Chemistry Review Flashcards
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards about the periodic table, atomic structure, chemical reactions, and factors affecting reaction rates, based on lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Atomic Number
The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom, which determines the atomic number.It also indicates the element's identity and its position in the periodic table.
number of protons = number of electrons = atomic number
Atomic Mass
The total number of particles in the nucleus (protons + neutrons together).
Mass number = total number of particles in nucleus
Isotopes
Atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons.
Radioactive
Unstable atomic nuclei that emit radiation to become more stable.
Law of Conservation of Mass
The principle stating that matter cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed.
Closed System
A system that does not exchange matter with its surroundings but may exchange energy.
Ionic Compounds
Compounds formed through electrostatic attraction between ions, typically involving a metal and nonmetal.
Covalent Compounds
Compounds formed by sharing valence electrons between atoms, typically involving nonmetals.
Synthesis Reaction
A reaction where two or more reactants combine to form a single product. (A + B → AB)
Decomposition Reaction
A reaction where a single reactant breaks down into two or more products. (AB → A + B)
Displacement Reaction
A reaction where atoms are exchanged between reactants to form new products.
Single Displacement Reaction
A displacement reaction where a single element replaces another in a compound.(AB + C → CB + A)
Double Displacement Reaction
A displacement reaction where two different atoms in different compounds switch places.(AB + CD → AD + BC)
Neutralization Reaction
A double displacement reaction between an acid and a base, forming water and a salt.
Concentration
A measure of the amount of a substance in a defined space.
Surface Area
The total area of a solid exposed to the reactants.
Catalyst
A substance that speeds up a reaction without being consumed in the process.
Calculating numbers of subatomic particles
number of protons = atomic number
number of electrons = atomic number
number of neutrons = mass number - atomic number
Atoms
The basic unit of matter, comprised of protons (p+), neutrons (n), and electrons(e-). combine to form molecules, making up all substances. are also electrically neutral and must have the same number of electrons as protons.
Protons
Positively charged subatomic particles found in the nucleus of an atom; they determine the atomic number and identity of an element.
Neutrons
Neutral subatomic particles located in the nucleus of an atom; they contribute to the mass number but do not affect the atom's charge.
Electrons
Negatively charged subatomic particles that orbit the nucleus of an atom; they play a key role in chemical bonding and determine the atom's charge.
Nucleus
The central part of an atom, consisting of protons and neutrons, which contains most of the atom's mass.
Atom structure
Electrons spin fast around the nucleus in a region of empty space. Opposite charges attract each other and this keeps the electrons from spinning out from the atom.
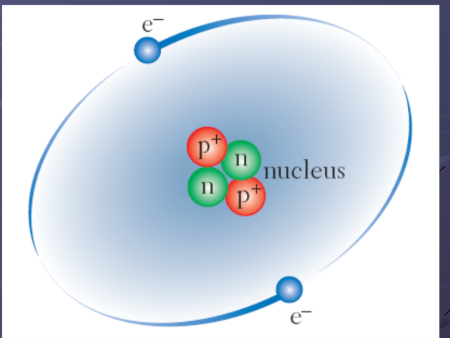

Working it out
Mass number is 19, Atomic number 9
The atom Fluorine has 9 protons and 9 electrons and 10 neutrons (19-9=10)
Elements
Each element is made up of one type of atom. e.g. Oxygen only contains oxygen atoms. If atoms belong to the same element, they have the same atomic number.
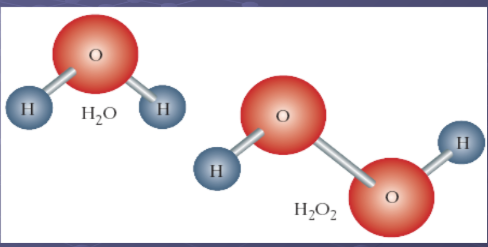
Compounds
Pure substances made up of two or more elements chemically bonded together in a fixed proportion. The simplest form of is a molecule.
Mixtures
can be separated by simple physical techniques such as filtration or evaporation since it is made of different elements or compounds simply thrown together. No formula can be written.
Examples include salt water, a can of cola, soil, air and blood.
Molecules
A group of atoms bonded or joined together.
Compound formulas
They write chemical formulas using element symbols, with subscripts to show how many of each atom there are in the compound. Water has two atoms of the element hydrogen and one atom of the element oxygen, so the formula for water becomes H2O ( we don’t write in ones).
Chemical Reactions
happen when atoms bump into each other. The protons and neutrons are relatively unaffected by the bump, being at the centre of the atom in the nucleus. The outermost electrons, however, are greatly affected and are easily ‘grabbed’ or shared by other atoms.
Ions
If the number of electrons changes in an atom, it becomes electrically charged and we call it an ion
• If an atom loses electrons, it becomes a positive ion.
• If an atom gains electrons, it becomes a negative ion.
The Noble Gases
The nobles gases are colourless gases that occur naturally in the atmosphere. All can be separated by distillation of liquid air. They are very stable and react only in rare and extreme circumstances.
The Halogens
• form ions with a charge of –1.
• are never found in their pure form in nature but
are in various types of salts, including sea salt
• have coloured and poisonous vapours
• all form molecules, each being made up of two
atoms.
As we move down the group the atoms get bigger and become less reactive.
The Alkali Metals
• form +1 ions
• are far too reactive to be found free in nature, but
are found in mineral salts
• have typical metallic properties
• display similar chemically extreme behaviours.
Lithium, sodium and potassium are light enough to float on water and are so soft that they can be cut with a knife.