functional Reorganization
After a stroke or neural injury, patients often recover due to reorganization of intact circuits
Does not reflect the regrowth or replacement or damaged neurons
Regrowth of Axons
→Requires reactivation of the process for axon growth and synapse formation
Seen primarily when sensory and motor nerves are damaged in the periphery
→ Leaves nerve cell bodies intact
Central nerve cell restoration
→ Sprouting → new dendrites, axons, and synapses must grow from an existing cell body
Generally fails, except over limited distances
→ Because of local overgrowth of glial cells and the production of signals that inhibit growth
Genesis of Neurons
Occurs rarely in adults → Peripheral olfactory receptor neurons
→ Nervous tissue must keep stem cells
→ Stem cells must be present in a region that keeps an appropriate environment for genesis and differentiation
→ Regeneration must keep the ability to repeat the migration and synapse formation during growth in order to regrowth local and long-distance connections
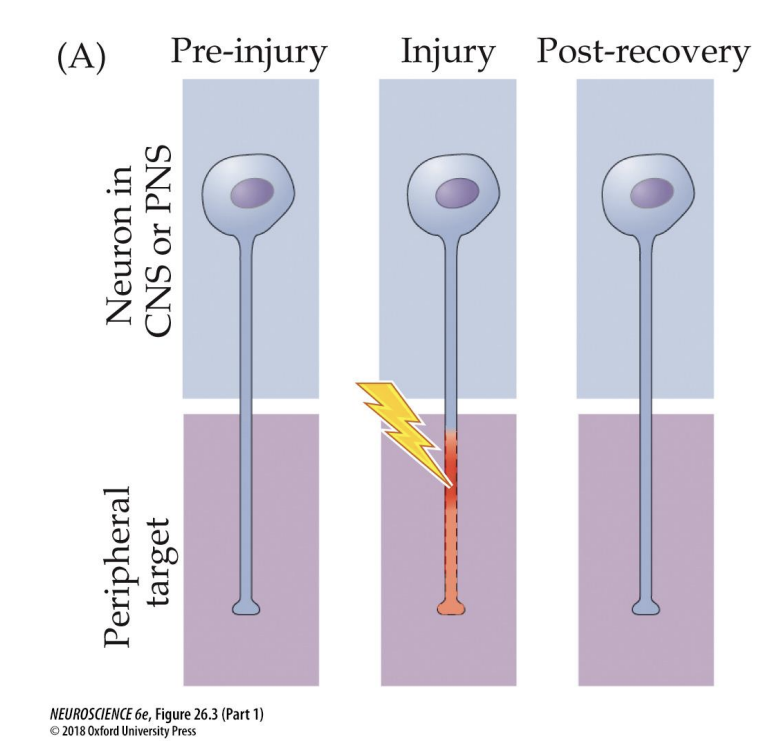
Peripheral nerve regeneration
A type of axon regrowth that results in a gradual, but usually incomplete restoration of sensory and motor function
Can be facilitated by surgical reapposition of the 2 ends of the severed nerve
Regeneration is more efficient after crushing vs cutting a nerve
Henry’s Head
A peripheral nerve regeneration experiment that monitored the return of sensation
Gradual return of sensitivity to pressure & touch that was not well localized starting ~6 weeks into recovery
→ Light touch, temperature discrimination, two-point discrimination recovered more slowly and less restoration
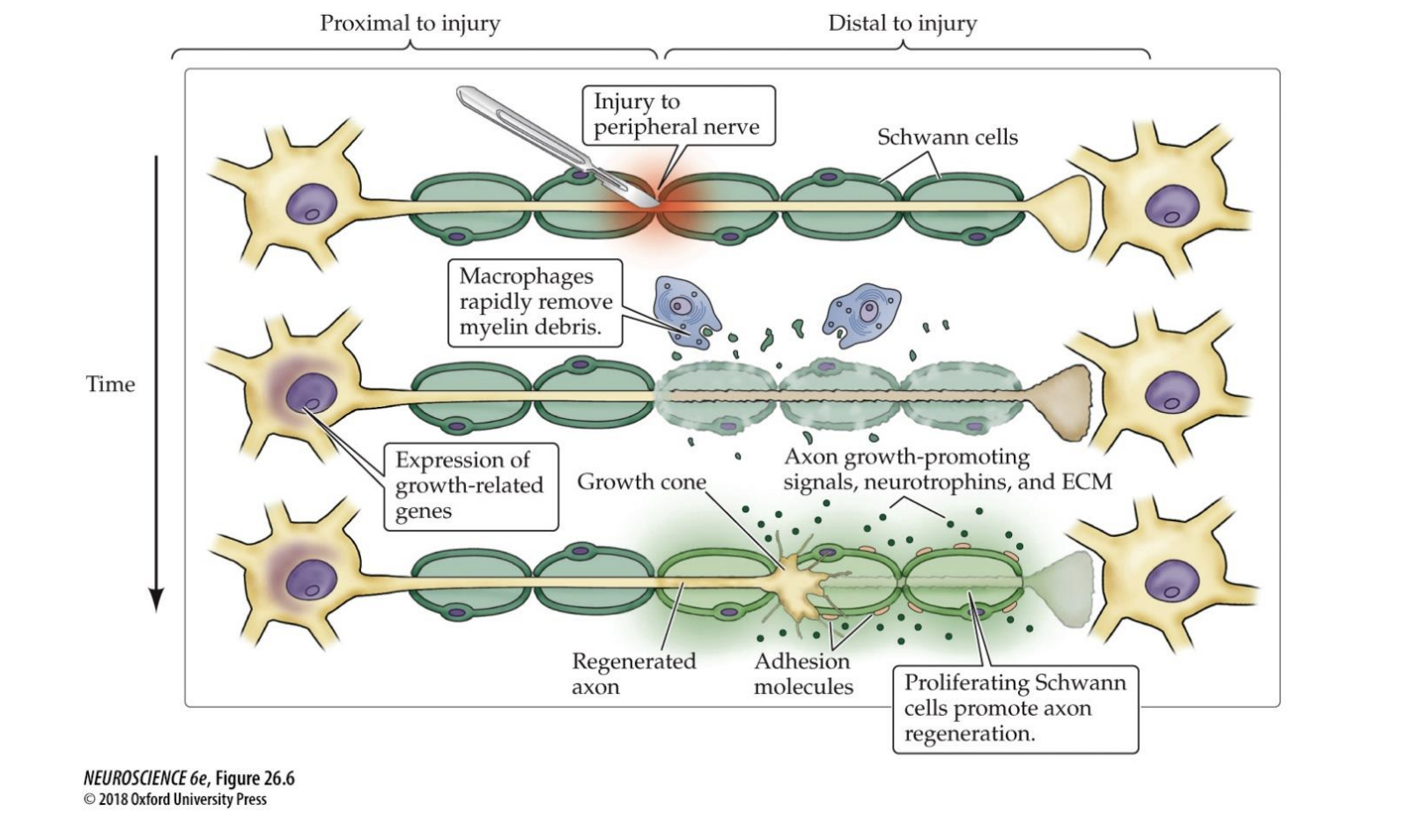
Schwann Cells
The glial cells that myelinate peripheral axons
Macrophages
The immune system cells that clear the degenerating remains of severed axons
Severed Peripheral Axon
• Axon segment distal to the cut degenerates
• Debris left by the dead axon is cleared by macrophages
• Proximal axon stump transforms into a growth cone
• Schwann cells proliferate & secrete growth-promoting signaling molecules
Peripheral Nerve graft
A treatment that can be used to treat a severed axon in the optic nerve
Offers the Schwann cell and connective tissue components that support Peripheral nerve regeneration
→ Central axons grow through the peripheral nerve graft
Limited effects → low # of synapses and functional capacity to restore vision
Peripheral nerve regeneration steps
• Extension of axons is the first step in peripheral nerve regeneration
• Next essential event: reinnervation of appropriate target tissues and reestablishment of synaptic connections
→Fair degree of imprecision in the reinnervation of specific targets
• Subsequent regeneration can (or cannot) be fairly faithful to the original pattern
CNS damage
Physical trauma (blunt force to the head)
Hypoxia (lack of oxygen, Ex: stroke)
Neurodegenerative diseases (Alzheimers, Parkinson’s, ALS)
Limited Regeneration CNS
1. Damage to brain tissue engages the mechanisms that lead to necrotic and apoptotic cell death for nearby neurons whose processes have been severed
2. A combination of glial growth and proliferation and microglial activity (immune functions that lead to local inflammation) actively inhibits growth
3. Upregulation of growth-inhibiting molecules
Glial Scarring
Caused due to extensive growth of processes from glial cells around the site of the injury
→ Local overgrowth & sustained concentrations of astrocytes & oligodendrocytes
Neurogenesis Regions
The olfactory bulb & the hippocampus
→ These are primarily GABAergic interneurons
Neurogenesis Components
• A low level of glial cell proliferation does continue throughout life
→ Astrocytes & oligodendrocytes
• Neural stem cells are often found in close proximity to blood vessels
→ Suggests they may be regulated by circulating as well as local signaling molecules
• Neuron replacement is gradual
• The limited capacity to replace neurons in an adult brain has offered some promise that, under the right conditions, neuron replacement might be used to repair the injured brain
• The CNS likely puts a premium on the stability of connections to ensure that learned behaviors are maintained
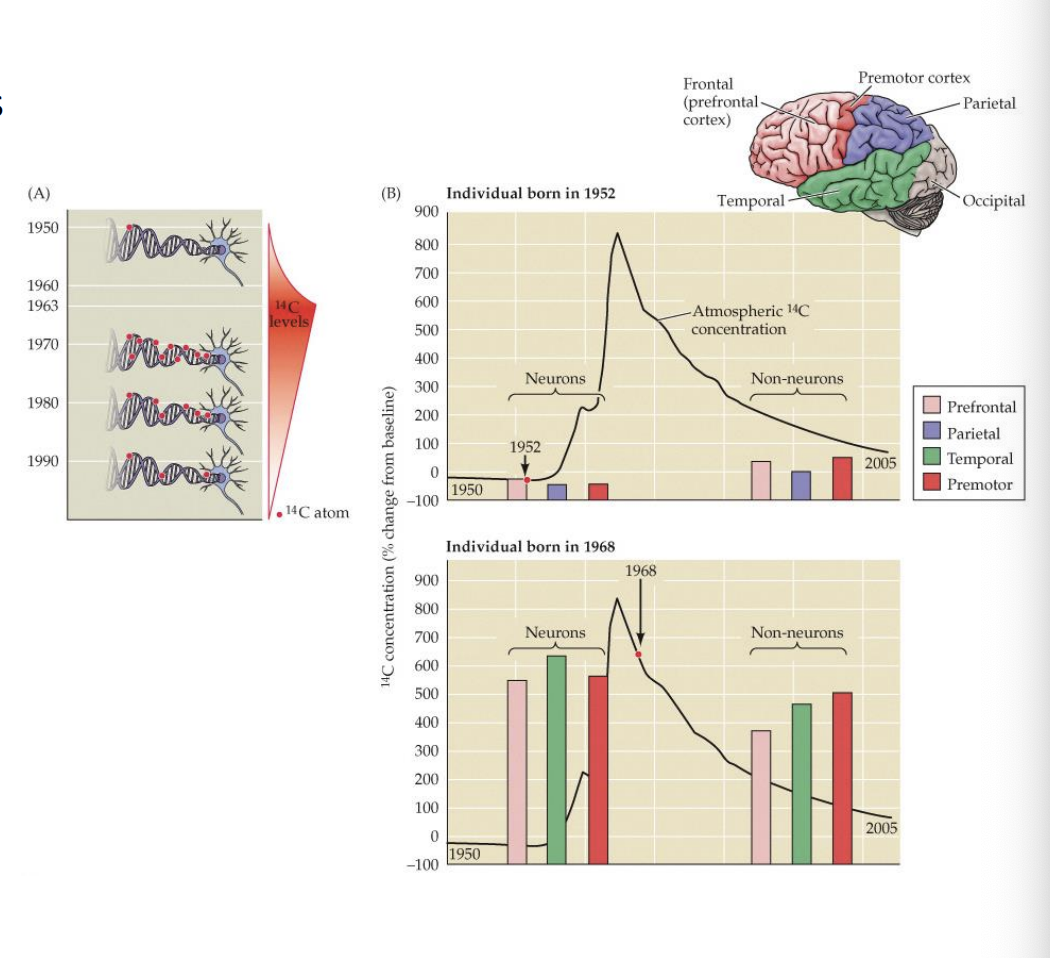
Nuclear Weapons and Neurogenesis
Fluctuations in environmental exposure to radioisotopes from nuclear weapons testing
Different levels of 14C in the brain due to weapons testing